|
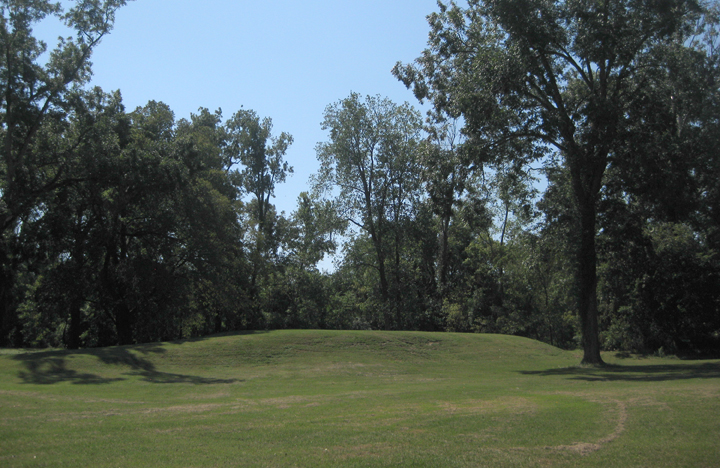
Mazique Archeological Site
The Mazique Archeological Site ( 22 AD 502), also known as White Apple Village, is a prehistoric Coles Creek culture archaeological site located in Adams County, Mississippi. It is also the location of the historic period White Apple Village of the Natchez people and the Mazique Plantation. It was added to the NRHP on October 23, 1991, as NRIS number 91001529. Description The site is located on the west bank of Second Creek, a tributary of the Homochitto River and consisted of three platform mounds and a central plaza. It was occupied during both the Coles Creek period (700–1000 CE) and the later Plaquemine Mississippian period (1000–1680 CE), when it was recorded in historic times as the White Apple village of the Natchez. Mound A sits directly on the bank of Second Creek and more than half of its mass has been lost due to the creek eroding into it. It is currently in height but was recorded as being in height and in circumference by Montroville W. Dickeson in 1841 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibley, Mississippi
Sibley is an unincorporated community in Adams County, Mississippi, United States. There is a post office located on U.S. Route 61 in Sibley, ZIP code 39165. Places The St. Catherine Creek National Wildlife Refuge is located west of Sibley, and the Mazique Archeological Site is located north. East of the hamlet are the "Sibley Oil Fields", and to the south is the "Plantation Oaks Landfill", opened in 1991. Notable people Sibley is the birthplace of brothers Theodis, YZ, and Melwyn Ealey, whose musical achievements are acknowledged on a Mississippi Blues Trail marker in Natchez Natchez may refer to: Places * Natchez, Alabama, United States * Natchez, Indiana, United States * Natchez, Louisiana, United States * Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States * Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o .... In popular culture Sibley is mentioned in Peter Orner's award-winning novel ''Esther Stories''. Notes Unincorporated communities in Adams Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaquemine Culture Pottery
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture (circa 1200 to 1700 CE) centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek (700-1200 CE) and Troyville cultures (400-700 CE) to the Marksville culture (100 BCE to 400 CE). The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi. History Definition The Plaquemine culture was a Mississippian culture variant centered on the Mississippi River valley, stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to just south of its junction with the Arkansas River, encompassing the Yazoo River basin and Natchez Bluffs in western Mississippi, and the lower Ouachita and Red River valleys in southeastern Arkansas, and eastern Louisiana. They were primarily agriculturists who grew maize, pumpkins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Rosalie
Fort Rosalie was built by the French in 1716 within the territory of the Natchez Native Americans and it was part of the French colonial empire in the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi. Early history As part of the peace terms that ended the First Natchez War in 1716, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville required the Natchez to build a fort by providing materials and labor. Sited close to the main Natchez settlement of Grand Village, Fort Rosalie served as the primary French stronghold and trading post among the Natchez. French settlements and tobacco plantations were established in Natchez territory, with the fort serving as the local seat of colonial government. Growing tension between the French and the Natchez erupted into violence several times during the 1720s, culminating in a massive Natchez attack on November 29, 1729. They destroyed the entire French settlement, killing nearly all the men and taking hundreds of women and children captive. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foster's Mound
Foster's Mound ( 22 AD 503) is a Plaquemine culture archaeological site located in Adams County, Mississippi northeast of Natchez off US 61. It is the type site for the ''Foster Phase (1350-1500 CE)'' of the Natchez Bluffs Plaquemine culture chronology. It was added to the NRHP on September 2, 1982 as NRIS number 82003091. The mounds are listed on the Mississippi Mound Trail. Description The Foster's site has two platform mounds and is located on the northern bank of St. Catherine Creek near its confluence with the Mississippi River. The largest mound, Mound A, is in height and by at its base and has had a plantation house on its summit since the 1790s. Its dimensions were originally smaller but it was enlarged to accommodate the veranda of the plantation house. Mound B is to the south across a large plaza area. It is an amorphous blob about at its highest point. It has been seriously eroded by the creek and is barely recognizable as a rectangular platform mound. The site sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerald Mound Site
The Emerald Mound site ( 22 AD 504), also known as the '' Selsertown site'', is a Plaquemine culture Mississippian period archaeological site located on the Natchez Trace Parkway near Stanton, Mississippi, United States. The site dates from the period between 1200 and 1730 CE. It is the type site for the ''Emerald Phase (1500 to 1680 CE)'' of the Natchez Bluffs Plaquemine culture chronology and was still in use by the later historic Natchez people for their main ceremonial center. The platform mound is the second-largest Mississippian period earthwork in the country, after Monk's Mound at Cahokia, Illinois. The mound covers eight acres, measuring by at the base and is in height. Emerald Mound has a flat top with two smaller secondary mounds at each end. It was constructed around a natural hill. Travelers in the early 19th century noted a number of adjoining mounds and an encircling ditch that are no longer present. This site once had six other secondary mounds which were los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River, where they settled mostly in present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were hunter-ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
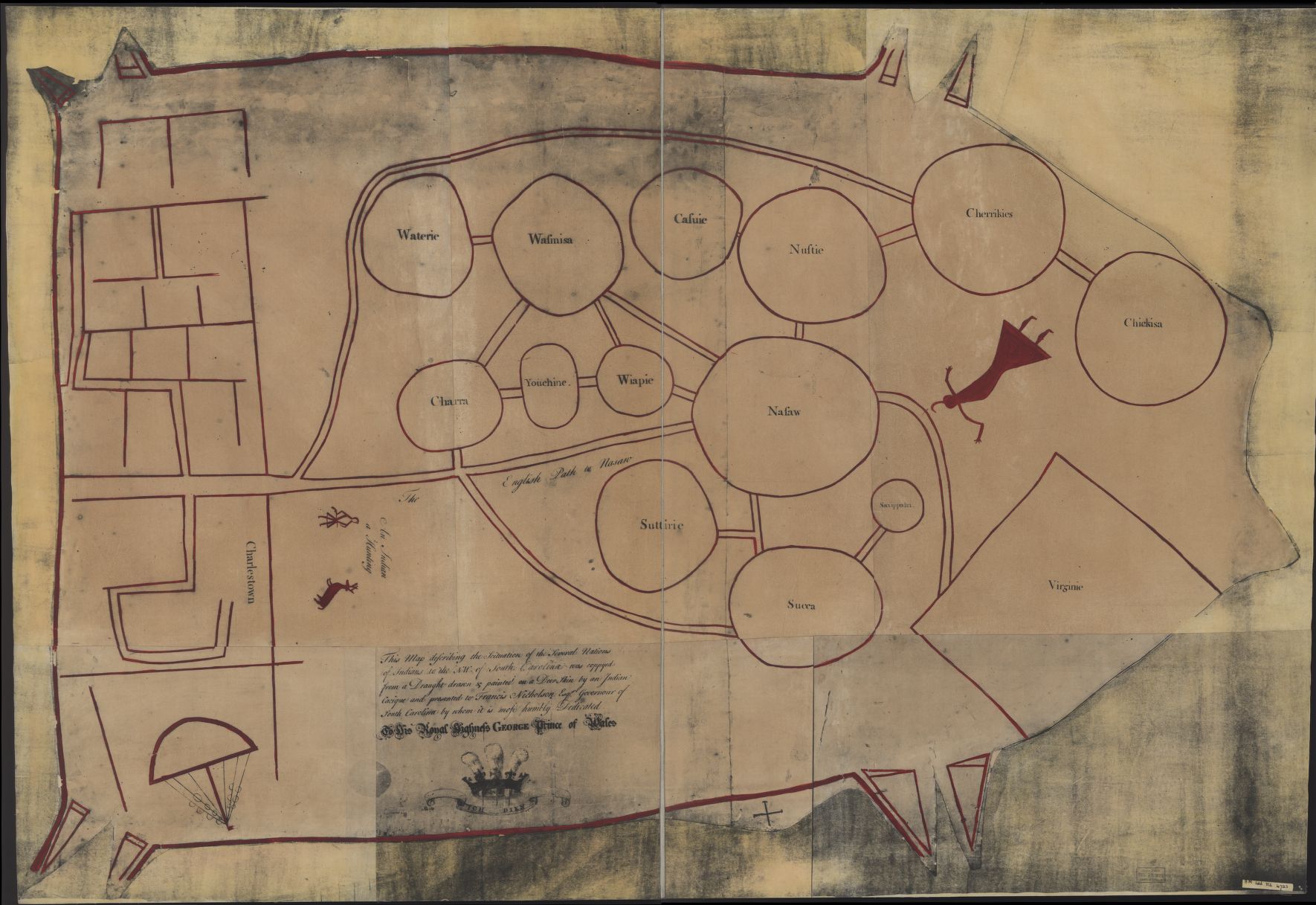
Grand Village Of The Natchez
Grand Village of the Natchez, ( 22 AD 501) also known as the Fatherland Site, is a site encompassing a prehistoric indigenous village and earthwork mounds in present-day south Natchez, Mississippi. The village complex was constructed starting about 1200 CE by members of the prehistoric Plaquemine culture. They built the three platform mounds in stages. Another phase of significant construction work by these prehistoric people has been dated to the mid-15th century. It was named for the historic Natchez people, who used the site in the 17th and 18th centuries. and In the early 18th century, when the historic Natchez people occupied the site, they added to the mounds. The village was the Natchez tribe's main political and religious ceremonial center in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, according to historical and archaeological evidence. It replaced the Emerald Mound site in this role. After suffering a 1730 military defeat by French settlers, the Natchez abandon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattooed Serpent
Tattooed Serpent (died 1725) (Natchez: Obalalkabiche; French: Serpent Piqué) was the war chief of the Natchez people of Grand Village, which was located near Natchez in what is now the U.S. state of Mississippi. He and his brother, the paramount chief Great Sun, allied his people with the French colonists. He was a friend of the colonist and chronicler Antoine-Simon Le Page du Pratz. Le Page du Pratz described their friendship and Tattooed Serpent's death and funeral in detail in his chronicle. Source of the name The name ''Obalalkabiche'' (Tattooed Serpent) was traditionally adopted by the War Chief of the Natchez, who was always the younger brother of the Paramount Chief, whose official name was ''Yak-stalchil'' (Great Sun). Thus, the Tattooed Serpent who died in 1725 and was a friend of Le Page du Pratz was preceded by his own maternal uncle (died 1700), who was also called Tattooed Serpent while in office. On his death in 1725, Tattooed Serpent was succeeded by his sister's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris. The vast territory of ''New France'' consisted of five colonies at its peak in 1712, each with its own administration: Canada, the most developed colony, was divided into the districts of Québec, Trois-Rivières, and Montréal; Hudson Bay; Acadie in the northeast; Plaisance on the island of Newfoundland; and Louisiane. It extended from Newfoundland to the Canadian Prairies and from Hudson Bay to the Gulf of Mexico, including all the Great Lakes of North America. In the 16th century, the lands were used primarily to draw from the wealth of natural resources such as furs through trade with the various indigenous peoples. In the seventeenth century, successful settlements began in Acadia and in Quebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke Colony, Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America. The British Empire's colonial territories in North America were greatly expanded in connection with the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally concluded the Seven Years' War, referred to by the English colonies in North America as the French and Indian War, and by the French colonies as . With the ultimate acquisition of most of New France (), Territorial evolution of North America since 1763, British territory in North America was more than doubled in size, and the exclusion of France also dramatically altered the political landscape of the continent. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |