|
San Juan Basin
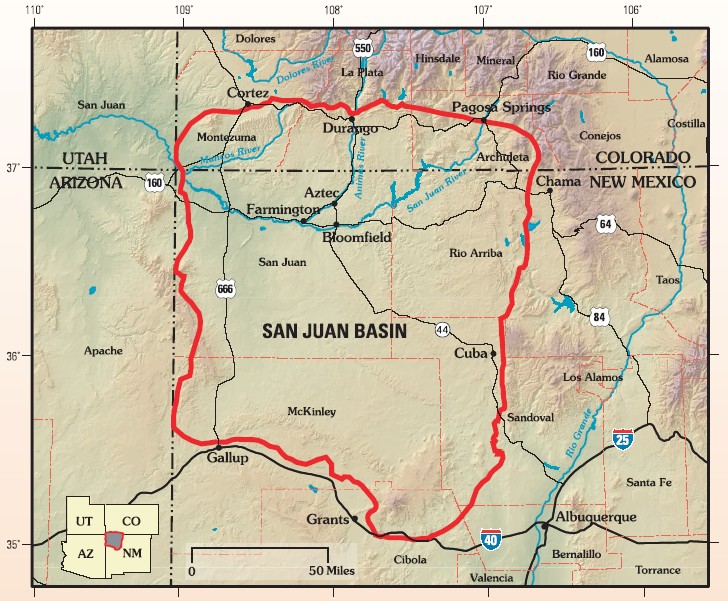
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly N-S and E-W. The San Juan Basin is an asymmetric structural depression in the Colorado Plateau province, with varying elevation and nearly in topographic relief. Its most striking features include Chaco Canyon (northwestern New Mexico, between Farmington and Santa Fe) and Chacra Mesa. The basin lies west of the Continental Divide, and its main drainage is the southwest- to west-flowing San Juan River, which eventually joins the Colorado River in Utah. Climate of the basin is arid to semiarid, with an annual precipitation of and an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important pre-Columbian cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major center of culture for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requiring generations of astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and also the northwestern part of Scotland, known as the Hebridean Terrane. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and itself consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of Early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today. The craton is named after the Laurentian Shield, through the Laurentian Mountains, which received their name from the Saint Lawrence River, named after Lawrence of Rome. Interior platform In eastern and central Canada, much of the stable craton is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalbed Methane In The United States
The 2017 production of coalbed methane in the United States was 0.98 trillion cubic feet (TCF), 3.6 percent of all US dry gas production that year. The 2017 production was down from the peak of 1.97 TCF in 2008. Most coalbed methane production came from the Rocky Mountain states of Colorado, Wyoming, and New Mexico. Coalbed methane reserve estimates vary; however a 1997 estimate from the U.S. Geological Survey predicts more than of methane within the US. At a natural gas price of US$6.05 per million Btu (US$5.73/GJ), that volume is worth US$4.37 trillion. At least of it is economically viable to produce. The EIA reports 2017 reserves at 11,878 billion cubic feet (BCF) or 11.878 trillion cubic feet, which at a current market price of US $2.97 as of May 14, 2021, are worth approximately $36.2 Billion USD. History Coalbed methane grew out of venting methane from coal seams. Some coal beds have long been known to be "gassy," and as a safety measure, boreholes were drilled into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, so odorizers such as mercaptan (which smells like sulfur or rotten eggs) are commonly added to natural gas supplies for safety so that leaks can be readily detected. Natural gas is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) decompose under anaerobic conditions and are subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other hydrocarbons. Natural gas can be burned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most arid climates straddle the Equator; these regions include parts of Africa, Asia, South America, North America, and Australia. Change over time The distribution of aridity at any time is largely the result of the general circulation of the atmosphere. The latter does change significantly over time through climate change. For example, temperature increase by 1.5–2.1 percent across the Nile Basin over the next 30–40 years could change the region from semi-arid to arid, significantly reducing the land usable for agriculture. In addition, changes in land use can increase demands on soil water and thereby increase aridity. See also * Arid Forest Research Institute * Aridity index * Desert climate * Desiccation tolerance * Drought * Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. states and two Mexican states. The name Colorado derives from the Spanish language for "colored reddish" due to its heavy silt load. Starting in the central Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it flows generally southwest across the Colorado Plateau and through the Grand Canyon before reaching Lake Mead on the Arizona–Nevada border, where it turns south toward the Mexico–United States border, international border. After entering Mexico, the Colorado approaches the mostly dry Colorado River Delta at the tip of the Gulf of California between Baja California and Sonora. Known for its dramatic canyons, whitewater rapids, and eleven National parks of the United States, U.S. National Parks, the Colorado River and its tributaries are a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan River (Colorado River)
The San Juan River is a major tributary of the Colorado River in the Southwestern United States, providing the chief drainage for the Four Corners region of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Arizona. Originating as snowmelt in the San Juan Mountains (part of the Rocky Mountains) of Colorado, it flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed March 21, 2011, through the deserts of northern New Mexico and southeastern Utah to join the Colorado River at Glen Canyon. The river drains a high, arid region of the Colorado Plateau. Along its length, it is often the only significant source of fresh water for many miles. The San Juan is also one of the muddiest rivers in North America, carrying an average of 25 million US tons (22.6 million t) of silt and sediment each year. Historically, the San Juan formed the border between the territory of the Navajo in the south and the Ute in the north. Although Europeans explored th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Divide Of The Americas
The Continental Divide of the Americas (also known as the Great Divide, the Western Divide or simply the Continental Divide; ) is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and (in northern North America) Arctic oceans (including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea and Hudson Bay). Although there are many other hydrological divides in the Americas, the Continental Divide is by far the most prominent of these because it tends to follow a line of high peaks along the main ranges of the Rocky Mountains and Andes, at a generally much higher elevation than the other hydrological divisions. Geography Beginning at the westernmost point of the Americas’ mainland (Cape Prince of Wales, just south of the Arctic Circle), the Conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)







