IBM Z14 (microprocessor) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
International Business Machines Corporation (using the
 The
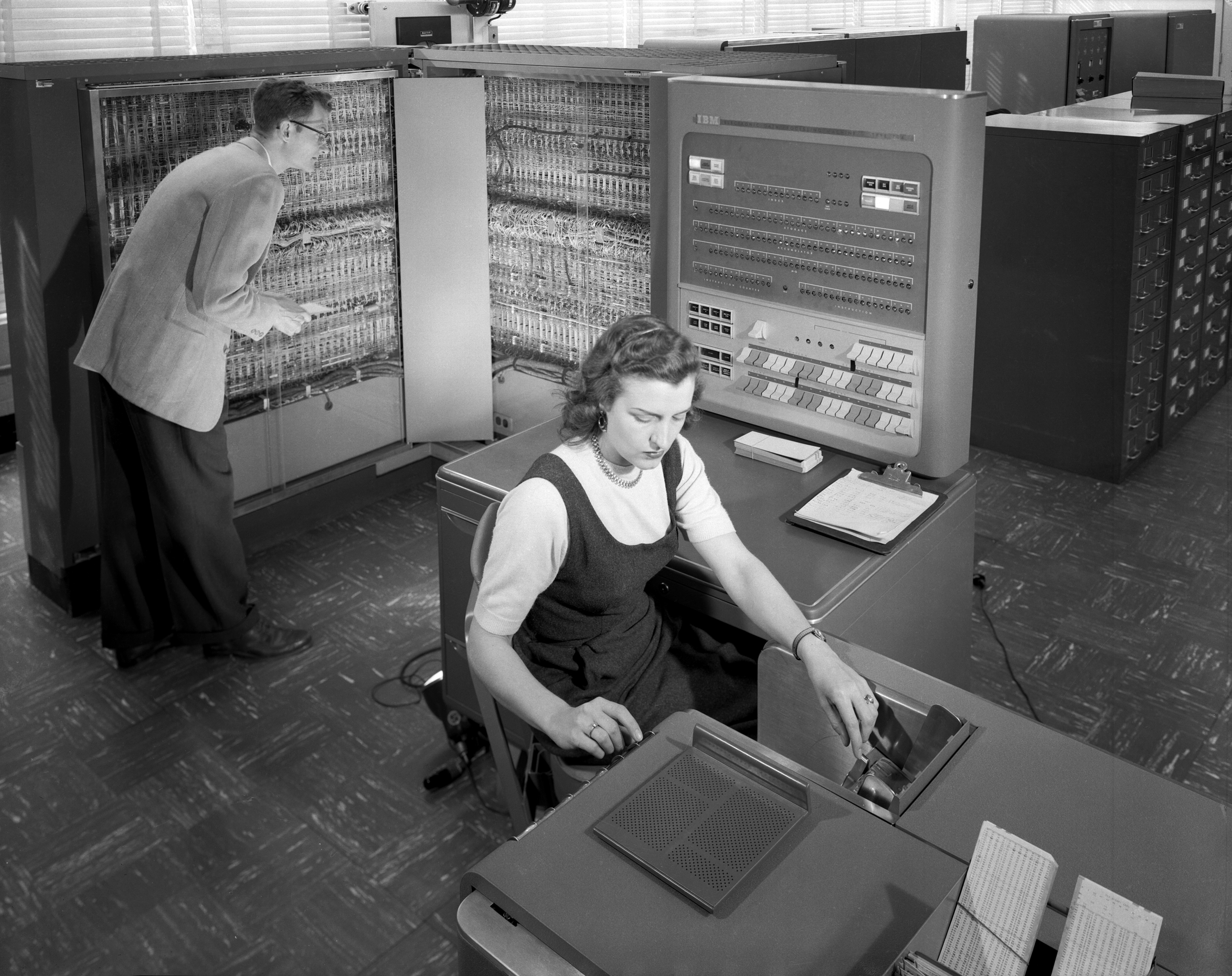
The ''model T'' of computing, because it was the first computer with over ten thousand unit sales by IBM.
In 1956, the company demonstrated the first practical example of

 On April 7, 1964, IBM launched the first computer system family, the
On April 7, 1964, IBM launched the first computer system family, the
 In 1998, IBM merged the enterprise-oriented Personal Systems Group of the IBM PC Co. into IBM's own Global Services personal computer consulting and customer service division. The resulting merged business units then became known simply as IBM Personal Systems Group. A year later, IBM stopped selling their computers at retail outlets after their market share in this sector had fallen considerably behind competitors
In 1998, IBM merged the enterprise-oriented Personal Systems Group of the IBM PC Co. into IBM's own Global Services personal computer consulting and customer service division. The resulting merged business units then became known simply as IBM Personal Systems Group. A year later, IBM stopped selling their computers at retail outlets after their market share in this sector had fallen considerably behind competitors
 IBM has a large and diverse portfolio of products and services. , these offerings fall into the categories of
IBM has a large and diverse portfolio of products and services. , these offerings fall into the categories of
 Research has been part of IBM since its founding, and its organized efforts trace their roots back to 1945, when the Watson Scientific Computing Laboratory was founded at
Research has been part of IBM since its founding, and its organized efforts trace their roots back to 1945, when the Watson Scientific Computing Laboratory was founded at
 IBM is nicknamed ''Big Blue'' partly because of its blue logo and color scheme, and also in reference to its former ''de facto'' dress code of white shirts with blue suits. The company logo has undergone several changes over the years, with its current "8-bar" logo designed in 1972 by
IBM is nicknamed ''Big Blue'' partly because of its blue logo and color scheme, and also in reference to its former ''de facto'' dress code of white shirts with blue suits. The company logo has undergone several changes over the years, with its current "8-bar" logo designed in 1972 by
In February 2021, IBM committed to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2030.

 IBM is among the world's largest employers, with over 297,900 employees worldwide in 2022, with about 160,000 of those being tech consultants.
IBM's leadership programs include Extreme Blue, an internship program, and the
IBM is among the world's largest employers, with over 297,900 employees worldwide in 2022, with about 160,000 of those being tech consultants.
IBM's leadership programs include Extreme Blue, an internship program, and the
trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a Good (economics and accounting), product or Service (economics), service f ...
IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American multinational technology company
A technology company (or tech company) is a company that focuses primarily on the manufacturing, support, research and development of—most commonly computing, telecommunication and consumer electronics–based—technology-intensive products and ...
headquartered in Armonk, New York
Armonk is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Administrative divisions of New York#Town, town of North Castle, New York, North Castle, located in Westchester County, New York, United States. The corporate headquar ...
, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow (), is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.
The DJIA is one of the oldest and most commonly followed equity indice ...
. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
s generated by a business.
IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company
The Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR) was a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems; it was subsequently known as IBM.
In 1911, the financier and noted trust organizer Charles R. Flint, called the ...
(CTR), a holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the Security (finance), securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own Share ...
of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe
IBM mainframes are large computer systems produced by IBM since 1952. During the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the computer market with the 7000 series and the later System/360, followed by the System/370. Current mainframe computers in IBM' ...
, exemplified by the System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applicati ...
and its successors, was the world's dominant computing platform
A computing platform, digital platform, or software platform is the infrastructure on which software is executed. While the individual components of a computing platform may be obfuscated under layers of abstraction, the ''summation of the requi ...
, with the company producing 80 percent of computers in the U.S. and 70 percent of computers worldwide. Embracing both business and scientific computing, System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover a complete range of applications from small to large.
IBM debuted in the microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (P ...
market in 1981 with the IBM Personal Computer
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a ...
, — its DOS software provided by Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
, which became the basis for the majority of personal computers
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
to the present day. The company later also found success in the portable
Portable may refer to:
General
* Portable building, a manufactured structure that is built off site and moved in upon completion of site and utility work
* Portable classroom, a temporary building installed on the grounds of a school to provide a ...
space with the ThinkPad
ThinkPad is a line of business-oriented laptop and Tablet computer, tablet computers produced since 1992. It was originally designed, created and manufactured by the American IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) Corporation. IBM Acquisit ...
. Since the 1990s, IBM has concentrated on computer services, software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, supercomputer
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instruc ...
s, and scientific research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and medieval world. The ...
; it sold its microcomputer division to Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, trading as Lenovo ( , zh, c=联想, p=Liánxiǎng), is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, personal computers, software, servers, conv ...
in 2005. IBM continues to develop mainframes, and its supercomputers have consistently ranked among the most powerful in the world in the 21st century. In 2018, IBM along with 91 additional ''Fortune'' 500 companies had "paid an effective federal tax rate of 0% or less" as a result of Donald Trump's Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017
The Act to provide for reconciliation pursuant to titles II and V of the concurrent resolution on the budget for fiscal year 2018, , is a congressional revenue act of the United States originally introduced in Congress as the Tax Cuts and Jobs ...
.
As one of the world's oldest and largest technology companies, IBM has been responsible for several technological innovation
Technological innovation is an extended concept of innovation. While innovation is a rather well-defined concept, it has a broad meaning to many people, and especially numerous understanding in the academic and business world.
Innovation refers to ...
s, including the Automated Teller Machine
An automated teller machine (ATM) is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transactions, such as cash withdrawals, deposits, funds transfers, balance inquiries or account ...
(ATM), Dynamic Random-Access Memory
Dynamics (from Greek language, Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power (disambiguation), power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and t ...
(DRAM), the floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
, the hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
, the magnetic stripe card
The term digital card can refer to a physical item, such as a memory card on a camera, or, increasingly since 2017, to the digital content hosted
as a virtual card or cloud card, as a digital virtual representation of a physical card. They shar ...
, the relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
, the SQL programming language, and the Universal Product Code
The Universal Product Code (UPC or UPC code) is a barcode#Symbologies, barcode symbology that is used worldwide for tracking trade items in stores.
The chosen symbology has bars (or spaces) of exactly 1, 2, 3, or 4 units wide each; each decimal ...
(UPC) barcode. The company has made inroads in advanced computer chips, quantum computing
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of wave-particle duality, both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using s ...
, artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
, and data infrastructure. IBM employees and alumni have won various recognitions for their scientific research and inventions, including six Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
s and six Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in the fi ...
s.
History
1910s–1950s
IBM originated with several technological innovations developed and commercialized in the late 19th century. Julius E. Pitrap patented the computing scale in 1885; Alexander Dey invented the dial recorder (1888);Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, in ...
patented the Electric Tabulating Machine
The tabulating machine was an electromechanical machine designed to assist in summarizing information stored on punched cards. Invented by Herman Hollerith, the machine was developed to help process data for the U.S. Census, 1890, 1890 U.S. Cens ...
(1889); and Willard Bundy invented a time clock to record workers' arrival and departure times on a paper tape (1889). On June 16, 1911, their four companies were amalgamated in New York State by Charles Ranlett Flint forming a fifth company, the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company
The Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR) was a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems; it was subsequently known as IBM.
In 1911, the financier and noted trust organizer Charles R. Flint, called the ...
(CTR) based in Endicott, New York. The five companies had 1,300 employees and offices and plants in Endicott and Binghamton, New York; Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
; Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
; Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
; and Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
, Canada.
Collectively, the companies manufactured a wide array of machinery for sale and lease, ranging from commercial scales and industrial time recorders, meat and cheese slicers, to tabulators and punched cards. Thomas J. Watson, Sr., fired from the National Cash Register Company (NCR) by John Henry Patterson, called on Flint and, in 1914, was offered a position at CTR. Watson joined CTR as general manager and then, 11 months later, was made President when antitrust
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust l ...
cases relating to his time at NCR were resolved. Having learned Patterson's pioneering business practices, Watson proceeded to put the stamp of NCR onto CTR's companies. He implemented sales conventions, "generous sales incentives, a focus on customer service, an insistence on well-groomed, dark-suited salesmen and had an evangelical fervor for instilling company pride and loyalty in every worker". His favorite slogan, " THINK", became a mantra for each company's employees. During Watson's first four years, revenues reached $9 million ($ today) and the company's operations expanded to Europe, South America, Asia and Australia. Watson never liked the clumsy hyphenated name "Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company" and chose to replace it with the more expansive title "International Business Machines" which had previously been used as the name of CTR's Canadian Division;Belden (1962) p. 125 the name was changed on February 14, 1924. By 1933, most of the subsidiaries had been merged into one company, IBM.
 The
The Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
made extensive use of Hollerith punch card and alphabetical accounting equipment and IBM's majority-owned German subsidiary, Deutsche Hollerith Maschinen GmbH ( Dehomag), supplied this equipment from the early 1930s. This equipment was critical to Nazi efforts to categorize citizens of both Germany and other nations that fell under Nazi control through ongoing censuses. These census data were used to facilitate the round-up of Jews and other targeted groups, and to catalog their movements through the machinery of the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
, including internment in the concentration camps. Black contends that IBM's dealings with Nazis through its New York City headquarters persisted during World War II. Nazi concentration camps operated a Hollerith department called Hollerith Abteilung, which had IBM machines, including calculating and sorting machines.
IBM as a military contractor produced 6% of the M1 Carbine
The M1 carbine (formally the United States carbine, caliber .30, M1) is a lightweight semi-automatic carbine chambered in the .30 carbine (7.62×33mm) cartridge that was issued to the U.S. military during World War II, the Korean War, and t ...
rifles used in World War II, about 346,500 of them, between August 1943 and May 1944. IBM built the Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator, an electromechanical computer, during World War II. It offered its first commercial stored-program computer, the vacuum tube based IBM 701
The IBM 701 Electronic Data Processing Machine, known as the Defense Calculator while in development, was IBM’s first commercial scientific computer and its first series production mainframe computer, which was announced to the public on May 2 ...
, in 1952. The IBM 305 RAMAC introduced the hard disk drive in 1956. The company switched to transistorized designs with the 7000 and 1400
Year 1400 ( MCD) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The year 1400 was not a leap year in the Proleptic Gregorian calendar, it was a common year starting on Wednesday.
Events
January–March
* January 4 ...
series, beginning in 1958. In which, IBM considered the 1400
Year 1400 ( MCD) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The year 1400 was not a leap year in the Proleptic Gregorian calendar, it was a common year starting on Wednesday.
Events
January–March
* January 4 ...
series the artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
when Arthur L. Samuel of IBM's Poughkeepsie, New York, laboratory programmed an IBM 704
The IBM 704 is the model name of a large digital computer, digital mainframe computer introduced by IBM in 1954. Designed by John Backus and Gene Amdahl, it was the first mass-produced computer with hardware for floating-point arithmetic. The I ...
not merely to play checkers but "learn" from its own experience. In 1957, the FORTRAN scientific programming language was developed.
1960s–1980s
In 1961, IBM developed the SABRE reservation system forAmerican Airlines
American Airlines, Inc. is a major airlines of the United States, major airline in the United States headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, and is the Largest airlines in the world, largest airline in the ...
and introduced the highly successful Selectric typewriter.
Also in 1961 IBM used the IBM 7094 to generate the first song sung completely by a computer using synthesizers. The song was Daisy Bell (Bicycle Built for Two).
In 1963, IBM employees and computers helped NASA track the orbital flights of the Mercury astronauts. A year later, it moved its corporate headquarters from New York City to Armonk, New York
Armonk is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Administrative divisions of New York#Town, town of North Castle, New York, North Castle, located in Westchester County, New York, United States. The corporate headquar ...
. The latter half of the 1960s saw IBM continue its support of space exploration, participating in the 1965 Gemini flights, 1966 Saturn flights, and 1969 lunar mission. IBM also developed and manufactured the Saturn V's Instrument Unit and Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
spacecraft guidance computers.

 On April 7, 1964, IBM launched the first computer system family, the
On April 7, 1964, IBM launched the first computer system family, the IBM System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applicati ...
. It spanned the complete range of commercial and scientific applications from large to small, allowing companies for the first time to upgrade to models with greater computing capability without having to rewrite their applications. It was followed by the IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a range of IBM mainframe computers announced as the successors to the IBM System/360, System/360 family on June 30, 1970. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migrati ...
in 1970. Together the 360 and 370 made the IBM mainframe
IBM mainframes are large computer systems produced by IBM since 1952. During the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the computer market with the 7000 series and the later System/360, followed by the System/370. Current mainframe computers in IBM' ...
the dominant mainframe computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise ...
and the dominant computing platform in the industry throughout this period and into the early 1980s. They and the operating systems that ran on them such as OS/VS1 and MVS, and the middleware built on top of those such as the CICS
IBM CICS (Customer Information Control System) is a family of mixed-language application servers that provide online business transaction management, transaction management and connectivity for applications on IBM mainframe systems under z/OS ...
transaction processing monitor, had a near-monopoly-level market share and became the thing IBM was most known for during this period.
In 1969, the United States of America alleged that IBM violated the Sherman Antitrust Act by monopolizing or attempting to monopolize the general-purpose electronic digital computer system market, specifically computers designed primarily for business, and subsequently alleged that IBM violated the antitrust laws in IBM's actions directed against leasing companies and plug-compatible peripheral manufacturers. Shortly after, IBM unbundled its software and services in what many observers believed was a direct result of the lawsuit, creating a competitive market for software. In 1982, the Department of Justice dropped the case as "without merit".
Also in 1969, IBM engineer Forrest Parry invented the magnetic stripe card
The term digital card can refer to a physical item, such as a memory card on a camera, or, increasingly since 2017, to the digital content hosted
as a virtual card or cloud card, as a digital virtual representation of a physical card. They shar ...
that would become ubiquitous for credit/debit/ATM cards, driver's licenses, rapid transit cards and a multitude of other identity and access control applications. IBM pioneered the manufacture of these cards, and for most of the 1970s, the data processing systems and software for such applications ran exclusively on IBM computers. In 1974, IBM engineer George J. Laurer developed the Universal Product Code
The Universal Product Code (UPC or UPC code) is a barcode#Symbologies, barcode symbology that is used worldwide for tracking trade items in stores.
The chosen symbology has bars (or spaces) of exactly 1, 2, 3, or 4 units wide each; each decimal ...
. IBM and the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
first introduced financial swaps to the public in 1981, when they entered into a swap agreement.
IBM entered the microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (P ...
market in the 1980s with the IBM Personal Computer
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a ...
(IBM 5150). The computer, which spawned a long line of successors, had a profound influence on the development of the personal computer market and became one of IBM's best selling products of all time. Because of a lack of foresight by IBM, the PC was not well protected by intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
laws. As a consequence, IBM quickly began losing its market dominance to emerging, compatible competitors in the PC market.
In 1985, IBM collaborated with Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
to develop a new operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
, which was released as OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
. Following a dispute, Microsoft severed the collaboration and IBM continued development of OS/2 on its own but it failed in the marketplace against Microsoft's Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
during the mid-1990s.
1990s–2000s
In 1991 IBM began spinning off its many divisions into autonomous subsidiaries (so-called "Baby Blues") in an attempt to make the company more manageable and to streamline IBM by having other investors finance those companies. These included AdStar, dedicated to disk drives and other data storage products; IBM Application Business Systems, dedicated to mid-range computers; IBM Enterprise Systems, dedicated to mainframes; Pennant Systems, dedicated to mid-range and large printers; Lexmark, dedicated to small printers; and more. Lexmark was acquired by Clayton & Dubilier in aleveraged buyout
A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition of a company using a significant proportion of borrowed money (Leverage (finance), leverage) to fund the acquisition with the remainder of the purchase price funded with private equity. The assets of t ...
shortly after its formation.
In September 1992, IBM completed the spin-off of its various non-mainframe and non-midrange, personal computer manufacturing divisions, combining them into an autonomous wholly-owned subsidiary known as the IBM Personal Computer Company (IBM PC Co.). This corporate restructuring came after IBM reported a sharp drop in profit margins during the second quarter of fiscal year 1992; market analysts attributed the drop to a fierce price war in the personal computer market over the summer of 1992. The corporate restructuring was one of the largest and most expensive in history up to that point. By the summer of 1993, the IBM PC Co. had divided into multiple business units itself, including Ambra Computer Corporation and the IBM Power Personal Systems Group, the former an attempt to design and market " clone" computers of IBM's own architecture and the latter responsible for IBM's PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
-based workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
s. IBM PC Co. introduced the ThinkPad
ThinkPad is a line of business-oriented laptop and Tablet computer, tablet computers produced since 1992. It was originally designed, created and manufactured by the American IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) Corporation. IBM Acquisit ...
clone computers, which IBM would heavily market and would eventually become one of the best-selling series of notebook computers.
In 1993, IBM posted an $8 billion loss – at the time the biggest in American corporate history. Lou Gerstner was hired as CEO from RJR Nabisco
R. J. Reynolds Nabisco, Inc., doing business as RJR Nabisco, was an American conglomerate, selling tobacco and food products, headquartered in the Calyon Building in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. R. J. Reynolds Nabisco stopped ...
to turn the company around. In 1995, IBM purchased Lotus Software
Lotus Software (called Lotus Development Corporation before its acquisition by IBM) was an American software company based in Massachusetts; it was sold to India's HCL Technologies in 2018.
Lotus is most commonly known for the Lotus 1-2-3 sprea ...
, best known for its Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles ...
spreadsheet software. During the decade, IBM was working on a new operating system, named the Workplace OS project. Despite a large amount of money spent on the project, it was cancelled in 1996.
 In 1998, IBM merged the enterprise-oriented Personal Systems Group of the IBM PC Co. into IBM's own Global Services personal computer consulting and customer service division. The resulting merged business units then became known simply as IBM Personal Systems Group. A year later, IBM stopped selling their computers at retail outlets after their market share in this sector had fallen considerably behind competitors
In 1998, IBM merged the enterprise-oriented Personal Systems Group of the IBM PC Co. into IBM's own Global Services personal computer consulting and customer service division. The resulting merged business units then became known simply as IBM Personal Systems Group. A year later, IBM stopped selling their computers at retail outlets after their market share in this sector had fallen considerably behind competitors Compaq
Compaq Computer Corporation was an American information technology, information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced some of the first IBM PC compati ...
and Dell
Dell Inc. is an American technology company that develops, sells, repairs, and supports personal computers (PCs), Server (computing), servers, data storage devices, network switches, software, computer peripherals including printers and webcam ...
. Immediately afterwards, the IBM PC Co. was dissolved and merged into IBM Personal Systems Group.
In 2002 IBM acquired PwC Consulting, the consulting arm of PwC
PricewaterhouseCoopers, also known as PwC, is a Multinational corporation, multinational professional services network based in London, United Kingdom.
It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is one of the Big Fo ...
which was merged into its IBM Global Services
IBM Consulting, rebranded in 2021 from IBM Global Business Services, is the professional services and consulting arm of IBM. It provides services to companies, global government organizations, Nonprofit organization, non-profits and Non-government ...
. On September 14, 2004, LG and IBM announced that their business alliance in the South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
n market would end at the end of that year. Both companies stated that it was unrelated to the charges of bribery earlier that year. Xnote was originally part of the joint venture and was sold by LG in 2012.
Continuing a trend started in the 1990s of downsizing its operations and divesting from commodity production, IBM sold all of its personal computer business to Chinese technology company Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, trading as Lenovo ( , zh, c=联想, p=Liánxiǎng), is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, personal computers, software, servers, conv ...
and, in 2009, it acquired software company SPSS Inc. Later in 2009, IBM's Blue Gene
Blue Gene was an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with relatively low power consumption.
The project created three generations of supercomputers, Blue Gene/L, Blue ...
supercomputing program was awarded the National Medal of Technology and Innovation
The National Medal of Technology and Innovation (formerly the National Medal of Technology) is an honor granted by the president of the United States to American inventors and innovators who have made significant contributions to the development ...
by U.S. President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
.
2010s–present
In 2011, IBM gained worldwide attention for its artificial intelligence program Watson, which was exhibited on ''Jeopardy!
''Jeopardy!'' is an American television game show created by Merv Griffin. The show is a quiz competition that reverses the traditional question-and-answer format of many quiz shows. Rather than being given questions, contestants are instead g ...
'' where it won against game-show champions Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter. The company also celebrated its 100th anniversary in the same year on June 16. In 2012, IBM announced it had agreed to buy Kenexa and Texas Memory Systems, and a year later it also acquired SoftLayer Technologies, a web hosting service
A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service that hosts websites for clients, i.e. it offers the facilities required for them to create and maintain a site and makes it accessible on the World Wide Web. Companies providing web h ...
, in a deal worth around $2 billion. Also that year, the company designed a video surveillance system for Davao City
Davao City, officially the City of Davao, is a City of the Philippines#Legal classification, highly urbanized city in the Davao Region, Philippines. The city has a total land area of , making it the List of Philippine cities and municipalities ...
.
In 2014 IBM announced it would sell its x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
server division to Lenovo for $2.1 billion. while continuing to offer Power ISA
Power ISA is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) currently developed by the OpenPOWER Foundation, led by IBM. It was originally developed by IBM and the now-defunct Power.org industry group. Power IS ...
-based servers. Also that year, IBM began announcing several major partnerships with other companies, including Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Comput ...
, Twitter, Facebook, Tencent
Tencent Holdings Ltd. ( zh, s=腾讯, p=Téngxùn) is a Chinese Multinational corporation, multinational technology Conglomerate (company), conglomerate and holding company headquartered in Shenzhen. It is one of the highest grossing multimed ...
, Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, s ...
, UnderArmour, Box
A box (plural: boxes) is a container with rigid sides used for the storage or transportation of its contents. Most boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides (typically rectangular prisms). Boxes can be very small (like a matchbox) or v ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
, VMware, CSC, Macy's
Macy's is an American department store chain founded in 1858 by Rowland Hussey Macy. The first store was located in Manhattan on Sixth Avenue between 13th and 14th Streets, south of the present-day flagship store at Herald Square on West 34 ...
, Sesame Workshop
Sesame Workshop (SW), originally known as the Children's Television Workshop (CTW), is an American nonprofit organization and Television station, television company that has been responsible for the production of several educational children's ...
, the parent company of Sesame Street
''Sesame Street'' is an American educational television, educational children's television series that combines live-action, sketch comedy, animation, and puppetry. It is produced by Sesame Workshop (known as the Children's Television Worksh ...
, and Salesforce.com.
In 2015, its chip division transitioned to a fabless
Fabless manufacturing is the design and sale of hardware devices and semiconductor chips while outsourcing their fabrication (or ''fab'') to a specialized manufacturer called a semiconductor foundry. These foundries are typically, but not exclu ...
model with semiconductors design, offloading manufacturing to GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company located in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD in March 2009, the ...
.
In 2015, IBM announced three major acquisitions: Merge Healthcare for $1 billion, data storage vendor Cleversafe, and all digital assets from The Weather Company, including Weather.com and The Weather Channel
The Weather Channel (TWC) is an American pay television television channel, channel owned by Weather Group, LLC, a subsidiary of Allen Media Group. The channel's headquarters are located in Atlanta, Georgia. Launched on May 2, 1982, the channel ...
mobile app. Also that year, IBM employees created the film '' A Boy and His Atom'', which was the first molecule movie to tell a story. In 2016, IBM acquired video conferencing service Ustream
IBM Watson Media (formerly Ustream and IBM Cloud Video) is an American virtual events platform company which is a division of IBM. Prior to the IBM acquisition, it had more than 180 employees across San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Budapest office ...
and formed a new cloud video unit. In April 2016, it posted a 14-year low in quarterly sales. The following month, Groupon
Groupon, Inc. is an American global e-commerce marketplace connecting subscribers with local merchants by offering activities, travel, goods and services in 13 countries. Based in Chicago, Groupon was launched there in November 2008, launching ...
sued IBM accusing it of patent infringement, two months after IBM accused Groupon of patent infringement in a separate lawsuit.
In 2015, IBM bought the digital part of The Weather Company, Truven Health Analytics for $2.6 billion in 2016, and in October 2018, IBM announced its intention to acquire Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
for $34 billion, which was completed on July 9, 2019.
In February 2020, IBM's John Kelly III joined Brad Smith of Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
to sign a pledge with the Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Geography
* Vatican City, an independent city-state surrounded by Rome, Italy
* Vatican Hill, in Rome, namesake of Vatican City
* Ager Vaticanus, an alluvial plain in Rome
* Vatican, an unincorporated community in the ...
to ensure the ethical use and practice of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
IBM announced in October 2020 that it would divest the Managed Infrastructure Services unit of its Global Technology Services division into a new public company. The new company, Kyndryl, will have 90,000 employees, 4,600 clients in 115 countries, with a backlog of $60 billion. IBM's spin-off was greater than any of its previous divestitures, and welcomed by investors. IBM appointed Martin Schroeter, who had been IBM's CFO from 2014 through the end of 2017, as CEO of Kyndryl.
In 2021, IBM announced the acquisition of the enterprise software company Turbonomic for $1.5 billion. In January 2022, IBM announced it would sell Watson Health to private equity firm Francisco Partners
Francisco Partners Management, L.P., doing business as Francisco Partners, is an American private equity firm focused exclusively on investments in technology and technology-enabled services businesses. It was founded in August 1999 and based in ...
.
On March 7, 2022, a few days after the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
, IBM CEO Arvind Krishna published a Ukrainian flag and announced that "we have suspended all business in Russia". All Russian articles were also removed from the IBM website. On June 7, Krishna announced that IBM would carry out an "orderly wind-down" of its operations in Russia.
In late 2022, IBM started a collaboration with new Japanese manufacturer Rapidus, which led GlobalFoundries to file a lawsuit against IBM the following year.
In 2023, IBM acquired Manta Software Inc. to complement its data and A.I. governance capabilities for an undisclosed amount. On November 16, 2023, IBM suspended ads on Twitter after ads were found next to pro-Nazi content.
In August 2023, IBM agreed to sell The Weather Company to Francisco Partners for an undisclosed sum. The sale was finalized on February 1, 2024, and the cost was disclosed as $1.1 billion, with $750 million in cash, $100 million deferred over seven years, and $250 million in contingent consideration.
In December 2023, IBM announced it would acquire Software AG's StreamSets and webMethods platforms for €2.13 billion ($2.33 billion).
Corporate affairs
Business trends
IBM's market capitalization was valued at over $153 billion as of May 2024. Despite its relative decline within the technology sector, IBM remains the seventh largest technology company by revenue, and 67th largest overall company by revenue in the United States. IBM ranked No. 38 on the 2020Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States Joint-stock company#Closely held corporations and publicly traded corporations, corporations by ...
rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. In 2014, IBM was accused of using "financial engineering" to hit its quarterly earnings targets rather than investing for the longer term.
The key trends of IBM are (as at the financial year ending December 31):
Board and shareholders
The company's 15-member board of directors are responsible for overall corporate management and includes the current or former CEOs ofAnthem
An anthem is a musical composition of celebration, usually used as a symbol for a distinct group, particularly the national anthems of countries. Originally, and in music theory and religious contexts, it also refers more particularly to sho ...
, Dow Chemical
The Dow Chemical Company is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Midland, Michigan, United States. The company was among the three largest chemical producers in the world in 2021. It is the operating subsidiary of Dow Inc., ...
, Johnson and Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and Medical device, medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publi ...
, Royal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company, headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New ...
, UPS, and Vanguard
The vanguard (sometimes abbreviated to van and also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force.
...
as well as the president of Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
and a retired U.S. Navy admiral. Vanguard Group is the largest shareholder of IBM and as of March 31, 2023, held 15.7% of total shares outstanding.
In 2011, IBM became the first technology company Warren Buffett
Warren Edward Buffett ( ; born August 30, 1930) is an American investor and philanthropist who currently serves as the chairman and CEO of the conglomerate holding company Berkshire Hathaway. As a result of his investment success, Buffett is ...
's holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the Security (finance), securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own Share ...
Berkshire Hathaway
Berkshire Hathaway Inc. () is an American multinational conglomerate holding company headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. Originally a textile manufacturer, the company transitioned into a conglomerate starting in 1965 under the management of c ...
invested in. Initially he bought 64 million shares costing $10.5 billion. Over the years, Buffett increased his IBM holdings, but by the end of 2017 had reduced them by 94.5% to 2.05 million shares; by May 2018, he was completely out of IBM.
Headquarters and offices
IBM is headquartered inArmonk, New York
Armonk is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Administrative divisions of New York#Town, town of North Castle, New York, North Castle, located in Westchester County, New York, United States. The corporate headquar ...
, a community north of Midtown Manhattan. A nickname for the company is the "Colossus of Armonk". Its principal building, referred to as CHQ, is a glass and stone edifice on a parcel amid a 432-acre former apple orchard the company purchased in the mid-1950s. There are two other IBM buildings within walking distance of CHQ: the North Castle office, which previously served as IBM's headquarters; and the Louis V. Gerstner, Jr., Center for Learning (formerly known as IBM Learning Center (ILC)), a resort hotel and training center, which has 182 guest rooms, 31 meeting rooms, and various amenities.
IBM operates in 174 countries , with mobility centers in smaller market areas and major campuses in the larger ones. In New York City, IBM has several offices besides CHQ, including the IBM Watson
IBM Watson is a computer system capable of answering questions posed in natural language. It was developed as a part of IBM's DeepQA project by a research team, led by principal investigator David Ferrucci. Watson was named after IBM's fou ...
headquarters at Astor Place
Astor Place is a street in NoHo/ East Village, in the lower part of the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is divided into two sections: One segment runs from Broadway in the west (just below East 8th Street) to Lafayette Street, an ...
in Manhattan. Outside of New York, major campuses in the United States include Austin, Texas
Austin ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Texas. It is the county seat and most populous city of Travis County, Texas, Travis County, with portions extending into Hays County, Texas, Hays and W ...
; Research Triangle Park (Raleigh-Durham), North Carolina; Rochester, Minnesota
Rochester is a city in Olmsted County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. It is located along rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a popul ...
; and Silicon Valley, California.
IBM's real estate holdings are varied and globally diverse. Towers occupied by IBM include 1250 René-Lévesque (Montreal, Canada) and One Atlantic Center (Atlanta, Georgia, US). In Beijing, China, IBM occupies Pangu Plaza, the city's seventh tallest building and overlooking Beijing National Stadium ("Bird's Nest"), home to the 2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and officially branded as Beijing 2008 (), were an international multisport event held from 8 to 24 August 2008, in Beijing, China. A total of 10,942 athletes fro ...
.
IBM India Private Limited is the Indian subsidiary of IBM, which is headquartered at Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
, Karnataka. It has facilities in Coimbatore
Coimbatore (Tamil: kōyamputtūr, ), also known as Kovai (), is one of the major Metropolitan cities of India, metropolitan cities in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Noyy ...
, Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and ...
, Kochi
Kochi ( , ), List of renamed Indian cities and states#Kerala, formerly known as Cochin ( ), is a major port city along the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea. It is part of the Ernakulam district, district of Ernakulam in the ...
, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
, Pune
Pune ( ; , ISO 15919, ISO: ), previously spelled in English as Poona (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1978), is a city in the state of Maharashtra in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan plateau in Western ...
, Gurugram
Gurgaon (), officially named Gurugram (), is a satellite city of Delhi and administrative headquarters of Gurgaon district, located in the northern Indian state of Haryana. It is situated near the Delhi–Haryana border, about southwest o ...
, Noida
Noida (), short for New Okhla Industrial Development Authority (ISO: ), is a city located in Gautam Buddha Nagar district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. As per provisional reports of Census of India, the population of Noida in 2011 was ...
, Bhubaneshwar, Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
, Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam (; List of renamed places in India, formerly known as Vizagapatam, and also referred to as Vizag, Visakha, and Waltair) is the largest and most populous metropolitan city in the States and union territories of India, Indian stat ...
, Hyderabad
Hyderabad is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. With an average altitude of , much ...
, Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
and Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (; ), also known as Tatanagar, is a major industrial city in eastern India. It is the List of cities in Jharkhand by population, largest city in the state of Jharkhand. With a population of 629,658 in the city limits and 1.3 million ...
.
Other notable buildings include the IBM Rome Software Lab (Rome, Italy), Hursley House (Winchester, UK), 330 North Wabash (Chicago, Illinois, United States), the Cambridge Scientific Center (Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States), the IBM Toronto Software Lab (Toronto, Canada), the IBM Building, Johannesburg (Johannesburg, South Africa), the IBM Building (Seattle) (Seattle, Washington, United States), the IBM Hakozaki Facility (Tokyo, Japan), the IBM Yamato Facility (Yamato, Japan), the IBM Canada Head Office Building (Ontario, Canada) and the Watson IoT Headquarters (Munich, Germany). Defunct IBM campuses include the IBM Somers Office Complex (Somers, New York), Spango Valley (Greenock, Scotland), and Tour Descartes (Paris, France). The company's contributions to industrial architecture and design include works by Marcel Breuer
Marcel Lajos Breuer ( ; 21 May 1902 – 1 July 1981) was a Hungarian-American modernist architect and furniture designer. He moved to the United States in 1937 and became a naturalized American citizen in 1944.
At the Bauhaus he designed the Was ...
, Eero Saarinen
Eero Saarinen (, ; August 20, 1910 – September 1, 1961) was a Finnish-American architect and industrial designer who created a wide array of innovative designs for buildings and monuments, including the General Motors Technical Center; the pa ...
, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
Ludwig Mies van der Rohe ( ; ; born Maria Ludwig Michael Mies; March 27, 1886August 17, 1969) was a German-American architect, academic, and interior designer. He was commonly referred to as Mies, his surname. He is regarded as one of the pionee ...
, I.M. Pei and Ricardo Legorreta. Van der Rohe's building in Chicago was recognized with the 1990 Honor Award from the National Building Museum.
Products
 IBM has a large and diverse portfolio of products and services. , these offerings fall into the categories of
IBM has a large and diverse portfolio of products and services. , these offerings fall into the categories of cloud computing
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for ...
, artificial intelligence, commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
, data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
and analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
, Internet of things
Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks. The IoT encompasse ...
(IoT), IT infrastructure
Information technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT) components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components (Computer hardware, computer and networking hardware and facilitie ...
, mobile, digital workplace and cybersecurity
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and networks from thr ...
.
Hardware
Mainframe computers
Since 1954, IBM sellsmainframe computers
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterpris ...
, the latest being the IBM z
IBM Z is a family name used by IBM for all of its z/Architecture mainframe computers.
In July 2017, with another generation of products, the official family was changed to IBM Z from IBM z Systems; the IBM Z family will soon include the newes ...
series. The most recent model, the IBM z17, was released in 2024.
Microprocessors
In 1990, IBM released the Power microprocessors, which were designed into many console gaming systems, includingXbox 360
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the Xbox (console), original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was officially unveiled on MTV on May 12, 2005, with detail ...
, PlayStation 3
The PlayStation 3 (PS3) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment (SCE). It is the successor to the PlayStation 2, and both are part of the PlayStation brand of consoles. The PS3 was first released on ...
, and Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's Wii U
The Wii U ( ) is a home video game console developed by Nintendo as the successor to the Wii. Released in late 2012, it is the first eighth-generation video game console and competed with Microsoft's Xbox One and Sony's PlayStation 4.
The W ...
. IBM Secure Blue is encryption hardware that can be built into microprocessors, and in 2014, the company revealed TrueNorth
A cognitive computer is a computer that hardwires artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into an integrated circuit that closely reproduces the behavior of the human brain. It generally adopts a neuromorphic engineering approach. ...
, a neuromorphic CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
and announced a $3 billion investment over the following five years to design a neural chip that mimics the human brain, with 10 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses, but that uses just 1 kilowatt of power. In 2016, the company launched all-flash arrays designed for small and midsized companies, which includes software for data compression, provisioning, and snapshots across various systems.
Quantum computing
In January 2019, IBM introduced its first commercial quantum computer: IBM Q System One. In March 2020, it was announced that IBM would build Europe's first quantum computer in Ehningen,Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. The center, operated by the Fraunhofer Society
The Fraunhofer Society () is a German publicly-owned research organization with 76institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science (as opposed to the Max Planck Society, which works primarily on Basic re ...
, was opened in 2024.
Software
Since 2009, IBM has ownedSPSS
SPSS Statistics is a statistical software suite developed by IBM for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and criminal investigation. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. Versi ...
, a software package used for statistical analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of ...
in the social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
s. IBM also owned The Weather Company, which provides weather forecasting and includes weather.com and Weather Underground, which was sold in 2024.
Cloud services
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud (formerly known as Bluemix) is a set of cloud computing services for business offered by the information technology company IBM.
Services
As of 2021, IBM Cloud contains more than 170 services including compute, storage, networkin ...
includes infrastructure as a service
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service model where a cloud services vendor provides computing resources such as storage, network, servers, and virtualization (which emulates computer hardware). This service frees users fr ...
(IaaS), software as a service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a cloud computing service model where the provider offers use of application software to a client and manages all needed physical and software resources. SaaS is usually accessed via a web application. Unlike o ...
(SaaS) and platform as a service
Platform as a service (PaaS) or application platform as a service (aPaaS) or platform-based service is a cloud computing service model where users provision, instantiate, run and manage a modular bundle of a computing platform and applications, w ...
(PaaS) offered through public, private and hybrid cloud delivery models. For instance, the IBM Bluemix PaaS enables developers to quickly create complex websites on a pay-as-you-go model. IBM SoftLayer is a dedicated server, managed hosting and cloud computing
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for ...
provider, which in 2011 reported hosting more than 81,000 servers for more than 26,000 customers. IBM also provides Cloud Data Encryption Services (ICDES), using cryptographic splitting to secure customer data.
In May 2022, IBM announced the company had signed a multi-year Strategic Collaboration Agreement with Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Amazon that provides Software as a service, on-demand cloud computing computing platform, platforms and Application programming interface, APIs to individuals, companies, and gover ...
to make a wide variety of IBM software available as a service on AWS Marketplace. Additionally, the deal includes both companies making joint investments that make it easier for companies to consume IBM's offering and integrate them with AWS, including developer training and software development for select markets.
Artificial intelligence
IBM Watson
IBM Watson is a computer system capable of answering questions posed in natural language. It was developed as a part of IBM's DeepQA project by a research team, led by principal investigator David Ferrucci. Watson was named after IBM's fou ...
is a technology platform that uses natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
and machine learning to reveal insights from large amounts of unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
. Watson was debuted in 2011 on the American game show ''Jeopardy!
''Jeopardy!'' is an American television game show created by Merv Griffin. The show is a quiz competition that reverses the traditional question-and-answer format of many quiz shows. Rather than being given questions, contestants are instead g ...
'', where it competed against champions Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter in a three-game tournament and won. Watson has since been applied to business, healthcare, developers, and universities. For example, IBM has partnered with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center to assist with considering treatment options for oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's Etymology, etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγ ...
patients and for doing melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
screenings. Several companies use Watson for call centers, either replacing or assisting customer service agents.
IBM also provides infrastructure for the New York City Police Department
The City of New York Police Department, also referred to as New York City Police Department (NYPD), is the primary law enforcement agency within New York City. Established on May 23, 1845, the NYPD is the largest, and one of the oldest, munic ...
through their IBM Cognos Analytics
IBM Cognos Analytics (aka ''Cognos Analytics'', formerly known as ''IBM Cognos Analytics with Watson'' and ''IBM Cognos Business Intelligence'') is a web-based integrated business intelligence suite by IBM. It provides a toolset for reporting, ...
to perform data visualizations of CompStat
CompStat (also written COMPSTAT) is a police management system created by the New York City Police Department in 1994 with assistance from the New York City Police Foundation. Today, variations of the system are used in police departments worldwid ...
crime data.
In June 2020, IBM announced that it was exiting the facial recognition business. In a letter to congress, IBM's Chief Executive Officer Arvind Krishna told lawmakers, "now is the time to begin a national dialogue on whether and how facial recognition technology should be employed by domestic law enforcement agencies."
In May 2023, IBM revealed Watsonx, a Generative AI toolkit that is powered by IBM's own Granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
models with option to use other publicly available LLMs. Watsonx has multiple services for training and fine tuning models based on confidential data. A year later, IBM open-sourced Granite code models and put them on Hugging Face
Hugging Face, Inc. is a French-American company based in List of tech companies in the New York metropolitan area, New York City that develops computation tools for building applications using machine learning. It is most notable for its Transf ...
for public use. In October 2024, IBM introduced Granite 3.0, an open-source large language model designed for enterprise AI applications.
Consulting
With 160,000 consultants globally as of 2024, IBM is one of the ten largest consulting companies in the world, with capabilities spanning strategy andmanagement consulting
Management consulting is the practice of providing consulting services to organizations to improve their performance or in any way to assist in achieving organizational objectives. Organizations may draw upon the services of management consultant ...
, experience design, technology and systems integration
System integration is defined in engineering as the process of bringing together the component sub-systems into one system (an aggregation of subsystems cooperating so that the system is able to deliver the overarching functionality) and ensuring ...
, and operations. IBM's consulting business was valued at $20 billion, as of 2024.
Research
 Research has been part of IBM since its founding, and its organized efforts trace their roots back to 1945, when the Watson Scientific Computing Laboratory was founded at
Research has been part of IBM since its founding, and its organized efforts trace their roots back to 1945, when the Watson Scientific Computing Laboratory was founded at Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
in New York City, converting a renovated fraternity house on Manhattan's West Side into IBM's first laboratory. Now, IBM Research
IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American Multinational corporation, multinational information technology company. IBM Research is headquartered at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York ...
constitutes the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 12 labs on 6 continents. IBM Research is headquartered at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in New York, and facilities include the Almaden lab in California, Austin lab in Texas, Australia lab in Melbourne, Brazil lab in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, China lab in Beijing and Shanghai, Ireland lab in Dublin, Haifa lab in Israel, India lab in Delhi and Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
, Tokyo lab, Zurichlab and Africa lab in Nairobi
Nairobi is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kenya. The city lies in the south-central part of Kenya, at an elevation of . The name is derived from the Maasai language, Maasai phrase , which translates to 'place of cool waters', a ...
.
In terms of investment, IBM's R&D expenditure totals several billion dollars each year. In 2012, that expenditure was approximately $6.9 billion. Recent allocations have included $1 billion to create a business unit for Watson in 2014, and $3 billion to create a next-gen semiconductor along with $4 billion towards growing the company's "strategic imperatives" (cloud, analytics, mobile, security, social) in 2015.
IBM has been a leading proponent of the Open Source Initiative
The Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a California public benefit corporation "actively involved in Open Source community-building, education, and public advocacy to promote awareness and the importance of non-proprietary software".
Governance
The ...
, and began supporting Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
in 1998. The company invests billions of dollars in services and software based on Linux through the IBM Linux Technology Center, which includes over 300 Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
developers. IBM has also released code under different open-source license
Open-source licenses are software licenses that allow content to be used, modified, and shared. They facilitate free and open-source software (FOSS) development. Intellectual property (IP) laws restrict the modification and sharing of creative ...
s, such as the platform-independent software framework
In computer programming, a software framework is a software abstraction that provides generic functionality which developers can extend with custom code to create applications. It establishes a standard foundation for building and deploying soft ...
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
(worth approximately $40 million at the time of the donation), the three-sentence International Components for Unicode ( ICU) license, and the Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
-based relational database management system
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
(RDBMS) Apache Derby
Apache Derby (previously distributed as IBM Cloudscape) is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by the Apache Software Foundation that can be embedded in Java programs and used for online transaction processing. It has a 3.5 ...
. IBM's open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
involvement has not been trouble-free, however (see '' SCO v. IBM'').
Famous invention
An invention is a unique or novelty (patent), novel machine, device, Method_(patent), method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It m ...
s and developments by IBM include: the automated teller machine (ATM), Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM), the electronic keypunch, the financial swap, the floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
, the hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
, the magnetic stripe card
The term digital card can refer to a physical item, such as a memory card on a camera, or, increasingly since 2017, to the digital content hosted
as a virtual card or cloud card, as a digital virtual representation of a physical card. They shar ...
, the relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
, RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
, the SABRE airline reservation system, SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced ''S-Q-L''; or alternatively as "sequel")
is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling s ...
, the Universal Product Code (UPC) bar code, and the virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
. Additionally, in 1990 company scientists used a scanning tunneling microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of scanning probe microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in ...
to arrange 35 individual xenon atoms to spell out the company acronym, marking the first structure assembled one atom at a time. A major part of IBM research is the generation of patents
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
. Since its first patent for a traffic signaling device, IBM has been one of the world's most prolific patent sources. In 2021, the company held the record for most patents
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
generated by a business for 29 consecutive years for the achievement.
Patents
As of 2021, IBM holds the record for most annualU.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
s generated by a business for 29 consecutive years.
In 2001, IBM became the first company to generate more than 3,000 patents in one year, beating this record in 2008 with over 4,000 patents. As of 2022, the company held 150,000 patents. IBM has also been criticized as being a patent troll.
Brand and reputation
 IBM is nicknamed ''Big Blue'' partly because of its blue logo and color scheme, and also in reference to its former ''de facto'' dress code of white shirts with blue suits. The company logo has undergone several changes over the years, with its current "8-bar" logo designed in 1972 by
IBM is nicknamed ''Big Blue'' partly because of its blue logo and color scheme, and also in reference to its former ''de facto'' dress code of white shirts with blue suits. The company logo has undergone several changes over the years, with its current "8-bar" logo designed in 1972 by graphic designer
A graphic designer is a practitioner who follows the discipline of graphic design, either within companies or organizations or independently. They are professionals in design and visual communication, with their primary focus on transforming ...
Paul Rand
Paul Rand (born Peretz Rosenbaum; August 15, 1914 – November 26, 1996) was an American art director and graphic designer. He was best known for his corporate logo designs, including the logos for IBM, United Parcel Service, UPS, Enron, Morni ...
. It was a general replacement for a 13-bar logo, since period photocopiers did not render narrow (as opposed to tall) stripes well. Aside from the logo, IBM used Helvetica
Helvetica, also known by its original name Neue Haas Grotesk, is a widely-used sans-serif typeface developed in 1957 by Swiss typeface designer Max Miedinger and Eduard Hoffmann.
Helvetica is a neo-grotesque design, one influenced by the f ...
as a corporate typeface for 50 years, until it was replaced in 2017 by the custom-designed IBM Plex.
IBM has a valuable brand as a result of over 100 years of operations and marketing campaigns. Since 1996, IBM has been the exclusive technology partner for the Masters Tournament
The Masters Tournament (usually referred to as simply the Masters, or as the U.S. Masters outside North America) is one of the four men's major championships in professional golf. Scheduled for the first full week in April, the Masters is the ...
, one of the four major championships in professional golf, with IBM creating the first Masters.org (1996), the first course cam (1998), the first iPhone
The iPhone is a line of smartphones developed and marketed by Apple that run iOS, the company's own mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then–Apple CEO and co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007, at ...
app with live streaming (2009), and first-ever live 4K Ultra High Definition feed in the United States for a major sporting event (2016). As a result, IBM CEO Ginni Rometty became the third female member of the Master's governing body, the Augusta National Golf Club. IBM is also a major sponsor in professional tennis, with engagements at the U.S. Open, Wimbledon
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* W ...
, the Australian Open, and the French Open. The company also sponsored the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
from 1960 to 2000, and the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
from 2003 to 2012. In Japan, IBM employees also have an American football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
team complete with pro stadium, cheerleaders and televised games, competing in the Japanese X-League as the " Big Blue".
Environmental
In 2004, concerns were raised related to IBM's contribution in its early days to pollution in its original location inEndicott, New York
Endicott is a Village (New York), village within the town of Union, New York, Union in Broome County, New York, United States. The population was 13,392 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Binghamton metropolitan area. The village is named after ...
. IBM reported its total CO2e emissions (direct and indirect) for the twelve months ending December 31, 2020 at 621 kilotons (-324 /-34.3% year-on-year).Alt URLIn February 2021, IBM committed to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2030.
Tax avoidance
In 2018, IBM along with 91 additional ''Fortune'' 500 companies had "paid an effective federal tax rate of 0% or less" as a result of Donald Trump´sTax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017
The Act to provide for reconciliation pursuant to titles II and V of the concurrent resolution on the budget for fiscal year 2018, , is a congressional revenue act of the United States originally introduced in Congress as the Tax Cuts and Jobs ...
.
People and culture
Employees

 IBM is among the world's largest employers, with over 297,900 employees worldwide in 2022, with about 160,000 of those being tech consultants.
IBM's leadership programs include Extreme Blue, an internship program, and the
IBM is among the world's largest employers, with over 297,900 employees worldwide in 2022, with about 160,000 of those being tech consultants.
IBM's leadership programs include Extreme Blue, an internship program, and the IBM Fellow
An IBM Fellow is a position at IBM appointed by the CEO. Typically only four to nine (eleven in 2014) IBM Fellows are appointed each year, in May or June. Fellow is the highest honor a scientist, engineer, or programmer at IBM can achieve.
Over ...
award, offered since 1963 based on technical achievement.
Notable current and former employees
Many IBM employees have achieved notability outside of work and after leaving IBM. In business, former IBM employees includeApple Inc.
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Comput ...
CEO Tim Cook
Timothy Donald Cook (born November 1, 1960) is an American business executive who is the current chief executive officer of Apple Inc. Cook had previously been the company's chief operating officer under its co-founder Steve Jobs. Cook joined ...
, former EDS CEO and politician Ross Perot
Henry Ross Perot ( ; June 27, 1930 – July 9, 2019) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive officer of Electronic Data Systems and Perot Systems. He ran an Independent politician ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
chairman John W. Thompson, SAP co-founder Hasso Plattner, Gartner
Gartner, Inc. is an American research and advisory firm focusing on business and technology topics. Gartner provides its products and services through research reports, conferences, and consulting. Its clients include large corporations, gover ...
founder Gideon Gartner, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) CEO Lisa Su, Cadence Design Systems
Cadence Design Systems, Inc. (stylized as cādence)Investor's Business DailCEO Lip-Bu Tan Molds Troubled Cadence Into Long-Term LeaderRetrieved November 12, 2020 is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology and computational ...
CEO Anirudh Devgan, former Citizens Financial Group CEO Ellen Alemany, former Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
chairman Alfred Amoroso, former AT&T
AT&T Inc., an abbreviation for its predecessor's former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the w ...
CEO C. Michael Armstrong, former Xerox Corporation
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduction of the Xerox ...
CEOs David T. Kearns and G. Richard Thoman, former Fair Isaac Corporation CEO Mark N. Greene, Citrix Systems co-founder Ed Iacobucci, ASOS.com chairman Brian McBride, former Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, trading as Lenovo ( , zh, c=联想, p=Liánxiǎng), is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, personal computers, software, servers, conv ...
CEO Steve Ward, and former Teradata
Teradata Corporation is an American software company that provides cloud database and Analytics, analytics-related software, products, and services. The company was formed in 1979 in Brentwood, California, as a collaboration between researchers a ...
CEO Kenneth Simonds
Kenneth Wayne Simonds (May 5, 1935 – October 11, 2009) was an American businessman and philanthropist.
Life
He began his career in 1958 at IBM and was the youngest IBM manager when promoted to Green Bay, Wisconsin, Green Bay, Wisconsin. He lef ...
.
In government, Patricia Roberts Harris served as United States Secretary of Housing and Urban Development
The United States secretary of housing and urban development is the head of the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development, a member of the Cabinet of the United States, and thirteenth in the presidential line of succession. T ...
, the first African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
woman
A woman is an adult female human. Before adulthood, a female child or Adolescence, adolescent is referred to as a girl.
Typically, women are of the female sex and inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and women with functi ...
to serve in the United States Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United States is the principal official advisory body to the president of the United States. The Cabinet generally meets with the president in Cabinet Room (White House), a room adjacent to the Oval Office in the West Wing of ...
. Samuel K. Skinner served as U.S. Secretary of Transportation and as the White House Chief of Staff
The White House chief of staff is the head of the Executive Office of the President of the United States, a position in the federal government of the United States.
The chief of staff is a Political appointments in the United States, politi ...
. Alumni also include U.S. Senators Mack Mattingly and Thom Tillis; Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
governor Scott Walker; former U.S. Ambassadors Vincent Obsitnik (Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
), Arthur K. Watson (France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
), and Thomas Watson Jr. (Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
); and former U.S. Representatives Todd Akin, Glenn Andrews
Arthur Glenn Andrews (January 15, 1909 – September 25, 2008) was an American politician and a United States representative from Alabama.
Biography
Andrews was born in Anniston in Calhoun County in North Alabama, a son of Roger Lee Andrews ...
, Robert Garcia, Katherine Harris
Katherine Harris (born April 5, 1957) is an American politician from Florida. A Republican, she served in the Florida Senate from 1994 to 1998, as Secretary of State of Florida from 1999 to 2002, and as a member of the United States House of Re ...
, Amo Houghton, Jim Ross Lightfoot, Thomas J. Manton, Donald W. Riegle Jr., and Ed Zschau.
Other former IBM employees include NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
astronaut Michael J. Massimino, Canadian astronaut and former Governor General Julie Payette
Julie Payette (; born October 20, 1963) is a Canadian engineer, scientist and former astronaut who served from 2017 to 2021 as Governor General of Canada, the List of governors general of Canada, 29th since Canadian Confederation.
Payette holds ...
, noted musician Dave Matthews, Harvey Mudd College president Maria Klawe, Western Governors University president emeritus Robert Mendenhall, former University of Kentucky
The University of Kentucky (UK, UKY, or U of K) is a Public University, public Land-grant University, land-grant research university in Lexington, Kentucky, United States. Founded in 1865 by John Bryan Bowman as the Agricultural and Mechanical ...
president Lee T. Todd Jr., former University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (U of I, UIowa, or Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized int ...
president Bruce Harreld, NFL referee Bill Carollo, former Rangers F.C. chairman John McClelland, and recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature
The Nobel Prize in Literature, here meaning ''for'' Literature (), is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in ...
J. M. Coetzee
John Maxwell Coetzee Order of Australia, AC Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature, FRSL Order of Mapungubwe, OMG (born 9 February 1940) is a South African and Australian novelist, essayist, linguist, and translator. The recipient of the 2003 ...
. Thomas Watson Jr. also served as the 11th national president of the Boy Scouts of America
Scouting America is the largest scouting organization and one of the largest List of youth organizations, youth organizations in the United States, with over 1 million youth, including nearly 200,000 female participants. Founded as the Boy Sco ...
.
Five IBM employees have received the Nobel Prize: Leo Esaki, of the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, N.Y., in 1973, for work in semiconductors; Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer
Heinrich Rohrer (6 June 1933 – 16 May 2013) was a Swiss physicist who shared half of the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics with Gerd Binnig for the design of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM). The other half of the Prize was awarded to Ernst R ...
, of the Zurich Research Center, in 1986, for the scanning tunneling microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of scanning probe microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in ...
; and Georg Bednorz and Alex Müller, also of Zurich, in 1987, for research in superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ord ...
. Six IBM employees have won the Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in the fi ...
, including the first female recipient Frances E. Allen. Ten National Medals of Technology (USA) and five National Medals of Science (USA) have been awarded to IBM employees.
Workplace culture
Employees are often referred to as "IBMers". IBM's culture has evolved significantly over its century of operations. In its early days, a dark (or gray) suit, white shirt, and a "sincere" tie constituted the public uniform for IBM employees. During IBM's management transformation in the 1990s, CEO Louis V. Gerstner Jr. relaxed these codes, normalizing the dress and behavior of IBM employees. The company's culture has also given to different plays on the company acronym (IBM), with some saying it stands for "I've Been Moved," based on frequent relocations, others saying it stands for "I'm By Myself" pursuant to a prevalent work-from-anywhere norm, and others saying it stands for "I'm Being Mentored" in reference to the company's open door policy and encouragement for mentoring at all levels. The company has traditionally resisted labor union organizing, although unions represent some IBM workers outside the United States.Leadership
President
# Thomas J. Watson, 1911–1949 # John George Phillips, 1949–1951 # Thomas J. Watson Jr., 1951–1961 # Albert Lynn Williams, 1961–1966 # T. Vincent Learson, 1966–1971 # Frank T. Cary, 1971–1974 # John R. Opel, 1974–1983 # John Fellows Akers, 1983–1989 # Jack Kuehler, 1989– # Samuel J. Palmisano, 2000–2012 # Ginni Rometty, 2012–2020 #Arvind Krishna
Arvind Krishna (born November 23, 1962) is an American business executive, and the chairman and CEO of IBM. He has been CEO of IBM since April 2020 and chairman since January 2021. Arvind began his career at IBM in 1990, at its Thomas J. Watso ...
, 2020–present
Chairman of the Board
# George Winthrop Fairchild, 1915–1949 # Thomas J. Watson, 1949–1961 # Thomas J. Watson Jr., 1961–1971 # T. Vincent Learson, 1971–1972 # Frank T. Cary, 1972–1983 # John R. Opel, 1983–1986 # John Fellows Akers, 1986–1993 # Lou Gerstner, 1993–2002 # Samuel J. Palmisano, 2003–2012 # Ginni Rometty, 2012–2020 #Arvind Krishna
Arvind Krishna (born November 23, 1962) is an American business executive, and the chairman and CEO of IBM. He has been CEO of IBM since April 2020 and chairman since January 2021. Arvind began his career at IBM in 1990, at its Thomas J. Watso ...
, 2020–present
See also
* List of electronics brands *List of largest Internet companies
This is a list of Internet companies by revenue and market capitalization. The list is limited to dot-com companies, defined as a company that does the majority of its business on the Internet, with annual revenues exceeding US$1 billion. It excl ...
* List of largest manufacturing companies by revenue
* Tech companies in the New York City metropolitan region
* Top 100 US Federal Contractors
The Top 100 Contractors Report (TCR 100) is a list developed annually by the General Services Administration as part of its tracking of U.S. federal government procurement. It features the "Top 100" contractors with the U.S. government.
In 20 ...
* Quantum Energy Teleportation using IBM superconducting computers
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * . * * * * *External links
* * * {{Portalbar, Companies, Telecommunication, Electronics, Technology 1911 establishments in New York (state) Technology companies established in 1911 American companies established in 1911 Cloud computing providers Collier Trophy recipients Companies based in Westchester County, New York Companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average Companies in the Dow Jones Global Titans 50 Companies in the S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats Companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange Computer companies of the United States Computer hardware companies Computer systems companies Data companies Data quality companies Display technology companies Electronics companies of the United States Information technology consulting firms of the United States Multinational companies headquartered in the United States National Medal of Technology recipients Outsourcing companies Point of sale companies Software companies based in New York (state) Storage Area Network companies Software companies of the United States International information technology consulting firms Tax avoidance in the United States