The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the
State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. It consists of three service branches: the
Israeli Ground Forces, the
Israeli Air Force, and the
Israeli Navy. It is the sole military wing of the
Israeli security apparatus, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel. The IDF is headed by the
Chief of the General Staff, who is subordinate to the
Israeli Defense Minister.
On the orders of
David Ben-Gurion, the IDF was formed on 26 May 1948 and began to operate as a
conscript military, drawing its initial recruits from the already-existing paramilitaries of the
Yishuv—namely
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the ...
, the
Irgun, and
Lehi
Lehi (; he, לח"י – לוחמי חרות ישראל ''Lohamei Herut Israel – Lehi'', "Fighters for the Freedom of Israel – Lehi"), often known pejoratively as the Stern Gang,"This group was known to its friends as LEHI and to its enemie ...
. Since its formation shortly after the
Israeli Declaration of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive ...
, the IDF has participated in
every armed conflict involving Israel. While it originally operated on three major fronts—against
Lebanon and
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in the north, against
Jordan and
Iraq in the east, and against
Egypt in the south—the IDF has primarily shifted its focus to
southern Lebanon and the
Palestinian Territories since the
1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty and
1994 Israel–Jordan peace treaty. However, notable
Israeli–Syrian border incidents have occurred frequently since 2011 due to regional instability caused by the ongoing multi-sided
Syrian Civil War.
The IDF is unique among the militaries of the world due to
its regulated conscription of women since its formation. It is one of the most prominent institutions in Israeli society due to its influence on the country's economy and political scene. It uses several technologies developed within Israel, with many of them made specifically to cater to its needs in its operational environment in the
Levant. Prominent Israeli-developed military equipment includes: the
Merkava, a
main battle tank; the
Achzarit, an
armored personnel carrier;
Iron Dome, an
air defense system;
Trophy
A trophy is a tangible, durable reminder of a specific achievement, and serves as a recognition or evidence of merit. Trophies are often awarded for sporting events, from youth sports to professional level athletics. In many sports medals (or, in ...
, an
active protection system
An active protection system is a system designed to actively prevent certain anti-tank weapons from destroying a vehicle.
Countermeasures that either conceal the vehicle from, or disrupt the guidance of an incoming guided missile threat are design ...
; the
IMI Galil and
IWI Tavor families of
assault rifles; and the
Uzi, a family of
submachine gun
A submachine gun (SMG) is a magazine-fed, automatic carbine designed to fire handgun cartridges. The term "submachine gun" was coined by John T. Thompson, the inventor of the Thompson submachine gun, to describe its design concept as an autom ...
s. Since 1967, the IDF has had
a close security relationship with the United States, including in research and development cooperation, with joint efforts on the
F-15I, the
Tactical High-Energy Laser, and the
Arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
, among others.
The IDF is believed to have maintained
an operational nuclear weapons capability since 1967, possibly possessing between 80 and 400
nuclear warheads;
[There are a wide range of estimates as to the size of the Israeli nuclear arsenal. For a compiled list of estimates, see Avner Cohen, ''The Worst-Kept Secret: Israel's bargain with the Bomb'' (Columbia University Press, 2010), Table 1, page xxvii and page 82.] its nuclear-delivery system structure is widely suspected of having been successfully developed into a
nuclear triad, primarily consisting of
Jericho
Jericho ( ; ar, أريحا ; he, יְרִיחוֹ ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank. It is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It is the administrative seat of the Jericho Gove ...
land-based
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s,
Popeye Turbo maritime-based
submarine-launched cruise missile
A submarine-launched cruise missile (SLCM) is a cruise missile that is launched from a submarine (especially a SSG or SSGN). Current versions are typically standoff weapons known as land-attack cruise missiles (LACMs), which are used to attack p ...
s, and various
delivery-capable aircraft.
Etymology
The
Israeli cabinet
The Cabinet of Israel (officially: he, ממשלת ישראל ''Memshelet Yisrael'') exercises executive authority in the State of Israel. It consists of ministers who are chosen and led by the prime minister. The composition of the governmen ...
ratified the name "Israel Defense Forces" ( he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל), ''Tzva HaHagana LeYisra'el'', literally "army for the defense of Israel," on 26 May 1948. The other main contender was ''Tzva Yisra'el'' ( he, צְבָא יִשְׂרָאֵל). The name was chosen because it conveyed the idea that the army's role was defense, and because it incorporated the name
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the ...
, the pre-state defensive organization upon which the new army was based.
Among the primary opponents of the name were Minister
Haim-Moshe Shapira and the
Hatzohar party, both in favor of ''Tzva Yisra'el''.
History
The IDF traces its roots to Jewish paramilitary organizations in the
New Yishuv, starting with the
Second Aliyah (1904 to 1914). The first such organization was
Bar-Giora
Bar-Giora ( he, בר גיורא) was a Jewish militia of the Second Aliyah, the precursor of Hashomer.
History
Bar Giora's founder, Israel Shochat made his Aliyah to Ottoman Palestine in 1904. He already had experience of underground militias ...
, founded in September 1907. Bar-Giora was transformed into
Hashomer in April 1909, which operated until the
British Mandate of Palestine came into being in 1920. Hashomer was an elitist organization with narrow scope, and was mainly created to protect against criminal gangs seeking to steal property. The
Zion Mule Corps and the
Jewish Legion, both part of the
British Army of
World War I, would further bolster the Yishuv with military experience and manpower, forming the basis for later paramilitary forces. After the
1920 Palestine riots
The 1920 Nebi Musa riots or 1920 Jerusalem riots took place in British-controlled part of Occupied Enemy Territory Administration between Sunday, 4 April, and Wednesday, 7 April 1920 in and around the Old City of Jerusalem. Five Jews and four Ar ...
against Jews in April 1920, the Yishuv leadership realized the need for a nationwide underground defense organization, and the
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the ...
was founded in June of the same year. The Haganah became a full-scale defense force after the
1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine, later known as The Great Revolt (''al-Thawra al- Kubra'') or The Great Palestinian Revolt (''Thawrat Filastin al-Kubra''), was a popular nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine a ...
with an organized structure, consisting of three main units—the
Field Corps,
Guard Corps, and the
Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Companies") was the elite fighting force of the Haganah, the underground army of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of the British Mandate for Palestine. The Palmach ...
. During World War II, the Yishuv participated in the British war effort, culminating in the formation of the
Jewish Brigade. These would eventually form the backbone of the Israel Defense Forces, and provide it with its initial manpower and doctrine.
Following Israel's
Declaration of Independence, Prime Minister and Defense Minister
David Ben-Gurion issued an order for the formation of the Israel Defense Forces on 26 May 1948. Although Ben-Gurion had no legal authority to issue such an order, the order was made legal by
the cabinet on 31 May. The same order called for the disbandment of all other Jewish armed forces.
The two other Jewish underground organizations,
Irgun and
Lehi
Lehi (; he, לח"י – לוחמי חרות ישראל ''Lohamei Herut Israel – Lehi'', "Fighters for the Freedom of Israel – Lehi"), often known pejoratively as the Stern Gang,"This group was known to its friends as LEHI and to its enemie ...
, agreed to join the IDF if they would be able to form independent units and agreed not to make independent arms purchases. This was the background for the
Altalena Affair
The ''Altalena'' Affair was a violent confrontation that took place in June 1948 by the newly created Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively ref ...
, a confrontation surrounding weapons purchased by the Irgun resulting in a standoff between Irgun members and the newly created IDF. The affair came to an end when ''Altalena'', the ship carrying the arms, was shelled by the IDF. Following the affair, all independent Irgun and Lehi units were either disbanded or merged into the IDF. The Palmach, a leading component of the Haganah, also joined the IDF with
provisions, and Ben Gurion responded by disbanding its staff in 1949, after which many senior Palmach officers retired, notably its first commander,
Yitzhak Sadeh.
The new army organized itself when the
1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine escalated into the
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
, which saw neighboring Arab states attack. Twelve
infantry and
armored brigades formed:
Golani,
Carmeli,
Alexandroni,
Kiryati,
Givati,
Etzioni, the
7th, and
8th armored brigades,
Oded,
Harel Harel is both a surname and a given name. Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Alon Harel (1957-), Israeli law professor
* Dan Harel (1955-), general in the Israeli Defense Force
* David Harel (1950-), computer sciences professor
* Eden ...
,
Yiftach, and
Negev.
After the war, some of the brigades were converted to reserve units, and others were disbanded. Directorates and corps were created from corps and services in the Haganah, and this basic structure in the IDF
still exists today.
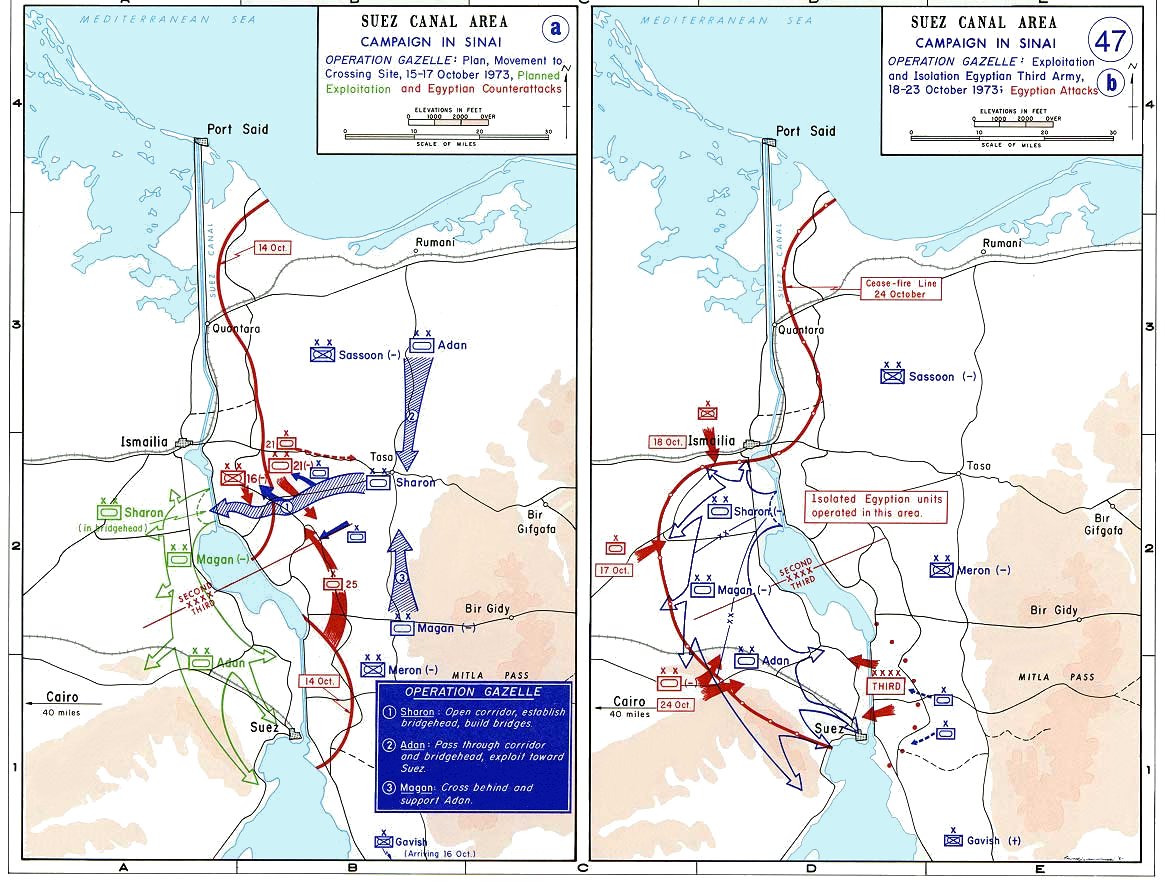
Immediately after the 1948 war, the
Israel-Palestinian conflict shifted to a
low intensity conflict between the IDF and
Palestinian fedayeen
Palestinian fedayeen (from the Arabic ''fidā'ī'', plural ''fidā'iyūn'', فدائيون) are militants or guerrillas of a nationalist orientation from among the Palestinian people. Most Palestinians consider the fedayeen to be " freedom fig ...
. In the 1956
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
, the IDF's first serious test of strength after 1949, the new army captured the
Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, which was later returned. In the 1967
Six-Day War, Israel conquered the Sinai Peninsula,
Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
,
West Bank (including
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel.
Jerusalem was envisaged as a separat ...
) and
Golan Heights from the surrounding Arab states, changing the balance of power in the region as well as the role of the IDF. In the following years leading up to the
Yom Kippur War, the IDF fought in the
War of Attrition against Egypt in the Sinai and a border war against the
Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establ ...
(PLO) in
Jordan, culminating in the
Battle of Karameh.
The surprise of the Yom Kippur War and its aftermath completely changed the IDF's procedures and approach to warfare. Organizational changes were made and more time was dedicated to training for
conventional warfare. However, in the following years the army's role slowly shifted again to low-intensity conflict,
urban warfare and
counter-terrorism. An example of the latter was the successful 1976
Operation Entebbe commando raid to free hijacked airline passengers being held captive in
Uganda. During this era, the IDF also mounted a
successful bombing mission in
Iraq to destroy its nuclear reactor. It was involved in the
Lebanese Civil War, initiating
Operation Litani and later the
1982 Lebanon War
The 1982 Lebanon War, dubbed Operation Peace for Galilee ( he, מבצע שלום הגליל, or מבצע של"ג ''Mivtsa Shlom HaGalil'' or ''Mivtsa Sheleg'') by the Israeli government, later known in Israel as the Lebanon War or the First L ...
, where the IDF ousted Palestinian guerrilla organizations from
Lebanon. For twenty-five years the IDF maintained a
security zone
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercive change) caused by others, by restraining the freedom of others to act. Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be of persons and social ...
inside South Lebanon with their allies the
South Lebanon Army. Palestinian militancy has been the main focus of the IDF ever since, especially during the
First and
Second Intifada
The Second Intifada ( ar, الانتفاضة الثانية, ; he, האינתיפאדה השנייה, ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada ( ar, انتفاضة الأقصى, label=none, '), was a major Palestinian uprising against Israel. ...
s,
Operation Defensive Shield
Operation "Defensive Shield" ( he, מִבְצָע חוֹמַת מָגֵן, ''Mivtza Homat Magen'', literally "Operation Shield Wall") was a large-scale military operation conducted by the Israel Defense Forces in 2002 during the Second Intifada ...
, the
Gaza War,
Operation Pillar of Defense,
Operation Protective Edge, and
Operation Guardian of the Walls, causing the IDF to change many of its values and publish the
IDF Spirit. The Lebanese
Shia organization
Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
has also been a growing threat, against which the IDF fought an
asymmetric conflict
Asymmetric warfare (or asymmetric engagement) is the term given to describe a type of war between belligerents whose relative military power, strategy or tactics differ significantly. This is typically a war between a standing, professional ar ...
between 1982 and 2000, as well as a
full-scale war in 2006.
Organization

All branches of the IDF answer to a single
General Staff
A military staff or general staff (also referred to as army staff, navy staff, or air staff within the individual services) is a group of officers, enlisted and civilian staff who serve the commander of a division or other large military un ...
. The
Chief of the General Staff is the only serving officer having the rank of
Lieutenant General (''Rav Aluf''). He reports directly to the
Defense Minister and indirectly to the
Prime Minister of Israel and the cabinet. Chiefs of Staff are formally appointed by the cabinet, based on the Defense Minister's recommendation, for three years, but the government can vote to extend their service to four (and on rare occasions even five) years. The current chief of staff is
Aviv Kochavi
Rav-Aluf (Lieutenant General) Aviv Kochavi ( he, אביב כוכבי; born 23 April 1964) is the Chief of General Staff of the Israel Defense Forces, having taken the oath of office on January 15, 2019. He was the commander of the Gaza Division, ...
. He replaced
Gadi Eizenkot in 2019.
Structure
The IDF includes the following bodies (those whose respective heads are members of the
General Staff
A military staff or general staff (also referred to as army staff, navy staff, or air staff within the individual services) is a group of officers, enlisted and civilian staff who serve the commander of a division or other large military un ...
are in bold):
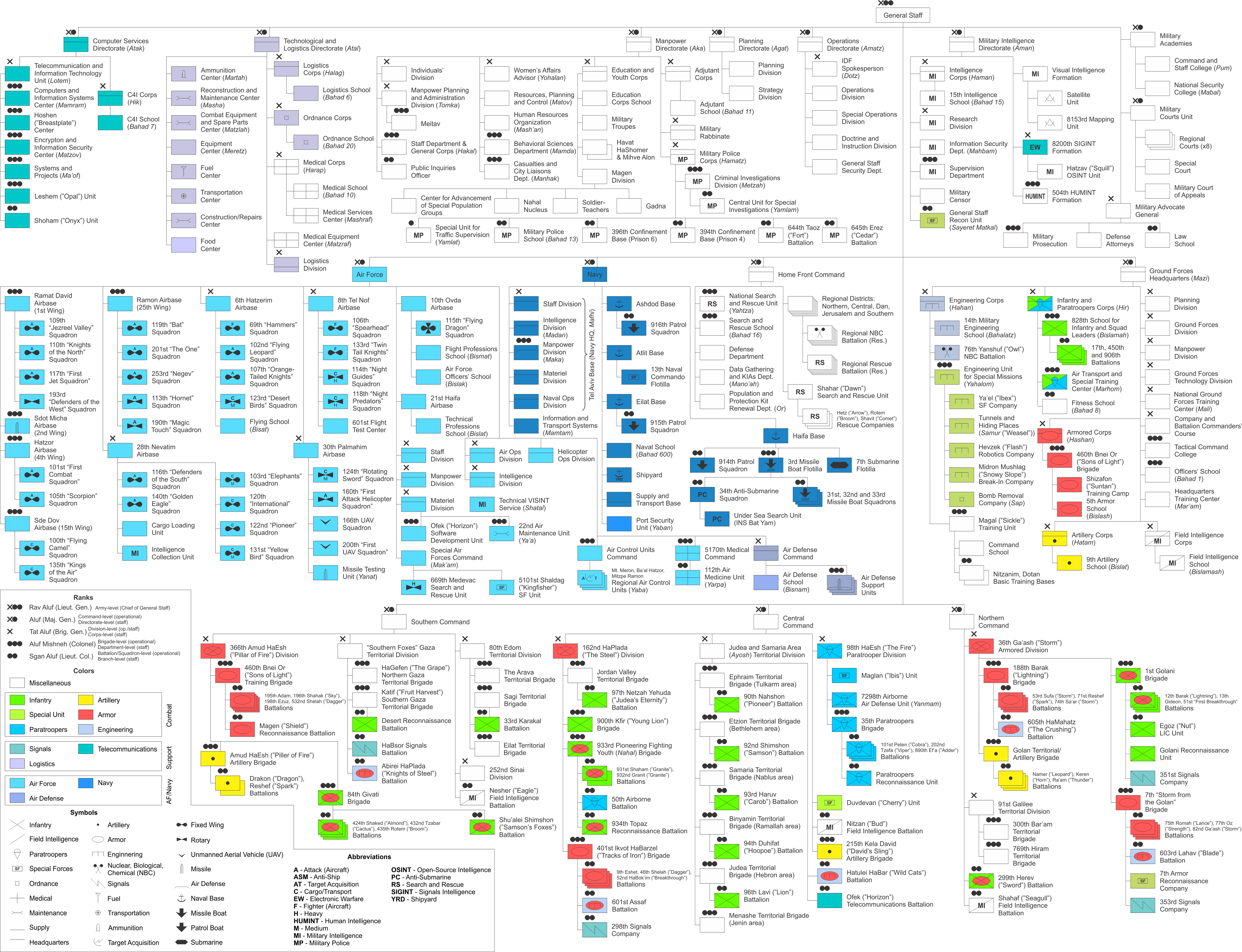
Regional commands
*
Northern Command
*
Central Command
*
Southern Command
*
Home Front Command
Arms
Ground Arm
*
Infantry Corps
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and ma ...
**
1st Golani Brigade
**
35th Paratroopers Brigade
**
84th Nahal Brigade
**
89th Commando Brigade
**
900th Kfir Brigade
**
933rd Givati Brigade
*
Armored Corps
An armoured corps (also mechanized corps or tank corps) is a specialized military organization whose role is to conduct armoured warfare. The units belonging to an armoured corps include military staff, and are equipped with tanks and other armou ...
**
7th Sa'ar Armored Brigade
**
188th Barak Armored Brigade
**
401st Ikvot HaBarzel Armored Brigade
**
460th Sons of Light Armored Brigade
*
Artillery Corps
*
Combat Engineering Corps
*
Combat Intelligence Collection Corps
Air and Space Arm
*
Air Force
:*
Air Defense Network
Sea Arm
*
Israeli Navy
Administrative branches
General Staff
A military staff or general staff (also referred to as army staff, navy staff, or air staff within the individual services) is a group of officers, enlisted and civilian staff who serve the commander of a division or other large military un ...
*
Planning Directorate (split in 2020)
:*Multi-Branch Force Buildup Directorate
:*
*
Operations Directorate
**
IDF Spokesperson
**
The Dado Center for Interdisciplinary Military Studies
*
Intelligence Directorate
**
Intelligence Corps
**
Military Censor
*
Depth Headquarters
*
Manpower Directorate
The Israeli Personnel Directorate (, ''Agaf Koakh Adam'', abbreviated to AKA), formerly called the Manpower Directorate and the Human Resources Directorate, is the Israel Defense Forces body that holds responsibility for planning and coordination ...
**
Military Police Corps
**
Education and Youth Corps
**
Adjutant Corps
**
General Corps
**
Military Rabbinate
**
Women's Affairs advisor
**
Manpower Planning and Administration brigade
**
Individuals' Department
**
Staff Department
**
Chief Reserve Officer
*
Military Courts / Tribunals Unit
**
Military Court / Tribunal
**
Military Advocate General
**
Military Court of Appeals
*
Computer Service Directorate
**
Teleprocessing and Signal Corps (C4I Corps)
*
Technological and Logistics Directorate
**
Ordnance Corps
**
Maintenance, Supply and Logistics Corps
**
Medical Corps
Other bodies
Military:
* Military Academies
**
Tactical Command College
**
Command and Staff College
**
National Security College
*
Coordinator of Government Activities in the Territories
*
Financial Advisor to the Chief of Staff
*
Military Secretary to the Prime Minister
Civilian:
*
Director-general of the
Ministry of Defense
*
Defense Establishment Comptroller Unit
*
Administration for the Development of Weapons and the Technological Industry
*
Engineering and Construction Department of the Ministry of Defense
Units
Ranks, uniforms and insignia
Ranks

Unlike most militaries, the IDF uses the same rank names in all corps, including the air force and navy. For ground forces' officers, rank insignia are brass on a red background; for the air force, silver on a blue background; and for the navy, the standard gold worn on the sleeve. Officer insignia are worn on epaulets on top of both shoulders. Insignia distinctive to each service are worn on the cap (see fig. 15).


Enlisted grades wear rank insignia on the sleeve, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. For the army and air force, the insignia are white with blue interwoven threads backed with the appropriate corps color. Navy personnel wear gold-colored rank insignia sewn on navy blue material.
From the formation of the IDF until the late 1980s,
sergeant major was a particularly important
warrant officer rank, in line with usage in other armies. However, in the 1980s and 1990s the proliferating ranks of sergeant major became devalued, and now all professional
non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
ranks are a variation on sergeant major (''rav samal'') with the exception of ''rav nagad''.
All translations here are the official translations of the IDF's website.
s (''Hogrim'') (Conscript ranks may be gained purely on time served)
*
Private (''Turai'')
*
Corporal (''Rav Turai'') (also called ''rabat'')
*
Sergeant
Sergeant (abbreviated to Sgt. and capitalized when used as a named person's title) is a rank in many uniformed organizations, principally military and policing forces. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and other uni ...
(''Samal'')
*
First Sergeant (''Samal Rishon'')
Warrant Officers (''Nagadim'')
*
Sergeant First Class (''Rav Samal'')
*
Master Sergeant (''Rav Samal Rishon'')
*
Sergeant Major (''Rav Samal Mitkadem'')
*
Warrant Officer (''Rav Samal Bakhir'')
*
Master Warrant Officer
Master warrant officer (MWO) is a senior military rank in the Bangladesh Armed Forces, the Canadian Forces, Singapore Armed Forces, the South African National Defence Force and the Israel Defense Forces.
Bangladesh Armed Forces
Bangladesh-army- ...
(''Rav Nagad Mishneh'')
*
Chief Warrant Officer (''Rav Nagad'')
Academic officers (''Ktzinim Akadema'im'')
* Professional Academic Officer (''Katzin Miktzo'i Akadema'i'')
* Senior Academic Officer (''Katzin Akadema'i Bakhir'')
Officers (''Ktzinim'')
*
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
(''Segen Mishneh'')
951–Present*
Lieutenant (''Segen'')
*
Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
(''Seren'')
*
Major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
(''Rav Seren'')
*
Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
(''Sgan Aluf'')
*
Colonel (''Aluf Mishneh'')
950–Present 95 or 95th may refer to:
* 95 (number)
* one of the years 95 BC, AD 95, 1995, 2095, etc.
* 95th Division (disambiguation)
* 95th Regiment
** 95th Regiment of Foot (disambiguation)
* 95th Squadron (disambiguation)
* Atomic number 95: americium
*Mi ...
*
Brigadier General (''Tat Aluf'')
968–Present*
Major General (''
Aluf'')
948–Present*
Lieutenant General (''Rav Aluf'')
Uniforms


The Israel Defense Forces has several types of uniforms:
*
Service dress (מדי אלף ''Madei Alef'' – Uniform "A") – the everyday uniform, worn by everybody.
*
Field dress (מדי ב ''Madei Bet'' – Uniform "B") – worn into combat, training, work on base.
The first two resemble each other but the Madei Alef is made of higher quality materials in a golden-olive while the madei bet is in
olive drab.
The dress uniforms may also exhibit a surface shine
* Officers / Ceremonial dress (מדי שרד ''madei srad'') – worn by officers, or during special events/ceremonies.
*
Dress uniform and
mess dress – worn only abroad. There are several dress uniforms depending on the season and the branch.
The service uniform for all ground forces personnel is
olive green; navy and air force uniforms are
beige/
tan (also once worn by the ground forces). The uniforms consist of a two-pocket shirt,
combat trousers
Cargo pants or cargo trousers, also sometimes called combat pants or combat trousers after their original purpose as military workwear, are loosely cut pants originally designed for rough work environments and outdoor activities, distinguished b ...
,
sweater, jacket or blouse, and shoes or boots. The navy also has an all white dress uniform. The green fatigues are the same for winter and summer and heavy winter gear is issued as needed. Women's dress parallels the men's but may substitute a skirt for the trousers and a blouse for the shirt.

Headgear included a service cap for dress and semi-dress and a
field cap
A patrol hat, also known as a field cap, is a soft kepi constructed similarly to a baseball cap, with a stiff, rounded visor but featuring a flat top, worn by military personnel of some countries in the field when a combat helmet is not required.
...
or
"Kova raful" bush hat worn with fatigues. Many IDF personnel once wore the
tembel as a field hat. IDF personnel generally wear
berets in lieu of the service cap and there are many beret colors issued to IDF personnel.
Paratroopers are issued a maroon beret,
Golani brown,
Givati purple,
Nahal
Nahal ( he, נח"ל) (acronym of ''Noar Halutzi Lohem'', lit. Fighting Pioneer Youth) is a program that combines military service with mostly social welfare and informal education projects such as youth movement activities, as well as training ...
lime green,
Kfir camouflage, Combat Engineers gray, navy blue for IDF Naval and dark gray for IDF Air Force personnel. Other beret colors are: black for armored corps, turquoise for artillery personnel; olive drab for infantry; gray for combat engineers. For all other army personnel, except combat units, the beret for men was green and for women, black. Women in the navy wear a black beret with gold insignia. Males in the navy once wore a blue/black beret but replaced it with the
US Navy's
sailor cap.
In combat uniforms the
Orlite helmet has replaced the British
Brodie helmet Mark II/Mark III,
RAC Mk II modified helmet with chin web jump harness (used by
paratroopers and similar to the
HSAT Mk II/Mk III paratrooper helmets), US
M1 helmet, and French
Modèle 1951 helmet
The Modèle 1951 helmet was a military helmet used by the French military (Army, Navy, Air Force and Gendarmerie), iconic of the Algerian War. It replaced a variety of helmets used during the Second World War, including the Adrian helmet, Modè ...
– previously worn by Israeli infantry and airborne troops from the late 1940s to the mid-1970s and early 1980s.
Some corps or units have small variations in their uniforms – for instance,
military police wear a white belt and
police hat, Naval personnel have dress whites for parades, paratroopers are issued a four pocket tunic (yarkit/yerkit) worn untucked with a pistol belt cinched tight around the waist over the shirt.
The IDF Air Corps has a dress uniform consisting of a pale blue shirt with dark blue trousers.
Most IDF soldiers are issued black leather
combat boots, certain units issue
reddish-brown leather boots for historical reasons — the paratroopers,
combat medics, Nahal and Kfir Brigades, as well as some
Special Forces units (
Sayeret Matkal,
Oketz,
Duvdevan,
Maglan, and the
Counter-Terror School). Women were also formerly issued
sandals, but this practice has ceased.
Insignia
IDF soldiers have three types of insignia (other than rank insignia) which identify their corps, specific unit, and position.
A pin attached to the beret identifies a soldier's corps. Soldiers serving in staffs above corps level are often identified by the General Corps pin, despite not officially belonging to it, or the pin of a related corps. New recruits undergoing ''
tironut'' (basic training) do not have a pin. Beret colors are also often indicative of the soldier's corps, although most non-combat corps do not have their own beret, and sometimes wear the color of the corps to which the post they're stationed in belongs. Individual units are identified by a shoulder tag attached to the left
shoulder strap. Most units in the IDF have their own tags, although those that do not, generally use tags identical to their command's tag (corps, directorate, or regional command).
While one cannot always identify the position/job of a soldier, two optional factors help make this identification: an
aiguillette attached to the left shoulder strap and shirt pocket, and a pin indicating the soldier's work type (usually given by a professional course). Other pins may indicate the corps or additional courses taken. Finally, an optional battle pin indicates a war that a soldier has fought in.
Service


Military service routes
The military service is held in three different tracks:
*
Regular service (שירות חובה): mandatory military service which is held according to the
Israeli security service law
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli (b ...
.
*
Permanent service (שירות קבע): military service which is held as part of a contractual agreement between the IDF and the permanent position-holder.
*
Reserve service (שירות מילואים): a military service in which citizens are called for active duty of at most a month every year (in accordance with the Reserve Service Law), for training and ongoing military activities and especially for the purpose of increasing the military forces in case of a war.
Sometimes the IDF would also hold pre-military courses (קורס קדם צבאי or קד"צ) for soon-to-be regular service soldiers.
Special service routes
*
Shoher (שוחר), a person enrolled in pre-military studies (high school, technical college up to engineering degree, some of the קד"ץ courses) – after completing the twelfth study year will do a two-month boot-camp and, if allowed, enter a program of education to qualify as a
practical engineer, with at least two weeks of training following each study year. Successful candidates will continue for an engineering
bachelor degree. The Shoher will be enrolled into regular service if he dropped out before finished their P.A. education or in any finishing education stage (after high school, after P.A. or after receiving the bachelor's degree). Another example of a Shoher is a
programmer
A computer programmer, sometimes referred to as a software developer, a software engineer, a programmer or a coder, is a person who creates computer programs — often for larger computer software.
A programmer is someone who writes/creates ...
that is under the programming course of School for Computer Professions ( he, בית הספר למקצועות המחשב, abbr. Basmach he, בסמ"ח). The course usually lasts about six months, and at its peak, the Shoher receives a programmer badge. The Shoher will have the ability to serve in R&D units without having the engineering credentials if an officer finds him as worthy, and could recommend him for the R&D units. R&D units have the option to provide he, על תקן מהנדס certificate for few selected personal to allow the person to work on life-saving or flight equipment without having an Eng. license (the certificate is not valid for medical R&D machinery). The certificate is provided by the highest in command in the research field (as an example for the Air Force it is the Chief of Equipment Group).
* Civilian working for the IDF ( he, אזרח עובד צה"ל), a civilian working for the military.
The
Israeli Manpower Directorate ( he, אגף משאבי אנוש) at the
Israeli General Staff is the body which coordinates and assembles activities related to the control over human resources and its placement.
Regular service
National military service is mandatory for all
Israeli citizens over the age of 18, although
Arab (but not
Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
) citizens are exempted if they so please, and other exceptions may be made on religious, physical or psychological grounds (see
Profile 21). The
Tal law, which exempts ultra-Orthodox Jews from service, has been the subject of several court cases as well as considerable legislative controversy.
Until the draft of July 2015, men served three years in the IDF. Men drafted as of July 2015 and later will serve two years and eight months (32 months), with some roles requiring an additional four months of Permanent service. Women serve two years. The IDF women who volunteer for several combat positions often serve for three years, due to the longer period of training. Women in other positions, such as programmers, who also require lengthy training time, may also serve three years.
Many
Religious Zionist
Religious Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת דָּתִית, translit. ''Tziyonut Datit'') is an ideology that combines Zionism and Orthodox Judaism. Its adherents are also referred to as ''Dati Leumi'' ( "National Religious"), and in Israel, the ...
men (and many
Modern Orthodox who make
Aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel ...
) elect to do
Hesder, a five-year program envisioned by Rabbi
Yehuda Amital which combines
Torah learning
Torah study is the study of the Torah, Hebrew Bible, Talmud, responsa, rabbinic literature, and similar works, all of which are Judaism's religious texts. According to Rabbinic Judaism, the study is done for the purpose of the ''mitzvah'' ("comma ...
and
military service.
Some distinguished recruits are selected to be trained in order to eventually become members of
special forces units. Every brigade in the IDF has its own special force branch.
Career soldiers are paid on average
NIS 23,000 a month, fifty times the NIS 460 paid to conscripts.
In 1998–2000, only about 9% of those who
refused to serve in the Israeli military were granted exemption.
Permanent service
Permanent service is designed for soldiers who choose to continue serving in the army after their regular service, for a short or long period, and in many cases making the military their career. Permanent service usually begins immediately after the mandatory Regular service period, but there are also soldiers who get released from military at the end of the mandatory Regular service period and who get recruited back to the military as Permanent service soldiers in a later period.
Permanent service is based on a contractual agreement between the IDF and the permanent position holder. The service contract defines how long the soldier's service would be, and towards the end of the contract period a discussion may rise on the extension of the soldier's service duration. Many times, regular service soldiers are required to commit to a permanent service after the mandatory Regular service period, in exchange for assigning them in military positions which require a long training period.
In exchange for the Permanent service, the Permanent service soldiers receive full wages, and when serving for a long period as a permanent service soldier, they are also entitled for a pension from the army. This right is given to the Permanent service soldiers in a relatively early stage of their life in comparison to the rest of the Israeli retirees.
Reserve service

After personnel complete their regular service, they are either granted permanent exemption from military service, or assigned a position in the reserve forces. No distinction is made between the assignment of men or women to reserve service.
The IDF may call up reservists for:
* reserve service of up to one month every three years, until the age of 40 (enlisted) or 45 (officers). Reservists may volunteer after this age, with approval of the Manpower Directorate.
* immediate active duty in wartime.
All Israelis who served in the IDF and are under the age of 40, unless otherwise exempt, are eligible for reserve duty. However, only those who completed at least 20 days of reserve duty within the past three years are considered active reservists.
In most cases, the reserve duty is carried out in the same unit for years, in many cases the same unit as the active service and by the same people. Many soldiers who have served together in active service continue to meet in reserve duty for years after their discharge, causing reserve duty to become a strong
male bonding experience in Israeli society.
Although still available for call-up in times of crisis, most Israeli men, and virtually all women, do not actually perform reserve service in any given year. In 2015, only 26% of the population eligible for reserve duty held an active reserve status. The IDF has reduced the number of reserve soldiers called up to improve efficiency and cut costs. Units do not always call up all of their reservists every year, and a variety of exemptions are available if called for regular reserve service. Virtually no exemptions exist for reservists called up in a time of crisis, but experience has shown that in such cases (most recently, the 2014
Operation Protective Edge) exemptions are rarely requested or exercised; units generally achieve recruitment rates above those considered fully manned.

Legislation (approved in April 2008) has reformed the reserve service, lowering the maximum service age to 40 for enlisted, and 45 for officers, designating it as an emergency and security force (disallowing routine duties that may be carried out by the active forces), as well as many other changes to the structure (although the Defense Minister can suspend any portion of it at any time for security reasons). The age threshold for many reservists whose positions are listed and updated yearly by the Knesset through the Occupations executive order is fixed at 45 or 49, depending on their military occupation and position.
Non-IDF service
Other than the civil, i.e. non-military "National Service" (''
Sherut Leumi''), IDF conscripts may serve in bodies other than the IDF in a number of ways.
The combat option is
Israel Border Police (''Magav'' – the exact translation from Hebrew means "border guard") service, part of the
Israel Police. Some soldiers complete their IDF combat training and later undergo additional
counter terror and Border Police training. These are assigned to Border Police units. The Border Police units fight side by side with the regular IDF combat units though to a lower capacity. They are also responsible for security in heavy urban areas such as
Jerusalem and security and crime fighting in rural areas.
Non-combat services include the (''Shaham'', שח"מ) program, where youth serve in the
Israeli Police
The Israel Police ( he, משטרת ישראל, ''Mišteret Yisra'el''; ar, شرطة إسرائيل, ''Shurtat Isrāʼīl'') is the civilian police force of Israel. As with most other police forces in the world, its duties include crime fightin ...
,
Israel Prison Service, or other wings of the
Israeli Security Forces instead of the regular army service.
Women



Israel is one of only a few nations that conscript women or deploy them in combat roles, although in practice, women can avoid conscription through a religious exemption and over a third of Israeli women do so. As of 2010, 88% of all roles in the IDF are open to female candidates, and women could be found in 69% of all IDF positions.
According to the IDF, 535 female Israeli soldiers were killed during service in the period 1962–2016, and dozens before then. The IDF says that fewer than 4 percent of women are in combat positions. Rather, they are concentrated in "combat-support" positions which command a lower compensation and status than combat positions.
[Gaza: It's a Man's War](_blank)
The Atlantic, 7 August 2014
Civilian pilot and aeronautical engineer Alice Miller successfully petitioned the High Court of Justice to take the Israeli Air Force pilot training exams, after being rejected on grounds of gender. Though president
Ezer Weizman, a former IAF commander, told Miller that she would be better off staying home and darning socks, the court eventually ruled in 1996 that the IAF could not exclude qualified women from pilot training. Even though Miller would not pass the exams, the ruling was a watershed, opening doors for women in new IDF roles. Female legislators took advantage of the momentum to draft a bill allowing women to volunteer for any position, if they could qualify.
In 2000 the Equality amendment to the Military Service law stated that the right of women to serve in any role in the IDF is equal to the right of men.
Women have served in the military since before the founding of the state of Israel in 1948.
Women started to enter combat support and light combat roles in a few areas, including the Artillery Corps, infantry units and armored divisions. A few platoons named Karakal were formed for men and women to serve together in light infantry. By 2000 Karakal became a
full-fledged battalion, with a second mixed-gender battalion, Lions of the Jordan (אריות הירדן, Arayot Ha-Yarden) formed in 2015. Many women also joined the
Border Police
A border guard of a country is a national security agency that performs border security. Some of the national border guard agencies also perform coast guard (as in Germany, Italy or Ukraine) and rescue service duties.
Name and uniform
In diff ...
.
In June 2011 Maj. General
Orna Barbivai became the first female major general in the IDF, replacing head of the directorate Maj. General Avi Zamir. Barbivai stated, "I am proud to be the first woman to become a major general and to be part of an organization in which equality is a central principle. Ninety percent of jobs in the IDF are open to women and I am sure that there are other women who will continue to break down barriers."
In 2013 the IDF announced they would, for the first time, allow a (MTF) transgender woman to serve in the army as a female soldier.
Elana Sztokman notes it would be "difficult to claim that women are equals in the IDF". "And tellingly, there is only one female general in the entire IDF," she adds.
In 2012 religious soldiers claimed they were promised they would not have to listen to women sing or lecture, but IAF Chief Rabbi Moshe Raved resigned because male religious soldiers were being required to do so. In January 2015 three women IDF singers performed in one of the IDF's units. The performance was first disrupted by fifteen religious soldiers, who left in protest and then the Master Sergeant forced the women to end the performance because it was disturbing the religious soldiers. An IDF spokesperson announced an investigation of the incident: "We are aware of the incident and already began examining it. The exclusion of woman is not consistent with the values of the IDF." Defense Minister
Moshe Ya'alon has also arranged for women to be excluded from recruitment centers catering to religious males. As the IDF recruits more religious soldiers, the rights of male religious soldiers and of women in the IDF come into conflict. Brig. Gen. Zeev Lehrer, who served on the chief of staff's panel of the integration of women, noted "There is a clear process of 'religionization' in the army, and the story of the women is a central piece of it. There are very strong pressures at work to halt the process of integrating women into the army, and they are coming from the direction of religion."
Sex segregation is allowed in the IDF, which reached what it considers a "new milestone" in 2006, creating the first company of soldiers segregated in an all female unit, the Nachshol (Hebrew for "giant wave") Reconnaissance Company. "We are the only unit in the world made up entirely of female combat soldiers," said Nachshol Company Commander Cpt. Dana Ben-Ezra. "Our effectiveness and the dividends we earn are the factors by which we are measured, not our gender."
Minorities in the IDF
Non-Jewish minorities tended to serve in one of several special units: the
Sword Battalion
The Sword Battalion ( he, גדוד חרב, translit=Gdud Herev; ar, كتيبة السيف), formerly Unit 300 and also known as the IDF Minorities Unit, was an Arabic-speaking battalion of the Israel Defense Forces.
History
Unit 300 was formed ...
, also known as Unit 300 or the Minorities Unit, until it was disbanded in 2015; the Druze Reconnaissance Unit; and the Trackers Unit, composed mostly of
Negev Bedouins. In 1982 the IDF general staff decided to integrate the armed forces by opening up other units to minorities, while placing some Jewish conscripts in the Minorities Unit. Until 1988 the intelligence corps and the air force remained closed to minorities.
Druze and Circassians

Although Israel has a majority of Jewish soldiers, all citizens including large numbers of
Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
and
Circassian men are subject to mandatory conscription. Originally, they served in the framework of a special unit called "The Minorities' Unit", which operated until 2015 in the form of the independent Herev Gdud
("Sword") battalion. However, since the 1980s Druze soldiers have increasingly protested this practice, which they considered a means of segregating them and denying them access to elite units (like
sayeret units). The army has increasingly admitted Druze soldiers to regular combat units and promoted them to higher ranks from which they had been previously excluded. In 2015 Rav Aluf
Gadi Eizenkot ordered the unit's closure in order to assimilate the Druze soldiers no differently than Jewish soldiers, as part of an ongoing reorganization of the army. Several Druze officers reached ranks as high as Major General, and many received commendations for distinguished service. In proportion to their numbers, the Druze people achieve much higher—documented—levels in the Israeli army than other soldiers. Nevertheless, some Druze still charge that discrimination continues, such as exclusion from the
Air Force, although the official low security classification for Druze has been abolished for some time. The first Druze aircraft navigator completed his training course in 2005; like all air force pilots, his identity is not disclosed. During the
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
, many Druze who had initially sided with the Arabs deserted their ranks to either return to their villages or side with Israel in various capacities.
Since the late 1970s the
Druze Initiative Committee
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of Ha ...
, centered at the village of
Beit Jan
Beit Jann ( ar, بيت جن; he, בֵּיתּ גַ'ן) is a Druze village on Mount Meron in northern Israel. At 940 meters above sea level, Beit Jann is one of the highest inhabited locations in the country. In it had a population of .
Etym ...
and linked to
Maki, has campaigned to abolish Druze conscription.
Military service is a tradition among some of the Druze population, with most opposition in Druze communities of the
Golan Heights; 83 percent of Druze boys serve in the army, according to the IDF's statistics. According to the Israeli army in 2010, 369 Druze soldiers had been killed in combat operations since 1948.
Bedouins and Israeli Arabs
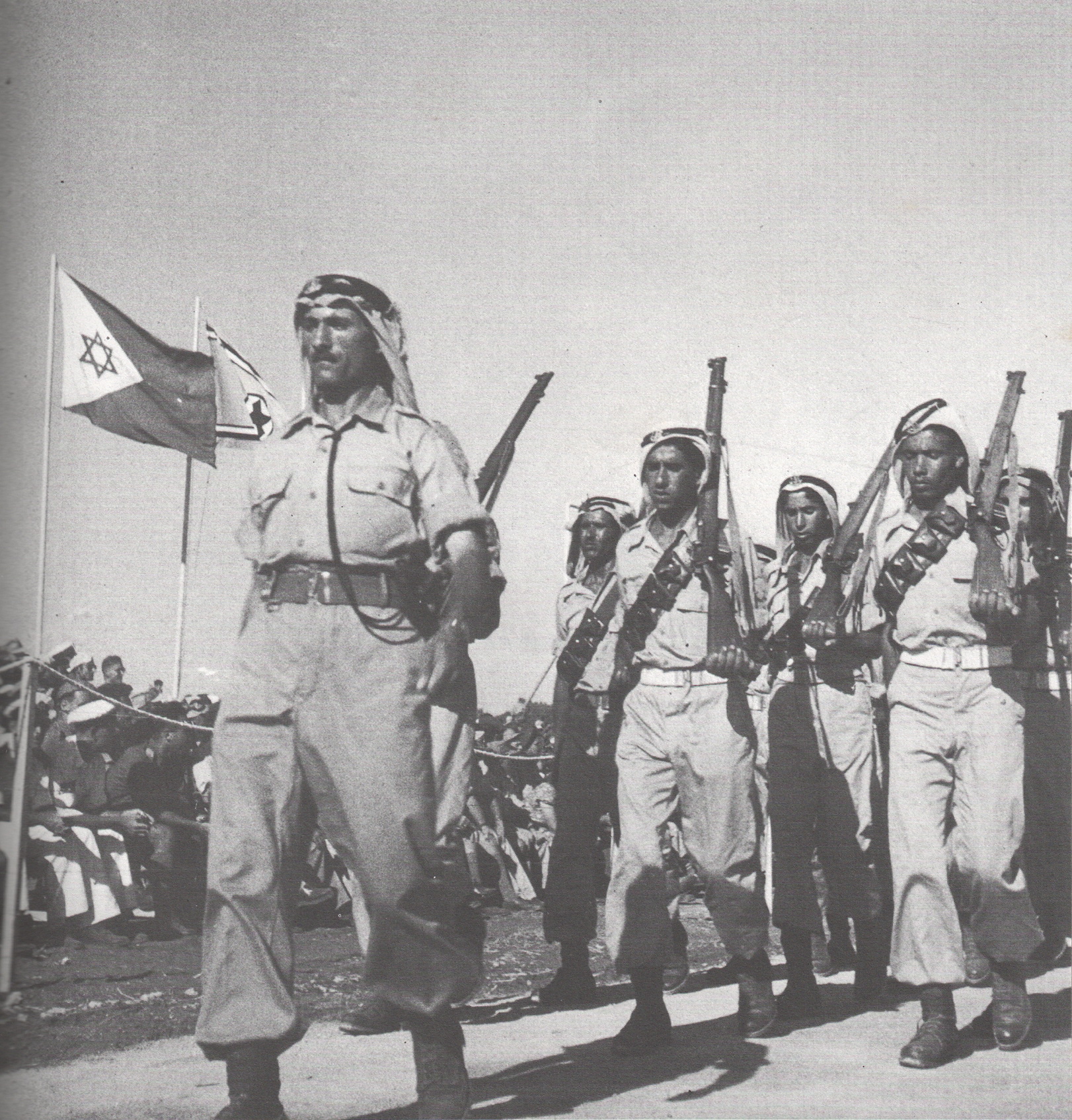



By law, all Israeli citizens are subject to conscription. The Defense Minister has complete discretion to grant exemption to individual citizens or classes of citizens. A long-standing policy dating to Israel's early years extends an exemption to all other Israeli minorities (most notably
Israeli Arabs). However, there is a long-standing government policy of encouraging
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
s to volunteer and of offering them various inducements, and in some impoverished Bedouin communities a military career seems one of the few means of (relative) social mobility available. Also, Muslims and Christians are accepted as volunteers, even if older than 18.
From among non-Bedouin Arab citizens, the number of volunteers for military service—some
Christian Arabs and even a few Muslim Arabs—is minute, and the government makes no special effort to increase it. Six Israeli Arabs have received orders of distinction as a result of their military service; of them the most famous is a Bedouin officer, Lieutenant Colonel Abd el-Majid Hidr (also known as
Amos Yarkoni), who received the Order of Distinction. Vahid el Huzil was the first Bedouin to be a battalion commander.
Until the second term of
Yitzhak Rabin as Prime Minister (1992–1995), social benefits given to families in which at least one member (including a grandfather, uncle, or cousin) had served at some time in the armed forces were significantly higher than to "non-military" families, which was considered a means of blatant discrimination between Jews and Arabs. Rabin led the abolition of the measure, in the teeth of strong opposition from the Right. At present, the only official advantage from military service is the attaining of security clearance and serving in some types of government positions (in most cases, security-related), as well as some indirect benefits.
Rather than perform army service, Israeli Arab youths have the option to volunteer to
national service and receive benefits similar to those received by discharged soldiers. The volunteers are generally allocated to Arab populations, where they assist with social and community matters. 1,473 Arabs were volunteering for national service. According to sources in the national service administration, Arab leaders are counseling youths to refrain from performing services to the state. According to a National Service official, "For years the Arab leadership has demanded, justifiably, benefits for Arab youths similar to those received by discharged soldiers. Now, when this opportunity is available, it is precisely these leaders who reject the state's call to come and do the service, and receive these benefits."
Although Arabs are not obliged to serve in IDF, any Arab can volunteer. In 2008 a Muslim Arab woman was serving as a medic with unit 669.
Cpl.
Elinor Joseph from
Haifa became the first female Arab combat soldier for IDF.
Other Arab-Muslim officers who have served in the IDF are
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
Hisham Abu Varia
and
Major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
Ala Wahib, the highest ranking Muslim officer in the IDF in 2013.

In October 2012 the IDF promoted Mona Abdo to become the first female Christian Arab to the rank of combat commander. Abdo had voluntarily enlisted in the IDF, which her family had encouraged, and transferred from the
Ordnance Corps to the
Caracal Battalion, a mixed-gender unit with both Jewish and Arab soldiers.
In 2014 an increase of Israeli Christian Arabs joining the army was reported.
Muslim Arabs have also been drafted into the Israel Defense Forces in increasing numbers in recent years. In 2020, 606 Muslim Arabs were drafted, compared to 489 in 2019 and 436 in 2018. More than half of those who have drafted have gone into combat roles.
Ethiopian Jews
The IDF carried out extended missions in
Ethiopia and neighboring states, whose purpose was to protect
Ethiopian Jews
The Beta Israel ( he, בֵּיתֶא יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Bēteʾ Yīsrāʾēl''; gez, ቤተ እስራኤል, , modern ''Bēte 'Isrā'ēl'', EAE: "Betä Ǝsraʾel", "House of Israel" or "Community of Israel"), also known as Ethiopian Jews ...
(Beta Israel) and to help their immigration to Israel. The IDF adopted policies and special activities for absorption and integration of Ethiopian immigrant soldiers, reported to have much improved the achievements and integration of those soldiers in the army, and Israeli society in general. Statistical research showed that the Ethiopian soldiers are esteemed as excellent soldiers and many aspire to be recruited to combat units.
Haredim

Men in the
Haredi community may choose to defer service while enrolled in ''
yeshivot'' (see
Tal committee); many avoid conscription altogether. This special arrangement is called
Torato Omanuto, and has given rise
to tensions between the Israeli religious and secular communities. While options exist for Haredim to serve in the IDF in an
atmosphere accommodating to their religious convictions, most Haredim do not choose to serve in the IDF.
Haredi males have the option of serving in the
97th "Netzah Yehuda" Infantry Battalion. This unit is a standard IDF infantry battalion focused on the
Jenin
Jenin (; ar, ') is a Palestinian city in the northern West Bank. It serves as the administrative center of the Jenin Governorate of the State of Palestine and is a major center for the surrounding towns. In 2007, Jenin had a population of app ...
region. To facilitate Haredi soldiers to serve, the Netzah Yehuda military bases follow the standards of
Jewish dietary laws; the only women permitted on these bases are wives of soldiers and officers. Additionally, some Haredim serve in the IDF via the
Hesder system, principally designed for the
Religious Zionist
Religious Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת דָּתִית, translit. ''Tziyonut Datit'') is an ideology that combines Zionism and Orthodox Judaism. Its adherents are also referred to as ''Dati Leumi'' ( "National Religious"), and in Israel, the ...
sector; it is a 5-year program which includes 2 years of religious studies, 1½ years of military service and 1½ years of religious studies during which the soldiers can be recalled to active duty at any moment. Haredi soldiers may join other units of the IDF, but rarely do.
The IDF has identified a gap of hundreds of soldiers in their technical units that might be filled by the Haredi. The IAF is currently using
defense contractors to fill in the gaps and continue operations.
Although the IDF claims it will not discriminate against women, it is offering Haredim "
women free and secular free" recruitment centers. Defense Minister Moshe Ya'alon expressed his willingness to relax regulations to meet the demands of ultra-Orthodox rabbis. Regulations regarding
gender equality had already been relaxed so that Haredim could be assured that men would not receive physical exams from female medical staff.
LGBT people
Israel is one of 24 nations that allow openly gay individuals to serve in the military. Since the early 1990s, sexual identity presents no formal barrier in terms of soldiers' military specialization or eligibility for promotion.
Until the 1980s the IDF tended to discharge soldiers who were openly gay. In 1983 the IDF permitted homosexuals to serve, but banned them from intelligence and top-secret positions. A decade later, Professor Uzi Even,
an IDF reserves officer and chairman of
Tel Aviv University's Chemistry Department, revealed that his rank had been revoked and that he had been barred from researching sensitive topics in military intelligence, solely because of his sexual orientation. His testimony to the
Knesset in 1993 raised a political storm, forcing the IDF to remove such restrictions against gays.
The chief of staff's policy states that it is strictly forbidden to harm or hurt anyone's dignity or feeling based on their gender or sexual orientation in any way, including signs, slogans, pictures, poems, lectures, any means of guidance, propaganda, publishing, voicing, and utterance. Moreover, gays in the IDF have additional rights, such as the right to take a shower alone if they want to. According to a
University of California, Santa Barbara study,
a brigadier general stated that Israelis show a "great tolerance" for gay soldiers. Consul
David Saranga at the Israeli Consulate in New York, who was interviewed by the ''St. Petersburg Times'', said, "It's a non-issue. You can be a very good officer, a creative one, a brave one, and be gay at the same time."
A study published by the
Israel Gay Youth (IGY) Movement in January 2012 found that half of the homosexual soldiers who serve in the IDF suffer from violence and homophobia, although the head of the group said that "I am happy to say that the intention among the top brass is to change that."
Deaf and hard-of-hearing people
Israel is the only country in the world that requires deaf and hard-of-hearing people to serve in the military. Sign language interpreters are provided during training, and many of them serve in non-combat capacities such as mapping and office work. The major language spoken by deaf in Israel is
Israeli Sign Language (also called Shassi)–a language related to
German Sign Language but not Hebrew or any other local language–though Israel and Palestine are home to numerous sign languages spoken by various populations like Bedouins'
Al-Sayyid Bedouin Sign Language.
Vegans
According to a
Care2 report, vegans in the IDF may refuse vaccination if they oppose animal testing.
They are given artificial leather boots and a black fleece beret.
Until 2014, vegan soldiers in the IDF received special allowances to buy their own food, when this policy was replaced with vegan food being provided in all bases, as well as vegan combat rations being offered to vegan combat soldiers.
Volunteers
In cases when a citizen cannot be normally drafted by the law (old age, served as a soldier in a different country, severe health problems, handicaps, autism, etc.), the person could enroll as a volunteer in places where his knowledge can be used or in cases where there is a base that accepts volunteer service from one day per week up to full-time service based upon a volunteer's abilities and wishes.
Overseas volunteers
Non-immigrating foreign volunteers typically serve with the IDF in one of five ways:
* The
Mahal program targets young non-Israeli Jews or Israeli citizens who grew up abroad (men younger than 24 and women younger than 21). The program consists typically of 18 months of IDF service, including a lengthy training for those in combat units or (for 18 months) one month of non-combat training and additional two months of learning
Hebrew after enlisting, if necessary. There are two additional subcategories of Mahal, both geared solely for religious men: Mahal
Nahal Haredi (18 months), and Mahal
Hesder, which combines yeshiva study of 5 months with IDF service of 16 months, for a total of 21 months. Similar IDF programs exist for Israeli overseas residents. To be accepted as a Mahal Volunteer, one must be of Jewish descent (at least one Jewish grandparent).
*
Sar-El, an organization subordinate to the Israeli
Logistics Corps, provides a volunteer program for non-Israeli citizens who are 17 years or older (or 15 if accompanied by a parent). The program is also aimed at Israeli citizens, aged 30 years or older, living abroad who did not serve in the Israeli Army and who now wish to finalize their status with the military. The program usually consists of three weeks of volunteer service on different rear army bases, doing non-combative work.
*
Garin Tzabar
Garin Tzabar () is a program that facilitates service in the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) and provides a support system for Israelis and Diaspora Jews who do not have parents in Israel. Soldiers who do not have at least one parent living in Israel a ...
offers a program mainly for Israelis who emigrated with their parents to the United States at a young age. Although a basic knowledge of the Hebrew language is not mandatory, it is helpful. Of all the programs listed, only Garin Tzabar requires full-length service in the IDF. The program is set up in stages: first the participants go through five seminars in their country of origin, then have an absorption period in Israel at a
kibbutz
A kibbutz ( he, קִבּוּץ / , lit. "gathering, clustering"; plural: kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1909, was Degania. Today, farming h ...
. Each delegation is adopted by a kibbutz in Israel and has living quarters designated for it. The delegation shares responsibilities in the kibbutz when on military leave. Participants start the program three months before being enlisted in the army at the beginning of August.
*
Marva is short-term basic training for two months.
*
Lev LaChayal
Lev may refer to:
Common uses
*Bulgarian lev, the currency of Bulgaria
*an abbreviation for Leviticus, the third book of the Hebrew Bible and the Torah
People and fictional characters
*Lev (given name)
*Lev (surname)
Places
*Lev, Azerbaijan, a ...
is a program based at
Yeshivat Lev Hatorah
Yeshivat Lev HaTorah ( he, ישיבת ההסדר לב התורה) is a Religious Zionist yeshiva, located in Ramat Shilo, a sub-district of Ramat Bet Shemesh, Israel.
Notable alumni
* Adam Edelman (born 1991), American-born four-time Israeli N ...
which takes a holistic approach to preparation for service. Being as ready as possible for integrating into Israeli culture, handling the physical challenges of the military, and maintaining religious values require a multi-pronged approach. The beit midrash learning, classes, physical training, and even the recreational activities are designed to allow for maximum readiness.
Mission
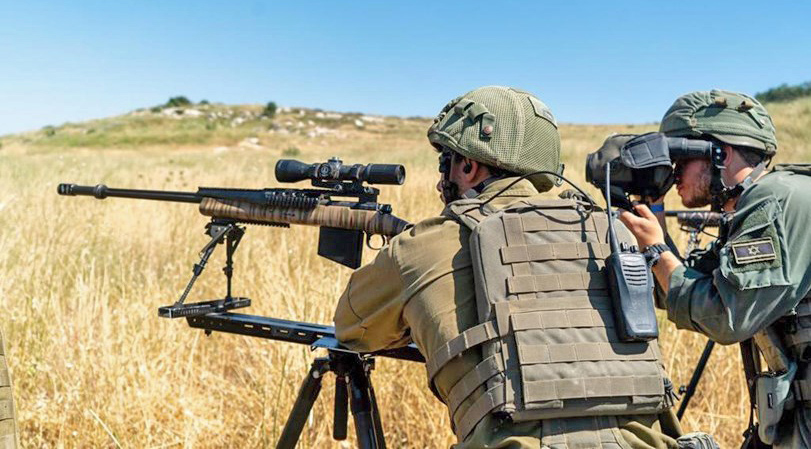



The IDF's mission is to "defend the existence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the state of Israel. To protect the inhabitants of Israel and to combat all forms of terrorism which threaten the daily life." The Israeli military's primary principles derive from Israel's need to combat numerically superior opponents. One such principle, is the concept that Israel cannot afford to lose a single war. The IDF believes that this is possible if it can rapidly mobilize troops to insure that they engage the enemy in enemy territory. In the 21st Century, various nonconventional threats including terrorist organizations,
subterranean infrastructure operated by Hamas, etc. have forced the IDF to modify its official defense doctrine.
Doctrine
Main doctrine
The main doctrine consists of the following principles:
Basic points
* Israel cannot afford to lose a single war
* Defensive on the strategic level, no territorial ambitions
* Desire to avoid war by political means and a credible deterrent posture
* Preventing escalation
* Determine the outcome of war quickly and decisively
* Combating terrorism
* Very low casualty ratio
Prepare for defense
* A small
standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or n ...
with an early warning capability, regular air force and navy
* An efficient reserve mobilization and transportation system
Move to counterattack
* Multi-arm coordination
* Transferring the battle to enemy territory quickly
* Quick attainment of war objectives
Code of conduct
In 1992, the IDF drafted a Code of Conduct that combines international law, Israeli law, Jewish heritage and the IDF's own traditional ethical code—the IDF Spirit ( he, רוח צה"ל, ''Ru'ah Tzahal'').
Stated values of the IDF
The document defines four core values for all IDF soldiers to follow, as well as ten secondary values (the first being most important, and the others appearing sorted in Hebrew alphabetical order):
;Core values:
# Defense of the State, its Citizens and its Residents
# Love of the Homeland and Loyalty to the Country
# Human Dignity
# Stateliness
;Other values:


* Tenacity of Purpose in Performing Missions and Drive to Victory
* Responsibility
* Credibility
* Personal Example
* Human Life
*
Purity of Arms
*
Professionalism
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and skil ...
* Discipline
* Comradeship
* Sense of Mission
Military ethics of fighting terror
In 2005,
Asa Kasher and
Amos Yadlin co-authored a noticed article published in the ''Journal of Military Ethics'' under the title: "Military Ethics of Fighting Terror: An Israeli Perspective". The article was meant as an "extension of the classical Just War Theory", and as a "
eededthird model" or missing paradigm besides which of "classical war (army) and law enforcement (police).", resulting in a "doctrine (...) on the background of the IDF fight against acts and activities of terror performed by Palestinian individuals and organizations."
In this article, Kasher and Yadlin came to the conclusion that
targeted killings of terrorists were justifiable, even at the cost of hitting nearby civilians. In a 2009 interview to ''
Haaretz
''Haaretz'' ( , originally ''Ḥadshot Haaretz'' – , ) is an Israeli newspaper. It was founded in 1918, making it the longest running newspaper currently in print in Israel, and is now published in both Hebrew and English in the Berliner f ...
'', Asa Kasher later confirmed, pointing to the fact that in an area in which the IDF does not have effective security control (e.g., Gaza, vs. East-Jerusalem), soldiers' lives protection takes priority over avoiding injury to enemy civilians. Some, along with
Avishai Margalit and
Michael Walzer
Michael Laban Walzer (born 1935) is an American political theorist and public intellectual. A professor emeritus at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey, he is editor emeritus of ''Dissent'', an intellectual magazine ...
, have recused this argument, advancing that such position was "contrary to centuries of theorizing about the morality of war as well as international humanitarian law", since drawing "a sharp line between combatants and noncombatants" would be "the only morally relevant distinction that all those involved in a war can agree on."
As of today "The Spirit of the IDF" (cf. supra) is still considered the only binding moral code that formally applies to the IDF troops. In 2009,
Amos Yadlin (then head of
Military Intelligence) suggested that the article he co-authored with
Asa Kasher be ratified as a formal binding code, arguing that "the current code
The Spirit of the IDF'does not sufficiently address one of the army's most pressing challenges:
asymmetric warfare against terrorist organizations that operate amid a civilian population".
Budget
During 1950–66, Israel spent an average of 9% of its GDP on defense. Defense expenditures increased dramatically after both the 1967 and 1973 wars. They reached a high of about 30% of GDP in 1975, but have since come down significantly, following the signing of peace agreements with Jordan and Egypt.
On 30 September 2009 Defense Minister Ehud Barak, Finance Minister Yuval Steinitz and Prime Minister
Benjamin Netanyahu endorsed an additional NIS 1.5 billion for the defense budget to help Israel address problems regarding Iran. The budget changes came two months after Israel had approved its current two-year budget. The defense budget in 2009 stood at NIS 48.6 billion and NIS 53.2 billion for 2010 – the highest amount in Israel's history. The figure constituted 6.3% of expected gross domestic product and 15.1% of the overall budget, even before the planned NIS 1.5 billion addition.
However, in 2011, the prime minister
Benjamin Netanyahu reversed course and moved to make significant cuts in the defense budget in order to pay for social programs. The General Staff concluded that the proposed cuts endangered the battle readiness of the armed forces. In 2012, Israel spent $15.2 billion on its armed forces, one of the highest ratios of defense spending to GDP among developed countries ($1,900 per person). However, Israel's spending per capita is below that of the US.
Field rations
Field rations, called ''manot krav'', usually consist of canned
tuna,
sardines,
beans,
stuffed vine leaves
Dolma (Turkish for “stuffed”) is a family of stuffed dishes associated with Ottoman cuisine, and common in modern national cuisines of regions and countries that once were part of the Ottoman Empire. Some types of dolma are made with whol ...
,
maize and
fruit cocktail and bars of
halva
Halva (also halvah, halwa, and other spellings, Persian : حلوا) is a type of confectionery originating from Persia and widely spread throughout the Middle East. The name is used for a broad variety of recipes, generally a thick paste made f ...
. Packets of fruit flavored drink powder are also provided along with condiments like
ketchup,
mustard, chocolate spread and jam. Around 2010, the IDF announced that certain freeze dried
MREs served in water activated disposable heaters like
goulash, turkey
schwarma
Shawarma (; ar, شاورما) is a popular Middle Eastern dish that originated in the Ottoman Empire, consisting of meat cut into thin slices, stacked in a cone-like shape, and roasted on a slowly-turning vertical rotisserie or spit. Traditiona ...
and
meatballs
A meatball is ground meat rolled into a ball, sometimes along with other ingredients, such as bread crumbs, minced onion, eggs, butter, and seasoning. Meatballs are cooked by frying, baking, steaming, or braising in sauce. There are many types ...
would be introduced as field rations.
One staple of these rations was ''
loof Loof or Lööf (Swedish variant) is a Germanic surname that may refer to:
*Anders Lööf (born 1961), Swedish male curler
*Annie Lööf (born 1983), Swedish politician
* Annika Lööf (born 1966), Swedish female curler
* Augustine Loof (born 1996), ...
'', a type of Kosher
spam
Spam may refer to:
* Spam (food), a canned pork meat product
* Spamming, unsolicited or undesired electronic messages
** Email spam, unsolicited, undesired, or illegal email messages
** Messaging spam, spam targeting users of instant messaging ( ...
made from chicken or beef that was phased out around 2008. Food historian Gil Marks has written that: "Many Israeli soldiers insist that Loof uses all the parts of the cow that the hot dog manufacturers will not accept, but no one outside of the manufacturer and the kosher supervisors actually know what is inside."
Weapons and equipment
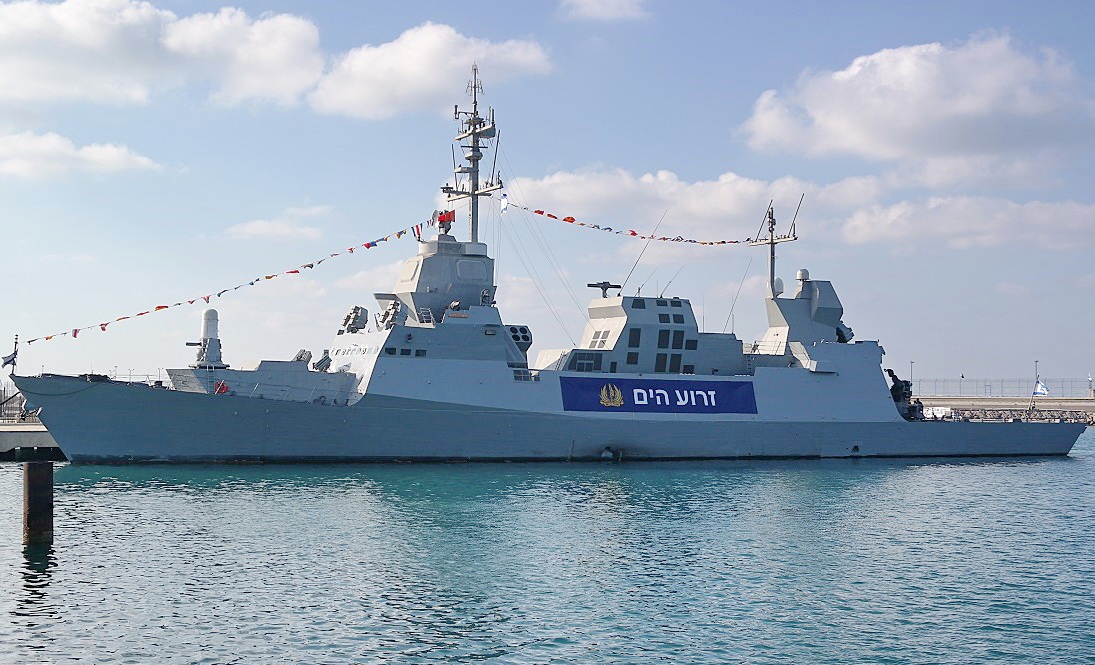




Military equipment
The IDF possesses various foreign and domestically produced weapons and computer systems. Some gear comes from the US (with some equipment modified for IDF use) such as the
M4A1 and
M16
The M16 rifle (officially designated Rifle, Caliber 5.56 mm, M16) is a family of military rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States military. The original M16 rifle was a 5.56×45mm automatic rifle with a 20-roun ...
assault rifles, the
M24 SWS
The M24 Sniper Weapon System (SWS) or M24 is the military and police version of the Remington Model 700 rifle, ''M24'' being the model name assigned by the United States Army after adoption as their standard sniper rifle in 1988. The M24 is refe ...
7.62 mm
bolt action sniper rifle
A sniper rifle is a high-precision, long-range rifle. Requirements include accuracy, reliability, mobility, concealment and optics for anti-personnel, anti-materiel and surveillance uses of the military sniper. The modern sniper rifle is a por ...
, the
SR-25 7.62 mm semi-automatic sniper rifle, the
F-15 Eagle
The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle is an American twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter aircraft designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing). Following reviews of proposals, the United States Air Force selected McDonnell Douglas's ...
and
F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful ...
fighter jets, and the
AH-1 Cobra and
AH-64D Apache attack helicopter
An attack helicopter is an armed helicopter with the primary role of an attack aircraft, with the offensive capability of engaging ground targets such as enemy infantry, military vehicles and fortifications. Due to their heavy armament they ...
s. Israel has also developed its own independent weapons industry, which has developed weapons and vehicles such as the
Merkava battle tank series,
Nesher and
Kfir fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
, and various small arms such as the
Galil and
Tavor assault rifles, and the
Uzi submachine gun
A submachine gun (SMG) is a magazine-fed, automatic carbine designed to fire handgun cartridges. The term "submachine gun" was coined by John T. Thompson, the inventor of the Thompson submachine gun, to describe its design concept as an autom ...
. Israel has also installed a variant of the
Samson RCWS
The Samson Remote Controlled Weapon Station (RCWS), also known as Katlanit (קטלנית in Hebrew: "lethal", female inflection) is a Remote Weapon System that enables a variety of devices to be operated automatically or by remote control, includ ...
, a remote controlled weapons platform, which can include machine guns, grenade launchers, and anti-tank missiles on a remotely operated turret, in
pillboxes along the
Israeli Gaza Strip barrier intended to prevent
Palestinian militants from entering its territory. Israel has developed observation
balloons
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the per ...
equipped with sophisticated cameras and surveillance systems used to thwart terror attacks from Gaza. The IDF also possesses advanced
combat engineering equipment which include the
IDF Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozer
The armored bulldozer is a basic tool of combat engineering. These combat engineering vehicles combine the earth moving capabilities of the bulldozer with armor which protects the vehicle and its operator in or near combat. Most are civilian bu ...
,
IDF Puma CEV,
Tzefa Shiryon and
CARPET minefield breaching rockets, and a variety of
robots and explosive devices.
The IDF also has several large internal
research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
departments, and it purchases many technologies produced by the Israeli security industries including
IAI
, abbreviated , is a Japanese martial art that emphasizes being aware and capable of quickly drawing the sword and responding to sudden attacks.Christensen, Karen and Allen Guttmann et.al (2001) ''International Encyclopedia of Women and Sports ...
,
IMI,
Elbit Systems
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an Israel-based international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land ...
,
Rafael, and dozens of smaller firms. Many of these developments have been battle-tested in Israel's numerous military engagements, making the relationship mutually beneficial, the IDF getting tailor-made solutions and the industries a good reputation.
In response to the price overruns on the US
Littoral Combat Ship program, Israel is considering producing their own
warships, which would take a decade and depend on diverting US financing to the project.
Main developments
Israel's military technology is most famous for its firearms,
armored fighting vehicles (
tanks, tank-converted
armored personnel carriers (APCs),
armored bulldozer
The armored bulldozer is a basic tool of combat engineering. These combat engineering vehicles combine the earth moving capabilities of the bulldozer with armor which protects the vehicle and its operator in or near combat. Most are civilian bu ...
s, etc.),
unmanned aerial vehicles, and rocketry (missiles and rockets). Israel also has manufactured aircraft including the
Kfir (reserve),
IAI Lavi (canceled), and the
IAI Phalcon Airborne early warning System
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, ...
, and naval systems (patrol and missile ships). Much of the IDF's electronic systems (intelligence, communication, command and control, navigation etc.) are Israeli-developed, including many systems installed on foreign platforms (esp. aircraft, tanks and submarines), as are many of its
precision-guided munition
A precision-guided munition (PGM, smart weapon, smart munition, smart bomb) is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gul ...
s. Israel is the world's largest exporter of
drones.
[Israel is world's largest exporter of drones, study finds](_blank)
''Haaretz'', Gili Cohen Published: 19 May 2013
Israel Military Industries
, former_name = Israel Military Industries
, type = State-owned enterprise
, industry = Arms industry
, fate = Acquired by Elbit Systems
, successor = Elbit Systems Land
, founded =
, founder =
, defunct =
, hq_location_city = Ramat ...
(IMI) is known for its firearms. The
IMI Galil, the
Uzi, the
IMI Negev light machine gun and the new
Tavor TAR-21
The IWI Tavor TAR-21 is an Israeli bullpup assault rifle chambered in 5.56×45mm NATO caliber with a selective fire system, selecting between semi-automatic mode and full automatic fire mode. The Tavor is designed and produced by Israel Weap ...
Bullpup assault rifle are used by the IDF. The
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Spike missile
Spike (Hebrew: ספייק) is an Israeli fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile and anti-personnel missile with a tandem-charge high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead. , it is in its fourth generation. It was developed and designed by the Is ...
is one of the most widely exported
ATGMs in the world.
[Spike Anti-Tank Missile, Israel](_blank)
army-technology.com
Israel is the only country in the world with an operational anti-ballistic missile defense system on the national level – the
Arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
system, jointly funded and produced by Israel and the United States. The
Iron Dome system against short-range
rockets is operational and proved to be successful, intercepting hundreds of
Qassam,
122 mm Grad and
Fajr-5
The Fajr-5 (rarely Fadjr-5, fa, فجر-۵, "Dawn") is an Iranian 333 mm long-range multiple launch rocket system (MLRS). The Fajr-5 was developed during the 1990s and has since been exported to various armed actors in the Middle East.
The F ...
artillery
rockets fire by Palestinian militants from the Gaza Strip.
, an anti-missile system designed to counter
medium range rockets, became operational in 2017. Israel has also worked with the US on development of a tactical high energy
laser system against medium range rockets (called Nautilus or
THEL
The Tactical High-Energy Laser, or THEL, was a laser developed for military use, also known as the Nautilus laser system. The mobile version is the Mobile Tactical High-Energy Laser, or MTHEL. In 1996, the United States and Israel entered into a ...
).
Israel has the independent capability of launching
reconnaissance satellites into orbit, a capability shared with Russia, the United States, the United Kingdom, France, South Korea, Italy, Germany, the People's Republic of China, India, Japan, Brazil and Ukraine. Israeli security industries developed both the satellites (
Ofeq) and the launchers (
Shavit).
Israel is known to have developed
nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
.
Israel
does not officially acknowledge its nuclear weapons program. It is thought Israel possesses between one hundred and four hundred nuclear warheads.
It is believed that
Jericho intercontinental ballistic missiles are capable of delivering nuclear warheads with a superior degree of accuracy and a range of 11,500 km.
[Missile Proliferation and Defences: Problems and Prospects](_blank)
(PDF). Retrieved 4 June 2011. Israeli
F-15I and
F-16
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine Multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it ...
fighter-bomber aircraft also have been cited as possible nuclear delivery systems (these aircraft types are nuclear capable in the
US Air Force).
The
U.S. Air Force F-15E has
tactical nuclear weapon (B61 and B83 bombs) capability. It has been asserted that
Dolphin-class submarines have been adapted to carry
Popeye Turbo Submarine-launched cruise missile
A submarine-launched cruise missile (SLCM) is a cruise missile that is launched from a submarine (especially a SSG or SSGN). Current versions are typically standoff weapons known as land-attack cruise missiles (LACMs), which are used to attack p ...
s with nuclear warheads, so as to give Israel a
second strike
In nuclear strategy, a retaliatory strike or second-strike capability is a country's assured ability to respond to a nuclear attack with powerful nuclear retaliation against the attacker. To have such an ability (and to convince an opponent of it ...
capacity.
From 2006 Israel deployed the
Wolf Armoured Vehicle
The Wolf Armoured Vehicle ( he, זאב) is an armoured personnel carrier, used mainly by the Israeli Defence Force. It was created to provide a better handling and better protected armoured vehicle than the M113 (Bardelas). The Wolf is a heavily ...
APC for use in
urban warfare and to protect
VIPs.
File:M4A1 ACOG.png, M4A1 carbine
File:IDF Tavor X95 Flattop - Zachi Evenor 2019.jpg, Tavor X95 flattop 380
File:IWI-Negev-Zachi-Evenor-01-white.jpg, IWI Negev LMG
File:IDF-M24-SWS-2018.jpg, M24 Sniper Weapon System (2018)
PEO M2E2-QCB HMG.jpg, M2HQCB 0.5
File:סער 4.5.JPG, Sa'ar 4.5-class missile boat
The Sa'ar 4.5-class missile boats ( he, סער 4.5) is a class of Israeli Sea Corps missile boats designed and built by Israel Shipyards Ltd. as an improved and stretched . There are two different subclasses that are both named Sa'ar 4.5. The fir ...
File:Elbit Hermes 900s.JPG, Hermes 900 UAV
File:Flickr - Israel Defense Forces - Becoming A Soldier of the Caracal Battalion (59).jpg, Soldier armed with the IWI Tavor assault rifle
File:SPIKE ATGM.jpg, Spike ATGM
File:Arrow anti-ballistic missile launch.jpg, Arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventiona ...
File:Zeev-jeep002.jpg, Wolf Armoured Vehicle
The Wolf Armoured Vehicle ( he, זאב) is an armoured personnel carrier, used mainly by the Israeli Defence Force. It was created to provide a better handling and better protected armoured vehicle than the M113 (Bardelas). The Wolf is a heavily ...
File:Gulfstream 5 (2669062652).jpg, Israel Aerospace Industries EL/W-2085
The EL/W-2085 is an airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) multi-band radar system developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) and Elta Electronics Industries of Israel. Its primary objective is to provide intelligence to maintain air sup ...
, a development of the EL/M-2075
File:Ah-64d.jpg, "Saraph" AH-64D Apache Longbow
File:D9--Our-IDF-2018-IZE-211.jpg, IDF Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozer
The armored bulldozer is a basic tool of combat engineering. These combat engineering vehicles combine the earth moving capabilities of the bulldozer with armor which protects the vehicle and its operator in or near combat. Most are civilian bu ...
File:Operation Guardian of the Walls, May 2021. XVIII.jpeg, Iron Dome anti-rocket system launcher
File:Typhoon25mm001.jpg, Typhoon Weapon Station armed with 25 mm gun
File:Python5-missile001.jpg, The Python missile
The Rafael Python is a family of air-to-air missiles (AAMs) built by the Israeli weapons manufacturer Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, formerly RAFAEL Armament Development Authority. Originally starting with the ''Shafrir'' ( he, שפריר, loos ...
series.
File:IAI Harop PAS 2013 01.jpg, IAI Harop
The IAI Harop is a loitering munition developed by the MBT division of Israel Aerospace Industries. Loitering munitions are designed to loiter above the battlefield and attack targets by crashing into them and exploding.
Overview
The IAI Harop ...
.
File:Litening_Pod_on_FA-18.jpg, The LITENING targeting pod, which is today used by more than 20 international air-forces.
File:David-Sling-0001.jpg, David's Sling Weapons System Stunner Missile
File:Merkava4m-Windbreaker-0036a.jpg, Merkava Mk 4m with Trophy active protection system, the first operationally tested Active Protection System for tanks.
File:M2-Catlanit002.jpg, M2 Browning on Catlanit RCWS
Commemoration
Commemoration

 Yom Hazikaron
Yom Hazikaron, Israel's day of remembrance for fallen soldiers, is observed on the 4th day of the month of
Iyar of the
Hebrew calendar, the day before the celebration of
Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
. Memorial services are held in the presence of Israel's top military personnel. A two-minute siren is heard at 11:00, which marks the opening of the official military memorial ceremonies and private remembrance gatherings at each cemetery where soldiers are buried. Many Israelis visit the graves of family members and friends who were killed in action. On the evening before the remembrance day all shops, restaurants and entertainment places must close gates to the public no later than 7 P.M. (the same routine and law applies to the day of remembrance of the Holocaust which takes place a week earlier).
The main museum for Israel's armored corps is the
Yad La-Shiryon in
Latrun, which houses one of the largest tank museums in the world. Other significant military museums are the
Israel Defense Forces History Museum (Batei Ha-Osef) in
Tel Aviv, the
Palmach Museum
The Palmach Museum ( he, מוזיאון הפלמ"ח) is a museum located in Ramat Aviv, Israel dedicated to the Palmach, the strike-force of the pre-state underground Haganah defense organization, which was later integrated into the Israel Defense ...
, and the Beit HaTotchan of artillery in
Zikhron Ya'akov. The
Israeli Air Force Museum is located at
Hatzerim Airbase in the
Negev Desert
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
, and the Israeli Clandestine Immigration and Naval Museum, is in
Haifa.
Israel's National Military Cemetery is at
Mount Herzl. Other Israeli military cemeteries include
Kiryat Shaul Military Cemetery in Tel Aviv, and Sgula military cemetery at
Petah Tikva
Petah Tikva ( he, פֶּתַח תִּקְוָה, , ), also known as ''Em HaMoshavot'' (), is a city in the Central District (Israel), Central District of Israel, east of Tel Aviv. It was founded in 1878, mainly by Haredi Judaism, Haredi Jews of ...
.
Parades
Israel Defense Forces parades took place on Independence Day, during the first 25 years of the State of Israel's existence. They were canceled after 1973 due to financial and security concerns. The Israel Defense Forces still has weapon exhibitions country-wide on Independence Day, but they are stationary.
Foreign military relations
France
Starting on
Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
on 14 May 1948 (5 Iyar 5708), a strong military, commercial and political relationship were established between France and Israel until 1969. The highest level of the military collaboration was reached between 1956 and 1966. At this time France provided almost all the aircraft, tanks and military ships. In 1969 the French president
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
limited the export of weapons to Israel. This was the end of the "golden age" 20 years of relations between Israel and France.
United States

In 1983, the United States and Israel established a
Joint Political Military Group, which convenes twice a year. Both the U.S. and Israel participate in joint military planning and combined exercises, and have collaborated on military research and weapons development. Additionally the
U.S. military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
maintains two classified, pre-positioned
War Reserve Stocks in Israel valued at $493 million.
Israel has the official distinction of being an American
Major non-NATO ally.
Since 1976, Israel had been the largest annual recipient of U.S. foreign assistance. In 2009, Israel received $2.55 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) grants from the Department of Defense.
All but 26% of this military aid is for the purchase of military hardware from American companies only.
In October 2012, United States and Israel began their biggest joint air and missile defense exercise, known as
Austere Challenge 12, involving around 3,500 U.S. troops in the region along with 1,000 IDF personnel. Germany and Britain also participated.
Since mid 2017, the United States operates an anti-missile system in the
Negev region of Southern Israel, which is manned by 120 US Army personnel. It is a facility used by the U.S. inside a larger
Mashabim Israeli Air Force base.
India
India and Israel enjoy strong military and strategic ties. Israeli authorities consider Indian citizens to be the most pro-Israel people in the world.
[ by Martin Sherman, The Jewish Institute for National Security Affairs] Apart from being Israel's second-largest economic partner in Asia, India is also the largest customer of Israeli arms in the world.
In 2006, annual military sales between India and Israel stood at US$900 million. Israeli defense firms had the largest exhibition at the 2009
Aero India show, during which Israel offered several state-of-the art weapons to India. The first major military deal between the two countries was the sale of Israeli
Phalcon airborne warning and control system (AWACS) radars to the
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
in 2004. In March 2009, India and Israel signed a US$1.4 billion deal under which Israel would sell India an advanced air-defense system. India and Israel have also embarked on extensive space cooperation. In 2008, India's
ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman ...
launched Israel's most technologically advanced
spy satellite TecSAR.
In 2009, India reportedly developed a high-tech spy satellite
RISAT-2 with significant assistance from Israel. The satellite was successfully launched by India in April 2009.
According to a Los Angeles Times news story the
2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks (also referred to as 26/11, pronounced "twenty six eleven") were a series of Terrorism, terrorist attacks that took place in November 2008, when 10 members of Lashkar-e-Taiba, an Islamist terrorist organisation from P ...
were an attack on the growing India-Israel partnership. It quotes retired Indian Vice Admiral Premvir S. Das thus "Their aim was to... tell the Indians clearly that your growing linkage with Israel is not what you should be doing..." In the past, India and Israel have held numerous joint anti-terror training exercises
Germany
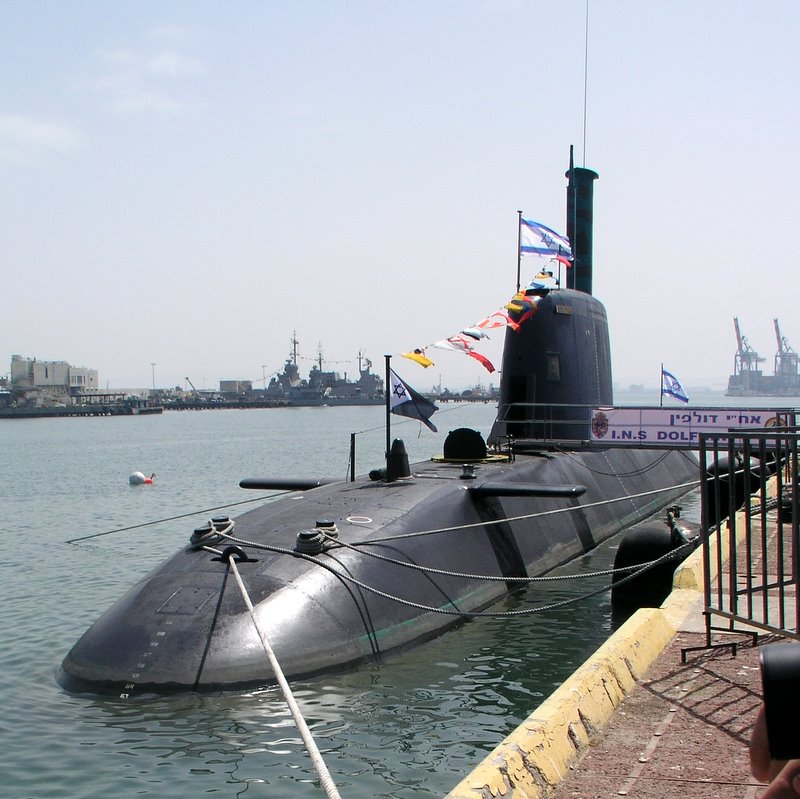

Germany developed the
Dolphin submarine and supplied it to Israel. Two submarines were donated by Germany. The military co-operation has been discreet but mutually profitable:
Israeli intelligence, for example, sent captured
Warsaw Pact armor to West Germany to be analyzed. The results aided the German development of an
anti-tank system. Israel also trained members of
GSG 9
, formerly (), is the police tactical unit of the German Federal Police ''(Bundespolizei (Germany), Bundespolizei)''. The state police (''Landespolizei'') maintain their own tactical units known as the ''Special Deployment Commando, Spezialein ...
, a German counter-terrorism and special operations unit. The Israeli
Merkava MK IV tank uses a German
V12 engine produced under license.
In 2008, the website DefenseNews revealed that Germany and Israel had been jointly developing a nuclear warning system, dubbed Operation Bluebird.

United Kingdom
During a secret operation in 1966, two British made "Chieftain" MBTs were brought to Israel for a 4 years long evaluation for service with the IDF. The plan was for the IDF not only to purchase the British MBTs, but for IMI (Israeli Military Industries) to buy production rights. As part of the deal during the early 60's Israel purchased second hand "Centurion" MBTs from the British, that used that money in the "Chieftain" development. After the trials were done Israeli improvement and ideas were implemented by the British manufacturer, but British politicians canceled the agreement with Israel and the program was shut down. The knowledge earned during the improvements on the "Chieftain", together with earlier experiments in tank improvements, gave the last push for the development and production of the "Merkava" tank.
United Kingdom has supplied equipment and spare parts for
Sa'ar 4.5-class missile boat
The Sa'ar 4.5-class missile boats ( he, סער 4.5) is a class of Israeli Sea Corps missile boats designed and built by Israel Shipyards Ltd. as an improved and stretched . There are two different subclasses that are both named Sa'ar 4.5. The fir ...
s and
F-4 Phantom fighter-bombers, components for small-caliber artillery ammunition and air-to-surface missiles, and engines for
Elbit Hermes 450 Unmanned aerial vehicles. British arms sales to Israel mainly consist of light weaponry, and ammunition and components for helicopters, tanks, armored personnel carriers, and combat aircraft.
Russia
On 19 October 1999, Defense Minister of China, General
Chi Haotian, after meeting with Syrian Defense Minister
Mustafa Tlass
Mustafa Abdul Qadir Tlass ( ar, مُصْطَفَى عَبْد الْقَادِر طَلَاس, Musṭafā ʿAbd al-Qādir Ṭalās; 11 May 1932 – 27 June 2017) was a Syrian senior military officer and politician who was Syria's minister of defe ...
in
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
,
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, to discuss expanding military ties between Syria and China, then flew directly to Israel and met with
Ehud Barak
Ehud Barak ( he-a, אֵהוּד בָּרָק, Ehud_barak.ogg, link=yes, born Ehud Brog; 12 February 1942) is an Israeli general and politician who served as the tenth prime minister from 1999 to 2001. He was leader of the Labor Party until Jan ...
, the then Prime Minister and Defense Minister of Israel where they discussed military relations. Among the military arrangements was a $1 billion Israeli Russian sale of military aircraft to China, which were to be jointly produced by Russia and Israel.
Russia has bought drones from Israel.
China
Israel is the second-largest foreign supplier of arms to the People's Republic of China, only after the
Russian Federation. China has purchased a wide array of military hardware from Israel, including
Unmanned aerial vehicles and
communications satellites. China has become an extensive market for Israel's military industries and arms manufacturers, and trade with Israel has allowed it to obtain "dual-use" technology which the United States and
European Union were reluctant to provide. In 2010
Yair Golan Yair may refer to:
*A spelling variant of the Jewish name Jair or Ya'ir
*Yair (name), list of people with the name Yair
*Yair, Scottish Borders
Yair, also known as The Yair, is an estate in the Scottish Borders. It stands by the River Tweed in ...
, head of
IDF Home Front Command visited China to strengthen military ties. In 2012,
IDF Chief of Staff Benny Gantz visited China for high-level talks with the Chinese defense establishment.
Cyprus
As closely neighboring countries, Israel and Cyprus have enjoyed greatly improving diplomatic relations since 2010. During the
Mount Carmel Forest Fire, Cyprus dispatched two aviation assets to assist fire-fighting operations in Israel – the first time Cypriot Government aircraft were permitted to operate from Israeli airfields in a non-civil capacity. In addition, Israel and Cyprus have closely cooperated in maritime activities relating to Gaza, since 2010, and have reportedly begun an extensive sharing program of regional intelligence to support mutual security concerns. On 17 May 2012, it was widely reported that the Israeli Air Force had been granted unrestricted access to the Nicosia Flight Information Region of Cyprus, and that Israeli aviation assets may have operated over the island itself. Cyprus, as a former
S-300 air-defense system operator, was speculated by Greek media to have assisted Israel in strategic planning to challenge such air-defense systems, alongside shorter-range
SAM
Sam, SAM or variants may refer to:
Places
* Sam, Benin
* Sam, Boulkiemdé, Burkina Faso
* Sam, Bourzanga, Burkina Faso
* Sam, Kongoussi, Burkina Faso
* Sam, Iran
* Sam, Teton County, Idaho, United States, a populated place
People and fictional ...
systems, although this remains unconfirmed.
Greece


Israel and Greece have enjoyed a very cordial military relationship since 2008, including military drills ranging from Israel to the island of Crete. Drills include air-to-air long-distance refueling, long-range flights, and most importantly aiding Israel in outmaneuvering the
S-300 which Greece has. Recent purchases include 100 million euro deal between Greece and Israel for the purchase of
SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 pound bomb kits. They have also signed many defense agreements, including Cyprus, in order to establish stability for transporting gas from Israel-Cyprus to Greece and on to the European Union-a paramount objective to the future stability and prosperity of all three countries, threatened by Turkey.
Turkey
Israel has provided extensive military assistance to Turkey. Israel sold Turkey
IAI Heron
The IAI Heron (Machatz-1) is a medium-altitude long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed by the Malat
(UAV) division of Israel Aerospace Industries. It is capable of Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) operations of up to 52 h ...
Unmanned aerial vehicles, and modernized Turkey's
F-4 Phantom and
Northrop F-5 aircraft at the cost of $900 million. Turkey's
main battle tank is the Israeli-made
Sabra tank, of which Turkey has 170. Israel later upgraded them for $500 million. Israel has also supplied Turkey with Israeli-made missiles, and the two nations have engaged in naval cooperation. Turkey allowed Israeli pilots to practice long-range flying over mountainous terrain in Turkey's Konya firing range, while Israel trains Turkish pilots at Israel's computerized firing range at
Nevatim Airbase. Until 2009, the Turkish military was one of Israel's largest defense customers. Israel defense companies have sold unmanned aerial vehicles and long-range targeting pods.
However, relations have been strained in recent times. In the last two years, the Turkish military has declined to participate in the annual joint naval exercise with Israel and the United States. The exercise, known as "Reliant Mermaid" was started in 1998 and included the Israeli, Turkish and American navies. The objective of the exercise is to practice search-and-rescue operations and to familiarize each navy with international partners who also operate in the
Mediterranean Sea.
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan and Israel have engaged in intense cooperation since 1992. Israeli military have been a major provider of battlefield aviation, artillery, antitank, and anti-infantry weaponry to Azerbaijan. In 2009, Israeli President
Shimon Peres
Shimon Peres (; he, שמעון פרס ; born Szymon Perski; 2 August 1923 – 28 September 2016) was an Israeli politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Israel from 1984 to 1986 and from 1995 to 1996 and as the ninth president of ...
made a visit to Azerbaijan where military relations were expanded further, with the Israeli company
Aeronautics Defense Systems Ltd announcing it was going to build a factory in
Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world a ...
. In 2012, Israel and Azerbaijan signed an agreement according to which state-run
Israel Aerospace Industries would sell $1.6 billion in drones and anti-aircraft and missile defense systems to Azerbaijan. In March 2012, the magazine ''
Foreign Policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
'' reported that the
Israeli Air Force may be preparing to use the
Sitalchay Military Airbase, located from the Iranian border, for air strikes against the
nuclear program of Iran
The nuclear program of Iran is an ongoing scientific effort by Iran to research nuclear technology that can be used to make nuclear weapons. Iran has several research sites, two uranium mines, a research reactor, and uranium processing facilit ...
,
later backed up by other media.
Other countries
Israel has also sold to or received supplies of military equipment from the
Czech Republic,
Argentina,
Portugal,
Spain,
Slovakia,
Italy,
South Africa,
Canada,
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
,
Poland,
Slovenia,
Romania,
Hungary,
Belgium,
Austria,
Serbia,
Montenegro,
Bosnia and Herzegovina,
,
Vietnam and
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, among others.
Future

The IDF is planning a number of technological upgrades and structural reforms for the future for its land, air, and sea branches. Training has been increased, including in cooperation between ground, air, and naval units.
The Israeli Army is phasing out the M-16 rifle from all ground units in favor of the
IMI Tavor variants, most recently the
IWI Tavor X95 flat-top ("Micro-Tavor Dor Gimel"). In addition, the IDF is now replacing its outdated
M113 armored personnel carriers in favor of new
Namer APCs, with 200 ordered in 2014, the
Eitan AFV, and is upgrading its
IDF Achzarit APCs. The IDF also announced plans to streamline its military bureaucracy so as to better maintain its reserve force, which a 2014 State Comptroller report noted was under-trained and may not be able to fulfill wartime missions. As part of the plans, 100,000 reservists and will be discharged, and training for the remainder will be improved. The officer corps will be slashed by 5,000. In addition, infantry and light artillery brigades will be reduced to increase training standards among the rest. The backbone of the IDF Artillery Corps, the
M109 howitzer, will be phased out in favor of a still-undecided replacement, with the
ATMOS 2000 and
Artillery Gun Module under primary consideration. The IDF is also planning a future tank to replace the Merkava. The new tank will be able to fire lasers and electromagnetic pulses, run on a hybrid engine, run with a crew as small as two, will be faster, and will be better-protected, with emphasis on protection systems such as the Trophy over armor. The
Combat Engineering Corps assimilated new technologies, mainly in tunnel detection and
unmanned ground vehicles and
military robots, such as remote-controlled
IDF Caterpillar D9T "Panda" armored bulldozers,
Sahar engineering scout robot and improved
Remotec ANDROS robots.
The
Israeli Air Force will purchase as many as 100
F-35 Lightning II fighter jets from the United States. The aircraft will be modified and designated F-35I. They will use Israeli-built electronic warfare systems, outer-wings, guided bombs, and air-to-air missiles. As part of a 2013 arms deal, the IAF will purchase
KC-135 Stratotanker aerial refueling aircraft and
V-22 Osprey
The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, tiltrotor military aircraft with both vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities. It is designed to combine the functionality of a convention ...
multi-mission aircraft from the United States, as well as advanced radars for warplanes and missiles designed to take out radars. In April 2013, an Israeli official stated that within 40–50 years, piloted aircraft would be phased out of service by
unmanned aerial vehicles capable of executing nearly any operation that can be performed by piloted combat aircraft. Israel's military industries are reportedly on the path to developing such technology in a few decades. Israel will also manufacture tactical satellites for military use.
The
Israeli Navy is currently expanding its submarine fleet, with a planned total of six
Dolphin class submarines. Currently, five have been delivered, with the sixth, INS Drakon, expected to be delivered in 2020. It is also upgrading and expanding its surface fleet. It is planning to upgrade the electronic warfare systems of its
Sa'ar 5-class corvettes and
Sa'ar 4.5 class missile boat
The Sa'ar 4.5-class missile boats ( he, סער 4.5) is a class of Israeli Sea Corps missile boats designed and built by Israel Shipyards Ltd. as an improved and stretched . There are two different subclasses that are both named Sa'ar 4.5. The fir ...
s, and has ordered two new classes of warship: the
Sa'ar 6-class corvette (a variant of the
Braunschweig-class corvette
The K130 ''Braunschweig'' class (sometimes Korvette 130) is Germany's newest class of ocean-going corvettes. Five ships have replaced the of the German Navy.
In October 2016 it was announced that a second batch of five more corvettes, original ...
) and the
Sa'ar 72-class corvette (an improved and enlarged version of the Sa'ar 4.5-class). It plans to acquire four Saar 6-class corvettes and three Sa'ar 72-class corvettes. Israel is also developing marine artillery, including a gun capable of firing satellite-guided 155mm rounds between 75 and 120 kilometers.
See also
Security forces
*
Intelligence Community
**
Shabak
**
Mossad
Mossad ( , ), ; ar, الموساد, al-Mōsād, ; , short for ( he, המוסד למודיעין ולתפקידים מיוחדים, links=no), meaning 'Institute for Intelligence and Special Operations'. is the national intelligence agency ...
**
National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
*
Israeli police
The Israel Police ( he, משטרת ישראל, ''Mišteret Yisra'el''; ar, شرطة إسرائيل, ''Shurtat Isrāʼīl'') is the civilian police force of Israel. As with most other police forces in the world, its duties include crime fightin ...
*
Knesset Guard
Defense industry of Israel
*
Defense industry of Israel
*
Plasan
*
Soltam
Strategic communication
*
IDF Spokesperson's Unit
*
Public diplomacy of Israel
Related subjects
*
Arab–Israeli conflict
*
Israel and weapons of mass destruction
Israel is widely believed to possess weapons of mass destruction, and to be one of four nuclear-armed countries not recognized as a Nuclear Weapons State by the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). The US Congress Office of Technology Assessment has re ...
*
Israeli casualties of war
*
Krav Maga
*
List of brigades of the Israel Defense Forces
*
Military equipment of Israel
*
Military history of Israel
The history of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) intertwines in its early stages with history of the Haganah.
Before 1948
Following the 1947 UN Partition Plan, which divided the British Mandate of Palestine, the country became increasingly vo ...
*
Palestinian political violence
*
Prayer for the IDF
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branc ...
*
Sherut Leumi, the non-military (civil) national service
References and footnotes
Further reading
* Marcus, Raphael D. ''Israel's Long War with Hezbollah: Military Innovation and Adaptation under Fire'' (Georgetown UP, 2018
online review*
*
*
*
*
* Roislien, Hanne Eggen (2013)
"Religion and Military Conscription: The Case of the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF)," Armed Forces & Society 39, No. 3, pp. 213–232.
* Country Briefing: Israel,
Jane's Defence Weekly, 19 June 1996
External links
*
Israel Defense Forces ranks and insigniaIDF Blog – news and updates from the field* Moshe Yaalon
The IDF and the Israeli SpiritPalestinian violence and terror attacks since September 2000A list of civilians and soldiers who died during Palestinian terror attacks since September 2000CNN.com Special – Victims of Terrorisayeret.com– The Israeli Special Forces Database
Israeli WeaponsOriginal Letters and Manuscripts: Ben-Gurion on the IDFShapell Manuscript Foundation
Jerusalem volunteer Border GuardTsahal-Miniature
IDF photosIsrael's War HistoryIsrael Military Forum*
{{Authority control
1948 establishments in Israel
Military units and formations established in 1948
Israel Prize in education recipients
Israel Prize recipients that are organizations
 Immediately after the 1948 war, the Israel-Palestinian conflict shifted to a low intensity conflict between the IDF and
Immediately after the 1948 war, the Israel-Palestinian conflict shifted to a low intensity conflict between the IDF and  All branches of the IDF answer to a single
All branches of the IDF answer to a single 
 Unlike most militaries, the IDF uses the same rank names in all corps, including the air force and navy. For ground forces' officers, rank insignia are brass on a red background; for the air force, silver on a blue background; and for the navy, the standard gold worn on the sleeve. Officer insignia are worn on epaulets on top of both shoulders. Insignia distinctive to each service are worn on the cap (see fig. 15).
Unlike most militaries, the IDF uses the same rank names in all corps, including the air force and navy. For ground forces' officers, rank insignia are brass on a red background; for the air force, silver on a blue background; and for the navy, the standard gold worn on the sleeve. Officer insignia are worn on epaulets on top of both shoulders. Insignia distinctive to each service are worn on the cap (see fig. 15).

 Enlisted grades wear rank insignia on the sleeve, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. For the army and air force, the insignia are white with blue interwoven threads backed with the appropriate corps color. Navy personnel wear gold-colored rank insignia sewn on navy blue material.
From the formation of the IDF until the late 1980s, sergeant major was a particularly important warrant officer rank, in line with usage in other armies. However, in the 1980s and 1990s the proliferating ranks of sergeant major became devalued, and now all professional
Enlisted grades wear rank insignia on the sleeve, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. For the army and air force, the insignia are white with blue interwoven threads backed with the appropriate corps color. Navy personnel wear gold-colored rank insignia sewn on navy blue material.
From the formation of the IDF until the late 1980s, sergeant major was a particularly important warrant officer rank, in line with usage in other armies. However, in the 1980s and 1990s the proliferating ranks of sergeant major became devalued, and now all professional 
 The Israel Defense Forces has several types of uniforms:
* Service dress (מדי אלף ''Madei Alef'' – Uniform "A") – the everyday uniform, worn by everybody.
* Field dress (מדי ב ''Madei Bet'' – Uniform "B") – worn into combat, training, work on base.
The first two resemble each other but the Madei Alef is made of higher quality materials in a golden-olive while the madei bet is in olive drab. The dress uniforms may also exhibit a surface shine
* Officers / Ceremonial dress (מדי שרד ''madei srad'') – worn by officers, or during special events/ceremonies.
* Dress uniform and mess dress – worn only abroad. There are several dress uniforms depending on the season and the branch.
The service uniform for all ground forces personnel is olive green; navy and air force uniforms are beige/ tan (also once worn by the ground forces). The uniforms consist of a two-pocket shirt,
The Israel Defense Forces has several types of uniforms:
* Service dress (מדי אלף ''Madei Alef'' – Uniform "A") – the everyday uniform, worn by everybody.
* Field dress (מדי ב ''Madei Bet'' – Uniform "B") – worn into combat, training, work on base.
The first two resemble each other but the Madei Alef is made of higher quality materials in a golden-olive while the madei bet is in olive drab. The dress uniforms may also exhibit a surface shine
* Officers / Ceremonial dress (מדי שרד ''madei srad'') – worn by officers, or during special events/ceremonies.
* Dress uniform and mess dress – worn only abroad. There are several dress uniforms depending on the season and the branch.
The service uniform for all ground forces personnel is olive green; navy and air force uniforms are beige/ tan (also once worn by the ground forces). The uniforms consist of a two-pocket shirt,  Headgear included a service cap for dress and semi-dress and a
Headgear included a service cap for dress and semi-dress and a 

 After personnel complete their regular service, they are either granted permanent exemption from military service, or assigned a position in the reserve forces. No distinction is made between the assignment of men or women to reserve service.
The IDF may call up reservists for:
* reserve service of up to one month every three years, until the age of 40 (enlisted) or 45 (officers). Reservists may volunteer after this age, with approval of the Manpower Directorate.
* immediate active duty in wartime.
All Israelis who served in the IDF and are under the age of 40, unless otherwise exempt, are eligible for reserve duty. However, only those who completed at least 20 days of reserve duty within the past three years are considered active reservists.
In most cases, the reserve duty is carried out in the same unit for years, in many cases the same unit as the active service and by the same people. Many soldiers who have served together in active service continue to meet in reserve duty for years after their discharge, causing reserve duty to become a strong male bonding experience in Israeli society.
Although still available for call-up in times of crisis, most Israeli men, and virtually all women, do not actually perform reserve service in any given year. In 2015, only 26% of the population eligible for reserve duty held an active reserve status. The IDF has reduced the number of reserve soldiers called up to improve efficiency and cut costs. Units do not always call up all of their reservists every year, and a variety of exemptions are available if called for regular reserve service. Virtually no exemptions exist for reservists called up in a time of crisis, but experience has shown that in such cases (most recently, the 2014 Operation Protective Edge) exemptions are rarely requested or exercised; units generally achieve recruitment rates above those considered fully manned.
After personnel complete their regular service, they are either granted permanent exemption from military service, or assigned a position in the reserve forces. No distinction is made between the assignment of men or women to reserve service.
The IDF may call up reservists for:
* reserve service of up to one month every three years, until the age of 40 (enlisted) or 45 (officers). Reservists may volunteer after this age, with approval of the Manpower Directorate.
* immediate active duty in wartime.
All Israelis who served in the IDF and are under the age of 40, unless otherwise exempt, are eligible for reserve duty. However, only those who completed at least 20 days of reserve duty within the past three years are considered active reservists.
In most cases, the reserve duty is carried out in the same unit for years, in many cases the same unit as the active service and by the same people. Many soldiers who have served together in active service continue to meet in reserve duty for years after their discharge, causing reserve duty to become a strong male bonding experience in Israeli society.
Although still available for call-up in times of crisis, most Israeli men, and virtually all women, do not actually perform reserve service in any given year. In 2015, only 26% of the population eligible for reserve duty held an active reserve status. The IDF has reduced the number of reserve soldiers called up to improve efficiency and cut costs. Units do not always call up all of their reservists every year, and a variety of exemptions are available if called for regular reserve service. Virtually no exemptions exist for reservists called up in a time of crisis, but experience has shown that in such cases (most recently, the 2014 Operation Protective Edge) exemptions are rarely requested or exercised; units generally achieve recruitment rates above those considered fully manned.
 Legislation (approved in April 2008) has reformed the reserve service, lowering the maximum service age to 40 for enlisted, and 45 for officers, designating it as an emergency and security force (disallowing routine duties that may be carried out by the active forces), as well as many other changes to the structure (although the Defense Minister can suspend any portion of it at any time for security reasons). The age threshold for many reservists whose positions are listed and updated yearly by the Knesset through the Occupations executive order is fixed at 45 or 49, depending on their military occupation and position.
Legislation (approved in April 2008) has reformed the reserve service, lowering the maximum service age to 40 for enlisted, and 45 for officers, designating it as an emergency and security force (disallowing routine duties that may be carried out by the active forces), as well as many other changes to the structure (although the Defense Minister can suspend any portion of it at any time for security reasons). The age threshold for many reservists whose positions are listed and updated yearly by the Knesset through the Occupations executive order is fixed at 45 or 49, depending on their military occupation and position.


 Although Israel has a majority of Jewish soldiers, all citizens including large numbers of
Although Israel has a majority of Jewish soldiers, all citizens including large numbers of 

 By law, all Israeli citizens are subject to conscription. The Defense Minister has complete discretion to grant exemption to individual citizens or classes of citizens. A long-standing policy dating to Israel's early years extends an exemption to all other Israeli minorities (most notably Israeli Arabs). However, there is a long-standing government policy of encouraging
By law, all Israeli citizens are subject to conscription. The Defense Minister has complete discretion to grant exemption to individual citizens or classes of citizens. A long-standing policy dating to Israel's early years extends an exemption to all other Israeli minorities (most notably Israeli Arabs). However, there is a long-standing government policy of encouraging  In October 2012 the IDF promoted Mona Abdo to become the first female Christian Arab to the rank of combat commander. Abdo had voluntarily enlisted in the IDF, which her family had encouraged, and transferred from the Ordnance Corps to the Caracal Battalion, a mixed-gender unit with both Jewish and Arab soldiers.
In 2014 an increase of Israeli Christian Arabs joining the army was reported.
Muslim Arabs have also been drafted into the Israel Defense Forces in increasing numbers in recent years. In 2020, 606 Muslim Arabs were drafted, compared to 489 in 2019 and 436 in 2018. More than half of those who have drafted have gone into combat roles.
In October 2012 the IDF promoted Mona Abdo to become the first female Christian Arab to the rank of combat commander. Abdo had voluntarily enlisted in the IDF, which her family had encouraged, and transferred from the Ordnance Corps to the Caracal Battalion, a mixed-gender unit with both Jewish and Arab soldiers.
In 2014 an increase of Israeli Christian Arabs joining the army was reported.
Muslim Arabs have also been drafted into the Israel Defense Forces in increasing numbers in recent years. In 2020, 606 Muslim Arabs were drafted, compared to 489 in 2019 and 436 in 2018. More than half of those who have drafted have gone into combat roles.
 Men in the Haredi community may choose to defer service while enrolled in '' yeshivot'' (see Tal committee); many avoid conscription altogether. This special arrangement is called Torato Omanuto, and has given rise to tensions between the Israeli religious and secular communities. While options exist for Haredim to serve in the IDF in an atmosphere accommodating to their religious convictions, most Haredim do not choose to serve in the IDF.
Haredi males have the option of serving in the 97th "Netzah Yehuda" Infantry Battalion. This unit is a standard IDF infantry battalion focused on the
Men in the Haredi community may choose to defer service while enrolled in '' yeshivot'' (see Tal committee); many avoid conscription altogether. This special arrangement is called Torato Omanuto, and has given rise to tensions between the Israeli religious and secular communities. While options exist for Haredim to serve in the IDF in an atmosphere accommodating to their religious convictions, most Haredim do not choose to serve in the IDF.
Haredi males have the option of serving in the 97th "Netzah Yehuda" Infantry Battalion. This unit is a standard IDF infantry battalion focused on the 

 The IDF's mission is to "defend the existence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the state of Israel. To protect the inhabitants of Israel and to combat all forms of terrorism which threaten the daily life." The Israeli military's primary principles derive from Israel's need to combat numerically superior opponents. One such principle, is the concept that Israel cannot afford to lose a single war. The IDF believes that this is possible if it can rapidly mobilize troops to insure that they engage the enemy in enemy territory. In the 21st Century, various nonconventional threats including terrorist organizations, subterranean infrastructure operated by Hamas, etc. have forced the IDF to modify its official defense doctrine.
The IDF's mission is to "defend the existence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the state of Israel. To protect the inhabitants of Israel and to combat all forms of terrorism which threaten the daily life." The Israeli military's primary principles derive from Israel's need to combat numerically superior opponents. One such principle, is the concept that Israel cannot afford to lose a single war. The IDF believes that this is possible if it can rapidly mobilize troops to insure that they engage the enemy in enemy territory. In the 21st Century, various nonconventional threats including terrorist organizations, subterranean infrastructure operated by Hamas, etc. have forced the IDF to modify its official defense doctrine.

 * Tenacity of Purpose in Performing Missions and Drive to Victory
* Responsibility
* Credibility
* Personal Example
* Human Life
* Purity of Arms
*
* Tenacity of Purpose in Performing Missions and Drive to Victory
* Responsibility
* Credibility
* Personal Example
* Human Life
* Purity of Arms
* 




 Yom Hazikaron, Israel's day of remembrance for fallen soldiers, is observed on the 4th day of the month of Iyar of the Hebrew calendar, the day before the celebration of
Yom Hazikaron, Israel's day of remembrance for fallen soldiers, is observed on the 4th day of the month of Iyar of the Hebrew calendar, the day before the celebration of  In 1983, the United States and Israel established a Joint Political Military Group, which convenes twice a year. Both the U.S. and Israel participate in joint military planning and combined exercises, and have collaborated on military research and weapons development. Additionally the
In 1983, the United States and Israel established a Joint Political Military Group, which convenes twice a year. Both the U.S. and Israel participate in joint military planning and combined exercises, and have collaborated on military research and weapons development. Additionally the 

 Israel and Greece have enjoyed a very cordial military relationship since 2008, including military drills ranging from Israel to the island of Crete. Drills include air-to-air long-distance refueling, long-range flights, and most importantly aiding Israel in outmaneuvering the S-300 which Greece has. Recent purchases include 100 million euro deal between Greece and Israel for the purchase of SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 pound bomb kits. They have also signed many defense agreements, including Cyprus, in order to establish stability for transporting gas from Israel-Cyprus to Greece and on to the European Union-a paramount objective to the future stability and prosperity of all three countries, threatened by Turkey.
Israel and Greece have enjoyed a very cordial military relationship since 2008, including military drills ranging from Israel to the island of Crete. Drills include air-to-air long-distance refueling, long-range flights, and most importantly aiding Israel in outmaneuvering the S-300 which Greece has. Recent purchases include 100 million euro deal between Greece and Israel for the purchase of SPICE 1000 and SPICE 2000 pound bomb kits. They have also signed many defense agreements, including Cyprus, in order to establish stability for transporting gas from Israel-Cyprus to Greece and on to the European Union-a paramount objective to the future stability and prosperity of all three countries, threatened by Turkey.
 The IDF is planning a number of technological upgrades and structural reforms for the future for its land, air, and sea branches. Training has been increased, including in cooperation between ground, air, and naval units.
The Israeli Army is phasing out the M-16 rifle from all ground units in favor of the IMI Tavor variants, most recently the IWI Tavor X95 flat-top ("Micro-Tavor Dor Gimel"). In addition, the IDF is now replacing its outdated M113 armored personnel carriers in favor of new Namer APCs, with 200 ordered in 2014, the Eitan AFV, and is upgrading its IDF Achzarit APCs. The IDF also announced plans to streamline its military bureaucracy so as to better maintain its reserve force, which a 2014 State Comptroller report noted was under-trained and may not be able to fulfill wartime missions. As part of the plans, 100,000 reservists and will be discharged, and training for the remainder will be improved. The officer corps will be slashed by 5,000. In addition, infantry and light artillery brigades will be reduced to increase training standards among the rest. The backbone of the IDF Artillery Corps, the M109 howitzer, will be phased out in favor of a still-undecided replacement, with the ATMOS 2000 and Artillery Gun Module under primary consideration. The IDF is also planning a future tank to replace the Merkava. The new tank will be able to fire lasers and electromagnetic pulses, run on a hybrid engine, run with a crew as small as two, will be faster, and will be better-protected, with emphasis on protection systems such as the Trophy over armor. The Combat Engineering Corps assimilated new technologies, mainly in tunnel detection and unmanned ground vehicles and military robots, such as remote-controlled IDF Caterpillar D9T "Panda" armored bulldozers, Sahar engineering scout robot and improved Remotec ANDROS robots.
The Israeli Air Force will purchase as many as 100 F-35 Lightning II fighter jets from the United States. The aircraft will be modified and designated F-35I. They will use Israeli-built electronic warfare systems, outer-wings, guided bombs, and air-to-air missiles. As part of a 2013 arms deal, the IAF will purchase KC-135 Stratotanker aerial refueling aircraft and
The IDF is planning a number of technological upgrades and structural reforms for the future for its land, air, and sea branches. Training has been increased, including in cooperation between ground, air, and naval units.
The Israeli Army is phasing out the M-16 rifle from all ground units in favor of the IMI Tavor variants, most recently the IWI Tavor X95 flat-top ("Micro-Tavor Dor Gimel"). In addition, the IDF is now replacing its outdated M113 armored personnel carriers in favor of new Namer APCs, with 200 ordered in 2014, the Eitan AFV, and is upgrading its IDF Achzarit APCs. The IDF also announced plans to streamline its military bureaucracy so as to better maintain its reserve force, which a 2014 State Comptroller report noted was under-trained and may not be able to fulfill wartime missions. As part of the plans, 100,000 reservists and will be discharged, and training for the remainder will be improved. The officer corps will be slashed by 5,000. In addition, infantry and light artillery brigades will be reduced to increase training standards among the rest. The backbone of the IDF Artillery Corps, the M109 howitzer, will be phased out in favor of a still-undecided replacement, with the ATMOS 2000 and Artillery Gun Module under primary consideration. The IDF is also planning a future tank to replace the Merkava. The new tank will be able to fire lasers and electromagnetic pulses, run on a hybrid engine, run with a crew as small as two, will be faster, and will be better-protected, with emphasis on protection systems such as the Trophy over armor. The Combat Engineering Corps assimilated new technologies, mainly in tunnel detection and unmanned ground vehicles and military robots, such as remote-controlled IDF Caterpillar D9T "Panda" armored bulldozers, Sahar engineering scout robot and improved Remotec ANDROS robots.
The Israeli Air Force will purchase as many as 100 F-35 Lightning II fighter jets from the United States. The aircraft will be modified and designated F-35I. They will use Israeli-built electronic warfare systems, outer-wings, guided bombs, and air-to-air missiles. As part of a 2013 arms deal, the IAF will purchase KC-135 Stratotanker aerial refueling aircraft and