
The history of the Roman Empire covers the
history of ancient Rome from the fall of the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingd ...
in 27 BC until the abdication of
Romulus Augustulus in AD 476 in the West, and the
Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had beg ...
in the East in AD 1453. Ancient Rome became a territorial empire while still a republic, but was then ruled by
Roman emperors beginning with
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
(), becoming the Roman Empire following the death of the last republican
dictator
A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a small clique. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in ti ...
, the first emperor's adoptive father
Julius Caesar.
Rome had begun expanding shortly after the founding of the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingd ...
in the 6th century BC, though it did not expand outside the
Italian Peninsula until the 3rd century BC. Civil war engulfed the Roman state in the mid 1st century BC, first between Julius Caesar and
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, and finally between
Octavian and
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the ...
. Antony was defeated at the
Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ne ...
in 31 BC. In 27 BC, the
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
made Octavian ''
imperator'' ("commander") thus beginning the
Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate ...
, the first epoch of Roman imperial history usually dated from 27 BC to AD 284; they later awarded him the name Augustus, "the venerated". Subsequent emperors all took this name as the imperial title ''
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
''.
The success of Augustus in establishing principles of dynastic succession was limited by his outliving a number of talented potential heirs; the
Julio-Claudian dynasty
, native_name_lang= Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type=Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estat ...
lasted for four more emperors—
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
,
Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanic ...
,
Claudius, and
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unt ...
—before it yielded in AD 69 to the strife-torn
Year of the Four Emperors
The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from ...
, from which
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Em ...
emerged as victor. Vespasian became the founder of the brief
Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
, to be followed by the
Nerva–Antonine dynasty which produced the "
Five Good Emperors
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
5, five or number 5 may also refer to:
* AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era
* 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era
Literature
* ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram
* ''5'' (comics), an awa ...
":
Nerva,
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
,
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman '' municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispan ...
,
Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
and the philosophically inclined
Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
. In the view of the Greek historian
Dio Cassius, a contemporary observer, the accession of the emperor
Commodus in AD 180 marked the descent "from a kingdom of gold to one of rust and iron"—a famous comment which has led some historians, notably
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is ...
, to take Commodus' reign as the beginning of the
decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
.
In 212, during the reign of
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor ...
,
Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
was granted to all freeborn inhabitants of the Empire. Despite this gesture of universality, the
Severan dynasty was tumultuous—an emperor's reign was ended routinely by his murder or execution—and following its collapse, the Roman Empire was engulfed by the
Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensi ...
, a period of invasions, civil strife, economic disorder, and epidemic disease. In defining
historical epochs, this crisis is typically viewed as marking the start of the
Later Roman Empire,
and also the transition from
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
to
Late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
. In the reign of
Philip the Arab
Philip the Arab ( la, Marcus Julius Philippus "Arabs"; 204 – September 249) was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. He was born in Aurantis, Arabia, in a city situated in modern-day Syria. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Phili ...
(), Rome celebrated the thousandth anniversary of her founding by
Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and Remus (, ) are twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the founding of the city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his fratricide of Remus. The image of a she-wolf sucklin ...
with the
Saecular Games.
Diocletian () restored stability to the empire, modifying the role of ''princeps'' and becoming the first emperor to be addressed by
Roman citizens as ''domine'', "master" or "lord" or referred to as ''dominus noster'' "our lord". Diocletian's reign also brought the Empire's most concerted effort against the perceived threat of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, the
"Great Persecution". The state of
absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constituti ...
that began with Diocletian endured until the fall of the
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
in 1453.
Diocletian divided the empire into four regions, each ruled by an emperor (the
Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
). Confident that he fixed the disorders plaguing Rome, he abdicated along with his co-''augustus'', and the Tetrarchy eventually collapsed in the
civil wars of the Tetrarchy
The Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy were a series of conflicts between the co-emperors of the Roman Empire, starting in 306 AD with the usurpation of Maxentius and the defeat of Severus and ending with the defeat of Licinius at the hands of C ...
. Order was eventually restored by the victories of
Constantine, who became the first emperor to
convert to Christianity, and who founded
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
as a new capital for the empire after defeating his co-emperor
Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan, AD 313, that granted official toleration to ...
. The reign of
Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
, who under the influence of his adviser
Mardonius attempted to restore
Classical Roman and
Hellenistic religion
The concept of Hellenistic religion as the late form of Ancient Greek religion covers any of the various systems of beliefs and practices of the people who lived under the influence of ancient Greek culture during the Hellenistic period and the ...
, only briefly interrupted the succession of Christian emperors of the
Constantinian dynasty
The Constantinian dynasty is an informal name for the ruling family of the Roman Empire from Constantius Chlorus (died 306) to the death of Julian in 363. It is named after its most famous member, Constantine the Great, who became the sole ruler ...
. During the decades of the
Valentinianic and
Theodosian dynasties, the established practice of multiple emperors was continued.
Theodosius I, the last emperor to rule over both the
Eastern empire and the whole
Western empire, died in AD 395 after making Christianity the
official religion of the Empire.
The Western Roman Empire began to
disintegrate
Disintegration or disintegrate may refer to:
Music Albums
* ''Disintegrate'' (Zyklon album) or the title song, 2006
* ''Disintegration'' (The Cure album) or the title song, 1989
* ''Disintegration'', by I've Sound, 2002
Songs
* "Disintegrate ...
in the early 5th century as the
Germanic migrations and invasions of the
Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
overwhelmed the capacity of the Empire to assimilate the immigrants and fight off the invaders.
Most chronologies place the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476, when
Romulus Augustulus was
forced to abdicate to the Germanic warlord
Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustu ...
. By placing himself under the rule of the eastern emperor
Zeno, rather than naming himself or a puppet ruler as emperor, as other Germanic chiefs, had done, Odoacer ended the separate Roman government of the Western empire. The Eastern empire exercised diminishing control over the west over the course of the next century. The empire in the east—known today as the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, but referred to in its time as the "Roman Empire" or by various other names—ended in 1453 with the death of
Constantine XI and the
fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had beg ...
to the
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
.
27 BC–AD 14: Augustus
 Octavian
Octavian, the grandnephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar, had made himself a central military figure during the chaotic period following
Caesar's assassination. In 43 BC, at the age of twenty he became one of the three members of the
Second Triumvirate, a political alliance with
Marcus Lepidus
Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (; c. 89 BC – late 13 or early 12 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who formed the Second Triumvirate alongside Octavian and Mark Antony during the final years of the Roman Republic. Lepidus had previously be ...
and
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the ...
. Octavian and Antony defeated the last of Caesar's assassins in 42 BC at the
Battle of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Wars of the Second Triumvirate between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, at ...
, although after this point tensions began to rise between the two. The triumvirate ended in 32 BC, torn apart by the competing ambitions of its members: Lepidus was forced into exile and Antony, who had allied himself with his lover Queen
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. ...
of
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, committed suicide in 30 BC following his defeat at the
Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ne ...
(31 BC) by the fleet of Octavian. Octavian subsequently annexed Egypt to the empire.
Now sole ruler of Rome, Octavian began a full-scale reformation of military, fiscal and political matters. The
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
granted him power over appointing its membership and several successive
consulship
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the '' cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which polit ...
s, allowing him to operate within the existing constitutional machinery and thus reject titles that Romans associated with monarchy, such as ''rex'' ("king"). The
dictatorship
A dictatorship is a form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, which holds governmental powers with few to no limitations on them. The leader of a dictatorship is called a dictator. Politics in a dictatorship a ...
, a military office in the early Republic typically lasting only for the six-month military campaigning season, had been resurrected first by
Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla ha ...
in the late 80s BC and then by Julius Caesar in the mid-40s; the title ''dictator'' was never again used. As the adopted heir of Julius Caesar, Octavian had taken "Caesar" as a component of his name, and handed down the name to his heirs of the Julio-Claudian dynasty. With Vespasian, one of the first emperors outside the dynasty, Caesar evolved from a family name to the imperial title ''
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
''.
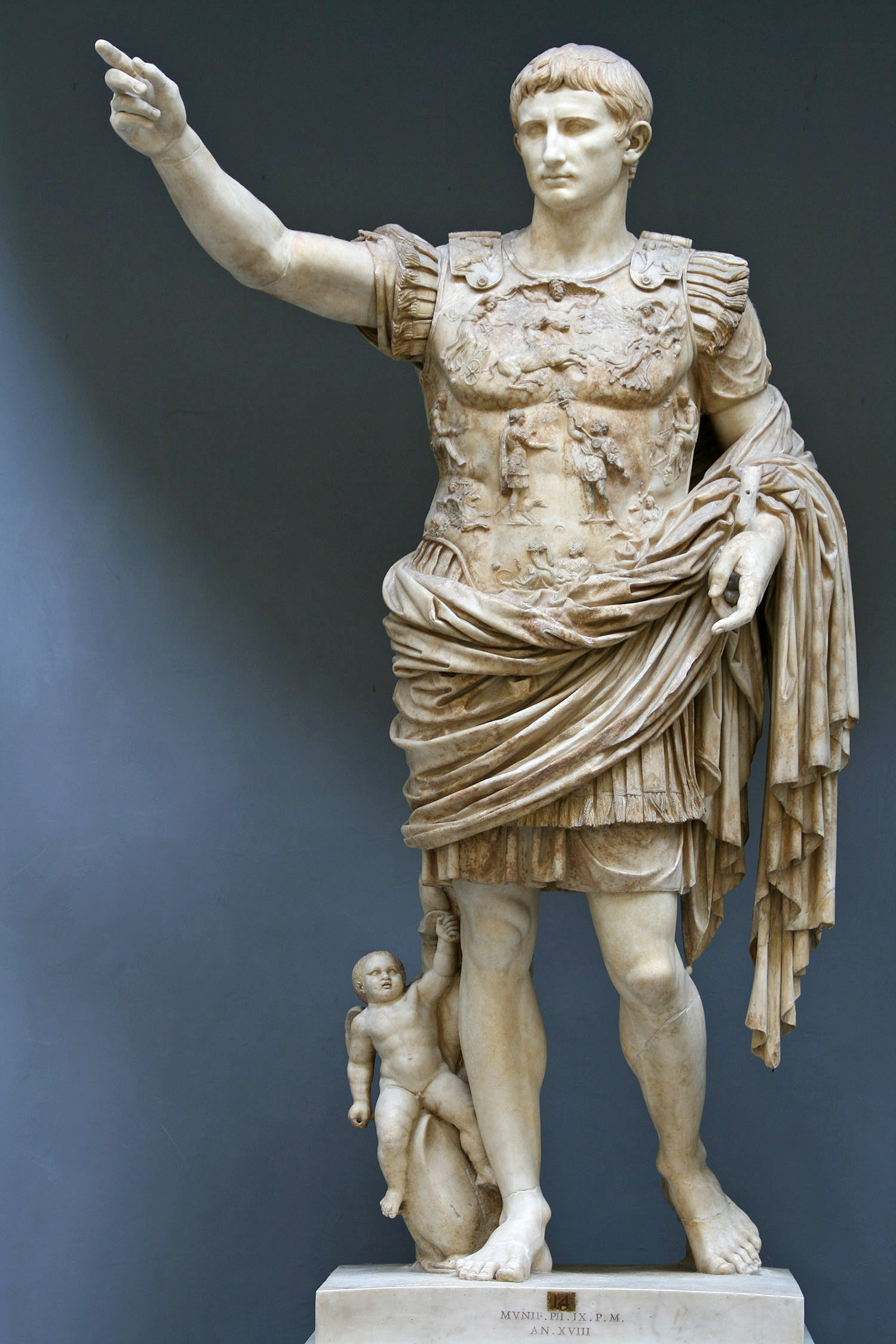

Augustus created his novel and historically unique position by consolidating the constitutional powers of several Republican offices. He renounced his
consulship
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the '' cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which polit ...
in 23 BC, but retained his consular ''
imperium
In ancient Rome, ''imperium'' was a form of authority held by a citizen to control a military or governmental entity. It is distinct from '' auctoritas'' and '' potestas'', different and generally inferior types of power in the Roman Republic ...
'', leading to a second compromise between Augustus and the Senate known as the
Second settlement. Augustus was granted the authority of a
tribune (''tribunicia potestas''), though not the title, which allowed him to call together the Senate and people at will and lay business before it, veto the actions of either the Assembly or the Senate, preside over elections, and it gave him the right to speak first at any meeting. Also included in Augustus's tribunician authority were powers usually reserved for the
Roman censor
The censor (at any time, there were two) was a magistrate in ancient Rome who was responsible for maintaining the census, supervising public morality, and overseeing certain aspects of the government's finances.
The power of the censor was abso ...
; these included the right to supervise public morals and scrutinise laws to ensure they were in the public interest, as well as the ability to hold a census and determine the membership of the Senate. No tribune of Rome ever had these powers, and there was no precedent within the Roman system for consolidating the powers of the tribune and the censor into a single position, nor was Augustus ever elected to the office of Censor. Whether censorial powers were granted to Augustus as part of his tribunician authority, or he simply assumed those, is a matter of debate.
In addition to those powers, Augustus was granted sole ''
imperium
In ancient Rome, ''imperium'' was a form of authority held by a citizen to control a military or governmental entity. It is distinct from '' auctoritas'' and '' potestas'', different and generally inferior types of power in the Roman Republic ...
'' within the city of
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
itself; all armed forces in the city, formerly under the control of the
prefects, were now under the sole authority of Augustus. Additionally, Augustus was granted ''imperium proconsulare maius'' (literally: "eminent proconsular command"), the right to interfere in any
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
and override the decisions of any
governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
. With ''imperium maius'', Augustus was the only individual able to grant a
triumph to a successful general as he was ostensibly the leader of the entire
Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
.
The Senate re-classified the provinces at the frontiers (where the vast majority of the legions were stationed) as
imperial provinces, and gave control of those to Augustus. The peaceful provinces were re-classified as
senatorial provinces, governed as they had been during the Republic by members of the Senate sent out annually by the central government. Senators were prohibited from so much as visiting
Roman Egypt, given its great wealth and history as a base of power for opposition to the new emperor. Taxes from the imperial provinces went into the ''
fiscus'', the fund administrated by persons chosen by and answerable to Augustus. The revenue from senatorial provinces continued to be sent to the state treasury ''(
aerarium),'' under the supervision of the Senate.
The
Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of t ...
s, which had reached an unprecedented 50 in number because of the civil wars, were reduced to 28. Several legions, particularly those with members of doubtful loyalties, were simply disbanded. Other legions were united, a fact hinted by the title ''Gemina'' (Twin). Augustus also created nine special
cohorts
Cohort or cohortes may refer to:
* Cohort (educational group), a group of students working together through the same academic curriculum
* Cohort (floating point), a set of different encodings of the same numerical value
* Cohort (military unit), ...
to maintain peace in
Italia
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, with three, the
Praetorian Guard
The Praetorian Guard (Latin: ''cohortēs praetōriae'') was a unit of the Imperial Roman army that served as personal bodyguards and intelligence agents for the Roman emperors. During the Roman Republic, the Praetorian Guard were an escort f ...
, kept in Rome. Control of the ''fiscus'' enabled Augustus to ensure the loyalty of the legions through their pay.

Augustus completed the conquest of
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: His ...
, while subordinate generals expanded Roman possessions in
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
. Augustus' final task was to ensure an orderly succession of his powers. His stepson
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
had conquered
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
,
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
,
Raetia, and temporarily
Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north ...
for the Empire, and was thus a prime candidate. In 6 BC, Augustus granted some of his powers to his stepson, and soon after he recognised Tiberius as his heir. In AD 13, a law was passed which extended Augustus' powers over the provinces to Tiberius, so that Tiberius' legal powers were equivalent to, and independent from, those of Augustus.
Attempting to secure the borders of the Empire upon the rivers
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
and
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Rep ...
, Augustus ordered the invasions of
Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
,
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
, and Pannonia (south of the Danube), and Germania (west of the Elbe). At first everything went as planned, but then disaster struck. The
Illyrian tribes revolted and had to be crushed, and three full legions under the command of
Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus ( Cremona, 46 BC – Teutoburg Forest, AD 9) was a Roman general and politician under the first Roman emperor Augustus. Varus is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions when ambushed by Germanic tribe ...
were ambushed and destroyed at the
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctil ...
in AD 9 by Germanic tribes led by
Arminius. Being cautious, Augustus secured all territories west of the
Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
and contented himself with retaliatory raids. The rivers Rhine and Danube became the permanent borders of the Roman empire in the North.
In AD 14, Augustus died at the age of seventy-five, having ruled the Empire for forty years, and was succeeded as emperor by
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
.
Sources
The
Augustan Age is not as well documented as the age of Caesar and
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the est ...
.
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
wrote his history during Augustus's reign and covered all of Roman history through to 9 BC, but only
epitome
An epitome (; gr, ἐπιτομή, from ἐπιτέμνειν ''epitemnein'' meaning "to cut short") is a summary or miniature form, or an instance that represents a larger reality, also used as a synonym for embodiment. Epitomacy represents "t ...
s survive of his coverage of the late Republican and Augustan periods. Important primary sources for the Augustan period include:
*''
Res Gestae Divi Augusti'', Augustus's highly partisan autobiography,
*''Historiae Romanae'' by
Velleius Paterculus, the best
annals of the Augustan period,
*''Controversiae'' and ''Suasoriae'' of
Seneca the Elder
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Elder (; c. 54 BC – c. 39 AD), also known as Seneca the Rhetorician, was a Roman writer, born of a wealthy equestrian family of Corduba, Hispania. He wrote a collection of reminiscences about the Roman schools of rhe ...
.
Works of poetry such as
Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the ...
's ''
Fasti
In ancient Rome, the ''fasti'' (Latin plural) were chronological or calendar-based lists, or other diachronic records or plans of official and religiously sanctioned events. After Rome's decline, the word ''fasti'' continued to be used for si ...
'' and
Propertius's Fourth Book, legislation and engineering also provide important insights into Roman life of the time. Archaeology, including
maritime archaeology
Maritime archaeology (also known as marine archaeology) is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, s ...
,
aerial surveys
Aerial survey is a method of collecting geomatics or other imagery by using airplanes, helicopters, UAVs, balloons or other aerial methods. Typical types of data collected include aerial photography, Lidar, remote sensing (using various visible ...
,
epigraphic inscriptions on buildings, and Augustan
coinage, has also provided valuable evidence about economic, social and military conditions.
Secondary ancient sources on the Augustan Age include
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
, Dio Cassius,
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ...
and
Lives of the Twelve Caesars by
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; c. AD 69 – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire.
His most important surviving work is a set of biographies ...
.
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly d ...
's ''
Jewish Antiquities'' is the important source for
Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous south ...
, which became a
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
during Augustus's reign.
14–68: Julio-Claudian Dynasty

Augustus had three grandsons by his daughter
Julia the Elder
Julia the Elder (30 October 39 BC – AD 14), known to her contemporaries as Julia Caesaris filia or Julia Augusti filia (Classical Latin: IVLIA•CAESARIS•FILIA or IVLIA•AVGVSTI•FILIA), was the daughter and only biological child of August ...
:
Gaius Caesar,
Lucius Caesar and
Agrippa Postumus. None of the three lived long enough to succeed him. He therefore was succeeded by his stepson Tiberius. Tiberius was the son of
Livia
Livia Drusilla (30 January 59 BC – 28 September AD 29) was a Roman empress from 27 BC to AD 14 as the wife of Emperor Augustus Caesar. She was known as Julia Augusta after her formal adoption into the Julian family in AD 14.
Livia was the da ...
, the third wife of Augustus, by her first marriage to
Tiberius Nero. Augustus was a scion of the ''
gens
In ancient Rome, a gens ( or , ; plural: ''gentes'' ) was a family consisting of individuals who shared the same nomen and who claimed descent from a common ancestor. A branch of a gens was called a ''stirps'' (plural: ''stirpes''). The ''gen ...
''
Julia (the Julian family), one of the most ancient
patrician clans of
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, while Tiberius was a scion of the ''gens''
Claudia, only slightly less ancient than the Julians. Their three immediate successors were all descended both from the ''gens'' Claudia, through Tiberius' brother
Nero Claudius Drusus, and from ''gens'' Julia, either through Julia the Elder, Augustus' daughter from his first marriage (
Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanic ...
and Nero), or through Augustus' sister
Octavia Minor (Claudius). Historians thus refer to their dynasty as "Julio-Claudian".
14–37: Tiberius
The early years of Tiberius's reign were relatively peaceful. Tiberius secured the overall power of Rome and enriched its treasury. However, his rule soon became characterised by
paranoia. He began a series of treason trials and executions, which continued until his death in 37. He left power in the hands of the commander of the guard,
Lucius Aelius Sejanus. Tiberius himself retired to live at his villa on the island of
Capri
Capri ( , ; ; ) is an island located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the Sorrento Peninsula, on the south side of the Gulf of Naples in the Campania region of Italy. The main town of Capri that is located on the island shares the name. It has bee ...
in 26, leaving administration in the hands of Sejanus, who carried on the persecutions with contentment. Sejanus also began to consolidate his own power; in 31 he was named co-consul with Tiberius and married
Livilla, the emperor's niece. At this point he was "hoist by his own
petard": the emperor's paranoia, which he had so ably exploited for his own gain, turned against him. Sejanus was put to death, along with many of his associates, the same year. The persecutions continued until Tiberius' death in 37.
37–41: Caligula
At the time of Tiberius's death most of the people who might have succeeded him had been killed. The logical successor (and Tiberius' own choice) was his 24-year-old grandnephew,
Gaius, better known as "Caligula" ("little boots"). Caligula was a son of
Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the pat ...
and
Agrippina the Elder. His paternal grandparents were
Nero Claudius Drusus and
Antonia Minor, and his maternal grandparents were
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa (; BC – 12 BC) was a Roman general, statesman, and architect who was a close friend, son-in-law, and lieutenant to the Roman emperor Augustus. He was responsible for the construction of some of the most notable build ...
and
Julia the Elder
Julia the Elder (30 October 39 BC – AD 14), known to her contemporaries as Julia Caesaris filia or Julia Augusti filia (Classical Latin: IVLIA•CAESARIS•FILIA or IVLIA•AVGVSTI•FILIA), was the daughter and only biological child of August ...
. He was thus a descendant of both Augustus and Livia.

Caligula started out well, by putting an end to the persecutions and burning his uncle's records. Unfortunately, he quickly lapsed into illness. The Caligula that emerged in late 37 demonstrated features of mental instability that led modern commentators to diagnose him with such illnesses as
encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hal ...
, which can cause mental derangement,
hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidis ...
, or even a nervous breakdown (perhaps brought on by the stress of his position). Whatever the cause, there was an obvious shift in his reign from this point on, leading his biographers to label him as insane.
Most of what history remembers of Caligula comes from
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; c. AD 69 – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire.
His most important surviving work is a set of biographies ...
, in his book ''Lives of the Twelve Caesars''. According to Suetonius, Caligula once planned to appoint his favourite horse
Incitatus to the Roman Senate. He ordered his soldiers to invade
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
to fight the sea god
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, but changed his mind at the last minute and had them pick sea shells on the northern end of France instead. It is believed he carried on
incest
Incest ( ) is human sexual activity between family members or close relatives. This typically includes sexual activity between people in consanguinity (blood relations), and sometimes those related by affinity ( marriage or stepfamily), ado ...
uous relations with his three sisters:
Julia Livilla,
Drusilla and
Agrippina the Younger
Julia Agrippina (6 November AD 15 – 23 March AD 59), also referred to as Agrippina the Younger, was Roman empress from 49 to 54 AD, the fourth wife and niece of Emperor Claudius.
Agrippina was one of the most prominent women in the Julio-Cl ...
. He ordered a statue of himself to be erected in
Herod's Temple at
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, which would have undoubtedly led to revolt had he not been dissuaded from this plan by his friend king
Agrippa I
Herod Agrippa (Roman name Marcus Julius Agrippa; born around 11–10 BC – in Caesarea), also known as Herod II or Agrippa I (), was a grandson of Herod the Great and King of Judea from AD 41 to 44. He was the father of Herod Agrippa II, the l ...
. He ordered people to be secretly killed, and then called them to his palace. When they did not appear, he would jokingly remark that they must have committed suicide.
In 41, Caligula was assassinated by the commander of the guard
Cassius Chaerea. Also killed were his fourth wife
Caesonia and their daughter
Julia Drusilla. For two days following his assassination, the Senate debated the merits of restoring the Republic.
41–54: Claudius
Claudius was a younger brother of Germanicus, and had long been considered a weakling and a fool by the rest of his family. The Praetorian Guard, however, acclaimed him as emperor. Claudius was neither paranoid like his uncle Tiberius, nor insane like his nephew Caligula, and was therefore able to administer the Empire with reasonable ability. He improved the bureaucracy and streamlined the citizenship and senatorial rolls. He ordered the construction of a winter port at
Ostia Antica for Rome, thereby providing a place for
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legu ...
from other parts of the Empire to be brought in inclement weather.
Claudius ordered the suspension of further attacks across the Rhine,
[Goldsworthy, ''In the Name of Rome'', p. 269.] setting what was to become the permanent limit of the Empire's expansion in that direction.
[Luttwak, ''The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire'', p. 38.] In 43, he resumed the
Roman conquest of Britannia that Julius Caesar had begun in the 50s BC, and incorporated more Eastern provinces into the empire.
In his own family life, Claudius was less successful. His wife
Messalina
Valeria Messalina (; ) was the third wife of Roman emperor Claudius. She was a paternal cousin of Emperor Nero, a second cousin of Emperor Caligula, and a great-grandniece of Emperor Augustus. A powerful and influential woman with a reputation ...
cuckolded him; when he found out, he had her executed and married his niece, Agrippina the Younger. She, along with several of his
freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
, held an inordinate amount of power over him, and although there are conflicting accounts about his death, she may very well have poisoned him in 54. Claudius was deified later that year. The death of Claudius paved the way for Agrippina's own son, the 17-year-old Lucius Domitius Nero.
54–68: Nero

Nero ruled from 54 to 68. During his rule, Nero focused much of his attention on diplomacy, trade, and increasing the cultural capital of the empire. He ordered the building of theatres and promoted athletic games. His reign included the
Roman–Parthian War (a successful war and negotiated peace with the
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conq ...
(58–63)), the suppression of a revolt led by
Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. Sh ...
in
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Gr ...
(60–61) and the improvement of cultural ties with Greece. However, he was egotistical and had severe troubles with his mother, who he felt was controlling and over-bearing. After several attempts to kill her, he finally had her stabbed to death. He believed himself a god and decided to build an opulent palace for himself. The so-called
Domus Aurea
The Domus Aurea (Latin, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor Nero largely on the Oppian Hill in the heart of ancient Rome after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.Roth (1993)
It repla ...
, meaning golden house in Latin, was constructed atop the burnt remains of Rome after the
Great Fire of Rome (64). Because of the convenience of this many believe that Nero was ultimately responsible for the fire, spawning the legend of him fiddling while Rome burned which is almost certainly untrue. The Domus Aurea was a colossal feat of construction that covered a huge space and demanded new methods of construction in order to hold up the golden, jewel-encrusted ceilings. By this time Nero was hugely unpopular despite his attempts to blame the Christians for most of his regime's problems.
A military coup drove Nero into hiding. Facing execution at the hands of the Roman Senate, he reportedly committed suicide in 68. According to
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, Nero's last words were "Jupiter, what an artist perishes in me!"
68–69: Year of the Four Emperors
Since he had no heir, Nero's suicide was followed by a brief period of civil war, known as the "
Year of the Four Emperors
The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from ...
". Between and , Rome witnessed the successive rise and fall of
Galba,
Otho and
Vitellius
Aulus Vitellius (; ; 24 September 1520 December 69) was Roman emperor for eight months, from 19 April to 20 December AD 69. Vitellius was proclaimed emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of c ...
until the final accession of
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Em ...
, first ruler of the
Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
. The military and political anarchy created by this civil war had serious implications, such as the outbreak of the
Batavian rebellion. These events showed that a military power alone could create an emperor. Augustus had established a standing army, where individual soldiers served under the same military governors over an extended period of time. The consequence was that the soldiers in the provinces developed a degree of loyalty to their commanders, which they did not have for the emperor. Thus the Empire was, in a sense, a union of inchoate principalities, which could have disintegrated at any time.
Through his sound fiscal policy, the emperor Vespasian was able to build up a surplus in the treasury, and began construction on the
Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world ...
.
Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
, Vespasian's son and successor, quickly proved his merit, although his short reign was marked by disaster, including the eruption of Mount
Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma- stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
in
Pompeii. He held the opening ceremonies in the still unfinished Colosseum, but died in 81. His brother
Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavi ...
succeeded him. Having exceedingly poor relations with the Senate, Domitian was murdered in September 96.
69–96: Flavian dynasty
The Flavians, although a relatively short-lived dynasty, helped restore stability to an empire on its knees. Although all three have been criticised, especially based on their more centralised style of rule, they issued reforms that created a stable enough empire to last well into the 3rd century. However, their background as a military dynasty led to further marginalisation of the Roman Senate, and a conclusive move away from ''princeps'', or first citizen, and toward ''imperator'', or emperor.
69–79: Vespasian
Vespasian was a remarkably successful Roman general who had been given rule over much of the eastern part of the Roman Empire. He had supported the imperial claims of Galba, after whose death Vespasian became a major contender for the throne. Following the suicide of Otho, Vespasian was able to take control of
Rome's winter grain supply in Egypt, placing him in a good position to defeat his remaining rival, Vitellius. On 20 December 69, some of Vespasian's partisans were able to occupy Rome. Vitellius was murdered by his own troops and, the next day, Vespasian, then sixty years old, was confirmed as emperor by the Senate.
Although Vespasian was considered an
autocrat by the Senate, he mostly continued the weakening of that body begun in the reign of Tiberius. The degree of the Senate's subservience can be seen from the post-dating of his accession to power, by the Senate, to 1 July, when his troops proclaimed him emperor, instead of 21 December, when the Senate confirmed his appointment. Another example was his assumption of the censorship in 73, giving him power over the make up of the Senate. He used that power to expel dissident senators. At the same time, he increased the number of senators from 200 (at that low level because of the actions of Nero and the year of crisis that followed), to 1,000; most of the new senators came not from Rome but from Italy and the urban centres within the western provinces.

Vespasian was able to liberate Rome from the financial burdens placed upon it by Nero's excesses and the civil wars. To do this, he not only increased taxes, but created new forms of taxation. Also, through his power as censor, he was able to carefully examine the fiscal status of every city and province, many paying taxes based upon information and structures more than a century old. Through this sound fiscal policy, he was able to build up a surplus in the treasury and embark on public works projects. It was he who first commissioned the ''Amphitheatrum Flavium'' (
Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world ...
); he also built the Forum of Vespasian, whose centrepiece was the
Temple of Peace. In addition, he allotted sizeable subsidies to the arts, and created a chair of rhetoric at Rome.
Vespasian was also an effective emperor for the provinces, having posts all across the empire, both east and west. In the west he gave considerable favouritism to Hispania (the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, comprising modern
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
) in which he granted
Latin Rights to over three hundred towns and cities, promoting a new era of urbanisation throughout the western (formerly barbarian) provinces. Through the additions he made to the Senate he allowed greater influence of the provinces in the Senate, helping to promote unity in the empire. He also extended the borders of the empire, mostly done to help strengthen the frontier defences, one of Vespasian's main goals.
The crisis of 69 had wrought havoc on the army. One of the most marked problems had been the support lent by provincial legions to men who supposedly represented the best will of their province. This was mostly caused by the placement of native auxiliary units in the areas they were recruited in, a practice Vespasian stopped; he mixed
auxiliary units with men from other areas of the empire or moved the units away from where they were recruited. Also, to reduce further the chances of another military coup, he broke up the legions and, instead of placing them in singular concentrations, spread them along the border. Perhaps the most important military reform he undertook was the extension of legion recruitment from exclusively Italy to
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
and Hispania, in line with the Romanisation of those areas.
79–81: Titus
Titus, the eldest son of Vespasian, had been groomed to rule. He had served as an effective general under his father, helping to secure the east and eventually taking over the command of Roman armies in
Syria and
Iudaea, quelling a significant
First Jewish–Roman War at the time. He shared the consulship for several years with his father and received the best tutelage. Although there was some trepidation when he took office because of his known dealings with some of the less respectable elements of Roman society, he quickly proved his merit, even recalling many exiled by his father as a show of good faith.
However, his short reign was marked by disaster: in 79,
Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma- stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
erupted in
Pompeii, and in 80, a fire destroyed much of Rome. His generosity in rebuilding after these tragedies made him very popular. Titus was very proud of his work on the vast amphitheatre begun by his father. He held the opening ceremonies in the still unfinished edifice during the year 80, celebrating with a lavish show that featured 100
gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s and lasted 100 days. Titus died in 81 at the age of 41 of what is presumed to be illness; it was rumoured that his brother Domitian murdered him in order to become his successor, although these claims have little merit. Whatever the case, he was greatly mourned and missed.
81–96: Domitian

All of the Flavians had rather poor relations with the Senate due to their autocratic rule; however, Domitian was the only one who encountered significant problems. His continuous control as consul and censor throughout his rule—the former his father shared in much the same way as his Julio-Claudian forerunners, the latter presented difficulty even to obtain—were unheard of. In addition, he often appeared in full military regalia as an
imperator, an affront to the idea of what the Principate-era emperor's power was based upon: the emperor as the
princeps
''Princeps'' (plural: ''principes'') is a Latin word meaning "first in time or order; the first, foremost, chief, the most eminent, distinguished, or noble; the first man, first person". As a title, ''princeps'' originated in the Roman Republic w ...
. His reputation in the Senate aside, he kept the people of Rome happy through various measures, including donations to every resident of Rome, wild spectacles in the newly finished Colosseum, and the continuation of the public works projects of his father and brother. He also apparently had the good fiscal sense of his father; although he spent lavishly, his successors came to power with a well-endowed treasury. Domitian repelled the
Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often cons ...
in
his Dacian War; the Dacians had sought to conquer
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
, south of the Danube in the Roman
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
.
Toward the end of his reign Domitian became extremely paranoid, which probably had its roots in the treatment he received by his father: although given significant responsibility, he was never trusted with anything important without supervision. This flowered into the severe and perhaps pathological repercussions following the short-lived rebellion in 89 of
Lucius Antonius Saturninus
Lucius Antonius Saturninus was a Roman senator and general during the reign of Vespasian and his sons. While governor of the province called Germania Superior, motivated by a personal grudge against Emperor Domitian, he led a rebellion known as ...
, a governor and commander in
Germania Superior. Domitian's paranoia led to a large number of arrests, executions, and seizures of property (which might help explain his ability to spend so lavishly). Eventually it reached the point where even his closest advisers and family members lived in fear. This led to his murder in 96, orchestrated by his enemies in the Senate, Stephanus (the steward of the deceased
Julia Flavia), members of the Praetorian Guard and the empress
Domitia Longina.
96–180: Five Good Emperors

The next century came to be known as the period of the "Five Good Emperors", in which the succession was peaceful and the Empire prosperous. The emperors of this period were
Nerva (96–98),
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
(98–117),
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman '' municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispan ...
(117–138),
Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
(138–161) and
Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
(161–180), each one adopted by his predecessor as his successor during the former's lifetime. While their respective choices of successor were based upon the merits of the individual men they selected rather than
dynastic
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
, it has been argued that the real reason for the lasting success of the adoptive scheme of succession lay more with the fact that none but the last had a natural heir.
The last two emperors of the "Five Good Emperors" and
Commodus are also called
Antonines.
96–98: Nerva
After his accession, Nerva set a new tone: he released those imprisoned for treason, banned future prosecutions for treason, restored much confiscated property, and involved the Roman Senate in his rule. He probably did so as a means to remain relatively popular and therefore alive, but this did not completely aid him. Support for Domitian in the army remained strong, and in October 97 the Praetorian Guard laid siege to the Imperial Palace on the
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; la, Collis Palatium or Mons Palatinus; it, Palatino ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." ...
and took Nerva hostage. He was forced to submit to their demands, agreeing to hand over those responsible for Domitian's death and even giving a speech thanking the rebellious Praetorians. Nerva then adopted Trajan, a commander of the armies on the German frontier, as his successor shortly thereafter in order to bolster his own rule.
Casperius Aelianus
Casperius Aelianus who served as Praetorian Prefect under the emperors Domitian and Nerva, was a Praetorian Prefect loyal to the Roman Emperor Domitian, the last of the Flavian dynasty. After Domitian's murder and the ascension of the Emperor ...
, the Guard Prefect responsible for the mutiny against Nerva, was later executed under Trajan.
98–117: Trajan

Upon his accession to the throne, Trajan prepared and launched
a carefully planned military invasion in
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ...
, a region north of the lower Danube whose inhabitants the Dacians had long been an opponent to Rome. In 101, Trajan personally crossed the Danube and defeated the armies of the Dacian king
Decebalus at the
Battle of Tapae. The emperor decided not to press on towards a final conquest as his armies needed reorganisation, but he did impose very hard peace conditions on the Dacians. At Rome, Trajan was received as a hero and he took the name of ''Dacicus'', a title that appears on his coinage of this period.
Decebalus complied with the terms for a time, but before long he began inciting revolt. In 105 Trajan once again invaded and after a yearlong invasion ultimately defeated the Dacians by conquering their capital,
Sarmizegetusa Regia
Sarmizegetusa Regia, also Sarmisegetusa, Sarmisegethusa, Sarmisegethuza, Ζαρμιζεγεθούσα (''Zarmizegethoúsa'') or Ζερμιζεγεθούση (''Zermizegethoúsē''), was the capital and the most important military, religious an ...
. King Decebalus, cornered by the Roman cavalry, eventually committed suicide rather than being captured and humiliated in Rome. The conquest of Dacia was a major accomplishment for Trajan, who ordered 123 days of celebration throughout the empire. He also constructed
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Trajan's Dacian Wars, Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision o ...
in the middle of
Trajan's Forum
Trajan's Forum ( la, Forum Traiani; it, Foro di Traiano) was the last of the Imperial fora to be constructed in ancient Rome. The architect Apollodorus of Damascus oversaw its construction.
History
This forum was built on the order of the empe ...
in Rome to glorify the victory.
In 112, Trajan was provoked by the decision of
Osroes I
Osroes I (also spelled Chosroes I or Khosrow I; xpr, 𐭇𐭅𐭎𐭓𐭅 ''Husrōw'') was a Parthian contender, who ruled the western portion of the Parthian Empire from 109 to 129, with a one-year interruption. For the whole of his reign he con ...
to put his own nephew
Axidares
Axidares or Ashkhadar also known as Exedares or Exedates (flourished second half of the 1st century & first half of the 2nd century, died 113) was a Parthian Prince who served as a Roman Client King of Armenia.
Axidares was one of the three son ...
on the throne of the
Kingdom of Armenia. The
Arsacid dynasty of Armenia was a branch of the Parthian royal family established in 54. Since then, the two great empires had shared hegemony of Armenia. The encroachment on the traditional Roman sphere of influence by Osroes ended the peace which had lasted for some 50 years.

Trajan first invaded Armenia. He deposed the king and annexed it to the Roman Empire. Then he turned south into Parthian territory in
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, taking the cities of
Babylon,
Seleucia and finally the capital of
Ctesiphon in 116, while suppressing the
Kitos War, a Jewish uprising across the eastern provinces. He continued southward to the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
, whence he took
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
as a new province of the empire and lamented that he was too old to follow in the steps of
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and continue his invasion eastward.
But he did not stop there. In 116, he captured the great city of
Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
. He deposed the emperor Osroes I and put his own puppet ruler
Parthamaspates on the throne. Not until the reign of Heraclius would the Roman army push so far to the east, and Roman territory never again reached so far eastward. During his rule, the Roman Empire reached its greatest extent; it was quite possible for a Roman to travel from
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
to the Persian Gulf without leaving Roman territory.
117–138: Hadrian

Despite his own excellence as a military administrator, Hadrian's reign was marked more by the defence of the empire's vast territories, rather than major military conflicts. He surrendered Trajan's conquests in Mesopotamia, considering them to be indefensible. There was almost a war with
Vologases III of Parthia
Vologases III ( xpr, 𐭅𐭋𐭂𐭔 ''Walagash'') was king of the Parthian Empire from 110 to 147. He was the son and successor of Pacorus II ().
Vologases III's reign was marked by civil strife and warfare. At his ascension, he had to deal ...
around 121, but the threat was averted when Hadrian succeeded in negotiating a peace. Hadrian's army crushed the
Bar Kokhba revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''Mereḏ Bar Kōḵḇāʾ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Judea (Roman province), Roman province of Judea, led b ...
, a massive Jewish uprising in Judea (132–135).
Hadrian was the first emperor to extensively tour the provinces, donating money for local construction projects as he went. In Britain, he ordered the construction of a wall, the famous
Hadrian's Wall as well as various other such defences in
Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north ...
and
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
. His domestic policy was one of relative peace and prosperity.
138–161: Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius's reign was comparatively peaceful; there were several military disturbances throughout the Empire in his time, in
Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
,
Judaea, and amongst the
Brigantes in Britain, but none of them are considered serious. The unrest in Britain is believed to have led to the construction of the
Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some ...
from the
Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meanin ...
to the
Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
, although it was soon abandoned.
161–180: Marcus Aurelius and Lucius Verus
Germanic tribes and other people launched many raids along the long north European border, particularly into Gaul and across the Danube; Germans, in turn, may have been under attack from more warlike tribes farther east, driving them into the empire. His campaigns against them are commemorated on the
Column of Marcus Aurelius.
In Asia, a revitalised Parthian Empire renewed its assault. Marcus Aurelius sent his co-emperor
Lucius Verus to command the legions in the East. Lucius was authoritative enough to command the full loyalty of the troops, but already powerful enough that he had little incentive to overthrow Marcus. The plan succeeded—Verus remained loyal until his death, while on campaign, in 169.
In 175, while on campaign in northern Germany in the
Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars (Latin: ''bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum'', "German and Sarmatian War") were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi ...
, Marcus was forced to contend with a rebellion by
Avidius Cassius, a general who had been an officer during the wars against Persia. Cassius proclaimed himself Roman Emperor and took the provinces of
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
and
Syria as his part of the Empire. It is said that Cassius had revolted as he had heard word that Marcus was dead. After three months Cassius was assassinated and Marcus restored the eastern part of the Empire.
In the last years of his life Marcus, a philosopher as well as an emperor, wrote his book of
Stoic philosophy known as the ''
Meditations
''Meditations'' () is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from AD 161 to 180, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy.
Marcus Aurelius wrote the 12 books of the ''Meditations'' in Koin ...
''. The book has since been hailed as Marcus' great contribution to philosophy.
When Marcus died in 180 the throne passed to his son
Commodus, who had been elevated to the rank of co-emperor in 177. This ended the succession plan of the previous four emperors where the emperor would adopt his successor, although Marcus was the first emperor since
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Em ...
to have a natural son that could succeed him, which probably was the reason he allowed the throne to pass to Commodus and not adopt a successor from outside his family.

It is possible that an alleged
Roman embassy from "
Daqin" that arrived in
Eastern Han China in 166 via a
Roman maritime route into the
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
, landing at
Jiaozhou Jiaozhou may refer to:
* Jiaozhou Bay, a sea gulf in Qingdao, Shandong, China
* Jiaozhou City, a county-level city near the bay
* Jiaozhou (region), an ancient region which included modern North Vietnam, Guangxi, Guangdong, and Hainan
** Jiaozhi (northern
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
) and bearing gifts for the
Emperor Huan of Han
Emperor Huan of Han (; 132 – 25 January 168) was the 27th emperor of the Han dynasty after he was enthroned by the Empress Dowager and her brother Liang Ji on 1 August 146. He was a great-grandson of Emperor Zhang. He was the 11th Emperor of ...
(), was sent by Marcus Aurelius, or his predecessor Antoninus Pius (the confusion stems from the transliteration of their names as "Andun",
Chinese: 安敦).
The embassy was perhaps simply a group of Roman merchants, not official diplomats. Other Roman embassies of the 3rd century supposedly visited China by sailing along the same maritime route.
These were preceded by the appearance of
Roman glasswares in Chinese tombs, the earliest piece found at
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong ...
(along the coast of the South China Sea) and dating to the 1st century BC. The earliest
Roman coins found in China date to the 4th century AD and appear to have come by way of the
Silk Road through
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
. However, Roman golden
medal
A medal or medallion is a small portable artistic object, a thin disc, normally of metal, carrying a design, usually on both sides. They typically have a commemorative purpose of some kind, and many are presented as awards. They may be int ...
lions from the reign of Antoninus Pius, and possibly his successor Marcus Aurelius, have been discovered at
Óc Eo (in southern Vietnam), which was then part of the kingdom of
Funan
Funan (; km, ហ៊្វូណន, ; vi, Phù Nam, Chữ Hán: ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in mai ...
near Chinese-controlled
Jiaozhi (northern Vietnam) and the region where
Chinese historical texts claim the Romans first landed before venturing further into China to conduct diplomacy.
[Gary K. Young (2001), ''Rome's Eastern Trade: International Commerce and Imperial Policy, 31 BC – AD 305'', London & New York: Routledge, , p. 29.][For further information on the ]Kingdom of Funan
Funan (; km, ហ៊្វូណន, ; vi, Phù Nam, Chữ Hán: ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in mai ...
and discoveries at Oc Eo, see Milton Osborne (2006), ''The Mekong: Turbulent Past, Uncertain Future'', Crows Nest: Allen & Unwin, revised edition, first published in 2000, , pp. 24–25. Furthermore, in his ''
Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
'' (),
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
described the location of the
Golden Chersonese
The Golden Chersonese or Golden Khersonese ( grc, Χρυσῆ Χερσόνησος, ''Chrysḗ Chersónēsos''; la, Chersonesus Aurea), meaning the Golden Peninsula, was the name used for the Malay Peninsula by Greek and Roman geographers in cla ...
, now known as the
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The are ...
, and beyond this a trading port called
Kattigara.
Ferdinand von Richthofen
Baron Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen (5 May 18336 October 1905), better known in English as was a German traveller, geographer, and scientist. He is noted for coining the terms "Seidenstraße" and "Seidenstraßen" = " Silk Road(s)" or "Silk ...
assumed this as
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi i ...
, yet the Roman and Mediterranean artefacts found at Óc Eo suggest this location instead.
180–193: Commodus and the Year of the Five Emperors
Commodus

The period of the "Five Good Emperors" was brought to an end by the reign of Commodus from 180 to 192. Commodus was the son of Marcus Aurelius, making him the first direct successor in a century, breaking the scheme of adoptive successors that had worked so well. He was co-emperor with his father from 177. When he became sole emperor upon the death of his father in 180, it was at first seen as a hopeful sign by the people of the Roman Empire. Nevertheless, as generous and magnanimous as his father was, Commodus was just the opposite. In ''
The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' by
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is ...
, it is noted that Commodus at first ruled the Empire well. However, after an assassination attempt, involving a conspiracy by certain members of his family, Commodus became paranoid and slipped into insanity. The ''
Pax Romana'', or "Roman Peace", ended with the reign of Commodus. One could argue that the assassination attempt began the long decline of the Roman Empire. When Commodus' behaviour became increasingly erratic throughout the early 190s,
Pertinax
Publius Helvius Pertinax (; 1 August 126 – 28 March 193) was Roman emperor for the first three months of 193. He succeeded Commodus to become the first emperor during the tumultuous Year of the Five Emperors.
Born the son of a freed sl ...
is thought to have been implicated in the conspiracy that led to Commodus' assassination on 31 December 192. The plot was carried out by the
Praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
Quintus Aemilius Laetus, Commodus' mistress
Marcia, and his chamberlain Eclectus.
Pertinax
After the murder had been carried out, Pertinax, who was serving as
urban prefect at this time, was hurried to the
Praetorian Camp and proclaimed emperor the following morning. His short reign (86 days) was an uneasy one. He attempted to emulate the restrained practices of Marcus Aurelius, and made an effort to reform the
welfare programme for poor children but he faced antagonism from many quarters.

His
monetary reform
Monetary reform is any movement or theory that proposes a system of supplying money and financing the economy that is different from the current system.
Monetary reformers may advocate any of the following, among other proposals:
* A return ...
was far-sighted, but would not survive his death. He attempted to impose stricter military discipline upon the pampered Praetorians. In early March he narrowly averted one conspiracy by a group to replace him with the consul
Quintus Pompeius Sosius Falco while he was in
Ostia
Ostia may refer to:
Places
*Ostia (Rome), a municipio (also called ''Ostia Lido'' or ''Lido di Ostia'') of Rome
*Ostia Antica, a township and port of ancient Rome
*Ostia Antica (district), a district of the commune of Rome
Arts and entertainment ...
inspecting the arrangements for grain shipments.
[Dio, 74:8.] The plot was betrayed; Falco himself was pardoned but several of the officers behind the coup were executed.
On 28 March 193, Pertinax was at his palace when a contingent of some three hundred soldiers of the Praetorian Guard rushed the gates (two hundred according to Cassius Dio). Sources suggest that they had received only half their promised pay.
Neither the guards on duty nor the palace officials chose to resist them. Pertinax sent Laetus to meet them, but he chose to side with the insurgents instead and deserted the emperor. Although advised to flee, he then attempted to reason with them, and was almost successful before being struck down by one of the soldiers. The Praetorian Guards auctioned off the imperial position, which senator
Didius Julianus
Marcus Didius Julianus (; 29 January 133 or 137 – 2 June 193) was Roman emperor for nine weeks from March to June 193, during the Year of the Five Emperors. Julianus had a promising political career, governing several provinces, including Da ...
won and became the new emperor.
Didius Julianus
Upon his accession, Julianus immediately devalued the
Roman currency
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, de ...
by decreasing the silver purity of the
denarius
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
from 87% to 81.5%. After the initial confusion had subsided, the population did not tamely submit to the dishonour brought upon Rome. Whenever Julianus appeared in public he was saluted with groans, imprecations, and shouts of "robber and parricide." The mob tried to obstruct his progress to the
Capitol, and even threw stones. When news of the public anger in Rome spread across the Empire, the generals
Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was Roman Emperor from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a ri ...
in Syria,
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary succ ...
in Pannonia, and
Clodius Albinus in Britain, each having three
legions under his command, refused to recognise the authority of Julianus. Julianus declared Severus a public enemy because he was the nearest of the three and, therefore, the most dangerous foe. Deputies were sent from the Senate to persuade the soldiers to abandon him; a new general was nominated to supersede him, and a
centurion dispatched to take his life.
The Praetorian Guard, lacking discipline and sunk in debauchery and sloth, were incapable of offering any effectual resistance. Julianus, now desperate, attempted negotiation and offered to share the empire with his rival. Severus ignored these overtures and pressed forward, all Italy declaring for him as he advanced. At last the Praetorians, having received assurances that they would suffer no punishment – provided they surrendered the actual murderers of Pertinax – seized the ringleaders of the conspiracy and reported what they had done to Silius Messala, the consul, by whom the Senate was summoned and informed of the proceedings. Julianus was killed in the palace by a soldier in the third month of his reign (1 June 193). Severus dismissed the Praetorian Guard and executed the soldiers who had killed Pertinax. According to
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, who lived in Rome during the period, Julianus's last words were "But what evil have I done? Whom have I killed?" His body was given to his wife and daughter, who buried it in his great-grandfather's tomb by the fifth milestone on the
Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. It seems possible that the road at first led to Tusculum, that it was then extended to Labici, and later still became a road for through traffic; it may even have ...
.
193–235: Severan dynasty
Septimius Severus (193–211)
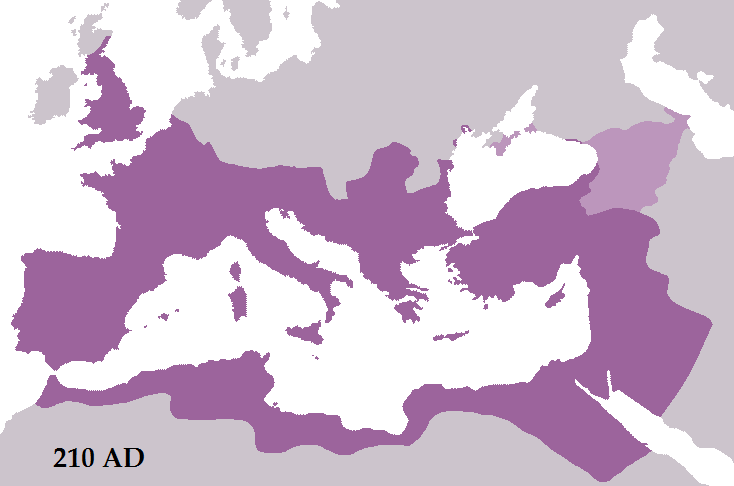
Lucius Septimius Severus was born to a family of Phoenician
equestrian rank in the Roman province of
Africa proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. He rose through military service to
consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states th ...
ar rank under the later
Antonines. Proclaimed emperor in 193 by his legionaries in
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nort ...
during the political unrest that followed the death of Commodus, he secured sole rule over the empire in 197 after defeating his last rival,
Clodius Albinus, at the
Battle of Lugdunum. In securing his position as emperor, he founded the
Severan dynasty.
Severus fought a successful war against the
Parthians and campaigned with success against barbarian incursions in
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
, rebuilding Hadrian's Wall. In Rome, his relations with the Senate were poor, but he was popular with the commoners, as with his soldiers, whose salary he raised. Starting in 197, the influence of his
Praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus was a negative influence; the latter was executed in 205. One of Plautianus's successors was the jurist
Papinian. Severus continued official persecution of
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
and
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
, as they were the only two groups who would not assimilate their beliefs to the official
syncretistic creed. Severus died while campaigning in Britain. He was succeeded by his sons
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor ...
and
Geta, whom he made his co-Augusti and who reigned under the influence of their mother,
Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of pries ...
.
Caracalla and Geta (198–217)

The eldest son of Severus, Caracalla was born Lucius Septimius Bassianus in
Lugdunum, Gaul. "Caracalla" was a nickname referring to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore even when he slept. Before his father's death, Caracalla was proclaimed co-emperor with his father and brother Geta. Conflict between the two culminated in the assassination of the latter. Unlike the much more successful joint reign of Marcus Aurelius and his brother
Lucius Verus in the previous century, relations were hostile between the two Severid brothers from childhood. Geta was assassinated in his mother's apartments by order of Caracalla, who thereafter ruled as sole ''Augustus''.
Reigning alone, Caracalla was noted for lavish bribes to the legionaries and unprecedented cruelty, authorising numerous assassinations of perceived enemies and rivals. He campaigned with indifferent success against the
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pr ...
. The
Baths of Caracalla in Rome are the most enduring monument of his rule. His reign was also notable for the
Antonine Constitution (
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
: ''Constitutio Antoniniana''), also known as the ''Edict of Caracalla'', which granted
Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
to nearly all freemen throughout the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
.
He was assassinated while en route to a campaign against the Parthians by the Praetorian Guard.
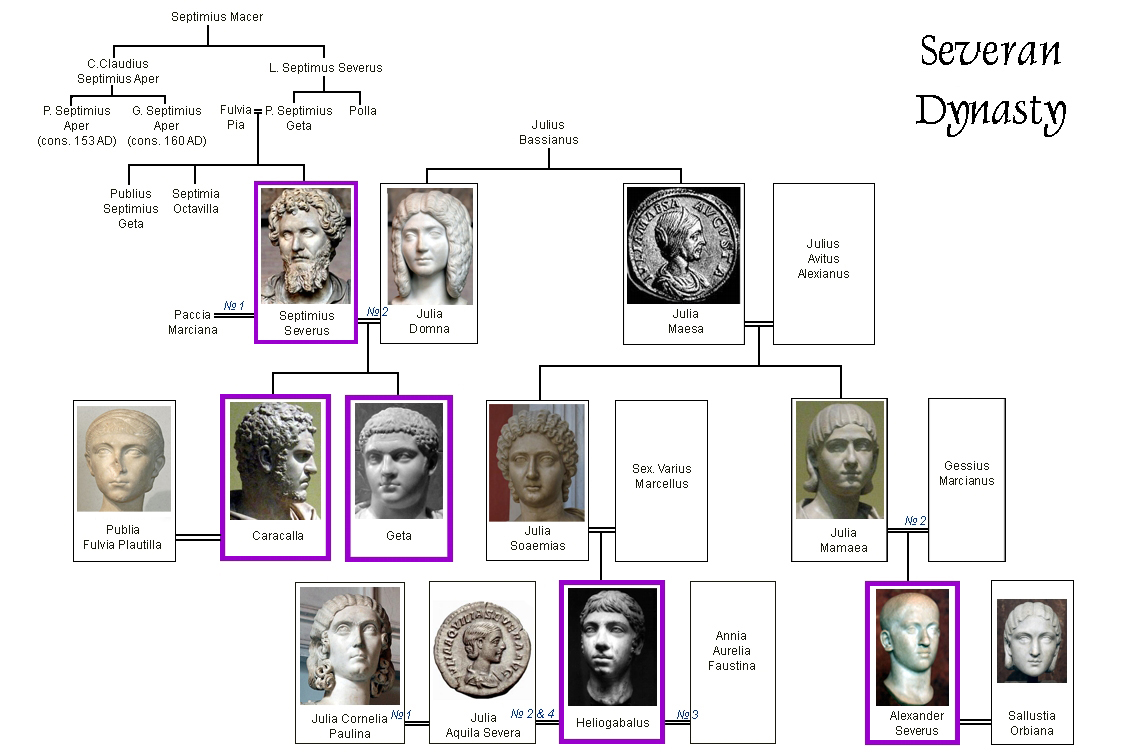
Interlude: Macrinus and Diadumenian (217–218)
Macrinus was born in 164 at Caesarea. Although coming from a humble background that was ''not'' dynastically related to the Severan dynasty, he rose through the imperial household until, under the emperor Caracalla, he was made prefect of the Praetorian Guard. On account of the cruelty and treachery of the emperor, Macrinus became involved in a conspiracy to kill him, and ordered the Praetorian Guard to do so. On 8 April 217, Caracalla was assassinated travelling to
Carrhae. Three days later, Macrinus was declared ''Augustus''.
Diadumenian was the son of Macrinus, born in 208. He was given the title ''Caesar'' in 217, when his father became ''Augustus'', and raised to co-Augustus the following year.
His most significant early decision was to make peace with the Parthian Empire, but many thought that the terms were degrading to the Romans. However, his downfall was his refusal to award the pay and privileges promised to the eastern troops by Caracalla. He also kept those forces wintered in Syria, where they became attracted to the young
Elagabalus
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus, 204 – 11/12 March 222), better known by his nickname "Elagabalus" (, ), was Roman emperor from 218 to 222, while he was still a teenager. His short reign was conspicuous for s ...
. After months of mild rebellion by the bulk of the army in Syria, Macrinus took his loyal troops to meet the army of Elagabalus near
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
. Despite a good fight by the Praetorian Guard, his soldiers were defeated. Macrinus managed to escape to Chalcedon, but his authority was lost: he was betrayed and executed after a short reign of just 14 months. After his father's defeat outside Antioch,
Diadumenian tried to escape east to
Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Mede ...
, but was captured and killed.
Elagabalus (218–222)

Born Varius Avitus Bassianus on 16 May 205, known later as M. Aurelius Antonius, he was appointed at an early age to be priest of the sun god,
Elagabalus
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus, 204 – 11/12 March 222), better known by his nickname "Elagabalus" (, ), was Roman emperor from 218 to 222, while he was still a teenager. His short reign was conspicuous for s ...
, represented by a large, dark rock called a
baetyl, by which name he is known to historians (his name is sometimes written "Heliogabalus"). He was proclaimed emperor by the troops of Emesa, his hometown, who were instigated to do so by Elagabalus's grandmother,
Julia Maesa. She spread a rumour that Elagabalus was the secret son of Caracalla. This revolt spread to the entire Syrian army (which, at the time, was swollen with troops raised by the emperor Caracalla, and not fully loyal to
Macrinus), and eventually they were to win the short struggle that followed by defeating Macrinus at a battle just outside Antioch. Elagabalus was then accepted by the Senate, and he began the slow journey to Rome.
His reign in Rome has long been known for outrageousness, although the historical sources are few, and in many cases not to be fully trusted. He is said to have smothered guests at a banquet by flooding the room with rose petals; married his male lover – who was then referred as the 'empress's husband'; and married one of the
Vestal Virgins. Some say he was
transgender
A transgender (often abbreviated as trans) person is someone whose gender identity or gender expression does not correspond with their sex assigned at birth. Many transgender people experience dysphoria, which they seek to alleviate through ...
, and one ancient text states that he offered half the empire to the physician who could give him female genitalia.
The running of the Empire during this time was mainly left to his grandmother and mother (Julia Soaemias). Seeing that her grandson's outrageous behaviour could mean the loss of power, Julia Maesa persuaded Elagabalus to accept his cousin
Severus Alexander
Marcus Aurelius Severus Alexander (1 October 208 – 21/22 March 235) was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 222 until 235. He was the last emperor from the Severan dynasty. He succeeded his slain cousin Elagabalus in 222. Alexander himself wa ...
as ''Caesar'' (and thus the nominal emperor-to-be). However, Alexander was popular with the troops, who viewed their new emperor with dislike: when Elagabalus, jealous of this popularity, removed the title of ''Caesar'' from his nephew, the enraged Praetorian Guard swore to protect him. Elagabalus and his mother were murdered in a Praetorian Guard camp mutiny.
Severus Alexander (222–235)
Severus Alexander was adopted as son and ''Caesar'' by his slightly older and very unpopular cousin, the emperor Elagabalus at the urging of the influential and powerful Julia Maesa — who was grandmother of both cousins and who had arranged for the emperor's acclamation by the Third Legion. On March 6, 222, when Alexander was just fourteen, a rumour went around the city troops that Alexander had been killed, triggering a revolt of the guards that had sworn his safety from Elegabalus and his accession as emperor. The eighteen-year-old Emperor Elagabalus and his mother were both taken from the palace, dragged through the streets, murdered and thrown in the river
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the Ri ...
by the Praetorian Guard, who then proclaimed Severus Alexander as ''Augustus''.
Ruling from the age of fourteen under the influence of his able mother,
Julia Avita Mamaea, Alexander restored, to some extent, the moderation that characterised the rule of Septimius Severus. The rising strength of the
Sasanian Empire (226–651) heralded perhaps the greatest external challenge that Rome faced in the 3rd century. His prosecution of the war against a German invasion of Gaul led to his overthrow by the troops he was leading, whose regard the twenty-seven-year-old had lost during the campaign.
235–284: Crisis of the Third Century
The situation of the Roman Empire became dire in AD 235, when the emperor Severus Alexander was murdered by his own troops. Many
Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of t ...
s had been defeated during a campaign against
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
raiding across the borders, while the emperor was focused primarily on the dangers from the
Sassanid Persian Empire. Leading his troops personally, Alexander resorted to diplomacy and the paying of tribute in an attempt to pacify the
Germanic chieftains quickly. According to
Herodian
Herodian or Herodianus ( el, Ἡρωδιανός) of Syria, sometimes referred to as "Herodian of Antioch" (c. 170 – c. 240), was a minor Roman civil servant who wrote a colourful history in Greek titled ''History of the Empire from the Death ...
this cost him the respect of his troops, who may have felt they should be punishing the tribes who were intruding on Rome's territory.
In the years following the emperor's death, generals of the Roman army fought each other for control of the Empire and neglected their duties in preventing invasions. Provincials became victims of frequent raids by foreign tribes, such as the
Carpians,
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
,
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
, and
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pr ...
, along the Rhine and Danube Rivers in the western part of the empire, as well as attacks from
Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
in the eastern part of the Empire. Additionally, in 251, the
Plague of Cyprian (possibly
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
) broke out, causing large-scale mortality which may have seriously affected the ability of the Empire to defend itself.

By 258, the Roman Empire broke up into three competing states. The
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
s of
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
, Britain and Hispania broke off to form the
Gallic Empire
The Gallic Empire or the Gallic Roman Empire are names used in modern historiography for a breakaway part of the Roman Empire that functioned ''de facto'' as a separate state from 260 to 274. It originated during the Crisis of the Third Century, ...
and, two years later in 260, the eastern provinces of Syria,
Palestine and
Aegyptus became independent as the
Palmyrene Empire, leaving the remaining Italian-centred Roman Empire-proper in the middle.
An invasion by a vast host of Goths was beaten back at the
Battle of Naissus in 269. This victory was significant as the turning point of the crisis, when a series of tough, energetic soldier-emperors took power. Victories by the emperor
Claudius Gothicus over the next two years drove back the Alamanni and recovered Hispania from the Gallic Empire. When Claudius died in 270 of the plague,
Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited ...
, who had commanded the cavalry at
Naissus, succeeded him as the emperor and continued the restoration of the Empire.
Aurelian reigned (270–275) through the worst of the crisis, defeating the Vandals, the
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, the
Palmyrenes, the Persians, and then the remainder of the Gallic Empire. By late 274, the Roman Empire was reunited into a single entity, and the frontier troops were back in place. More than a century would pass before Rome again lost military ascendancy over its external enemies. However, dozens of formerly thriving cities, especially in the western empire, had been ruined, their populations dispersed and, with the breakdown of the economic system, could not be rebuilt. Major cities and towns, even Rome itself, had not needed fortifications for many centuries; many then surrounded themselves with thick walls.
Finally, although Aurelian had played a significant role in restoring the Empire's borders from external threat, more fundamental problems remained. In particular, the right of succession had never been clearly defined in the Roman Empire, leading to continuous civil wars as competing factions in the military, Senate and other parties put forward their favoured candidate for emperor. Another issue was the sheer size of the Empire, which made it difficult for a single autocratic ruler to effectively manage multiple threats at the same time. These continuing problems would be radically addressed by
Diocletian, allowing the Empire to continue to survive in the West for over a century and in the East for over a millennium.
Late Roman Empire
As a matter of historical convention, the late Roman Empire emerged from the
Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate ...
(the early Roman Empire), with the accession of Diocletian in 284, following the
Third Century Crisis of AD 235–284.
The end of the late Empire is usually marked in the west with the collapse of the western empire in AD 476, while in the
east its end is disputed, as either occurring at the close of the reign of
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
(AD 565) or of
Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
(AD 641). The subsequent period of centuries of the Roman Empire's history is conventionally labelled the "
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
", with the reign of Heraclius beginning the Middle Byzantine period, which lasted until the
Fourth Crusade.
284–301: Diocletian and the Tetrarchy

The transition to divided western and eastern halves of the empire was gradual. In July 285, Diocletian defeated rival emperor
Carinus and briefly became sole emperor of the Roman Empire. Diocletian's reign stabilised the empire and marked the end of the Crisis of the Third Century. Diocletian appointed a co-emperor in 286 and delegated further with two junior-emperors.
Diocletian secured the empire's borders and purged it of all threats to his power. He defeated the
Sarmatians and
Carpi during several campaigns between 285 and 299, the Alamanni in 288, and usurpers in
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
between 297 and 298. Galerius, aided by Diocletian, campaigned successfully against
Sassanid Persia
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
, the empire's traditional enemy. In 299, he sacked their capital, Ctesiphon. Diocletian led the subsequent negotiations and achieved a lasting and favourable peace. Diocletian separated and enlarged the empire's civil and military services and reorganised the empire's provincial divisions, establishing the largest and most
bureaucratic
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
government in the history of the empire. He established new administrative centres in
Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocleti ...
,
Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, an ...
, Antioch, and
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
, closer to the empire's frontiers than the traditional capital at Rome had been. Building on third-century trends towards
absolutism
Absolutism may refer to:
Government
* Absolute monarchy, in which a monarch rules free of laws or legally organized opposition
* Absolutism (European history), period c. 1610 – c. 1789 in Europe
** Enlightened absolutism, influenced by the E ...
, he styled himself an autocrat, elevating himself above the empire's masses with imposing forms of court ceremonies and architecture. Bureaucratic and military growth, constant campaigning, and construction projects increased the state's expenditures and necessitated a comprehensive tax reform. From at least 297 on, imperial taxation was standardised, made more equitable, and levied at generally higher rates.
Diocletian saw that the vast Roman Empire was ungovernable by a single emperor in the face of internal pressures and military threats on two fronts. He therefore split the Empire in half along a northwest axis just east of Italy, and created two equal emperors to rule under the title of ''augustus''. Diocletian himself was the ''augustus'' of the eastern half, and he made his long-time friend
Maximian
Maximian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maximianus; c. 250 – c. July 310), nicknamed ''Herculius'', was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then '' Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his ...
''augustus'' of the western half. In doing so, he effectively created what would become the western empire and the eastern empire.

On 1 March 293, authority was further divided. Each ''augustus'' took a junior emperor called a ''caesar'' to aid him in administrative matters, and to provide a line of succession.
Galerius
Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. During his reign he campaigned, aided by Diocletian, against the Sasanian Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across the D ...
became ''caesar'' for Diocletian and
Constantius Chlorus
Flavius Valerius Constantius "Chlorus" ( – 25 July 306), also called Constantius I, was Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as caesar from 293 ...
''caesar'' for Maximian. This constituted what is called the Tetrarchy by modern scholars, as each emperor would rule over a quarter-division of the empire. After the empire had been plagued by bloody disputes about the supreme authority, this finally formalised a peaceful succession of the emperor: in each half a ''caesar'' would rise up to replace the ''augustus'' and select a new ''caesar''. On May 1, 305, Diocletian and Maximian abdicated in favour of their ''caesares''. Galerius named the two new ''caesares'': his nephew
Maximinus Daia
Galerius Valerius Maximinus, born as Daza (20 November 270 – July 313), was Roman emperor from 310 to 313 CE. He became embroiled in the Civil wars of the Tetrarchy between rival claimants for control of the empire, in which he was defeated ...
for himself, and
Valerius Severus
Flavius Valerius Severus (died September 307), also called Severus II, was a Roman emperor from 306 to 307. After failing to besiege Rome, he fled to Ravenna. It is thought that he was killed there or executed near Rome.
Background and earl ...
for Constantius. The arrangement worked well under Diocletian and Maximian and shortly thereafter. The internal tensions within the Roman government were less acute than they had been. In ''
The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. It traces Western civilization (as well as the Islamic and Mongolian conquests) from the height of the Roman Empire to t ...
'',
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is ...
notes that this arrangement worked well because of the affinity the four rulers had for each other. Gibbon says that this arrangement has been compared to a "chorus of music". With the retirement of Diocletian and Maximian, this harmony disappeared.
After an initial period of tolerance, Diocletian, who was a fervent pagan and was worried about the ever-increasing numbers of Christians in the Empire,
persecuted them with zeal unknown since the time of Nero; this was to be one of the greatest persecutions the Christians endured in history. Not all of Diocletian's plans were successful: the
Edict on Maximum Prices (301), his attempt to curb
inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
via
price controls, was counterproductive and quickly ignored. Although effective while he ruled, Diocletian's tetrarchic system collapsed after his abdication under the competing dynastic claims of
Maxentius
Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maxentius (c. 283 – 28 October 312) was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 306 until his death in 312. Despite ruling in Italy and North Africa, and having the recognition of the Senate in Rome, he was not recognized ...
and Constantine, sons of Maximian and Constantius respectively. The
Diocletianic Persecution
The Diocletianic or Great Persecution was the last and most severe persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. In 303, the emperors Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius issued a series of edicts rescinding Christians' legal ri ...
(303–11), the empire's last, largest, and bloodiest official persecution of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, did not destroy the empire's Christian community; indeed, after 324 Christianity became the empire's preferred religion under its first Christian emperor, Constantine.

In spite of his failures, Diocletian's reforms fundamentally changed the structure of Roman imperial government and helped stabilise the empire economically and militarily, enabling the empire to remain essentially intact for another hundred years despite being near the brink of collapse in Diocletian's youth. Weakened by illness, Diocletian left the imperial office on 1 May 305, and became the first Roman emperor to voluntarily abdicate the position (
John VI retired to a monastery in the 14th century). He lived out his retirement in
his palace on the Dalmatian coast, tending to his vegetable gardens. His palace eventually became the core of the modern-day city of
Split.
The peaceful Tetrarchy would effectively collapse with the death of Constantius Chlorus on July 25, 306. Constantius's troops in
Eboracum
Eboracum () was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimate ...
immediately proclaimed his son
Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
as ''augustus''. In August 306, Galerius promoted Severus to the position of ''augustus''. A revolt in Rome supported another claimant to the same title: Maxentius, son of Maximian, who was proclaimed ''augustus'' on October 28, 306. His election was supported by the Praetorian Guard and the Roman Senate. This left the Empire with five rulers: four ''augusti'' (Galerius, Constantine, Severus and Maxentius) and one ''caesar'' (Maximinus).
The year 307 saw the return of Maximian to the rank of ''augustus'' alongside his son Maxentius, creating a total of six rulers of the Empire. Galerius and Severus campaigned against them in Italy. Severus was killed under command of Maxentius on September 16, 307. The two ''augusti'' of Italy also managed to ally themselves with Constantine by having Constantine marry
Fausta
Flavia Maxima Fausta ''Augusta'' (289–326 AD) was a Roman empress. She was the daughter of Maximian and second wife of Constantine the Great, who had her executed and excluded from all official accounts for unknown reasons. Historians Zosim ...
, the daughter of Maximian and sister of Maxentius. At the end of 307, the Empire had four ''augusti'' (Maximian, Galerius, Constantine and Maxentius) and a sole ''caesar''.
In 311, Galerius's
Edict of Serdica officially put an end to the persecution of Christians, though the persecution continued in the territory of Maximinius Daia until his death in 313. Constantine and his co-''augustus''
Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan, AD 313, that granted official toleration to ...
legalised Christianity definitively in 313 in the so-called
Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan ( la, Edictum Mediolanense; el, Διάταγμα τῶν Μεδιολάνων, ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 AD agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. ( ...
. In 317, Constantine and Licinius elevated three of the grandchildren of Constantius to ''caesar'': Constantine's eldest sons
Crispus
Flavius Julius Crispus (; 300 – 326) was the eldest son of the Roman emperor Constantine I, as well as his junior colleague ( ''caesar'') from March 317 until his execution by his father in 326. The grandson of the ''augustus'' Constantius ...
and
Constantine II, and his nephew, Licinius's son
Licinius II
Licinius II, also called Licinius Junior or Licinius Caesar (Latin: ''Valerius Licinianus Licinius''; – ), was the son of the Roman emperor Licinius I. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' between March 317 and September 324, while his fat ...
. Constantine defeated his brother-in-law in 324 and executed both him and his son. This unified the empire under his control as sole ''augustus'', with only his young sons as co-emperors; he raised his son
Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
to ''caesar'' in 324.
324–363: Constantinian dynasty
Constantine and his sons
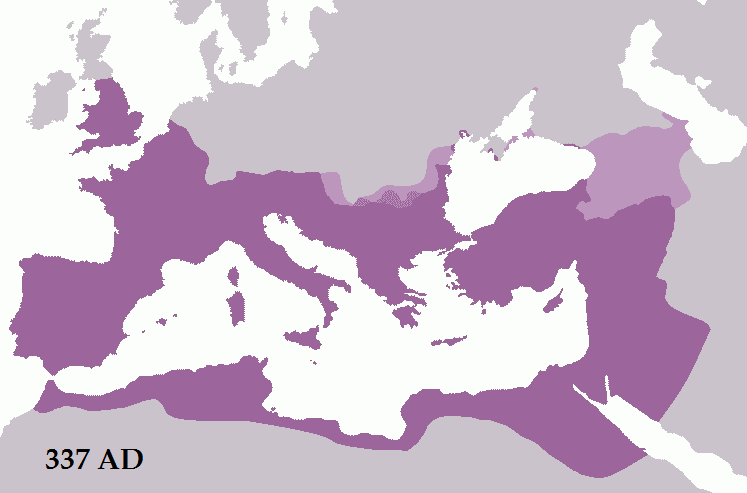
Having executed his eldest son and ''caesar'' Crispus in 326, Constantine also elevated his son
Constans to ''caesar'' in 333, as well as appointing his relatives
Dalmatius and
Hannibalianus to ''caesar'' and ''
King of Kings'' respectively. Constantine would rule until his death on 22 May 337. On their father's death, an interregnum followed during which Constantine II, Constantius II, and Constans eliminated most of the Constantinian dynasty in a struggle for power that ended with the elevation of the three brothers as co-''augusti'' in September 337. The empire was parted again among his three surviving sons.
Constantine II was killed in conflict with his youngest brother in 340. Constans was himself killed in conflict with the rebel ''augustus''
Magnentius
Magnus Magnentius ( 303 – 11 August 353) was a Roman general and usurper against Constantius II from 350 to 353. Of Germanic descent, Magnentius served with distinction in Gaul under the Western emperor Constans. On 18 January 350 Magnentiu ...
on 18 January 350. Magnentius was at first opposed in the city of Rome by self-proclaimed ''augustus''
Nepotianus, a paternal first cousin of Constans. Nepotianus was killed alongside his mother
Eutropia. His other first cousin Constantia convinced
Vetranio to proclaim himself ''caesar'' in opposition to Magnentius. Vetranio served a brief term from 1 March to 25 December 350. He was then forced to abdicate by the legitimate ''augustus'' Constantius. The
usurper Magnentius would continue to rule the western Roman Empire until 353 while in conflict with Constantius. His eventual defeat and suicide left Constantius as sole emperor until the nomination of his cousin
Constantius Gallus as his ''caesar'' and co-emperor.
Constantius's rule would, however, be opposed again in 360. After his execution of Constantius Gallus, the ''augustus'' Constantius had named his paternal half-cousin and brother-in-law
Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
as his ''caesar'' in 355, sending him to rule from Trier. During the following five years, Julian had a series of victories against invading
Germanic tribes, including the
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pr ...
. This allowed him to secure the Rhine frontier. His victorious
Gallic troops thus ceased campaigning. Constantius sent orders for the troops to be transferred to the east as reinforcements for his own currently unsuccessful campaign against
Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The List of longest-reigning monarchs, longest ...
of Persia. This order led the Gallic troops to an
insurrection. They
acclaimed, invested, and crowned their commanding officer Julian as ''augustus'' after the decisive
Battle of Strasbourg
The Battle of Strasbourg, also known as the Battle of Argentoratum, was fought in 357 between the Western Roman army under the '' Caesar'' (deputy emperor) Julian and the Alamanni tribal confederation led by the joint paramount King Chnodomar ...
, a distinction he had previously been offered but declined. Both ''augusti'' readied their troops for another Roman civil war, but the timely demise of Constantius on 3 November 361 and his deathbed recognition of Julian as co-''augustus'' prevented the
Roman civil war of 350–353
The Roman civil war of 350–353 AD was a war fought between the Roman emperor Constantius II and the usurper Magnentius.
Background
With the death of Constantine I in 337 AD, the empire was divided between his three sons from his marriage t ...
from reaching Constantinople.
361–363: Julian

Julian would serve as the sole emperor for two years. He had been raised by the
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
slave
Mardonius, a great admirer of
ancient Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
and
literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to inclu ...
. Julian had received his
baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
as a Christians, Christian years before, but no longer considered himself one. His reign would see the ending of restrictions and violence against paganism introduced by his uncle and father-in-law Constantine I and his cousins and brothers-in-law Constantine II, Constans and Constantius II. He instead placed similar restrictions on Christianity, and some unofficial violence against Christians occurred. His edict of toleration in 362 ordered the reopening of pagan Temple (Roman), temples and the reinstitution of alienated temple properties, and, more problematically for the Christian Church, the recalling of previously exiled Christian bishops. Returning orthodox and Arian bishops resumed their conflicts, thus further weakening the Church as a whole.
Julian himself was not a traditional pagan. His personal beliefs were largely influenced by Neoplatonism and Theurgy; he reputedly believed he was the reincarnation of
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. He produced works of philosophy arguing his beliefs. His brief renaissance of paganism would, however, end with his death. Julian eventually resumed the war against
Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The List of longest-reigning monarchs, longest ...
of Persia. He received a mortal wound in battle and died on June 26, 363.
According to Gibbon in ''The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', upon being mortally wounded by a dart, he was carried back to his camp. He gave a farewell speech, in which he refused to name a successor. He then proceeded to debate the philosophical nature of the soul with his generals. He then requested water and, shortly after drinking it, died. He was considered a hero by pagan sources of his time and a villain by Christian ones. Gibbon wrote quite favourably about Julian. Contemporary historians have treated him as a controversial figure.
364: Jovian
Julian died childless and with no designated successor. The officers of his army elected the rather obscure officer Jovian (Emperor), Jovian emperor. He is remembered for signing an unfavourable peace treaty with the
Sasanian Empire, ceding territories won from the Persians, dating back to
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
. He restored the privileges of Christianity. He is considered a Christian himself, though little is known of his beliefs. Jovian himself died on 17 February 364.
364–392: Valentinianic dynasty
Valentinian and Valens
The role of choosing a new ''augustus'' fell again to army officers. On 28 February 364,
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
n officer Valentinian I was elected ''augustus'' in İznik, Nicaea, Bithynia. The army had been left leaderless twice in less than a year, and the officers demanded Valentinian choose a co-ruler. On 28 March, Valentinian chose his own younger brother Valens and the two new ''augusti'' parted the empire in the pattern established by Diocletian: Valentinian would administer the western provinces, while Valens took control over the eastern empire.
The election of Valens was soon disputed. Procopius (usurper), Procopius, a Cilician maternal cousin of Julian, had been considered a likely heir to his cousin but was never designated as such. He had been in hiding since the election of Jovian. In 365, while Valentinian was at Paris and then at Rheims to direct the operations of his generals against the Alamanni, Procopius managed to bribery, bribe two
legions assigned to Constantinople and take control of Constantinople. He was acclaimed ''augustus'' on September 28 and soon extended his control to both Thrace and Bithynia. War between the rival emperors continued until Procopius was defeated. Valens had him executed on 27 May 366.
On 4 August 367, the eight-year-old Gratian was proclaimed as a third ''augustus'' by his father Valentinian, who had fallen ill, a nominal co-ruler and means to secure succession.
In April 375, Valentinian I led his army in a campaign against the Quadi, a Germanic tribes, Germanic tribe which had invaded his native region of Pannonia. According to Ammianus Marcellinus, during an audience with an Diplomatic mission, embassy from the Quadi at Brigetio on the Danube, Valentinian suffered a burst blood vessel in his brain while angrily yelling at the people gathered,
resulting in his death on 17 November 375. Gratian was then a 16-year-old and arguably ready to act as emperor, but the troops in Pannonia proclaimed his infant half-brother emperor under the title Valentinian II. Valens and Gratian acquiesced in their choice. While the senior ''augustus'' administered the eastern empire, Gratian governed the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. The Praetorian prefecture of Italy, praetorian prefecture of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa were officially administrated by infant brother and Gratian's stepmother Justina (empress), Justina. However the division was merely nominal, actual authority in the west still rested with Gratian, and with Valens as the senior emperor.
=Battle of Adrianople (378)
=

Meanwhile, the Eastern Roman Empire faced its own problems with Germanic tribes. The Thervings, Thervingi, an Germanic peoples, East Germanic tribe, fled their former lands following an invasion by the Huns. Their leaders Alavivus and Fritigern led them to seek refuge in the Eastern Roman Empire. Valens allowed them to settle as foederati on the southern bank of the Danube in 376. However, the newcomers faced problems from allegedly Political corruption, corrupted provincial commanders and a series of hardships. Their dissatisfaction led them to revolt against their Roman hosts.
Conflicts continued for the following two years. Valens led a campaign against them in 378. Gratian provided his uncle with reinforcements from the western Roman army. However, this campaign proved disastrous for the Romans. The two armies approached each other near Adrianople. Valens was apparently overconfident of the numerical superiority of his own forces over the Goths. Some of his officers advised caution and to await the arrival of Gratian, others urged an immediate attack and eventually prevailed over Valens, who, eager to have all of the glory for himself, rushed into battle. On 9 August 378, the Battle of Adrianople resulted in the crushing defeat of the Romans and the death of Valens. Contemporary historian Ammianus Marcellinus estimated that two-thirds of the Roman army were lost in the battle.
The battle had far-reaching consequences. Veteran soldiers and valuable administrators were among the heavy casualties. There were few available replacements at the time, leaving the Empire with the problem of finding suitable leadership. The
Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
also started to face recruiting problems. In the following century much of the Roman army would consist of Germanic mercenaries.
Gratian and Valentinian II
The death of Valens left Gratian and Valentinian II as the sole ''augusti''. Gratian was now effectively responsible for the whole empire. He sought a replacement ''augustus'' for the Eastern Roman Empire. His choice was Theodosius I, son of formerly distinguished ''magister equitum'' Count Theodosius. The elder Theodosius had been executed in early 375 for unclear reasons. The younger Theodosius was named Gratian and Valentinian's junior co-''augustus'' on January 19, 379, at Sirmium.
Gratian governed the western Roman Empire with energy and success for some years, but he gradually sank into indolence. He is considered to have become a figurehead while Franks, Frankish general Merobaudes (magister peditum), Merobaudes and bishop Ambrose of Milan jointly acted as the power behind the throne. Gratian lost favour with factions of the Roman Senate by prohibiting traditional paganism at Rome and relinquishing his title of Pontifex maximus. The senior ''augustus'' also became unpopular with his own Roman troops because of his close association with so-called barbarians. He reportedly recruited Alans to his personal service and adopted the guise of a Scythian warrior for public appearances.
Meanwhile, Gratian, Valentinian II and Theodosius were joined by a fourth ''augustus''. Theodosius elevated his oldest son Arcadius to ''augustus'' in January 383, in an obvious attempt to secure succession. The boy was still only five or six years old and held no actual authority. Nevertheless, he was recognised as a co-emperor by all three ''augusti''.
= 383–388: rebellion of Magnus Maximus
=
The increasing unpopularity of Gratian would cause the four ''augusti'' problems later that same year. Magnus Maximus, a general from Hispania, stationed in
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
, was proclaimed ''augustus'' by his troops in 383 and, rebelling against Gratian, he invaded Gaul. Gratian fled from Lutetia (Paris) to Lugdunum (Lyon), where he was assassinated on 25 August 383, at the age of 25.
Maximus was a firm believer of the Nicene Creed and introduced state persecution on charges of heresy, which brought him into conflict with Pope Siricius, who argued that the ''augustus'' had no authority over church matters. But he was an emperor with popular support, as is attested in Romano-British tradition, where he gained a place in the ''Mabinogion'', compiled about a thousand years after his death.
Following Gratian's death, Maximus had to deal with Valentinian II, at the time only twelve years old, as the senior ''augustus''. During the first few years, the Alps would serve as the borders between the respective territories of the two rival western Roman emperors. Maximus controlled the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. He assumed the government at Augusta Treverorum (
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
), the prefecture's capital.
Maximus soon entered negotiations with Valentinian II and Theodosius, attempting to gain their official recognition. By 384 negotiations were unfruitful and Maximus tried to press the matter by settling succession as only a legitimate emperor could do: proclaiming his own infant son Flavius Victor an ''augustus''. The end of the year found the Empire having five ''augusti'' (Valentinian II, Theodosius I, Arcadius, Magnus Maximus and Flavius Victor) with relations between them yet to be determined. Theodosius was left a widower in 385, following the sudden death of Aelia Flaccilla, his ''augusta'' and the mother of Arcadius and Honorius (emperor), Honorius.
In 386, Maximus and Victor finally received official recognition by Theodosius but not by Valentinian. In 387, Maximus apparently decided to rid himself of his Italian rival. He crossed the Alps into the valley of the Po River, Po and threatened Milan. Theodosius was remarried to the sister of Valentinian II, Galla, after their mother Justina fled with the young emperor to Theodosius's territory to escape Magnus Maximus's invasion of Italy. The marriage secured closer relations between the two ''augusti.'' Theodosius indeed campaigned west in 388 and was victorious against Maximus. Maximus himself was captured and executed in Aquileia on 28 July 388. The ''magister militum'' Arbogast (magister militum), Arbogast was sent to Trier with orders to also kill Flavius Victor. Theodosius restored Valentinian to power and through his influence had him converted to orthodox catholic Christianity. Theodosius continued supporting Valentinian and protecting him from a variety of usurpations.
379–457: Valentinianic–Theodosian dynasty

392–394: rebellion of Eugenius
In 392 Valentinian II died mysteriously in Vienne. Arbogast, who may have killed him, arranged for the appointment of Eugenius as emperor. However, the eastern emperor Theodosius I, Theodosius refused to recognise Eugenius as emperor and invaded the West, defeating and killing Arbogast and Eugenius at the Battle of the Frigidus. He thus reunited the entire Roman Empire under his rule, the last emperor who had practical power over the whole empire. On his death in February 395, the two halves of the Empire went to his two sons Arcadius and Honorius (emperor), Honorius.
395–423: Arcadius and Honorius
Arcadius became ruler in the East, with his capital in Constantinople, and Honorius became ruler in the West, with his capital in Milan and later Ravenna. The Roman state would continue to have two different emperors with different seats of power throughout the 5th century, though the eastern Romans considered themselves to be the only ones who were fully Roman. Latin was used in official writings as much as, if not more than, Greek and the two halves were nominally, culturally and historically, if not politically, the same state. Arcadius died in 408, having already elevated his infant son Theodosius II to ''augustus'' in 402. Theodosius II reigned for more than forty years.
Theodosius had two sons and a daughter, Pulcheria (daughter of Theodosius I), Pulcheria, from his first wife, Aelia Flacilla. His daughter and wife had died in 385. By his second wife, Galla, the daughter of Valentinian the Great, he had a daughter, Galla Placidia; his son Gratian did not survive infancy. Galla Placidia, having grown up at Constantinople, married first Athaulf, king of the Visigoths, and then the future Constantius III. Both her husbands died not long after the marriages, and Constantius III, who succeeded Honorius as ''augustus'', reigned for less than a year. Galla Placidia and Constantius had two children: the future Valentinian III, who became ''augustus'' in the western empire, and Justa Grata Honoria.
On the death of Honorius, the official Joannes seized power in Italy and Thedosius II appointed Valentinian III his ''caesar'' and dispatched him to the western empire with an army, which deposed Joannes and whose commander elevated Valentinian to ''augustus'' on the first anniversary of his appointment as ''caesar''. His mother the ''augusta'' Galla Placidia was regent during his youth. Valentinian III married Theodosius II's daughter Licinia Eudoxia and reigned for three decades until his murder by the rebel ''augustus'' Petronius Maximus and his ''caesar'' Palladius (Caesar), Palladius, who forced Valentinian's wife Licinia and daughter Placidia to marry them.
On the death of Theodosius II, the military officer Marcian was acclaimed Valentinian III's co-''augustus'' and married the late emperor's elder sister, the ''augusta'' Pulcheria. Marcian was the last of the Theodosians to rule in the east, and only connected to them by marriage to the ''augusta''. When Pulcheria died in 453 and Marcian died in 457, ending the Theodosian line, the court at Constantinople selected the general Leo I (emperor), Leo I as his successor as ''augustus'', beginning the reign of the Leonid dynasty.
457–518: Leonid dynasty
The Leonid dynasty established by Leo I (emperor), Leo I was continued by his daughters by the ''augusta'' Verina: Ariadne (empress), Ariadne and Leontia Porphyrogenita, Leontia. Ariadne married
Zeno and their son together, Leo II (emperor), Leo II, was elevated to ''augustus'' on the death of his grandfather (or shortly beforehand) in 474. Leo II, still a child, also died that year, but not before crowning his own father Zeno his co-emperor. Zeno, who was then sole ''augustus'', faced numerous rebellions because of his tenuous claim to the throne, including a usurpation by Basiliscus, Leo I's brother-in-law, that briefly ousted Zeno from Constantinople. Other claimants were descended from Marcia Euphemia, the daughter of the emperor Marcian from his first marriage, before becoming emperor. Marcia Euphemia married Anthemius, who became ''augustus'' in the west in 467, and had several sons: Anthemiolus was killed fighting the Goths in the west, but his brothers Romulus (son of Anthemius), Romulus, Procopius Anthemius (emperor's son), Procopius Anthemius, and Marcianus (son of Anthemius), Marcianus, who married Leontia, sought to overthrow Zeno, as did the generals Illus and Leontius (usurper), Leontius, though each failed to dislodge the emperor. A relative of Leo I's wife Verina Julius Nepos's wife, whose name is lost was married to Julius Nepos, Julius, the future emperor, who took the name ''Nepos'', 'nephew', from his wife's relationship with the imperial dynasty.
When Zeno died in 491, his widow Ariadne remarried, wedding a ''silentiarius'', Anastasius Dicorus, who was then acclaimed and crowned emperor. Anastasius built the Anastasian Wall as an outer defensive works for the fortification Walls of Constantinople.
Decline of the Western Roman Empire


After 395, the emperors in the western empire were usually figureheads, while the actual rulers were military strongmen who took the title of ''magister militum'', ''Patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician'' or both—Stilicho from 395 to 408, Constantius III, Constantius from about 411 to 421, Flavius Aëtius, Aëtius from 433 to 454 and Ricimer from about 457 to 472.
The year 476 is generally accepted as the formal end of the Western Roman Empire. That year, Orestes (father of Romulus Augustulus), Orestes, having stolen power from the emperor Julius Nepos the year before, refused the request of Germanic mercenaries in his service for lands in Italy. The dissatisfied mercenaries, including the Heruli, revolted. The revolt was led by the Germanic chieftain
Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustu ...
. Odoacer and his men captured and executed Orestes; weeks later they captured Ravenna and deposed Orestes' usurper son, Romulus Augustus. This event has been traditionally considered the fall of the Roman Empire in the west. Odoacer quickly conquered the remaining provinces of Italy.
Odoacer returned the western imperial regalia to the eastern emperor, Zeno. Zeno soon received two deputations. One was from Odoacer requesting that his control of Italy be formally recognised by the empire, in which case he would in turn acknowledge Zeno's supremacy. The other deputation was from Julius Nepos, requesting support to regain the throne. Zeno granted Odoacer the title
patrician. Zeno told Odoacer and the Roman Senate to take Nepos back, but Nepos never returned from Dalmatia, even though Odoacer issued coins in his name. Upon Nepos's death in 480, Zeno claimed Dalmatia for the East; J. B. Bury considers this the real end of the Western Roman Empire. Odoacer attacked Dalmatia, and the ensuing war ended with Theodoric the Great, King of the Ostrogoths, conquering Italy under Zeno's authority and forming the Ostrogothic Kingdom, with its capital at Ostrogothic Ravenna, Ravenna.
518–602: Justinian dynasty
When Anastasius himself died, the court at Constantinople ignored potential claimants from the Valentinianic–Theodosian dynasty and elevated instead a senior officer of the imperial guard, Justin I, as ''augustus''.
Map gallery
Empire
File:Roman expansion 264 BC Shepherd.jpg
File:Augusto 30aC - 6dC 55%CS jpg.JPG
File:RomanEmpire 117.svg
File:Roman Empire full - Referenced.jpg
File:Roman Empire full map.jpg
File:Roman Empire with provinces in 210 AD.png
File:Roman Empire with dioceses in 300 AD.png
File:Butler Migrations of the Barbarians.jpg
Orient
File:RomanPowerAsiaMinor63BCE.JPG
File:RomanEmpire 117-oriente.svg
File:Heinrich Kiepert. Asia citerior.jpg
File:Asia minor-Shepherd 1923.JPG
File:Dioecesis Orientis 400 AD.png
See also
*History of Rome
*Timeline of Roman history
*Legacy of the Roman Empire
*Succession of the Roman Empire
*History of the Byzantine Empire
Notes
References
;Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
;References
External links
*
{{Authority control
History of the Roman Empire,
Roman Empire, History
 The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of ancient Rome from the fall of the
The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of ancient Rome from the fall of the  Octavian, the grandnephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar, had made himself a central military figure during the chaotic period following Caesar's assassination. In 43 BC, at the age of twenty he became one of the three members of the Second Triumvirate, a political alliance with
Octavian, the grandnephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar, had made himself a central military figure during the chaotic period following Caesar's assassination. In 43 BC, at the age of twenty he became one of the three members of the Second Triumvirate, a political alliance with  Augustus created his novel and historically unique position by consolidating the constitutional powers of several Republican offices. He renounced his
Augustus created his novel and historically unique position by consolidating the constitutional powers of several Republican offices. He renounced his  Augustus completed the conquest of
Augustus completed the conquest of  Augustus had three grandsons by his daughter
Augustus had three grandsons by his daughter  Caligula started out well, by putting an end to the persecutions and burning his uncle's records. Unfortunately, he quickly lapsed into illness. The Caligula that emerged in late 37 demonstrated features of mental instability that led modern commentators to diagnose him with such illnesses as
Caligula started out well, by putting an end to the persecutions and burning his uncle's records. Unfortunately, he quickly lapsed into illness. The Caligula that emerged in late 37 demonstrated features of mental instability that led modern commentators to diagnose him with such illnesses as  Nero ruled from 54 to 68. During his rule, Nero focused much of his attention on diplomacy, trade, and increasing the cultural capital of the empire. He ordered the building of theatres and promoted athletic games. His reign included the Roman–Parthian War (a successful war and negotiated peace with the
Nero ruled from 54 to 68. During his rule, Nero focused much of his attention on diplomacy, trade, and increasing the cultural capital of the empire. He ordered the building of theatres and promoted athletic games. His reign included the Roman–Parthian War (a successful war and negotiated peace with the  Vespasian was able to liberate Rome from the financial burdens placed upon it by Nero's excesses and the civil wars. To do this, he not only increased taxes, but created new forms of taxation. Also, through his power as censor, he was able to carefully examine the fiscal status of every city and province, many paying taxes based upon information and structures more than a century old. Through this sound fiscal policy, he was able to build up a surplus in the treasury and embark on public works projects. It was he who first commissioned the ''Amphitheatrum Flavium'' (
Vespasian was able to liberate Rome from the financial burdens placed upon it by Nero's excesses and the civil wars. To do this, he not only increased taxes, but created new forms of taxation. Also, through his power as censor, he was able to carefully examine the fiscal status of every city and province, many paying taxes based upon information and structures more than a century old. Through this sound fiscal policy, he was able to build up a surplus in the treasury and embark on public works projects. It was he who first commissioned the ''Amphitheatrum Flavium'' ( The next century came to be known as the period of the "Five Good Emperors", in which the succession was peaceful and the Empire prosperous. The emperors of this period were Nerva (96–98),
The next century came to be known as the period of the "Five Good Emperors", in which the succession was peaceful and the Empire prosperous. The emperors of this period were Nerva (96–98),  Upon his accession to the throne, Trajan prepared and launched a carefully planned military invasion in
Upon his accession to the throne, Trajan prepared and launched a carefully planned military invasion in  Despite his own excellence as a military administrator, Hadrian's reign was marked more by the defence of the empire's vast territories, rather than major military conflicts. He surrendered Trajan's conquests in Mesopotamia, considering them to be indefensible. There was almost a war with
Despite his own excellence as a military administrator, Hadrian's reign was marked more by the defence of the empire's vast territories, rather than major military conflicts. He surrendered Trajan's conquests in Mesopotamia, considering them to be indefensible. There was almost a war with  It is possible that an alleged Roman embassy from " Daqin" that arrived in Eastern Han China in 166 via a Roman maritime route into the
It is possible that an alleged Roman embassy from " Daqin" that arrived in Eastern Han China in 166 via a Roman maritime route into the  The period of the "Five Good Emperors" was brought to an end by the reign of Commodus from 180 to 192. Commodus was the son of Marcus Aurelius, making him the first direct successor in a century, breaking the scheme of adoptive successors that had worked so well. He was co-emperor with his father from 177. When he became sole emperor upon the death of his father in 180, it was at first seen as a hopeful sign by the people of the Roman Empire. Nevertheless, as generous and magnanimous as his father was, Commodus was just the opposite. In '' The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' by
The period of the "Five Good Emperors" was brought to an end by the reign of Commodus from 180 to 192. Commodus was the son of Marcus Aurelius, making him the first direct successor in a century, breaking the scheme of adoptive successors that had worked so well. He was co-emperor with his father from 177. When he became sole emperor upon the death of his father in 180, it was at first seen as a hopeful sign by the people of the Roman Empire. Nevertheless, as generous and magnanimous as his father was, Commodus was just the opposite. In '' The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' by  His
His  Lucius Septimius Severus was born to a family of Phoenician equestrian rank in the Roman province of
Lucius Septimius Severus was born to a family of Phoenician equestrian rank in the Roman province of  The eldest son of Severus, Caracalla was born Lucius Septimius Bassianus in Lugdunum, Gaul. "Caracalla" was a nickname referring to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore even when he slept. Before his father's death, Caracalla was proclaimed co-emperor with his father and brother Geta. Conflict between the two culminated in the assassination of the latter. Unlike the much more successful joint reign of Marcus Aurelius and his brother Lucius Verus in the previous century, relations were hostile between the two Severid brothers from childhood. Geta was assassinated in his mother's apartments by order of Caracalla, who thereafter ruled as sole ''Augustus''.
Reigning alone, Caracalla was noted for lavish bribes to the legionaries and unprecedented cruelty, authorising numerous assassinations of perceived enemies and rivals. He campaigned with indifferent success against the
The eldest son of Severus, Caracalla was born Lucius Septimius Bassianus in Lugdunum, Gaul. "Caracalla" was a nickname referring to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore even when he slept. Before his father's death, Caracalla was proclaimed co-emperor with his father and brother Geta. Conflict between the two culminated in the assassination of the latter. Unlike the much more successful joint reign of Marcus Aurelius and his brother Lucius Verus in the previous century, relations were hostile between the two Severid brothers from childhood. Geta was assassinated in his mother's apartments by order of Caracalla, who thereafter ruled as sole ''Augustus''.
Reigning alone, Caracalla was noted for lavish bribes to the legionaries and unprecedented cruelty, authorising numerous assassinations of perceived enemies and rivals. He campaigned with indifferent success against the 
 Born Varius Avitus Bassianus on 16 May 205, known later as M. Aurelius Antonius, he was appointed at an early age to be priest of the sun god,
Born Varius Avitus Bassianus on 16 May 205, known later as M. Aurelius Antonius, he was appointed at an early age to be priest of the sun god,  By 258, the Roman Empire broke up into three competing states. The
By 258, the Roman Empire broke up into three competing states. The  The transition to divided western and eastern halves of the empire was gradual. In July 285, Diocletian defeated rival emperor Carinus and briefly became sole emperor of the Roman Empire. Diocletian's reign stabilised the empire and marked the end of the Crisis of the Third Century. Diocletian appointed a co-emperor in 286 and delegated further with two junior-emperors.
Diocletian secured the empire's borders and purged it of all threats to his power. He defeated the Sarmatians and Carpi during several campaigns between 285 and 299, the Alamanni in 288, and usurpers in
The transition to divided western and eastern halves of the empire was gradual. In July 285, Diocletian defeated rival emperor Carinus and briefly became sole emperor of the Roman Empire. Diocletian's reign stabilised the empire and marked the end of the Crisis of the Third Century. Diocletian appointed a co-emperor in 286 and delegated further with two junior-emperors.
Diocletian secured the empire's borders and purged it of all threats to his power. He defeated the Sarmatians and Carpi during several campaigns between 285 and 299, the Alamanni in 288, and usurpers in  On 1 March 293, authority was further divided. Each ''augustus'' took a junior emperor called a ''caesar'' to aid him in administrative matters, and to provide a line of succession.
On 1 March 293, authority was further divided. Each ''augustus'' took a junior emperor called a ''caesar'' to aid him in administrative matters, and to provide a line of succession.  In spite of his failures, Diocletian's reforms fundamentally changed the structure of Roman imperial government and helped stabilise the empire economically and militarily, enabling the empire to remain essentially intact for another hundred years despite being near the brink of collapse in Diocletian's youth. Weakened by illness, Diocletian left the imperial office on 1 May 305, and became the first Roman emperor to voluntarily abdicate the position ( John VI retired to a monastery in the 14th century). He lived out his retirement in his palace on the Dalmatian coast, tending to his vegetable gardens. His palace eventually became the core of the modern-day city of Split.
The peaceful Tetrarchy would effectively collapse with the death of Constantius Chlorus on July 25, 306. Constantius's troops in
In spite of his failures, Diocletian's reforms fundamentally changed the structure of Roman imperial government and helped stabilise the empire economically and militarily, enabling the empire to remain essentially intact for another hundred years despite being near the brink of collapse in Diocletian's youth. Weakened by illness, Diocletian left the imperial office on 1 May 305, and became the first Roman emperor to voluntarily abdicate the position ( John VI retired to a monastery in the 14th century). He lived out his retirement in his palace on the Dalmatian coast, tending to his vegetable gardens. His palace eventually became the core of the modern-day city of Split.
The peaceful Tetrarchy would effectively collapse with the death of Constantius Chlorus on July 25, 306. Constantius's troops in 
 Having executed his eldest son and ''caesar'' Crispus in 326, Constantine also elevated his son Constans to ''caesar'' in 333, as well as appointing his relatives Dalmatius and Hannibalianus to ''caesar'' and '' King of Kings'' respectively. Constantine would rule until his death on 22 May 337. On their father's death, an interregnum followed during which Constantine II, Constantius II, and Constans eliminated most of the Constantinian dynasty in a struggle for power that ended with the elevation of the three brothers as co-''augusti'' in September 337. The empire was parted again among his three surviving sons.
Constantine II was killed in conflict with his youngest brother in 340. Constans was himself killed in conflict with the rebel ''augustus''
Having executed his eldest son and ''caesar'' Crispus in 326, Constantine also elevated his son Constans to ''caesar'' in 333, as well as appointing his relatives Dalmatius and Hannibalianus to ''caesar'' and '' King of Kings'' respectively. Constantine would rule until his death on 22 May 337. On their father's death, an interregnum followed during which Constantine II, Constantius II, and Constans eliminated most of the Constantinian dynasty in a struggle for power that ended with the elevation of the three brothers as co-''augusti'' in September 337. The empire was parted again among his three surviving sons.
Constantine II was killed in conflict with his youngest brother in 340. Constans was himself killed in conflict with the rebel ''augustus''  Julian would serve as the sole emperor for two years. He had been raised by the
Julian would serve as the sole emperor for two years. He had been raised by the  Meanwhile, the Eastern Roman Empire faced its own problems with Germanic tribes. The Thervings, Thervingi, an Germanic peoples, East Germanic tribe, fled their former lands following an invasion by the Huns. Their leaders Alavivus and Fritigern led them to seek refuge in the Eastern Roman Empire. Valens allowed them to settle as foederati on the southern bank of the Danube in 376. However, the newcomers faced problems from allegedly Political corruption, corrupted provincial commanders and a series of hardships. Their dissatisfaction led them to revolt against their Roman hosts.
Conflicts continued for the following two years. Valens led a campaign against them in 378. Gratian provided his uncle with reinforcements from the western Roman army. However, this campaign proved disastrous for the Romans. The two armies approached each other near Adrianople. Valens was apparently overconfident of the numerical superiority of his own forces over the Goths. Some of his officers advised caution and to await the arrival of Gratian, others urged an immediate attack and eventually prevailed over Valens, who, eager to have all of the glory for himself, rushed into battle. On 9 August 378, the Battle of Adrianople resulted in the crushing defeat of the Romans and the death of Valens. Contemporary historian Ammianus Marcellinus estimated that two-thirds of the Roman army were lost in the battle.
The battle had far-reaching consequences. Veteran soldiers and valuable administrators were among the heavy casualties. There were few available replacements at the time, leaving the Empire with the problem of finding suitable leadership. The
Meanwhile, the Eastern Roman Empire faced its own problems with Germanic tribes. The Thervings, Thervingi, an Germanic peoples, East Germanic tribe, fled their former lands following an invasion by the Huns. Their leaders Alavivus and Fritigern led them to seek refuge in the Eastern Roman Empire. Valens allowed them to settle as foederati on the southern bank of the Danube in 376. However, the newcomers faced problems from allegedly Political corruption, corrupted provincial commanders and a series of hardships. Their dissatisfaction led them to revolt against their Roman hosts.
Conflicts continued for the following two years. Valens led a campaign against them in 378. Gratian provided his uncle with reinforcements from the western Roman army. However, this campaign proved disastrous for the Romans. The two armies approached each other near Adrianople. Valens was apparently overconfident of the numerical superiority of his own forces over the Goths. Some of his officers advised caution and to await the arrival of Gratian, others urged an immediate attack and eventually prevailed over Valens, who, eager to have all of the glory for himself, rushed into battle. On 9 August 378, the Battle of Adrianople resulted in the crushing defeat of the Romans and the death of Valens. Contemporary historian Ammianus Marcellinus estimated that two-thirds of the Roman army were lost in the battle.
The battle had far-reaching consequences. Veteran soldiers and valuable administrators were among the heavy casualties. There were few available replacements at the time, leaving the Empire with the problem of finding suitable leadership. The 
