|
Diffusiophoresis
Diffusiophoresis is the spontaneous motion of colloidal particles or molecules in a fluid, induced by a concentration gradient of a different substance. In other words, it is motion of one species, A, in response to a concentration gradient in another species, B. Typically, A is colloidal particles which are in aqueous solution in which B is a dissolved salt such as sodium chloride, and so the particles of A are much larger than the ions of B. But both A and B could be polymer molecules, and B could be a small molecule. For example, concentration gradients in ethanol solutions in water move 1 μm diameter colloidal particles with diffusiophoretic velocities _ of order 0.1 to 1 μm/s, the movement is towards regions of the solution with lower ethanol concentration (and so higher water concentration). Both species A and B will typically be diffusing but diffusiophoresis is distinct from simple diffusion: in simple diffusion a species A moves down a gradient in its own concentration. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrokinetic Phenomena
Electrokinetic phenomena are a family of several different effects that occur in heterogeneous fluids, or in porous bodies filled with fluid, or in a fast flow over a flat surface. The term heterogeneous here means a fluid containing particles. Particles can be solid, liquid or gas bubbles with sizes on the scale of a micrometer or nanometer.Dukhin, A. S. and Goetz, P. J. ''Characterization of liquids, nano- and micro- particulates and porous bodies using Ultrasound'', Elsevier, 2017 There is a common source of all these effects—the so-called interfacial 'double layer' of charges. Influence of an external force on the diffuse layer generates tangential motion of a fluid with respect to an adjacent charged surface. This force might be electric, pressure gradient, concentration gradient, or gravity. In addition, the moving phase might be either continuous fluid or dispersed phase. Family Various combinations of the driving force and moving phase determine various electrokinetic ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic Of Particle Illustrating Diffusiophoresis
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermophoresis
Thermophoresis (also thermomigration, thermodiffusion, the Soret effect, or the Ludwig–Soret effect) is a phenomenon observed in mixtures of mobile particles where the different particle types exhibit different responses to the force of a temperature gradient. This phenomenon tends to move light molecules to hot regions and heavy molecules to cold regions. The term ''thermophoresis'' most often applies to aerosol mixtures whose mean free path \lambda is comparable to its characteristic length scale L, but may also commonly refer to the phenomenon in all phases of matter. The term ''Soret effect'' normally applies to liquid mixtures, which behave according to different, less well-understood mechanisms than gaseous mixtures. Thermophoresis may not apply to thermomigration in solids, especially multi-phase alloys. Thermophoretic force The phenomenon is observed at the scale of one millimeter or less. An example that may be observed by the naked eye with good lighting is when the hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. The electrokinetic phenomenon of electrophoresis was observed for the first time in 1807 by Russian professors Peter Ivanovich Strakhov and Ferdinand Frederic Reuss at Moscow University, who noticed that the application of a constant electric field caused clay particles dispersed in water to migrate. It is ultimately caused by the presence of a charged interface between the particle surface and the surrounding fluid. It is the basis for analytical techniques used in chemistry for separating molecules by size, charge, or binding affinity. Electropho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. The electrokinetic phenomenon of electrophoresis was observed for the first time in 1807 by Russian professors Peter Ivanovich Strakhov and Ferdinand Frederic Reuss at Moscow University, who noticed that the application of a constant electric field caused clay particles dispersed in water to migrate. It is ultimately caused by the presence of a charged interface between the particle surface and the surrounding fluid. It is the basis for analytical techniques used in chemistry for separating molecules by size, charge, or binding affinity. Electropho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field D resulting from an applied electric field E is :\mathbf = \varepsilon \mathbf. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity ''ε''r which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity ''ε'' and the vacuum permittivity ''ε''0 :\kappa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface. Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal dispersions. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta (ζ), hence ''ζ-potential''. The usual units are volts (V) or, more commonly, millivolts (mV). From a theoretical viewpoint, the zeta potential is the electric potential in the interfacial double layer (DL) at the location of the slipping plane relative to a point in the bulk fluid away from the interface. In other words, zeta potential is the potential difference between the dispersion medium and the stationary layer of fluid attached to the dispersed particle. The zeta potential is caused by the net electrical charge contained within the region bounded by the slipping plane, and also depends on the location of that plane. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug Flow
In fluid mechanics, plug flow is a simple model of the velocity profile of a fluid flowing in a pipe. In plug flow, the velocity of the fluid is assumed to be constant across any cross-section of the pipe perpendicular to the axis of the pipe. The plug flow model assumes there is no boundary layer adjacent to the inner wall of the pipe. The plug flow model has many practical applications. One example is in the design of chemical reactors. Essentially no back mixing is assumed with "plugs" of fluid passing through the reactor. This results in differential equations that need to be integrated to find the reactor conversion and outlet temperatures. Other simplifications used are perfect radial mixing and a homogeneous bed structure. An advantage of the plug flow model is that no part of the solution of the problem can be perpetuated "upstream". This allows one to calculate the exact solution to the differential equation knowing only the initial conditions. No further iteration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs when two solutions containing different concentrations of solute are separated by a selectively permeable membrane. Solvent molecules pass preferentially through the membrane from the low-concentration solution to the solution with higher solute concentration. The transfer of solvent molecules will continue until equilibrium is attained. Theory and measurement Jacobus van 't Hoff found a quantitative relationship between osmotic pressure and solute concentration, expressed in the following equation: :\Pi = icRT where \Pi is osmotic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Flow
Stokes flow (named after George Gabriel Stokes), also named creeping flow or creeping motion,Kim, S. & Karrila, S. J. (2005) ''Microhydrodynamics: Principles and Selected Applications'', Dover. . is a type of fluid flow where advective inertial forces are small compared with viscous forces. The Reynolds number is low, i.e. \mathrm \ll 1. This is a typical situation in flows where the fluid velocities are very slow, the viscosities are very large, or the length-scales of the flow are very small. Creeping flow was first studied to understand lubrication. In nature this type of flow occurs in the swimming of microorganisms, sperm and the flow of lava. In technology, it occurs in paint, MEMS devices, and in the flow of viscous polymers generally. The equations of motion for Stokes flow, called the Stokes equations, are a linearization of the Navier–Stokes equations, and thus can be solved by a number of well-known methods for linear differential equations. The primary Green's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
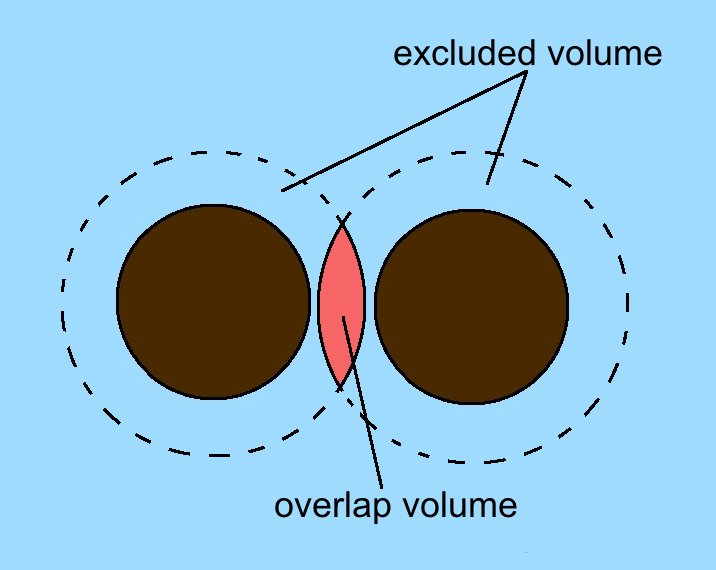
Depletion Force
A depletion force is an effective attractive force that arises between large colloidal particles that are suspended in a dilute solution of ''depletants'', which are smaller solutes that are preferentially excluded from the vicinity of the large particles. One of the earliest reports of depletion forces that lead to particle coagulation is that of Bondy, who observed the separation or "creaming" of rubber latex upon addition of polymer depletant molecules (sodium alginate) to solution. More generally, depletants can include polymers, micelles, osmolytes, ink, mud, or paint dispersed in a continuous phase. Depletion forces are often regarded as entropic forces, as was first explained by the established Asakura–Oosawa model. In this theory the depletion force arises from an increase in osmotic pressure of the surrounding solution when colloidal particles get close enough such that the excluded cosolutes (depletants) cannot fit in between them. Because the particles were consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |