Jungfrau Railway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Jungfrau Railway (german: Jungfraubahn, JB) is a mountain railway in the

 *1896 construction began. The construction work proceeded briskly.
*1898 the Jungfrau Railway opened as far as the Eigergletscher railway station, at the foot of the
*1896 construction began. The construction work proceeded briskly.
*1898 the Jungfrau Railway opened as far as the Eigergletscher railway station, at the foot of the
 * Kleine Scheidegg,
* Eigergletscher,
*
* Kleine Scheidegg,
* Eigergletscher,
*
 Since most of the railway is inside a tunnel, it was designed to be powered by electricity from conception. The current rolling stock consists of twin-unit motorcoaches carrying up to 230 people per train which operate at 12.5 km/h on the steepest parts of the ascent. The motors function at two speeds which allows the units to operate at double this speed on the less steep part of the ascent (above Eismeer station).
The motors will operate in a regenerative mode which allows the trains to generate electricity during the descent, which is fed back into the power distribution system. Approximately 50% of the energy required for an ascent is recovered during the descent. It is this generation that regulates the descent speed.
Motive power delivered since 1992 (numbers 211...224) no longer has directly fed three phase motors but is equipped similarly to a normal single phase locomotive. This rolling stock can travel at variable speed and this allowed a reduction in journey time from 52 to 35 min with the timetable starting 11 December 2016.
Since most of the railway is inside a tunnel, it was designed to be powered by electricity from conception. The current rolling stock consists of twin-unit motorcoaches carrying up to 230 people per train which operate at 12.5 km/h on the steepest parts of the ascent. The motors function at two speeds which allows the units to operate at double this speed on the less steep part of the ascent (above Eismeer station).
The motors will operate in a regenerative mode which allows the trains to generate electricity during the descent, which is fed back into the power distribution system. Approximately 50% of the energy required for an ascent is recovered during the descent. It is this generation that regulates the descent speed.
Motive power delivered since 1992 (numbers 211...224) no longer has directly fed three phase motors but is equipped similarly to a normal single phase locomotive. This rolling stock can travel at variable speed and this allowed a reduction in journey time from 52 to 35 min with the timetable starting 11 December 2016.Official Swiss timetable publication
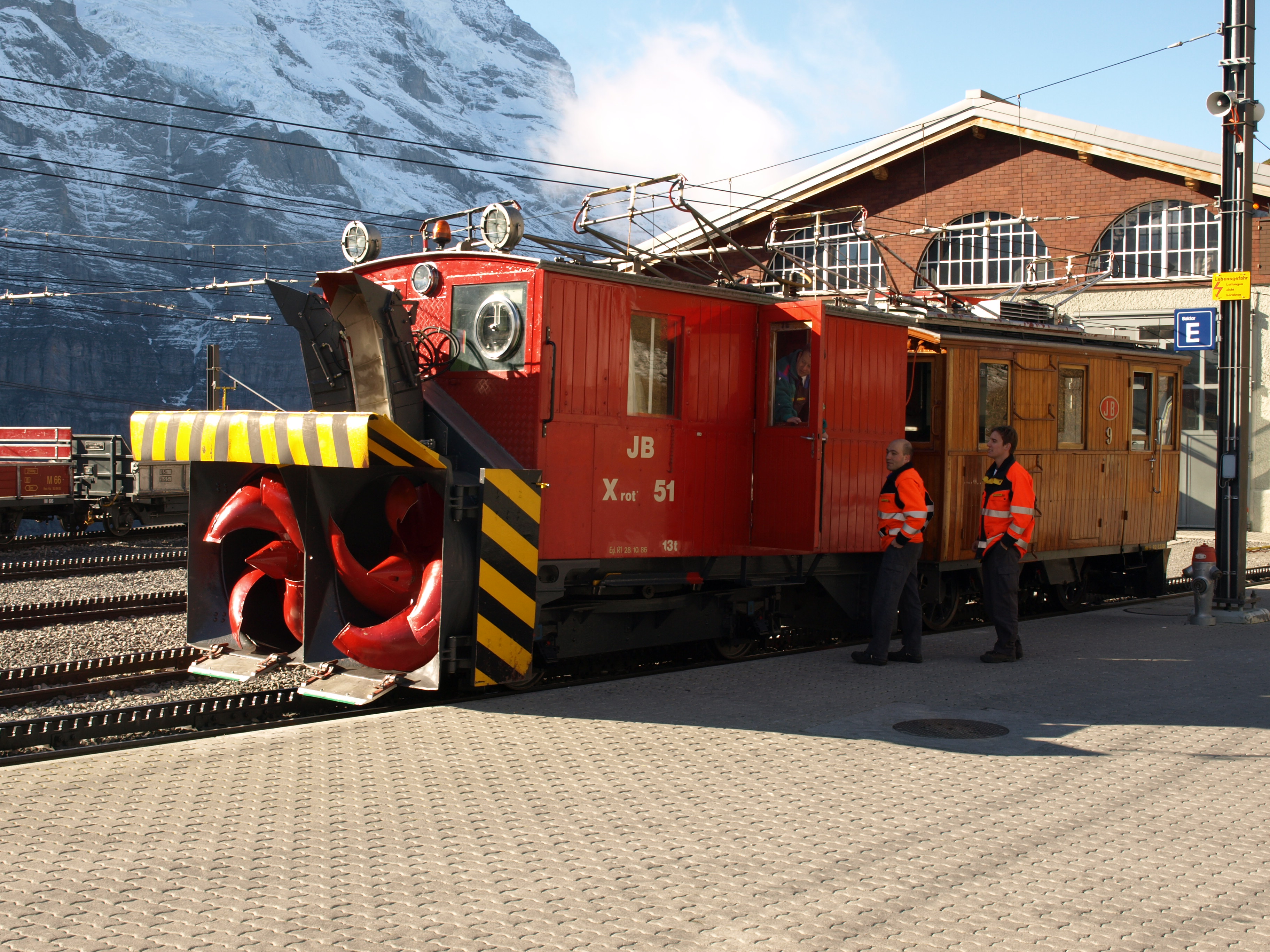
/ref> Pre-1992 rolling stock can no longer be used in regular traffic and most of the earlier trains have been scrapped. Snow clearing equipment is essential on the open section of line between Kleine Scheidegg railway station and Eigergletscher railway station. Originally snow ploughs were used but more recently snow blowing equipment has been brought into service. The railway also operates some dedicated freight vehicles to supply the visitor facilities at

Jungfrau Railways website
''Jungfraurailway: Why the highest of Europe didn't end higher''
'Tim Travel' on
"Alpine Climbing by Railroad"
''Popular Mechanics'', December 1911, pp. 830–831. {{Authority control Transport in the Alps Bernese Oberland Mountain railways Metre gauge railways in Switzerland Railway companies of Switzerland Electric railways in Switzerland Railway lines in Switzerland Railways using three-phase power Railway lines opened in 1898 Rack railways in Switzerland Transport in the canton of Bern Transport in Valais Tourist attractions in the Canton of Bern 1898 establishments in Switzerland Companies listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange
Bernese Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo
, photo=BerneseAlps.jpg
, photo_caption=The Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau
, country= Switzerland
, subdivision1_type= Cantons
, subdivision1=
, parent= Western Alps
, borders_on=
, ...
, connecting Kleine Scheidegg in the Bernese Oberland
The Bernese Oberland ( en, Bernese Highlands, german: Berner Oberland; gsw, Bärner Oberland; french: Oberland bernois), the highest and southernmost part of the canton of Bern, is one of the canton's five administrative regions (in which context ...
to the Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
, across the Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
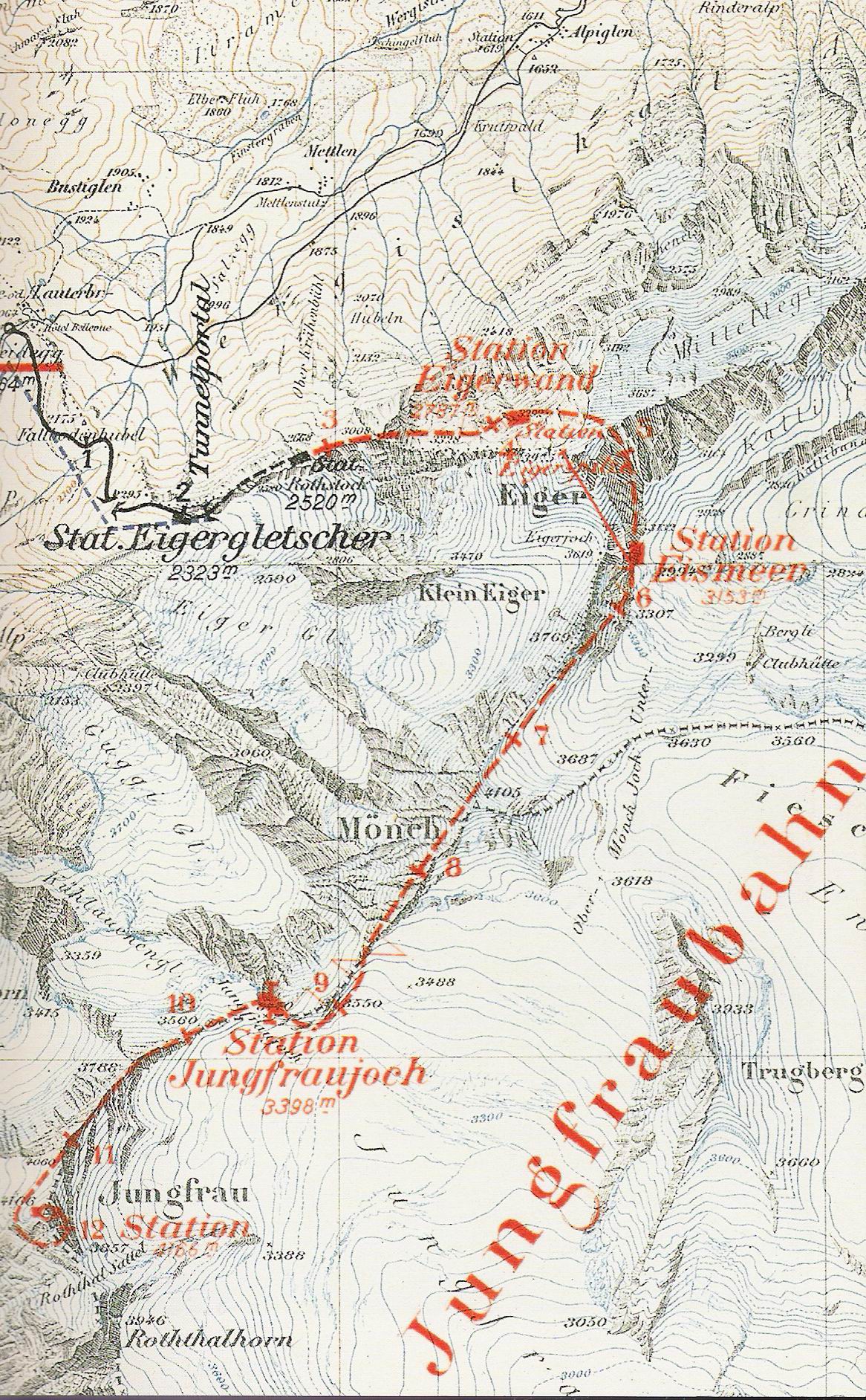
border. The railway, which uses a and racks, runs from the station of Kleine Scheidegg () to the Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
(). It is the highest railway in Switzerland and Europe, the Jungfraujoch being the highest railway station on the continent and well above the perennial snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
. As a consequence, the railway runs essentially within the Jungfrau Tunnel, built into the neighbouring Eiger
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that exte ...
and Mönch, to protect the line from snow and extreme weather. Another particularity of the Jungfrau Railway is the high elevation of its starting point, at the hub of Kleine Scheidegg, also the highest in Europe.
The Jungfrau Railway got its name from the highest of the three high peaks above it: the Jungfrau ( en, maiden, virgin; ), the latter mountain being the initial goal of the project. A lift connecting the summit of the Jungfrau with an underground railway was planned. In 1912, the project finally ended at the Jungfraujoch, the saddle between the Mönch and Jungfrau. It was nevertheless one of the highest railways in the world at the time of inauguration.
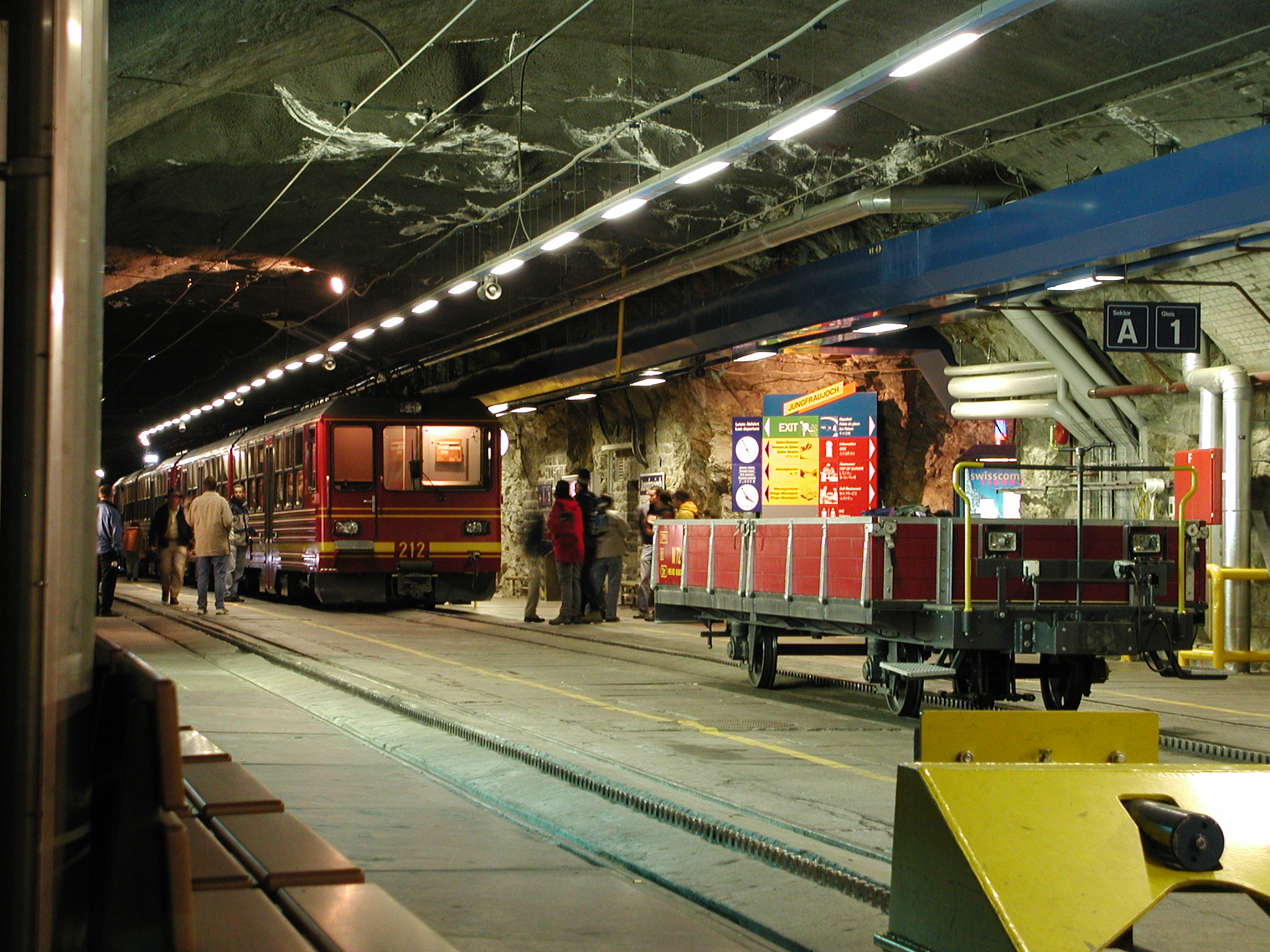
The Jungfrau Railway includes three additional stations. The initial open-air section culminates just after Eigergletscher (2,320 m), at around 2,350 metres, which makes it the second highest open-air railway in Switzerland. The two other stations are located in the Jungfrau Tunnel, where passengers can disembark for a short time to observe the neighbouring mountains through windows built into the mountainside. The lower one, Eigerwand
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that extends a ...
, gives access to windows in the north face of the Eiger. The upper one, Eismeer, gives access to windows in the east face of the Eiger, overlooking the Eismeer (the "sea of ice"). The line is electrified at 3-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral r ...
1,125 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference ( voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
D ...
s 50 Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one her ...
, and is one of four lines in the world using three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral ...
.
At Kleine Scheidegg the JB connects with the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), which has two routes down the mountain, running respectively to the villages of Lauterbrunnen and Grindelwald
Grindelwald is a village and municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Berne. In addition to the village of Grindelwald, the municipality also includes the settlements of Alpiglen, Burglauenen, Grund, Itram ...
. From both villages, branches of the Berner Oberland-Bahn (BOB) connect to the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
at Interlaken
, neighboring_municipalities= Bönigen, Därligen, Matten bei Interlaken, Ringgenberg, Unterseen
, twintowns = Scottsdale (USA), Ōtsu (Japan), Třeboň (Czech Republic)
Interlaken (; lit.: ''between lakes'') is a Swiss town and mun ...
.
The line is owned by the ''Jungfraubahn AG'', a subsidiary of the ''Jungfraubahn Holding AG'', a holding company that owns several mountain railways, cable railways, hotels, restaurants and travel agencies in the same region. Through that holding company it is part of the ''Allianz - Jungfrau Top of Europe'' marketing alliance, which also includes the separately owned Berner Oberland-Bahn and Schynige Platte-Bahn.
History
*1860 (approximately) - there were many different plans for a mountain railway on the Jungfrau, which failed due to financial problems. *1894 the industrialistAdolf Guyer-Zeller
Adolf Guyer-Zeller (1 May 1839 – 3 April 1899) was a Swiss entrepreneur.
Born in Bäretswil, Switzerland on 1 May 1839, Guyer-Zeller was the son of an owner of spinning mill and creator of a textile export trade in Zürich. After the death of ...
received a concession for a rack railway, which began from the Kleine Scheidegg railway station of the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), with a long tunnel through the Eiger
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that exte ...
and Mönch up to the summit of the Jungfrau.

 *1896 construction began. The construction work proceeded briskly.
*1898 the Jungfrau Railway opened as far as the Eigergletscher railway station, at the foot of the
*1896 construction began. The construction work proceeded briskly.
*1898 the Jungfrau Railway opened as far as the Eigergletscher railway station, at the foot of the Eiger
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that exte ...
.
*1899 Six workers are killed in an explosion. There is a four-month strike by workers. Adolf Guyer-Zeller
Adolf Guyer-Zeller (1 May 1839 – 3 April 1899) was a Swiss entrepreneur.
Born in Bäretswil, Switzerland on 1 May 1839, Guyer-Zeller was the son of an owner of spinning mill and creator of a textile export trade in Zürich. After the death of ...
dies in Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich () i ...
on 3 April. The section from Eigergletscher station to Rotstock station opens on 2 August
*1903 The section from Rotstock station to Eigerwand station opens on 28 June.
*1905 The section from Eigerwand station to Eismeer station opens on 25 July
*1908 There is an explosion at Eigerwand station.
*1912 21 February, sixteen years after work commenced, the tunneling crew finally breaks through the glacier in Jungfraujoch. Jungfraujoch station was inaugurated on 1 August.
*1924 "The house above the clouds" at Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
is opened on 14 September.
*1931 The research station at the Jungfraujoch is opened.
*1937 The Sphinx Observatory is opened. A snowblower is purchased and this results in year-round operation.
*1942 Relocation of the company offices from Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich () i ...
to Interlaken
, neighboring_municipalities= Bönigen, Därligen, Matten bei Interlaken, Ringgenberg, Unterseen
, twintowns = Scottsdale (USA), Ōtsu (Japan), Třeboň (Czech Republic)
Interlaken (; lit.: ''between lakes'') is a Swiss town and mun ...
.
*1950 The dome is installed on the Sphinx Observatory.
*1951 The adhesion section between Eismeer station and Jungfraujoch station is converted to rack operation.
*1955 A second depot at Kleine Scheidegg is constructed. The post office inaugurates its relay station on the Jungfraujoch.
*1972 The panoramic windows are installed at Eigerwand and Eismeer. The Jungfraujoch mountain house and tourist house are destroyed by fire on 21 October.
*1975 A new tourist house is opened.
*1987 A new mountain house is opened on 1 August.
*1991 A new station hall is opened at the Jungfraujoch.
*1993 The small Kleine Scheidegg depot is extended.
*1996 The covered observation deck at the Sphinx Observatory is opened.
*1997 For the first time the annual visitor numbers exceed 500,000.
*2000 On 1 June a daily record number of 8,148 visitors is achieved.
Stations
 * Kleine Scheidegg,
* Eigergletscher,
*
* Kleine Scheidegg,
* Eigergletscher,
*Eigerwand
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that extends a ...
,
* Eismeer,
*Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
,
Source:
Openings
*Rotstock Station (closed in 1903) *StollenlochLift proposal and aerial cableway
In early 2008, Jungfraubahn Holding AG announced it was exploring the idea of an efficient fast form of access to the Jungfraujoch, using the world's longest tunnel-lift system, as an alternative to the rack railway. A feasibility study was undertaken to determine if and how such a system - for example as a fast lift or funicular - from the Lauterbrunnen Valley to theJungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
could be realised without disturbing the unique landscape of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
. These plans were later abandoned and in 2017 the company announced plans to build an aerial cableway between , a new station on the Interlaken-Grindelwald line, and from where the Jungfrau railway could be joined for the journey to the summit. This aerial cableway, known as the Eiger Express, opened to the public on 5 December 2020. and provides an alternative, faster, way to access the Jungfraujoch from the valley.
Rolling stock
/ref> Pre-1992 rolling stock can no longer be used in regular traffic and most of the earlier trains have been scrapped. Snow clearing equipment is essential on the open section of line between Kleine Scheidegg railway station and Eigergletscher railway station. Originally snow ploughs were used but more recently snow blowing equipment has been brought into service. The railway also operates some dedicated freight vehicles to supply the visitor facilities at
Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphi ...
, including a tank to transport additional water.
Main characteristics

See also
* List of mountain railways in Switzerland *Rail transport in Switzerland
The Swiss rail network is noteworthy for its density, its coordination between services, its integration with other modes of transport, timeliness and a thriving domestic and trans-alp freight system. This is made necessary by strong regulations ...
* Wetterhorn Elevator
The Wetterhorn Elevator (german: Wetterhorn-Aufzug) was an aerial tramway in the valley of Grindelwald. It connected the base of the Upper Grindelwald Glacier to a higher location in the Wetterhorn massif. The tramway was inaugurated in 1908, mak ...
, another ambitious project in the region aiming at the Wetterhorn
References
External links
Jungfrau Railways website
''Jungfraurailway: Why the highest of Europe didn't end higher''
'Tim Travel' on
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second most ...
"Alpine Climbing by Railroad"
''Popular Mechanics'', December 1911, pp. 830–831. {{Authority control Transport in the Alps Bernese Oberland Mountain railways Metre gauge railways in Switzerland Railway companies of Switzerland Electric railways in Switzerland Railway lines in Switzerland Railways using three-phase power Railway lines opened in 1898 Rack railways in Switzerland Transport in the canton of Bern Transport in Valais Tourist attractions in the Canton of Bern 1898 establishments in Switzerland Companies listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange