
The immune system is a network of
biological process
Biological processes are those processes that are vital for an organism to live, and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in the ...
es that protects an
organism from
diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that ar ...
. It detects and responds to a wide variety of
pathogens, from
viruses to
parasitic worms, as well as
cancer cells
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these d ...
and objects such as wood
splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy
tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The
innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The
adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use
molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
and
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
to perform their functions.
Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system.
Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of
enzymes that protect against
virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient
plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include
phagocytosis,
antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ...
called
defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, ...
s, and the
complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
.
Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt to recognize pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates an
immunological memory leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of
vaccination.
Dysfunction of the immune system can cause
autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s,
inflammatory diseases and
cancer.
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can be the result of a
genetic disease such as
severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as
HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
/
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
, or the use of
immunosuppressive medication.
Autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include
Hashimoto's thyroiditis,
rheumatoid arthritis,
diabetes mellitus type 1, and
systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
.
Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.
Layered defense
The immune system protects its host from
infection with layered defenses of increasing specificity. Physical barriers prevent pathogens such as
bacteria and
viruses from entering the organism. If a pathogen breaches these barriers, the
innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
provides an immediate, but non-specific response. Innate immune systems are found in all
animals.
If pathogens successfully evade the innate response, vertebrates possess a second layer of protection, the
adaptive immune system, which is activated by the innate response. Here, the immune system adapts its response during an infection to improve its recognition of the pathogen. This improved response is then retained after the pathogen has been eliminated, in the form of an
immunological memory, and allows the adaptive immune system to mount faster and stronger attacks each time this pathogen is encountered.
Both innate and adaptive immunity depend on the ability of the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self
molecules. In immunology, ''self'' molecules are components of an organism's body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Conversely, ''non-self'' molecules are those recognized as foreign molecules. One class of non-self molecules are called antigens (originally named for being ''anti''body ''gen''erators) and are defined as substances that bind to specific
immune receptors and elicit an immune response.
Surface barriers
Several barriers protect organisms from infection, including mechanical, chemical, and biological barriers. The waxy
cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
of most leaves, the
exoskeleton of insects, the
shells and membranes of externally deposited eggs, and
skin are examples of mechanical barriers that are the first line of defense against infection. Organisms cannot be completely sealed from their environments, so systems act to protect body openings such as the
lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s,
intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
s, and the
genitourinary tract. In the lungs, coughing and sneezing mechanically eject pathogens and other
irritants from the
respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
. The flushing action of
tears and
urine also mechanically expels pathogens, while
mucus secreted by the respiratory and
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
serves to trap and entangle
microorganisms.
Chemical barriers also protect against infection. The skin and respiratory tract secrete
antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ...
such as the β-
defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, ...
s.
Enzymes such as
lysozyme and
phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyse the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid “tail” and the glyce ...
in
saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
, tears, and
breast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates ( lacto ...
are also
antibacterials.
Vaginal secretions serve as a chemical barrier following
menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility.
Gir ...
, when they become slightly
acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic, while
semen contains defensins and
zinc to kill pathogens. In the
stomach,
gastric acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
serves as a chemical defense against ingested pathogens.
Within the genitourinary and gastrointestinal tracts,
commensal flora serve as biological barriers by competing with pathogenic bacteria for food and space and, in some cases, changing the conditions in their environment, such as
pH or available iron. As a result, the probability that pathogens will reach sufficient numbers to cause illness is reduced.
Innate immune system
Microorganisms or toxins that successfully enter an organism encounter the cells and mechanisms of the innate immune system. The innate response is usually triggered when microbes are identified by
pattern recognition receptors, which recognize components that are conserved among broad groups of microorganisms,
or when damaged, injured or stressed cells send out alarm signals, many of which are recognized by the same receptors as those that recognize pathogens.
Innate immune defenses are non-specific, meaning these systems respond to pathogens in a generic way. This system does not confer long-lasting
immunity against a pathogen. The innate immune system is the dominant system of host defense in most organisms,
and the only one in plants.
Immune sensing
Cells in the innate immune system use
pattern recognition receptors to recognize molecular structures that are produced by pathogens.
They are
proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of the
innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils and epithelial cells to identify two classes of molecules:
pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are associated with microbial
pathogens, and
damage-associated molecular patterns
Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are molecules within cells that are a component of the innate immune response released from damaged or dying cells due to trauma or an infection by a pathogen. They are also known as danger-associated ...
(DAMPs), which are associated with components of host's cells that are released during cell damage or cell death.
Recognition of extracellular or endosomal PAMPs is mediated by
transmembrane proteins known as
toll-like receptors (TLRs).
TLRs share a typical structural motif, the
leucine rich repeats (LRR), which give them a curved shape. Toll-like receptors were first discovered in ''
Drosophila'' and trigger the synthesis and secretion of
cytokines and activation of other host defense programs that are necessary for both innate or adaptive immune responses. Ten toll-like receptors have been described in humans.
Cells in the innate immune system have pattern recognition receptors, which detect infection or cell damage, inside. Three major classes of these "cytosolic" receptors are
NOD–like receptors,
RIG (retinoic acid-inducible gene)-like receptors, and cytosolic DNA sensors.
Innate immune cells

Some
leukocytes (white blood cells) act like independent, single-celled organisms and are the second arm of the innate immune system. The innate leukocytes include the
"professional" phagocytes (
macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s,
neutrophils, and
dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s). These cells identify and eliminate pathogens, either by attacking larger pathogens through contact or by engulfing and then killing microorganisms. The other cells involved in the innate response include
innate lymphoid cells,
mast cells,
eosinophils,
basophils, and
natural killer cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and repres ...
s.
Phagocytosis is an important feature of cellular innate immunity performed by cells called phagocytes that engulf pathogens or particles. Phagocytes generally patrol the body searching for pathogens, but can be called to specific locations by cytokines. Once a pathogen has been engulfed by a phagocyte, it becomes trapped in an intracellular
vesicle called a
phagosome, which subsequently fuses with another vesicle called a
lysosome to form a
phagolysosome. The pathogen is killed by the activity of digestive enzymes or following a
respiratory burst that releases
free radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron.
With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spont ...
into the phagolysosome. Phagocytosis evolved as a means of acquiring
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s, but this role was extended in phagocytes to include engulfment of pathogens as a defense mechanism. Phagocytosis probably represents the oldest form of host defense, as phagocytes have been identified in both vertebrate and invertebrate animals.
Neutrophils and macrophages are phagocytes that travel throughout the body in pursuit of invading pathogens. Neutrophils are normally found in the
bloodstream and are the most abundant type of phagocyte, representing 50% to 60% of total circulating leukocytes. During the acute phase of
inflammation, neutrophils migrate toward the site of inflammation in a process called
chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
, and are usually the first cells to arrive at the scene of infection. Macrophages are versatile cells that reside within tissues and produce an array of chemicals including enzymes,
complement proteins, and cytokines, while they can also act as scavengers that rid the body of worn-out cells and other debris, and as
antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using ...
s (APC) that activate the adaptive immune system.
Dendritic cells are phagocytes in tissues that are in contact with the external environment; therefore, they are located mainly in the
skin,
nose, lungs, stomach, and intestines.
They are named for their resemblance to
neuronal
dendrites, as both have many spine-like projections. Dendritic cells serve as a link between the bodily tissues and the innate and adaptive immune systems, as they
present antigens to
T cells, one of the key cell types of the adaptive immune system.
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are
cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They ha ...
s are leukocytes that have granules in their cytoplasm. In this category are neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. Mast cells reside in
connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
s and
mucous membranes, and regulate the inflammatory response. They are most often associated with
allergy and
anaphylaxis.
Basophils and
eosinophils are related to neutrophils. They secrete chemical mediators that are involved in defending against
parasites and play a role in allergic reactions, such as
asthma.
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a group of
innate immune cells that are derived from
common lymphoid progenitor and belong to the
lymphoid lineage. These cells are defined by absence of antigen specific
B or
T cell receptor (TCR) because of the lack of
recombination activating gene. ILCs do not express myeloid or dendritic cell markers.
Natural killer cells (NK) are lymphocytes and a component of the innate immune system which does not directly attack invading microbes.
Rather, NK cells destroy compromised host cells, such as tumor cells or virus-infected cells, recognizing such cells by a condition known as "missing self." This term describes cells with low levels of a cell-surface marker called MHC I (
major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are calle ...
)—a situation that can arise in viral infections of host cells. Normal body cells are not recognized and attacked by NK cells because they express intact self MHC antigens. Those MHC antigens are recognized by killer cell immunoglobulin receptors which essentially put the brakes on NK cells.
Inflammation
Inflammation is one of the first responses of the immune system to infection.
The symptoms of inflammation are redness, swelling, heat, and pain, which are caused by increased blood flow into tissue. Inflammation is produced by
eicosanoids and
cytokines, which are released by injured or infected cells. Eicosanoids include
prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s that produce
fever and the
dilation of
blood vessels associated with inflammation, and
leukotrienes that attract certain
white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s (leukocytes).
Common cytokines include
interleukins that are responsible for communication between white blood cells;
chemokines that promote
chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
; and
interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten the ...
s that have
anti-viral effects, such as shutting down
protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the product ...
in the host cell.
s and cytotoxic factors may also be released. These cytokines and other chemicals recruit immune cells to the site of infection and promote healing of any damaged tissue following the removal of pathogens.
The pattern-recognition receptors called
inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes (consisting of an NLR, the adaptor protein ASC, and the effector molecule pro-caspase-1) that form in response to cytosolic PAMPs and DAMPs, whose function is to generate active forms of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18.
Humoral defenses
The complement system is a
biochemical cascade that attacks the surfaces of foreign cells. It contains over 20 different proteins and is named for its ability to "complement" the killing of pathogens by
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
. Complement is the major humoral component of the innate immune response.
Many species have complement systems, including non-
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s like plants, fish, and some
invertebrates. In humans, this response is activated by complement binding to antibodies that have attached to these microbes or the binding of complement proteins to
carbohydrates on the surfaces of
microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s. This recognition
signal triggers a rapid killing response. The speed of the response is a result of signal amplification that occurs after sequential
proteolytic activation of complement molecules, which are also proteases. After complement proteins initially bind to the microbe, they activate their protease activity, which in turn activates other complement proteases, and so on. This produces a
catalytic cascade that amplifies the initial signal by controlled
positive feedback. The cascade results in the production of peptides that attract immune cells, increase
vascular permeability, and
opsonize (coat) the surface of a pathogen, marking it for destruction. This deposition of complement can also kill cells directly by disrupting their
plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
.
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system evolved in early vertebrates and allows for a stronger immune response as well as
immunological memory, where each pathogen is "remembered" by a signature antigen. The adaptive immune response is antigen-specific and requires the recognition of specific "non-self" antigens during a process called
antigen presentation. Antigen specificity allows for the generation of responses that are tailored to specific pathogens or pathogen-infected cells. The ability to mount these tailored responses is maintained in the body by "memory cells". Should a pathogen infect the body more than once, these specific memory cells are used to quickly eliminate it.
Recognition of antigen
The cells of the adaptive immune system are special types of leukocytes, called lymphocytes.
B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
s and T cells are the major types of lymphocytes and are derived from
hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within t ...
s in the
bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
. B cells are involved in the
humoral immune response, whereas T cells are involved in
cell-mediated immune response
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibody, antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific Cytotoxic T cell, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the rel ...
. Killer T cells only recognize antigens coupled to
Class I MHC
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on plat ...
molecules, while helper T cells and regulatory T cells only recognize antigens coupled to
Class II MHC molecules. These two mechanisms of antigen presentation reflect the different roles of the two types of T cell. A third, minor subtype are the
γδ T cells
Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) are T cells that have a γδ T-cell receptor (TCR) on their surface. Most T cells are αβ (alpha beta) T cells with TCR composed of two glycoprotein chains called α (alpha) and β (beta) TCR chains. In contrast, ...
that recognize intact antigens that are not bound to MHC receptors.
The double-positive T cells are exposed to a wide variety of
self-antigens in the
thymus, in which
iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
is necessary for its thymus development and activity.
In contrast, the B cell antigen-specific receptor is an antibody molecule on the B cell surface and recognizes native (unprocessed) antigen without any need for
antigen processing. Such antigens may be large molecules found on the surfaces of pathogens, but can also be small
haptens (such as penicillin) attached to carrier molecule. Each lineage of B cell expresses a different antibody, so the complete set of B cell antigen receptors represent all the antibodies that the body can manufacture. When B or T cells encounter their related antigens they multiply and many "clones" of the cells are produced that target the same antigen. This is called
clonal selection.
Antigen presentation to T lymphocytes
Both B cells and T cells carry receptor molecules that recognize specific targets. T cells recognize a "non-self" target, such as a pathogen, only after antigens (small fragments of the pathogen) have been processed and presented in combination with a "self" receptor called a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule.
Cell mediated immunity
There are two major subtypes of T cells: the
killer T cell and the
helper T cell. In addition there are
regulatory T cells which have a role in modulating immune response.
Killer T cells
Killer T cells are a sub-group of T cells that kill cells that are infected with viruses (and other pathogens), or are otherwise damaged or dysfunctional. As with B cells, each type of T cell recognizes a different antigen. Killer T cells are activated when their
T-cell receptor binds to this specific antigen in a complex with the MHC Class I receptor of another cell. Recognition of this MHC:antigen complex is aided by a
co-receptor on the T cell, called
CD8. The T cell then travels throughout the body in search of cells where the MHC I receptors bear this antigen. When an activated T cell contacts such cells, it releases
cytotoxins, such as
perforin, which form pores in the target cell's
plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
, allowing
ions, water and toxins to enter. The entry of another toxin called
granulysin Granulysin (GNLY) is a protein expressed in most mammals which functions as an antimicrobial peptide released by killer lymphocytes in cytotoxic granules. It is a pore-forming peptide, as it can puncture a microbial cell wall, allowing for other dea ...
(a protease) induces the target cell to undergo
apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
.
T cell killing of host cells is particularly important in preventing the replication of viruses. T cell activation is tightly controlled and generally requires a very strong MHC/antigen activation signal, or additional activation signals provided by "helper" T cells (see below).
Helper T cells
Helper T cells regulate both the innate and adaptive immune responses and help determine which immune responses the body makes to a particular pathogen. These cells have no cytotoxic activity and do not kill infected cells or clear pathogens directly. They instead control the immune response by directing other cells to perform these tasks.
Helper T cells express T cell receptors that recognize antigen bound to Class II MHC molecules. The MHC:antigen complex is also recognized by the helper cell's
CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
co-receptor, which recruits molecules inside the T cell (such as
Lck) that are responsible for the T cell's activation. Helper T cells have a weaker association with the MHC:antigen complex than observed for killer T cells, meaning many receptors (around 200–300) on the helper T cell must be bound by an MHC:antigen to activate the helper cell, while killer T cells can be activated by engagement of a single MHC:antigen molecule. Helper T cell activation also requires longer duration of engagement with an antigen-presenting cell. The activation of a resting helper T cell causes it to release cytokines that influence the activity of many cell types. Cytokine signals produced by helper T cells enhance the microbicidal function of macrophages and the activity of killer T cells. In addition, helper T cell activation causes an upregulation of molecules expressed on the T cell's surface, such as CD40 ligand (also called
CD154), which provide extra stimulatory signals typically required to activate antibody-producing B cells.
Gamma delta T cells
Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) possess an alternative T-cell receptor (TCR) as opposed to CD4+ and CD8+ (αβ) T cells and share the characteristics of helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. The conditions that produce responses from γδ T cells are not fully understood. Like other 'unconventional' T cell subsets bearing invariant TCRs, such as
CD1d-restricted
natural killer T cells, γδ T cells straddle the border between innate and adaptive immunity. On one hand, γδ T cells are a component of adaptive immunity as they
rearrange TCR genes to produce receptor diversity and can also develop a memory phenotype. On the other hand, the various subsets are also part of the innate immune system, as restricted TCR or NK receptors may be used as
pattern recognition receptors. For example, large numbers of human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells respond within hours to
common molecules produced by microbes, and highly restricted Vδ1+ T cells in
epithelia respond to stressed epithelial cells.
Humoral immune response

A
B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
identifies pathogens when antibodies on its surface bind to a specific foreign antigen.
This antigen/antibody complex is taken up by the B cell and processed by
proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called protease ...
into
peptides. The B cell then displays these antigenic peptides on its surface MHC class II molecules. This combination of MHC and antigen attracts a matching helper T cell, which releases
lymphokines and activates the B cell. As the activated B cell then begins to
divide, its offspring (
plasma cells)
secrete millions of copies of the antibody that recognizes this antigen. These antibodies circulate in
blood plasma and
lymph, bind to pathogens expressing the antigen and mark them for destruction by
complement activation
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
or for uptake and destruction by
phagocytes. Antibodies can also neutralize challenges directly, by binding to bacterial toxins or by interfering with the receptors that viruses and bacteria use to infect cells.
Newborn infants have no prior exposure to microbes and are particularly vulnerable to infection. Several layers of passive protection are provided by the mother. During pregnancy, a particular type of antibody, called
IgG, is transported from mother to baby directly through the
placenta, so human babies have high levels of antibodies even at birth, with the same range of antigen specificities as their mother. Breast milk or
colostrum also contains antibodies that are transferred to the gut of the infant and protect against bacterial infections until the newborn can synthesize its own antibodies. This is
passive immunity because the
fetus does not actually make any memory cells or antibodies—it only borrows them. This passive immunity is usually short-term, lasting from a few days up to several months. In medicine, protective passive immunity can also be
transferred artificially from one individual to another.
Immunological memory
When B cells and T cells are activated and begin to replicate, some of their offspring become long-lived memory cells. Throughout the lifetime of an animal, these memory cells remember each specific pathogen encountered and can mount a strong response if the pathogen is detected again. This is "adaptive" because it occurs during the lifetime of an individual as an adaptation to infection with that pathogen and prepares the immune system for future challenges. Immunological memory can be in the form of either passive short-term memory or active long-term memory.
Physiological regulation

The immune system is involved in many aspects of physiological regulation in the body. The immune system interacts intimately with other systems, such as the
endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
and the
nervous systems. The immune system also plays a crucial role in
embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
(development of the embryo), as well as in
tissue repair and
regeneration.
Hormones
Hormones can act as
immunomodulators, altering the sensitivity of the immune system. For example,
female sex hormones
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects ar ...
are known
immunostimulators of both adaptive and innate immune responses. Some autoimmune diseases such as
lupus erythematosus strike women preferentially, and their onset often coincides with
puberty. By contrast,
male sex hormones such as
testosterone seem to be
immunosuppressive. Other hormones appear to regulate the immune system as well, most notably
prolactin,
growth hormone and
vitamin D.
Vitamin D
Although cellular studies indicate that vitamin D has receptors and probable functions in the immune system, there is no
clinical evidence to prove that
vitamin D deficiency increases the risk for immune diseases or vitamin D
supplementation lowers immune disease risk.
A 2011 United States
Institute of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, E ...
report stated that "outcomes related to ... immune functioning and
autoimmune disorders, and infections ... could not be linked reliably with calcium or vitamin D intake and were often conflicting."
Sleep and rest
The immune system is affected by sleep and rest, and
sleep deprivation
Sleep deprivation, also known as sleep insufficiency or sleeplessness, is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep to support decent alertness, performance, and health. It can be either chronic or acute and may vary ...
is detrimental to immune function. Complex feedback loops involving
cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
, such as
interleukin-1 and
tumor necrosis factor-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
produced in response to infection, appear to also play a role in the regulation of non-rapid eye movement (
REM
Rem or REM may refer to:
Music
* R.E.M., an American rock band
* ''R.E.M.'' (EP), by Green
* "R.E.M." (song), by Ariana Grande
Organizations
* La République En Marche!, a French centrist political party
* Reichserziehungsministerium, in Nazi G ...
) sleep. Thus the immune response to infection may result in changes to the sleep cycle, including an increase in
slow-wave sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both St ...
relative to REM sleep.
In people with sleep deprivation,
active immunization
Active immunization is the induction of immunity after exposure to an antigen. Antibodies are created by the recipient and may be stored permanently.
Active immunization can occur naturally when microbes or other antigen are received by a person ...
s may have a diminished effect and may result in lower antibody production, and a lower immune response, than would be noted in a well-rested individual.
Additionally, proteins such as
NFIL3
Nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated, also known as NFIL3 or E4BP4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NFIL3'' gene.
Function
Expression of interleukin-3 ( IL-3) is restricted to activated T cells, natural killer ( NK) cells, a ...
, which have been shown to be closely intertwined with both T-cell differentiation and
circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
s, can be affected through the disturbance of natural light and dark cycles through instances of sleep deprivation. These disruptions can lead to an increase in chronic conditions such as heart disease, chronic pain, and asthma.
In addition to the negative consequences of sleep deprivation, sleep and the intertwined circadian system have been shown to have strong regulatory effects on immunological functions affecting both innate and adaptive immunity. First, during the early slow-wave-sleep stage, a sudden drop in blood levels of
cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
,
epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
, and
norepinephrine causes increased blood levels of the hormones
leptin
Leptin (from Ancient Greek, Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate Energy homeostasis, energy balance by inhib ...
,
pituitary growth hormone
Growth hormone 1, also known as pituitary growth hormone or simply as growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GH1'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin fam ...
, and
prolactin. These signals induce a pro-inflammatory state through the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1,
interleukin-12,
TNF-alpha and
IFN-gamma. These cytokines then stimulate immune functions such as immune cell activation, proliferation, and
differentiation. During this time of a slowly evolving adaptive immune response, there is a peak in undifferentiated or less differentiated cells, like naïve and central memory T cells. In addition to these effects, the milieu of hormones produced at this time (leptin, pituitary growth hormone, and prolactin) supports the interactions between APCs and T-cells, a shift of the
Th1/Th2 cytokine balance towards one that supports T
h1, an increase in overall T
h cell proliferation, and naïve T cell migration to lymph nodes. This is also thought to support the formation of long-lasting immune memory through the initiation of Th1 immune responses.
During wake periods, differentiated effector cells, such as cytotoxic natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, peak to elicit an effective response against any intruding pathogens. Anti-inflammatory molecules, such as cortisol and
catecholamines, also peak during awake active times. Inflammation would cause serious cognitive and physical impairments if it were to occur during wake times, and inflammation may occur during sleep times due to the presence of
melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle.
In vertebrates ...
. Inflammation causes a great deal of
oxidative stress and the presence of melatonin during sleep times could actively counteract free radical production during this time.
Physical exercise
Physical exercise has a positive effect on the immune system and depending on the frequency and intensity, the pathogenic effects of diseases caused by bacteria and viruses are moderated.
Immediately after intense exercise there is a transient immunodepression, where the number of circulating lymphocytes decreases and antibody production declines. This may give rise to a window of opportunity for infection and reactivation of latent virus infections,
but the evidence is inconclusive.
Changes at the cellular level

During exercise there is an increase in circulating
white blood cells of all types. This is caused by the frictional force of blood flowing on the
endothelial cell
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
surface and
catecholamines affecting
β-adrenergic receptors (βARs).
The number of
neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
in the blood increases and remains raised for up to six hours and
immature forms are present. Although the increase in neutrophils ("
neutrophilia") is similar to that seen during bacterial infections, after exercise the cell population returns to normal by around 24 hours.
The number of circulating
lymphocytes (mainly
natural killer cells
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represe ...
) decreases during intense exercise but returns to normal after 4 to 6 hours. Although up to 2% of the cells
die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
most migrate from the blood to the tissues, mainly the intestines and lungs, where
pathogens are most likely to be encountered.
Some
monocytes leave the blood circulation and migrate to the muscles where they differentiate and become
macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s.
These cells differentiate into two types: proliferative macrophages, which are responsible for increasing the number of
stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
s and restorative macrophages, which are involved their maturing to muscle cells.
Repair and regeneration
The immune system, particularly the innate component, plays a decisive role in tissue repair after an
insult
An insult is an expression or statement (or sometimes behavior) which is disrespectful or scornful. Insults may be intentional or accidental. An insult may be factual, but at the same time pejorative, such as the word "inbred".
Jocular exc ...
. Key actors include
macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s and
neutrophils, but other cellular actors, including γδ T cells,
innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), and
regulatory T cells (Tregs), are also important. The plasticity of immune cells and the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals are crucial aspects of efficient tissue repair. Immune components and pathways are involved in regeneration as well, for example in
amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s such as in
axolotl limb regeneration. According to one hypothesis, organisms that can regenerate (''e.g.'',
axolotls) could be less immunocompetent than organisms that cannot regenerate.
Disorders of human immunity
Failures of host defense occur and fall into three broad categories: immunodeficiencies, autoimmunity, and hypersensitivities.
Immunodeficiencies
Immunodeficiencies
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
occur when one or more of the components of the immune system are inactive. The ability of the immune system to respond to pathogens is diminished in both the young and the
elderly
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage ...
, with immune responses beginning to decline at around 50 years of age due to
immunosenescence.
In
developed countries,
obesity,
alcoholism, and drug use are common causes of poor immune function, while
malnutrition is the most common cause of immunodeficiency in
developing countries.
Diets lacking sufficient protein are associated with impaired cell-mediated immunity, complement activity, phagocyte function,
IgA Iga may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ambush at Iga Pass, a 1958 Japanese film
* Iga no Kagemaru, Japanese manga series
* Iga, a set of characters from the Japanese novel '' The Kouga Ninja Scrolls''
Biology
* ''Iga'' (beetle), a gen ...
antibody concentrations, and cytokine production. Additionally, the loss of the
thymus at an early age through
genetic mutation or surgical removal results in severe immunodeficiency and a high susceptibility to infection. Immunodeficiencies can also be inherited or '
acquired'.
Severe combined immunodeficiency is a rare
genetic disorder characterized by the disturbed development of functional T cells and B cells caused by numerous genetic mutations.
, where
phagocytes have a reduced ability to destroy pathogens, is an example of an inherited, or
congenital, immunodeficiency.
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
and some types of
cancer cause acquired immunodeficiency.
Autoimmunity
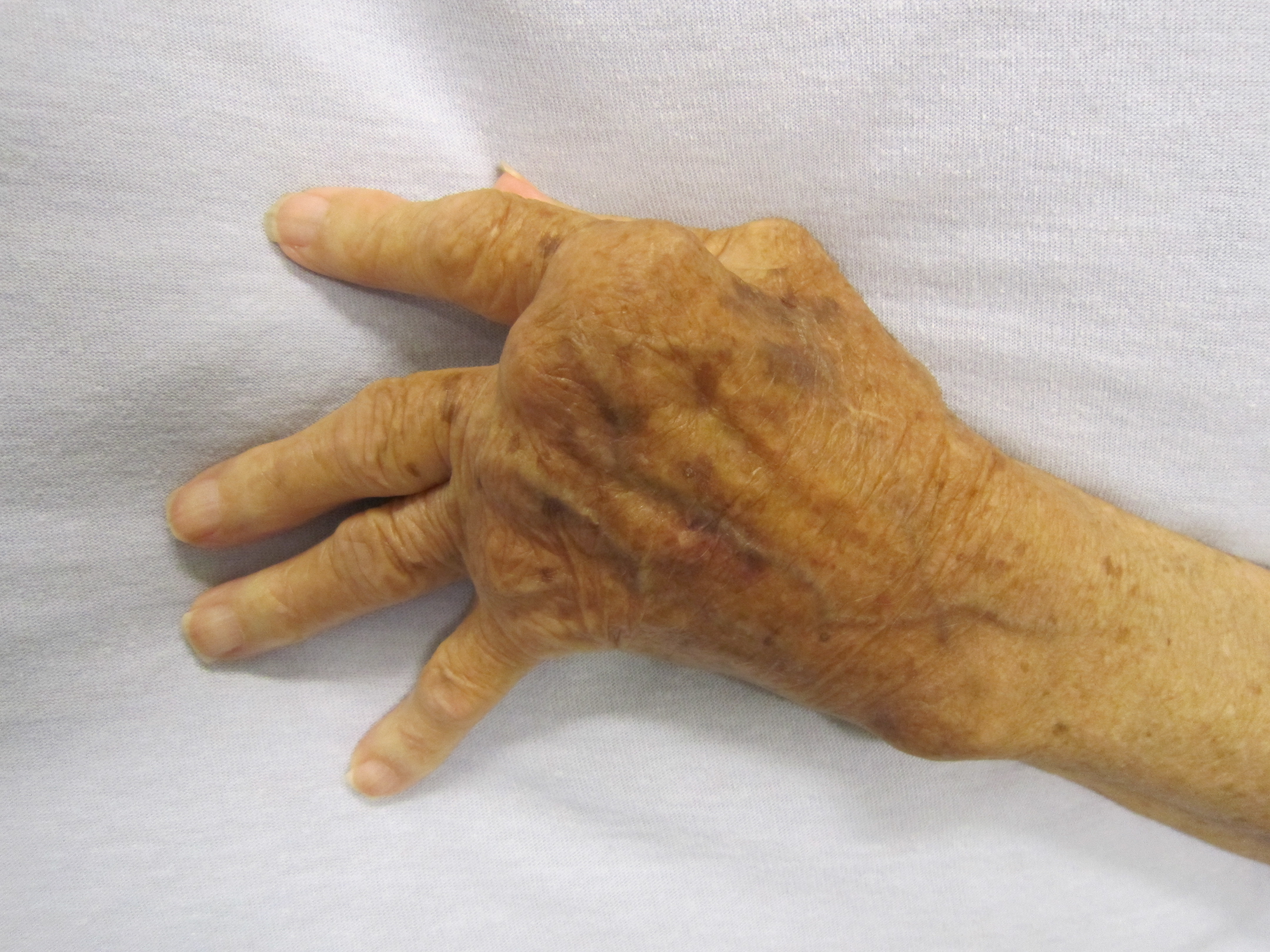
Overactive immune responses form the other end of immune dysfunction, particularly the
autoimmune disorders. Here, the immune system fails to properly distinguish between
self and non-self, and attacks part of the body. Under normal circumstances, many T cells and antibodies react with "self" peptides. One of the functions of specialized cells (located in the
thymus and bone marrow) is to present young lymphocytes with
self antigens produced throughout the body and to eliminate those cells that recognize
self-antigens, preventing autoimmunity.
Common autoimmune diseases include
Hashimoto's thyroiditis,
,
,
and
systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
.
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity is an immune response that damages the body's own tissues. It is divided into four classes (Type I – IV) based on the mechanisms involved and the time course of the hypersensitive reaction. Type I hypersensitivity is an immediate or
anaphylactic reaction, often associated with allergy. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to death. Type I hypersensitivity is mediated by
IgE, which triggers degranulation of
mast cells and
basophils when cross-linked by antigen.
Type II hypersensitivity occurs when antibodies bind to antigens on the individual's own cells, marking them for destruction. This is also called antibody-dependent (or cytotoxic) hypersensitivity, and is mediated by
IgG and
IgM antibodies.
es (aggregations of antigens, complement proteins, and IgG and IgM antibodies) deposited in various tissues trigger Type III hypersensitivity reactions.
Type IV hypersensitivity (also known as cell-mediated or ''delayed type hypersensitivity'') usually takes between two and three days to develop. Type IV reactions are involved in many autoimmune and infectious diseases, but may also involve
contact dermatitis. These reactions are mediated by
T cells,
monocytes, and
macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s.
Idiopathic inflammation
Inflammation is one of the first responses of the immune system to infection,
but it can appear without known cause.
Inflammation is produced by
eicosanoids and
cytokines, which are released by injured or infected cells. Eicosanoids include
prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s that produce fever and the
dilation of blood vessels associated with inflammation, and
leukotrienes that attract certain white blood cells (leukocytes).
Common cytokines include
interleukins that are responsible for communication between white blood cells;
chemokines that promote
chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
; and
interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten the ...
s that have anti-viral effects, such as shutting down
protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the product ...
in the host cell.
s and cytotoxic factors may also be released. These cytokines and other chemicals recruit immune cells to the site of infection and promote healing of any damaged tissue following the removal of pathogens.
Manipulation in medicine

The immune response can be manipulated to suppress unwanted responses resulting from autoimmunity, allergy, and
transplant rejection, and to stimulate protective responses against pathogens that largely elude the immune system (see
immunization) or cancer.
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
s are used to control autoimmune disorders or
inflammation when excessive tissue damage occurs, and to prevent rejection after an
organ transplant.
drugs are often used to control the effects of inflammation.
Glucocorticoids are the most powerful of these drugs and can have many undesirable
side effects, such as
central obesity,
hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
, and
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone ...
. Their use is tightly controlled. Lower doses of anti-inflammatory drugs are often used in conjunction with cytotoxic or immunosuppressive drugs such as
methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
or
azathioprine.
Cytotoxic drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemoth ...
inhibit the immune response by killing dividing cells such as activated T cells. This killing is indiscriminate and other
constantly dividing cells
In cellular biology, labile cells are cells that continuously multiply and divide throughout life. This continual division of labile cells allows them to reproduce new stem cells and replace functional cells that are lost in the body. Functional c ...
and their organs are affected, which causes toxic side effects.
Immunosuppressive drugs such as
cyclosporin prevent T cells from responding to signals correctly by inhibiting
signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
pathways.
Immunostimulation
Claims made by marketers of various products and
alternative health providers, such as
chiropractors,
homeopaths, and
acupuncturists
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scient ...
to be able to stimulate or "boost" the immune system generally lack meaningful explanation and evidence of effectiveness.
Vaccination

Long-term ''active'' memory is acquired following infection by activation of B and T cells. Active immunity can also be generated artificially, through
vaccination. The principle behind vaccination (also called
immunization) is to introduce an
antigen from a pathogen to stimulate the immune system and develop
specific immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune syste ...
against that particular pathogen without causing disease associated with that organism. This deliberate induction of an immune response is successful because it exploits the natural specificity of the immune system, as well as its inducibility. With infectious disease remaining one of the leading causes of death in the human population, vaccination represents the most effective manipulation of the immune system mankind has developed.
Many vaccines are based on
acellular components of micro-organisms, including harmless
toxin components. Since many antigens derived from acellular vaccines do not strongly induce the adaptive response, most bacterial vaccines are provided with additional
adjuvants that activate the
antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using ...
s of the innate immune system and maximize
immunogenicity.
Tumor immunology
Another important role of the immune system is to identify and eliminate
tumors. This is called immune surveillance. The ''transformed cells'' of tumors express
antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
that are not found on normal cells. To the immune system, these antigens appear foreign, and their presence causes immune cells to attack the transformed tumor cells. The antigens expressed by tumors have several sources;
some are derived from
oncogenic
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
viruses like
human papillomavirus, which causes cancer of the
cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during ...
,
vulva,
vagina,
penis,
anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
,
mouth, and throat,
while others are the organism's own proteins that occur at low levels in normal cells but reach high levels in tumor cells. One example is an enzyme called
tyrosinase that, when expressed at high levels, transforms certain skin cells (for example,
melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and heart.
...
s) into tumors called
melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
s.
A third possible source of tumor antigens are proteins normally important for regulating
cell growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than ...
and survival, that commonly mutate into cancer inducing molecules called
oncogenes.

The main response of the immune system to tumors is to destroy the abnormal cells using killer T cells, sometimes with the assistance of helper T cells.
Tumor antigens are presented on MHC class I molecules in a similar way to viral antigens. This allows killer T cells to recognize the tumor cell as abnormal.
NK cells also kill tumorous cells in a similar way, especially if the tumor cells have fewer MHC class I molecules on their surface than normal; this is a common phenomenon with tumors. Sometimes antibodies are generated against tumor cells allowing for their destruction by the
complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
.
Some tumors evade the immune system and go on to become cancers.
Tumor cells often have a reduced number of MHC class I molecules on their surface, thus avoiding detection by killer T cells.
Some tumor cells also release products that inhibit the immune response; for example by secreting the cytokine
TGF-β, which suppresses the activity of
macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s and
lymphocytes.
In addition,
immunological tolerance may develop against tumor antigens, so the immune system no longer attacks the tumor cells.
Paradoxically, macrophages can promote tumor growth when tumor cells send out cytokines that attract macrophages, which then generate cytokines and growth factors such as
tumor-necrosis factor alpha that nurture tumor development or promote stem-cell-like plasticity.
In addition, a combination of hypoxia in the tumor and a cytokine produced by macrophages induces tumor cells to decrease production of a protein that blocks
metastasis and thereby assists spread of cancer cells.
Anti-tumor M1 macrophages are recruited in early phases to tumor development but are progressively differentiated to M2 with pro-tumor effect, an immunosuppressor switch. The hypoxia reduces the cytokine production for the anti-tumor response and progressively macrophages acquire pro-tumor M2 functions driven by the tumor microenvironment, including IL-4 and IL-10.
Cancer immunotherapy covers the medical ways to stimulate the immune system to attack cancer tumors.
Predicting immunogenicity
Some drugs can cause a neutralizing immune response, meaning that the immune system produces
neutralizing antibodies that counteract the action of the drugs, particularly if the drugs are administered repeatedly, or in larger doses. This limits the effectiveness of drugs based on larger peptides and proteins (which are typically larger than 6000
Da).
In some cases, the drug itself is not immunogenic, but may be co-administered with an immunogenic compound, as is sometimes the case for
Taxol. Computational methods have been developed to predict the immunogenicity of peptides and proteins, which are particularly useful in designing therapeutic antibodies, assessing likely virulence of mutations in viral coat particles, and validation of proposed peptide-based drug treatments. Early techniques relied mainly on the observation that
hydrophilic amino acids are overrepresented in
epitope regions than
hydrophobic amino acids;
however, more recent developments rely on
machine learning techniques using databases of existing known epitopes, usually on well-studied virus proteins, as a
training set.
A publicly accessible database has been established for the cataloguing of epitopes from pathogens known to be recognizable by B cells.
The emerging field of
bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combi ...
-based studies of immunogenicity is referred to as ''
immunoinformatics''.
Immunoproteomics
Immunoproteomics is the study of large sets of proteins (proteomics) involved in the immune response.
Examples of common applications of immunoproteomics include:
* The isolation and mass spectrometric identification of MHC (major histocompatibil ...
is the study of large sets of proteins (
proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In ...
) involved in the immune response.
Evolution and other mechanisms
Evolution of the immune system
It is likely that a multicomponent, adaptive immune system arose with the first
vertebrates, as
invertebrates do not generate lymphocytes or an antibody-based humoral response.
Many species, however, use mechanisms that appear to be precursors of these aspects of vertebrate immunity. Immune systems appear even in the structurally simplest forms of life, with bacteria using a unique defense mechanism, called the
restriction modification system to protect themselves from viral pathogens, called
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
s.
Prokaryotes (
bacteria and
archea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebact ...
) also possess acquired immunity, through a system that uses
CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacte ...
sequences to retain fragments of the genomes of phage that they have come into contact with in the past, which allows them to block virus replication through a form of
RNA interference. Prokaryotes also possess other defense mechanisms. Offensive elements of the immune systems are also present in
unicellular eukaryotes, but studies of their roles in defense are few.
Pattern recognition receptors are proteins used by nearly all organisms to identify molecules associated with pathogens.
Antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ...
called
defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, ...
s are an evolutionarily conserved component of the innate immune response found in all animals and plants, and represent the main form of invertebrate systemic immunity.
The
complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
and phagocytic cells are also used by most forms of invertebrate life.
Ribonucleases and the
RNA interference pathway are conserved across all
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s, and are thought to play a role in the immune response to viruses.
Unlike animals, plants lack phagocytic cells, but many plant immune responses involve systemic chemical signals that are sent through a plant.
Individual plant cells respond to molecules associated with pathogens known as
pathogen-associated molecular patterns or PAMPs. When a part of a plant becomes infected, the plant produces a localized
hypersensitive response, whereby cells at the site of infection undergo rapid
apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
to prevent the spread of the disease to other parts of the plant.
Systemic acquired resistance is a type of defensive response used by plants that renders the entire plant
resistant to a particular infectious agent.
mechanisms are particularly important in this systemic response as they can block
virus replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome an ...
.
Alternative adaptive immune system
Evolution of the adaptive immune system occurred in an ancestor of the
jawed vertebrates
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living ...
. Many of the classical molecules of the adaptive immune system (for example,
immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
s and
T-cell receptors) exist only in jawed vertebrates. A distinct
lymphocyte-derived molecule has been discovered in primitive
jawless vertebrates, such as the
lamprey and
hagfish. These animals possess a large array of molecules called
Variable lymphocyte receptors (VLRs) that, like the antigen receptors of jawed vertebrates, are produced from only a small number (one or two) of
genes. These molecules are believed to bind pathogenic
antigens in a similar way to
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
, and with the same degree of specificity.
Manipulation by pathogens
The success of any pathogen depends on its ability to elude host immune responses. Therefore, pathogens evolved several methods that allow them to successfully infect a host, while evading detection or destruction by the immune system.
Bacteria often overcome physical barriers by secreting enzymes that digest the barrier, for example, by using a
type II secretion system
The type 2 secretion system (often referred to as the type II secretion system or by the initials T2SS) is a type of protein secretion machinery found in various species of Gram-negative bacteria, including many human pathogens such as ''Pseudomo ...
. Alternatively, using a
type III secretion system, they may insert a hollow tube into the host cell, providing a direct route for proteins to move from the pathogen to the host. These proteins are often used to shut down host defenses.
An evasion strategy used by several pathogens to avoid the innate immune system is to hide within the cells of their host (also called
intracellular pathogenesis). Here, a pathogen spends most of its
life-cycle inside host cells, where it is shielded from direct contact with immune cells, antibodies and complement. Some examples of intracellular pathogens include viruses, the
food poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease) ...
bacterium ''
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is fur ...
'' and the
eukaryotic parasites that cause
malaria (''
Plasmodium spp.'') and
leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most freq ...
(''
Leishmania
''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...
spp.''). Other bacteria, such as ''
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'', live inside a protective capsule that prevents
lysis
Lysis ( ) is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular bio ...
by complement. Many pathogens secrete compounds that diminish or misdirect the host's immune response.
Some bacteria form
biofilms to protect themselves from the cells and proteins of the immune system. Such biofilms are present in many successful infections, such as the chronic ''
Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''
Burkholderia cenocepacia
''Burkholderia cenocepacia'' is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in soil and water environments and may also be associated with plants and animals, particularly as a human pathogen. It is one of over 20 species in the ...
'' infections characteristic of
cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
. Other bacteria generate surface proteins that bind to antibodies, rendering them ineffective; examples include ''
Streptococcus'' (protein G), ''
Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive ...
'' (protein A), and ''
Peptostreptococcus magnus'' (protein L).
The mechanisms used to evade the adaptive immune system are more complicated. The simplest approach is to rapidly change non-essential
epitopes (
amino acids and/or sugars) on the surface of the pathogen, while keeping essential epitopes concealed. This is called
antigenic variation. An example is HIV, which mutates rapidly, so the proteins on its
viral envelope that are essential for entry into its host target cell are constantly changing. These frequent changes in antigens may explain the failures of
vaccines directed at this virus. The parasite ''
Trypanosoma brucei'' uses a similar strategy, constantly switching one type of surface protein for another, allowing it to stay one step ahead of the antibody response. Masking antigens with host molecules is another common strategy for avoiding detection by the immune system. In HIV, the envelope that covers the
virion is formed from the outermost membrane of the host cell; such "self-cloaked" viruses make it difficult for the immune system to identify them as "non-self" structures.
History of immunology
 Immunology
Immunology is a science that examines the structure and function of the immune system. It originates from
medicine and early studies on the causes of immunity to disease. The earliest known reference to immunity was during the
plague of Athens in 430 BC.
Thucydides noted that people who had recovered from a previous bout of the disease could nurse the sick without contracting the illness a second time. In the 18th century,
Pierre-Louis Moreau de Maupertuis experimented with scorpion venom and observed that certain dogs and mice were immune to this venom. In the 10th century, Persian physician
al-Razi (also known as Rhazes) wrote the first recorded theory of acquired immunity,
noting that a
smallpox bout protected its survivors from future infections. Although he explained the immunity in terms of "excess moisture" being expelled from the blood—therefore preventing a second occurrence of the disease—this theory explained many observations about smallpox known during this time.
These and other observations of acquired immunity were later exploited by
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization, the latter of which was named afte ...
in his development of vaccination and his proposed
germ theory of disease. Pasteur's theory was in direct opposition to contemporary theories of disease, such as the
miasma theory
The miasma theory (also called the miasmatic theory) is an obsolete medical theory that held that diseases—such as cholera, chlamydia, or the Black Death—were caused by a ''miasma'' (, Ancient Greek for 'pollution'), a noxious form of "bad ...
. It was not until
Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( , ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera (though the Vibrio ...
's 1891
proofs, for which he was awarded a
Nobel Prize in 1905, that microorganisms were confirmed as the cause of
infectious disease. Viruses were confirmed as human pathogens in 1901, with the discovery of the
yellow fever virus by
Walter Reed.
Immunology made a great advance towards the end of the 19th century, through rapid developments in the study of
humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it in ...
and
cellular immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in ...
.
Particularly important was the work of
Paul Ehrlich, who proposed the
side-chain theory to explain the specificity of the
antigen-antibody reaction Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process call ...
; his contributions to the understanding of humoral immunity were recognized by the award of a joint Nobel Prize in 1908, along with the founder of cellular immunology,
Elie Metchnikoff.
In 1974,
Niels Kaj Jerne developed the
immune network theory; he shared a Nobel Prize in 1984 with
Georges J. F. Köhler
Georges Jean Franz Köhler (; 17 April 1946 – 1 March 1995) was a German biologist.
Together with César Milstein and Niels Kaj Jerne, Köhler won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984, "for work on the immune system and the prod ...
and
César Milstein
César Milstein, CH, FRS (8 October 1927 – 24 March 2002) was an Argentine biochemist in the field of antibody research. Milstein shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984 with Niels Kaj Jerne and Georges J. F. Köhler for d ...
for theories related to the immune system.
See also
*
Fc receptor
*
Immune system receptors
*
Immunostimulator
*
Neuroimmune system
*
Original antigenic sin – when the immune system uses immunological memory upon encountering a slightly different pathogen
*
Plant disease resistance
*
Polyclonal response
*
Tumor antigens
References
Citations
General bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* (The book'
sourcesare only online.) A popular science explanation of the immune system.
External links
– from the
University of South Carolina School of Medicine (undergraduate level)
{{Authority control
 The immune system is a network of
The immune system is a network of  Some leukocytes (white blood cells) act like independent, single-celled organisms and are the second arm of the innate immune system. The innate leukocytes include the "professional" phagocytes (
Some leukocytes (white blood cells) act like independent, single-celled organisms and are the second arm of the innate immune system. The innate leukocytes include the "professional" phagocytes ( The adaptive immune system evolved in early vertebrates and allows for a stronger immune response as well as immunological memory, where each pathogen is "remembered" by a signature antigen. The adaptive immune response is antigen-specific and requires the recognition of specific "non-self" antigens during a process called antigen presentation. Antigen specificity allows for the generation of responses that are tailored to specific pathogens or pathogen-infected cells. The ability to mount these tailored responses is maintained in the body by "memory cells". Should a pathogen infect the body more than once, these specific memory cells are used to quickly eliminate it.
The adaptive immune system evolved in early vertebrates and allows for a stronger immune response as well as immunological memory, where each pathogen is "remembered" by a signature antigen. The adaptive immune response is antigen-specific and requires the recognition of specific "non-self" antigens during a process called antigen presentation. Antigen specificity allows for the generation of responses that are tailored to specific pathogens or pathogen-infected cells. The ability to mount these tailored responses is maintained in the body by "memory cells". Should a pathogen infect the body more than once, these specific memory cells are used to quickly eliminate it.
 A
A  During exercise there is an increase in circulating white blood cells of all types. This is caused by the frictional force of blood flowing on the
During exercise there is an increase in circulating white blood cells of all types. This is caused by the frictional force of blood flowing on the  Long-term ''active'' memory is acquired following infection by activation of B and T cells. Active immunity can also be generated artificially, through vaccination. The principle behind vaccination (also called immunization) is to introduce an antigen from a pathogen to stimulate the immune system and develop
Long-term ''active'' memory is acquired following infection by activation of B and T cells. Active immunity can also be generated artificially, through vaccination. The principle behind vaccination (also called immunization) is to introduce an antigen from a pathogen to stimulate the immune system and develop  The main response of the immune system to tumors is to destroy the abnormal cells using killer T cells, sometimes with the assistance of helper T cells. Tumor antigens are presented on MHC class I molecules in a similar way to viral antigens. This allows killer T cells to recognize the tumor cell as abnormal. NK cells also kill tumorous cells in a similar way, especially if the tumor cells have fewer MHC class I molecules on their surface than normal; this is a common phenomenon with tumors. Sometimes antibodies are generated against tumor cells allowing for their destruction by the
The main response of the immune system to tumors is to destroy the abnormal cells using killer T cells, sometimes with the assistance of helper T cells. Tumor antigens are presented on MHC class I molecules in a similar way to viral antigens. This allows killer T cells to recognize the tumor cell as abnormal. NK cells also kill tumorous cells in a similar way, especially if the tumor cells have fewer MHC class I molecules on their surface than normal; this is a common phenomenon with tumors. Sometimes antibodies are generated against tumor cells allowing for their destruction by the  Immunology is a science that examines the structure and function of the immune system. It originates from medicine and early studies on the causes of immunity to disease. The earliest known reference to immunity was during the plague of Athens in 430 BC. Thucydides noted that people who had recovered from a previous bout of the disease could nurse the sick without contracting the illness a second time. In the 18th century, Pierre-Louis Moreau de Maupertuis experimented with scorpion venom and observed that certain dogs and mice were immune to this venom. In the 10th century, Persian physician al-Razi (also known as Rhazes) wrote the first recorded theory of acquired immunity, noting that a smallpox bout protected its survivors from future infections. Although he explained the immunity in terms of "excess moisture" being expelled from the blood—therefore preventing a second occurrence of the disease—this theory explained many observations about smallpox known during this time.
These and other observations of acquired immunity were later exploited by
Immunology is a science that examines the structure and function of the immune system. It originates from medicine and early studies on the causes of immunity to disease. The earliest known reference to immunity was during the plague of Athens in 430 BC. Thucydides noted that people who had recovered from a previous bout of the disease could nurse the sick without contracting the illness a second time. In the 18th century, Pierre-Louis Moreau de Maupertuis experimented with scorpion venom and observed that certain dogs and mice were immune to this venom. In the 10th century, Persian physician al-Razi (also known as Rhazes) wrote the first recorded theory of acquired immunity, noting that a smallpox bout protected its survivors from future infections. Although he explained the immunity in terms of "excess moisture" being expelled from the blood—therefore preventing a second occurrence of the disease—this theory explained many observations about smallpox known during this time.
These and other observations of acquired immunity were later exploited by