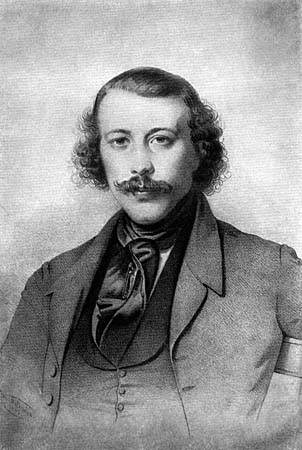|
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician. Life Born in Warsaw to a Polonized German family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 1814 he became a lecturer in history, with a brief sojourn at Warsaw, 1818–1821, where he joined the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning. His lectures on Polish history created great enthusiasm, as shown in some lines addressed to him by Adam Mickiewicz that led to Lelewel's removal by the Russians in 1824. Five years later, Lelewel returned to Warsaw, where he was elected a deputy to the Sejm of Congress Poland. He joined the November 1830 Uprising with more enthusiasm than energy, though Tsar Nicholas I identified him as one of the most dangerous rebels. He is considered the author of the motto: "For our freedom and yours". On the suppression of the rebellion, Lelewel made his way in disguise to Germany and subsequently reached Pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official (the Pope or the Ecumenical Patriarch)—but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". It lends its name to a system of government, tsarist autocracy or tsarism. "Tsar" and its variants were the official titles of the following states: * Bulgarian Empire (First Bulgarian Empire in 681–1018, Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185–1396), and also used in Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria, in 1908–1946 * Serbian Empire, in 1346–1371 * Tsardom of Russia, in 1547–1721 (replaced in 1721 by ''imperator'' in Russian Empire, but still re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urban area, which stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 718,507 (as of 2020), while according to the Vilnius territorial health insurance fund, there were 753,875 permanent inhabitants as of November 2022 in Vilnius city and Vilnius district municipalities combined. Vilnius is situated in southeastern Lithuania and is the second-largest city in the Baltic states, but according to the Bank of Latvia is expected to become the largest before 2025. It is the seat of Lithuania's national government and the Vilnius District Municipality. Vilnius is known for the architecture in its Old Town, declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The city was noted for its multicultural population already in the time of the Polish–Lithuanian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasos Cemetery
Rasos Cemetery ( lt, Rasų kapinės, pl, cmentarz Na Rossie, be, Могілкі Росы) is the oldest and most famous cemetery in the city of Vilnius, Lithuania. It is named after the Rasos district where it is located. It is separated into two parts, the old and the new cemeteries, by a narrow Sukilėliai Street. The total area is 10.8 ha. Since 1990 new burials are allowed only to family graves. History The year 1769 is cited in many sources as the date when the cemetery was founded. However, some historians believe it is a typo and the real date should be 1796. On April 24, 1801, the new cemetery was consecrated. Two days later Jan Müller, the mayor of Vilnius, became the first person to be buried there. A formal document was signed in July 1801. It specified that the cemetery received of land and that the cemetery will be free of charge to all city residents. It was the first cemetery in Vilnius not located next to a church. In 1802-1807 two columbariums were built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodytel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promoting university e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessarily limited to, governments, nation states, and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with stateless societies or other forms of free associations. As a historically left-wing movement, usually placed on the farthest left of the political spectrum, it is usually described alongside communalism and libertarian Marxism as the libertarian wing (libertarian socialism) of the socialist movement. Humans lived in societies without formal hierarchies long before the establishment of formal states, realms, or empires. With the rise of organised hierarchical bodies, scepticism toward authority also rose. Although traces of anarchist thought are found throughout history, modern anarchism emerged from the Enlightenm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet ''The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków Uprising
The Kraków uprising (Polish: ''powstanie krakowskie'', ''rewolucja krakowska''; German: ''Krakauer Aufstand''; Russian: ''краковское восстание'') of 1846 was an attempt, led by Polish insurgents such as Jan Tyssowski and Edward Dembowski, to incite a fight for national independence. The uprising was centered on the city of Kraków, the capital of a small state of Free City of Krakow. It was directed at the powers that partitioned Poland, in particular the nearby Austrian Empire. The uprising lasted about nine days and ended with Austrian victory. Background The uprising was primarily organized and supported by members of the Polish nobility and middle class, who desired the restoration of Polish independence after the 1795 partitions of Poland ended its existence as a sovereign state; there was also support for various political and social reforms (such as the demands for the emancipation of peasants and an end to serfdom). Many of the insurgents' ideas we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region (within which it forms an enclave) and the Walloon Region. Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest GDP per capita, it has the lowest available income per household. The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million. The five times larger metropolitan area of Brusse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Philippe Of France
Louis Philippe (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850) was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France. As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding troops during the Revolutionary Wars and was promoted to lieutenant general by the age of nineteen, but he broke with the Republic over its decision to execute King Louis XVI. He fled to Switzerland in 1793 after being connected with a plot to restore France's monarchy. His father Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (Philippe Égalité) fell under suspicion and was executed during the Reign of Terror. Louis Philippe remained in exile for 21 years until the Bourbon Restoration. He was proclaimed king in 1830 after his cousin Charles X was forced to abdicate by the July Revolution (and because of the Spanish renounciation). The reign of Louis Philippe is known as the July Monarchy and was dominated by wealthy industrialists and bankers. He followed conservative policies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)