|
Equilibrium Chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid–base, host–guest, metal–complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria. Thermodynamic equilibrium A chemical system is said to be in equilibrium when the quantities of the chemical entities involved do not and ''cannot'' change in time without the application of an external influence. In this sense a system in chemical equilibrium is in a stable state. The system at chemical equilibrium will be at a constant temperature, pressure or volume and a composition. It will be insulated from exchange of heat with the surroundings, that is, it is a closed system. A change of te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both the reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time, so that there is no observable change in the properties of the system. This state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but they are equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactants and products. Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium. Historical introduction The concept of chemical equilibrium was developed in 1803, after Berthollet found that some chemical reactions are reversible. For any reaction mixture to exist at equilibrium, the rates of the forward and backward (reverse) reactions must be equal. In the following chemical equation, arrows point both ways to indicate equilibrium. A and B are reactant chemical species, S and T are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decay Chain
In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to a series of radioactive decays of different radioactive decay products as a sequential series of transformations. It is also known as a "radioactive cascade". Most radioisotopes do not decay directly to a stable state, but rather undergo a series of decays until eventually a stable isotope is reached. Decay stages are referred to by their relationship to previous or subsequent stages. A ''parent isotope'' is one that undergoes decay to form a ''daughter isotope''. One example of this is uranium (atomic number 92) decaying into thorium (atomic number 90). The daughter isotope may be stable or it may decay to form a daughter isotope of its own. The daughter of a daughter isotope is sometimes called a ''granddaughter isotope''. The time it takes for a single parent atom to decay to an atom of its daughter isotope can vary widely, not only between different parent-daughter pairs, but also randomly between identical pairings of parent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
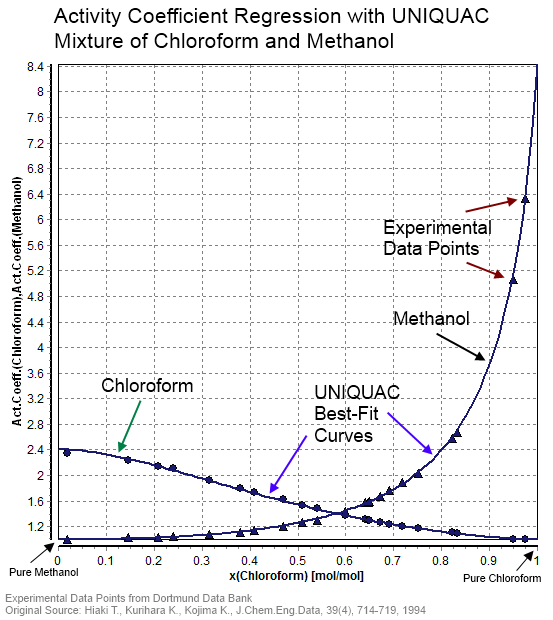
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given by :\mu_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Quotient
In chemical thermodynamics, the reaction quotient (''Q''r or just ''Q'') is a dimensionless quantity that provides a measurement of the relative amounts of products and reactants present in a reaction mixture for a reaction with well-defined overall stoichiometry, at a particular point in time. Mathematically, it is defined as the ratio of the activities (or molar concentrations) of the product species over those of the reactant species involved in the chemical reaction, taking stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction into account as exponents of the concentrations. In equilibrium, the reaction quotient is constant over time and is equal to the equilibrium constant. A general chemical reaction in which ''α'' moles of a reactant A and ''β'' moles of a reactant B react to give ''ρ'' moles of a product R and ''σ'' moles of a product S can be written as :\it \alpha\,\rm A + \it \beta\,\rm B \it \rho\,\rm R + \it \sigma\,\rm S. The reaction is written as an equilibrium even t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard State
In chemistry, the standard state of a material (pure substance, mixture or solution) is a reference point used to calculate its properties under different conditions. A superscript circle ° (degree symbol) or a Plimsoll (⦵) character is used to designate a thermodynamic quantity in the standard state, such as change in enthalpy (Δ''H''°), change in entropy (Δ''S''°), or change in Gibbs free energy (Δ''G''°). The degree symbol has become widespread, although the Plimsoll is recommended in standards, see discussion about typesetting below. In principle, the choice of standard state is arbitrary, although the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends a conventional set of standard states for general use. The standard state should not be confused with standard temperature and pressure (STP) for gases, nor with the standard solutions used in analytical chemistry. STP is commonly used for calculations involving gases that approximate an ideal gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Constant
The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol or . It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, i.e. the pressure–volume product, rather than energy per temperature increment per ''particle''. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation. The gas constant is the constant of proportionality that relates the energy scale in physics to the temperature scale and the scale used for amount of substance. Thus, the value of the gas constant ultimately derives from historical decisions and accidents in the setting of units of energy, temperature and amount of substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity (symbol ) is a measure of the "effective concentration" of a species in a mixture, in the sense that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution. The term "activity" in this sense was coined by the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis in 1907. By convention, activity is treated as a dimensionless quantity, although its value depends on customary choices of standard state for the species. The activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solid or liquids) is normally taken as unity (the number 1). Activity depends on temperature, pressure and composition of the mixture, among other things. For gases, the activity is the effective partial pressure, and is usually referred to as fugacity. The difference between activity and other measures of concentration arises because the interactions between different types of molecules in non-ideal gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometric Coefficient
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and chemical formulas. The reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between the entities in both the reactants and the products, and an arrow that points towards the products to show the direction of the reaction. The chemical formulas may be symbolic, structural (pictorial diagrams), or intermixed. The coefficients next to the symbols and formulas of entities are the absolute values of the stoichiometric numbers. The first chemical equation was diagrammed by Jean Beguin in 1615. Structure A chemical equation (see an example below) consists of a list of reactants (the starting substances) on the left-hand side, an arrow symbol, and a list of products (substances formed in the chemical reaction) on the right-hand side. Each substance is specified by its chemical formula, optionally preceded by a number called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
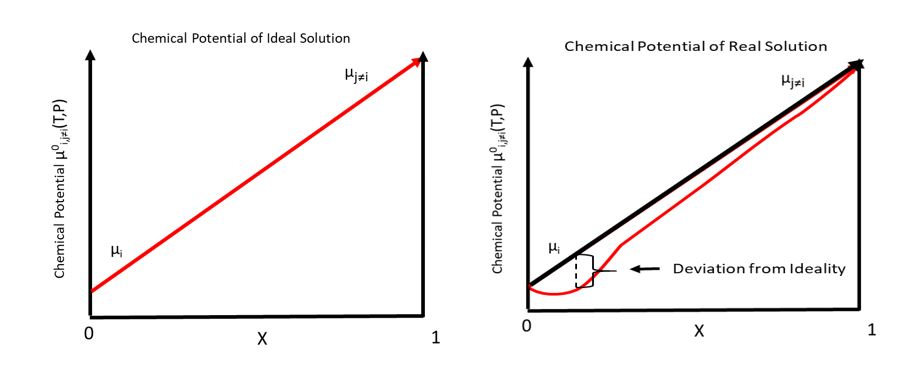
Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum. In a system in diffusion equilibrium, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work required to establish the system's physical dimensions, i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; bond, lattice, solvation and other "energies" in chemistry are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure, and volume, not on the path taken to achieve it. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for enthalpy is the joule. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Solution
In chemistry, an ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution that exhibits thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of mixing is zero as is the volume change on mixing by definition; the closer to zero the enthalpy of mixing is, the more "ideal" the behavior of the solution becomes. The vapor pressures of the solvent and solute obey Raoult's law and Henry's law, respectively, and the activity coefficient (which measures deviation from ideality) is equal to one for each component. The concept of an ideal solution is fundamental to chemical thermodynamics and its applications, such as the explanation of colligative properties. Physical origin Ideality of solutions is analogous to ideality for gases, with the important difference that intermolecular interactions in liquids are strong and cannot simply be neglected as they can for ideal gases. Instead we assume that the mean strength of the interactions are the same between all the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |