History Of Native Americans In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of
 According to the most generally accepted theory of the
According to the most generally accepted theory of the
 The Paleo-Indian or Lithic stage lasted from the first arrival of people in the Americas until about (in North America). Three major migrations occurred, as traced by linguistic and genetic data; the early Paleoamericans soon spread throughout the Americas, diversifying into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes. By the North American climate was very similar to today's.J. Imbrie and K.P. Imbrie, ''Ice Ages: Solving the Mystery'' (Short Hills, NJ: Enslow Publishers) 1979. A study published in 2012 gives genetic backing to the 1986 theory put forward by linguist
The Paleo-Indian or Lithic stage lasted from the first arrival of people in the Americas until about (in North America). Three major migrations occurred, as traced by linguistic and genetic data; the early Paleoamericans soon spread throughout the Americas, diversifying into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes. By the North American climate was very similar to today's.J. Imbrie and K.P. Imbrie, ''Ice Ages: Solving the Mystery'' (Short Hills, NJ: Enslow Publishers) 1979. A study published in 2012 gives genetic backing to the 1986 theory put forward by linguist  The
The
Joe W. Saunders, Rolfe D. Mandel, Roger T. Saucier, E. Thurman Allen, C. T. Hallmark, Jay K. Johnson, Edwin H. Jackson, Charles M. Allen, Gary L. Stringer, Douglas S. Frink, James K. Feathers, Stephen Williams, Kristen J. Gremillion, Malcolm F. Vidrine, and Reca Jones, ''Science'', September 19, 1997: Vol. 277 no. 5333, pp. 1796–99, accessed 2011-10-27
 The term "Woodland" was coined in the 1930s and refers to prehistoric sites dated between the Archaic period and the
The term "Woodland" was coined in the 1930s and refers to prehistoric sites dated between the Archaic period and the  The
The  The
The
''Encyclopædia Britannica.'' Retrieved 4 June 2012. It is believed that the Ancestral Puebloans developed, at least in part, from the
 After 1492
After 1492
Frederick W. Hodge, ''Handbook of American Indians'', 1906. Most mainstream scholars believe that, among the various contributing factors,
 After European explorers reached the West Coast in the 1770s, smallpox rapidly killed at least 30% of Northwest Coast Native Americans. For the next 80 to 100 years, smallpox and other diseases devastated native populations in the region.
After European explorers reached the West Coast in the 1770s, smallpox rapidly killed at least 30% of Northwest Coast Native Americans. For the next 80 to 100 years, smallpox and other diseases devastated native populations in the region.
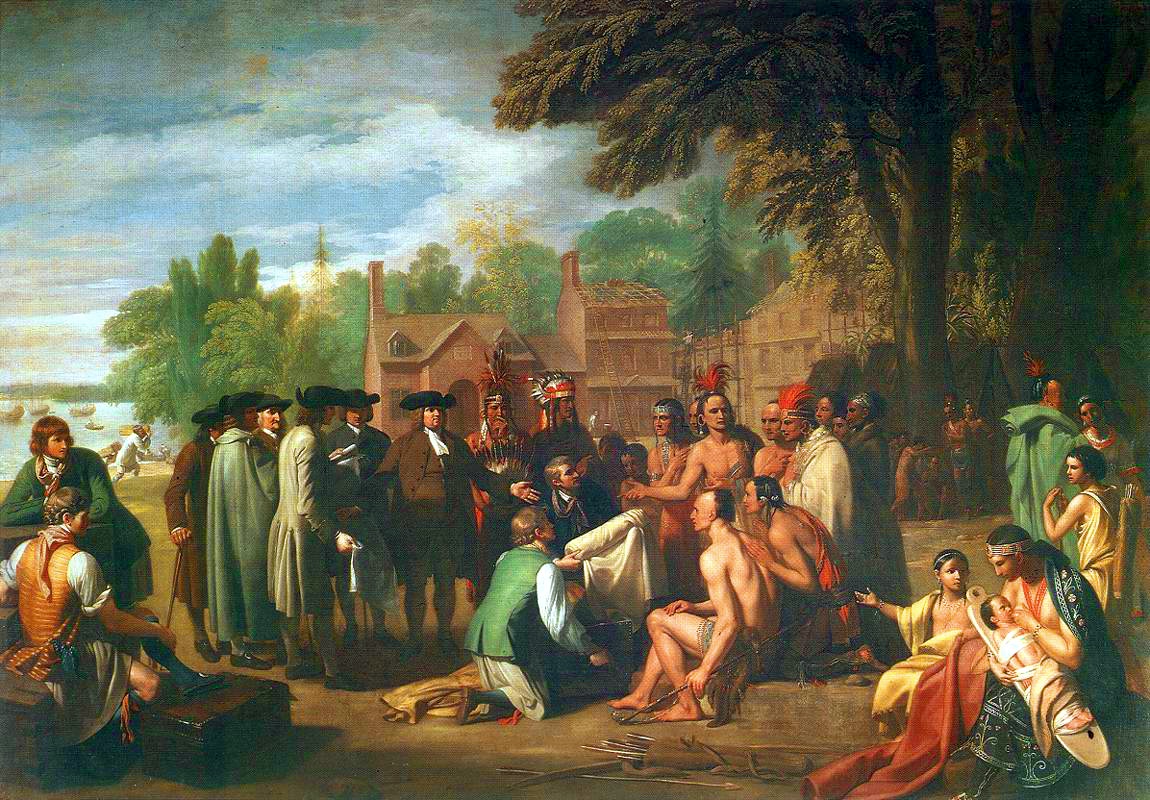 Native American culture began to have an influence on European thought in this period. Some Europeans considered Native American societies to be representative of a golden age known to them only in folk history.
The political theorist
Native American culture began to have an influence on European thought in this period. Some Europeans considered Native American societies to be representative of a golden age known to them only in folk history.
The political theorist
''History News Network'', July 5, 2005, accessed 2012-01-17 Secondly, he notes: "All the key political concepts that were the stuff of American political discourse before the Revolution and after, had obvious European antecedents and referents: bicameralism, separation of powers, confederations, and the like."
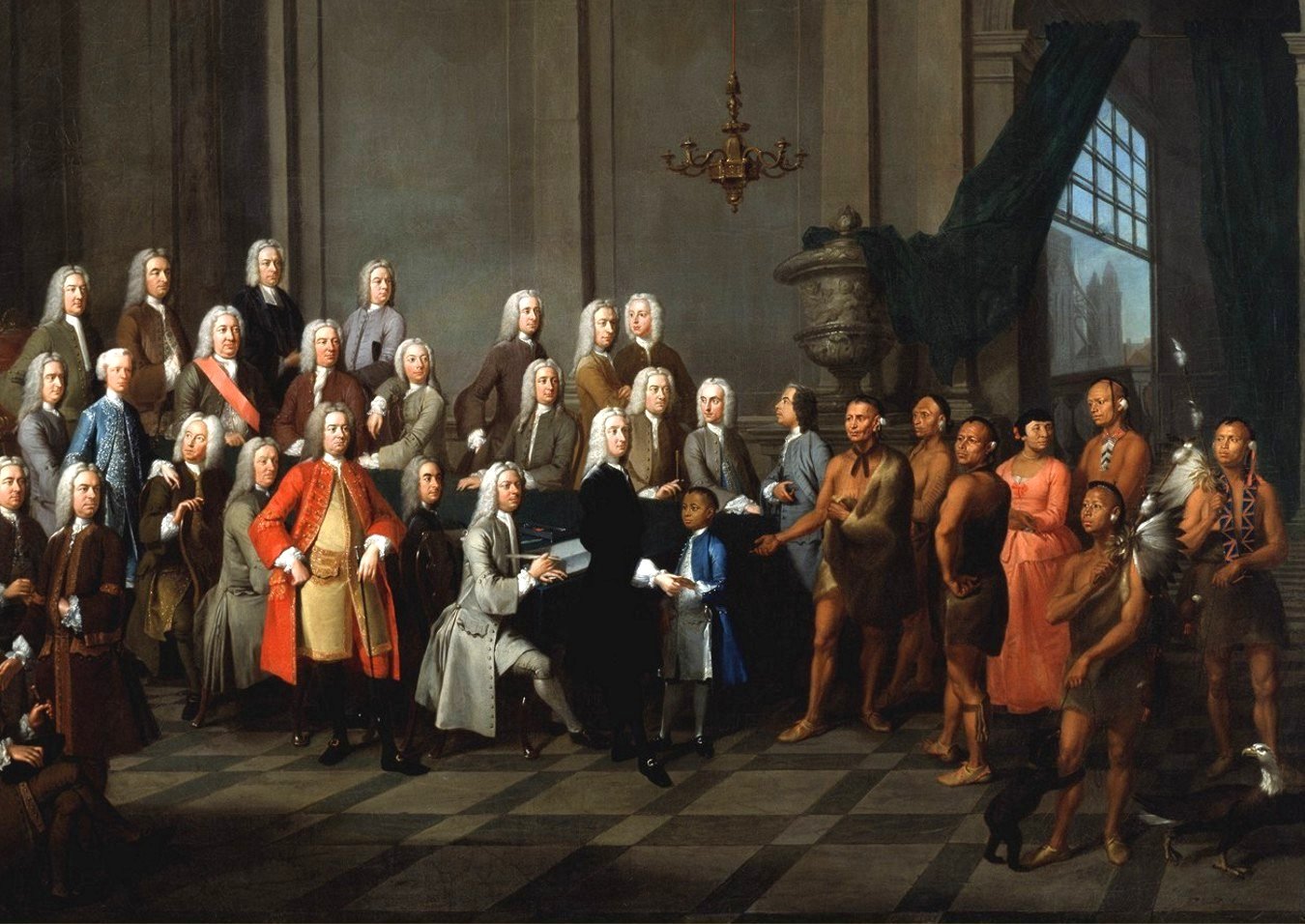 During the
During the  The British made peace with the Americans in the
The British made peace with the Americans in the
 During this time, what came to be called The
During this time, what came to be called The  In the late 18th century, reformers starting with Washington and Knox, supported educating native children and adults, in efforts to "
In the late 18th century, reformers starting with Washington and Knox, supported educating native children and adults, in efforts to "
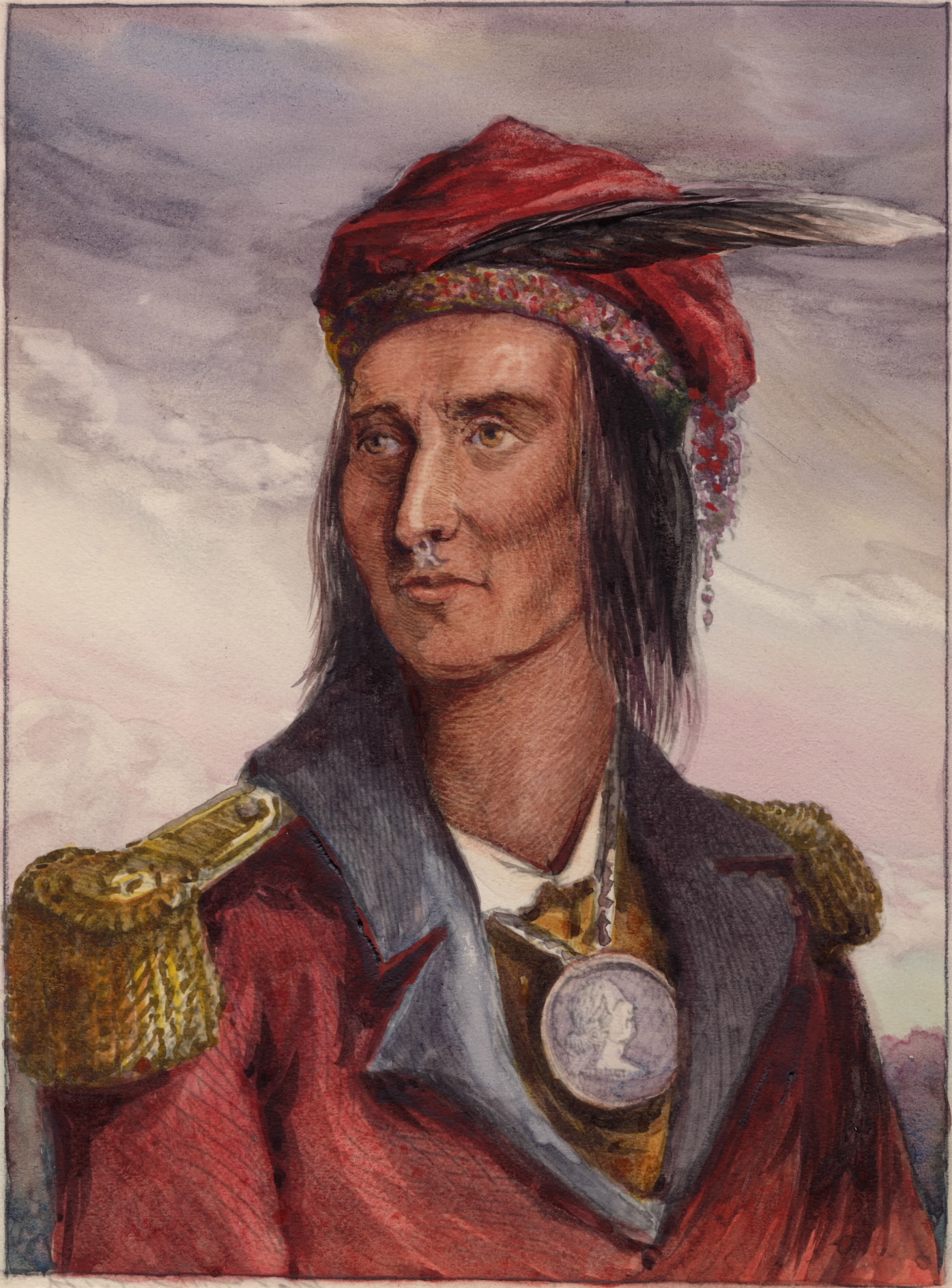 As American expansion continued, Native Americans resisted settlers' encroachment in several regions of the new nation (and in unorganized territories), from the Northwest to the Southeast, and then in the West, as settlers encountered the tribes of the
As American expansion continued, Native Americans resisted settlers' encroachment in several regions of the new nation (and in unorganized territories), from the Northwest to the Southeast, and then in the West, as settlers encountered the tribes of the
 In July 1845, the New York newspaper editor John L. O’Sullivan coined the phrase, "Manifest Destiny," as the "design of Providence" supporting the territorial expansion of the United States.
In July 1845, the New York newspaper editor John L. O’Sullivan coined the phrase, "Manifest Destiny," as the "design of Providence" supporting the territorial expansion of the United States.  After a decade of wars between the U.S and the tribes of the Great Plains, including
After a decade of wars between the U.S and the tribes of the Great Plains, including
 Many Native Americans served in the military during the
Many Native Americans served in the military during the  General Ely S. Parker, a member of the
General Ely S. Parker, a member of the
 Some 44,000 Native Americans served in the
Some 44,000 Native Americans served in the
''Indian Country Today,'' 4 September 2013; accessed 5 November 2016 By 2012, "the Justice and Interior departments had reached settlements totaling more than $1 billion with 41 tribes for claims of mismanagement."Alysa Landry, "Barack Obama: ‘Emotionally and Intellectually Committed to Indian Country’"
''Indian Country Today,'' 1 November 2016; accessed 5 November 2016 The Navajo Nation gained the largest settlement with a single tribe, of $554 million. It is the largest tribe in the United States. In 2013 under renewal of the Violence Against Women Act#2012–13 legislative battle and reauthorization, Violence Against Women Act, the federal government strengthened protection of Native American women, as it established authority for tribes to prosecute non-Natives who commit crimes on Indian land. Domestic and sexual abuse of Native American women has been a problem in many areas, but previous laws prevented arrest or prosecution by tribal police or courts of non-native abusive partners. Native American migration to urban areas continued to grow: 70% of Native Americans lived in urban areas in 2012, up from 45% in 1970, and 8% in 1940. Urban areas with significant Native American populations include Rapid City, South Dakota, Rapid City,
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United State ...
began before the founding of the country, tens of thousands of years ago with the settlement of the Americas
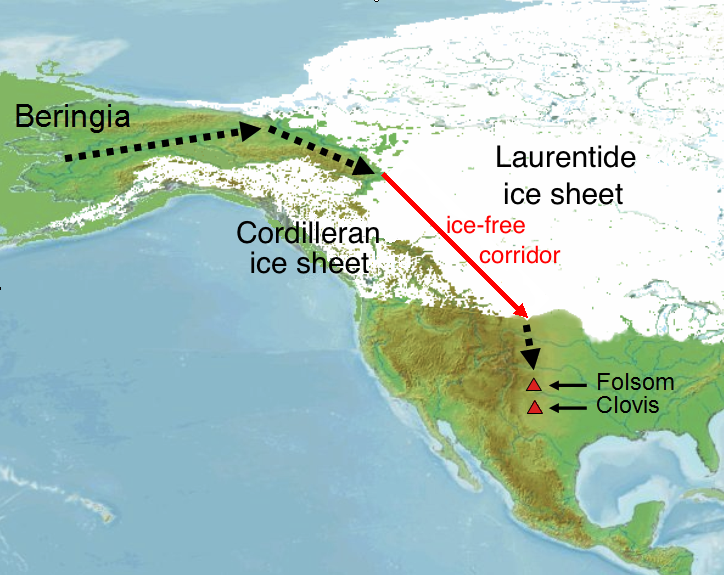
The settlement of the Americas began when Paleolithic hunter-gatherers entered North America from the North Asian Mammoth steppe via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia and western Alaska due to the lowering of ...
by the Paleo-Indians. Anthropologists and archeologists have identified and studied a wide variety of cultures that existed during this era. Their subsequent contact with Europeans had a profound impact on their history afterwards.
Eurasian migration
Migration to the Continent
 According to the most generally accepted theory of the
According to the most generally accepted theory of the settlement of the Americas
The settlement of the Americas began when Paleolithic hunter-gatherers entered North America from the North Asian Mammoth steppe via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia and western Alaska due to the lowering of ...
, migrations of humans from Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
to the Americas took place via Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
, a land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and Colonisation (biology), colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regre ...
which connected the two continents across what is now the Bering Strait. The number and if amin was part
of the migrations is still being debated.Ehlers, J., and P.L. Gibbard, 2004a, ''Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 2: Part II North America'', Elsevier, Amsterdam. . Falling sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
s associated with an intensive period of Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe ...
created the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
that joined Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
to Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
about 60–25,000 years ago. The latest this migration could have taken place is 12,000 years ago; the earliest remains undetermined.
The archaeological periods used are the classifications of archaeological periods and cultures established in Gordon Willey
Gordon Randolph Willey (7 March 1913 – 28 April 2002) was an American archaeologist who was described by colleagues as the "dean" of New World archaeology.Sabloff 2004, p.406 Willey performed fieldwork at excavations in South America, Central A ...
and Philip Phillips' 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology'' which divided the archaeological record in the Americas into five phases; see Archaeology of the Americas
The archaeology of the Americas is the study of the archaeology of the Western Hemisphere, including North America (Mesoamerica), Central America, South America and the Caribbean. This includes the study of pre-historic/Pre-Columbian and histor ...
.
Paleo-India or Lithic stage
 The Paleo-Indian or Lithic stage lasted from the first arrival of people in the Americas until about (in North America). Three major migrations occurred, as traced by linguistic and genetic data; the early Paleoamericans soon spread throughout the Americas, diversifying into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes. By the North American climate was very similar to today's.J. Imbrie and K.P. Imbrie, ''Ice Ages: Solving the Mystery'' (Short Hills, NJ: Enslow Publishers) 1979. A study published in 2012 gives genetic backing to the 1986 theory put forward by linguist
The Paleo-Indian or Lithic stage lasted from the first arrival of people in the Americas until about (in North America). Three major migrations occurred, as traced by linguistic and genetic data; the early Paleoamericans soon spread throughout the Americas, diversifying into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes. By the North American climate was very similar to today's.J. Imbrie and K.P. Imbrie, ''Ice Ages: Solving the Mystery'' (Short Hills, NJ: Enslow Publishers) 1979. A study published in 2012 gives genetic backing to the 1986 theory put forward by linguist Joseph Greenberg
Joseph Harold Greenberg (May 28, 1915 – May 7, 2001) was an American linguist, known mainly for his work concerning linguistic typology and the genetic classification of languages.
Life Early life and education
Joseph Greenberg was born on ...
that the Americas must have been populated in three waves, based on language differences.
The Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 ...
, a megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
hunting culture, is primarily identified by use of fluted spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
points. Artifacts from this culture were first excavated in 1932 near Clovis, New Mexico
Clovis is a city in and the county seat of Curry County, New Mexico, Curry County, New Mexico. The city had a population of 37,775 as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, and a 2019 estimated population of 38,319. Clovis is located in th ...
. The Clovis culture ranged over much of North America and also appeared in South America. The culture is identified by the distinctive Clovis point, a flaked flint spear-point with a notched flute, by which it was inserted into a shaft. Dating of Clovis materials has been by association with animal bones and by the use of carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
methods. Recent reexaminations of Clovis materials using improved carbon-dating methods produced results of 11,050 and 10,800 radiocarbon years BP (roughly 9100 to 8850 BCE).
Numerous Paleoindian cultures occupied North America, with some arrayed around the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
and Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
of the modern United States of America and Canada, as well as adjacent areas to the West and Southwest. According to the oral histories of many of the indigenous peoples of the Americas, they have been living on this continent since their genesis, described by a wide range of traditional creation stories
A creation myth (or cosmogonic myth) is a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop ...
. Other tribes have stories that recount migrations across long tracts of land and a great river believed to be the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. Genetic and linguistic data connect the indigenous people of this continent with ancient northeast Asians. Archeological and linguistic data has enabled scholars to discover some of the migrations within the Americas.
 The
The Folsom tradition
The Folsom Complex is a Paleo-Indian archaeological culture that occupied much of central North America from c. 8500 BCE to c. 4000 BCE. The term was first used in 1927 by Jesse Dade Figgins, director of the Colorado Museum of Natural History.
...
was characterized by the use of Folsom point
Folsom points are projectile points associated with the Folsom tradition of North America. The style of tool-making was named after the Folsom site located in Folsom, New Mexico, where the first sample was found in 1908 by George McJunkin within t ...
s as projectile tips and activities known from kill sites, where slaughter and butchering of bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
took place. Folsom tools were left behind between 9000 BCE and 8000 BCE.
Na-Dené
Na-Dene (; also Nadene, Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit, Tlina–Dene) is a family of Native American languages that includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. Haida was formerly included, but is now considere ...
-speaking peoples entered North America starting around , reaching the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
by , and from there migrating along the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
and into the interior. Linguists, anthropologists, and archeologists believe their ancestors constituted a separate migration into North America, later than the first Paleo-Indians. They migrated into Alaska and northern Canada, south along the Pacific Coast, into the interior of Canada, and south to the Great Plains and the American Southwest.
They were the earliest ancestors of the Athabascan
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Co ...
-speaking peoples, including the present-day and historical Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
and Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño an ...
. They constructed large multi-family dwellings in their villages, which were used seasonally. People did not live there year-round, but for the summer to hunt and fish, and to gather food supplies for the winter.
Meso-Indian or Archaic stage
The Archaic period lasted until about . A major culture of the Archaic stage was theMound builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
, who stretched from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
to the Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
and Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
rivers. Since the 1990s, archeologists have explored and dated eleven Middle Archaic sites in present-day Louisiana and Florida at which early cultures built complexes with multiple earthwork mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher el ...
s; they were societies of hunter-gatherers rather than the settled agriculturalists believed necessary according to the theory of Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
to sustain such large villages over long periods. Native American cultures are not included in characterizations of advanced Stone Age cultures as "Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
," which is a category that more often includes only the cultures in Eurasia, Africa, and other regions.
The prime example is Watson Brake in northern Louisiana, whose 11-mound complex is dated to , making it the oldest dated site in the Americas for such complex construction. It is nearly 2,000 years older than the Poverty Point
Poverty Point State Historic Site/Poverty Point National Monument (french: Pointe de Pauvreté; 16 WC 5) is a prehistoric earthwork constructed by the Poverty Point culture, located in present-day northeastern Louisiana, though evidence of t ...
site. Construction of the mounds went on for 500 years until was abandoned about , probably due to changing environmental conditions."A Mound Complex in Louisiana at 5400–5000 Years Before the Present"Joe W. Saunders, Rolfe D. Mandel, Roger T. Saucier, E. Thurman Allen, C. T. Hallmark, Jay K. Johnson, Edwin H. Jackson, Charles M. Allen, Gary L. Stringer, Douglas S. Frink, James K. Feathers, Stephen Williams, Kristen J. Gremillion, Malcolm F. Vidrine, and Reca Jones, ''Science'', September 19, 1997: Vol. 277 no. 5333, pp. 1796–99, accessed 2011-10-27
Poverty Point culture
The Poverty Point culture is the archaeological culture of a prehistoric indigenous peoples who inhabited a portion of North America's lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 1730 – 1350 BC.
Archeologists have identified ...
is a Late Archaic archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
that inhabited the area of the lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf Coast. The culture thrived from to , during the Late Archaic period. Evidence of this culture has been found at more than 100 sites, from the major complex at Poverty Point, Louisiana (a UNESCO World Heritage site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
) across a range to the Jaketown Site
Jaketown Site ( 22 HU 505) is an archaeological site with two prehistoric earthwork mounds in Humphreys County, Mississippi, United States. While the mounds have not been excavated, distinctive pottery shards found in the area lead scholars t ...
near Belzoni, Mississippi
Belzoni ( ) is a city in Humphreys County, Mississippi, United States, in the Mississippi Delta region, on the Yazoo River. The population was 2,235 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Humphreys County. It was named for the 19th-centur ...
.
Poverty Point is a complex of six major earthwork concentric rings, with additional platform mounds at the site. Artifacts show the people traded with other Native Americans located from Georgia to the Great Lakes region. This is one among numerous mound sites of complex indigenous cultures throughout the Mississippi and Ohio valleys. They were one of several succeeding cultures often referred to as mound builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
.
The Oshara tradition
Oshara Tradition, the northern tradition of the Picosa culture, was a Southwestern Archaic tradition centered in the area now called New Mexico and Colorado. Cynthia Irwin-Williams developed the sequence of Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic ...
people lived from to . They were part of the Southwestern Archaic tradition The Archaic Southwest was the culture of the North American Southwest between 6500 BC and 200 AD (approximately).
Paleo-Indian era
The Paleo-Indian tradition before that dates from 10,500 BC to 7500 BC. The Southwestern United States during the A ...
centered in north-central New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, the San Juan Basin
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah a ...
, the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
Valley, southern Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, and southeastern Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
.
Post-Archaic stage
The Post-Archaic stage includes the Formative, Classic and Post-Classic stages in Willey and Phillipp's scheme. The Formative stage lasted from until about , the Classic from about to , while the Post-Classic refers to until the present day. It also includes theWoodland period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European con ...
of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, th ...
, whose culture refers to the time period from roughly to in the eastern part of North America.
 The term "Woodland" was coined in the 1930s and refers to prehistoric sites dated between the Archaic period and the
The term "Woodland" was coined in the 1930s and refers to prehistoric sites dated between the Archaic period and the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
s. The Adena culture
The Adena culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharing ...
was a Native American culture that existed from to , in a time known as the Early Woodland period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologi ...
. The Adena culture refers to what was probably a number of related Native American societies sharing a burial complex and ceremonial system.
The Hopewell tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 1 ...
is the term for the common aspects of the Woodland period culture that flourished along rivers in the Eastern Woodlands
The Eastern Woodlands is a cultural area of the indigenous people of North America. The Eastern Woodlands extended roughly from the Atlantic Ocean to the eastern Great Plains, and from the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico, which is now p ...
from to . The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
or society, but a widely dispersed set of related populations, who were connected by a common network of trade routes, known as the Hopewell Exchange System. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell exchange system ran from the Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the nor ...
into the northern shores of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
. Within this area, societies participated in a high degree of exchange; most activities was conducted along the waterways that served as their major transportation routes. The Hopewell exchange system traded materials from all over North America.
 The
The Coles Creek culture
Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population i ...
was an indigenous development of the Lower Mississippi Valley that took place between the late Woodland period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European con ...
and the later Plaquemine culture
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture (circa 1200 to 1700 CE) centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek (700-1200 CE) and Troyville culture ...
period. The period is marked by the increased use of flat-topped platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s arranged around central plazas, more complex political institutions, and a subsistence strategy still grounded in the Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex in the woodlands of eastern North America was one of about 10 independent centers of plant domestication in the pre-historic world. Incipient agriculture dates back to about 5300 BCE. By about 1800 BCE the Native ...
and hunting rather than on the maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
plant as would happen in the succeeding Plaquemine Mississippian period. The culture was originally defined by the unique decoration on grog-tempered ceramic ware by James A. Ford after his investigations at the Mazique Archeological Site. He had studied both the Mazique and Coles Creek Sites, and almost went with the ''Mazique culture'', but decided on the less historically involved sites name. It is ancestral to the Plaquemine culture
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture (circa 1200 to 1700 CE) centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek (700-1200 CE) and Troyville culture ...
.
The Mississippian culture which extended throughout the Ohio and Mississippi valleys and built sites throughout the Southeast created the largest earthworks
Earthworks may refer to:
Construction
*Earthworks (archaeology), human-made constructions that modify the land contour
* Earthworks (engineering), civil engineering works created by moving or processing quantities of soil
*Earthworks (military), m ...
in North America north of Mexico, most notably at Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south- ...
, on a tributary of the Mississippi River in present-day Illinois.
* The ten-story Monks Mound
Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900–955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collinsvil ...
at Cahokia has a larger perimeter than the Pyramid of the Sun
The Pyramid of the Sun is the largest building in Teotihuacan, and one of the largest in Mesoamerica. It is believed to have been constructed about 200 AD. Found along the Avenue of the Dead, in between the Pyramid of the Moon and the Ciudadel ...
at Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'') (; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is ...
, and roughly the same as the Great Pyramid
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. The city complex was based on the culture's cosmology; it included more than 100 mounds, positioned to support their sophisticated knowledge of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
, and built with knowledge of varying soil types. The society began building at this site about 950 CE, and reached its peak population in 1,250 CE of 20,000–30,000 people, which was not equalled by any city in the present-day United States until after 1800.
* Cahokia was a major regional chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
, with trade and tributary chiefdoms located in a range of areas from bordering the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
.
* Kincaid c. 1050–1400 CE, is one of the largest settlements of the Mississippian culture, it was located at the southern tip of present-day U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
. Kincaid Mounds has been notable for both its significant role in native North American prehistory and for the central role the site has played in the development of modern archaeological techniques. The site had at least 11 substructure platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s (ranking fifth for mound-culture pyramids). Artifacts from the settlement link its major habitation and the construction of the mounds to the Mississippian period, but it was also occupied earlier during the Woodland period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European con ...
.
* Etowah Indian Mounds
Etowah Indian Mounds ( 9BR1) are a archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia, south of Cartersville. Built and occupied in three phases, from 1000–1550 CE, the prehistoric site is located on the north shore of the Etowah River.
Etow ...
( 9BR1) are a archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
in Bartow County, Georgia
Bartow County is located in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 108,901, up from 100,157 in 2010. The county seat is Cartersville.
Traditionally considered part of northwest Georgia, B ...
south of Cartersville
Cartersville is a city in Bartow County, Georgia, Bartow County, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, United States; it is located within the northwest edge of the Atlanta metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the city ha ...
, in the United States. Built and occupied in three phases, from , the prehistoric site is on the north shore of the Etowah River
The Etowah River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 27, 2011 waterway that rises northwest of Dahlonega, Georgia, north of Atlanta. On Matthew Carey's 1795 ...
.
* The Mississippian culture developed the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their ado ...
, the name which archeologists have given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
, ceremonies
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin '' caerimonia''.
Church and civil (secular) ...
and myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
ology. The rise of the complex culture was based on the people's adoption of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
agriculture, development of greater population densities, and chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
-level complex social organization from to .
* The Mississippian pottery are some of the finest and most widely spread ceramics north of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. Cahokian pottery was espically fine, with smooth surfaces, very thin walls and distinctive tempering, slips and coloring.
 The
The Hohokam culture
Hohokam () was a culture in the North American Southwest in what is now part of Arizona, United States, and Sonora, Mexico. It existed between 300 and 1500 AD, with cultural precursors possibly as early as 300 BC. Archaeologists disagree about ...
was centered along American Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, N ...
.Chenault, Mark, Rick Ahlstrom, and Tom Motsinger, (1993) ''In the Shadow of South Mountain: The Pre-Classic Hohokam of 'La Ciudad de los Hornos','' Part I and II. The early Hohokam founded a series of small villages along the middle Gila River
The Gila River (; O'odham ima Keli Akimel or simply Akimel, Quechan: Haa Siʼil, Maricopa language: Xiil) is a tributary of the Colorado River flowing through New Mexico and Arizona in the United States. The river drains an arid watershed of n ...
. They raised corn, squash, and beans. The communities were near good arable land, with dry farming
Dryland farming and dry farming encompass specific agricultural techniques for the non-irrigated cultivation of crops. Dryland farming is associated with drylands, areas characterized by a cool wet season (which charges the soil with virtuall ...
common in the earlier years of this period. They were known for their pottery, using the paddle-and-anvil technique. The Classical period of the culture saw the rise in architecture and ceramics. Buildings were grouped into walled compounds, as well as earthen platform mounds. Platform mounds were built along river as well as irrigation canal systems, suggesting these sites were administrative centers allocating water and coordinating canal labor. Polychrome pottery appeared, and inhumation burial replaced cremation. The trade included that of shells and other exotics. Social and climatic factors led to a decline and abandonment of the area after .
The Ancestral Puebloan culture covered present-day Four Corners
The Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. The Four Corners area ...
region of the United States, comprising southern Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, northern Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, northwestern New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, and southwestern Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
."Ancestral Pueblo culture."''Encyclopædia Britannica.'' Retrieved 4 June 2012. It is believed that the Ancestral Puebloans developed, at least in part, from the
Oshara tradition
Oshara Tradition, the northern tradition of the Picosa culture, was a Southwestern Archaic tradition centered in the area now called New Mexico and Colorado. Cynthia Irwin-Williams developed the sequence of Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic ...
, who developed from the Picosa culture. They lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger clan type structures, grand pueblos
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zu ...
, and cliff sited dwellings. The Ancestral Puebloans possessed a complex network that stretched across the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of ...
linking hundreds of communities and population centers. The culture is perhaps best known for the stone and earth dwellings built along cliff walls, particularly during the Pueblo II and Pueblo III eras.
* Three UNESCO World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in the United States are credited to the Pueblos: Mesa Verde National Park
Mesa Verde National Park is an American national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan archaeological sites in the United States.
Established ...
, Chaco Culture National Historical Park
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote ca ...
and Taos Pueblo
Taos Pueblo (or Pueblo de Taos) is an ancient pueblo belonging to a Taos-speaking (Tiwa) Native American tribe of Puebloan people. It lies about north of the modern city of Taos, New Mexico. The pueblos are considered to be one of the oldest c ...
.
* The best-preserved examples of the stone dwellings are in National Parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual ...
(US), examples being, Navajo National Monument
Navajo National Monument is a National Monument located within the northwest portion of the Navajo Nation territory in northern Arizona, which was established to preserve three well-preserved cliff dwellings of the Ancestral Puebloan people: Keet ...
, Chaco Culture National Historical Park, Mesa Verde National Park, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument
Canyons of the Ancients National Monument is a national monument protecting an archaeologically-significant landscape located in the southwestern region of the U.S. state of Colorado. The monument's are managed by the Bureau of Land Management, ...
, Aztec Ruins National Monument
The Aztec Ruins National Monument in northwestern New Mexico, USA consists of preserved structures constructed by the Pueblo Indians. The national monument lies on the western bank of the Animas River in Aztec, New Mexico, about northeast of F ...
, Bandelier National Monument
Bandelier National Monument is a United States National Monument near Los Alamos in Sandoval and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico. The monument preserves the homes and territory of the Ancestral Puebloans of a later era in the Southwest. Most ...
, Hovenweep National Monument
Hovenweep National Monument is located on land in southwestern Colorado and southeastern Utah, between Cortez, Colorado and Blanding, Utah on the Cajon Mesa of the Great Sage Plain. Shallow tributaries run through the wide and deep canyons into t ...
, and Canyon de Chelly National Monument
Canyon de Chelly National Monument ( ) was established on April 1, 1931, as a unit of the National Park Service. Located in northeastern Arizona, it is within the boundaries of the Navajo Nation and lies in the Four Corners region. Reflecting on ...
.
The Iroquois League of Nations or "People of the Long House", based in present-day upstate and western New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, had a confederacy model from the mid-15th century. It has been suggested that their culture contributed to political thinking during the development of the later United States government. Their system of affiliation was a kind of federation, different from the strong, centralized European monarchies.
* Long-distance trading did not prevent warfare and displacement among the indigenous peoples, and their oral histories tell of numerous migrations to the historic territories where Europeans encountered them. The Iroquois invaded and attacked tribes in the Ohio River area of present-day Kentucky and claimed the hunting grounds. Historians have placed these events as occurring as early as the 13th century, or in the 17th century Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
.
* Through warfare, the Iroquois drove several tribes to migrate west to what became known as their historically traditional lands west of the Mississippi River. Tribes originating in the Ohio Valley who moved west included the Osage, Kaw
Kaw or KAW may refer to:
Mythology
* Kaw (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology
* Johnny Kaw, mythical settler of Kansas, US
* Kaw (character), in ''The Chronicles of Prydain''
People
* Kaw people, a Native American tribe
Places
* Kaw, Fr ...
, Ponca
The Ponca ( Páⁿka iyé: Páⁿka or Ppáⁿkka pronounced ) are a Midwestern Native American tribe of the Dhegihan branch of the Siouan language group. There are two federally recognized Ponca tribes: the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska and the Ponca ...
and Omaha people
The Omaha ( Omaha-Ponca: ''Umoⁿhoⁿ'') are a federally recognized Midwestern Native American tribe who reside on the Omaha Reservation in northeastern Nebraska and western Iowa, United States. There were 5,427 enrolled members as of 2012. Th ...
. By the mid-17th century, they had resettled in their historical lands in present-day Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
and Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
. The Osage warred with Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, wh ...
-speaking Native Americans, displacing them in turn by the mid-18th century and dominating their new historical territories.
European exploration and colonization
 After 1492
After 1492 European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
exploration and colonization of the Americas revolutionized how the Old
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Mai ...
and New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
s perceived themselves. One of the first major contacts, in what would be called the American Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, occurred when the conquistador Juan Ponce de León landed in La Florida in April 1513. He was later followed by other Spanish explorers, such as Pánfilo de Narváez in 1528 and Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
in 1539. The subsequent European colonists in North America often rationalized their expansion of empire with the assumption that they were saving a barbaric, pagan world by spreading Christian civilization
Christianity has been intricately intertwined with the history and formation of Western society. Throughout its long history, the Church has been a major source of social services like schooling and medical care; an inspiration for art, cultur ...
.
In the Spanish colonization of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions ...
, the policy of Indian Reductions
Reductions ( es, reducciones, also called ; , pl. ) were settlements created by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such re ...
resulted in the forced conversions to Catholicism of the indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
in northern ''Nueva España
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
.'' They had long-established spiritual and religious traditions
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, tra ...
and theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
beliefs. What developed during the colonial years and since has been a syncretic Catholicism that absorbed and reflected indigenous beliefs; the religion changed in New Spain.
Impact on native populations
From the 16th through the 19th centuries, the population of Native Americans declined in the following ways: epidemic diseases brought from Europe;violence
Violence is the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy. Other definitions are also used, such as the World Health Organization's definition of violence as "the intentional use of physical force or Power (social and p ...
and warfare. at the hands of European explorers and colonists, as well as between tribes; displacement from their lands; internal warfare, enslavement
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
; and a high rate of intermarriage."Indian Mixed-Blood"Frederick W. Hodge, ''Handbook of American Indians'', 1906. Most mainstream scholars believe that, among the various contributing factors,
epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
was the overwhelming cause of the population decline of the American natives because of their lack of immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
to new diseases brought from Europe. With the rapid declines of some populations and continuing rivalries among their nations, Native Americans sometimes re-organized to form new cultural groups, such as the Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, an ...
s of Florida in the 19th century and the Mission Indians
Mission Indians are the indigenous peoples of California who lived in Southern California and were forcibly relocated from their traditional dwellings, villages, and homelands to live and work at 15 Franciscan missions in Southern California and ...
of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
. Some scholars characterize the treatment of Native Americans by the US as genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
or genocidal
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
whilst others dispute this characterization. uenter Lewy, "Were American Indians the Victims of Genocide?" History News Network, 11–22–04.
Estimating the number of Native Americans living in what is today the United States of America before the arrival of the European explorers and settlers has been the subject of much debate. While it is difficult to determine exactly how many Natives lived in North America before Columbus, estimates range from a low of 2.1 million ( Ubelaker 1976) to 7 million people (Russell Thornton) to a high of 18 million ( Dobyns 1983). A low estimate of around 1 million was first posited by the anthropologist James Mooney
James Mooney (February 10, 1861 – December 22, 1921) was an American ethnographer who lived for several years among the Cherokee. Known as "The Indian Man", he conducted major studies of Southeastern Indians, as well as of tribes on the Gr ...
in the 1890s, by calculating population density of each culture area based on its carrying capacity
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as t ...
.
In 1965, the American anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and ...
Henry F. Dobyns
Henry Farmer Dobyns, Jr. (July 3, 1925 – June 21, 2009) was an anthropologist, author and researcher specializing in the ethnohistory and demography of native peoples in the American hemisphere.
published studies estimating the original population to have been 10 to 12 million. By 1983, he increased his estimates to 18 million. Historian David Henige
David Patrick Henige (born 1938) is an American historian, bibliographer, academic librarian and Africanist scholar. The majority of Henige's academic career has been spent in affiliation with the University of Wisconsin–Madison, where for over ...
criticized higher estimates such as those of Dobyns', writing that many population figures are the result of arbitrary formulas selectively applied to numbers from unreliable historical sources. By 1800, the Native population of the present-day United States had declined to approximately 600,000, and only 250,000 Native Americans remained in the 1890s.

Chicken pox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab ...
and measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
but rarely fatal among Europeans (long after being introduced from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
), often proved deadly to Native Americans. Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
s often immediately followed European exploration and sometimes destroyed entire village populations. While precise figures are difficult to determine, some historians estimate that at least 30% (and sometimes 50% to 70%) of some Native populations died after first contact due to Eurasian smallpox. One element of the Columbian exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
suggests explorers from the Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
expedition contracted syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
from indigenous peoples and carried it back to Europe, where it spread widely. Other researchers believe that the disease existed in Europe and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
before Columbus and his men returned from exposure to indigenous peoples of the Americas, but that they brought back a more virulent form.
In the 100 years following the arrival of the Spanish to the Americas, large disease epidemics depopulated large parts of the Eastern Woodlands in the 15th century. In 1618–1619, smallpox killed 90% of the Native Americans in the area of the Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its ...
. Historians believe many Mohawk in present-day New York became infected after contact with children of Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
traders in Albany in 1634. The disease swept through Mohawk villages, reaching the Onondaga at Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
by 1636, and the lands of the western Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
by 1679, as it was carried by Mohawk and other Native Americans who traveled the trading routes. The high rate of fatalities caused breakdowns in Native American societies and disrupted generational exchange of culture.
 After European explorers reached the West Coast in the 1770s, smallpox rapidly killed at least 30% of Northwest Coast Native Americans. For the next 80 to 100 years, smallpox and other diseases devastated native populations in the region.
After European explorers reached the West Coast in the 1770s, smallpox rapidly killed at least 30% of Northwest Coast Native Americans. For the next 80 to 100 years, smallpox and other diseases devastated native populations in the region. Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected ma ...
area populations, once estimated as high as 37,000 people, were reduced to only 9,000 survivors by the time settlers arrived en masse in the mid-19th century. The Spanish missions in California
The Spanish missions in California ( es, Misiones españolas en California) comprise a
series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of California. Founded by Catholic priests o ...
did not have a large effect on the overall population of Native Americans because the small number of missions was concentrated in a small area along the southern and central coast. The numbers of indigenes decreased more rapidly after California ceased to be a Spanish colony, especially during the second half of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th (see chart on the right).
Smallpox epidemics in 1780–1782 and 1837–1838 brought devastation and drastic depopulation among the Plains Indians
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of N ...
. By 1832, the federal government established a smallpox vaccination
The smallpox vaccine is the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. In 1796, British physician Edward Jenner demonstrated that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus conferred immunity against the deadly smallpox ...
program for Native Americans (''The Indian Vaccination Act of 1832''). It was the first federal program created to address a health problem of Native Americans.
Animal introductions
With the meeting of two worlds, animals, insects, and plants were carried from one to the other, both deliberately and by chance, in what is called theColumbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
. Sheep, pigs, horses, and cattle were all Old World animals that were introduced to contemporary Native Americans who never knew such animals.
In the 16th century, Spaniards and other Europeans brought horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
s to Mexico. Some of the horses escaped and began to breed and increase their numbers in the wild. The early American horse
American Horse ( lkt, Wašíčuŋ Tȟašúŋke) (a/k/a "American Horse the Younger") (1840 – December 16, 1908) was an Oglala Lakota chief, statesman, educator and historian. American Horse is notable in American history as a U.S. Army Indian S ...
had been game for the earliest humans on the continent. It was hunted to extinction about , just after the end of the last glacial period. Native Americans benefited from the reintroduction of horses, as they adopted the use of the animals, they began to change their cultures in substantial ways, especially by extending their nomadic ranges for hunting.
The reintroduction of the horse to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
had a profound impact on Native American culture of the Great Plains. The tribes trained and used horses to ride and to carry packs or pull travois
A travois (; Canadian French, from French , a frame for restraining horses; also obsolete travoy or travoise) is a historical frame structure that was used by indigenous peoples, notably the Plains Aboriginals of North America, to drag loads ov ...
. The people fully incorporated the use of horses into their societies and expanded their territories. They used horses to carry goods for exchange with neighboring tribes, to hunt game
A game is a structured form of play (activity), play, usually undertaken for enjoyment, entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator s ...
, especially bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
, and to conduct wars and horse raids.
16th century
The 16th century saw the first contacts between Native Americans in what was to become the United States and European explorers and settlers.Southeast
One of the first major contacts, in what would be called the AmericanDeep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, occurred when the conquistador Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León (, , , ; 1474 – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Florida and for serving as the first governor of Puerto Rico. He was born in Santervá ...
landed in La Florida in April 1513. There he encountered the Timucuan and Ais peoples. De León returned in 1521 in an attempt at colonization, but after fierce resistance from the Calusa
The Calusa ( ) were a Native American people of Florida's southwest coast. Calusa society developed from that of archaic peoples of the Everglades region. Previous indigenous cultures had lived in the area for thousands of years.
At the time of ...
people, the attempt was abandoned. He was later followed by other Spanish explorers, such as Pánfilo de Narváez
Pánfilo de Narváez (; 147?–1528) was a Spanish '' conquistador'' and soldier in the Americas. Born in Spain, he first embarked to Jamaica in 1510 as a soldier. He came to participate in the conquest of Cuba and led an expedition to Camagü ...
in 1528 and Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
in 1539.
Southwest
In 1536 a group of four Spanish explorers and one enslaved black Moorish man, found themselves stranded on the coast of what is now Texas. The group was led byÁlvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca (; 1488/90/92"Cabeza de Vaca, Alvar Núñez (1492?-1559?)." American Eras. Vol. 1: Early American Civilizations and Exploration to 1600. Detroit: Gale, 1997. 50-51. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 Decembe ...
, and for a time they were held in semi captivity by the coastal natives. The enslaved Moor, whose name was Esterban, later became a scout who had encounters with the Zunis
The Zuni ( zun, A:shiwi; formerly spelled ''Zuñi'') are Native American Pueblo peoples native to the Zuni River valley. The Zuni are a Federally recognized tribe and most live in the Pueblo of Zuni on the Zuni River, a tributary of the Lit ...
. Rumors of the fabled Seven Cities of Gold
The myth of the Seven Cities of Gold, also known as the Seven Cities of Cibola (), was popular in the 16th century and later featured in several works of popular culture. According to legend, the seven cities of gold referred to Aztec mythology r ...
being located in the northern area of New Spain began to emerge amongst the Spaniards. And in 1540 Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, using the information gained by the scouting expeditions of Esterban and Fray Marcos, set out to conquer Cíbola. Coronado and his band of over one thousand found no cities of gold. What the conquistadors did encounter was Hawikuh, a Zuni town. There the Zuni people, having never seen horses or a band of this size before, were frightened. Although Coronado had been explicitly instructed not to harm the natives, when the Zuni refused his insistence for food and supplies, Coronado ordered an attack on the town.
17th century
Through the mid 17th century theBeaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
were fought over the fur trade between the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
and the Hurons
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario w ...
, the northern Algonquians
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. Historically, the peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. T ...
, and their French allies. During the war the Iroquois destroyed several large tribal confederacies—including the Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
, Neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
, Erie
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 a ...
, Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
, and Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
, and became dominant in the region and enlarged their territory.
King Philip's War
King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England coloni ...
, also called Metacom
Metacomet (1638 – August 12, 1676), also known as Pometacom, Metacom, and by his adopted English name King Philip,New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
and English colonists and their Native American allies from 1675 to 1676. It continued in northern New England (primarily on the Maine frontier) even after King Philip was killed, until a treaty was signed at Casco Bay
Casco Bay is an inlet of the Gulf of Maine on the southern coast of Maine, New England, United States. Its easternmost approach is Cape Small and its westernmost approach is Two Lights in Cape Elizabeth. The city of Portland sits along its south ...
in April 1678. According to a combined estimate of loss of life in Schultz and Tougias' ''King Philip's War, The History and Legacy of America's Forgotten Conflict'' (based on sources from the Department of Defense, the Bureau of Census, and the work of Colonial historian Francis Jennings), 800 out of 52,000 English colonists of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
(1 out of every 65) and 3,000 out of 20,000 natives (3 out of every 20) lost their lives due to the war, which makes it proportionately one of the bloodiest and costliest in the history of America. More than half of New England's 90 towns were assaulted by Native American warriors. One in ten soldiers on both sides were wounded or killed.
The war is named after the main leader of the Native American side, Metacomet
Metacomet (1638 – August 12, 1676), also known as Pometacom, Metacom, and by his adopted English name King Philip,Pokanoket
The Pokanoket (also spelled PakanokickKathleen J. Bragdon, ''Native People of Southern New England, 1500–1650'', page 21) was the village governed by Massasoit (Wampanoag, c. 1581–1661). The term broadened to refer to all peoples and lands go ...
Tribe/Pokanoket Federation and Wampanoag
The Wampanoag , also rendered Wôpanâak, are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands based in southeastern Massachusetts and historically parts of eastern Rhode Island,Salwen, "Indians of Southern New England and Long Island," p. 17 ...
Nation. Upon their loss to the Colonists, many managed to flee to the North to continue their fight against the British (Massachusetts Bay Colony) by joining with the Abenaki Tribes and Wabanaki Federation.
18th century
Between 1754 and 1763, many Native American tribes were involved in theFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
/Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
. Those involved in the fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
in the northern areas tended to ally with French forces against British colonial militias. Native Americans fought on both sides of the conflict. The greater number of tribes fought with the French in the hopes of checking British expansion. The British had made fewer allies, but it was joined by some tribes that wanted to prove assimilation and loyalty in support of treaties to preserve their territories. They were often disappointed when such treaties were later overturned. The tribes had their own purposes, using their alliances with the European powers to battle traditional Native enemies.
Native American influence
 Native American culture began to have an influence on European thought in this period. Some Europeans considered Native American societies to be representative of a golden age known to them only in folk history.
The political theorist
Native American culture began to have an influence on European thought in this period. Some Europeans considered Native American societies to be representative of a golden age known to them only in folk history.
The political theorist Jean Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
wrote that the idea of freedom and democratic ideals was born in the Americas because "it was only in America" that Europeans from 1500 to 1776 knew of societies that were "truly free."
In the 20th century, some writers have credited the Iroquois nations' political confederacy and democratic government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
as being influences for the development of the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
and the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
.
In October 1988, the U.S. Congress passed Concurrent Resolution 331 to recognize the influence of the Iroquois Constitution upon the U.S. Constitution and Bill of Rights.
However, leading historians of the period note that historic evidence is lacking to support such an interpretation. Gordon Wood wrote, "The English colonists did not need the Indians to tell them about federalism or self-government. The New England Confederation was organized as early as 1643." The historian Jack Rakove
Jack Norman Rakove (born June 4, 1947) is an American historian, author and professor at Stanford University. He is a Pulitzer Prize winner.
Biography
Rakove was born in Chicago to Political Science Professor Milton L. Rakove (1918–1983) ...
, a specialist in early American history, in 2005 noted that the voluminous documentation of the Constitutional proceedings "contain no significant reference to Iroquois."Jack Rakove, "Did the Founding Fathers Really Get Many of Their Ideas of Liberty from the Iroquois?"''History News Network'', July 5, 2005, accessed 2012-01-17 Secondly, he notes: "All the key political concepts that were the stuff of American political discourse before the Revolution and after, had obvious European antecedents and referents: bicameralism, separation of powers, confederations, and the like."
American Revolution
 During the
During the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
, the newly proclaimed United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
competed with the British for the allegiance of Native American nations east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. Most Native Americans who joined the struggle sided with the British, based both on their trading relationships and hopes that colonial defeat would result in a halt to further colonial expansion onto Native American land. Many native communities were divided over which side to support in the war and others wanted to remain neutral. Seeking out treaties with the Indigenous inhabitants soon became a very pressing matter. It was during the American Revolution that the newly forming United States would sign its first treaty as a nation with the Indigenous inhabitants. In a bid to gain ground near the British stronghold of Detroit the Continental Congress reached out to the Leni Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory includ ...
, also known as the Delawares, to form an alliance. Understanding a treaty would be the best way to secure this alliance, in 1778 The Treaty with The Delawares was signed by representatives from the Congress and the Lenape. For the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
Confederacy, based in New York, the American Revolution resulted in civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. The only Iroquois tribes to ally with the colonials were the Oneida and Tuscarora.
Frontier warfare during the American Revolution
The Western theater of the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) was the area of conflict west of the Appalachian Mountains, the region which became the Northwest Territory of the United States as well as what would become the states of Ke ...
was particularly brutal, with noncombatants suffering greatly. Both sides committed numerous atrocities and destroyed villages and food supplies to reduce the ability of people to fight, as in frequent raids in the Mohawk Valley
The Mohawk Valley region of the U.S. state of New York is the area surrounding the Mohawk River, sandwiched between the Adirondack Mountains and Catskill Mountains, northwest of the Capital District. As of the 2010 United States Census, th ...
and western New York. The largest of these expeditions was the Sullivan Expedition
The 1779 Sullivan Expedition (also known as the Sullivan-Clinton Expedition, the Sullivan Campaign, and the Sullivan-Clinton Genocide) was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 1779 ...
of 1779, in which American colonial troops destroyed more than 40 Iroquois villages to neutralize Iroquois raids in upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Is ...
. The expedition failed to have the desired effect: Native American activity became even more determined.
 The British made peace with the Americans in the
The British made peace with the Americans in the Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of George III, King George III of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and representatives of the United States, United States of America on September 3, 1783, officially ended the Ame ...
, through which they ceded vast Native American territories to the United States without informing or consulting with the Native Americans. Within the Peace Treaty of Paris of 1783, no mention of Indigenous peoples or their rights were made. The United States initially treated the Native Americans who had fought as allies with the British as a conquered people who had lost their lands. Although most members of the Iroquois tribes went to Canada with the Loyalists, others tried to stay in New York and western territories to maintain their lands. The state of New York made a separate treaty with Iroquois nations and put up for sale of land that had previously been their territories. The state established small reservations in western New York for the remnant peoples.
After the formation of the United States
The United States was eager to expand, to develop farming and settlements in new areas, and to satisfy land hunger of settlers from New England and new immigrants. The belief and inaccurate presumption was that the land was not settled and existed in a state of nature and therefore was free to be settled by citizens of the newly formed United States. In the years after the American Revolution, the newly formed nation set about acquiring lands in the Northwest Territory through a multitude oftreaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
with Native nations. The coercive tactics used to obtain these treaties often left the Native Nations with the option to sell the land or face war. The states and settlers were frequently at odds with this policy. Congress passed the Northwest Ordinance in 1787, which was conceived to allow for the United States to sell lands inhabited by the Native nations to settlers willing to move into that area.
 During this time, what came to be called The
During this time, what came to be called The Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern ...
also began, led by the Native nations of the Ohio country trying to repulse American settlers and halt the seizure of land by the Continental Congress. Leaders such as Little Turtle and Blue Jacket lead the allied tribes of the Miamis and Shawnees, who were among the tribes that had been disregarded during the signing of the Peace Treaty of Paris.
European nations sent Native Americans (sometimes against their will) to the Old World as objects of curiosity. They often entertained royalty and were sometimes prey to commercial purposes. Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of Native Americans was a charted purpose for some European colonies.
United States policy toward Native Americans had continued to evolve after the American Revolution. George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
and Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
believed that Native Americans were equals but that their society was inferior. Washington formulated a policy to encourage the "civilizing" process.
Washington had a six-point plan for civilization which included:
# impartial justice toward Native Americans
# regulated buying of Native American lands
# promotion of commerce
# promotion of experiments to civilize or improve Native American society
# presidential authority to give presents
# punishing those who violated Native American rights.
Robert Remini
Robert Vincent Remini (July 17, 1921 – March 28, 2013) was an American historian and a professor emeritus at the University of Illinois at Chicago. He wrote numerous books about President Andrew Jackson and the Jacksonian era, most notably a th ...
, a historian, wrote that "once the Indians adopted the practice of private property, built homes, farmed, educated their children, and embraced Christianity, these Native Americans would win acceptance from white Americans."
The United States appointed agents, like Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite ...
, to live among the Native Americans and to teach them how to live like whites.
 In the late 18th century, reformers starting with Washington and Knox, supported educating native children and adults, in efforts to "
In the late 18th century, reformers starting with Washington and Knox, supported educating native children and adults, in efforts to "civilize
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of State (polity), a state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and Symbol, symbolic systems of communication beyond natural language, natur ...
" or otherwise assimilate Native Americans to the larger society (as opposed to relegating them to reservations). The Civilization Fund Act of 1819 promoted this civilization policy by providing funding to societies (mostly religious) who worked on Native American improvement.
The end of the 18th century also saw the revival of spirituality among the Iroquois society and other nations of the eastern seaboard. After years of war and uncertainty, despair and demoralization led some within these communities to turn to alcohol. In 1799, the Seneca warrior Handsome Lake
Handsome Lake ( Cayuga language: Sganyadái:yo, Seneca language: Sganyodaiyo) (Θkanyatararí•yau• in Tuscarora) (1735 – 10 August 1815) was a Seneca religious leader of the Iroquois people. He was a half-brother to Cornplanter, a Seneca ...
, who suffered from depression and alcoholism himself, received a spiritual vision. This vision led Handsome Lake to travel among the Seneca as a religious prophet. He preached about a revival of the traditional ceremonies of the Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
nations and a renouncement of drinking. This movement, which also carried some elements of Christianity, came to be known as Gaiwiio, or Good Word.
19th century
Resistance
 As American expansion continued, Native Americans resisted settlers' encroachment in several regions of the new nation (and in unorganized territories), from the Northwest to the Southeast, and then in the West, as settlers encountered the tribes of the
As American expansion continued, Native Americans resisted settlers' encroachment in several regions of the new nation (and in unorganized territories), from the Northwest to the Southeast, and then in the West, as settlers encountered the tribes of the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
.
East of the Mississippi River, an intertribal army led by Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and ...
, a Shawnee chief and noted orator, fought a number of engagements in the Northwest during the period 1811–12, known as Tecumseh's War
Tecumseh's War or Tecumseh's Rebellion was a conflict between the United States and Tecumseh's Confederacy, led by the Shawnee leader Tecumseh in the Indiana Territory. Although the war is often considered to have climaxed with William Henry Har ...
. In the latter stages, Tecumseh's group allied with the British forces in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
and was instrumental in the conquest of Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at th ...
. Conflicts in the Southeast include the Creek War
The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Indigenous American Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in modern-day Alabama ...
and Seminole Wars
The Seminole Wars (also known as the Florida Wars) were three related military conflicts in Geography of Florida, Florida between the United States and the Seminole, citizens of a Native Americans in the United States, Native American nation whi ...
, both before and after the Indian Removals of most members of the Five Civilized Tribes
The term Five Civilized Tribes was applied by European Americans in the colonial and early federal period in the history of the United States to the five major Native American nations in the Southeast—the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek ...
beginning in the 1830s under President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
's policies.
Native American nations on the plains in the west engaged in armed conflicts with the United States throughout the 19th century, through what were called generally "Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
." The Battle of Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota people, Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and also commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lako ...
(1876) was one of the greatest Native American victories. Defeats included the Sioux Uprising
The Dakota War of 1862, also known as the Sioux Uprising, the Dakota Uprising, the Sioux Outbreak of 1862, the Dakota Conflict, the U.S.-Dakota War of 1862, or Little Crow's War, was an armed conflict between the United States and several ban ...
of 1862, the Sand Creek Massacre (1864) and Wounded Knee in 1890. Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
continued into the early 20th century.
According to the U.S. Bureau of the Census (1894), "The Indian wars under the government of the United States have been more than 40 in number. They have cost the lives of about 19,000 white men, women and children, including those killed in individual combats, and the lives of about 30,000 Indians. The actual number of killed and wounded Indians must be very much higher than the given... Fifty percent additional would be a safe estimate..."
American expansion
 In July 1845, the New York newspaper editor John L. O’Sullivan coined the phrase, "Manifest Destiny," as the "design of Providence" supporting the territorial expansion of the United States.
In July 1845, the New York newspaper editor John L. O’Sullivan coined the phrase, "Manifest Destiny," as the "design of Providence" supporting the territorial expansion of the United States. Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
had serious consequences for Native Americans, since continental expansion for the United States took place at the cost of their occupied land. Manifest Destiny was a justification for expansion and westward movement, or, in some interpretations, an ideology or doctrine that helped to promote the progress of civilization. Advocates of Manifest Destiny believed that expansion was not only good, but that it was obvious and certain. The term was first used primarily by Jacksonian Democrats
Jacksonian democracy was a 19th-century political philosophy in the United States that expanded suffrage to most white men over the age of 21, and restructured a number of federal institutions. Originating with the seventh U.S. president, And ...
in the 1840s to promote the annexation of much of what is now the Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
(the Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Ori ...
, the Texas Annexation
The Texas annexation was the 1845 annexation of the Republic of Texas into the United States. Texas was admitted to the Union as the 28th state on December 29, 1845.
The Republic of Texas declared independence from the Republic of Mexico on ...
, and the Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession ( es, Cesión mexicana) is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico originally controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War ...
).
In 1851, delegates from the federal government and upwards of ten thousand Indigenous peoples, consisting of various Plains tribes including the Sioux, Cheyenne and Crow among many others, assembled. They gathered for the purpose of signing the Treaty of Fort Laramie which would set the definitive boundaries of the tribal territories, and tribes were to agree to leave travelers through the territory unharmed. In 1853 members of the tribes from the southern Plains such as the Comanches, Kiowas, and Kiowa Apaches signed treaties similar to the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851.
In the years following the 1851 treaty, tracks were laid for the Union Pacific Railroad and gold was discovered in Montana and Colorado. These factors amongst others led to increased traffic through tribal land which in turn disrupted the game animals that were necessary for the Plains’ nations survival. Conflicts between the U.S. Army, settlers and Native Americans continued, however in 1864 after the massacre of a Cheyenne village along the banks of Sand Cheek, war between the U.S and the tribes of the Great Plains was inevitable.
 After a decade of wars between the U.S and the tribes of the Great Plains, including
After a decade of wars between the U.S and the tribes of the Great Plains, including Red Cloud's War
Red Cloud's War (also referred to as the Bozeman War or the Powder River War) was an armed conflict between an alliance of the Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, and Northern Arapaho peoples against the United States that took place in the Wyoming and Mo ...
in 1866, the federal government again called for a treaty. In 1868 the Peace Treaty of Fort Laramie was signed, with one of the terms of the treaty being that the Sioux would settle on the Black hills Reservation in Dakota Territory.
In 1874 gold was discovered within the Black Hills, land which is to this day most sacred to the Sioux. The Black Hills were at this time also the center of the Sioux Nation, the federal government offered six million dollars for the land, however Sioux leaders refused to sell. (In the Hands) By 1877 the Black Hills were confiscated, and the land that had once been the Sioux Nation was further divided into six smaller reservations.
The age of Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
, which came to be associated with extinguishing American Indian territorial claims and moving them to reservations, gained ground as the United States population explored and settled west of the Mississippi River. Although Indian Removal from the Southeast had been proposed by some as a humanitarian measure to ensure their survival away from Americans, conflicts of the 19th century led some European-Americans to regard the natives as "savages".
The period of the Gold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Z ...
was marked by the California Genocide
The California genocide was the killing of thousands of indigenous peoples of California by United States government agents and private citizens in the 19th century. It began following the American Conquest of California from Mexico, and the ...
. Under US sovereignty, the indigenous population plunged from approximately 150,000 in 1848 to 30,000 in 1870 and reached its nadir of 16,000 in 1900. Thousands of California Native Americans, including women and children, are documented to have been killed by non-Native Americans in this period. The dispossession and murder of California Native Americans was aided by institutions of the state of California, which encouraged indigenous peoples to be killed with impunity.
Civil War
 Many Native Americans served in the military during the
Many Native Americans served in the military during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, on both sides. By fighting with the whites, Native Americans hoped to gain favor with the prevailing government by supporting the war effort.
 General Ely S. Parker, a member of the
General Ely S. Parker, a member of the Seneca tribe
The Seneca () ( see, Onödowáʼga:, "Great Hill People") are a group of Indigenous Iroquoian-speaking people who historically lived south of Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes in North America. Their nation was the farthest to the west w ...
, transcribed the terms of the articles of surrender which General Robert E. Lee signed at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865. Gen. Parker, who served as Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's military secretary and was a trained attorney, was once rejected for Union military service because of his race. At Appomattox, Lee is said to have remarked to Parker, "I am glad to see one real American here," to which Parker replied, "We are all Americans." General Stand Watie
Brigadier-General Stand Watie ( chr, ᏕᎦᏔᎦ, translit=Degataga, lit=Stand firm; December 12, 1806September 9, 1871), also known as Standhope Uwatie, Tawkertawker, and Isaac S. Watie, was a Cherokee politician who served as the second princ ...
, a leader of the Cherokee Nation
The Cherokee Nation (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᎯ ᎠᏰᎵ ''Tsalagihi Ayeli'' or ᏣᎳᎩᏰᎵ ''Tsalagiyehli''), also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It ...
and Confederate Indian cavalry
Indian cavalry is the name collectively given to the Midwest and Eastern American Indians who fought during the American Civil War, most of them on horseback and for the Confederate States of America.
Indian units in the CS Armed forces Cherokee ...
commander, was the last Confederate General to surrender his troops.
Removals and reservations
In the 19th century, the incessant westward expansion of the United States incrementally compelled large numbers of Native Americans to resettle further west, often by force, almost always reluctantly. Native Americans believed this forced relocation illegal, given the Hopewell Treaty of 1785. Under PresidentAndrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
passed the Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
of 1830, which authorized the President to conduct treaties to exchange Native American land east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
for lands west of the river.
As many as 100,000 Native Americans relocated to the West as a result of this Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a de ...
policy. In theory, relocation was supposed to be voluntary and many Native Americans did remain in the East. In practice, great pressure was put on Native American leaders to sign removal treaties.
The most egregious violation of the stated intention of the removal policy took place under the Treaty of New Echota
The Treaty of New Echota was a treaty signed on December 29, 1835, in New Echota, Georgia, by officials of the United States government and representatives of a minority Cherokee political faction, the Treaty Party.
The treaty established terms ...
, which was signed by a dissident faction of Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
s but not the principal chief. The following year, the Cherokee conceded to removal, but Georgia included their land in a lottery for European-American settlement before that. President Jackson used the military to gather and transport the Cherokee to the west, whose timing and lack of adequate supplies led to the deaths of an estimated 4,000 Cherokees on the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
. About 17,000 Cherokees, along with approximately 2,000 enslaved blacks held by Cherokees, were taken by force migration to Indian Territory.
Tribes were generally located to reservations where they could more easily be separated from traditional life and pushed into European-American society. Some southern states additionally enacted laws in the 19th century forbidding non-Native American settlement on Native American lands, with the intention to prevent sympathetic white missionaries from aiding the scattered Native American resistance.
Native Americans and U.S. citizenship
In 1817, the Cherokee became the first Native Americans recognized as U.S. citizens. Under Article 8 of the 1817 Cherokee treaty, "Upwards of 300 Cherokees (Heads of Families) in the honest simplicity of their souls, made an election to become American citizens." The next earliest recorded date of Native Americans' becoming U.S. citizens was in 1831, when some MississippiChoctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
became citizens after the United States Congress ratified the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek
The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States Government. This treaty was the first removal treaty wh ...
.
Article 22 sought to put a Choctaw representative in the U.S. House of Representatives. Under article XIV of that treaty, any Choctaw who elected not to move with the Choctaw Nation could become an American citizen when he registered and if he stayed on designated lands for five years after treaty ratification. Through the years, Native Americans became U.S. citizens by:
1. Treaty provision (as with the Cherokee)In 1857, Chief Justice
2. Registration and land allotment under the Dawes Act of February 8, 1887
3. Issuance of Patent inFee simple In English law, a fee simple or fee simple absolute is an estate in land, a form of freehold ownership. A "fee" is a vested, inheritable, present possessory interest in land. A "fee simple" is real property held without limit of time (i.e., perm ...
4. Adopting Habits of Civilized Life
5. Minor Children
6. Citizenship by Birth
7. Becoming Soldiers and Sailors in the U.S. Armed Forces
8. Marriage to a U.S. citizen
9. Special Act of Congress.
Roger B. Taney
Roger Brooke Taney (; March 17, 1777 – October 12, 1864) was the fifth chief justice of the United States, holding that office from 1836 until his death in 1864. Although an opponent of slavery, believing it to be an evil practice, Taney belie ...
expressed the opinion of the court that since Native Americans were "free and independent people," they could become U.S. citizens.
Taney asserted that Native Americans could be naturalized and join the "political community" of the United States.
After the American Civil War, the Civil Rights Act of 1866
The Civil Rights Act of 1866 (, enacted April 9, 1866, reenacted 1870) was the first United States federal law to define citizenship and affirm that all citizens are equally protected by the law. It was mainly intended, in the wake of the Amer ...
states, "that all persons born in the United States, and not subject to any foreign power, excluding Indians not taxed, are hereby declared to be citizens of the United States".(McCool 3) This was affirmed by the ratification of the Fourteenth Amendment. But the concept of Native Americans as U.S. citizens fell out of favor among politicians at the time. Senator Jacob Howard
Jacob Merritt Howard (July 10, 1805 – April 2, 1871) was an American attorney and politician. He was most notable for his service as a U.S. Representative and U.S. Senator from the state of Michigan, and his political career spanned the Ameri ...
of Michigan commented, “I am not yet prepared to pass a sweeping act of naturalization by which all the Indian savages, wild or tame, belonging to a tribal relation, are to become my fellow-citizens and go to the polls and vote with me". (''Congressional Globe'', 1866, 2895)McCool, Daniel, Susan M. Olson, and Jennifer L. Robinson. ''Native Vote'', Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 2007. In a Senate floor debate regarding the Fourteenth Amendment, James Rood Doolittle
James Rood Doolittle (January 3, 1815July 27, 1897) was an American politician who served as a U.S. Senator from Wisconsin from March 4, 1857, to March 4, 1869. He was a strong supporter of President Abraham Lincoln's administration during the ...
of Wisconsin stated, " ... all those wild Indians to be citizens of the United States, the Great Republic of the world, whose citizenship should be a title as proud as that of king, and whose danger is that you may degrade that citizenship (''Congressional Globe'', 1866, 2892)."
Indian Appropriations Act of 1871
In 1871 Congress added a rider to theIndian Appropriations Act
The Indian Appropriations Act is the name of several acts passed by the United States Congress. A considerable number of acts were passed under the same name throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, but the most notable landmark acts cons ...
ending United States recognition of additional Native American tribes or independent nations, and prohibiting additional treaties.
Education and boarding schools
After the Indian wars in the late 19th century, the United States establishedNative American boarding schools
American Indian boarding schools, also known more recently as American Indian residential schools, were established in the United States from the mid 17th to the early 20th centuries with a primary objective of "civilizing" or assimilating Na ...
, initially run primarily by or affiliated with Christian missionaries. At this time American society thought that Native American children needed to be acculturated to the general society. The boarding school
A boarding school is a school where pupils live within premises while being given formal instruction. The word "boarding" is used in the sense of "room and board", i.e. lodging and meals. As they have existed for many centuries, and now exten ...
experience often proved traumatic to Native American children, who were forbidden to speak their native languages, taught Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and denied the right to practice their native religions, and in numerous other ways forced to abandon their Native American identities and adopt European-American culture.
Since the late 20th century, investigations have documented cases of sexual, physical and mental abuse occurring at such schools. While problems were documented as early as the 1920s, some of the schools continued into the 1960s. Since the rise of self-determination for Native Americans, they have generally emphasized education of their children at schools near where they live. In addition, many federally recognized tribes have taken over operations of such schools and added programs of language retention and revival to strengthen their cultures. Beginning in the 1970s, tribes have also founded colleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
at their reservations, controlled and operated by Native Americans, to educate their young for jobs as well as to pass on their cultures.
20th century
On August 29, 1911Ishi
Ishi ( – March 25, 1916) was the last known member of the Native American Yahi people from the present-day state of California in the United States. The rest of the Yahi (as well as many members of their parent tribe, the Yana) were kill ...
, generally considered to have been the last Native American to live most of his life without contact with European-American
European Americans (also referred to as Euro-Americans) are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes people who are descended from the first European settlers in the United States as well as people who are descended from more recent Eu ...
culture, was discovered near Oroville, California
Oroville (''Oro'', Spanish for "Gold" and ''Ville'', French for "town") is the county seat of Butte County, California, United States. The population of the city was 15,506 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, up from 13,004 in the 200 ...
after a forest fire drove him from nearby mountains. He was the last of his tribe, the rest having been massacred by a party of White "Indian fighters" in 1865 when he was a boy. After being jailed in protective custody, Ishi was released to anthropologists led by Alfred L. Kroeber
Alfred Louis Kroeber (June 11, 1876 – October 5, 1960) was an American cultural anthropologist. He received his PhD under Franz Boas at Columbia University in 1901, the first doctorate in anthropology awarded by Columbia. He was also the first ...
at the University of California. They studied his Southern Yahi language and culture, and provided him a home until his death from tuberculosis five years later.
On June 2, 1924 U.S. Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
President Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican lawyer ...
signed the Indian Citizenship Act
The Indian Citizenship Act of 1924, (, enacted June 2, 1924) was an Act of the United States Congress that granted US citizenship to the indigenous peoples of the United States. While the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution ...
, which made citizens of the United States of all Native Americans born in the United States and its territories and who were not already citizens. Prior to passage of the act, nearly two-thirds of Native Americans were already U.S. citizens.
American Indians today have all the rights guaranteed in the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
, can vote in elections, and run for political office. There has been controversy over how much the federal government has jurisdiction over tribal affairs, sovereignty, and cultural practices.
World War II
United States military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
: at the time, one-third of all able-bodied Indian men from 18 to 50 years of age.
The entry of young men into the United States military during World War II has been described as the first large-scale exodus of indigenous peoples from the reservations. It involved more people than any migration since the removals
A moving company, removalist or van line is a company that helps people and businesses move their goods from one place to another. It offers all-inclusive services for relocations, like packing, loading, moving, unloading, unpacking, and a ...
from areas east of the Mississippi River of the early 19th century.
The men's service with the US military in the international conflict was a turning point in Native American history. The overwhelming majority of Native Americans welcomed the opportunity to serve; they had a voluntary enlistment rate that was 40% higher than those who were drafted. War Department officials said that if the entire population had enlisted in the same proportion as the Native Americans, the response would have rendered the draft unnecessary.
Their fellow soldiers often held them in high esteem, in part since the legend of the tough Native American warrior had become a part of the fabric of American historical legend. White servicemen sometimes showed a lighthearted respect toward Native American comrades by calling them "chief". Native American cultures were profoundly changed after their young men returned home, because of their wide contact with the world outside of the reservation system. "The war", said the U.S. Indian Commissioner in 1945, "caused the greatest disruption of Native life since the beginning of the reservation era", affecting the habits, views, and economic well-being of tribal members.
The most significant of these changes was the opportunity—as a result of wartime labor shortages—to find well-paying work in cities. After the war many Native Americans relocated to urban areas, particularly on the West Coast with the buildup of the defense industry. In the 1950s the federal government had a relocation policy encouraging them to do so because of economic opportunity in cities. But Native Americans struggled with discrimination and the great cultural changes in leaving their reservations behind.
There were also losses as a result of the war. For instance, a total of 1,200 Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
men served in World War II; only about half came home alive. In addition many more Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
served as Code talker
A code talker was a person employed by the military during wartime to use a little-known language as a means of secret communication. The term is now usually associated with United States service members during the world wars who used their k ...
s for the military in the Pacific. The code they made, although cryptologically very simple, was never cracked by the Japanese.
Self-determination
Military service and urban residency contributed to the rise of American Indian activism, particularly after the 1960s and theoccupation of Alcatraz Island
The Occupation of Alcatraz (November 20, 1969 – June 11, 1971) was a 19-month long protest when 89 Native Americans and their supporters occupied Alcatraz Island. The protest was led by Richard Oakes, LaNada Means, and others, while John ...
(1969–1971) by a student Indian group from San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
. In the same period, the American Indian Movement
The American Indian Movement (AIM) is a Native American grassroots movement which was founded in Minneapolis, Minnesota in July 1968, initially centered in urban areas in order to address systemic issues of poverty, discrimination, and police ...
(AIM) was founded in Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origins ...
, and chapters were established throughout the country, where American Indians combined spiritual and political activism. Political protests gained national media attention and the sympathy of the American public.
Through the mid-1970s, conflicts between governments and Native Americans occasionally erupted into violence. A notable late 20th-century event was the Wounded Knee incident
The Wounded Knee Occupation, also known as Second Wounded Knee, began on February 27, 1973, when approximately 200 Oglala Lakota (sometimes referred to as Oglala Sioux) and followers of the American Indian Movement (AIM) seized and occupied ...
on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation
The Pine Ridge Indian Reservation ( lkt, Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke), also called Pine Ridge Agency, is an Oglala Lakota Indian reservation located entirely within the U.S. state of South Dakota. Originally included within the territory of the Gr ...
. Upset with tribal government and the failures of the federal government to enforce treaty rights, about 300 Oglala Lakota
The Oglala (pronounced , meaning "to scatter one's own" in Lakota language) are one of the seven subtribes of the Lakota people who, along with the Dakota people, Dakota, make up the Sioux, Očhéthi Šakówiŋ (Seven Council Fires). A majority ...
and American Indian Movement
The American Indian Movement (AIM) is a Native American grassroots movement which was founded in Minneapolis, Minnesota in July 1968, initially centered in urban areas in order to address systemic issues of poverty, discrimination, and police ...
(AIM) activists took control of Wounded Knee on February 27, 1973.
Indian activists from around the country joined them at Pine Ridge, and the occupation became a symbol of rising American Indian identity and power. Federal law enforcement officials and the national guard cordoned off the town, and the two sides had a standoff for 71 days. During much gunfire, one United States Marshal
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforcem ...
was wounded and paralyzed. In late April a Cherokee and local Lakota man were killed by gunfire; the Lakota elders ended the occupation to ensure no more lives were lost.
In June 1975, two FBI agents seeking to make an armed robbery arrest at Pine Ridge Reservation were wounded in a firefight, and killed at close range. The AIM activist Leonard Peltier
Leonard Peltier (born September 12, 1944) is a Native American activist and militant member of the American Indian Movement (AIM) who, following a controversial trial, was convicted of two counts of first-degree murder in the deaths of two Fe ...
was sentenced in 1976 to two consecutive terms of life in prison in the FBI deaths.
In 1968 the government enacted the Indian Civil Rights Act
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a landmark law in the United States signed into law by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles II through VII comprise the Indian Civil Rights Act, which applie ...
. This gave tribal members most of the protections against abuses by tribal governments that the Bill of Rights accords to all U.S. citizens with respect to the federal government. In 1975 the U.S. government passed the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act
The Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975 (Public Law 93-638) authorized the Secretary of the Interior, the Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare, and some other government agencies to enter into contracts with, a ...
, marking the culmination of 15 years of policy changes. It resulted from American Indian activism, the Civil Rights Movement, and community development aspects of President Lyndon Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
's social programs of the 1960s. The Act recognized the right and need of Native Americans for self-determination. It marked the U.S. government's turn away from the 1950s policy of termination of the relationship between tribes and the government. The U.S. government encouraged Native Americans' efforts at self-government and determining their futures. Tribes have developed organizations to administer their own social, welfare and housing programs, for instance. Tribal self-determination has created tension with respect to the federal government's historic trust obligation to care for Indians, however, the Bureau of Indian Affairs has never lived up to that responsibility.
By this time, tribes had already started to establish community schools to replace the BIA boarding schools. Led by the Navajo Nation
The Navajo Nation ( nv, Naabeehó Bináhásdzo), also known as Navajoland, is a Native American reservation in the United States. It occupies portions of northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southeastern Utah; at roughly , the ...
in 1968, tribes started tribal colleges and universities
In the United States, tribal colleges and universities (TCUs) are a Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, category of higher education, Minority Serving Institution, minority-serving institutions defined in the Higher Educa ...
, to build their own models of education on reservations, preserve and revive their cultures, and develop educated workforces. In 1994 the U.S. Congress passed legislation recognizing the tribal colleges as land-grant colleges
A land-grant university (also called land-grant college or land-grant institution) is an institution of higher education in the United States designated by a state to receive the benefits of the Morrill Acts of 1862 and 1890.
Signed by Abraha ...
, which provided opportunities for funding. Thirty-two tribal colleges in the United States belong to the American Indian Higher Education Consortium
The American Indian Higher Education Consortium (AIHEC) was established in 1972 to represent the interests of the newly developed tribal colleges, which are controlled and operated by American Indian nations. The four founders were Gerald One F ...
. By the early 21st century, tribal nations had also established numerous language revival programs in their schools.
In addition, Native American activism has led major universities across the country to establish Native American studies programs and departments, increasing awareness of the strengths of Indian cultures, providing opportunities for academics, and deepening research on history and cultures in the United States. Native Americans have entered academia; journalism and media; politics at local, state and federal levels; and public service, for instance, influencing medical research and policy to identify issues related to American Indians.
In 1981, Tim Giago
Timothy Antoine Giago Jr. (July 12, 1934 – July 24, 2022), also known as Nanwica Kciji, was an American Oglala Lakota journalist and publisher. In 1981, he founded the ''Lakota Times'' with Doris Giago at the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, w ...
founded the '' Lakota Times'', an independent Native American newspaper, located at the Pine Ridge Reservation but not controlled by tribal government. He later founded the Native American Journalists Association
The Native American Journalists Association, based in Norman, Oklahoma, on the campus of the University of Oklahoma, is an organization dedicated to supporting Native Americans in journalism. The organization hosts the annual National Native Media ...
. Other independent newspapers and media corporations have been developed, so that Native American journalists are contributing perspective on their own affairs and other policies and events.
In 2004 Senator Sam Brownback
Samuel Dale Brownback (born September 12, 1956) is an American attorney, politician, diplomat, and member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party who served as the United States Ambassador-at-Large for International Religious Fr ...
(Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
of Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
) introduced a joint resolution (Senate Joint Resolution 37) to "offer an apology to all Native Peoples on behalf of the United States" for past "ill-conceived policies" by the U.S. government regarding Indian Tribes. President Barack Obama signed the historic apology into law in 2009, as Section 8113 of the 2010 defense appropriations bill.
After years of investigation and independent work by Native American journalists, in 2003 the U.S. government indicted suspects in the December 1975 murder of Anna Mae Aquash at the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation. A ''Miꞌkmaq, Mi'kmaq,'' Aquash was the highest-ranking woman activist in the American Indian Movement
The American Indian Movement (AIM) is a Native American grassroots movement which was founded in Minneapolis, Minnesota in July 1968, initially centered in urban areas in order to address systemic issues of poverty, discrimination, and police ...
(AIM) at the time. She was killed several months after two FBI agents had been killed at the reservation. Many Lakota believe that she was killed by AIM on suspicion of having been an FBI informant, but she never worked for the FBI. Arlo Looking Cloud was convicted in federal court in 2004. In 2007 the United States Extradition, extradited AIM activist John Graham (Canadian activist), John Graham from Canada to stand trial for her murder. He was also convicted and sentenced to life.
The Indian Arts and Crafts Act of 1990
The Indian Arts and Crafts Act of 1990 (P.L. 101-644) is a truth-in-advertising law that prohibits misrepresentation in marketing of Native Americans in the United States, American Indian or Alaska Natives, Alaska Native arts and crafts products within the United States, including dreamcatchers. It is illegal to offer or display for sale, or sell any art or craft product in a manner that falsely suggests it is Indian produced.21st century
Native American tribes and individuals began to file suits against the federal government over a range of issues, especially land claims and mismanagement of trust lands and fees. A number of longstanding cases were finally settled by the administration of President Barack Obama, who made a commitment to improve relations between the federal government and the tribes. Among these was ''Cobell v. Salazar,'' a class action suit settled in 2009, with Congress appropriating funds in 2010. Another was ''Keepseagle v. '', settled in April 2011. The $760 million settlement "designated $680 million for Native American farmers who had faced discrimination from the United States Department of Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture over a period of several years in the past.Rob Capriccioso, "Tribes Don't Like Keepseagle Lawyers Controlling $380 Million of Settlement"''Indian Country Today,'' 4 September 2013; accessed 5 November 2016 By 2012, "the Justice and Interior departments had reached settlements totaling more than $1 billion with 41 tribes for claims of mismanagement."Alysa Landry, "Barack Obama: ‘Emotionally and Intellectually Committed to Indian Country’"
''Indian Country Today,'' 1 November 2016; accessed 5 November 2016 The Navajo Nation gained the largest settlement with a single tribe, of $554 million. It is the largest tribe in the United States. In 2013 under renewal of the Violence Against Women Act#2012–13 legislative battle and reauthorization, Violence Against Women Act, the federal government strengthened protection of Native American women, as it established authority for tribes to prosecute non-Natives who commit crimes on Indian land. Domestic and sexual abuse of Native American women has been a problem in many areas, but previous laws prevented arrest or prosecution by tribal police or courts of non-native abusive partners. Native American migration to urban areas continued to grow: 70% of Native Americans lived in urban areas in 2012, up from 45% in 1970, and 8% in 1940. Urban areas with significant Native American populations include Rapid City, South Dakota, Rapid City,
Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origins ...
, Oklahoma City, Denver, Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Tucson, Arizona, Tucson, Seattle, Chicago, Houston, and New York City. Many have lived in poverty and struggled with discrimination. Racism, unemployment, drugs and gangs were common problems which Indian social service organizations, such as the Little Earth housing complex in Minneapolis, have attempted to address.
See also
* List of Native American firstsNotes
{{Authority control Native American people Native American history, History of the United States by topic