James Watt (New York Politician) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish

 When he was 18, Watt's mother died and his father's health began to fail. Watt travelled to
When he was 18, Watt's mother died and his father's health began to fail. Watt travelled to
 In 1759, Watt's friend, John Robison, called his attention to the use of steam as a source of motive power. The design of the Newcomen engine, in use for almost 50 years for pumping water from mines, had hardly changed from its first implementation. Watt began to experiment with steam, though he had never seen an operating steam engine. He tried constructing a model; it failed to work satisfactorily, but he continued his experiments and began to read everything he could about the subject. He came to realise the importance of latent heat—the thermal energy released or absorbed during a constant-temperature process—in understanding the engine, which, unknown to Watt, his friend Joseph Black had previously discovered years before. Understanding of the steam engine was in a very primitive state, for the science of thermodynamics would not be formalised for nearly another 100 years.
In 1763, Watt was asked to repair a model Newcomen engine belonging to the university. Even after repair, the engine barely worked. After much experimentation, Watt demonstrated that about three-quarters of the thermal energy of the steam was being consumed in heating the
In 1759, Watt's friend, John Robison, called his attention to the use of steam as a source of motive power. The design of the Newcomen engine, in use for almost 50 years for pumping water from mines, had hardly changed from its first implementation. Watt began to experiment with steam, though he had never seen an operating steam engine. He tried constructing a model; it failed to work satisfactorily, but he continued his experiments and began to read everything he could about the subject. He came to realise the importance of latent heat—the thermal energy released or absorbed during a constant-temperature process—in understanding the engine, which, unknown to Watt, his friend Joseph Black had previously discovered years before. Understanding of the steam engine was in a very primitive state, for the science of thermodynamics would not be formalised for nearly another 100 years.
In 1763, Watt was asked to repair a model Newcomen engine belonging to the university. Even after repair, the engine barely worked. After much experimentation, Watt demonstrated that about three-quarters of the thermal energy of the steam was being consumed in heating the 
 Despite a potentially workable design, there were still substantial difficulties in constructing a full-scale engine. This required more
Despite a potentially workable design, there were still substantial difficulties in constructing a full-scale engine. This required more
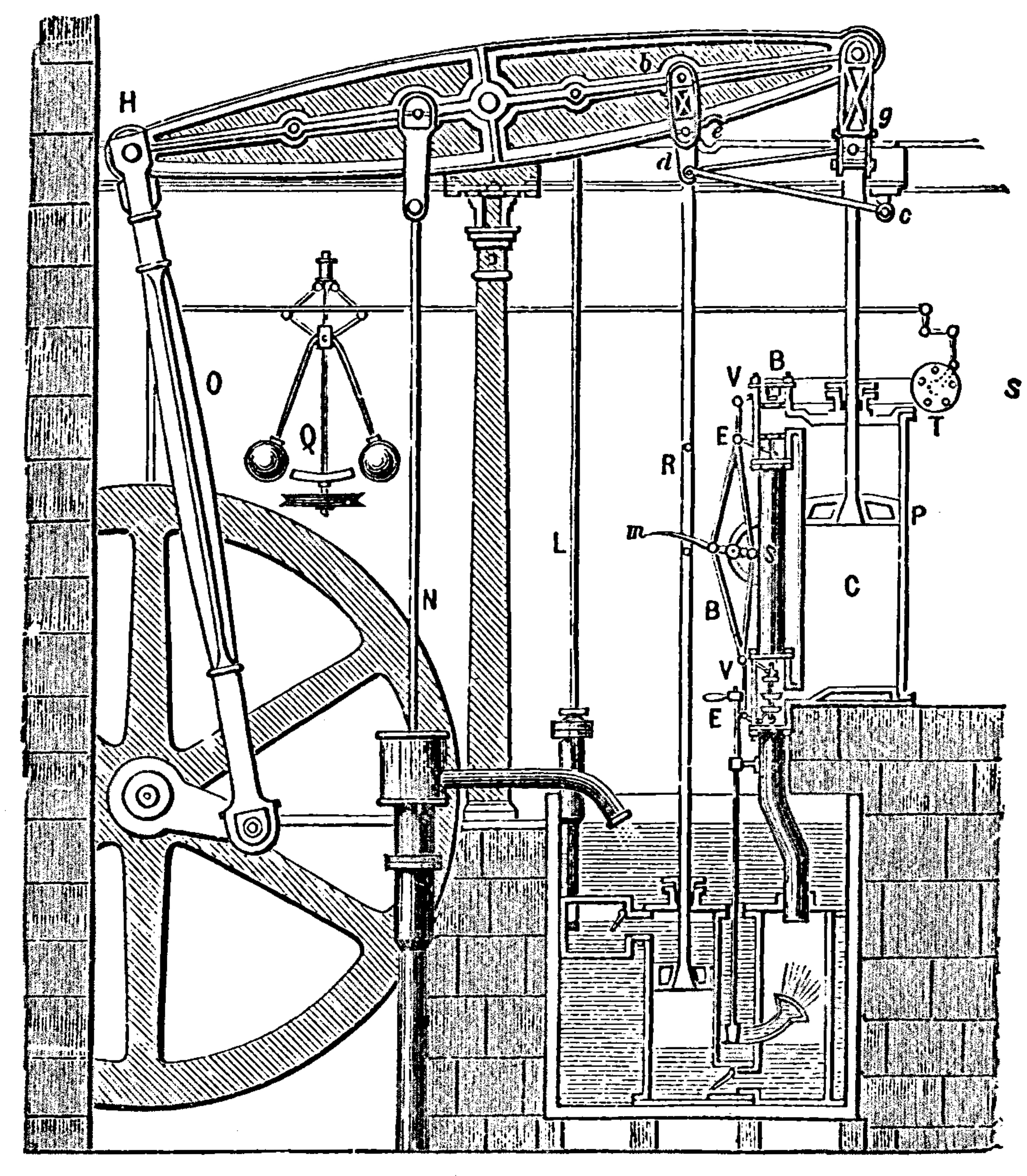 In 1776, the first engines were installed and working in commercial enterprises. These first engines were used to power pumps and produced only reciprocating motion to move the pump rods at the bottom of the shaft. The design was commercially successful, and for the next five years, Watt was very busy installing more engines, mostly in Cornwall, for pumping water out of mines.
These early engines were not manufactured by Boulton and Watt, but were made by others according to drawings made by Watt, who served in the role of
In 1776, the first engines were installed and working in commercial enterprises. These first engines were used to power pumps and produced only reciprocating motion to move the pump rods at the bottom of the shaft. The design was commercially successful, and for the next five years, Watt was very busy installing more engines, mostly in Cornwall, for pumping water out of mines.
These early engines were not manufactured by Boulton and Watt, but were made by others according to drawings made by Watt, who served in the role of

 Before 1780, there was no good method for making copies of letters or drawings. The only method sometimes used was a mechanical one using multiple linked pens. Watt at first experimented with improving this method, but soon gave up on this approach because it was so cumbersome. He instead decided to try to physically transfer ink from the front of the original to the back of another sheet, moistened with a solvent, and pressed to the original. The second sheet had to be thin, so that the ink could be seen through it when the copy was held up to the light, thus reproducing the original exactly.
Watt started to develop the process in 1779, and made many experiments to formulate the ink, select the thin paper, to devise a method for wetting the special thin paper, and to make a press suitable for applying the correct pressure to effect the transfer. All of these required much experimentation, but he soon had enough success to patent the process a year later. Watt formed another partnership with Boulton (who provided financing) and James Keir (to manage the business) in a firm called James Watt and Co. The perfection of the invention required much more development work before it could be routinely used by others, but this was carried out over the next few years. Boulton and Watt gave up their shares to their sons in 1794. It became a commercial success and was widely used in offices even into the 20th century.
Before 1780, there was no good method for making copies of letters or drawings. The only method sometimes used was a mechanical one using multiple linked pens. Watt at first experimented with improving this method, but soon gave up on this approach because it was so cumbersome. He instead decided to try to physically transfer ink from the front of the original to the back of another sheet, moistened with a solvent, and pressed to the original. The second sheet had to be thin, so that the ink could be seen through it when the copy was held up to the light, thus reproducing the original exactly.
Watt started to develop the process in 1779, and made many experiments to formulate the ink, select the thin paper, to devise a method for wetting the special thin paper, and to make a press suitable for applying the correct pressure to effect the transfer. All of these required much experimentation, but he soon had enough success to patent the process a year later. Watt formed another partnership with Boulton (who provided financing) and James Keir (to manage the business) in a firm called James Watt and Co. The perfection of the invention required much more development work before it could be routinely used by others, but this was carried out over the next few years. Boulton and Watt gave up their shares to their sons in 1794. It became a commercial success and was widely used in offices even into the 20th century.

 He was a rather poor businessman, and especially hated bargaining and negotiating terms with those who sought to use the steam engine. In a letter to William Small in 1772, Watt confessed that "he would rather face a loaded cannon than settle an account or make a bargain." Until he retired, he was always very concerned about his financial affairs, and was something of a worrier. His health was often poor and he suffered frequent nervous headaches and depression. When he retired in 1800, he became a rich enough man to pass the business on to his sons.
He was a rather poor businessman, and especially hated bargaining and negotiating terms with those who sought to use the steam engine. In a letter to William Small in 1772, Watt confessed that "he would rather face a loaded cannon than settle an account or make a bargain." Until he retired, he was always very concerned about his financial affairs, and was something of a worrier. His health was often poor and he suffered frequent nervous headaches and depression. When he retired in 1800, he became a rich enough man to pass the business on to his sons.

 Watt retired in 1800, the same year that his fundamental patent and partnership with Boulton expired. The famous partnership was transferred to the men's sons, Matthew Robinson Boulton and James Watt Jr.. Longtime firm engineer William Murdoch was soon made a partner and the firm prospered.
Watt continued to invent other things before and during his semi-retirement. Within his home in Handsworth, Staffordshire, Watt made use of a garret room as a workshop, and it was here that he worked on many of his inventions. Among other things, he invented and constructed machines for copying sculptures and medallions which worked very well, but which he never patented. One of the first sculptures he produced with the machine was a small
Watt retired in 1800, the same year that his fundamental patent and partnership with Boulton expired. The famous partnership was transferred to the men's sons, Matthew Robinson Boulton and James Watt Jr.. Longtime firm engineer William Murdoch was soon made a partner and the firm prospered.
Watt continued to invent other things before and during his semi-retirement. Within his home in Handsworth, Staffordshire, Watt made use of a garret room as a workshop, and it was here that he worked on many of his inventions. Among other things, he invented and constructed machines for copying sculptures and medallions which worked very well, but which he never patented. One of the first sculptures he produced with the machine was a small
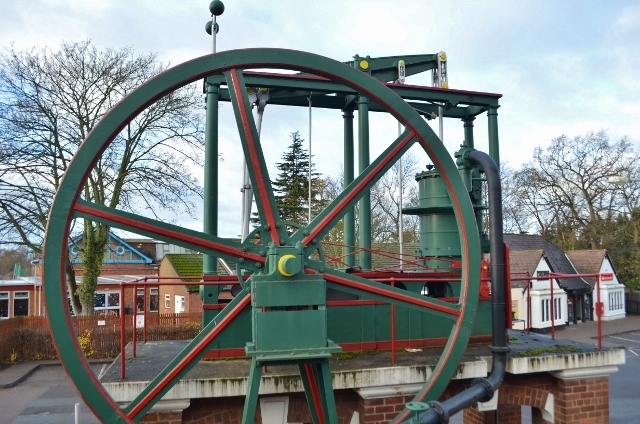 As one author states, James Watt's improvements to the steam engine "converted it from a prime mover of marginal efficiency into the mechanical workhorse of the Industrial Revolution".
As one author states, James Watt's improvements to the steam engine "converted it from a prime mover of marginal efficiency into the mechanical workhorse of the Industrial Revolution".
 Watt was buried in the grounds of
Watt was buried in the grounds of  There is a statue of James Watt in
There is a statue of James Watt in
Chapter 3: Mathematical Instrument Maker
fro
Steam Engine Library
of University of Rochester Department of History. * Marshall, Thomas H. (1925
''James Watt''
University of Rochester Department of History. * * * Roll, Erich (1930). ''An Early Experiment in Industrial Organisation : being a History of the Firm of Boulton & Watt.'' 1775–1805. Longmans, Green and Co. * Smiles, Samuel, ''Lives of the Engineers'', (London, 1861–62, new edition, five volumes, 1905). ;Related topics * *
James Watt by Andrew Carnegie (1905)
Librivox audiobook: James Watt by Andrew Carnegie (1905)
James Watt by Thomas H. Marshall (1925)
Archives of Soho
at Birmingham Central Library.
BBC History: James Watt
Revolutionary Players website
Cornwall Record Office Boulton and Watt letters
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Watt, James 18th-century British engineers 18th-century British scientists 18th-century Scottish people 1736 births 1819 deaths Alumni of the University of Glasgow Fellows of the Royal Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Industrial Revolution in England Industrial Revolution in Scotland Members of the Lunar Society of Birmingham People associated with energy People associated with Heriot-Watt University People from Greenock People of the Scottish Enlightenment Scottish business theorists Scottish businesspeople Scottish chemists Scottish deists Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame inductees Scottish inventors Scottish Presbyterians Scottish surveyors Astronomical instrument makers
 James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
, mechanical engineer, and chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
who improved on Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen (; February 1664 – 5 August 1729) was an English inventor who created the atmospheric engine, the first practical fuel-burning engine in 1712. He was an ironmonger by trade and a Baptist lay preacher by calling.
He ...
's 1712 Newcomen steam engine
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to as the Newcomen fire engine (see below) or simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creati ...
with his Watt steam engine
The Watt steam engine design became synonymous with steam engines, and it was many years before significantly new designs began to replace the basic Watt design.
The first steam engines, introduced by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, were of the "at ...
in 1776, which was fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world.
While working as an instrument maker at the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
, Watt became interested in the technology of steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s. He realised that contemporary engine designs wasted a great deal of energy by repeatedly cooling and reheating the cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
. Watt introduced a design enhancement, the separate condenser, which avoided this waste of energy and radically improved the power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of steam engines. Eventually, he adapted his engine to produce rotary motion, greatly broadening its use beyond pumping water.
Watt attempted to commercialise his invention, but experienced great financial difficulties until he entered a partnership with Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton (; 3 September 172817 August 1809) was an English manufacturer and business partner of Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton & Watt steam engine ...
in 1775. The new firm of Boulton and Watt
Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the Engli ...
was eventually highly successful and Watt became a wealthy man. In his retirement, Watt continued to develop new inventions though none was as significant as his steam engine work.
As Watt developed the concept of horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the ...
, the SI unit of power, the watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
, was named after him.
Biography
Early life and education
James Watt was born on 19 January 1736 inGreenock
Greenock (; sco, Greenock; gd, Grianaig, ) is a town and administrative centre in the Inverclyde council areas of Scotland, council area in Scotland, United Kingdom and a former burgh of barony, burgh within the Counties of Scotland, historic ...
, Renfrewshire, the eldest of the five surviving children of Agnes Muirhead (1703–1755) and James Watt (1698–1782). His mother came from a distinguished family, was well educated and said to be of forceful character, while his father was a shipwright
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
, ship owner and contractor, and served as the Greenock's chief baillie in 1751. The Watt family's wealth came in part from Watt's father's trading in slaves and slave-produced goods.
Watt's parents were Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
s and strong Covenanters
Covenanters ( gd, Cùmhnantaich) were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland, and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. The name is derived from ''Covenan ...
, but despite his religious upbringing he later became a deist. Watt's grandfather, Thomas Watt (1642–1734), was a teacher of mathematics, surveying and navigation and baillie to the Baron of Cartsburn
The barony of Cartsburn in the Baronage of Scotland was created for Thomas Crawfurd of Cartsburn in 1669, when the lands of Cartsburn in the Parish of Easter Greenock in the Shire of Renfrew were erected , as a free barony held of the Prince and G ...
.
Initially, Watt was educated at home by his mother, later going on to attend Greenock Grammar School. There he exhibited an aptitude for mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, while Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and Greek failed to interest him.
Watt is said to have suffered prolonged bouts of ill-health as a child and from frequent headaches all his life.
After leaving school, Watt worked in the workshops of his father's businesses, demonstrating considerable dexterity and skill in creating engineering models. After his father suffered unsuccessful business ventures, Watt left Greenock to seek employment in Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
as a mathematical instrument maker.

London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
and was able to obtain a period of training as an instrument maker for a year (1755–56), then returned to Scotland, settling in the major commercial city of Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
, intent on setting up his own instrument-making business. He was still very young and, having not had a full apprenticeship
Apprenticeship is a system for training a new generation of practitioners of a Tradesman, trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study (classroom work and reading). Apprenticeships can also enable practitioners ...
, did not have the usual connections via a former master to establish himself as a journeyman instrument maker.
Watt was saved from this impasse by the arrival from Jamaica of astronomical instruments bequeathed by Alexander MacFarlane to the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
– instruments that required expert attention. Watt restored them to working order and was remunerated. These instruments were eventually installed in the Macfarlane Observatory
The Macfarlane Observatory was established at the University of Glasgow in 1757. It was the first purpose-built university observatory in Britain.
History
The Observatory was named after Alexander MacFarlane, a merchant and slave-owner in Kin ...
. Subsequently, three professors offered him the opportunity to set up a small workshop within the university. It was initiated in 1757 and two of the professors, the physicist and chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
Joseph Black as well as the famed economist Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
, became Watt's friends.
At first, he worked on maintaining and repairing scientific instruments used in the university, helping with demonstrations, and expanding the production of quadrants. He made and repaired brass reflecting quadrants, parallel rulers
Parallel rulers are a drafting instrument used by navigators to draw parallel lines on charts. The tool consists of two straight edges joined by two arms which allow them to move closer or further away while always remaining parallel to each oth ...
, scales, parts for telescopes, and barometers, among other things.
It is sometimes falsely stated that he struggled to establish himself in Glasgow due to opposition from the Trades House
Trade is the voluntary exchange of goods, services, or both.
Trade or trading may also refer to:
Geography
* Trade, Tennessee, an unincorporated community, United States
* Trade City, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community, United States
* Tr ...
, but this myth has been thoroughly debunked by the historian Harry Lumsden. The records from this period are lost, but it is known that he was able to work and trade completely normally as a skilled metal worker
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale ...
so the Incorporation of Hammermen
Incorporation may refer to:
* Incorporation (business), the creation of a corporation
* Incorporation of a place, creation of municipal corporation such as a city or county
* Incorporation (academic), awarding a degree based on the student having ...
must have been satisfied that he met their requirements for membership. It is also known that other people in the metal trades were pursued for working without being members of the Incorporation well into the 19th century, so the rules were definitely being enforced when Watt was trading freely throughout the city.
In 1759, he formed a partnership with John Craig, an architect and businessman, to manufacture and sell a line of products including musical instruments and toys. This partnership lasted for the next six years, and employed up to 16 workers. Craig died in 1765. One employee, Alex Gardner, eventually took over the business, which lasted into the 20th century.
In 1764, Watt married his cousin Margaret (Peggy) Miller, with whom he had 5 children, 2 of whom lived to adulthood: James Jr. (1769–1848) and Margaret (1767–1796). His wife died in childbirth in 1773. In 1777, he married again, to Ann MacGregor, daughter of a Glasgow dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
-maker, with whom he had 2 children: Gregory (1777–1804), who became a geologist and mineralogist, and Janet (1779–1794). Ann died in 1832. Between 1777 and 1790 he lived in Regent Place, Birmingham.
Watt and the kettle
There is a popular story that Watt was inspired to invent the steam engine by seeing a kettle boiling, the steam forcing the lid to rise and thus showing Watt the power of steam. This story is told in many forms; in some Watt is a young lad, in others he is older, sometimes it's his mother's kettle, sometimes his aunt's. Watt did not actually ''invent'' the steam engine, as the story implies, but dramatically improved the efficiency of the existing Newcomen engine by adding a separate condenser. This is difficult to explain to someone not familiar with concepts of heat and thermal efficiency. It appears that the story was created, possibly by Watt's son James Watt Jr., and persists because it is easy for children to understand and remember. In this light, it can be seen as akin to the story of Isaac Newton and the falling apple and his discovery of gravity. Although it is often dismissed as a myth, the story of Watt and the kettle has a basis in fact. In trying to understand the thermodynamics of heat and steam, James Watt carried out many laboratory experiments and his diaries record that in conducting these, he used a kettle as a boiler to generate steam.Early experiments with steam

 In 1759, Watt's friend, John Robison, called his attention to the use of steam as a source of motive power. The design of the Newcomen engine, in use for almost 50 years for pumping water from mines, had hardly changed from its first implementation. Watt began to experiment with steam, though he had never seen an operating steam engine. He tried constructing a model; it failed to work satisfactorily, but he continued his experiments and began to read everything he could about the subject. He came to realise the importance of latent heat—the thermal energy released or absorbed during a constant-temperature process—in understanding the engine, which, unknown to Watt, his friend Joseph Black had previously discovered years before. Understanding of the steam engine was in a very primitive state, for the science of thermodynamics would not be formalised for nearly another 100 years.
In 1763, Watt was asked to repair a model Newcomen engine belonging to the university. Even after repair, the engine barely worked. After much experimentation, Watt demonstrated that about three-quarters of the thermal energy of the steam was being consumed in heating the
In 1759, Watt's friend, John Robison, called his attention to the use of steam as a source of motive power. The design of the Newcomen engine, in use for almost 50 years for pumping water from mines, had hardly changed from its first implementation. Watt began to experiment with steam, though he had never seen an operating steam engine. He tried constructing a model; it failed to work satisfactorily, but he continued his experiments and began to read everything he could about the subject. He came to realise the importance of latent heat—the thermal energy released or absorbed during a constant-temperature process—in understanding the engine, which, unknown to Watt, his friend Joseph Black had previously discovered years before. Understanding of the steam engine was in a very primitive state, for the science of thermodynamics would not be formalised for nearly another 100 years.
In 1763, Watt was asked to repair a model Newcomen engine belonging to the university. Even after repair, the engine barely worked. After much experimentation, Watt demonstrated that about three-quarters of the thermal energy of the steam was being consumed in heating the engine cylinder
In a reciprocating engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels.
The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is se ...
on every cycle. This energy was wasted because, later in the cycle, cold water was injected into the cylinder to condense the steam to reduce its pressure. Thus, by repeatedly heating and cooling the cylinder, the engine wasted most of its thermal energy rather than converting it into mechanical energy.
Watt's critical insight, arrived at in May 1765 as he crossed Glasgow Green park, was to cause the steam to condense in a separate chamber apart from the piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
, and to maintain the temperature of the cylinder at the same temperature as the injected steam by surrounding it with a "steam jacket". Thus, very little energy was absorbed by the cylinder on each cycle, making more available to perform useful work. Watt had a working model later that same year.
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
, some of which came from Black. More substantial backing came from John Roebuck, the founder of the celebrated Carron Iron Works near Falkirk
Falkirk ( gd, An Eaglais Bhreac, sco, Fawkirk) is a large town in the Central Lowlands of Scotland, historically within the county of Stirlingshire. It lies in the Forth Valley, northwest of Edinburgh and northeast of Glasgow.
Falkirk had a ...
, with whom he now formed a partnership. Roebuck lived at Kinneil House in Bo'ness, during which time Watt worked at perfecting his steam engine in a cottage adjacent to the house. The shell of the cottage, and a very large part of one of his projects, still exist to the rear.
The principal difficulty was in machining the piston and cylinder. Iron workers of the day were more like blacksmiths than modern machinist
A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who not only operates machine tools, but also has the knowledge of tooling and materials required to create set ups on machine tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling ...
s, and were unable to produce the components with sufficient precision. Much capital was spent in pursuing a patent on Watt's invention. Strapped for resources, Watt was forced to take up employment—first as a surveyor
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
, then as a civil engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing ...
—for 8 years.
Roebuck went bankrupt, and Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton (; 3 September 172817 August 1809) was an English manufacturer and business partner of Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton & Watt steam engine ...
, who owned the Soho Manufactory works near Birmingham, acquired his patent rights. An extension of the patent to 1800 was successfully obtained in 1775.
Through Boulton, Watt finally had access to some of the best iron workers in the world. The difficulty of the manufacture of a large cylinder with a tightly fitting piston was solved by John Wilkinson, who had developed precision boring techniques for cannon making at Bersham, near Wrexham, North Wales. Watt and Boulton formed a hugely successful partnership, Boulton and Watt
Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the Engli ...
, which lasted for the next 25 years.
First engines
 In 1776, the first engines were installed and working in commercial enterprises. These first engines were used to power pumps and produced only reciprocating motion to move the pump rods at the bottom of the shaft. The design was commercially successful, and for the next five years, Watt was very busy installing more engines, mostly in Cornwall, for pumping water out of mines.
These early engines were not manufactured by Boulton and Watt, but were made by others according to drawings made by Watt, who served in the role of
In 1776, the first engines were installed and working in commercial enterprises. These first engines were used to power pumps and produced only reciprocating motion to move the pump rods at the bottom of the shaft. The design was commercially successful, and for the next five years, Watt was very busy installing more engines, mostly in Cornwall, for pumping water out of mines.
These early engines were not manufactured by Boulton and Watt, but were made by others according to drawings made by Watt, who served in the role of consulting engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the ...
. The erection of the engine and its shakedown was supervised by Watt, at first, and then by men in the firm's employ. These were large machines. The first, for example, had a cylinder with a diameter of 50 inches and an overall height of about 24 feet, and required the construction of a dedicated building to house it. Boulton and Watt charged an annual payment, equal to one-third of the value of the coal saved in comparison to a Newcomen engine performing the same work.
The field of application for the invention was greatly widened when Boulton urged Watt to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston to produce rotational power for grinding, weaving and milling. Although a crank
Crank may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Crank (mechanism), in mechanical engineering, a bent portion of an axle or shaft, or an arm keyed at right angles to the end of a shaft, by which motion is imparted to or received from it
* Crankset, the compone ...
seemed the obvious solution to the conversion, Watt and Boulton were stymied by a patent for this, whose holder, James Pickard and his associates proposed to cross-license the external condenser. Watt adamantly opposed this and they circumvented the patent by their sun and planet gear in 1781.
Over the next six years, he made other improvements and modifications to the steam engine. A double-acting engine, in which the steam acted alternately on both sides of the piston, was one. He described methods for working the steam "expansively" (i.e., using steam at pressures well above atmospheric). A compound engine, which connected two or more engines, was described. Two more patents were granted for these in 1781 and 1782. Numerous other improvements that made for easier manufacture and installation were continually implemented. One of these included the use of the steam indicator which produced an informative plot of the pressure in the cylinder against its volume, which he kept as a trade secret. Another important invention, one which Watt was most proud of, was the parallel motion linkage
In kinematics, the parallel motion linkage is a six-bar mechanical linkage invented by the Scottish engineer James Watt in 1784 for the double-acting Watt steam engine. It allows a rod moving practically straight up and down to transmit moti ...
, which was essential in double-acting engines as it produced the straight line motion required for the cylinder rod and pump, from the connected rocking beam, whose end moves in a circular arc. This was patented in 1784. A throttle valve to control the power of the engine, and a centrifugal governor, patented in 1788, to keep it from "running away" were very important. These improvements taken together produced an engine which was up to five times as fuel efficient as the Newcomen engine.
Because of the danger of exploding boilers, which were in a very primitive stage of development, and the ongoing issues with leaks, Watt restricted his use of high pressure steam – all of his engines used steam at near atmospheric pressure.
Patent trials

Edward Bull
Edward Bull (c.1759–1798) was an English engineer, noted for a modified type of steam engine known as the Bull engine. Working with Richard Trevithick, many of these were installed in mines in Cornwall.
Life
Bull was born about 1759. From 1779 ...
started constructing engines for Boulton and Watt in Cornwall in 1781. By 1792, he had started making engines of his own design, but which contained a separate condenser, and so infringed Watt's patents. Two brothers, Jabez Carter Hornblower and Jonathan Hornblower Jnr also started to build engines about the same time. Others began to modify Newcomen engines by adding a condenser, and the mine owners in Cornwall became convinced that Watt's patent could not be enforced. They started to withhold payments to Boulton and Watt, which by 1795 had fallen on hard times. Of the total £21,000 (equivalent to £ as of ) owed, only £2,500 had been received. Watt was forced to go to court to enforce his claims.
He first sued Bull in 1793. The jury found for Watt, but the question of whether or not the original specification of the patent was valid was left to another trial. In the meantime, injunctions were issued against the infringers, forcing their payments of the royalties
A royalty payment is a payment made by one party to another that owns a particular asset, for the right to ongoing use of that asset. Royalties are typically agreed upon as a percentage of gross or net revenues derived from the use of an asset o ...
to be placed in escrow. The trial on determining the validity of the specifications which was held in the following year was inconclusive, but the injunctions remained in force and the infringers, except for Jonathan Hornblower, all began to settle their cases. Hornblower was soon brought to trial in 1799, and the verdict of the four was decisively in favour of Watt. Their friend John Wilkinson, who had solved the problem of boring an accurate cylinder, was a particularly grievous case. He had erected about 20 engines without Boulton's and Watts' knowledge. They finally agreed to settle the infringement in 1796. Boulton and Watt never collected all that was owed them, but the disputes were all settled directly between the parties or through arbitration
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) that resolves disputes outside the judiciary courts. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons (the 'arbitrators', 'arbiters' or 'arbitral tribunal'), which renders the ' ...
. These trials were extremely costly in both money and time, but ultimately were successful for the firm.
Copying machine
 Before 1780, there was no good method for making copies of letters or drawings. The only method sometimes used was a mechanical one using multiple linked pens. Watt at first experimented with improving this method, but soon gave up on this approach because it was so cumbersome. He instead decided to try to physically transfer ink from the front of the original to the back of another sheet, moistened with a solvent, and pressed to the original. The second sheet had to be thin, so that the ink could be seen through it when the copy was held up to the light, thus reproducing the original exactly.
Watt started to develop the process in 1779, and made many experiments to formulate the ink, select the thin paper, to devise a method for wetting the special thin paper, and to make a press suitable for applying the correct pressure to effect the transfer. All of these required much experimentation, but he soon had enough success to patent the process a year later. Watt formed another partnership with Boulton (who provided financing) and James Keir (to manage the business) in a firm called James Watt and Co. The perfection of the invention required much more development work before it could be routinely used by others, but this was carried out over the next few years. Boulton and Watt gave up their shares to their sons in 1794. It became a commercial success and was widely used in offices even into the 20th century.
Before 1780, there was no good method for making copies of letters or drawings. The only method sometimes used was a mechanical one using multiple linked pens. Watt at first experimented with improving this method, but soon gave up on this approach because it was so cumbersome. He instead decided to try to physically transfer ink from the front of the original to the back of another sheet, moistened with a solvent, and pressed to the original. The second sheet had to be thin, so that the ink could be seen through it when the copy was held up to the light, thus reproducing the original exactly.
Watt started to develop the process in 1779, and made many experiments to formulate the ink, select the thin paper, to devise a method for wetting the special thin paper, and to make a press suitable for applying the correct pressure to effect the transfer. All of these required much experimentation, but he soon had enough success to patent the process a year later. Watt formed another partnership with Boulton (who provided financing) and James Keir (to manage the business) in a firm called James Watt and Co. The perfection of the invention required much more development work before it could be routinely used by others, but this was carried out over the next few years. Boulton and Watt gave up their shares to their sons in 1794. It became a commercial success and was widely used in offices even into the 20th century.
Chemical experiments
From an early age, Watt was very interested in chemistry. In late 1786, while in Paris, he witnessed an experiment by Claude Louis Berthollet in which he reacted hydrochloric acid withmanganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell ...
to produce chlorine. He had already found that an aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
of chlorine could bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
textiles, and had published his findings, which aroused great interest among many potential rivals. When Watt returned to Britain, he began experiments along these lines with hopes of finding a commercially viable process. He discovered that a mixture of salt, manganese dioxide and sulphuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
could produce chlorine, which Watt believed might be a cheaper method. He passed the chlorine into a weak solution of alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
, and obtained a turbid solution that appeared to have good bleaching properties. He soon communicated these results to James McGrigor, his father-in-law, who was a bleacher in Glasgow. Otherwise, he tried to keep his method a secret.
With McGrigor and his wife Annie, he started to scale up the process, and in March 1788, McGrigor was able to bleach of cloth to his satisfaction. About this time, Berthollet discovered the salt and sulphuric acid process, and published it, so it became public knowledge. Many others began to experiment with improving the process, which still had many shortcomings, not the least of which was the problem of transporting the liquid product. Watt's rivals soon overtook him in developing the process, and he dropped out of the race. It was not until 1799, when Charles Tennant patented a process for producing solid bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
) that it became a commercial success.
By 1794, Watt had been chosen by Thomas Beddoes to manufacture apparatuses to produce, clean and store gases for use in the new Pneumatic Institution at Hotwells
Hotwells is a district of the English port city of Bristol. It is located to the south of and below the high ground of Clifton, and directly to the north of the Floating Harbour. The southern entrance to the Avon Gorge, which connects the docks ...
in Bristol. Watt continued to experiment with various gases, but by 1797, the medical uses for the " factitious airs" (artificial gases) had come to a dead end.Personality
Watt combined theoretical knowledge of science with the ability to apply it practically. Chemist Humphry Davy said of him, "Those who consider James Watt only as a great practical mechanic form a very erroneous idea of his character; he was equally distinguished as a natural philosopher and a chemist, and his inventions demonstrate his profound knowledge of those sciences, and that peculiar characteristic of genius, the union of them for practical application". He was greatly respected by other prominent men of theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. He was an important member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham, and was a much sought-after conversationalist and companion, always interested in expanding his horizons. His personal relationships with his friends and business partners were always congenial and long-lasting.
According to Lord Liverpool (Prime Minister of the UK),
A more excllent and amikable man in all the relations of life I believe never existed.Watt was a prolific correspondent. During his years in Cornwall, he wrote long letters to Boulton several times per week. He was averse to publishing his results in, for example, the '' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' however, and instead preferred to communicate his ideas in
patents
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
. He was an excellent draughtsman A draughtsman (British spelling) or draftsman (American spelling) may refer to:
* An architectural drafter, who produced architectural drawings until the late 20th century
* An artist who produces drawings that rival or surpass their other types ...
.
 He was a rather poor businessman, and especially hated bargaining and negotiating terms with those who sought to use the steam engine. In a letter to William Small in 1772, Watt confessed that "he would rather face a loaded cannon than settle an account or make a bargain." Until he retired, he was always very concerned about his financial affairs, and was something of a worrier. His health was often poor and he suffered frequent nervous headaches and depression. When he retired in 1800, he became a rich enough man to pass the business on to his sons.
He was a rather poor businessman, and especially hated bargaining and negotiating terms with those who sought to use the steam engine. In a letter to William Small in 1772, Watt confessed that "he would rather face a loaded cannon than settle an account or make a bargain." Until he retired, he was always very concerned about his financial affairs, and was something of a worrier. His health was often poor and he suffered frequent nervous headaches and depression. When he retired in 1800, he became a rich enough man to pass the business on to his sons.
Soho Foundry
At first, the partnership made the drawings and specifications for the engines, and supervised the work to erect them on the customers' property. They produced almost none of the parts themselves. Watt did most of his work at his home in Harper's Hill in Birmingham, while Boulton worked at the Soho Manufactory. Gradually, the partners began to actually manufacture more and more of the parts, and by 1795, they purchased a property about a mile away from the Soho Manufactory, on the banks of the Birmingham Canal, to establish a new foundry for the manufacture of the engines. The Soho Foundry formally opened in 1796 at a time when Watt's sons, Gregory and James Jr. were heavily involved in the management of the enterprise. In 1800, the year of Watt's retirement, the firm made a total of 41 engines.Later years

 Watt retired in 1800, the same year that his fundamental patent and partnership with Boulton expired. The famous partnership was transferred to the men's sons, Matthew Robinson Boulton and James Watt Jr.. Longtime firm engineer William Murdoch was soon made a partner and the firm prospered.
Watt continued to invent other things before and during his semi-retirement. Within his home in Handsworth, Staffordshire, Watt made use of a garret room as a workshop, and it was here that he worked on many of his inventions. Among other things, he invented and constructed machines for copying sculptures and medallions which worked very well, but which he never patented. One of the first sculptures he produced with the machine was a small
Watt retired in 1800, the same year that his fundamental patent and partnership with Boulton expired. The famous partnership was transferred to the men's sons, Matthew Robinson Boulton and James Watt Jr.. Longtime firm engineer William Murdoch was soon made a partner and the firm prospered.
Watt continued to invent other things before and during his semi-retirement. Within his home in Handsworth, Staffordshire, Watt made use of a garret room as a workshop, and it was here that he worked on many of his inventions. Among other things, he invented and constructed machines for copying sculptures and medallions which worked very well, but which he never patented. One of the first sculptures he produced with the machine was a small head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
of his old professor friend Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
. He maintained his interest in civil engineering and was a consultant on several significant projects. He proposed, for example, a method for constructing a flexible pipe to be used for pumping water under the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
at Glasgow.
He and his second wife travelled to France and Germany, and he purchased an estate in mid-Wales at Doldowlod House, one mile south of Llanwrthwl, which he much improved.
In 1816, he took a trip on the paddle-steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses were w ...
'' Comet'', a product of his inventions, to revisit his home town of Greenock.
He died on 25 August 1819 at his home " Heathfield Hall" near Handsworth in Staffordshire (now part of Birmingham) at the age of 83. He was buried on 2 September in the graveyard of St Mary's Church, Handsworth
St Mary's Church, Handsworth, also known as Handsworth Old Church, is a Grade II* listed Anglican church in Handsworth, Birmingham, England. Its ten-acre (4 hectare) grounds are contiguous with Handsworth Park. It lies just off the Birmin ...
. The church has since been extended and his grave is now inside the church.
Family
On 16 July 1764, Watt married his cousin Margaret Miller (d. 1773). They had two children, Margaret (1767–1796) and James (1769–1848). In 1791, their daughter married James Miller. In September 1773, while Watt was working in the Scottish Highlands, he learned that his wife, who was pregnant with their third child, was seriously ill. He immediately returned home but found that she had died and their child was stillborn. In 1775, he married Ann MacGregor (d. 1832).Freemasonry
He was Initiated into Scottish Freemasonry in The Glasgow Royal Arch Lodge, No. 77, in 1763. The Lodge ceased to exist in 1810. A Masonic Lodge was named after him in his home town of Glasgow – Lodge James Watt, No. 1215.Murdoch's contributions
William Murdoch joined Boulton and Watt in 1777. At first, he worked in the pattern shop in Soho, but soon he was erecting engines in Cornwall. He became an important part of the firm and made many contributions to its success including important inventions of his own. John Griffiths, who wrote a biography of him in 1992, has argued that Watt's discouragement of Murdoch's work with high-pressure steam on his steam road locomotive experiments delayed its development: Watt rightly believed that boilers of the time would be unsafe at higher pressures. Watt patented the application of the sun and planet gear to steam in 1781 and asteam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
in 1784, both of which have strong claims to have been invented by Murdoch. The patent was never contested by Murdoch, however, and Boulton and Watt's firm continued to use the sun and planet gear in their rotative engines, even long after the patent for the crank expired in 1794. Murdoch was made a partner of the firm in 1810, where he remained until his retirement 20 years later at the age of 76.
Legacy
 As one author states, James Watt's improvements to the steam engine "converted it from a prime mover of marginal efficiency into the mechanical workhorse of the Industrial Revolution".
As one author states, James Watt's improvements to the steam engine "converted it from a prime mover of marginal efficiency into the mechanical workhorse of the Industrial Revolution".
Honours
Watt was much honoured in his own time. In 1784, he was made a fellow of theRoyal Society of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established i ...
, and was elected as a member of the Batavian Society for Experimental Philosophy The Batavian Society for Experimental Philosophy ( nl, Bataafsch Genootschap voor Proefondervindelijke Wijsbegeerte) is a Dutch learned society residing in Rotterdam.
History
The society was founded on June 3, 1769 after Steven Hoogendijk declare ...
, of Rotterdam, the Netherlands, in 1787. In 1789, he was elected to the elite group, the Smeatonian Society of Civil Engineers. In 1806, he was conferred the honorary Doctor of Laws by the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
. The French Academy elected him a Corresponding Member and he was made a Foreign Associate in 1814.
The watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
is named after James Watt for his contributions to the development of the steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
, and was adopted by the Second Congress of the British Association for the Advancement of Science
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chie ...
in 1889 and by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established i ...
in 1960 as the unit of power incorporated in the International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(or "SI").
On 29 May 2009, the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
announced that Boulton and Watt would appear on a new £50 note. The design is the first to feature a dual portrait on a Bank of England note, and presents the two industrialists side by side with images of Watt's steam engine and Boulton's Soho Manufactory. Quotes attributed to each of the men are inscribed on the note: "I sell here, sir, what all the world desires to have—POWER" (Boulton) and "I can think of nothing else but this machine" (Watt). The inclusion of Watt is the second time that a Scot has featured on a Bank of England note (the first was Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
on the 2007 issue £20 note). In September 2011, it was announced that the notes would enter circulation on 2 November.
In 2011, he was one of seven inaugural inductees to the Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame.
Memorials
 Watt was buried in the grounds of
Watt was buried in the grounds of St. Mary's Church, Handsworth
St Mary's Church, Handsworth, also known as Handsworth Old Church, is a Grade II* listed Church of England, Anglican church in Handsworth, West Midlands, Handsworth, Birmingham, England. Its ten-acre (4 hectare) grounds are contiguous with ...
, in Birmingham. Later expansion of the church, over his grave, means that his tomb is now buried ''inside'' the church.
The garret room workshop that Watt used in his retirement was left, locked and untouched, until 1853, when it was first viewed by his biographer J. P. Muirhead. Thereafter, it was occasionally visited, but left untouched, as a kind of shrine. A proposal to have it transferred to the Patent Office came to nothing. When the house was due to be demolished in 1924, the room and all its contents were presented to the Science Museum, where it was recreated in its entirety. It remained on display for visitors for many years, but was walled-off when the gallery it was housed in closed. The workshop remained intact, and preserved, and in March 2011 was put on public display as part of a new permanent Science Museum exhibition, "James Watt and our world".
The approximate location of James Watt's birth in Greenock is commemorated by a statue. Other memorials in Greenock include street names and the Watt Memorial Library, which was begun in 1816 with Watt's donation of scientific books, and developed as part of the Watt Institution by his son (which ultimately became the James Watt College). Taken over by the local authority in 1974, the library now also houses the local history collection and archives of Inverclyde, and is dominated by a large seated statue in the vestibule
Vestibule or Vestibulum can have the following meanings, each primarily based upon a common origin, from early 17th century French, derived from Latin ''vestibulum, -i n.'' "entrance court".
Anatomy
In general, vestibule is a small space or cavity ...
. Watt is additionally commemorated by statuary in George Square, Glasgow and Princes Street
Princes Street ( gd, Sràid nam Prionnsan) is one of the major thoroughfares in central Edinburgh, Scotland and the main shopping street in the capital. It is the southernmost street of Edinburgh's New Town, stretching around 1.2 km (three ...
, Edinburgh, as well as others in Birmingham, where he is also remembered by the Moonstones and a school is named in his honour.
The James Watt College has expanded from its original location to include campuses in Kilwinning (North Ayrshire), Finnart Street and The Waterfront in Greenock, and the Sports campus in Largs. Heriot-Watt University
Heriot-Watt University ( gd, Oilthigh Heriot-Watt) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1821 as the School of Arts of Edinburgh, the world's first mechanics' institute, and subsequently granted univ ...
near Edinburgh was at one time the School of Arts of Edinburgh, founded in 1821 as the world's first Mechanics Institute, but to commemorate George Heriot, the 16th-century financier to King James VI and I, and James Watt, after Royal Charter the name was changed to Heriot-Watt University. Dozens of university and college buildings (chiefly of science and technology) are named after him. Matthew Boulton's home, Soho House, is now a museum, commemorating the work of both men. The University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
's Faculty of Engineering has its headquarters in the James Watt Building, which also houses the department of Mechanical Engineering and the department of Aerospace Engineering. The huge painting ''James Watt contemplating the steam engine'' by James Eckford Lauder
James Eckford Lauder (15 August 1811 in Edinburgh – 27 March 1869 in Edinburgh) was a notable mid- Victorian Scottish artist, famous for both portraits and historical pictures.
Life and work
A younger brother of artist Robert Scott Laud ...
is now owned by the National Gallery of Scotland.
 There is a statue of James Watt in
There is a statue of James Watt in Piccadilly Gardens
Piccadilly Gardens is a green space in Manchester city centre, England, on the edge of the Northern Quarter.
It takes its name from the adjacent street, Piccadilly, which runs across the city centre from Market Street to London Road. The ga ...
, Manchester and City Square, Leeds.
A colossal statue of Watt by Francis Legatt Chantrey was placed in Westminster Abbey, and later was moved to St. Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Gr ...
. On the cenotaph, the inscription reads, in part, "JAMES WATT ... ENLARGED THE RESOURCES OF HIS COUNTRY, INCREASED THE POWER OF MAN, AND ROSE TO AN EMINENT PLACE AMONG THE MOST ILLUSTRIOUS FOLLOWERS OF SCIENCE AND THE REAL BENEFACTORS OF THE WORLD".
A bust of Watt is in the Hall of Heroes of the National Wallace Monument in Stirling, Scotland.
The French Navy submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
was named for Watt.
Patents
Watt was the sole inventor listed on his six patents:Hills, vol. 3, p. 13. * Patent 913: A method of lessening the consumption of steam in steam engines – the separate condenser. The specification was accepted on 5 January 1769; enrolled on 29 April 1769, and extended to June 1800 by an Act of Parliament in 1775. * Patent 1,244: A new method of copying letters. The specification was accepted on 14 February 1780 and enrolled on 31 May 1780. * Patent 1,306: New methods to produce a continued rotation motion – sun and planet. The specification was accepted on 25 October 1781 and enrolled on 23 February 1782. * Patent 1,321: New improvements upon steam engines – expansive and double acting. The specification was accepted on 14 March 1782 and enrolled on 4 July 1782. * Patent 1,432: New improvements upon steam engines – three bar motion and steam carriage. The specification was accepted on 28 April 1782 and enrolled on 25 August 1782. * Patent 1,485: Newly improved methods of constructing furnaces. The specification was accepted on 14 June 1785 and enrolled on 9 July 1785.Notes
References
Sources
* * Carnegie, Andrew, ''James Watt'' University Press of the Pacific (2001) (Reprinted from the 1913 ed.), . * * * Hills, Rev. Dr. Richard L., ''James Watt, Vol 1, His time in Scotland, 1736–1774'' (2002); Vol 2, ''The years of toil, 1775–1785''; Vol 3 ''Triumph through adversity 1785–1819.'' Landmark Publishing Ltd, . * * * Marsden, Ben. ''Watt's Perfect Engine'' Columbia University Press (New York, 2002), . * Marshall, Thomas H. (1925), ''James Watt''Chapter 3: Mathematical Instrument Maker
fro
Steam Engine Library
of University of Rochester Department of History. * Marshall, Thomas H. (1925
''James Watt''
University of Rochester Department of History. * * * Roll, Erich (1930). ''An Early Experiment in Industrial Organisation : being a History of the Firm of Boulton & Watt.'' 1775–1805. Longmans, Green and Co. * Smiles, Samuel, ''Lives of the Engineers'', (London, 1861–62, new edition, five volumes, 1905). ;Related topics * *
External links
James Watt by Andrew Carnegie (1905)
Librivox audiobook: James Watt by Andrew Carnegie (1905)
James Watt by Thomas H. Marshall (1925)
Archives of Soho
at Birmingham Central Library.
BBC History: James Watt
Revolutionary Players website
Cornwall Record Office Boulton and Watt letters
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Watt, James 18th-century British engineers 18th-century British scientists 18th-century Scottish people 1736 births 1819 deaths Alumni of the University of Glasgow Fellows of the Royal Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Industrial Revolution in England Industrial Revolution in Scotland Members of the Lunar Society of Birmingham People associated with energy People associated with Heriot-Watt University People from Greenock People of the Scottish Enlightenment Scottish business theorists Scottish businesspeople Scottish chemists Scottish deists Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame inductees Scottish inventors Scottish Presbyterians Scottish surveyors Astronomical instrument makers