|
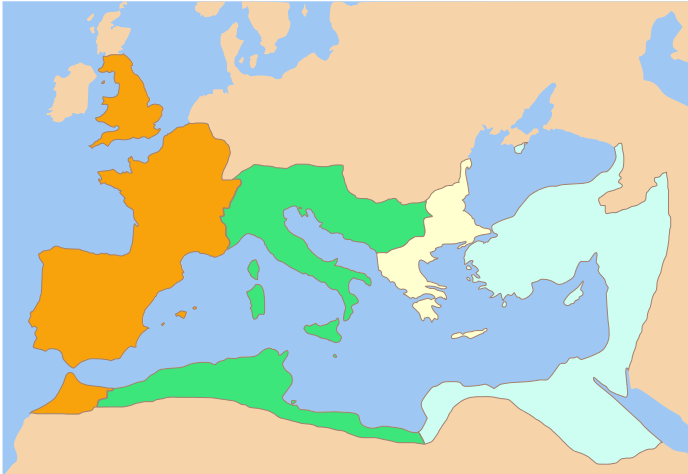
Constantine II (emperor)
Constantine II (; 316–340) was Roman emperor from 337 to 340. The son of the emperor Constantine I, he was proclaimed Caesar (title), ''caesar'' by his father shortly after his birth. He was associated with military victories over the Sarmatians, Alamanni and Goths during his career, for which he was granted a number of victory titles. He held the Roman consul, consulship four times – in 320, 321, 324, and 329. Constantine I had arranged for his sons to share power with their cousins Dalmatius and Hannibalianus, but this was not accepted by Constantine II and his brothers. As a result, Constantine II's brother Constantius II ordered the killings of numerous male relatives following Constantine I's death, including Dalmatius and Hannibalianus, thus eliminating any possible opponents to the succession of Constantine I's sons. Constantine II then ascended to the throne alongside his two younger brothers, ruling Roman Gaul, Gaul, Hispania, and Roman Britain, Britain. However, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piazza Del Campidoglio
Piazza del Campidoglio ("Capitoline Square") is a public square (piazza) on the top of the ancient Capitoline Hill, between the Roman Forum and the Campus Martius in Rome, Italy. The square includes three main buildings, the Palazzo Senatorio (Senatorial Palace) also known as the Comune di Roma Capitale (City Hall), and the two palaces that make up the Capitoline Museums, the Capitoline Hill#Palazzo dei Conservatori, Palazzo dei Conservatori and the Capitoline Hill#Palazzo Nuovo, Palazzo Nuovo, considered to be one of the oldest national museums, founded in 1471 when Pope Sixtus IV donated some of the museum's most impressive statues, the She-wolf, the Spinario, the Camillus and the colossal head of emperor Constantine. Over the centuries the museums' collection has grown to include many of ancient Roman's finest artworks and artifacts. If something was considered too valuable or fragile in Rome and a copy was made in its place for display, the original is likely now on display in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the second century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. It is currently a (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian (emperor)
Julian (; ; 331 – 26 June 363) was the Caesar of the West from 355 to 360 and Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplatonic Hellenism in its place, caused him to be remembered as Julian the Apostate in the Christian tradition. A nephew of Constantine the Great, Julian was one of few in the imperial family to survive the purges and civil wars during the reign of Constantius II, his cousin. Julian became an orphan as a child after his father was executed in 337, and spent much of his life under Constantius's close supervision. However, the emperor allowed Julian freedom to pursue an education in the Greek-speaking east. In 355, Constantius II summoned Julian to court and appointed him to rule Gaul. Julian was successful in his rule, defeating and counterattacking Germanic raids across the Rhine and encouraging the provinces' return to prosperity. In 360, he was proclaime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopography Of The Later Roman Empire
''Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire'' (abbreviated as ''PLRE'') is a work of Roman prosopography published in a set of three volumes collectively describing many of the people attested to have lived in the Roman Empire from AD 260, the date of the beginning of Gallienus' sole rule, to 641, the date of the death of Heraclius. Sources cited include histories, literary texts, inscriptions, and miscellaneous written sources. Individuals who are known only from dubious sources (e.g., the '), as well as identifiable people whose names have been lost, are included with signs indicating the reliability. A project of the British Academy, the work set out with the goal of doing The volumes were published by Cambridge University Press Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessme .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damnatio Memoriae
() is a modern Latin phrase meaning "condemnation of memory" or "damnation of memory", indicating that a person is to be excluded from official accounts. Depending on the extent, it can be a case of historical negationism. There are and have been many routes to including the destruction of depictions, the removal of names from inscriptions and documents, and even large-scale rewritings of history. The term can be applied to other instances of official scrubbing. The practice has been seen as early as the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period, where the Pharaohs Hatshepsut and Akhenaten were subject to it. After Herostratus set fire to the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, Seven Wonders of antiquity, the people of Ephesus banned the mention of his name. His name has since become an eponym for people who commit crimes for the purpose of gaining notoriety. Etymology Although the term is Latin, the phrase was not used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn Legitimacy (family law), legitimate child to inheritance, inherit all or most of their parent's estate (law), estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture), or firstborn child (absolute primogeniture). Its opposite analogue is partible inheritance. Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g., male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogenitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannibalianus
__NOTOC__ Flavius Hannibalianus (also Hanniballianus; died September 337) was a member of the Constantinian dynasty, which ruled over the Roman Empire in the 4th century. Hannibalianus was the son of Flavius Dalmatius, and thus nephew of Constantine the Great.Ammianus Marcellinus, xiv i.2.Aurelius Victor, 41.20 Hannibalianus and his brother Dalmatius were educated at Tolosa by rhetor Exuperius (who is probably not to be identified with St. Exuperius). In 320s, Constantine called Flavius Dalmatius and his sons to Constantinople. Hannibalianus married Constantine's elder daughter, Constantina, in 335, and was made '' nobilissimus''. He and Constantina may have had a daughter named Constantia, who would later marry Memmius Vitrasius Orfitus and become mother of Rusticiana, wife of Quintus Aurelius Symmachus. In occasion of the campaign of Constantine against the Sassanids (337), Hannibalianus was made '' Rex Regum et Ponticarum Gentium'', "King of the Kings and of the Pontic Peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatius
:''This article deals with the Caesar (335-337). For the censor Flavius Dalmatius, father of the Caesar, see Flavius Dalmatius. For saints with this name, see Saint Dalmatius (other).'' Flavius Dalmatius (died June 337), often spelled Delmatius on contemporary coins, was a ''Caesar'' of the Roman Empire from 335 to 337, and member of the Constantinian dynasty. Dalmatius was the nephew of Constantine the Great. His father, also named Flavius Dalmatius, was the half-brother of Constantine and served as censor. Dalmatius and his brother Hannibalianus were educated at Tolosa (Toulouse) by rhetor Exuperius. On 18 September 335, he was raised to the rank of ''Caesar'' by his uncle, with the control of Thracia, Achaea Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries. In the late 4th century, the lands of the Goths in present-day Ukraine were overwhelmed by a significant westward movement of Alans and Huns from the east. Large numbers of Goths subsequently concentrated upon the Roman border at the Lower Danube, seeking refuge inside the Roman Empire. After they entered the Empire, violence broke out, and Goth-led forces inflicted a devastating defeat upon the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, which by the eighth century were collectively referred to as '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by the Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, however, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4th century CE. The earliest known reference to the Sarmatians occurs in the Avesta, where they appear as ''Sairima-'', which in later Iranian sources becomes ''*Sarm'' and Salm (Shahnameh), ''Salm''. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BCE, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BCE. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BCE, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black Sea, Black and Caspian Sea, Caspian seas and the Caucasus to the south. In the first century CE, the Sarmatians beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |