Italian-language Television Stations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a
– Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Italian is included under the languages covered by the
Data for EU27
published in 2012. Including Italian speakers in non-EU European countries (such as Switzerland, Albania and the
 During this time, long-existing beliefs stemming from the teachings of the
During this time, long-existing beliefs stemming from the teachings of the
 Italian literature's first modern novel, ('' The Betrothed'') by
Italian literature's first modern novel, ('' The Betrothed'') by
 Italian is an official language of Italy and
Italian is an official language of Italy and  It formerly had official status in
It formerly had official status in  Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia. Although over 17 million Americans are of Italian descent, only a little over one million people in the United States speak Italian at home. Nevertheless, an Italian language media market does exist in the country. In Canada, Italian is the second most spoken non-official language when
Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia. Although over 17 million Americans are of Italian descent, only a little over one million people in the United States speak Italian at home. Nevertheless, an Italian language media market does exist in the country. In Canada, Italian is the second most spoken non-official language when
 From the late 19th to the mid-20th century, thousands of Italians settled in Argentina, Uruguay, Southern Brazil and Venezuela, as well as in Canada and the United States, where they formed a physical and cultural presence.
In some cases, colonies were established where variants of regional
From the late 19th to the mid-20th century, thousands of Italians settled in Argentina, Uruguay, Southern Brazil and Venezuela, as well as in Canada and the United States, where they formed a physical and cultural presence.
In some cases, colonies were established where variants of regional
 In Italy, almost all the other languages spoken as the vernacular—other than standard Italian and some languages spoken among immigrant communities—are often called "
In Italy, almost all the other languages spoken as the vernacular—other than standard Italian and some languages spoken among immigrant communities—are often called "
' ''; ''i'' is the plural of ''il''; and ''le'' is the plural of feminine ''la'' and ''l''
Il Nuovo De Mauro
* * Swadesh list in English and Italian * Italian proverbs *
Learn Italian
, '' BBC'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Language Fusional languages Languages attested from the 10th century Languages of Italy Languages of Monaco Languages of San Marino Languages of Sicily Languages of Switzerland Languages of Vatican City Languages of Slovenia Languages of Croatia Subject–verb–object languages
Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language fa ...
of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
that evolved from the Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
. Spoken by about 85 million people (2022), Italian is an official language in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Switzerland (Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and the Grisons), San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
, and Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
. It has an official minority status in western Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian and Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian, Italian and Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic betwee ...
(Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
).
Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia.Ethnologue report for language code:ita (Italy)– Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Italian is included under the languages covered by the
European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, ...
in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
and in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, although Italian is neither a co-official nor a protected language in these countries. Many speakers of Italian are native bilinguals of both Italian (either in its standard form or regional varieties) and another regional language of Italy.
Italian is a major language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
in Europe, being one of the official languages of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
and one of the working languages of the Council of Europe. It is the second-most-widely spoken native language in the European Union with 67 million speakers (15% of the EU population) and it is spoken as a second language by 13.4 million EU citizens (3%).Europeans and their LanguagesData for EU27
published in 2012. Including Italian speakers in non-EU European countries (such as Switzerland, Albania and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
) and on other continents, the total number of speakers is approximately 85 million. Italian is the main working language of the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
, serving as the lingua franca (common language) in the Roman Catholic hierarchy as well as the official language of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta. Italian has a significant use in musical terminology and opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libre ...
with numerous Italian words referring to music that have become international terms taken into various languages worldwide. Italian was adopted by the state after the Unification of Italy, having previously been a literary language
A literary language is the form (register) of a language used in written literature, which can be either a nonstandard dialect or a standardized variety of the language. Literary language sometimes is noticeably different from the spoken langu ...
based on Tuscan as spoken mostly by the upper class of Florentine society. Almost all native Italian words end with vowels and has a 7-vowel sound system ('e' and 'o' have mid-low and mid-high sounds). Italian has contrast between short and long consonants and gemination
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (), or consonant lengthening (from Latin 'doubling', itself from '' gemini'' 'twins'), is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from ...
(doubling) of consonants.
History
Origins
During theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the established written language in Europe was Latin, though the great majority of people were illiterate, and only a handful were well versed in the language. In the Italian Peninsula, as in most of Europe, most would instead speak a local vernacular. These dialects, as they are commonly referred to, evolved from Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
over the course of centuries, unaffected by formal standards and teachings. They are not in any sense "dialects" of standard Italian, which itself started off as one of these local tongues, but sister language
In historical linguistics, sister languages are cognate languages; that is, languages that descend from a common ancestral language, their so-called proto-language. Every language in a language family that descends from the same language as the o ...
s of Italian. Mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
with Italian varies widely, as it does with Romance languages in general. The Romance languages of Italy can differ greatly from Italian at all levels (phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
, morphology, syntax, lexicon, pragmatics
In linguistics and related fields, pragmatics is the study of how context contributes to meaning. The field of study evaluates how human language is utilized in social interactions, as well as the relationship between the interpreter and the in ...
) and are classified typologically as distinct languages.
The standard Italian language has a poetic and literary origin in the writings of Tuscan and Sicilian writers of the 12th century, and, even though the grammar and core lexicon are basically unchanged from those used in Florence in the 13th century, the modern standard of the language was largely shaped by relatively recent events. However, Romance vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
as language spoken in the Italian Peninsula has a longer history. In fact, the earliest surviving texts that can definitely be called vernacular (as distinct from its predecessor Vulgar Latin) are legal formulae known as the Placiti Cassinesi from the Province of Benevento that date from 960 to 963, although the Veronese Riddle, probably from the 8th or early 9th century, contains a late form of Vulgar Latin that can be seen as a very early sample of a vernacular dialect of Italy. The Commodilla catacomb inscription is also a similar case.
The Italian language has progressed through a long and slow process, which started after the Western Roman Empire's fall in the 5th century.
The language that came to be thought of as Italian developed in central Tuscany and was first formalized in the early 14th century through the works of Tuscan writer Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His '' Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ...
, written in his native Florentine. Dante's epic poems, known collectively as the ', to which another Tuscan poet Giovanni Boccaccio later affixed the title ', were read throughout the peninsula and his written dialect became the "canonical standard" that all educated Italians could understand. Dante is still credited with standardizing the Italian language. In addition to the widespread exposure gained through literature, the Florentine dialect also gained prestige due to the political and cultural significance of Florence at the time and the fact that it was linguistically an intermediate between the northern and the southern Italian dialects. Thus the dialect of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
became the basis for what would become the official language of Italy.
Italian was progressively made an official language of most of the Italian states predating unification, slowly replacing Latin, even when ruled by foreign powers (like Spain in the Kingdom of Naples, or Austria in the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
The Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia ( la, links=no, Regnum Langobardiae et Venetiae), commonly called the "Lombardo-Venetian Kingdom" ( it, links=no, Regno Lombardo-Veneto, german: links=no, Königreich Lombardo-Venetien), was a constituent land ...
), even though the masses kept speaking primarily their local vernaculars. Italian was also one of the many recognised languages in the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
.
Italy has always had a distinctive dialect for each city because the cities, until recently, were thought of as city-states. Those dialects now have considerable variety. As Tuscan-derived Italian came to be used throughout Italy, features of local speech were naturally adopted, producing various versions of Regional Italian
Regional Italian ( it, italiano regionale) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and ...
. The most characteristic differences, for instance, between Roman Italian and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 ...
ese Italian are syntactic gemination of initial consonants in some contexts and the pronunciation of stressed "e", and of "s" between vowels in many words: e.g. ' "all right" is pronounced by a Roman (and by any standard Italian speaker), by a Milanese (and by any speaker whose native dialect lies to the north of the La Spezia–Rimini Line); ' "at home" is for Roman, or for standard, for Milanese and generally northern.
In contrast to the Gallo-Italic linguistic panorama of Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
, the Italo-Dalmatian, Neapolitan and its related dialects were largely unaffected by the Franco- Occitan influences introduced to Italy mainly by bards from France during the Middle Ages, but after the Norman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern t ...
, Sicily became the first Italian land to adopt Occitan lyric moods (and words) in poetry. Even in the case of Northern Italian languages, however, scholars are careful not to overstate the effects of outsiders on the natural indigenous developments of the languages.
The economic might and relatively advanced development of Tuscany at the time (Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
) gave its language weight, though Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
remained widespread in medieval Italian commercial life, and Ligurian (or Genoese) remained in use in maritime trade alongside the Mediterranean. The increasing political and cultural relevance of Florence during the periods of the rise of the Medici Bank
The Medici Bank (Italian: ''Banco dei Medici'' ) was a financial institution created by the Medici family in Italy during the 15th century (1397–1494). It was the largest and most respected bank in Europe during its prime. There are some estim ...
, humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
, and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
made its dialect, or rather a refined version of it, a standard in the arts.
Renaissance
TheRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
era, known as in Italian, was seen as a time of rebirth, which is the literal meaning of both (from French) and (Italian).
 During this time, long-existing beliefs stemming from the teachings of the
During this time, long-existing beliefs stemming from the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
began to be understood from new perspectives as humanists—individuals who placed emphasis on the human body and its full potential—began to shift focus from the church to human beings themselves. The continual advancements in technology play a crucial role in the diffusion of languages. After the invention of the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
in the fifteenth century, the number of printing presses in Italy grew rapidly and by the year 1500 reached a total of 56, the biggest number of printing presses in all of Europe. This enabled the production of more pieces of literature at a lower cost and as the dominant language, Italian, spread.
Italian became the language used in the courts of every state in the Italian Peninsula, as well as the prestige variety
In sociolinguistics, prestige is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally con ...
used on the island of Corsica (but not in the neighboring Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label= Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, af ...
, which on the contrary underwent Italianization well into the late 18th century, under Savoyard sway: the island's linguistic composition, roofed by the prestige of Spanish among the Sardinians, would therein make for a rather slow process of assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
*Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
**Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the progre ...
to the Italian cultural sphere). The rediscovery of Dante's , as well as a renewed interest in linguistics in the 16th century, sparked a debate that raged throughout Italy concerning the criteria that should govern the establishment of a modern Italian literary and spoken language. This discussion, known as (i. e., the ''problem of the language''), ran through the Italian culture until the end of the 19th century, often linked to the political debate on achieving a united Italian state. Renaissance scholars divided into three main factions:
* The purists, headed by Venetian Pietro Bembo
Pietro Bembo, ( la, Petrus Bembus; 20 May 1470 – 18 January 1547) was an Italian scholar, poet, and literary theorist who also was a member of the Knights Hospitaller, and a cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. As an intellectual of the ...
(who, in his , claimed the language might be based only on the great literary classics, such as Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credite ...
and some part of Boccaccio). The purists thought the ''Divine Comedy'' was not dignified enough because it used elements from non-lyric registers of the language.
* Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
and other Florentines preferred the version spoken by ordinary people in their own times.
* The courtier
A courtier () is a person who attends the royal court of a monarch or other royalty. The earliest historical examples of courtiers were part of the retinues of rulers. Historically the court was the centre of government as well as the officia ...
s, like Baldassare Castiglione and Gian Giorgio Trissino
Gian Giorgio Trissino (8 July 1478 – 8 December 1550), also called Giovan Giorgio Trissino and self-styled as Giovan Giωrgio Trissino, was a Venetian Renaissance humanist, poet, dramatist, diplomat, grammarian, linguist, and philosopher. ...
, insisted that each local vernacular contribute to the new standard.
A fourth faction claimed that the best Italian was the one that the papal court adopted, which was a mixture of the Tuscan and Roman dialects. Eventually, Bembo's ideas prevailed, and the foundation of the in Florence (1582–1583), the official legislative body of the Italian language, led to publication of Agnolo Monosini's Latin tome in 1604 followed by the first Italian dictionary in 1612.
Modern era
An important event that helped the diffusion of Italian was the conquest and occupation of Italy by Napoleon in the early 19th century (who was himself of Italian-Corsican descent). This conquest propelled the unification of Italy some decades after and pushed the Italian language into a lingua franca used not only among clerks, nobility, and functionaries in the Italian courts but also by the bourgeoisie.Contemporary times
 Italian literature's first modern novel, ('' The Betrothed'') by
Italian literature's first modern novel, ('' The Betrothed'') by Alessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Antonio Manzoni (, , ; 7 March 1785 – 22 May 1873) was an Italian poet, novelist and philosopher. He is famous for the novel '' The Betrothed'' (orig. it, I promessi sposi) (1827), generally ranked among the maste ...
, further defined the standard by "rinsing" his Milanese "in the waters of the Arno" (Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
's river), as he states in the preface to his 1840 edition.
After unification, a huge number of civil servants and soldiers recruited from all over the country introduced many more words and idioms from their home languages— is derived from the Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
word ("slave", that is "your servant"), comes from the Lombard word , etc. Only 2.5% of Italy's population could speak the Italian standardized language properly when the nation was unified in 1861.
Classification
Italian is aRomance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language fa ...
, a descendant of Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
(colloquial spoken Latin). Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, especially its Florentine dialect, and is therefore an Italo-Dalmatian language, a classification that includes most other central and southern Italian languages and the extinct Dalmatian.
According to many sources, Italian is the closest language to Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
in terms of vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the la ...
. According to the Ethnologue, lexical similarity is 89% with French, 87% with Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
, 85% with Sardinian, 82% with Spanish, 80% with Portuguese, 78% with Ladin, 77% with Romanian. Estimates may differ according to sources.
One study (analyzing the degree of differentiation of Romance languages in comparison to Latin (comparing phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
, inflection
In linguistic morphology, inflection (or inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, animacy, and ...
, discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. ...
, syntax, vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the la ...
, and intonation) estimated that distance between Italian and Latin is higher than that between Sardinian and Latin. In particular, its vowels are the second-closest to Latin after Sardinian. As in most Romance languages, stress is distinctive.
Geographic distribution
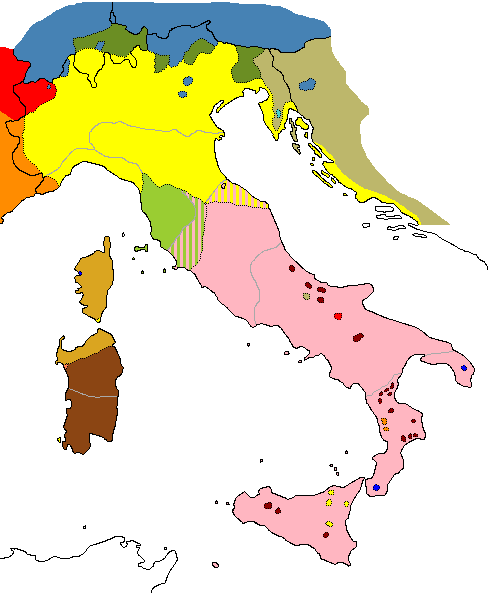
 Italian is an official language of Italy and
Italian is an official language of Italy and San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
and is spoken fluently by the majority of the countries' populations. Italian is the third most spoken language in Switzerland (after German and French), though its use there has moderately declined since the 1970s. It is official both on the national level and on regional level in two cantons: Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and the Grisons. In the latter canton, however, it is only spoken by a small minority, in the Italian Grisons. Ticino, which includes Lugano
Lugano (, , ; lmo, label=Ticinese dialect, Ticinese, Lugan ) is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Luga ...
, the largest Italian-speaking city outside Italy, is the only canton where Italian is predominant. Italian is also used in administration and official documents in Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
.
Italian is also spoken by a minority in Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word ...
and France, especially in the southeastern part of the country. Italian was the official language in Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
...
and in Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
until 1860, when they were both annexed by France under the Treaty of Turin, a development that triggered the " Niçard exodus", the emigration of a quarter of the Niçard Italians to Italy. Italian was the official language of Corsica until 1859. Italian is generally understood in Corsica by the population resident therein who speak Corsican, which is an Italo-Romance idiom similar to Tuscan. Italian was the official language in Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word ...
until 1860, when it was replaced by the French. This was due to the annexation of the surrounding County of Nice to France following the Treaty of Turin (1860).
It formerly had official status in Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
(because of the Venetian Albania), parts of Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
(because of the Venetian Istria and Venetian Dalmatia), parts of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
(because of the Venetian rule in the Ionian Islands and by the Kingdom of Italy in the Dodecanese). Italian is widely spoken in Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, where nearly two-thirds of the population can speak it fluently. Italian served as Malta's official language until 1934, when it was abolished by the British colonial administration amid strong local opposition. Italian language in Slovenia is an officially recognized minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) an ...
in the country. The official census, carried out in 2002, reported 2,258 ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians
Istrian Italians are an ethnic group from the Adriatic region of Istria in modern northwestern Croatia and southwestern Slovenia. Istrian Italians descend from the original Latinized population of Roman Histria, from the Venetian-speaking sett ...
) in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
(0.11% of the total population). Italian language in Croatia is an official minority language in the country, with many schools and public announcements published in both languages. The 2001 census in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
reported 19,636 ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) in the country (some 0.42% of the total population). Their numbers dropped dramatically after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
following the Istrian–Dalmatian exodus
The Istrian–Dalmatian exodus (; ; ) was the post-World War II exodus and departure of local ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) as well as ethnic Slovenes, Croats, and Istro-Romanians from the Yugoslav territory of J ...
, which caused the emigration of between 230,000 and 350,000 Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians. Italian was the official language of the Republic of Ragusa from 1492 to 1807.
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the ...
due to the annexation of the country to the Kingdom of Italy (1939–1943). Albania has a large population of non-native speakers, with over half of the population having some knowledge of the Italian language. The Albanian government has pushed to make Italian a compulsory second language in schools. The Italian language is well-known and studied in Albania, due to its historical ties and geographical proximity to Italy and to the diffusion of Italian television in the country.
Due to heavy Italian influence during the Italian colonial period, Italian is still understood by some in former colonies. Although it was the primary language in Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
since colonial rule, Italian greatly declined under the rule of Muammar Gaddafi, who expelled the Italian Libyan
Italian settlers in Libya ( it, Italo-libici, also called Italian Libyans) typically refers to Italians and their descendants, who resided or were born in Libya during the Italian colonial period.
History
Italian heritage in Libya can be dat ...
population and made Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
the sole official language of the country. A few hundred Italian settlers returned to Libya in the 2000s.
Italian was the official language of Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
during Italian colonisation. Italian is today used in commerce, and it is still spoken especially among elders; besides that, Italian words are incorporated as loan words in the main language spoken in the country (Tigrinya). The capital city of Eritrea, Asmara, still has several Italian schools, established during the colonial period. In the early 19th century, Eritrea was the country with the highest number of Italians abroad, and the Italian Eritreans
Italian Eritreans (or Eritrean Italians) are Eritrean-born descendants of Italian settlers as well as Italian long-term residents in Eritrea.
History
Their ancestry dates back from the beginning of the Italian colonization of Eritrea at the end o ...
grew from 4,000 during World War I to nearly 100,000 at the beginning of World War II. In Asmara there are two Italian schools, the Italian School of Asmara (Italian primary school with a Montessori department) and the Liceo Sperimentale "G. Marconi" (Italian international senior high school).
Italian was also introduced to Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
through colonialism and was the sole official language of administration and education during the colonial period but fell out of use after government, educational and economic infrastructure were destroyed in the Somali Civil War.
varieties of Chinese
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of ...
are not grouped together, with 375,645 claiming Italian as their mother tongue in 2016.
Italian immigrants to South America have also brought a presence of the language to that continent. According to some sources, Italian is the second most spoken language in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
after the official language of Spanish, although its number of speakers, mainly of the older generation, is decreasing. Italian bilingual speakers can be found in the Southeast of Brazil as well as in the South, corresponding to 2.07% of the total population of the country. In Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
, Italian is the most spoken language after Spanish and Portuguese, with around 200,000 speakers. In Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, people that speak Italian as their home language is 1.1% of the total population of the country. In Australia, Italian is the second most spoken foreign language after Chinese, with 1.4% of the population speaking it as their home language.
The main Italian-language newspapers published outside Italy are the ''L'Osservatore Romano
''L'Osservatore Romano'' (, 'The Roman Observer') is the daily newspaper of Vatican City State which reports on the activities of the Holy See and events taking place in the Catholic Church and the world. It is owned by the Holy See but is not ...
'' (Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
), the ''L'Informazione di San Marino'' (San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
), the ''Corriere del Ticino
''Corriere del Ticino'' is a regional daily newspaper in the canton of Ticino, Switzerland.
History and profile
''Corriere del Ticino'' was established in 1891. The paper is published in the Italian language in Muzzano, Ticino.
In the early ...
'' and the '' laRegione Ticino'' ( Switzerland), the '' La Voce del Popolo'' (Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
), the ''Corriere d'Italia'' (Germany), the ''L'italoeuropeo'' (United Kingdom), the ''Passaparola'' (Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
), the '' America Oggi'' (United States), the ''Corriere Canadese
''Corriere Canadese'' ("The Canadian Courier") is an Italian language, Italian-language daily newspaper published in Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The publication is distributed exclusively in Ontario and Quebec, primarily throughout the Gre ...
'' and the ''Corriere Italiano
''Corriere Italiano'' ("Italian Courier") is an Italian-language daily newspaper published in Montreal, Quebec.
The ''Corriere Italiano'' was founded by Alfredo Gagliardi, president of the Italian Order of Sons of Italy in Canada, in Montreal in ...
'' (Canada), the ''Il punto d'incontro'' (Mexico), the ''L'Italia del Popolo'' (Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
), the ''Fanfulla'' (Brazil), the ''Gente d'Italia'' (Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
), the ''La Voce d'Italia'' (Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
), the '' Il Globo'' (Australia) and the ''La gazzetta del Sud Africa'' (South Africa).
Education
Italian is widely taught in many schools around the world, but rarely as the first foreign language. In the 21st century, technology also allows for the continual spread of the Italian language, as people have new ways to learn how to speak, read, and write languages at their own pace and at any given time. For example, the free website and application Duolingo has 4.94 million English speakers learning the Italian language. According to the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, every year there are more than 200,000 foreign students who study the Italian language; they are distributed among the 90 Institutes of Italian Culture that are located around the world, in the 179 Italian schools located abroad, or in the 111 Italian lecturer sections belonging to foreign schools where Italian is taught as a language of culture.Influence and derived languages
languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gr ...
were used, and some continue to use this regional language. Examples are Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, where Talian is used, and the town of Chipilo near Puebla, Mexico; each continues to use a derived form of Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
dating back to the nineteenth century. Another example is Cocoliche, an Italian–Spanish pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from s ...
once spoken in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
and especially in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the Capital city, capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata ...
, and Lunfardo.
Lingua franca
Starting in latemedieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
times in much of Europe and the Mediterranean, Latin was replaced as the primary commercial language by Italian language variants (especially Tuscan and Venetian). These variants were consolidated during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
with the strength of Italy and the rise of humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
and the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both h ...
.
During that period, Italy held artistic sway over the rest of Europe. It was the norm for all educated gentlemen to make the Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tu ...
, visiting Italy to see its great historical monuments and works of art. It thus became expected to learn at least some Italian. In England, while the classical languages Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
were the first to be learned, Italian became the second most common modern language after French, a position it held until the late 18th century when it tended to be replaced by German. John Milton
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet and intellectual. His 1667 epic poem ''Paradise Lost'', written in blank verse and including over ten chapters, was written in a time of immense religious flux and polit ...
, for instance, wrote some of his early poetry in Italian.
Within the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Italian is known by a large part of the ecclesiastical hierarchy and is used in substitution for Latin in some official documents.
Italian loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
s continue to be used in most languages in matters of art and music (especially classical music including opera), in the design and fashion industries, in some sports like football and especially in culinary terms.
Languages and dialects

Italian dialects Italian dialects may refer to any of the following linguistic notions:
*the various dialects pertaining to different languages which are spoken in Italy, regardless of the origins thereof;
* the , which are related to Italian, but do not stem fro ...
", a label that can be very misleading if it is understood to mean "dialects ''of'' Italian". The Romance dialects of Italy are local evolutions of spoken Latin that pre-date the establishment of Italian, and as such are sister language
In historical linguistics, sister languages are cognate languages; that is, languages that descend from a common ancestral language, their so-called proto-language. Every language in a language family that descends from the same language as the o ...
s to the Tuscan that was the historical source of Italian. They can be quite different from Italian and from each other, with some belonging to different linguistic branches of Romance. The only exceptions to this are twelve groups considered " historical language minorities", which are officially recognized as distinct minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) an ...
s by the law. On the other hand, Corsican (a language spoken on the French island of Corsica) is closely related to medieval Tuscan, from which Standard Italian derives and evolved.
The differences in the evolution of Latin in the different regions of Italy can be attributed to the natural changes that all languages in regular use are subject to, and to some extent to the presence of three other types of languages: substrata, superstrata, and adstrata. The most prevalent were substrata (the language of the original inhabitants), as the Italian dialects were most likely simply Latin as spoken by native cultural groups. Superstrata and adstrata were both less important. Foreign conquerors of Italy that dominated different regions at different times left behind little to no influence on the dialects. Foreign cultures with which Italy engaged in peaceful relations with, such as trade, had no significant influence either.
Throughout Italy, regional variations of Standard Italian, called Regional Italian
Regional Italian ( it, italiano regionale) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and ...
, are spoken. Regional differences can be recognized by various factors: the openness of vowels, the length of the consonants, and influence of the local language (for example, in informal situations ', ' and ' replace the standard Italian ' in the area of Tuscany, Rome and Venice respectively for the infinitive "to go").
There is no definitive date when the various Italian variants of Latin—including varieties that contributed to modern Standard Italian—began to be distinct enough from Latin to be considered separate languages. One criterion for determining that two language variants are to be considered separate languages rather than variants of a single language is that they have evolved so that they are no longer mutually intelligible; this diagnostic is effective if mutual intelligibility is minimal or absent (e.g. in Romance, Romanian and Portuguese), but it fails in cases such as Spanish-Portuguese or Spanish-Italian, as educated native speakers of either pairing can understand each other well if they choose to do so; however, the level of intelligibility is markedly lower between Italian-Spanish, and considerably higher between the Iberian sister languages of Portuguese-Spanish. Speakers of this latter pair can communicate with one another with remarkable ease, each speaking to the other in his own native language without slang/jargon. Nevertheless, on the basis of accumulated differences in morphology, syntax, phonology, and to some extent lexicon, it is not difficult to identify that for the Romance varieties of Italy, the first extant written evidence of languages that can no longer be considered Latin comes from the ninth and tenth centuries C.E. These written sources demonstrate certain vernacular characteristics and sometimes explicitly mention the use of the vernacular in Italy. Full literary manifestations of the vernacular began to surface around the 13th century in the form of various religious texts and poetry.Although these are the first written records of Italian varieties separate from Latin, the spoken language had likely diverged long before the first written records appear, since those who were literate generally wrote in Latin even if they spoke other Romance varieties in person.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, the use of Standard Italian became increasingly widespread and was mirrored by a decline in the use of the dialects. An increase in literacy was one of the main driving factors (one can assume that only literates were capable of learning Standard Italian, whereas those who were illiterate had access only to their native dialect). The percentage of literates rose from 25% in 1861 to 60% in 1911, and then on to 78.1% in 1951. Tullio De Mauro, an Italian linguist, has asserted that in 1861 only 2.5% of the population of Italy could speak Standard Italian. He reports that in 1951 that percentage had risen to 87%. The ability to speak Italian did not necessarily mean it was in everyday use, and most people (63.5%) still usually spoke their native dialects. In addition, other factors such as mass emigration, industrialization, and urbanization, and internal migrations after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, contributed to the proliferation of Standard Italian. The Italians who emigrated during the Italian diaspora beginning in 1861 were often of the uneducated lower class, and thus the emigration had the effect of increasing the percentage of literates, who often knew and understood the importance of Standard Italian, back home in Italy. A large percentage of those who had emigrated also eventually returned to Italy, often more educated than when they had left.
The Italian dialects have declined in the modern era, as Italy unified under Standard Italian and continues to do so aided by mass media, from newspapers to radio to television.
Phonology
Italian has a seven-vowel system, consisting of , as well as 23 consonants. Compared with most other Romance languages, Italian phonology is conservative, preserving many words nearly unchanged fromVulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
. Some examples:
* Italian ' "fourteen" < Latin (cf. Spanish ', French ' , Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
and Portuguese )
* Italian ''settimana'' "week" < Latin (cf. Romanian ''săptămână'', Spanish and Portuguese ''semana'', French ''semaine'' , Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
''setmana'')
* Italian ''medesimo'' "same" < Vulgar Latin * (cf. Spanish ''mismo'', Portuguese ''mesmo'', French ''même'' , Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
''mateix''; note that Italian usually prefers the shorter ''stesso'')
* Italian ''guadagnare'' "to win, earn, gain" < Vulgar Latin * < Germanic (cf. Spanish ''ganar'', Portuguese ''ganhar'', French ''gagner'' , Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
''guanyar'')
The conservative nature of Italian phonology is partly explained by its origin. Italian stems from a literary language that is derived from the 13th-century speech of the city of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
in the region of Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
, and has changed little in the last 700 years or so. Furthermore, the Tuscan dialect is the most conservative of all Italian dialects Italian dialects may refer to any of the following linguistic notions:
*the various dialects pertaining to different languages which are spoken in Italy, regardless of the origins thereof;
* the , which are related to Italian, but do not stem fro ...
, radically different from the Gallo-Italian languages less than to the north (across the La Spezia–Rimini Line).
The following are some of the conservative phonological features of Italian, as compared with the common Western Romance languages (French, Spanish, Portuguese, Galician, Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
). Some of these features are also present in Romanian.
* Little or no phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
lenition of consonants between vowels, e.g. > ''vita'' "life" (cf. Romanian ''viață'', Spanish ''vida'' , French ''vie''), > ''piede'' "foot" (cf. Spanish ''pie'', French ''pied'' ).
* Preservation of geminate consonants, e.g. > "year" (cf. Spanish , French , Romanian , Portuguese ).
* Preservation of all Proto-Romance
Proto-Romance is the Comparative method, comparatively Linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed ancestor of all Romance languages. It reflects a late variety of Vulgar Latin, spoken Latin prior to regional fragmentation.
Phonology
Vowels
M ...
final vowels, e.g. > "peace" (cf. Romanian , Spanish , French ), > "eight" (cf. Romanian , Spanish , French ), > "I did" (cf. Romanian dialectal , Spanish , French ).
* Preservation of most intertonic vowels (those between the stressed syllable and either the beginning or ending syllable). This accounts for some of the most noticeable differences, as in the forms ''quattordici'' and ''settimana'' given above.
* Slower consonant development, e.g. > Italo-Western > ''foglia'' "leaf" (cf. Romanian ''foaie'' , Spanish ''hoja'' , French ''feuille'' ; but note Portuguese ''folha'' ).
Compared with most other Romance languages, Italian has many inconsistent outcomes, where the same underlying sound produces different results in different words, e.g. > ''lasciare'' and ''lassare'', > ''cacciare'' and ''cazzare'', > ''sdrucciolare'', ''druzzolare'' and ''ruzzolare'', > ''regina'' and ''reina''. Although in all these examples the second form has fallen out of usage, the dimorphism is thought to reflect the several-hundred-year period during which Italian developed as a literary language divorced from any native-speaking population, with an origin in 12th/13th-century Tuscan but with many words borrowed from languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
farther to the north, with different sound outcomes. (The La Spezia–Rimini Line, the most important isogloss in the entire Romance-language area, passes only about north of Florence.) Dual outcomes of Latin /p t k/ between vowels, such as > ''luogo'' but > ''fuoco'', was once thought to be due to borrowing of northern voiced forms, but is now generally viewed as the result of early phonetic variation within Tuscany.
Some other features that distinguish Italian from the Western Romance languages:
* Latin becomes rather than .
* Latin becomes rather than or : > ''otto'' "eight" (cf. Spanish ''ocho'', French ''huit,'' Portuguese ''oito'').
* Vulgar Latin becomes ''cchi'' rather than : > ''occhio'' "eye" (cf. Portuguese ''olho'' , French ''œil'' < ); but Romanian ''ochi'' .
* Final is not preserved, and vowel changes rather than are used to mark the plural: ''amico'', ''amici'' "male friend(s)", ''amica'', ''amiche'' "female friend(s)" (cf. Romanian ''amic'', ''amici'' and ''amică'', ''amice''; Spanish ''amigo(s)'' "male friend(s)", ''amiga(s)'' "female friend(s)"); → ''tre, sei'' "three, six" (cf. Romanian ''trei'', ''șase''; Spanish ''tres'', ''seis'').
Standard Italian also differs in some respects from most nearby Italian languages:
* Perhaps most noticeable is the total lack of metaphony, though metaphony is a feature characterizing nearly every other Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 8 ...
.
* No simplification of original , (which often became elsewhere).
Assimilation
Italian phonotactics do not usually permit verbs and polysyllabic nouns to end with consonants, except in poetry and song, so foreign words may receive extra terminal vowel sounds.Writing system
Italian has a shallow orthography, meaning very regular spelling with an almost one-to-one correspondence between letters and sounds. In linguistic terms, the writing system is close to being a phonemic orthography. The most important of the few exceptions are the following (see below for more details): * The letter c represents the sound at the end of words and before the letters a, o, and u but represents the sound (as the first sound in the English word ''chair'') before the letters e and i. * The letter g represents the sound at the end of words and before the letters a, o, and u but represents the sound (as the first sound in the English word ''gem'') before the letters e and i. * The letter n represents the phoneme , which is pronounced (as in the English word ''sink'' or the name ''Ringo'') before the letters c and g when these represent velar plosives or , as in ''banco'' �baŋko ''fungo'' �fuŋɡo The letter q represents /k/ pronounced thus n also represents �in the position preceding it: ''cinque'' �t͡ʃiŋkwe Elsewhere the letter n represents /n/ pronounced including before the affricates /t͡ʃ/ or /d͡ʒ/ (equivalent to the consonants of English ''church'' and ''judge'') spelled with c or g before the letters i and e : ''mancia'' �mant͡ʃa ''mangia'' �mand͡ʒa * The letter ''h'' is always silent: ''hotel'' /oˈtɛl/; ''hanno'' 'they have' and ''anno'' 'year' both represent /ˈanno/. It is used to form a digraph with ''c'' or ''g'' to represent /k/ or /g/ before ''i'' or ''e'': ''chi'' /ki/ 'who', ''che'' /ke/ 'what'; ''aghi'' /ˈagi/ 'needles', ''ghetto'' /ˈgetto/. * The spellings ''ci'' and ''gi'' represent only /tʃ/ (as in English ''church'') or /dʒ/ (as in English ''judge'') with no /i/ sound before another vowel (''ciuccio'' /ˈtʃuttʃo/ 'pacifier', ''Giorgio'' /ˈdʒɔrdʒo/) unless ''c'' or ''g'' precede stressed /i/ (''farmacia'' /farmaˈtʃia/ 'pharmacy', ''biologia'' /bioloˈdʒia/ 'biology'). Elsewhere ''ci'' and ''gi'' represent /tʃ/ and /dʒ/ followed by /i/: ''cibo'' /ˈtʃibo/ 'food', ''baci'' /ˈbatʃi/ 'kisses'; ''gita'' /ˈdʒita/ 'trip', ''Tamigi'' /taˈmidʒi/ 'Thames'.* The Italian alphabet is typically considered to consist of 21 letters. The letters j, k, w, x, y are traditionally excluded, though they appear in loanwords such as ''jeans'', ''whisky'', ''taxi'', ''xenofobo'', ''xilofono''. The letter has become common in standard Italian with the prefix ''extra-'', although ''(e)stra-'' is traditionally used; it is also common to use the Latin particle ''ex(-)'' to mean "former(ly)" as in: ''la mia ex'' ("my ex-girlfriend"), "Ex-Jugoslavia" ("Former Yugoslavia"). The letter appears in the first name ''Jacopo'' and in some Italian place-names, such as Bajardo, Bojano, Joppolo, Jerzu, Jesolo, Jesi, Ajaccio, among others, and in ''Mar Jonio'', an alternative spelling of ''Mar Ionio'' (the Ionian Sea). The letter may appear in dialectal words, but its use is discouraged in contemporary standard Italian. Letters used in foreign words can be replaced with phonetically equivalent native Italian letters and digraphs: , , or for ; or for (including in the standard prefix ''kilo-''); , or for ; , , , or for ; and or for . * The acute accent is used over word-final to indicate a stressed front close-mid vowel, as in ''perché'' "why, because". In dictionaries, it is also used over to indicate a stressed back close-mid vowel (''azióne''). The grave accent is used over word-final and to indicate a front open-mid vowel and a back open-mid vowel respectively, as in ''tè'' "tea" and ''può'' "(he) can". The grave accent is used over any vowel to indicate word-final stress, as in ''gioventù'' "youth". Unlike , which is a ''close''-mid vowel, a stressed final is almost always a back open-mid vowel (''andrò''), with a few exceptions, like ''metró'', with a stressed final back close-mid vowel, making for the most part unnecessary outside of dictionaries. Most of the time, the penultimate syllable is stressed. But if the stressed vowel is the final letter of the word, the accent is mandatory, otherwise it is virtually always omitted. Exceptions are typically either in dictionaries, where all or most stressed vowels are commonly marked. Accents can optionally be used to disambiguate words that differ only by stress, as for ''prìncipi'' "princes" and ''princìpi'' "principles", or ''àncora'' "anchor" and ''ancóra'' "still''/''yet". For monosyllabic words, the rule is different: when two orthographically identical monosyllabic words with different meanings exist, one is accented and the other is not (example: ''è'' "is", ''e'' "and"). * The letter distinguishes ''ho'', ''hai'', ''ha'', ''hanno'' (present indicative of ''avere'' "to have") from ''o'' ("or"), ''ai'' ("to the"), ''a'' ("to"), ''anno'' ("year"). In the spoken language, the letter is always silent. The in ''ho'' additionally marks the contrasting open pronunciation of the . The letter is also used in combinations with other letters. Nophoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
exists in Italian. In nativized foreign words, the is silent. For example, ''hotel'' and ''hovercraft'' are pronounced and respectively. (Where existed in Latin, it either disappeared or, in a few cases before a back vowel, changed to : ''traggo'' "I pull" ← Lat. .)
* The letters and can symbolize voiced or voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies v ...
consonants. symbolizes or depending on context, with few minimal pairs. For example: ''zanzara'' "mosquito" and ''nazione'' "nation". symbolizes word-initially before a vowel, when clustered with a voiceless consonant (), and when doubled; it symbolizes when between vowels and when clustered with voiced consonants. Intervocalic varies regionally between and , with being more dominant in northern Italy and in the south.
* The letters and vary in pronunciation between plosives and affricates
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop consonant, stop and releases as a fricative consonant, fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal consonant, coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop a ...
depending on following vowels. The letter symbolizes when word-final and before the back vowels . It symbolizes as in ''chair'' before the front vowels . The letter symbolizes when word-final and before the back vowels . It symbolizes as in ''gem'' before the front vowels . Other Romance languages and, to an extent, English have similar variations for . Compare hard and soft C, hard and soft G. (See also palatalization
Palatalization may refer to:
*Palatalization (phonetics), the phonetic feature of palatal secondary articulation
*Palatalization (sound change)
Palatalization is a historical-linguistic sound change that results in a palatalized articulation ...
.)
* The digraphs and indicate ( and ) before . The digraphs and indicate "softness" ( and , the affricate consonants of English ''church'' and ''judge'') before . For example:
:
:Note: is silent in the digraphs '' '', '' ''; and is silent in the digraphs and before unless the is stressed. For example, it is silent in ''ciao
''Ciao'' ( , ) is an informal salutation in the Italian language that is used for both "hello" and "goodbye".
Originally from the Venetian language, it has entered the vocabulary of English and of many other languages around the world. Its du ...
'' and cielo , but it is pronounced in ''farmacia'' and ''farmacie'' .
Italian has geminate, or double, consonants, which are distinguished by length and intensity. Length is distinctive for all consonants except for , , , , , which are always geminate when between vowels, and , which is always single.
Geminate plosives and affricates are realized as lengthened closures. Geminate fricatives, nasals, and are realized as lengthened continuants. There is only one vibrant phoneme but the actual pronunciation depends on context and regional accent. Generally one can find a flap consonant in unstressed position whereas is more common in stressed syllables, but there may be exceptions. Especially people from the Northern part of Italy (Parma
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
, Aosta Valley, South Tyrol) may pronounce as , , or .
Of special interest to the linguistic study of Regional Italian
Regional Italian ( it, italiano regionale) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and ...
is the '' gorgia toscana'', or "Tuscan Throat", the weakening or lenition of intervocalic , , and in the Tuscan language.
The voiced postalveolar fricative
A voiced postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The International Phonetic Association uses term ''voiced postalveolar fricative'' only for the sound , but it also describes the voiced postalveolar ...
is present as a phoneme only in loanwords: for example, ''garage'' . Phonetic is common in Central and Southern Italy as an intervocalic allophone of : ''gente'' 'people' but ''la gente'' 'the people', ''ragione'' 'reason'.
Grammar
Italiangrammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraint ...
is typical of the grammar of Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language f ...
in general. Cases exist for personal pronouns (nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of ...
, oblique, accusative
The accusative case ( abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb.
In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ‘th ...
, dative), but not for nouns.
There are two basic classes of nouns in Italian, referred to as genders
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures u ...
, masculine and feminine. Gender may be natural (''ragazzo'' 'boy', ''ragazza'' 'girl') or simply grammatical with no possible reference to biological gender (masculine ''costo'' 'cost', feminine ''costa'' 'coast'). Masculine nouns typically end in ''-o'' (''ragazzo'' 'boy'), with plural marked by ''-i'' (''ragazzi'' 'boys'), and feminine nouns typically end in ''-a'', with plural marked by ''-e'' (''ragazza'' 'girl', ''ragazze'' 'girls'). For a group composed of boys and girls, ''ragazzi'' is the plural, suggesting that ''-i'' is a general neutral plural. A third category of nouns is unmarked for gender, ending in ''-e'' in the singular and ''-i'' in the plural: ''legge'' 'law, f. sg.', ''leggi'' 'laws, f. pl.'; ''fiume'' 'river, m. sg.', ''fiumi'' 'rivers, m. pl.', thus assignment of gender is arbitrary in terms of form, enough so that terms may be identical but of distinct genders: ''fine'' meaning 'aim', 'purpose' is masculine, while ''fine'' meaning 'end, ending' (e.g. of a movie) is feminine, and both are ''fini'' in the plural, a clear instance of ''-i'' as a non-gendered default plural marker. These nouns often, but not always, denote inanimates. There are a number of nouns that have a masculine singular and a feminine plural, most commonly of the pattern m. sg. ''-o'', f. pl. ''-a'' (''miglio'' 'mile, m. sg.', ''miglia'' 'miles, f. pl.'; ''paio'' 'pair, m. sg., ''paia'' 'pairs, f. pl.'), and thus are sometimes considered neuter (these are usually derived from neuter
Neuter is a Latin adjective meaning "neither", and can refer to:
* Neuter gender, a grammatical gender, a linguistic class of nouns triggering specific types of inflections in associated words
*Neuter pronoun
*Neutering, the sterilization of an ...
Latin nouns). An instance of neuter gender also exists in pronouns of the third person singular.
Examples:
Nouns, adjectives, and articles inflect for gender and number (singular and plural).
Like in English, common nouns are capitalized when occurring at the beginning of a sentence. Unlike English, nouns referring to languages (e.g. Italian), speakers of languages, or inhabitants of an area (e.g. Italians) are not capitalized.
There are three types of adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
s: descriptive, invariable and form-changing. Descriptive adjectives are the most common, and their endings change to match the number and gender of the noun they modify. Invariable adjectives are adjectives whose endings do not change. The form changing adjectives "buono (good), bello (beautiful), grande (big), and santo (saint)" change in form when placed before different types of nouns. Italian has three degrees for comparison of adjectives: positive, comparative, and superlative.
The order of words in the phrase is relatively free compared to most European languages. The position of the verb in the phrase is highly mobile. Word order often has a lesser grammatical function in Italian than in English. Adjectives are sometimes placed before their noun and sometimes after. Subject nouns generally come before the verb. Italian is a null-subject language, so that nominative pronouns are usually absent, with subject indicated by verbal inflection
In linguistic morphology, inflection (or inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, animacy, and ...
s (e.g. ''amo'' 'I love', ''ama'' '(s)he loves', ''amano'' 'they love'). Noun objects normally come after the verb, as do pronoun objects after imperative verbs, infinitives and gerunds, but otherwise pronoun objects come before the verb.
There are both indefinite and definite articles
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
...
in Italian. There are four indefinite articles, selected by the gender of the noun they modify and by the phonological structure of the word that immediately follows the article. ''Uno'' is masculine singular, used before ''z'' ( or ), ''s+consonant'', ''gn'' (), or ''ps'', while masculine singular ''un'' is used before a word beginning with any other sound. The noun ''zio'' 'uncle' selects masculine singular, thus ''uno zio'' 'an uncle' or ''uno zio anziano'' 'an old uncle,' but ''un mio zio'' 'an uncle of mine'. The feminine singular indefinite articles are ''una'', used before any consonant sound, and its abbreviated form, written ''un','' used before vowels: ''una camicia'' 'a shirt', ''una camicia bianca'' 'a white shirt', ''un'altra camicia'' 'a different shirt'. There are seven forms for definite articles, both singular and plural. In the singular: ''lo'', which corresponds to the uses of ''uno''; ''il'', which corresponds to the uses with consonant of ''un''; ''la,'' which corresponds to the uses of ''una''; ''l','' used for both masculine and feminine singular before vowels. In the plural: ''gli'' is the masculine plural of ''lo and larticles
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
...
. There are numerous productive suffixes for diminutive
A diminutive is a root word that has been modified to convey a slighter degree of its root meaning, either to convey the smallness of the object or quality named, or to convey a sense of intimacy or endearment. A ( abbreviated ) is a word-form ...
, augmentative, pejorative, attenuating, etc., which are also used to create neologism
A neologism Greek νέο- ''néo''(="new") and λόγος /''lógos'' meaning "speech, utterance"] is a relatively recent or isolated term, word, or phrase that may be in the process of entering common use, but that has not been fully accepted int ...
s.
There are 27 pronouns, grouped in clitic and tonic pronouns. Personal pronouns are separated into three groups: subject, object (which take the place of both direct and indirect objects), and reflexive. Second person subject pronouns have both a polite and a familiar form. These two different types of address are very important in Italian social distinctions. All object pronouns have two forms: stressed and unstressed (clitics). Unstressed object pronouns are much more frequently used, and come before a verb conjugated for subject verb (''La vedi''. 'You see her.'), after (in writing, attached to) non-conjugated verbs (''vendendola'' 'seeing her'). Stressed object pronouns come after the verb, and are used when emphasis is required, for contrast, or to avoid ambiguity (''Vedo lui, ma non lei''. 'I see him, but not her'). Aside from personal pronouns, Italian also has demonstrative, interrogative, possessive, and relative pronouns. There are two types of demonstrative pronouns: relatively near (this) and relatively far (that). Demonstratives in Italian are repeated before each noun, unlike in English.
There are three regular sets of verbal conjugations, and various verbs are irregularly conjugated. Within each of these sets of conjugations, there are four simple (one-word) verbal conjugations by person/number in the indicative mood (present tense
The present tense ( abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present ...
; past tense
The past tense is a grammatical tense whose function is to place an action or situation in the past. Examples of verbs in the past tense include the English verbs ''sang'', ''went'' and ''washed''. Most languages have a past tense, with some hav ...
with imperfective aspect, past tense with perfective aspect
The perfective aspect ( abbreviated ), sometimes called the aoristic aspect, is a grammatical aspect that describes an action viewed as a simple whole; i.e., a unit without interior composition. The perfective aspect is distinguished from the i ...
, and future tense), two simple conjugations in the subjunctive mood (present tense and past tense), one simple conjugation in the conditional mood, and one simple conjugation in the imperative mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. To form the imperative mood, ...
. Corresponding to each of the simple conjugations, there is a compound conjugation involving a simple conjugation of "to be" or "to have" followed by a past participle. "To have" is used to form compound conjugation when the verb is transitive ("Ha detto", "ha fatto": he/she has said, he/she has made/done), while "to be" is used in the case of verbs of motion and some other intransitive verbs ("È andato", "è stato": he has gone, he has been). "To be" may be used with transitive verbs, but in such a case it makes the verb passive ("È detto", "è fatto": it is said, it is made/done). This rule is not absolute, and some exceptions do exist.
Words
Conversation
Note: the plural form of verbs could also be used as an extremely formal (for example to noble people in monarchies) singular form (seeroyal we
The royal ''we'', majestic plural (), or royal plural, is the use of a plural pronoun (or corresponding plural-inflected verb forms) used by a single person who is a monarch or holds a high office to refer to themselves. A more general term fo ...
).
Question words
Time
Numbers
Days of the week
Months of the year
See also
*Languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gr ...
(includes "Italian dialects", )
* Accademia della Crusca
* CELI
* CILS (Qualification)
* '' Enciclopedia Italiana''
* Italian alphabet
* Regional Italian
Regional Italian ( it, italiano regionale) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and ...
* Italian exonyms
* Italian grammar
* Italian honorifics
* List of countries and territories where Italian is an official language
The following is a list of countries and territories that have Italian as an official language.
Sovereign states
Country subdivisions
See also
* Language geography
* Geolinguistics
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Countries and territories
...
* The Italian Language Foundation (in the United States)
* Italian language in Croatia
* Italian language in Slovenia
* Italian language in the United States
An important part of Italian Americans, Italian American identity, the Italian language has been widely spoken in the United States, United States of America for more than one hundred years, due to Italian diaspora, large-scale immigration beginn ...
* Italian language in Venezuela
* Italian literature
* Italian musical terms
* Italian phonology
* Italian profanity
* Italian Sign Language
Italian Sign Language or LIS (''Lingua dei Segni Italiana'') is the visual language used by deaf people in Italy. Deep analysis of it began in the 1980s, along the lines of William Stokoe's research on American Sign Language in the 1960s. Unt ...
* Italian Studies
* Italian Wikipedia
* Italian-language international radio stations
* Lessico etimologico italiano
* Sicilian School
* Veronese Riddle
* Languages of the Vatican City
* Talian
* List of English words of Italian origin
* List of Italian musical terms used in English
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * M. Vitale, ''Studi di Storia della Lingua Italiana'', LED Edizioni Universitarie, Milano, 1992, * S. Morgana, ''Capitoli di Storia Linguistica Italiana'', LED Edizioni Universitarie, Milano, 2003, * J. Kinder, ''CLIC: Cultura e Lingua d'Italia in CD-ROM / Culture and Language of Italy on CD-ROM'', Interlinea, Novara, 2008, * (with a similar list of other Italian-modern languages dictionaries)External links
*Il Nuovo De Mauro
* * Swadesh list in English and Italian * Italian proverbs *
Learn Italian
, '' BBC'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Language Fusional languages Languages attested from the 10th century Languages of Italy Languages of Monaco Languages of San Marino Languages of Sicily Languages of Switzerland Languages of Vatican City Languages of Slovenia Languages of Croatia Subject–verb–object languages