The Jauch family of
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
is a
Hanseatic family which can be traced back till the
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
. At the end of the 17th century the family showed up in the
Free Imperial and
Hanseatic City of Hamburg. The members of the family acted as long-distance merchants. They became hereditary
grand burgher
Grand Burgher aleor Grand Burgheress emale(from German: Großbürger ale Großbürgerin emale is a specific conferred or inherited title of medieval German origin and legally defined preeminent status granting exclusive constitutional privile ...
s of Hamburg and were
Lords of
Wellingsbüttel Manor
Wellingsbüttel Manor (German: Rittergut Wellingsbüttel, since Danish times: Kanzleigut Wellingsbüttel) is a former manor with a baroque manor house (German: ''Herrenhaus'') in Hamburg, Germany, which once enjoyed imperial immediacy (''Reichsf ...
– nowadays a
quarter of Hamburg.
The Jauch have brought forth some notable
lineal descendant
A lineal descendant, in legal usage, is a blood relative in the direct line of descent – the children, grandchildren, great-grandchildren, etc. of a person. In a legal procedure sense, lineal descent refers to the acquisition of estate by in ...
s, both
patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritanc ...
and
matrilineal
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's Lineage (anthropology), lineage – and which can in ...
. They can trace the nearer
cognatic kinship
Cognatic kinship is a mode of descent calculated from an ancestor counted through any combination of male and female links, or a system of bilateral kinship where relations are traced through both a father and mother. Such relatives may be known ...
of the issue of the
progenitor
In genealogy, the progenitor (rarer: primogenitor; german: Stammvater or ''Ahnherr'') is the – sometimes legendary – founder of a family, line of descent, clan or tribe, noble house, or ethnic group..
Ebenda''Ahnherr:''"Stammvater eines G ...
Johann Christian Jauch the Elder (1638–1718) in the following centuries to a number of renowned contemporaries.
Overview
Pre-Hanseatic time
The Jauch originate from
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and larg ...
where as the first family member the widow Lena Joherrin
is chronicled 1495 in today's
Bad Sulza
Bad Sulza is a town in the Weimarer Land district, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated on the river Ilm, 15 km southwest of Naumburg, and 18 km north of Jena. The former municipality Ködderitzsch was merged into Bad Sulza in January 2 ...
.
Johann Christian Jauch the Elder (1638–1718) left Sulza and entered the service of the
Güstrow branch of the
Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg. Two of his sons joined the service of the
Electors of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
and
Kings of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
. These branches were since the lieutenant colonel of the Franz Georg Jauch (b. 1681) and the major general
Joachim Daniel Jauch (1688–1754) mistakenly regarded as members of the
aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At t ...
. They became extinct in the 18th century.

The members of the family who had served the
Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg left the
Residenz
Residenz () is a German word for "place of living", now obsolete except in the formal sense of an official residence. A related term, Residenzstadt, denotes a city where a sovereign ruler resided, therefore carrying a similar meaning as the modern ...
Güstrow
Güstrow (; la, Gustrovium) is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is capital of the Rostock district; Rostock itself is a district-free city and regiopolis.
It has a population of 28,999 (2020) and is the seventh largest town in Me ...
in 1696 and turned to
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
, which was equal to a
Free Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. In 1701 they gained the
citizenship
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
(german: Bürgerrecht) of Lüneburg. Even though the family there brought forth
cleric
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
s and
jurist
A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyses and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal qualification in law and often a legal practitioner. In the Uni ...
s thereunder a
canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
, a secular canon and a
dean
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
as well as a senator of
Hannover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German States of Germany, state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germa ...
it was not only confined to the urban educated middle class (german:
Bildungsbürgertum
''Bildungsbürgertum'' () is a social class that emerged in mid-18th-century Germany, as the educated social stratum of the bourgeoisie, men and women who had received an education based upon the metaphysical values of Idealism and Classical s ...
). Other members of the family acted as merchants – listed 1699 at the „Uraltes löbliches Kramer-Amt“, the Merchants
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
at Hamburg – and subsequently as internationally acting merchants.
Hanseatics
Grand Burghers of Hamburg

The trading firm was relocated in the middle of the 18th century by Carl Daniel Jauch (1714–1794) from the falling back Lüneburg to Hamburg, the ″Queen of the cities″. Since the 17th century Hamburg played a special role in Germany's economic history because thanks to its it came out of the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
as the wealthiest and
most populous of all German cities.
Hamburg was a strictly bourgeois
mercantile republic in which neither
nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
existed, which was exiled since 1276, nor
patricians
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after ...
in the strict sense of the formally defined class of governing elites found within the other
free imperial cities
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. In contrast to the mediatised
burgesses in the towns located in
monarchies
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), ...
which were governed by
authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political '' status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic vot ...
Hamburg was characterized by its free citizens tied to the
culture of England
The culture of England is defined by the cultural norms of England and the English people. Owing to England's influential position within the United Kingdom it can sometimes be difficult to differentiate English culture from the culture of the ...
. Although a republic the town was not a
democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose gov ...
moreover an
oligarchy
Oligarchy (; ) is a conceptual form of power structure in which power rests with a small number of people. These people may or may not be distinguished by one or several characteristics, such as nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, r ...
because it was governed solely by the
Hanseaten. They formed the small in Hamburg and
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
purely bourgeois upper class of society in the
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
and
republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
an states Hamburg,
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
and
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
.
These three cities built up between 1630 and 1650 the Hanseatic Community (german: Hanseatische Gemeinschaft). It was formed after the
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
became informally extinct in the beginning of the 17th century. Therefore, it has to be differentiated between the earlier Hanseatic merchants (german: Hansekaufmann) of the former Hanseatic League and the later
Hanseaten as a class of the three cities which built the Hanseatic Community.
Since the end of the 18th century the family belongs to the Hanseaten. (1765–1855) who is the
last common ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
of today's Jauch, gained at the end of the 18th century the
citizenship
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
(german: Bürgerrecht) of the Free Imperial and Hanseatic City of Hamburg and subsequently the hereditary
grand burghership (german: Großbürgerrecht).
Rittmeister
__NOTOC__
(German and Scandinavian for "riding master" or "cavalry master") is or was a military rank of a commissioned cavalry officer in the armies of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Scandinavia, and some other countries. A ''Rittmeister'' is typic ...
( en, captain of the cavalry) (1848–1930) was for almost twenty years till 1915 – when he volunteered regardless of his age for military service in the
Landwehr
''Landwehr'', or ''Landeswehr'', is a German language term used in referring to certain national army, armies, or militias found in nineteenth- and early twentieth-century Europe. In different context it refers to large-scale, low-strength fortif ...
cavalry - one of the last members of the
Hamburg Parliament
The Hamburg Parliament (german: Hamburgische Bürgerschaft; literally “Hamburgish Citizenry”) is the unicameral legislature of the German state of Hamburg according to the constitution of Hamburg. As of 2011 there were 121 members in the parli ...
, who were delegated as representatives of the grand burghers (german: Notabelnabgeordneter) and not contesting an election by the burghers.
In the
German Revolution of 1918–19
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
the workers' and soldiers' councils put the city administrations under their control ending the reign of the Hanseaten also in Hamburg.
Land Owners in Hamburg, Lords of Manors in the Kingdom of Denmark
The family owned on the
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Repu ...
next to the old Hamburg timber harbour and situated on the city's
dyke the Baroque house ''Stadtdeich'' number 10 and the nearby houses ''Stadtdeich'' 3 and ''Stadtdeich an der Elbseite'' (on the Elbside) 159. ''Stadtdeich'' 10 (sometimes referred to as ''Stadtdeich'' 9) was a which was destroyed in the
Operation Gomorrah
The Allied bombing of Hamburg during World War II included numerous attacks on civilians and civic infrastructure. As a large city and industrial centre, Hamburg's shipyards, U-boat pens, and the Hamburg-Harburg area oil refineries were attacke ...
end of July 1943 – the heaviest assault in the
history of aerial warfare
The history of aerial warfare began in ancient times, with the use of kites in China. In the third century, it progressed to balloon warfare. Airplanes were put to use for war starting in 1911, initially for reconnaissance, and then for aerial com ...
and later called the
Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
of Germany by British officials.

Destroyed along with this historical building were the family crypt on the former cemetery in
Hamm, Hamburg (german: Alter Hammer Friedhof) and the ''Auguste Jauch Woman's Home for Needy Widows'' (german: Auguste-Jauch-Stift für bedürftige Witwen) located ''Bürgerweide'' 59 there.
Around the
Outer Alster Lake the Jauch possessed the houses ''An der Alster'' 24, ''An der Alster'' 28 and ''Schwanenwik'' 18. In addition, they possessed country houses on the
Bille in
Reinbek
Reinbek (; probably from "Rainbek" = brook at the field margin; Northern Low Saxon: ''Reinbeek'') is a town located in Stormarn (district), Stormarn district in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein within the metropolitan regio ...
and in the then popular
garden suburb
The garden city movement was a 20th century urban planning movement promoting satellite communities surrounding the central city and separated with greenbelts. These Garden Cities would contain proportionate areas of residences, industry, and ...
Hamm
Hamm (, Latin: ''Hammona'') is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northeastern part of the Ruhr area. As of 2016 its population was 179,397. The city is situated between the A1 motorway and A2 motorway. Hamm railwa ...
.
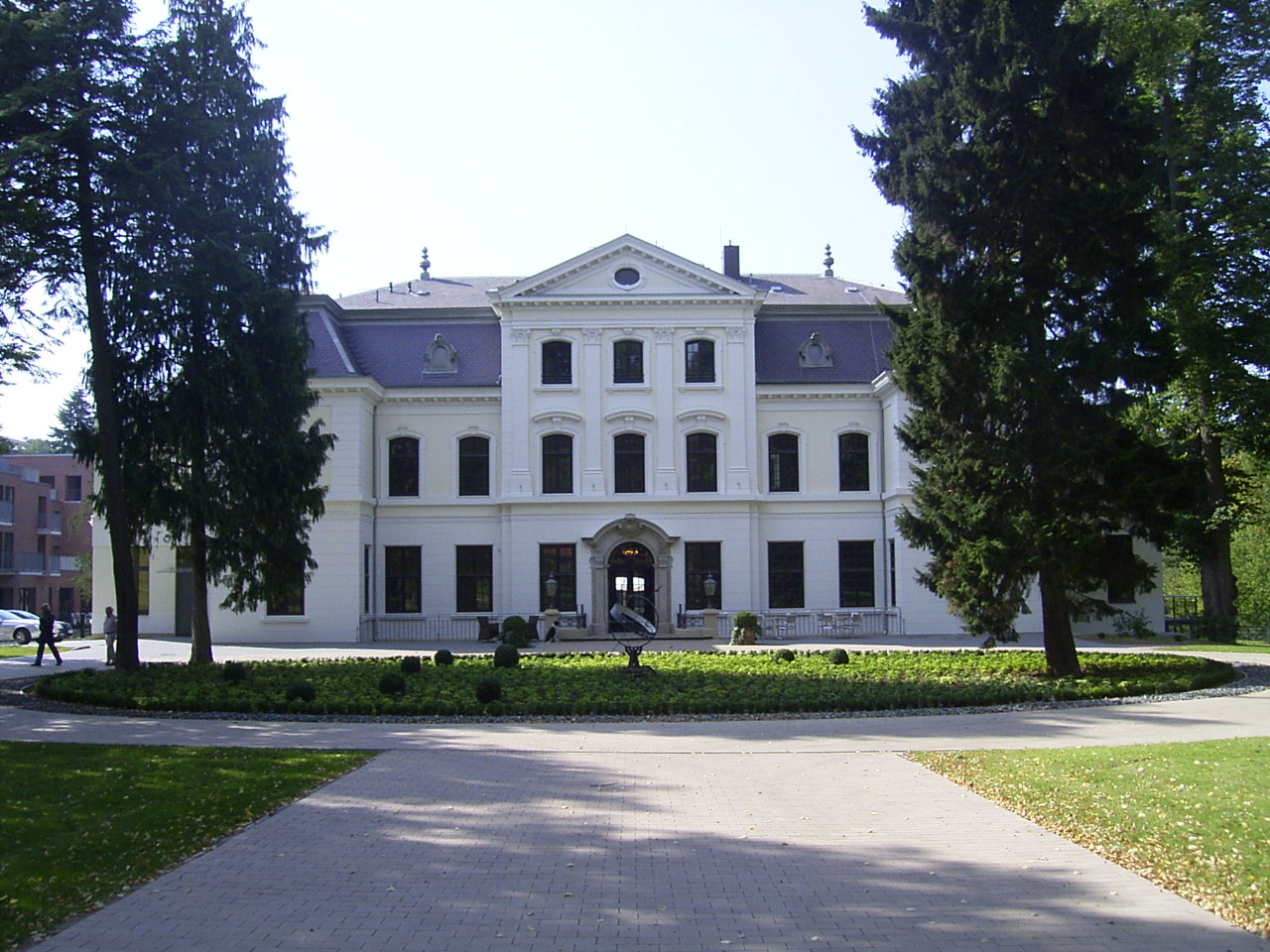

The regions surrounding Hamburg belonged to the
Duchy of Holstein
The Duchy of Holstein (german: Herzogtum Holstein, da, Hertugdømmet Holsten) was the northernmost state of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the present German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It originated when King Christian I of Denmark had his ...
and were since 1713 territory of the
Kingdom of Denmark
The Danish Realm ( da, Danmarks Rige; fo, Danmarkar Ríki; kl, Danmarkip Naalagaaffik), officially the Kingdom of Denmark (; ; ), is a sovereign state located in Northern Europe and Northern North America. It consists of Denmark, metropolitan ...
, later
Province of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein (german: Provinz Schleswig-Holstein ) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia (subsequently the Free State of Prussia after 1918) from 1868 to 1946.
History
It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and H ...
in the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Re ...
. Here became the property of the Jauch
Wellingsbüttel Manor
Wellingsbüttel Manor (German: Rittergut Wellingsbüttel, since Danish times: Kanzleigut Wellingsbüttel) is a former manor with a baroque manor house (German: ''Herrenhaus'') in Hamburg, Germany, which once enjoyed imperial immediacy (''Reichsf ...
, and
Krummbek Manor and the estates Fernsicht and Marienhof on the
Stör
The Stör () is a river in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, right tributary of the Elbe.
Its total length is . The Stör rises east of Neumünster, and flows west through Neumünster, Kellinghusen, and Itzehoe. The Stör joins the Elbe near Glücksta ...
at
Kellinghusen
Kellinghusen () is a town in the district of Steinburg in the ''Bundesland'' of Schleswig-Holstein.
Geography
Kellinghusen is located northeast of Itzehoe on both sides of the Stör River. The federal highway Bundesstraße 206 passes Kellingh ...
and Schwonendal in
Karby, Schleswig-Holstein.

Today the Jauch own the
Von Othegraven Winery. The
manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals w ...
, its
English garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
and the
vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards ...
Kanzemer Altenberg constitute a listed
cultural heritage site.
The manor house was heavily damaged at the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
by the
U.S. 10th Armored Division
The 10th Armored Division (nicknamed "Tiger Division") was an armored division of the United States Army in World War II. In the European Theater of Operations the 10th Armored Division was part of both the Twelfth United States Army Group an ...
shooting from the other side of the
Saar river
The Saar (; french: Sarre ) is a river in northeastern France and western Germany, and a right tributary of the Moselle. It rises in the Vosges mountains on the border of Alsace and Lorraine and flows northwards into the Moselle near Trier. It h ...
. It was restored and enlarged between 1954 and 1956. According to
Stuart Pigott
Stuart Pigott (born 26 May 1960 in Orpington, Kent) is a British wine critic and author who has lived in Berlin since 1993. Pigott mostly writes in German, and focuses on German wine. He writes for the specialist magazines ''Feinschmecker'' an ...
von Othegraven Winery ″is one of the most beautiful properties″ in the region.

The
plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
Armenia Lorena and other coffee plantations of the Jauch nearby
San Rafael Pie de la Cuesta in
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
were under severe pressure of the US government seized by the Guatemalan government in the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and expropriated without compensation in 1953.
Notables in the Hamburg Self-Government
While the
commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
s (german: Untertanen) in the landlocked
Imperial State
An Imperial State or Imperial Estate ( la, Status Imperii; german: Reichsstand, plural: ') was a part of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise si ...
s of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
were subjected to
bureaucracy
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
and its civil officialdom (german: Beamtentum), Hamburg was distinguished by its honorary self-government by the most respected of its free citizens, the Hamburg notables (german: Hamburger Notabeln).
The Jauch served mainly as honorary
almoner
An almoner (} ' (alms), via the popular Latin '.
History
Christians have historically been encouraged to donate one-tenth of their income as a tithe to their church and additional offerings as needed for the poor. The first deacons, mentioned ...
s (german: Armenpfleger) for Hamburg's , as provisors of the and as board members of their own and other humanitarian foundations. The Jauch belonged to the founding fathers of the ''Humanitarian Aid for ,
Hamm
Hamm (, Latin: ''Hammona'') is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northeastern part of the Ruhr area. As of 2016 its population was 179,397. The city is situated between the A1 motorway and A2 motorway. Hamm railwa ...
and
Horn
Horn most often refers to:
*Horn (acoustic), a conical or bell shaped aperture used to guide sound
** Horn (instrument), collective name for tube-shaped wind musical instruments
*Horn (anatomy), a pointed, bony projection on the head of various ...
'' (german: Hülfsverein für Borgfelde, Hamm und Horn), which took care of those poor who did not receive support from the city.
Keeping with the age-old Hanseatic tradition in setting up humanitarian foundations the Jauch maintained a daily
soup kitchen
A soup kitchen, food kitchen, or meal center, is a place where food is offered to the Hunger, hungry usually for free or sometimes at a below-market price (such as via coin donations upon visiting). Frequently located in lower-income neighborhoo ...
for the poor for free (german: Armenspeisung). They also built and maintained
almshouse
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) was charitable housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the medieval era. They were often targeted at the poor of a locality, at those from certain ...
s in Hamburg (german: Wohnstifte) and
Wellingsbüttel
Wellingsbüttel (), a quarter in the Wandsbek borough in the city of Hamburg in northern Germany, is a former independent settlement. In 2020 the population was 10,935.
History
The first records on Wellingsbüttel are from 1296. Wellingsbüttel ...
.

Johann Christian Jauch senior (1765–1855) served from 1820 until 1833 as
dyke-count and first dyke count (german: Ältester Deichgeschworener) of
Hamburg-Hammerbrook. He was in charge as first dyke count when the
dam failed during the
February flood of 1825 {{short description, Storm surge flood on the North Sea coast of Germany and the Netherlands
The February flood of 1825, also known in Germany as the Great Hallig Flood (''Große Halligflut''), was a devastating flood that occurred from 3 to 5 Febr ...
, 2.000 feet southeast of the Jauch house Stadtdeich 10 in Hamburg.

Cavalry Officers in the Hamburg Citizen Militia
In the
Hamburg Citizen Militia
The Hamburg Citizen Militia (german: Hamburger Bürgermilitär) or Hanseatic Citizen Guard (german: Hanseatische Bürgergarde) was a citizen militia of the States of the German Confederation, Free and Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Hamburg, fo ...
the
social class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the Upper class, upper, Middle class, middle and Working class, lower classes. Membership in a social class can for ...
and the
wealth
Wealth is the abundance of Value (economics), valuable financial assets or property, physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for financial transaction, transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the ...
of the individual predetermined the branch of his service and his
military rank
Military ranks are a system of hierarchical relationships, within armed forces, police, intelligence agencies or other institutions organized along military lines. The military rank system defines dominance, authority, and responsibility in a ...
– which was the opposite of the
Royal Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army (1701–1919, german: Königlich Preußische Armee) served as the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It became vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.
The Prussian Army had its roots in the cor ...
where the
officer rank
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent context ...
made the individual a member of the
upper class
Upper class in modern societies is the social class composed of people who hold the highest social status, usually are the wealthiest members of class society, and wield the greatest political power. According to this view, the upper class is gen ...
of
society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Socie ...
. The most prestigious citizens gladly served as officers in the militia.
The service in the cavalry was generally a badge of
high-ranking social status not least because of the high costs caused by maintaining the cavalry horses and the keeping of a groom which had to be borne by each cavalryman himself. All metal parts of a cavalry officer uniform had to be gilded. For these reasons the Hanseatic cavalry was the stomping ground for the
grand burgher
Grand Burgher aleor Grand Burgheress emale(from German: Großbürger ale Großbürgerin emale is a specific conferred or inherited title of medieval German origin and legally defined preeminent status granting exclusive constitutional privile ...
s.
The
conscripted
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
members of the family performed their service in the militia as
first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a s ...
s in the
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
under the cavalry commanders
Rittmeister
__NOTOC__
(German and Scandinavian for "riding master" or "cavalry master") is or was a military rank of a commissioned cavalry officer in the armies of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Scandinavia, and some other countries. A ''Rittmeister'' is typic ...
( en, captain of the cavalry)
Ernst Merck
Freiherr Ernst Merck (20 November 1811 – 6 July 1863) was a German businessman and politician.
Merck, born in Hamburg, was a member of the Frankfurt Parliament for a year from 1848 to 1849.
Merck was also the cavalry chief of the Hamburg Citize ...
and later Rittmeister Adolph
Godeffroy.
Ancestors from the Time of the Hanseatic League
Among the ancestors of the Hamburg branch of the family are several
First Mayors of the city-state of Hamburg, historically equivalent to a sovereign
head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
. One of these is (1470–1538) who was the head of the
Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
in Hamburg, implemented the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and became the first evangelical mayor of the city.
Progeny
Eleonora Maria Jauch (1732–1797) is the ancestress of the
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
to which belong her son the
burgomaster
Burgomaster (alternatively spelled burgermeister, literally "master of the town, master of the borough, master of the fortress, master of the citizens") is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chief m ...
(
head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
)
Christian Adolph Overbeck
Christian Adolph Overbeck (21 August 1755 in Lübeck – 9 March 1821 in Lübeck) was a German poet, and the Burgomaster of Lübeck.
Life
Family
Overbeck was the son of the lawyer, Georg Christian Overbeck (1713-1786) and his wife Eleonor ...
and her grandson the painter and head of the
Nazarene movement
The epithet Nazarene was adopted by a group of early 19th-century German Romantic painters who aimed to revive spirituality in art. The name Nazarene came from a term of derision used against them for their affectation of a biblical manner of c ...
Friedrich Overbeck.

Other offspring of the Jauch are the
Blessed
Blessed may refer to:
* The state of having received a blessing
* Blessed, a title assigned by the Roman Catholic Church to someone who has been beatified
Film and television
* ''Blessed'' (2004 film), a 2004 motion picture about a supernatural ...
Hanna Chrzanowska, the
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
-winning novelist
Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, especi ...
, the first International German Golf Champion , the
Barons Bolton, owners of the extinct duchy Bolton, branches of
Magnates of Poland
The magnates of Poland and Lithuania () were an aristocracy of Polish-Lithuanian nobility ('' szlachta'') that existed in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and, from the 1569 Union of Lublin, in the Polish–L ...
as the
Princes Czartoryski and the
Counts Potocki, as well as branches of the
Princes Podhorski and the .
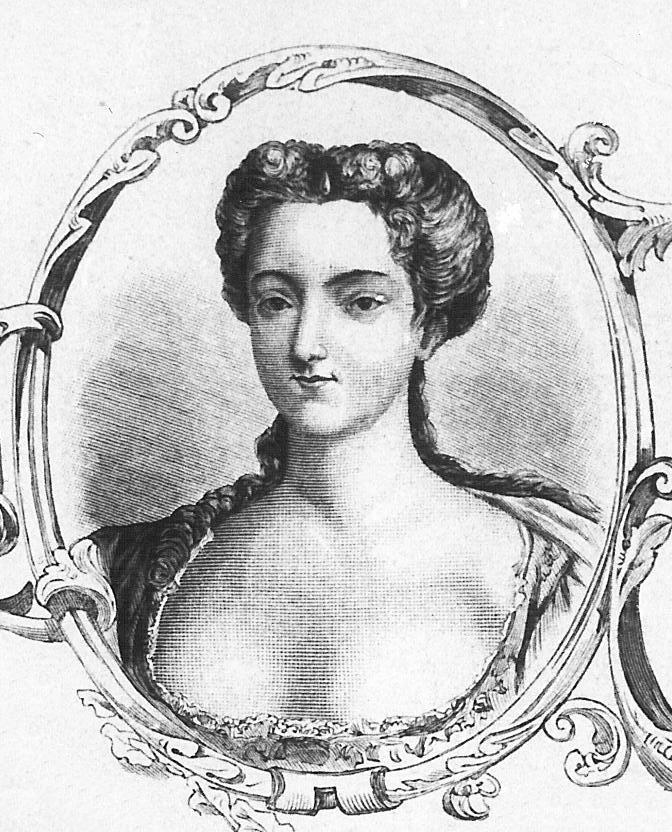

Constance Jauch (1722–1802) is the ancestress of the
Polish noble which was granted the
indygenat
''Indygenat'' or 'naturalization' in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was the grant of nobility to foreign nobles. To grant ''indygenat'', a foreign noble had to submit proof of their service to the Republic, together with proof of nobility is ...
by the
sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
. Her son Karol Mauricy Lelewel, godson of
King Augustus III of Poland
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
, belongs to the fathers of the
Constitution of May 3, 1791
The Constitution of 3 May 1791,; lt, Gegužės trečiosios konstitucija titled the Governance Act, was a constitution adopted by the Great Sejm ("Four-Year Sejm", meeting in 1788–1792) for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a dual mo ...
which is regarded to be the first modern constitution of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, grown out of the spirit of
Polish Enlightenment
The ideas of the Age of Enlightenment in Poland were developed later than in Western Europe, as the Polish bourgeoisie was weaker, and szlachta (nobility) culture (Sarmatism) together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth political system (Gol ...
. The Polish historian and rebel
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician.
Life
Born in Warsaw to a Polonized German family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 18 ...
(1786–1861), grandson of Constance Jauch, was creator of Poland's unofficial motto "
For our freedom and yours
For our freedom and yours ( pl, Za naszą i waszą wolność) is one of the unofficial mottos of Poland. It is commonly associated with the times when Polish soldiers, exiled from the partitioned Poland, fought in various independence movements ...
". He was member of Poland's Provisional Government in the
November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
1830.
Czar Nicholas I
, house = Romanov-Holstein-Gottorp
, father = Paul I of Russia
, mother = Maria Feodorovna (Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Gatchina Palace, Gatchina, Russian Empire
, death_date =
...
was dethroned in 1831 as
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
under his leadership as president of the radical . His brother Lieutenant Colonel
Jan Pawel Lelewel
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to:
Acronyms
* Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN
* Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code
* Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group
* Japanese Article Numb ...
(1796–1847) participated on 3 April 1833 in the
Frankfurter Wachensturm
The Frankfurter Wachensturm (German: charge of the Frankfurt guard house) on 3 April 1833 was a failed attempt to start a revolution in Germany.
Events
About 50 students attacked the soldiers and policemen of the Frankfurt Police offices '' Hau ...
, the attempt to start a revolution in all German states.
Colonel (1798–1859), son of Ludovica Jauch (1772–1805), was one of the thirtytwo members of the
Emperor Deputation on 3 April 1849 which offered Frederick William IV of Prussia the office of emperor. Lieutenant general of the
Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
Karl Fischer von Treuenfeld
Karl Freiherr von Fischer-Treuenfeld (31 March 1885 – 7 June 1946) was a German Waffen-SS commander. A brigade commander during the Nazi era, during the invasion of the Soviet Union, he commanded the 2 SS Infantry Brigade and the 1 SS Infant ...
, descendant of Eleonora Maria Jauch (1732–1797), was a close friend of
Erich Ludendorff
Erich Friedrich Wilhelm Ludendorff (9 April 1865 – 20 December 1937) was a German general, politician and military theorist. He achieved fame during World War I for his central role in the German victories at Liège and Tannenberg in 1914. ...
and one of the leading figures of the
Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch,Dan Moorhouse, ed schoolshistory.org.uk, accessed 2008-05-31.Known in German as the or was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party ( or NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff and othe ...
in 1923, a failed attempt by
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, to seize power in Germany. Charlotte Jauch's (1811–1872) grandson
Otto von Feldmann
Otto von Feldmann (6 August 1873, Berlin – 20 May 1945) was a German officer and politician
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, ...
(1873–1945) was policy officer of
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fro ...
and in charge of the campaign by which Hindenburg became
President of Germany
The president of Germany, officially the Federal President of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: link=no, Bundespräsident der Bundesrepublik Deutschland),The official title within Germany is ', with ' being added in international corres ...
in 1925.
History
Origins in Sulza
1512 Georg, Matthias and Nikolaus Jauch were registered as propertied men (german: Besessene Männer) in . Matthias Jauch Jauch there was
enfeoffed
In the Middle Ages, especially under the European feudal system, feoffment or enfeoffment was the deed by which a person was given land in exchange for a pledge of service. This mechanism was later used to avoid restrictions on the passage of ti ...
by the sovereign with the Segelitz estate. Georg Jauch (1606–1675) was
burgomaster
Burgomaster (alternatively spelled burgermeister, literally "master of the town, master of the borough, master of the fortress, master of the citizens") is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chief m ...
of
Sulza
Sulza is a municipality in the district Saale-Holzland, in Thuringia, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and ...
.
In Attendance on the Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg
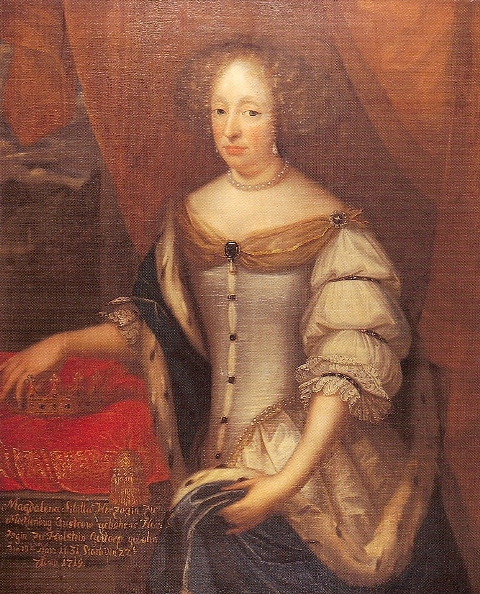

In the 17th century Sulza has been twice devastated, 1613 by the
and 1640 when it was plundered by Swedish troops. Johann Christian Jauch the Elder (1638–1718) left the fallen back Sulza and relocated to
Güstrow
Güstrow (; la, Gustrovium) is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is capital of the Rostock district; Rostock itself is a district-free city and regiopolis.
It has a population of 28,999 (2020) and is the seventh largest town in Me ...
where he entered 1662 the service of the
Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg at its residence
Güstrow Castle
Güstrow (; la, Gustrovium) is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is capital of the Rostock district; Rostock itself is a district-free city and regiopolis.
It has a population of 28,999 (2020) and is the seventh largest town in M ...
. He was a member of the ducal household of
Magdalena Sibylle, née Duchess of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorf, wife of
Gustav Adolph, Duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Gustav Adolph, Duke of Mecklenburg Güstrow(26 February 1633 – 6 October 1695) was the last ruler of Mecklenburg-Güstrow from 1636 until his death and last Lutheran Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg from 1636 to 1648.Jonathan ...
, until he became 1669 First
Valet de chambre
''Valet de chambre'' (), or ''varlet de chambre'', was a court appointment introduced in the late Middle Ages, common from the 14th century onwards. Royal households had many persons appointed at any time. While some valets simply waited on t ...
(german: Erster Lacquay und Taffeldecker) of Crown Prince Carl of
Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was a state of the Holy Roman Empire in Northern Germany, that existed on three occasions ruled by the House of Mecklenburg at Güstrow.
History
A first short-lived predecessor existed after the death of Henry IV, Duke of Me ...
. 1665 he married Ingborg Nicolai (†1696), who had come to Güstrow with the duchess Magdalena Sibylle from
Gottorf Castle
Gottorf Castle (german: Schloss Gottorf, da, Gottorp Slot, Low German: ''Gottorp'') is a castle and estate in the city of Schleswig, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is one of the most important secular buildings in Schleswig-Holstein, and ha ...
, serving her as
lady's maid and confidant. The social rank of a servant at these times mirrored the lordship − the higher the lordship, the better the opportunities for the servant to reach a prestigious position himself. A ducal valet de chambre ranked in
Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was a state of the Holy Roman Empire in Northern Germany, that existed on three occasions ruled by the House of Mecklenburg at Güstrow.
History
A first short-lived predecessor existed after the death of Henry IV, Duke of Me ...
equal to
The Very Reverend
The Very Reverend is a Style (manner of address), style given to members of the clergy. The definite article "The" should always precede "Reverend" as "Reverend" is a style or fashion and not a title.
Catholic
In the Catholic Church, the style i ...
, thus allowing the lordship to demonstrate its own rank. Suitably the first daughters of Johann Christian and Ingborg Jauch married members of the
nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
.
In 1688, Crown Prince Carl died without a male heir. Johann Christian Jauch the Elder quit the service and became
burgher
Burgher may refer to:
* Burgher (social class), a medieval, early modern European title of a citizen of a town, and a social class from which city officials could be drawn
** Burgess (title), a resident of a burgh in northern Britain
** Grand Bu ...
of the city of Güstrow, dealing at retail and being a court shoemaker, purveyor to the ducal family. His eldest son Johann Christopher Jauch (1669–1725) had been a stipendiary of the duke and carried out since the end of 1694 the function of a court chaplain (german: Hof- und Schlossprediger). After the death of the last Duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, Gustav Adolph, in 1695 the dukedom of
Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was a state of the Holy Roman Empire in Northern Germany, that existed on three occasions ruled by the House of Mecklenburg at Güstrow.
History
A first short-lived predecessor existed after the death of Henry IV, Duke of Me ...
became extinct. Though duchess Magdalena Sibylla maintained a small court until 1718 the residence Güstrow lost its splendour and relevance. Moreover, Ingborg Jauch had already died. Therefore, almost all family members left Güstrow 1696 and turned to
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
.
In Attendance on the House of Hanover
1701 the Jauchs became
burghers of
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
. At Lüneburg Johann Christopher Jauch (1669–1725) was
Royal British and Electoral Brunswick-Lüneburg Dean
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
of the Lutheran churches (german: Königlich Großbritannischer und Kurfürstlich Braunschweig-Lüneburgischer Stadtsuperintendent) at
St. John's Church, Lüneburg
The Church of John the Baptist (Germ. ''St. Johannis'' or ''Johanniskirche'') is the oldest Lutheran church in Lüneburg, Germany. It is located in the city centre. Lüneburg is on the European Route of Brick Gothic and the church is an example o ...
, while Johann Christian Jauch (1702–1778) became
canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
, 1754 subsenior collegii canonici, 1760
The Very Reverend
The Very Reverend is a Style (manner of address), style given to members of the clergy. The definite article "The" should always precede "Reverend" as "Reverend" is a style or fashion and not a title.
Catholic
In the Catholic Church, the style i ...
(german: Erster Domherr) and
vice-dean (german: Vizedekan) with the function of a
provost of the Lutheran cathedral of
Bardowick
Bardowick (''Bewick'' in Low Saxon) is a municipality in the district of Lüneburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is three miles north of Lüneburg on the navigable river Ilmenau. Bardowick is also the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective muni ...
. He married Clara Maria Rhüden (1710–1775), who was a great-great-grandchild of the
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
theologian of the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
(1559–1605), thereby ancestor of all later Jauchs, son of deacon Paul Gesner, who was taught by
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
and consecrated by
Johannes Bugenhagen
Johannes Bugenhagen (24 June 1485 – 20 April 1558), also called ''Doctor Pomeranus'' by Martin Luther, was a German theologian and Lutheran priest who introduced the Protestant Reformation in the Duchy of Pomerania and Denmark in the 16th ce ...
. Her great-great-grandfather, the professor of philosophy at Hamburg, Bernhard Werenberg (1577–1643), has been an opponent to the noted scientist
Joachim Jungius
Joachim Jungius (born Joachim Junge; 22 October 1587 – 23 September 1657) was a German mathematician, logician and philosopher of science.
Life
Jungius was a native of Lübeck. He studied metaphysics at the Universities of Rostock and Giess ...
at the same place. Her uncle was the predecessor of Johann Christopher Jauch and great-grandson of
Philipp Melanchthon
Philip Melanchthon. (born Philipp Schwartzerdt; 16 February 1497 – 19 April 1560) was a German Lutheran reformer, collaborator with Martin Luther, the first systematic theologian of the Protestant Reformation, intellectual leader of the Lu ...
Heinrich Jonathan Werenberg (1651–1713). Ludolph Friedrich Jauch (1698–1764), son of the dean Johann Christopher Jauch, was
Senior Pastor
A pastor (abbreviated as "Pr" or "Ptr" , or "Ps" ) is the leader of a Christianity, Christian congregation who also gives advice and counsel to people from the community or congregation. In Lutheranism, Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Or ...
of Lüneburg's St. Michael's Church (german: Michaeliskirche), his brother Tobias Christoph Jauch (1703–1776), was a legal practitioner and deputy (german: Stadt−Secretarius), member of the
municipal council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counci ...
(german: Magistrat) of Lüneburg. Carl Jauch (1735–1818) was Royal British and Electoral Brunswick-Lüneburg judge of the castle court of justice (german: Burggerichtsverwalter) in
Horneburg
Horneburg is a municipality southwest of Hamburg (Germany) in the Stade (district), district of Stade in Lower Saxony.
Horneburg is also the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Horneburg (Samtgemeinde), Horneburg.
History
Hor ...
and
canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
of the Cathedral of Bardowick, Friedrich August Jauch (1741–1796), son of the imperial
civil law notary
Civil-law notaries, or Latin notaries, are lawyers of noncontentious private civil law who draft, take, and record legal instruments for private parties, provide legal advice and give attendance in person, and are vested as public officers wit ...
Adolph Jauch (1705–1758), was senator and police governor of the city of
Hannover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German States of Germany, state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germa ...
.
Carl Jauch (1680–1755), merchant in
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
, has been a supporter of the theologian, alchemist and physician
Johann Konrad Dippel
Johann Konrad Dippel, also spelled Johann Conrad Dippel (10 August 1673 – 25 April 1734), was a German Pietist theologian, physician, alchemist and occultist.
Life
Dippel was born at Castle Frankenstein near Mühltal and Darmstadt, and theref ...
, by some authors debatably claimed to be the model for
Mary Shelley's novel ''
Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a sapient creature in an unorthodox scientific ex ...
''. After Dippel's expulsion from
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
1727 Carl Jauch gave shelter to the refugee who was 1729 expelled from Lüneburg, too. Carl Jauch was married to a grandniece of the
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
dean
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
(1640–1698), who strongly influenced the faith and the thinking of
Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard w ...
.
Eleonora Maria Jauch's (1732–1797) father-in-law was the
dean
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
of
Bardowick
Bardowick (''Bewick'' in Low Saxon) is a municipality in the district of Lüneburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is three miles north of Lüneburg on the navigable river Ilmenau. Bardowick is also the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective muni ...
, in whose foster-parental home
August Hermann Francke
August Hermann Francke (; 22 March 1663 – 8 June 1727) was a German Lutheran clergyman, theologian, philanthropist, and Biblical scholar.
Biography
Born in Lübeck, Francke was educated at the Illustrious Gymnasium in Gotha before he studie ...
1687 had been guest when he experienced his so-called "Lüneburg conversion" (german: Lüneburger Bekehrung), making him one of the earliest leaders of
Pietism
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy and ...
.
In Attendance on the Electors of Saxony and Kings of Poland
1698 Johann Christopher Jauch adjourned his function in
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
and served as court chaplain for
Christiane Eberhardine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
Christiane Eberhardine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (19 December 1671 – 4 September 1727) was Electress of Saxony from 1694 to 1727 (her death) and Queen Consort of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1697 to 1727 by marriage to Augustus I ...
, queen consort of Poland and grand duchess consort of Lithuania during her cure at
Pretzsch, encouraging her to keep at her
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
faith after the conversion of her husband to
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Christiane Eberhardine later was named by her Protestant countrymen "The Praying Pillar of Saxony" (german: Die Betsäule Sachsens)
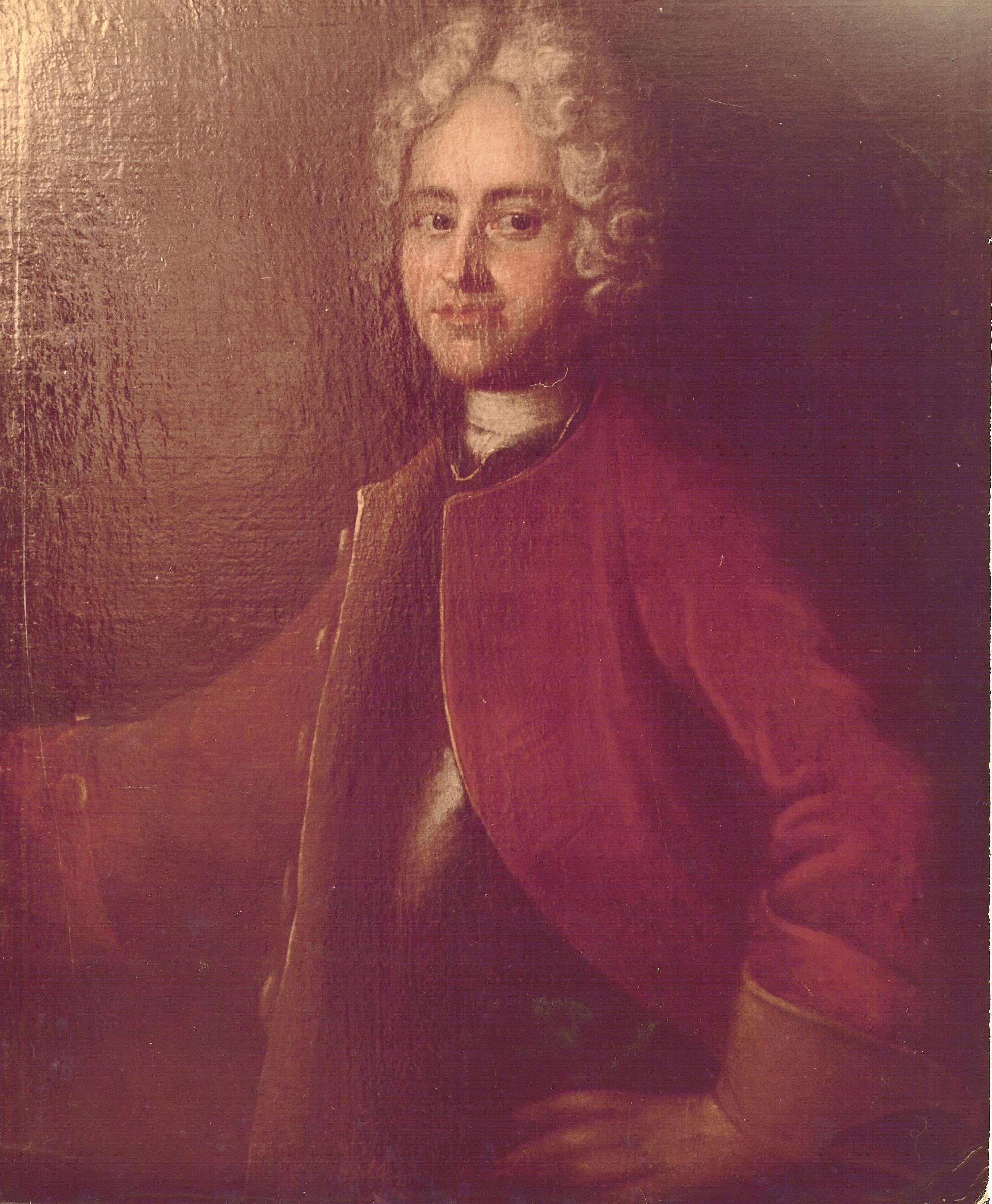


His brother
Joachim Daniel (1688–1754) served at first in the army of the
Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, before he changed 1705 as lieutenant into the Saxon army. He took part as a captain in the
first siege of Stralsund 1711–12 during the
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedi ...
. At the end he was contemporaneously royal Polish colonel (since 1736), electoral Saxon major general (since 1746), superintendent of the Saxon building authority in Poland (since 1721), with the title director (since 1736), remunerated for each function separately. His primary obligation was to supervise the baroque development of the city of
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
. Vital was his responsibility for the extensive merrymakings of the Saxon court at Warsaw.
When 1730 at the end of tremendous fireworks at
Zeithain
Zeithain is a municipality in the district of Meißen, in Saxony, Germany.
Historically, it is known for the Zeithain Encampment (''Zeithainer Zeltlager'' or ''Zeithainer Lustlager''), which was a huge agglomeration of tents and troops, involving ...
which lasted for five hours, instead of the correct "
VIVAT
''Viva'', ''vive'', and ''vivat'' are interjections used in the Romance languages. ''Viva'' in Spanish (plural ), Portuguese, and Italian (Also . in plural is rare), ''Vive'' in French, and ''Vivat'' in Latin (plural ) are subjunctive forms ...
" in front of 48 foreign princes and numerous other lords a mistake in writing occurred and a "FIFAT" was illuminated, he gained his cognomen "Fifat". He erected the Palais Jauch in Warsaw's suburb Solec and was architect for a number of prominent baroque buildings in
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
.
He married Eva Maria Münnich, said to be the daughter of the later Russian field marshal
Burkhard Christoph Count von Münnich (1683–1767), his predecessor as superintendent of the Saxon building authority. His son August von Jauch (b. 1731) was godson of King
Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as Ki ...
. The elaborate cradle endowed to his parents by the king, later the cradle for
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician.
Life
Born in Warsaw to a Polonized German family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 18 ...
, is exhibited in the
National Museum, Kraków
The National Museum in Kraków ( pl, Muzeum Narodowe w Krakowie), popularly abbreviated as MNK, is the largest museum in Poland, and the main branch of Poland's National Museum, which has several independent branches with permanent collections arou ...
.
Joachim Daniel Jauch is buried in the Capuchins Church in the
Miodowa
Miodowa (lit. ''Honey Street'') is a street in Warsaw's Old Town. More precisely, it links the Krakowskie (Cracow Suburb) Street in with Krasiński Square. It is also the name of a street in the Kazimierz district in Kraków.
History
In the 16 ...
in Warsaw.
Some members of the family followed Major General
Joachim Daniel von Jauch Joachim Daniel von Jauch (22 March 1688 – 3 May 1754) was a German-born architect who supervised the baroque development of Warsaw in Poland.
Early life and work
Joachim Daniel von Jauch was born into the Jauch family in Güstrow, Germany on 22 ...
(1688–1754) as officers into the Saxon and Polish army, two of them, Franz Georg Jauch (b. 1681) and Heinrich Georg Jauch (b. 1709), serving as lieutenant colonels – colonels in relation to the other regiments (german: Linienregimenter) – in the
Royal Guard
A royal guard is a group of military bodyguards, soldiers or armed retainers responsible for the protection of a royal person, such as the emperor or empress, king or queen, or prince or princess. They often are an elite unit of the regular arm ...
of King
Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as Ki ...
and King
Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
. Franz Georg Jauch 1724 was participating as a captain in the
Blood-Bath of Thorn, commanding a company of the .

Grand Burghers of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg
1699 Franz Jürgen Jauch and his brother Christian Jauch the Younger († 1720) served an apprenticeship as merchant in
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
. 1752 the merchant Joachim Daniel Jauch (1714–1795) moved his business from
Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
to Hamburg. Lt. Johann Georg Jauch (1727–1799) kidnapped 1754 Anna , daughter of the
Secretary of State of Hamburg Magnifizenz Johann Baptista Mutzenbecher (1691–1759), member of one of Hamburg's leading families and married her. Under Johann Christian Jauch senior (1765–1855), son of Johann Georg Jauch, the Jauchs became the most important and wealthiest wood traders of Hamburg who reached grand burghership status of the town. Thus, they became members of the ruling class, the
Hanseatics (''Hanseaten'') in one of the wealthiest cities of Germany, with whose financial capacity only
Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
could compete because of the local high nobility concentrating there and its wealth.
) on the left,
(b) Jauch's sawmill on the riverbank and another timber yard (german: Jauch's Holzsägerei und Lager) in the center,
(c) a
timber raft
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest mean ...
drifting down the Elbe in the middle left background bringing wood to Jauch
Christian Jauch senior's sons were founders of the three still existing branches of the family: Wellingsbüttel, Schönhagen und Fernsicht. His great-grandnephew was (1874–1923), naval architect and significant for the upgrowth of
submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s in
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, cousin of first
president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
of the
Federal Republic of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between ...
Theodor Heuss
Theodor Heuss (; 31 January 1884 – 12 December 1963) was a German liberal politician who served as the first president of West Germany from 1949 to 1959. His cordial nature – something of a contrast to the stern character of chancellor Ko ...
.
His eldest son Johann Christian Jauch junior (1802–1880) acquired the
Manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals w ...
Wellingsbüttel
Wellingsbüttel (), a quarter in the Wandsbek borough in the city of Hamburg in northern Germany, is a former independent settlement. In 2020 the population was 10,935.
History
The first records on Wellingsbüttel are from 1296. Wellingsbüttel ...
, previously domicile of the
penultimate
Penult is a linguistics term for the second to last syllable of a word. It is an abbreviation of ''penultimate'', which describes the next-to-last item in a series. The penult follows the antepenult and precedes the ultima. For example, the main ...
Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Beck, Friedrich Karl Ludwig, ancestor of the modern-day
British royal family. In addition to his land he leased the for hunting, which is today Hamburg's largest
nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
. Alongside his home in Hamburg he erected a deer park and a cage for the bears he brought with himself from his voyages to
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The poet Hebbel wrote to his long-time companion Elise Lensing, who had lived for many years in the house Stadtdeich 43, after she moved out:
1863 he was a patron of the international
agricultural exhibition on the
Heiligengeistfeld
Heiligengeistfeld (German: "Holy Ghost Field") is an area of Hamburg in the St. Pauli quarter. The ''Hamburger Dom'' funfair has been held there since 1893. When the area is not used for exhibitions, circuses or the Dom it is a car park. A buildi ...
.
His son Carl Jauch (1828–1888) was
Lord of Wellingsbüttel, too. He married Louise von Plessen (1827–1875), daughter of the
Grand Ducal Mecklenburg Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
(''Großherzoglich Mecklenburgischen Oberlanddrost'') Ulrich von Plessen und great-granddaughter of Baron (''
Reichsfreiherr
(; male, abbreviated as ), (; his wife, abbreviated as , literally "free lord" or "free lady") and (, his unmarried daughters and maiden aunts) are designations used as titles of nobility in the German-speaking areas of the Holy Roman Empire ...
'') Seneca von Gelting (1715–1786), who was married to a niece of
Johannes Thedens and had become highly wealthy as
chargé d'affaires
A ''chargé d'affaires'' (), plural ''chargés d'affaires'', often shortened to ''chargé'' (French) and sometimes in colloquial English to ''charge-D'', is a diplomat who serves as an embassy's chief of mission in the absence of the ambassador ...
of the
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
in
Cirebon
Cirebon (, formerly rendered Cheribon or Chirebon in English) is a port city on the northern coast of the Indonesian island of Java. It is the only coastal city of West Java, located about 40 km west of the provincial border with Central Java ...
. His grandfather Diederich Brodersen (1640–1717), ancestor of today's Jauchs of the Wellingsbüttel branch is also an ancestor to the composer
Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
. Because of this marriage the earliest notable ancestor is Helmoldus I de Huckelem, documented 1097 and connecting the Wellingsbüttel branch to numerous prominent other descendants of inter alia the von Plessen, von Moltke und von Oertzen families.
''Auguste Jauch'' (1822–1902) was one of the well known
benefactors to the poor of Hamburg. Colonel ''Hans Jauch'' (1883–1965), Commander of the
Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, regar ...
"Jauch", took part in putting down
communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
uprisings in 1920 and is founder of the Roman Catholic branch of the family.
Luise Jauch (1885–1933) was head nurse at
The Magic Mountain
''The Magic Mountain'' (german: Der Zauberberg, links=no, ) is a novel by Thomas Mann, first published in German in November 1924. It is widely considered to be one of the most influential works of twentieth-century German literature.
Mann st ...
at
Davos
, neighboring_municipalities= Arosa, Bergün/Bravuogn, Klosters-Serneus, Langwies, S-chanf, Susch
, twintowns =
}
Davos (, ; or ; rm, ; archaic it, Tavate) is an Alpine resort town and a municipality in the Prättigau/Davos R ...
, the second famous novel of Thomas Mann, when his wife
Katia Mann
Katia Mann (born Katharina Hedwig Pringsheim; July 24, 1883 – April 25, 1980) was the youngest child and only daughter (among four sons) of the German Jewish mathematician and artist Alfred Pringsheim and his wife Hedwig Pringsheim, who was ...
stood there 1912. Luise Jauch's traits have been utilized for the novel's head nurse Adritacia von Mylendonk.

In different polls
Günther Jauch
Günther Johannes Jauch (; born 13 July 1956) is a German television presenter, television producer, and journalist.
Career
Jauch is known for a unique style of informing and entertaining people that is generally considered witty and funny. ...
(b. 1956) was elected as “Most intelligent German” (2002), “Most wanted TV-star to become politician” (2003) and “Most popular German” (2005). He was awarded in 2001 the
World Award for entertainment. Since 2008 his sculpture is part of
Madame Tussauds
Madame Tussauds (, ) is a wax museum founded in 1835 by French wax sculptor Marie Tussaud in London, spawning similar museums in major cities around the world. While it used to be spelled as "Madame Tussaud's"; the apostrophe is no longer us ...
wax museum at Berlin.
Major Landowners in Guatemala
In Guatemala the coffee business was from the beginning in the hand of German investors. ″The US government forced the Guatemalan government to confiscate the German coffee holdings and to arrest German citizens. This allowed US companies to take control of the Guatemalan coffee industry.″
In the Times of the Third Reich
Heinrich Jauch, First State Attorney at Hamburg

Heinrich Jauch (1894–1945) was the Prosecuting Attorney of the Special Tribunal (german:
Sondergericht
A ''Sondergericht'' (plural: ''Sondergerichte'') was a German "special court". After taking power in 1933, the Nazis quickly moved to remove internal opposition to the Nazi regime in Germany. The legal system became one of many tools for this ai ...
) Hamburg in the criminal trial against the Soviet agent during the interwar period
Jan Valtin
Richard Julius Hermann Krebs (December 17, 1905 - January 1, 1951), better known by his alias Jan Valtin, was a German writer during the interwar period. He settled in the United States in 1938, and in 1940 (as Valtin) wrote his bestselling book '' ...
and 52 other defendants of whom nine were condemned to death. Jauch crushed with this trial the
Red Navy (german: Rote Marine) Hamburg. Valtin reports in his biography ''“Out of the Night”'', the US-bestseller of 1941 and the
TIME
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
“Book of the Year”, the trial and the executions:
The trial is regarded to be the model for the
Moscow Trials
The Moscow trials were a series of show trials held by the Soviet Union between 1936 and 1938 at the instigation of Joseph Stalin. They were nominally directed against "Trotskyists" and members of "Right Opposition" of the Communist Party of th ...
which were a series of three
show trial
A show trial is a public trial in which the judicial authorities have already determined the guilt or innocence of the defendant. The actual trial has as its only goal the presentation of both the accusation and the verdict to the public so th ...
s held in the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
at the instigation of
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
between 1936 and 1938. I these trials Stalin got rid of most of the surviving
Old Bolsheviks
Old Bolshevik (russian: ста́рый большеви́к, ''stary bolshevik''), also called Old Bolshevik Guard or Old Party Guard, was an unofficial designation for a member of the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Par ...
, as well as the former leadership of the Soviet
secret police
Secret police (or political police) are intelligence, security or police agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic of a ...
. In addition, it is believed that Heinrich Jauch has won the majority of the death sentences in Hamburg bevor he was called to
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
.
The first who were sentenced to death were executed on 19 May 1934. Formerly a
guillotine
A guillotine is an apparatus designed for efficiently carrying out executions by beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secured with stocks at th ...
had been used, but it had been discarded as a French method of decapitation. Since then people were put to death with an executioner's ax.
The executions under the direction of Heinrich Jauch became, entwined with the events of the
Altona Bloody Sunday
Altona Bloody Sunday (german: Altonaer Blutsonntag) is the name given to the events of 17 July 1932 when a recruitment march by the Nazi SA led to violent clashes between the police, the SA and supporters of the Communist Party of Germany ...
, the literary model for a novel and two films. The novelist
Arnold Zweig
Arnold Zweig (10 November 1887 – 26 November 1968) was a German writer, pacifist and socialist.
He is best known for his six-part cycle on World War I.
Life and work
Zweig was born in Glogau, Prussian Silesia (now Głogów, Poland), the son ...
red 1938 in a newspaper in
Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
the mistaken information that Dettmer and others had been executed by a master
butcher
A butcher is a person who may Animal slaughter, slaughter animals, dress their flesh, sell their meat, or participate within any combination of these three tasks. They may prepare standard cuts of meat and poultry for sale in retail or wholesal ...
named Fock who after a couple of months had committed suicide. Zweig made literary use of the
beheading
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the i ...
s and the alleged fate of the headsman and published 1943 the novel (''The axe of Wandsbek''). 1951 an
East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
film script,
The Axe of Wandsbek was adapted from the novel followed by the
West German
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
film . In memory of Jonny Dettmer a
Stolperstein
A (; plural ; literally 'stumbling stone', metaphorically a 'stumbling block') is a sett-size, concrete cube bearing a brass plate inscribed with the name and life dates of victims of Nazi extermination or persecution.
The project, initiat ...
was set into the ground in front of the house where he lived in
Hamburg-Eilbek
(former Eilbeck) is a quarter of the German city of Hamburg and part of the Wandsbek borough. It originated as a small village on the outskirts of Hamburg and was eventually incorporated when the city expanded. In 2020 the population was 22,235.
...
.
In 1937 Heinrich Jauch brought the charge against
Arnold Bernstein
Arnold Bernstein (23 January 1888, in Breslau, Silesia, German Empire – March 1971 in Ocean Ridge, Florida, U.S.[shipowner
A ship-owner is the owner of a merchant vessel (commercial ship) and is involved in the shipping industry. In the commercial sense of the term, a shipowner is someone who equips and exploits a ship, usually for delivering cargo at a certain frei ...]
and pioneer of transatlantic car transport. Bernstein was imprisoned on charges of foreign exchange offenses. At the time of his arrest, he was the owner of one of the largest Jewish businesses in Germany. The company was confiscated without compensation and after an additional payment of $30,000 in U.S. currency, Bernstein was allowed to leave Germany. The
show trial
A show trial is a public trial in which the judicial authorities have already determined the guilt or innocence of the defendant. The actual trial has as its only goal the presentation of both the accusation and the verdict to the public so th ...
is regarded to be the first major
Aryanization
Aryanization (german: Arisierung) was the Nazi term for the seizure of property from Jews and its transfer to non-Jews, and the forced expulsion of Jews from economic life in Nazi Germany, Axis-aligned states, and their occupied territories. I ...
of Jewish property.

Similarly, Heinrich Jauch organized that the Nazi state reached control over the trading firm
Alfred C. Toepfer Company owned by
Alfred Toepfer
Alfred Carl Toepfer (13 July 1894 in Hamburg – 8 October 1993 in Hamburg) was a German entrepreneur, owner of the company Toepfer International and founder of the Alfred Toepfer Foundation. He helped to shape the original internal markets of the ...
. He arrested Toepfer on charges of foreign exchange offenses between 1937 and 1938 until Toepfer gave up control over his firm.
Jauch & Hübener and the German Resistance to Nazism
Major General
Hans Oster
Hans Paul Oster (9 August 1887 – 9 April 1945) was a general in the ''Wehrmacht'' and a leading figure of the anti-Nazi German resistance from 1938 to 1943. As deputy head of the counter-espionage bureau in the ''Abwehr'' (German military inte ...
(1887–1945), one of the earliest and most determined opponents of
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
and
Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
, moving spirit of
German resistance German resistance can refer to:
* Freikorps, German nationalist paramilitary groups resisting German communist uprisings and the Weimar Republic government
* German resistance to Nazism
* Landsturm, German resistance groups fighting against France d ...
from 1938 to 1943, was a first cousin-in-law of
Rittmeister
__NOTOC__
(German and Scandinavian for "riding master" or "cavalry master") is or was a military rank of a commissioned cavalry officer in the armies of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Scandinavia, and some other countries. A ''Rittmeister'' is typic ...
( en, captain of the cavalry) (1888–1976). Walter Jauch was the founder of Jauch & Hübener, who were at the beginning of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
the largest
insurance broker
An insurance broker is an intermediary who sells, solicits, or negotiates insurance on behalf of a client for compensation. An insurance broker is distinct from an insurance agent in that a broker typically acts on behalf of a client by negoti ...
in
continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
. In the
Oster Conspiracy
The Oster Conspiracy (german: Septemberverschwörung, lit=September Conspiracy) of 1938 was a proposed plan to overthrow German ''Führer'' Adolf Hitler and the Nazi regime if Germany went to war with Czechoslovakia over the Sudetenland. It was led ...
Oster planned already in 1938 to assassinate German dictator
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, the leader of Nazi Germany. Oster and his opposition group including
Hans von Dohnányi
Hans von Dohnanyi (; originally ''Johann von Dohnányi'' ; 1 January 1902 – 8 or 9 April 1945) was a German jurist. He used his position in the Abwehr to help Jews escape Germany, worked with German resistance against the Nazi régim ...
were supported by Jauch & Hübener, today's German branch of
Aon Corporation
Aon PLC () is a British-American multinational financial services firm that sells a range of risk-mitigation products, including Commercial Risk, Investment, Wealth and Reinsurance solutions, as well as boutique strategy consulting through Aon ...
. Walter Jauch's co-founder was arrested 1945 in Hamburg and hanged in late April 1945 without trial, a few days before the end of
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
Robert Jauch, officer commanding in the battle of Stalingrad
Robert Jauch (1913–2000) fought as an officer, almost as an
artillery observer
An artillery observer, artillery spotter or forward observer (FO) is responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire onto a target. It may be a ''forward air controller'' (FAC) for close air support (CAS) and spotter for naval gunfire su ...
(german: Vorgeschobener Beobachter (VB)), ultimately as
first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a s ...
and
officer commanding
The officer commanding (OC), also known as the officer in command or officer in charge (OiC), is the commander of a sub-unit or minor unit (smaller than battalion size), principally used in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. In other countries, ...
(OC) of an
artillery battery
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to fac ...
of the Panzer-Artillerieregiment 16, part of the
16. Panzer-Division, in a number of major battles, including the
Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
, the
Battle of Kiev (1941)
The First Battle of Kiev was the German name for the operation that resulted in a huge encirclement of Soviet troops in the vicinity of Kiev during World War II. This encirclement is considered the largest encirclement in the history of warfar ...
, the
First Battle of Kharkov
The First Battle of Kharkov, so named by Wilhelm Keitel, was the 1941 battle for the city of Kharkov, Ukrainian SSR, during the final phase of Operation Barbarossa between the German 6th Army of Army Group South and the Soviet Southwestern F ...
and the
Battle of Kalach
The Battle of Kalach) and English-language historiography. The Soviet history of World War II (История второй мировой войны 1939–1945 в двенадцати томах) considers the battles at Kalach to have been ...
. In 1942–1943 he took part in the
Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
. Of about 400,000 German casualties during the battle about 150,000 fell in the "Cauldron" of Stalingrad itself. The surviving nearly 110,000 Germans of which 2,500 were officers were captured in Stalingrad. Among those was Robert Jauch, who surrendered on his thirtieth birthday, the 2 February 1943. Out of the 110,000 survivors only about 5,000 ever returned from Russia. Robert Jauch became a member of the League of German Officers (german:
Bund Deutscher Offiziere) (BDO), an anti-Nazi organization. He came back to Germany after seven years as a prisoner of war in
Yelabuga
Yelabuga (alternative spelling that reflects the Cyrillic spelling: Elabuga; russian: Елабуга; tt-Cyrl, Алабуга, ''Alabuğa'') is a town in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia, located on the right bank of the Kama River and east ...
,
Kuibishev and
Simferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, ...
as one of the ″
late homecomers″ (german: Spätheimkehrer) in 1950.
Casualties of World War I and World War II

Eight lineage holders of the Jauch, half of all lineage holders in these generations, died as soldiers on the different European battlefields of the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, seven of them
killed in action. They all with only one exception had no descendants.
Lt. Rudolf Jauch (1891–1915) died 1915 in the sinking of the submarine
U-40 by the submarine
HMS C24, cooperating with the
decoy-ship ''Taranki''. It was the first U-boot trap victory by the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
during the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The
Distinguished Service Cross The Distinguished Service Cross (D.S.C.) is a military decoration for courage. Different versions exist for different countries.
*Distinguished Service Cross (Australia)
The Distinguished Service Cross (DSC) is a military decoration awarded to ...
which has been awarded for this action to Commander Captain Frederick Henry Taylor is part of the collection of the
National Maritime Museum
The National Maritime Museum (NMM) is a maritime museum in Greenwich, London. It is part of Royal Museums Greenwich, a network of museums in the Maritime Greenwich World Heritage Site. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United ...
at Greenwich. The wreck was discovered a hundred years later approximately off
Eyemouth
Eyemouth ( sco, Heymooth) is a small town and civil parish in Berwickshire, in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland. It is east of the main north–south A1 road and north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
The town's name comes from its location at th ...
,
Berwickshire
Berwickshire ( gd, Siorrachd Bhearaig) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in south-eastern Scotland, on the English border. Berwickshire County Council existed from 1890 until 1975, when the area became part of th ...
, Scotland. It is placed as a controlled site under the
Protection of Military Remains Act 1986
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although th ...
. – Since their joint training als
officer cadet
Officer Cadet is a rank held by military cadets during their training to become commissioned officers. In the United Kingdom, the rank is also used by members of University Royal Naval Units, University Officer Training Corps and University Air ...
s on Rudolf Jauch was a friend of the later
pacifist
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaign ...
and
anti-war
An anti-war movement (also ''antiwar'') is a social movement, usually in opposition to a particular nation's decision to start or carry on an armed conflict, unconditional of a maybe-existing just cause. The term anti-war can also refer to pa ...
activist
Martin Niemöller
Friedrich Gustav Emil Martin Niemöller (; 14 January 18926 March 1984) was a German theologian and Lutheran pastor. He is best known for his opposition to the Nazi regime during the late 1930s and for his widely quoted 1946 poem " First they ca ...
.
First Lieutenant Günther Jauch (1919–1942), aid de camp of the Panzer-Artillerieregiment 227 was killed in action during the
Lyuban Offensive Operation
The Battle of Lyuban, Lyuban offensive operation or Battle of the Volkhov (7 January 1942 – 30 April 1942) (Russian: Любанская наступательная операция; German: Schlacht am Wolchow) was a Soviet offensive operatio ...
, a major Russian attack as part of the
Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
which was one of the longest and most destructive
sieges in history and overwhelmingly the
most costly in terms of casualties. His final resting place is since 2000 on the German
war cemetery
A war grave is a burial place for members of the armed forces or civilians who died during military campaigns or operations.
Definition
The term "war grave" does not only apply to graves: ships sunk during wartime are often considered to be ...
Sologubovka.
Daughters of the Jauch and their Descendants
Catharina Elisabeth Jauch (1671–1736) married von Naumann

Catharina Elisabeth Jauch (1671–1736) married the later colonel and architect of
King August the Strong,
Johann Christoph von Naumann
Johann Christoph von Naumann was the urban designer who, with Matthäus Daniel Pöppelmann, designed portions of the city of Warsaw, Poland, including the Saxon Axis and other important streetscapes. 1729-30 he modernized the town hall at Bautzen ...
. He was a member of the
diplomatic mission
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
of the
Holy League in the course of the
Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
1699 with the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, which ended the
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War (german: Großer Türkenkrieg), also called the Wars of the Holy League ( tr, Kutsal İttifak Savaşları), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Pola ...
.
Juliana Agnesa Jauch (1673 bis nach 1712) married Baroness von Schmiedel
Juliana Agnesa Jauch (1673–1712) married Baron (german:
Freiherr
(; male, abbreviated as ), (; his wife, abbreviated as , literally "free lord" or "free lady") and (, his unmarried daughters and maiden aunts) are designations used as titles of nobility in the German-speaking areas of the Holy Roman Empire ...
) Johann Rudolf von Schmiedel, Saxon district governor (german:
Amtshauptmann) and councillor of the board of domains (german: Landkammerrat), their son being Baron Franz Rudolf von Schmiedel, Lord Steward of the Household (german:
Hofmarschall
The ''Hofmarschall'' (plural: Hofmarschälle) was the administrative official in charge of a princely German court, supervising all its economic affairs.
Historically, every civil service was regarded as court service (e.g. the Russian nobility is ...
) of the extravagant
Ernest Augustus I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Ernest Augustus I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar (German: ''Ernst August I''; 19 April 1688 – 19 January 1748), was a duke of Saxe-Weimar and, from 1741, of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach.
Biography
He was the second but eldest surviving son of Johann Ernst ...
.
Constance Jauch (1722–1802) married von Lölhöffel

Joachim Daniel Jauch's daughter Constance Jauch (1722–1802) married Heinrich Lölhöffel von Löwensprung (1705–1763), privy councillor (german:
Hofrat
''Geheimrat'' was the title of the highest advising officials at the Imperial, royal or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic r ...
) and physician to the King
Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
. After the death of her father she erected 1755 by
Ephraim Schröger the
Lelewel Palace – her polonized name – in the
Miodowa
Miodowa (lit. ''Honey Street'') is a street in Warsaw's Old Town. More precisely, it links the Krakowskie (Cracow Suburb) Street in with Krasiński Square. It is also the name of a street in the Kazimierz district in Kraków.
History
In the 16 ...
. Regardless the early death of her husband in 1763 she enabled a splendid career for her children.
Her son Karol Maurycy Lelewel (1750–1830) married a daughter of the
starosta
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. Th ...
of Babice, niece of the
archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
and
metropolitan of the archdiocese of
Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
(1745–1831). Karol Mauricy Lelewel was a Royal Polish captain, reached the
indygenat
''Indygenat'' or 'naturalization' in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was the grant of nobility to foreign nobles. To grant ''indygenat'', a foreign noble had to submit proof of their service to the Republic, together with proof of nobility is ...
, the naturalisation as a Polish noble, and became a member of the
general sejm
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED O ...
. 1789 he became appointed as
cup-bearer
A cup-bearer was historically an officer of high rank in royal courts, whose duty was to pour and serve the drinks at the royal table. On account of the constant fear of plots and intrigues (such as poisoning), a person must have been regarded as ...
of the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
( pl,
Podczaszy wielki litewski), a title possessed prior by
Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch ...
before he was elected as the last king and grand duke of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Karol Mauricy was from 1778 until 1794 the lawyer and treasurer of the
Commission of National Education
The Commission of National Education ( pl, Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, KEN; lt, Edukacinė komisija) was the central educational authority in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, created by the Sejm and King Stanisław II August on October 14 ...
, which was because of its vast authority and autonomy considered the first Ministry of Education in European history. Lelwel was also centrally linked to another important achievement of the
Polish Enlightenment
The ideas of the Age of Enlightenment in Poland were developed later than in Western Europe, as the Polish bourgeoisie was weaker, and szlachta (nobility) culture (Sarmatism) together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth political system (Gol ...
, the
Constitution of May 3, 1791
The Constitution of 3 May 1791,; lt, Gegužės trečiosios konstitucija titled the Governance Act, was a constitution adopted by the Great Sejm ("Four-Year Sejm", meeting in 1788–1792) for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a dual mo ...
.
After 1789 during the
Sejm Wielki
The Great Sejm, also known as the Four-Year Sejm (Polish: ''Sejm Wielki'' or ''Sejm Czteroletni''; Lithuanian: ''Didysis seimas'' or ''Ketverių metų seimas'') was a Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was held in Wars ...
the reformers had to sacrifice many of their privileges in order to gain support for the Constitution of May the 3rd. Nevertheless, it is often argued, with quite some force, that because of the efforts of the Commission of National Education, the Polish language and culture did not disappear into oblivion, during the
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
- heavy
Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
and
Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationa ...
notwithstanding.

Constance Jauch's grandsons were Joachim, Prot und Jan Pawel Lelewel.
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician.
Life
Born in Warsaw to a Polonized German family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 18 ...
(1786–1861) became Poland's most famous historian. He was a rebel, creator of Poland's unofficial motto "
For our freedom and yours
For our freedom and yours ( pl, Za naszą i waszą wolność) is one of the unofficial mottos of Poland. It is commonly associated with the times when Polish soldiers, exiled from the partitioned Poland, fought in various independence movements ...
", member of
Poland's Provisional Government 1830, was jointly with
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
and
Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,["Engels"](_blank)
'' Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
(''Demokratische Gesellschaft zur Einigung und Verbrüderung aller Völker (Brüssel)''). The
anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not neces ...
Michail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary ...
was strongly influenced by him. He was a friend of
Gilbert du Motier, marquis de Lafayette
Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de La Fayette (6 September 1757 – 20 May 1834), known in the United States as Lafayette (, ), was a French aristocrat, freemasonry, freemason and military officer who fought in the Ameri ...
, who had given shelter to him in his manor Lagrange, where he was later arrested and then expelled from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. The 29 May is Lelewel's memorial day in the Jewish almanc for his commitment for the
Jewish emancipation
Jewish emancipation was the process in various nations in Europe of eliminating Jewish disabilities, e.g. Jewish quotas, to which European Jews were then subject, and the recognition of Jews as entitled to equality and citizenship rights. It incl ...
.
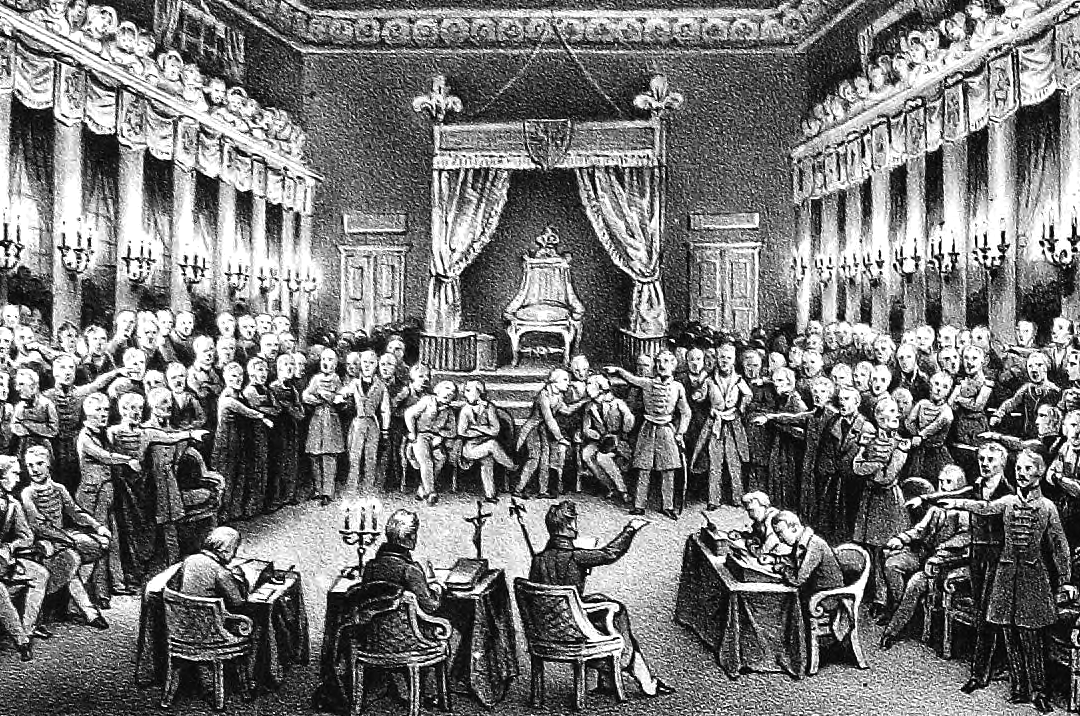
Prot Lelewel (1790–1884) served as a captain during the
French invasion of Russia
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental block ...
, participated 1812 in the
Battle of Berezina
The Battle of (the) Berezina (or Beresina) took place from 26 to 29 November 1812, between Napoleon's Grande Armée and the Imperial Russian Army under Field Marshal Wittgenstein and Admiral Chichagov. Napoleon was retreating back toward Pola ...
and 1813 in the
Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva ...
and was decorated as a chevalier of the
Légion d'honneur
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon ...
and with the silver medal of the
Virtuti Militari
The War Order of Virtuti Militari (Latin: ''"For Military Virtue"'', pl, Order Wojenny Virtuti Militari) is Poland's highest military decoration for heroism and courage in the face of the enemy at war. It was created in 1792 by Polish King Stan ...
. Lieutenant Colonel
Jan Pawel Lelewel
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to:
Acronyms
* Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN
* Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code
* Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group
* Japanese Article Numb ...
(1796–1847), was a Polish freedom fighter who unsuccessfully defended 1831
Praga
Praga is a district of Warsaw, Poland. It is on the east bank of the river Vistula. First mentioned in 1432, until 1791 it formed a separate town with its own city charter.
History
The historical Praga was a small settlement located at ...
against the Russian invasion and participated on 3 April 1833 in the
Frankfurter Wachensturm
The Frankfurter Wachensturm (German: charge of the Frankfurt guard house) on 3 April 1833 was a failed attempt to start a revolution in Germany.
Events
About 50 students attacked the soldiers and policemen of the Frankfurt Police offices '' Hau ...
, the attempt to start a revolution in all German states. 1816–1826 he modernized
Zamość Fortress
Zamość Fortress ( pl, Twierdza Zamość) is a set of fortifications constructed together with the city of Zamość (southeastern Poland). It was built between 1579 and 1618, and the construction was initiated by Chancellor and Hetman Jan Zamoys ...
, after his escape from Poland and Germany he became 1837–1947 head engineer of the
Canton of Bern
The canton of Bern or Berne (german: Kanton Bern; rm, Chantun Berna; french: canton de Berne; it, Canton Berna) is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. Its capital city, Bern, is also the ''de facto'' capital of Switzerland. ...
.
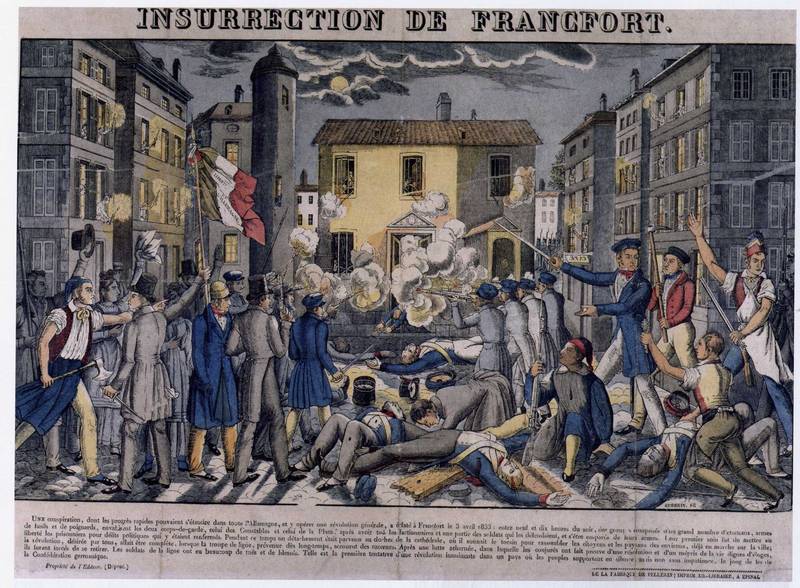

Constance Jauch's daughter Teresa Lelewelowna (1752–1814) married Adam Józef Cieciszowski (1743–1783), brother of the archbishop and metropolitan . He was
Great Scribe of Lithuania
Great Scribe of Lithuania ( lat, notarius magnus Lithuaniae) was a central, though non-Senatorial, office in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Great Scribe served as an adviser to the Grand Duke of Lithuania and his chancellor.
History ...
( la, notarius magnus Lithuaniae) and knight of the
Order of Saint Stanislaus
The Order of Saint Stanislaus ( pl, Order Św. Stanisława Biskupa Męczennika, russian: Орден Святого Станислава), also spelled Stanislas, was a Polish order of knighthood founded in 1765 by King Stanisław August Ponia ...
. Her granddaughter Aleksandra Franciszka Cieciszowska was married to the Polish
minister Jan Paweł Łuszczewski 1784–1795 private secretary of the last King and Grand Duke of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch ...
. He was nominated as count by the King
Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
. Their granddaughter
Jadwiga Łuszczewska
Jadwiga Łuszczewska (pen name: ''Deotyma'' ( Diotima); 1 July 1834 – 23 September 1908) was a Polish poet, novelist and salonniére. She was born and died in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abb ...
(1834–1908), daughter of the economist Wacław Józef Łuszczewski and the writer Magdalena Łuszczewska, was a Polish poet and novelist.
Great-grandson of Constance Jauch was the
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
-winning novelist, author of "
Quo vadis
''Quō vādis?'' (, ) is a Latin phrase meaning "Where are you marching?". It is also commonly translated as "Where are you going?" or, poetically, "Whither goest thou?"
The phrase originates from the Christian tradition regarding Saint Pete ...
",
Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, especi ...
(1846–1916). His daughter was the painter Jadwiga Sienkiewicz-Korniłowiczowa.
Another great-grandson was the founder of the Polish historical study of literature
Ignacy Chrzanowski (1866–1940), who died during the
Sonderaktion Krakau
''Sonderaktion Krakau'' was a German operation against professors and academics of the Jagiellonian University and other universities in German-occupied Kraków, Poland, at the beginning of World War II. It was carried out as part of the much bro ...
at
Sachsenhausen concentration camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners ...
. His son Lieutenant Bogdan Chrzanowski was murdered by Soviet soldiers, on the expressed orders of
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, in the
Katyn massacre
The Katyn massacre, "Katyń crime"; russian: link=yes, Катынская резня ''Katynskaya reznya'', "Katyn massacre", or russian: link=no, Катынский расстрел, ''Katynsky rasstrel'', "Katyn execution" was a series of m ...
. His daughter
Hanna Chrzanowska is being investigated by the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
for possible
saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
hood. The council of
cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
s in
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
has decreed that she has practised the
cardinal virtues
The cardinal virtues are four virtues of mind and character in both classical philosophy and Christian theology. They are prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance. They form a virtue theory of ethics. The term ''cardinal'' comes from the ...
of Faith, Hope and Charity to a heroic degree and, therefore, may be referred to as
Venerable
The Venerable (''venerabilis'' in Latin) is a style, a title, or an epithet which is used in some Western Christian churches, or it is a translation of similar terms for clerics in Eastern Orthodoxy and monastics in Buddhism.
Christianity
Cathol ...
Servant of God
"Servant of God" is a title used in the Catholic Church to indicate that an individual is on the first step toward possible canonization as a saint.
Terminology
The expression "servant of God" appears nine times in the Bible, the first five in th ...
.
Constance Jauch's granddaughter Anna Cieciszowska was sister-in-law of
Magdalena Agnieszka Sapieżyna (1739–1780), daughter of
Antoni Benedykt Lubomirski and informal consort of King Stanisław August Poniatowski. Great-aunt of Constance's progeny Lelewel was Jadwiga Walewska (b. 1740), sister-in-law of Countess
Maria Walewska
Marie Walewska, Countess Walewska (née Łączyńska; pl, Maria Walewska; 7 December 1786 – 11 December 1817) was a Poles, Polish noblewoman and an important figure at the court of Emperor Napoleon, Napoleon I with the role to influence him ...
(1786–1817), mistress of
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
.
Eleonora Maria Jauch (1732–1797) married Overbeck
Eleonora Maria Jauch (1732–1797), daughter of
The Very Reverend
The Very Reverend is a Style (manner of address), style given to members of the clergy. The definite article "The" should always precede "Reverend" as "Reverend" is a style or fashion and not a title.
Catholic
In the Catholic Church, the style i ...
and
vice-dean of the cathedral of
Bardowick
Bardowick (''Bewick'' in Low Saxon) is a municipality in the district of Lüneburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is three miles north of Lüneburg on the navigable river Ilmenau. Bardowick is also the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective muni ...
Johann Christian Jauch (1702–1788), married Georg Christian Overbeck (1713–1786), lawyer at
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
and son of the dean Caspar Nicolaus Overbeck. Her son was the mayor of Lübeck
Christian Adolph Overbeck
Christian Adolph Overbeck (21 August 1755 in Lübeck – 9 March 1821 in Lübeck) was a German poet, and the Burgomaster of Lübeck.
Life
Family
Overbeck was the son of the lawyer, Georg Christian Overbeck (1713-1786) and his wife Eleonor ...
(1755–1821). Before he was a senator of Lübeck and sent three times as ambassador Lübeck's to
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, where he attended on 1 April 1810 the marriage of
Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
and
Marie Louise, Duchess of Parma
french: Marie-Louise-Léopoldine-Françoise-Thérèse-Josèphe-Lucie it, Maria Luigia Leopoldina Francesca Teresa Giuseppa Lucia
, house = Habsburg-Lorraine
, father = Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Maria Theresa of ...
in the
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
and later the "banquet imperial" there, distorting in his ironical,
Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish Satire, satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whig (British political party), Whigs, then for the Tories (British political party), Tories), poe ...
citing comment a line of
Virgil's Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan_War#Sack_of_Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to ...
: "quaeque et pulcerrima vidi, et quorum pars parva fui.".


Her grandson was the painter and head of the
Nazarene movement
The epithet Nazarene was adopted by a group of early 19th-century German Romantic painters who aimed to revive spirituality in art. The name Nazarene came from a term of derision used against them for their affectation of a biblical manner of c ...
Johann Friedrich Overbeck
Johann Friedrich Overbeck (3 July 1789 – 12 November 1869) was a German painter. As a member of the Nazarene movement, he also made four etchings.
Early life and education
Born in Lübeck, his ancestors for three generations had been Protes ...
(1789–1869), decorated with the Prussian
Order Pour le Mérite for Sciences and Arts. On 7 February 1857
Pope Pius IX
Pope Pius IX ( it, Pio IX, ''Pio Nono''; born Giovanni Maria Mastai Ferretti; 13 May 1792 – 7 February 1878) was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878, the longest verified papal reign. He was notable for convoking the First Vatican ...
came for a personal visit in his home, the Villa Cancellotti next to the Via Merulana in
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. At that time he was painting the large-sized "Christ absconding from the Jews" (1858), a commission from Pius IX, and an
allegory
As a literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a hidden meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory th ...
on the pope's escape 1848 from Rome in disguise as a regular priest, originally on a ceiling in the
Quirinal Palace
The Quirinal Palace ( it, Palazzo del Quirinale ) is a historic building in Rome, Italy, one of the three current official residences of the president of the Italian Republic, together with Villa Rosebery in Naples and the Tenuta di Castelporzian ...
, later covered by the king, and now hanging in front of the Aula delle Benedizione in the
Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
. The Pope encouraged him:
) to
Friedrich Overbeck 1850
The archaeologist
Johannes Adolph Overbeck (1826–1895) was Constance Jauch's grand-grandson. Her great-granddaughter Cäcilie Lotte Eleonore Overbeck (1856-post 1920), married the anthropologist and ethnologist
Emil Ludwig Schmidt (1837–1906), who was personal physician of the hypochondriac "Cannon King"
Alfred Krupp
Alfred Krupp (born ''Alfried Felix Alwyn Krupp''; Essen, 26 April 1812 – Essen, 14 July 1887) was a German steel manufacturer and inventor; the largest arms supplier of his era, which earned him the nickname "The Cannon King".
Biography
Alf ...
. The great-granddaughter Wilhelmine Friederike Charlotte Overbeck (1829–1908) was wedded to the well known mechanical engineer
Franz Reuleaux
Franz Reuleaux (; ; 30 September 1829 – 20 August 1905), was a German mechanical engineer and a lecturer of the Berlin Royal Technical Academy, later appointed as the President of the Academy. He was often called the father of kinematics. He wa ...
(1829–1905), chairman of the German panel of judges for the
Centennial International Exhibition
The Centennial International Exhibition of 1876, the first official World's Fair to be held in the United States, was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from May 10 to November 10, 1876, to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the signing of the ...
in Philadelphia 1876. Great-great-granddaughter Agnes Elisabeth Overbeck (1870–1919), a pianist, was married under the pseudonym "Baron Eugen Borisowitsch Onégin" to the operatic contralto
Sigrid Onégin, who sang inter alia at
Metropolitan Opera
The Metropolitan Opera (commonly known as the Met) is an American opera company based in New York City, resident at the Metropolitan Opera House at Lincoln Center, currently situated on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. The company is operat ...
and
Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist si ...
.
=Buddenbrook-Nobility
=
The denotation ″Buddenbrook-Nobility″ traces back to
Thomas Mann's novel
Buddenbrooks
''Buddenbrooks'' () is a 1901 novel by Thomas Mann, chronicling the decline of a wealthy north German merchant family over the course of four generations, incidentally portraying the manner of life and mores of the Hanseatic bourgeoisie in th ...
which won Mann the
Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
in 1929. Mann portrayed the manner of life and mores of the
Hanseatics in the 19th century. The city where the Buddenbrook family lives shares so many of its street names and other details with Mann's hometown of
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
that the identification is perfect, although Mann carefully avoids explicit pronunciation of the name throughout the novel. In spite of this fact, many German readers, in particular such from Lübeck, and critics attacked Mann for writing about the "dirty laundry" of his hometown and his own family. However, for a long time that what had been attacked in the past was later regarded being an ennoblement. Those who have a close or distant relative, who has been portrayed in the Buddenbrooks, are half-ironically but at the same time respectfully counted among the "Buddenbrook-nobility".
Descendant Charlotte Leithoff (1819–1903) married consul Johann Heinrich Harms (1810–1893) (in the novel: ''August Möllendorpf''), brother of the senator Georg Friedrich Harms (1811–1892) (in the novel: ''Senator Möllendorpf''), who was married to the descendant Emma Wilhelmine Buck (1832–1896) (in the novel: ''Frau Möllendorpf geb. Langhals'') and father of Lorenz Harms (1840–1915) (in the novel: ''Konsul Kistenmaker''). Eleonora Maria Jauch's great-granddaughter Henriette Charlotte Harms (1842–1928) married the senator of Lübeck Johann Fehling (1835–1893), brother of the mayor of Lübeck (in the novel: ''Dr. Moritz Hagenström'') und brother-in-law of the mayor of Lübeck (in the novel: ''Bürgermeister Kaspar Oeverdieck''). He was a grandson of the poet
Emanuel Geibel
Emanuel von Geibel (17 October 18156 April 1884) was a German poet and playwright.
Life
Geibel was born at Lübeck, the son of a pastor. He was originally intended for his father's profession and studied at Bonn and Berlin, but his real interests ...
(in the novel: ''Jean Jacques Hoffstede''). Their daughter Emilie Charlotte Adele Fehling (1865–1890) married the novelist Lieutenant , brother of the Field Marshal und
President of Germany
The president of Germany, officially the Federal President of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: link=no, Bundespräsident der Bundesrepublik Deutschland),The official title within Germany is ', with ' being added in international corres ...
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fro ...
.
Ludovica Jauch (1772–1805)
=married Deetz
=
The granddaughter of
The Very Reverend
The Very Reverend is a Style (manner of address), style given to members of the clergy. The definite article "The" should always precede "Reverend" as "Reverend" is a style or fashion and not a title.
Catholic
In the Catholic Church, the style i ...
and
vice-dean of the cathedral of
Bardowick
Bardowick (''Bewick'' in Low Saxon) is a municipality in the district of Lüneburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is three miles north of Lüneburg on the navigable river Ilmenau. Bardowick is also the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective muni ...
Johann Christian Jauch (1702–1788), Margaretha Eleonora Ludovica Jauch (1772–1805) was married twice. Son from her first marriage with the merchant Johann Carl Deetz was Colonel (1772–1852) who became in 1847 town major of
Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon language, Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the Ri ...
. Later he became head of the central office of the
Prussian Minister of War
The Prussian War Ministry was gradually established between 1808 and 1809 as part of a series of reforms initiated by the Military Reorganization Commission created after the disastrous Treaties of Tilsit. The War Ministry was to help bring the ...
. 1848–1854 he was town major of
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
, member of the
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt Parliament (german: Frankfurter Nationalversammlung, literally ''Frankfurt National Assembly'') was the first freely elected parliament for all German states, including the German-populated areas of Austria-Hungary, elected on 1 Ma ...
and one of the thirtytwo members of the
Emperor Deputation, chosen by the National Assembly, which offered on 3 April 1849 the Imperial Crown of Germany to
Frederick William IV of Prussia
Frederick William IV (german: Friedrich Wilhelm IV.; 15 October 17952 January 1861), the eldest son and successor of Frederick William III of Prussia, reigned as King of Prussia from 7 June 1840 to his death on 2 January 1861. Also referred to ...
.
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
was at that time the Prussian envoy to the
Federal Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place in Philadelphia from May 25 to September 17, 1787. Although the convention was intended to revise the league of states and first system of government under the Articles of Confederation, the intention fr ...
in Frankfurt. His relationship to Albert Deetz as town commandant of Frankfurt and member of the Convention was distressed, because Deetz strictly refused to cooperate with him. Bismarck reported to Berlin:

Ludovica Jauch's great-great-grandson was Lieutenant Commander (german:
Korvettenkapitän
() is the lowest ranking senior officer in a number of Germanic-speaking navies.
Austro-Hungary
Belgium
Germany
Korvettenkapitän, short: KKpt/in lists: KK, () is the lowest senior officer rank () in the German Navy.
Address
The offici ...
)
Friedrich Deetz, commander of the
German submarine U-757, which was sunk 1944 in the North Atlantic, south-west of
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, by
depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive Shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth ...
s from the British frigate and the Canadian corvette . Another great-great-grandson, Colonel Günther Nentwig (1899–1943), bearer of the
Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II.
The Knight' ...
, was killed in action as commander of the 295. Infanterie-Division in the
Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
.
=married Griebel
=

After the death of her first husband Ludovica Jauch married the bassoonist of the
Royal Prussian Court Orchestra Johann Heinrich Griebel (1772–1852), stemming from a musical family whose members belonged to the royal orchestra of King
Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
. He was the first teacher of the composer
Albert Lortzing
Gustav Albert Lortzing (23 October 1801 – 21 January 1851) was a German composer, librettist, actor and singer. He is considered to be the main representative of the German ''Spieloper'', a form similar to the French '' opéra comique'', whic ...
, the main representative of the German
Spieloper
In the 19th century, Spieloper ('opera play') was understood to mean a light opera genre, developed from Singspiel. Works typical of the genre include those by Albert Lortzing, such as ''Zar und Zimmermann'', and Otto Nicolai's '' The Merry Wives ...
.
Her Stepchild
Frederick Griebel (1819–1859), who lived in
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
, was the first professional violinist in Canada. Even 20 years after his death his reputation survived as that of “the greatest violinist ever resident in this city.″
Her stepgrandchild was the
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
architect
George Henry Griebel (1846–1933), who built 1871 in
San Antonio, Texas
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
the quadrangle at
Fort Sam Houston
Fort Sam Houston is a U.S. Army post in San Antonio, Texas.
"Fort Sam Houston, TX • About Fort Sam Houston" (overview),
US Army, 2007, webpageSH-Army.
Known colloquially as "Fort Sam," it is named for the U.S. Senator from Texas, U.S. Represen ...
, later the
Dakota Building
The Dakota, also known as the Dakota Apartments, is a cooperative apartment building at 1 West 72nd Street on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City, United States. The Dakota was constructed between 1880 and 1884 in the Renaissance ...
in New York and the grand staircase in the Great Hall of the
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library is ...
.
Wilhelmine Jauch (1809–1893) married Avé-Lallemant
Wilhelmine Jauch (1809–1893) married
Theodor Avé-Lallemant, from his maternal side a descendant of the
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
leader in the
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estim ...
Gaspard II de Coligny
Gaspard de Coligny (16 February 1519 – 24 August 1572), Seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman, Admiral of France, and Huguenot leader during the French Wars of Religion. He served under kings Francis I and Henry II during the It ...
(1519–1572). Avé-Lallemant was a musician, music-teacher and music-critic. His wife's wealth enabled him, to become after getting married an important promoter of the music and to play for almost half a century a leading role in
Hamburg's music life. He was until his death the chief director of the
Hamburg Philharmonic Society (german: Philharmonische Gesellschaft). In 1841 he organized and directed the ''3rd North German Music Festival'' in 1841 in Hamburg, which was the biggest festival of its time.

Hans von Bülow
Freiherr Hans Guido von Bülow (8 January 1830 – 12 February 1894) was a German conductor, virtuoso pianist, and composer of the Romantic era. As one of the most distinguished conductors of the 19th century, his activity was critical for es ...
dedicated to Avé-Lallemant his ''Chant polonais Opus 12''.
Klaus Mann
Klaus Heinrich Thomas Mann (18 November 1906 – 21 May 1949) was a German writer and dissident. He was the son of Thomas Mann, a nephew of Heinrich Mann and brother of Erika Mann, with whom he maintained a lifelong close relationship, and Golo ...
describes in his novel ''Pathetic Symphony'' (french: Symphonie Pathétique) about the life of
Peter Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most popu ...
a meeting between Tchaikovsky and Avé-Lallemant. Tchaikovsky dedicated to his admirer Avé-Lallemant, for whom he had a lot of sympathy, his
5th Symphony.
Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
, who was a fourth
cousin
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, " ...
twice removed of Robert Jauch (1856–1909) and Bertha Jauch (1860–1935), and
Robert Schumann
Robert Schumann (; 8 June 181029 July 1856) was a German composer, pianist, and influential music critic. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Romantic era. Schumann left the study of law, intending to pursue a career a ...
became godfathers of two of Theodor Avé-Lallemant's and Wilhelmine Jauch's sons.
The collection of letters from a number of composers and scores by Brahms is since 2000 part of the collection of the
Brahms-Institut. Avé-Lallemant, who played the violin himself, possessed the
Cremonese
Cremona (, also ; ; lmo, label= Cremunés, Cremùna; egl, Carmona) is a city and ''comune'' in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po river in the middle of the ''Pianura Padana'' (Po Valley). It is the capital of the ...
violin of
Prince Louis Ferdinand of Prussia (1772–1806)
English: Frederick Louis Christian
, house = House of Hohenzollern
, father = Prince August Ferdinand of Prussia
, mother = Elisabeth Louise of Brandenburg-Schwedt
, birth_date = 18 November 1 ...
. Apart from being a soldier in the
Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, Louis Ferdinand was also a gifted musician and composer. The prince brought his violin also to military campaigns. He bequeathed it to his friend, Avé-Lallemant's father, the evening before his death in the
Battle of Saalfeld
The Battle of Saalfeld took place on 10 October 1806, at which a French force of 12,800 men commanded by Marshal Jean Lannes defeated a Prussian- Saxon force of 8,300 men under Prince Louis Ferdinand. The battle took place in Thuringia in wha ...
with the words: ″In case that I will not return from the battle.″
Charlotte Jauch (1811–1872) married Lührsen


Luise Jauch (1815–1881) married Halske
Bertha Jauch (1860–1935) married Knoop

Other known Families with the Name "Jauch"
Citizens of the Canton of Uri in the Old Swiss Confederacy
The from the
Canton of Uri
The canton of Uri (german: Kanton Uri rm, Chantun Uri; french: Canton d'Uri; it, Canton Uri) is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and a founding member of the Swiss Confederation. It is located in Central Switzerland. The canton's territ ...
in the
Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (German language, Modern German: ; historically , after the Swiss Reformation, Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ...
, are chronicled since 1368. They stepped up significantly for the first time with
Hans Jauch (1500–1568), who won 1531 during the
Reformation in Switzerland
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matte ...
for the
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, t ...
the
Second War of Kappel
The Second War of Kappel (german: Zweiter Kappelerkrieg) was an armed conflict in 1531 between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.
Cause
The tensions between the two part ...
.
The
Altdorf main branch of these Jauch became known as
Swiss mercenaries
The Swiss mercenaries (german: Reisläufer) were a powerful infantry force constituted by professional soldiers originating from the cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. They were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially among th ...
.
This family is not related to the Hanseatic Jauch covered here.
Commoners of the Grand Duchy of Baden
Neither are related to the Hanseatic Jauch the Jauch of
Villingen-Schwenningen and the surrounding municipalities in today's
Schwarzwald-Baar
Schwarzwald-Baar () is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the south of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from north clockwise) Ortenaukreis, Rottweil, Tuttlingen, Constance, the Swiss canton of Schaffhausen, and the districts ...
district, who were
commoners
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
of the
Grand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subs ...
.
Most Jauch spread over the world in present-day time descend from these Jauch, of whom a number due to poverty and famine emigrated with hundreds of other inhabitants in several waves from 1747–1754, 1801, 1817, 1847 and in the period thereafter until about 1890 to
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
,
Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
, the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
For example, Schwenningen sent in April 1847 about 200 further residents – including a few Jauch –, corresponding to 5 percent of of the time, across the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
. The municipality had calculated that it would cost less to send the poorest to America than it would to support them until the famine ended, which resulted from the
bad potato harvest in 1846.
To the Jauch of Schwennigen belongs – though stationed in Hamburg – the
SS Oberscharführer __NOTOC__
''Oberscharführer'' (, ) was a Nazi Party paramilitary rank that existed between 1932 and 1945. ''Oberscharführer'' was first used as a rank of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) and was created due to an expansion of the enlisted positions ...
, who was convicted and given the death sentence in 1946 because of his involvement in the killings in the subcamp
Bullenhuser Damm
The Bullenhuser Damm School is located at ''92–94 Bullenhuser Damm'' in the Rothenburgsort section of Hamburg, Germany – the site of the Bullenhuser Damm Massacre, the murder of 20 children and their adult caretakers at the very end of W ...
of the Neuengamme concentration camp.
Commoners of the Electorate of Saxony
Another Jauch family considered in the literature originates from
Pegau
Pegau () is a town in the Leipzig district in Saxony, Germany, situated in a fertile plain, on the White Elster, 18 m. S.W. from Leipzig by the railway to Zeitz.
It has two Evangelical churches, that of St. Lawrence being a fine Gothic structure ...
and spread to
Meißen
Meissen (in German orthography: ''Meißen'', ) is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrech ...
in the
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
. Their ancestor was the butcher Andreas Jauch (b. 1523) and their best known member was the jurist and controlling clerk of the 17th century Haubold Gottfried Jauch. There is no relationship to the Hanseatic Jauch family, too.
Family tree (under construction)
Bibliography
Family-related literature
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
General literature
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Films
* (→ The reconstruction of the
Potsdamer Stadtschloss (Potsdam City Palace) – completed in 2013 – around the old palace's Fortuna Gate, which was initiated by
Günther Jauch
Günther Johannes Jauch (; born 13 July 1956) is a German television presenter, television producer, and journalist.
Career
Jauch is known for a unique style of informing and entertaining people that is generally considered witty and funny. ...
, who donated the reconstruction of the Fortuna Gate in 2000–2001.)
* (→
Heinrich Jauch, First State Attorney at Hamburg and the persecution of the Red Marine.)
* (→ 700 Waffen-SS soldiers under the command of descendant Generalleutnant
Karl Fischer von Treuenfeld
Karl Freiherr von Fischer-Treuenfeld (31 March 1885 – 7 June 1946) was a German Waffen-SS commander. A brigade commander during the Nazi era, during the invasion of the Soviet Union, he commanded the 2 SS Infantry Brigade and the 1 SS Infant ...
laying siege to the
Church of Saints Cyril and Methodius
The Saints Cyril and Methodius Cathedral in Nové Město, Prague, the Czech Republic, is the principal Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church.
History Early history
According to oral tradition, the site where Saints Cyril and Methodius Cathedral sta ...
in Prague with Fischer von Treuenfeld inspecting the first dead paratroopers at 2:34.)
* (→
SM U-40 (Germany)
SM ''U-40'') and combined with the ''U'' for ''Unterseeboot'' would be translated as ''His Majesty's Submarine''., group=Note was a German Type U 31 U-boat of the German Imperial Navy (german: Kaiserliche Marine) during World War I.
Her constr ...
, whose second officer
lieutenant Rudolf Jauch died in the sinking.)
* (→ Father Robert Jauch
OFM, at the time living in the
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
in
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, in which the control of the building is
shared between several Christian churches in complicated arrangements, essentially unchanged for centuries ( la, status quo), provides an insight into his,
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, perspective of the life in the church.)
* (→
Günther Jauch
Günther Johannes Jauch (; born 13 July 1956) is a German television presenter, television producer, and journalist.
Career
Jauch is known for a unique style of informing and entertaining people that is generally considered witty and funny. ...
explains the history and the
Riesling
Riesling (, ; ) is a white grape variety that originated in the Rhine region. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet, and sparkling wh ...
wine of his
Von Othegraven Winery.)
* (→ The
Marmorpalais (Marble Palace) at Potsdam on the shores of the
Heiliger See (Holy Lake), situated directly opposite to the Villa Jauch on the shores of the lake. Since April 14, 2006 all 40 rooms have been renovated and opened to the public,
Günther Jauch
Günther Johannes Jauch (; born 13 July 1956) is a German television presenter, television producer, and journalist.
Career
Jauch is known for a unique style of informing and entertaining people that is generally considered witty and funny. ...
starting the renovation with a donation for the roof repairs.)
[
]
External links
References
{{Hanseaten
German families
Hanseatic families
 The members of the family who had served the Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg left the
The members of the family who had served the Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg left the  The trading firm was relocated in the middle of the 18th century by Carl Daniel Jauch (1714–1794) from the falling back Lüneburg to Hamburg, the ″Queen of the cities″. Since the 17th century Hamburg played a special role in Germany's economic history because thanks to its it came out of the
The trading firm was relocated in the middle of the 18th century by Carl Daniel Jauch (1714–1794) from the falling back Lüneburg to Hamburg, the ″Queen of the cities″. Since the 17th century Hamburg played a special role in Germany's economic history because thanks to its it came out of the  Destroyed along with this historical building were the family crypt on the former cemetery in Hamm, Hamburg (german: Alter Hammer Friedhof) and the ''Auguste Jauch Woman's Home for Needy Widows'' (german: Auguste-Jauch-Stift für bedürftige Witwen) located ''Bürgerweide'' 59 there.
Around the Outer Alster Lake the Jauch possessed the houses ''An der Alster'' 24, ''An der Alster'' 28 and ''Schwanenwik'' 18. In addition, they possessed country houses on the Bille in
Destroyed along with this historical building were the family crypt on the former cemetery in Hamm, Hamburg (german: Alter Hammer Friedhof) and the ''Auguste Jauch Woman's Home for Needy Widows'' (german: Auguste-Jauch-Stift für bedürftige Witwen) located ''Bürgerweide'' 59 there.
Around the Outer Alster Lake the Jauch possessed the houses ''An der Alster'' 24, ''An der Alster'' 28 and ''Schwanenwik'' 18. In addition, they possessed country houses on the Bille in  The regions surrounding Hamburg belonged to the
The regions surrounding Hamburg belonged to the  Today the Jauch own the Von Othegraven Winery. The
Today the Jauch own the Von Othegraven Winery. The  The
The  Johann Christian Jauch senior (1765–1855) served from 1820 until 1833 as dyke-count and first dyke count (german: Ältester Deichgeschworener) of Hamburg-Hammerbrook. He was in charge as first dyke count when the dam failed during the
Johann Christian Jauch senior (1765–1855) served from 1820 until 1833 as dyke-count and first dyke count (german: Ältester Deichgeschworener) of Hamburg-Hammerbrook. He was in charge as first dyke count when the dam failed during the  Constance Jauch (1722–1802) is the ancestress of the Polish noble which was granted the
Constance Jauch (1722–1802) is the ancestress of the Polish noble which was granted the  In the 17th century Sulza has been twice devastated, 1613 by the
and 1640 when it was plundered by Swedish troops. Johann Christian Jauch the Elder (1638–1718) left the fallen back Sulza and relocated to
In the 17th century Sulza has been twice devastated, 1613 by the
and 1640 when it was plundered by Swedish troops. Johann Christian Jauch the Elder (1638–1718) left the fallen back Sulza and relocated to  His brother Joachim Daniel (1688–1754) served at first in the army of the
His brother Joachim Daniel (1688–1754) served at first in the army of the 
 In different polls
In different polls  Heinrich Jauch (1894–1945) was the Prosecuting Attorney of the Special Tribunal (german:
Heinrich Jauch (1894–1945) was the Prosecuting Attorney of the Special Tribunal (german:  Similarly, Heinrich Jauch organized that the Nazi state reached control over the trading firm Alfred C. Toepfer Company owned by
Similarly, Heinrich Jauch organized that the Nazi state reached control over the trading firm Alfred C. Toepfer Company owned by  Eight lineage holders of the Jauch, half of all lineage holders in these generations, died as soldiers on the different European battlefields of the
Eight lineage holders of the Jauch, half of all lineage holders in these generations, died as soldiers on the different European battlefields of the  Catharina Elisabeth Jauch (1671–1736) married the later colonel and architect of King August the Strong,
Catharina Elisabeth Jauch (1671–1736) married the later colonel and architect of King August the Strong,  Joachim Daniel Jauch's daughter Constance Jauch (1722–1802) married Heinrich Lölhöffel von Löwensprung (1705–1763), privy councillor (german:
Joachim Daniel Jauch's daughter Constance Jauch (1722–1802) married Heinrich Lölhöffel von Löwensprung (1705–1763), privy councillor (german:  Constance Jauch's grandsons were Joachim, Prot und Jan Pawel Lelewel.
Constance Jauch's grandsons were Joachim, Prot und Jan Pawel Lelewel.

 Constance Jauch's daughter Teresa Lelewelowna (1752–1814) married Adam Józef Cieciszowski (1743–1783), brother of the archbishop and metropolitan . He was
Constance Jauch's daughter Teresa Lelewelowna (1752–1814) married Adam Józef Cieciszowski (1743–1783), brother of the archbishop and metropolitan . He was 
 Her grandson was the painter and head of the
Her grandson was the painter and head of the  Ludovica Jauch's great-great-grandson was Lieutenant Commander (german:
Ludovica Jauch's great-great-grandson was Lieutenant Commander (german:  After the death of her first husband Ludovica Jauch married the bassoonist of the Royal Prussian Court Orchestra Johann Heinrich Griebel (1772–1852), stemming from a musical family whose members belonged to the royal orchestra of King
After the death of her first husband Ludovica Jauch married the bassoonist of the Royal Prussian Court Orchestra Johann Heinrich Griebel (1772–1852), stemming from a musical family whose members belonged to the royal orchestra of King 

