Induced-charge Electrokinetics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Induced-charge electrokinetics in
Induced-charge electrokinetics in
 Induced-charge electrokinetics in
Induced-charge electrokinetics in physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
is the electrically
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
driven fluid flow and particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from ...
motion in a liquid electrolyte.V. G. Levich, Physicochemical Hydrodynamics. Englewood Cliffs, N.J., Prentice-Hall, (1962) Consider a metal particle (which is neutrally charged but electrically conducting) in contact with an aqueous solution in a chamber/channel. If different voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
s apply to the end of this chamber/channel, electric field will generate in this chamber/channel. This applied electric field passes through this metal particle and causes the free charges inside the particle migrate under the skin of particle. As a result of this migration, the negative charges moves to the side which is close to the positive (or higher) voltage while the positive charges moves to the opposite side of the particle. These charges under the skin of conducting particle attract the counter-ions of the aqueous solution; thus, the electric double layer (EDL) forms around the particle. The EDL sign on the surface of the conducting particle changes from positive to negative and the distribution of the charges varies along the particle geometry. Due to these variations, the EDL is non-uniform and has different signs. Thus, the induced zeta potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in coll ...
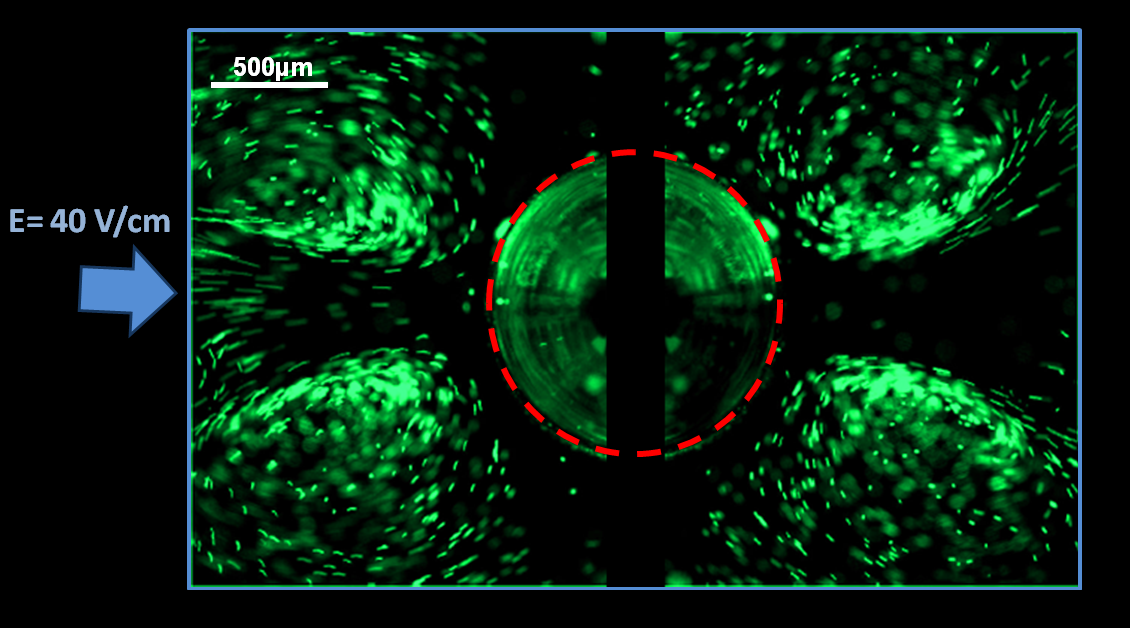
around the particle, and consequently slip velocity on the surface of the particle, vary as a function of local electric field. Differences in magnitude and direction of slip velocity on the surface of the conducting particle effects the flow pattern around this particle and causes micro vortices. Yasaman Daghighi and Dongqing Li, for the first time, experimentally illustrated these induced vortices around a 1.2mm diameter carbon-steel sphere under the 40V/cm direct current (DC) external electric filed.
Chenhui Peng et al. also experimentally showed the patterns of electro-osmotic flow around an Au sphere when alternating current (AC) is involved (E=10mV/μm, f=1 kHz).
Electrokinetics here refers to a branch of science related to the motion and reaction of charged particles to the applied electric filed and its effects on its environment. It is sometimes referred as non-linear electrokinetic phenomena as well.
History
Levich is one of the pioneers in induced-charge electrokinetic field. He calculated the perturbed slip profile around a conducting particle in contact with electrolyte. He also theoretically predicted that vortices induced around this particle once the electric filed is applied.Induced vortices around a conducting particle
The size and strength of the induced vortices around a conducting particle have direct relationship with the applied electric filed and also the size of the conducted surface. This phenomenon is experimentally and numerically proven by several studies, The vortices grow as the external electric field increases and generate "sinkhole" at the center of the each vortex while circulates the fluid faster. It is demonstrated that increasing the size of the conducting surface forms bigger induced vortices to the point that geometry does not limits this grows.Applications
The induced vortices have many applications in various aspects of electrokinetic microfluidics. There are many micro-mixers that are designed and fabricated based on the existence of their induced vortices in themicrofluidic
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field tha ...
s devices. Such micro-mixers which are used for biochemical, medicine, biology applications has no mechanical parts and only use conducting surfaces to generate induced vortices to mix the different fluid streams,M. Jain, A. Yeung and K. Nandakumar, Induced charge electro osmotic mixer: Obstacle shape optimization, Biomicrofluidics, 3 (2009)
This phenomenon even is used to trap the micron and submicron particles floating in flow inside a micro-channel. This method can be used to manipulate, detect, handle, and concentrate cells and virus in biomedical field; or, for colloidal particle assembly.
In addition the induced vortices around the conducting surfaces in a microfluidic system can be used as a micro-valve, micro-actuator, micro-motor and micro-regulator to control the direction and manipulation.
See also
* Surface charge *Electro-osmosis Electroosmotic flow (or electro-osmotic flow, often abbreviated EOF; synonymous with electroosmosis or electroendosmosis) is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or an ...
* Electrophoresis
* Diffusiophoresis
Diffusiophoresis is the spontaneous motion of colloidal particles or molecules in a fluid, induced by a concentration gradient of a different substance. In other words, it is motion of one species, A, in response to a concentration gradient in an ...
* Lab-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) is a device that integrates one or several laboratory functions on a single integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") of only millimeters to a few square centimeters to achieve automation and high-throughput screening. ...
References
{{Reflist, 2 Microfluidics Fluid dynamics Biotechnology Electrochemistry