Hydrolysation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
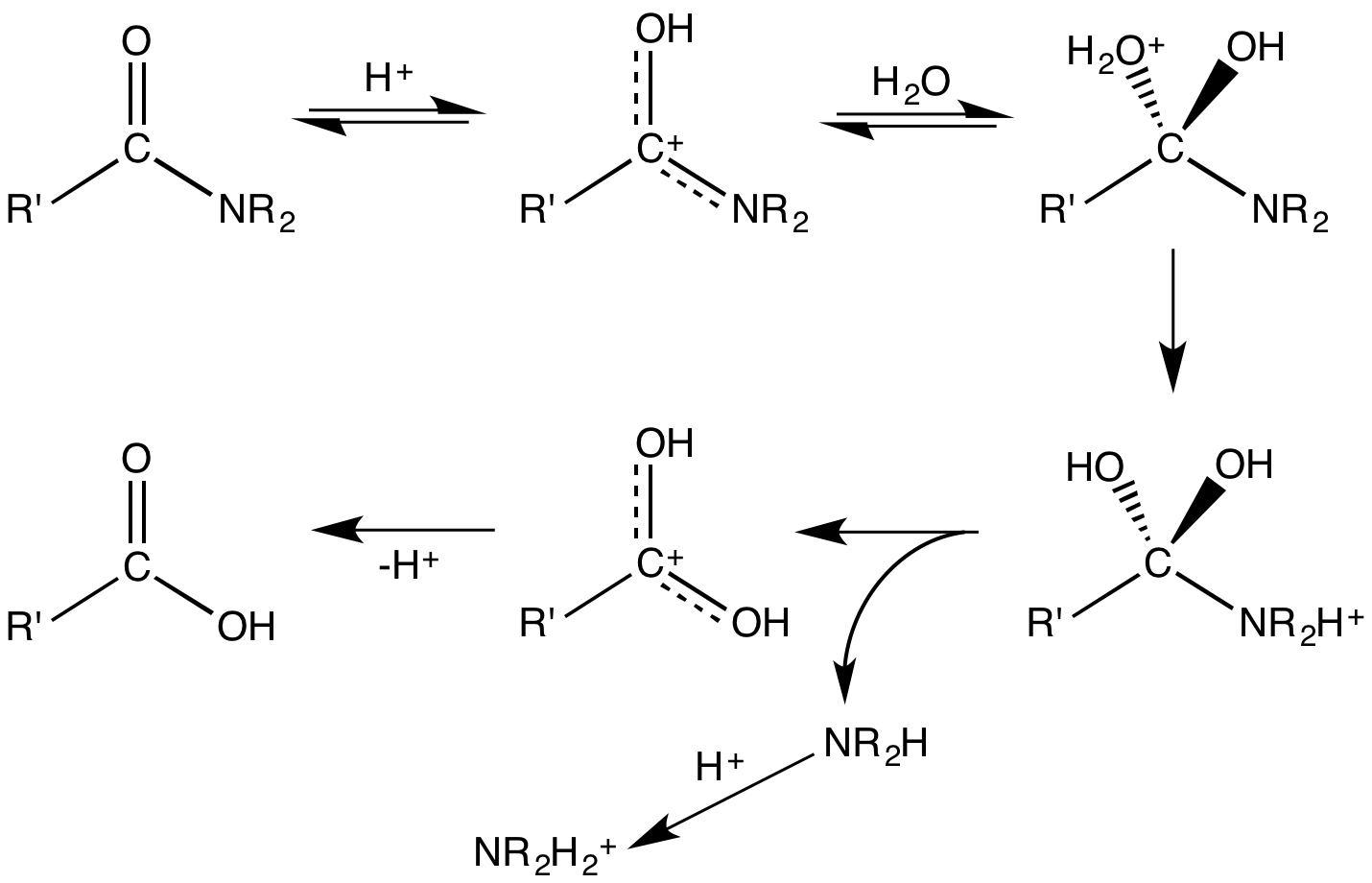 Upon hydrolysis, an amide converts into a
Upon hydrolysis, an amide converts into a
ATP + H2O -> ADP + P_
Secondly, the removal of a terminal diphosphate to yield adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate. The latter usually undergoes further cleavage into its two constituent phosphates. This results in biosynthesis reactions, which usually occur in chains, that can be driven in the direction of synthesis when the phosphate bonds have undergone hydrolysis.

M(H2O)_\mathit^ + H2O <=> M(H2O)_(OH)^ + H3O+
Thus the aqua
 Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution
Substitution may refer to:
Arts and media
*Chord substitution, in music, swapping one chord for a related one within a chord progression
* Substitution (poetry), a variation in poetic scansion
* "Substitution" (song), a 2009 song by Silversun Pi ...
, elimination
Elimination may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Elimination reaction, an organic reaction in which two functional groups split to form an organic product
*Bodily waste elimination, discharging feces, urine, or foreign substances from the bo ...
, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
.
Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
being broken down into glucose and fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
), this is recognized as saccharification.
Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water.
Types
Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In such reactions, one fragment of the target molecule (or parent molecule) gains a hydrogen ion. It breaks a chemical bond in the compound.Salts
A common kind of hydrolysis occurs when a salt of a weak acid or weak base (or both) is dissolved in water. Water spontaneously ionizes into hydroxide anions and hydronium cations. The salt also dissociates into its constituent anions and cations. For example, sodium acetate dissociates in water into sodium andacetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" als ...
ions. Sodium ions react very little with the hydroxide ions whereas the acetate ions combine with hydronium ions to produce acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
. In this case the net result is a relative excess of hydroxide ions, yielding a basic solution.
Strong acids also undergo hydrolysis. For example, dissolving sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
() in water is accompanied by hydrolysis to give hydronium and bisulfate, the sulfuric acid's conjugate base. For a more technical discussion of what occurs during such a hydrolysis, see Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.
Esters and amides
Acid–base-catalysed hydrolyses are very common; one example is the hydrolysis of amides or esters. Their hydrolysis occurs when thenucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
(a nucleus-seeking agent, e.g., water or hydroxyl ion) attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group of the ester or amide. In an aqueous base, hydroxyl ions are better nucleophiles than polar molecules such as water. In acids, the carbonyl group becomes protonated, and this leads to a much easier nucleophilic attack. The products for both hydrolyses are compounds with carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
groups.
Perhaps the oldest commercially practiced example of ester hydrolysis is saponification (formation of soap). It is the hydrolysis of a triglyceride (fat) with an aqueous base such as sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
(NaOH). During the process, glycerol is formed, and the fatty acids react with the base, converting them to salts. These salts are called soaps, commonly used in households.
In addition, in living systems, most biochemical reactions (including ATP hydrolysis) take place during the catalysis of enzymes. The catalytic action of enzymes allows the hydrolysis of proteins, fats, oils, and carbohydrates. As an example, one may consider proteases (enzymes that aid digestion by causing hydrolysis of peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
s in proteins). They catalyze the hydrolysis of interior peptide bonds in peptide chains, as opposed to exopeptidases (another class of enzymes, that catalyze the hydrolysis of terminal peptide bonds, liberating one free amino acid at a time).
However, proteases do not catalyze the hydrolysis of all kinds of proteins. Their action is stereo-selective: Only proteins with a certain tertiary structure are targeted as some kind of orienting force is needed to place the amide group in the proper position for catalysis. The necessary contacts between an enzyme and its substrates (proteins) are created because the enzyme folds in such a way as to form a crevice into which the substrate fits; the crevice also contains the catalytic groups. Therefore, proteins that do not fit into the crevice will not undergo hydrolysis. This specificity preserves the integrity of other proteins such as hormones, and therefore the biological system continues to function normally.
 Upon hydrolysis, an amide converts into a
Upon hydrolysis, an amide converts into a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
and an amine or ammonia (which in the presence of acid are immediately converted to ammonium salts). One of the two oxygen groups on the carboxylic acid are derived from a water molecule and the amine (or ammonia) gains the hydrogen ion. The hydrolysis of peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
gives amino acids.
Many polyamide polymers such as nylon 6,6 hydrolyze in the presence of strong acids. The process leads to depolymerization. For this reason nylon products fail by fracturing when exposed to small amounts of acidic water. Polyesters are also susceptible to similar polymer degradation reactions. The problem is known as environmental stress cracking
Environmental Stress Cracking (ESC) is one of the most common causes of unexpected brittle failure of thermoplastic (especially amorphous) polymers known at present. According to ASTM D883, stress cracking is defined as "an external or intern ...
.
ATP
Hydrolysis is related to energy metabolism and storage. All living cells require a continual supply of energy for two main purposes: thebiosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. ...
of micro and macromolecules, and the active transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes. The energy derived from the oxidation of nutrients is not used directly but, by means of a complex and long sequence of reactions, it is channeled into a special energy-storage molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The ATP molecule contains pyrophosphate linkages (bonds formed when two phosphate units are combined) that release energy when needed. ATP can undergo hydrolysis in two ways: Firstly, the removal of terminal phosphate to form adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbon ...
(ADP) and inorganic phosphate, with the reaction:
: Polysaccharides
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek ''monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water-solub ...
s can be linked together by glycosidic bonds, which can be cleaved by hydrolysis. Two, three, several or many monosaccharides thus linked form disaccharides, trisaccharide
''Trisaccharides'' are oligosaccharides composed of three monosaccharides with two glycosidic bonds connecting them. Similar to the disaccharides, each glycosidic bond can be formed between any hydroxyl group on the component monosaccharides. Even ...
s, oligosaccharides, or polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s, respectively. Enzymes that hydrolyze glycosidic bonds are called " glycoside hydrolases" or "glycosidases".
The best-known disaccharide is sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
(table sugar). Hydrolysis of sucrose yields glucose and fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
. Invertase is a sucrase Sucrase is a digestive enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose to its subunits fructose and glucose. One form, sucrase-isomaltase, is secreted in the small intestine on the brush border. The sucrase enzyme invertase, which occurs more commo ...
used industrially for the hydrolysis of sucrose to so-called invert sugar. Lactase is essential for digestive hydrolysis of lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix '' - ...
in milk; many adult humans do not produce lactase and cannot digest the lactose in milk.
The hydrolysis of polysaccharides to soluble sugars can be recognized as saccharification. Malt made from barley is used as a source of β-amylase to break down starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
into the disaccharide maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two- ...
, which can be used by yeast to produce beer. Other amylase enzymes may convert starch to glucose or to oligosaccharides. Cellulose is first hydrolyzed to cellobiose
Cellobiose is a disaccharide with the formula (C6H7(OH)4O)2O. It is classified as a reducing sugar. In terms of its chemical structure, it is derived from the condensation of a pair of β-glucose molecules forming a β(1→4) bond. It can be hyd ...
by cellulase and then cellobiose is further hydrolyzed to glucose by beta-glucosidase. Ruminants such as cows are able to hydrolyze cellulose into cellobiose and then glucose because of symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
bacteria that produce cellulases.
Metal aqua ions
Metal ions areLewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s, and in aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
they form metal aquo complexes of the general formula . The aqua ions undergo hydrolysis, to a greater or lesser extent. The first hydrolysis step is given generically as
:cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s behave as acids in terms of Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory. This effect is easily explained by considering the inductive effect of the positively charged metal ion, which weakens the bond of an attached water molecule, making the liberation of a proton relatively easy.
The dissociation constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (K_D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex fa ...
, pKa, for this reaction is more or less linearly related to the charge-to-size ratio of the metal ion. Ions with low charges, such as are very weak acids with almost imperceptible hydrolysis. Large divalent ions such as , , and have a pKa of 6 or more and would not normally be classed as acids, but small divalent ions such as undergo extensive hydrolysis. Trivalent ions like and are weak acids whose pKa is comparable to that of acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
. Solutions of salts such as or in water are noticeably acidic; the hydrolysis can be suppressed by adding an acid such as nitric acid, making the solution more acidic.
Hydrolysis may proceed beyond the first step, often with the formation of polynuclear species via the process of olation In inorganic chemistry, olation is the process by which metal ions form polymeric oxides in aqueous solution. The phenomenon is important for understanding the relationship between metal aquo complexes and metal oxides, which are represented by ma ...
. Some "exotic" species such as are well characterized. Hydrolysis tends to proceed as pH rises leading, in many cases, to the precipitation of a hydroxide such as or . These substances, major constituents of bauxite, are known as laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
s and are formed by leaching from rocks of most of the ions other than aluminium and iron and subsequent hydrolysis of the remaining aluminium and iron.
Mechanism strategies
Acetals, imines, and enamines can be converted back intoketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
s by treatment with excess water under acid-catalyzed conditions: ; ; .
See also
* Acid hydrolysis * Adenosine triphosphate * Alkaline hydrolysis (body disposal) *Catabolism
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipids, ...
* Condensation reaction
* Dehydration reaction
* Hydrolysis constant
* Inhibitor protein
The inhibitor protein (IP) is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and protects the cell against rapid ATP hydrolysis during momentary ischaemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ ...
* Polymer degradation
* Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called protease ...
* Saponification
* Sol–gel polymerisation
* Solvolysis
* Thermal hydrolysis
References
{{Authority control Chemical reactions Equilibrium chemistry