Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, located in the
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, the only state that is an
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
, and the only state geographically located within the
tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
.
Hawaii comprises
nearly the entire
Hawaiian archipelago
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, N─ü Mokupuni o HawaiŌĆśi) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
, 137
volcanic islands
Geologically, a high island or volcanic island is an island of volcanic origin. The term can be used to distinguish such islands from low islands, which are formed from sedimentation or the uplifting of coral reefs (which have often formed ...
spanning that are
physiographically and
ethnologically part of the
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and ╬Įß┐åŽā╬┐Žé () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, P┼Źr─½netia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the
fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are
Niihau
Niihau ( Hawaiian: ), anglicized as Niihau ( ), is the westernmost main and seventh largest inhabited island in Hawaii. It is southwest of Kaua╩╗i across the Kaulakahi Channel. Its area is . Several intermittent playa lakes provide wetland hab ...
,
Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Ni╩╗ihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island ...
,
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''O╩╗ahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of O╩╗ahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million peopleŌĆöover t ...
,
Molokai
Molokai , or Molokai (), is the fifth most populated of the eight major islands that make up the Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian Islands archipelago in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. It is 38 by 10 miles (61 by 16 km) at its greatest length an ...
,
L─ünai,
Kahoolawe
Kahoolawe (Hawaiian: ), anglicized as Kahoolawe (), is the smallest of the eight main volcanic islands in the Hawaiian Islands. Kahoolawe is located about southwest of Maui and also southeast of L─üna╩╗i, and it is long by wide, with a total ...
,
Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which ...
, and
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
ŌĆöthe last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited
Northwestern Hawaiian Islands
The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands or Leeward Hawaiian Islands are a series of islands and atolls in the Hawaiian island chain located northwest (in some cases, far to the northwest) of the islands of Kauai and Niihau. Politically, they are all p ...
make up most of the
Papah─ünaumoku─ükea Marine National Monument
The Papah─ünaumoku─ükea Marine National Monument (PMNM) (roughly ) is a World Heritage Site, World Heritage listed National Monument (United States), U.S. National Monument encompassing of ocean waters, including ten islands and atolls of th ...
, the United States'
largest protected area and the
fourth-largest in the world.
Of the 50
U.S. states
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
, Hawaii is the
eighth-smallest in land area and the
11th-least populous, but with 1.4million residents ranks
13th in population density. Two-thirds of the population lives on O'ahu, home to the state's capital and largest city,
Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
. Hawaii is among the country's most diverse states, owing to its central location in the Pacific and over two centuries of migration. As one of only six
majority-minority states, it has the country's only Asian American plurality, its largest
Buddhist community, and the largest proportion of
multiracial people
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
. Consequently, it is a unique
melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
of North American and
East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea a ...
cultures, in addition to its
indigenous Hawaiian heritage.
Settled by
Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
some time between 1000 and 1200 CE, Hawaii was home to numerous independent chiefdoms.
In 1778, British explorer
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October ŌĆō 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
was the first known non-Polynesian to arrive at the archipelago; early British influence is reflected in the
state flag
In vexillology, a state flag is either the flag of the government of a sovereign state, or the flag of an individual federated state (subnational administrative division).
Government flag
A state flag is a variant of a national flag (or occas ...
, which bears a
Union Jack
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
. An influx of European and American explorers, traders, and whalers arrived shortly after leading to the decimation of the once isolated Indigenous community by introducing diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, smallpox, measles, leprosy, and typhoid fever, reducing the native Hawaiian population from between 300,000 and one million to less than 40,000 by 1890.
Hawaii became a unified, internationally recognized
kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in 1810, remaining independent until
American and European businessmen overthrew the monarchy in 1893; this led to
annexation by the U.S. in 1898. As a strategically valuable
U.S. territory
In the United States, a territory is any extent of region under the sovereign jurisdiction of the federal government of the United States, including all waters (around islands or continental tracts). The United States asserts sovereign rights for ...
, Hawaii was
attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941, which brought it global and historical significance, and contributed to America's decisive entry into World War II. Hawaii is the most recent state to
join the union, on August 21, 1959. In 1993, the U.S. government
formally apologized for its role in the overthrow of Hawaii's government, which spurred the
Hawaiian sovereignty movement
The Hawaiian sovereignty movement ( haw, ke ea Hawai╩╗i), is a grassroots political and cultural campaign to re-establish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom of Hawaii due to desire for sovereignty, self-determination, and self-gove ...
.
Historically dominated by a
plantation economy
A plantation economy is an economy based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few commodity crops, grown on large farms worked by laborers or slaves. The properties are called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cas ...
, Hawaii remains a major agricultural exporter due to its fertile soil and uniquely tropical climate in the U.S. Its economy has gradually diversified since the mid-20th century, with tourism and military defense becoming the two largest sectors. The state attracts tourists, surfers, and scientists from around the world with its diverse natural scenery, warm tropical climate, abundance of public beaches, oceanic surroundings, active volcanoes, and clear skies on the Big Island. Hawaii hosts the
U.S. Pacific Fleet
The United States Pacific Fleet (USPACFLT) is a theater-level component command of the United States Navy, located in the Pacific Ocean. It provides naval forces to the Indo-Pacific Command. Fleet headquarters is at Joint Base Pearl HarborŌĆ ...
, the world's largest naval command, as well as 75,000 employees of the Defense Department.
Although its relative isolation results in one of the highest
costs of living
Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time can be operationalized in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a cer ...
in the United States, Hawaii is the third-wealthiest state.
Etymology
The State of Hawaii derives its name from the name of its largest island, . A common Hawaiian explanation of the name of is that it was named for , a legendary figure from Hawaiian myth. He is said to have discovered the islands when they were first settled.
The
Hawaiian language
Hawaiian (', ) is a Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language o ...
word is very similar to
Proto-Polynesian
Proto-Polynesian (abbreviated PPn) is the hypothetical proto-language from which all the modern Polynesian languages descend. It is a daughter language of the Proto-Austronesian language. Historical linguists have reconstructed the language using ...
''Sawaiki'', with the
reconstructed meaning "homeland".
Cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
s of are found in other Polynesian languages, including
M─üori
M─üori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the M─üori people
* M─üori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* M─üori language, the language of the M─üori people of New Zealand
* M─üori culture
* Cook Islanders, the M─üori people of the C ...
(),
Rarotongan () and
Samoan (). According to linguists Pukui and Elbert, "elsewhere in Polynesia, or a cognate is the name of the underworld or of the ancestral home, but in Hawaii, the name has no meaning".
Spelling of state name
In 1978, Hawaiian was added to the Constitution of the State of Hawaii as an official state language alongside English. The title of the state constitution is ''The Constitution of the State of Hawaii''. ArticleXV, Section1 of the Constitution uses ''The State of Hawaii''.
Diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
s were not used because the document, drafted in 1949, predates the use of the and the in modern Hawaiian orthography. The exact spelling of the state's name in the Hawaiian language is . In the
Hawaii Admission Act
The Admission Act, formally An Act to Provide for the Admission of the State of Hawaii into the Union () is a statute enacted by the United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower which dissolved the Territory of Haw ...
that granted Hawaiian statehood, the federal government recognized ''Hawaii'' as the official state name. Official government publications, department and office titles, and the
Seal of Hawaii
The Great Seal of the State of Hawaii was designated officially by Act 272 of the 1959 Territorial Legislature and is based on the territorial seal. Modifications to the territorial seal included the use of the words "State of Hawaii" at the top ...
use the traditional spelling with no symbols for glottal stops or vowel length.
Geography and environment
There are eight main Hawaiian islands. Seven are inhabited, but only six are open to tourists and locals. Niihau is privately managed by brothers Bruce and
Keith Robinson; access is restricted to those who have their permission. This island is also home to native Hawaiians. Access to uninhabited
Kaho╩╗olawe
Kahoolawe (Hawaiian: ), anglicized as Kahoolawe (), is the smallest of the eight main volcano, volcanic islands in the Hawaiian Islands. Kahoolawe is located about southwest of Maui and also southeast of Lanai, L─üna╩╗i, and it is long by wide ...
island is also restricted and anyone who enters without permission will be arrested. This island may also be dangerous since it was a military base during the world wars and could still have unexploded ordnance.
Topography

The Hawaiian
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
is southwest of the contiguous United States. Hawaii is the southernmost U.S. state and the second westernmost after
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: ąÉą╗čÅčüą║ą░, Alyaska; ale, Alax╠ésxax╠é; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, An├Īaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
. Hawaii, like Alaska, does not border any other U.S. state. It is the only U.S. state that is not geographically located in North America, the only state completely surrounded by water and that is entirely an archipelago, and the only state in which coffee is commercially cultivable.
In addition to the eight main islands, the state has many smaller islands and islets.
Kaula Kaula may refer to:
People
* Prithvi Nath Kaula (1924ŌĆō2009), Indian librarian
* William J. Kaula (1871ŌĆō1953), American watercolor painter
* William M. Kaula (1926ŌĆō2000), Australian-born American geophysicist
Other uses
* USS ''Kaula'' (AG-3 ...
is a small island near Niihau. The
Northwestern Hawaiian Islands
The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands or Leeward Hawaiian Islands are a series of islands and atolls in the Hawaiian island chain located northwest (in some cases, far to the northwest) of the islands of Kauai and Niihau. Politically, they are all p ...
is a group of nine small, older islands to the northwest of Kauai that extend from
Nihoa
Nihoa (; haw, N─½hoa ), also known as Bird Island or Moku Manu, is the tallest of ten islands and atolls in the uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands (NWHI). The island is located at the southern end of the NWHI chain, southeast of ...
to
Kure Atoll
Kure Atoll (; haw, H┼Źlanik┼½, translation=bringing forth heaven; haw, Mokup─üpapa, translation=flat island, label=none) or Ocean Island is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean west-northwest of Midway Atoll in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands ...
; these are remnants of once much larger volcanic mountains. Across the archipelago are around 130 small rocks and islets, such as
Molokini
Molokini is a crescent-shaped, partially submerged volcanic crater which forms a small, uninhabited islet located in ╩╗Alal─ükeiki Channel between the islands of Maui and Kahoolawe, Kahoolawe, within Maui County in Hawaii, Hawaii. It is the remai ...
, which are either volcanic, marine sedimentary or erosional in origin.
Hawaii's tallest mountain
Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea ( or ; ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a W─ükea''); is a dormant volcano on the island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the highest point in the state of Hawaii and second-highest peak of an island on Earth. The peak is ...
is above mean sea level; it is taller than
Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The ChinaŌĆōNepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation (snow heig ...
if measured from the base of the mountain, which lies on the floor of the Pacific Ocean and rises about .
Geology

The Hawaiian islands were formed by volcanic activity initiated at an undersea
magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
source called the
Hawaii hotspot
The Hawaii hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the ...
. The process is continuing to build islands; the
tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, Žä╬Ą╬║Žä╬┐╬Į╬╣╬║ŽīŽé, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
beneath much of the Pacific Ocean continually moves northwest and the hot spot remains stationary, slowly creating new volcanoes. Because of the hotspot's location, all currently active land volcanoes are located on the southern half of Hawaii Island. The newest volcano,
Kama╩╗ehuakanaloa (formerly L┼Źihi), is located south of the coast of Hawaii Island.
The last volcanic eruption outside Hawaii Island occurred at on Maui before the late 18thcentury, possibly hundreds of years earlier. In 1790,
K─½lauea exploded; it was the deadliest eruption known to have occurred in the modern era in what is now the United States. Up to 5,405 warriors and their families marching on
K─½lauea
K─½lauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. His ...
were killed by the eruption. Volcanic activity and subsequent erosion have created impressive geological features. Hawaii Island has the
second-highest point among the world's islands.
On the flanks of the volcanoes, slope instability has generated damaging earthquakes and related
tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, µ┤źµ│ó, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
s, particularly in
1868
Events
January–March
* January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries.
* January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Jap ...
and
1975
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. ...
.
Steep cliffs have been created by catastrophic
debris avalanche
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented rock rush down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. They generally ...
s on the submerged flanks of ocean island volcanoes.
erupted in May 2018, opening 22 fissure vents on its eastern
rift zone
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed t ...
. The
Leilani Estates
Leilani Estates is a census-designated place (CDP) in Hawai╩╗i County, Hawaii, United States located in the District of Puna. The subdivision was formed in 1964. The population was 1,139 at the 2020 census, down from 1,560 at the 2010 censu ...
and Lanipuna Gardens are situated within this territory. The eruption destroyed at least 36 buildings and this, coupled with the
lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
flows and the
sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
fumes, necessitated the evacuation of more than 2,000 local inhabitants from their neighborhoods.
Flora and fauna

The islands of Hawaii are distant from other land habitats, and life is thought to have arrived there by wind, waves (i.e., by ocean currents), and wings (i.e., birds, insects, and any seeds that they may have carried on their feathers). Hawaii has more endangered species and has lost a higher percentage of its endemic species than any other U.S. state. The endemic plant ''
Brighamia
The Hawaiian lobelioids are a group of flowering plants in the bellflower family, Campanulaceae, subfamily Lobelioideae, all of which are endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. This is the largest plant radiation in the Hawaiian Islands, and indeed t ...
'' now requires hand-pollination because its natural pollinator is presumed to be extinct. The two species of ''Brighamia''ŌĆö''B. rockii'' and ''B. insignis''ŌĆöare represented in the wild by around 120 individual plants. To ensure that these plants set seed, biologists rappel down cliffs to brush pollen onto their stigmas.
Terrestrial ecology
The extant main islands of the
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
have been above the surface of the ocean for fewer than 10million years; a fraction of the time
biological colonization
Colonisation or colonization is the process in biology by which a species spreads to new areas. Colonisation often refers to ''successful'' immigration where a population becomes integrated into an ecological community, having resisted initial ...
and evolution have occurred there. The islands are well known for the
environmental diversity that occurs on high mountains within a trade winds field. Native Hawaiians developed complex horticultural practices to utilize the surrounding ecosystem for agriculture. Cultural practices developed to enshrine values of environmental stewardship and reciprocity with the natural world, resulting in widespread biodiversity and intricate social and environmental relationships that persist to this day.
On a single island, the climate around the coasts can range from dry tropical (less than annual rainfall) to wet tropical; on the slopes, environments range from
tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season ŌĆō all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm ŌĆō and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
(more than per year), through a
temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5┬░ to 66.5┬░ N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
, to
alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
conditions with a cold, dry climate. The rainy climate impacts
soil development, which largely determines ground permeability, affecting the distribution of streams and
wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
.
Protected areas

Several areas in Hawaii are under the protection of the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
. Hawaii has two national parks:
Haleakal─ü National Park
Haleakal─ü National Park is an American national park located on the island of Maui in the state of Hawaii. Named after Haleakal─ü, a dormant volcano within its boundaries, the park covers an area of , of which is a wilderness area. The land wa ...
located near
Kula on the island of Maui, which features the dormant volcano Haleakal─ü that formed east Maui, and
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
in the southeast region of the Hawaii Island, which includes the active volcano K─½lauea and its rift zones.
There are three
national historical park
National Historic Site (NHS) is a designation for an officially recognized area of national historic significance in the United States. An NHS usually contains a single historical feature directly associated with its subject. The National Historic ...
s;
Kalaupapa National Historical Park
Kalaupapa National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park located in Kalaupapa, Hawaii, on the island of Molokai. Coterminous with the boundaries of Kalawao County and primarily on Kalaupapa peninsula, it was established by ...
in Kalaupapa, Molokai, the site of a former leper colony;
Kaloko-Honok┼Źhau National Historical Park
Kaloko-Honok┼Źhau National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park located in the Kona District on the Big island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It includes the National Historic Landmarked archaeological site known ...
in
Kailua-Kona
Kailua-Kona is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Hawaii County, Hawaii, United States. It is also known as Kailua (a name it shares with a community located on the windward side of Oahu), as Kona (a name it shares ...
on Hawaii Island; and
Puuhonua o H┼Źnaunau National Historical Park, an ancient place of refuge on Hawaii Island's west coast. Other areas under the control of the National Park Service include
Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail
Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail is a long trail located on the island of Hawaii. It is not yet a single continuous trail, but can be accessed at several broken segments along the coastline of the Big Island. The trail was established to acc ...
on Hawaii Island and the
USS ''Arizona'' Memorial at
Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Re ...
on Oahu.
The
Papah─ünaumoku─ükea Marine National Monument
The Papah─ünaumoku─ükea Marine National Monument (PMNM) (roughly ) is a World Heritage Site, World Heritage listed National Monument (United States), U.S. National Monument encompassing of ocean waters, including ten islands and atolls of th ...
was proclaimed by President
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
on June 15, 2006. The monument covers roughly of reefs, atolls, and shallow and deep sea out to offshore in the Pacific OceanŌĆöan area larger than all the national parks in the U.S. combined.
Climate

Hawaii has a tropical climate. Temperatures and humidity tend to be less extreme because of near-constant
trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
from the east. Summer highs usually reach around during the day, with the temperature reaching a low of at night. Winter day temperatures are usually around ; at low elevation they seldom dip below at night. Snow, not usually associated with the tropics, falls at on Mauna Kea and
Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
on Hawaii Island in some winter months. Snow rarely falls on Haleakal─ü.
Mount Waialeale
Mount Waialeale is a shield volcano and the second highest point on the island of Kauai in the Hawaiian Islands. Its name literally means "rippling water" or "overflowing water"
The mountain, at an elevation of , averages more than of rain ...
on Kauai has the second-highest average annual rainfall on Earth, about per year. Most of Hawaii experiences only two seasons; the dry season runs from May to October and the wet season is from October to April.
The warmest temperature recorded in the state, in
Pahala on April 27, 1931, is , making it tied with
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: ąÉą╗čÅčüą║ą░, Alyaska; ale, Alax╠ésxax╠é; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, An├Īaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
as the lowest record high temperature observed in a U.S. state.
Hawaii's record low temperature is observed in May1979, on the summit of
Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea ( or ; ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a W─ükea''); is a dormant volcano on the island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the highest point in the state of Hawaii and second-highest peak of an island on Earth. The peak is ...
. Hawaii is the only state to have never recorded sub-zero Fahrenheit temperatures.
Climates vary considerably on each island; they can be divided into
windward and leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
(''koolau'' and ''kona'', respectively) areas based upon location relative to the higher mountains. Windward sides face cloud cover.
Environmental issues
Hawaii has a decades-long history of hosting more military space for the United States than any other territory or state.
This record of military activity has taken a sharp toll on the environmental health of the Hawaiian archipelago, degrading its beaches and soil, and making some places entirely unsafe to go due to unexploded ordinances. According to scholar
Winona LaDuke
Winona LaDuke (born August 18, 1959) is an American economist, environmentalist, writer and industrial hemp grower, known for her work on tribal land claims and preservation, as well as sustainable development.
In 1996 and 2000, she ran for Vice ...
: "The vast militarization of Hawaii has profoundly damaged the land. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, there are more federal hazardous waste sites in Hawaii ŌĆō 31 ŌĆō than in any other U.S. state." Hawaii State Representative
Roy Takumi writes in "Challenging U.S. Militarism in Hawai'i and Okinawa" that these military bases and hazardous waste sites have meant "the confiscation of large tracts of land from native peoples" and quotes late Hawaiian activist George Helm as asking: "What is national defense when what is being destroyed is the very thing the military is entrusted to defend, the sacred land of Hawaii?"
Contemporary Indigenous Hawaiians are still protesting the occupation of their homelands and environmental degradation due to increased militarization in the wake of 9/11.
After the rise of sugarcane plantations in the mid 19th century, island ecology changed dramatically. Plantations require massive quantities of water, and European and American plantation owners transformed the land in order to access it; primarily through construction of tunnels to divert water from the mountains to the plantations, reservoir construction, and well digging.
These changes have made lasting impacts on the land and continue to contribute to resource scarcity for Native Hawaiians today.
According to Stanford scientist and scholar Sibyl Diver, Indigenous Hawaiians engage in a reciprocal relationship with the land, "based on principles of mutual caretaking, reciprocity and sharing".
This relationship ensures the longevity, sustainability, and natural cycles of growth and decay, as well as cultivating a sense of respect for the land and humility towards one's place in an ecosystem.
The ongoing expansion of the tourism industry and its pressure on local systems of ecology, cultural tradition and infrastructure in Hawaii is creating a conflict between economic and environmental health. In 2020, the Center for Biological Diversity reported on the plastic pollution of Hawaii's Kamilo beach, citing "massive piles of plastic waste". There are also issues such as the spread of invasive species, and the contamination of groundwater and coastal waters from chemical and pathogenic runoff.
History
Hawaii is one of two states that were widely recognized independent nations prior to joining the United States. The
Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawai╩╗i ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawai╩╗i Pae ╩╗─Ćina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island ...
was sovereign from 1810 until 1893 when
the monarchy was overthrown by resident American and European capitalists and landholders. Hawaii was an independent republic from 1894 until August 12, 1898, when it officially became a territory of the United States. Hawaii was admitted as a U.S. state on August 21, 1959.
First human settlement ŌĆō Ancient Hawaii (1000ŌĆō1778)
Based on archaeological evidence, the earliest habitation of the Hawaiian Islands dates to around 1000ŌĆō1200 CE, probably by Polynesian settlers from the
Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in th ...
.
A second wave of migration from
Raiatea
Raiatea or Ra'iatea ( Tahitian: ''RaŌĆśi─ütea'') is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the "centre" of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the ...
and
Bora Bora
Bora Bora ( French: ''Bora-Bora''; Tahitian: ''Pora Pora'') is an island group in the Leeward Islands. The Leeward Islands comprise the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, which is an overseas collectivity of the Frenc ...
took place in the century. The date of the human discovery and habitation of the Hawaiian Islands is the subject of academic debate. Some archaeologists and historians think it was a later wave of immigrants from
Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austr ...
around 1000 CE who introduced a new line of high chiefs, the
kapu Kapu may refer to:
* Kapu (Hawaiian culture), a Hawaiian code of conduct
* Kapu (caste), a social group of India
* Kapu, Karnataka, a town in Karnataka, India
** Kapu Assembly constituency
* Kapu, Arunachal Pradesh, a settlement in Tirap district, A ...
system, the practice of human sacrifice, and the building of ''
heiau
A ''heiau'' () is a Hawaiian temple. Made in different architectural styles depending upon their purpose and location, they range from simple earth terraces, to elaborately constructed stone platforms. There are heiau to treat the sick (''heia ...
''.
This later immigration is detailed in
Hawaiian mythology
Hawaiian religion refers to the indigenous religious beliefs and practices of native Hawaiians, also known as the kapu system. Hawaiian religion is based largely on the tapu religion common in Polynesia and likely originated among the Tahitian ...
(''moolelo'') about
Paao. Other authors say there is no archaeological or linguistic evidence for a later influx of Tahitian settlers and that Paao must be regarded as a myth.
The history of the islands is marked by a slow, steady growth in population and the size of the
chiefdoms
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
, which grew to encompass whole islands. Local chiefs, called
alii, ruled their settlements, and launched wars to extend their influence and defend their communities from predatory rivals. Ancient Hawaii was a
caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
-based society, much like that of Hindus in India. Population growth was facilitated by ecological and agricultural practices that combined upland agriculture (''manuka''), ocean fishing (''makai''),
fishponds
Fishponds is a large suburb in the north-east of the English city of Bristol, about from the city centre. It has two large Victorian-era parks: Eastville Park and Vassall's Park (once the Vassall Family estate, also known as Oldbury Court). T ...
and gardening systems. These systems were upheld by spiritual and religious beliefs, like the ''lokahi'', that linked cultural continuity with the health of the natural world.
According to Hawaiian scholar
Mililani Trask
Mililani Trask is a leader of the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and a politics, political Public speaking, speaker and Lawyer, attorney. One of Trask's contributions to the Hawaiian sovereignty movement was her founding of Na Koa Ikaika o Ka L─üh ...
, the ''lokahi'' symbolizes the "greatest of the traditions, values, and practices of our people ... There are three points in the triangleŌĆöthe Creator, ''Akua''; the peoples of the earth, ''Kanaka Maoli''; and the land, the ''aina''. These three things all have a reciprocal relationship."
European arrival
The 1778 arrival of British explorer
Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October ŌĆō 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
marked the first documented contact by a European explorer with Hawaii; early British influence can be seen in the design of the
flag of Hawaii
The flag of Hawaii ( Hawaiian: '), in addition to the current state design, previously had been used by the kingdom, protectorate, republic, and territory of Hawaii. It is the only U.S. state flag to include a foreign country's national flag. ...
, which bears the
Union Jack
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
in the top-left corner. Cook named the archipelago "the Sandwich Islands" in honor of his sponsor
John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich
John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, PC, FRS (13 November 1718 ŌĆō 30 April 1792) was a British statesman who succeeded his grandfather Edward Montagu, 3rd Earl of Sandwich as the Earl of Sandwich in 1729, at the age of ten. During his life ...
, publishing the islands' location and rendering the native name as ''Owyhee''. The form
'Owyhee' or 'Owhyhee' is preserved in the names of certain locations in the American part of the Pacific Northwest, among them
Owyhee County
Owyhee County ( ) is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Idaho. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,133. The county seat is Murphy, and its largest city is Homedale. In area it is the second-largest county in Ida ...
and
Owyhee Mountains
The Owyhee Mountains are a mountain range in Owyhee County, Idaho and Malheur County, Oregon.
Mahogany Mountain and the associated volcanic craters of the Lake Owyhee volcanic field are in the Owyhee Mountains of Oregon just east of the Owyhee R ...
in
Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the CanadaŌĆōUnited States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
, named after three native Hawaiian members of a trapping party who went missing in the area.
It is possible that
Spanish explorers
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
arrived in the Hawaiian Islands in the 16th century, two hundred years before Cook's first documented visit in 1778.
Ruy L├│pez de Villalobos
Ruy L├│pez de Villalobos (; ca. 1500 ŌĆō April 4, 1546) was a Spanish explorer who sailed the Pacific from Mexico to establish a permanent foothold for Spain in the East Indies, which was near the Line of Demarcation between Spain and Portugal a ...
commanded a fleet of six ships that left
Acapulco
Acapulco de Ju├Īrez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
in 1542 bound for the Philippines, with a Spanish sailor named Juan Gaetano aboard as pilot. Depending on the interpretation, Gaetano's reports describe an encounter with either Hawaii or the
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, ß╣éajeßĖĘ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolep─ün Aor┼Źkin ß╣éajeßĖĘ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Internati ...
.
If L├│pez de Villalobos' crew spotted Hawaii, Gaetano would thus be considered the first European to see the islands. Most scholars have dismissed these claims due to a lack of credibility.
Nonetheless, Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands at the same latitude as Hawaii, but with a longitude ten degrees east of the islands. In this manuscript, the island of Maui is named ''La Desgraciada'' (The Unfortunate Island), and what appears to be Hawaii Island is named ''La Mesa'' (The Table). Islands resembling
Kahoolawe',
L─ünai, and
Molokai
Molokai , or Molokai (), is the fifth most populated of the eight major islands that make up the Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian Islands archipelago in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. It is 38 by 10 miles (61 by 16 km) at its greatest length an ...
are named ''Los Monjes'' (The Monks). For two-and-a-half centuries,
Spanish galleons crossed the Pacific from Mexico along a route that passed south of Hawaii on their way to
Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers. Hawaii thus maintained independence, despite being situated on a sea route eastŌĆōwest between nations that were subjects of the
Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva Espa├▒a, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
, an empire that exercised jurisdiction over many subject civilizations and kingdoms on both sides of the Pacific.

Despite such contested claims, Cook is generally credited as being the first European to land at Hawaii, having visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as "firewood", and a minor chief and his men stole a boat from his ship. Cook abducted the
King of Hawaii Island,
Kalani┼Źpuu, and held him for ransom aboard his ship to gain return of Cook's boat, as this tactic had previously worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, the supporters of Kalani┼Źpuu attacked, killing Cook and four sailors as Cook's party retreated along the beach to their ship. The ship departed without retrieving the stolen boat.
After Cook's visit and the publication of several books relating his voyages, the Hawaiian Islands attracted many European and American visitors: explorers, traders, and eventually whalers, who found the islands to be a convenient harbor and source of supplies. These visitors introduced diseases to the once-isolated islands, causing the Hawaiian population to drop precipitously.
Native Hawaiians had no resistance to Eurasian diseases, such as
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
,
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
and
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10ŌĆō12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7ŌĆō10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
. By 1820, disease, famine and wars between the chiefs killed more than half of the Native Hawaiian population. During the 1850s, measles killed a fifth of Hawaii's people.
Historical records indicated the earliest Chinese immigrants to Hawaii originated from
Guangdong Province
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
; a few sailors had arrived in 1778 with Captain Cook's journey, and more arrived in 1789 with an American trader who settled in Hawaii in the late 18th century. It is said that leprosy was introduced by Chinese workers by 1830, and as with the other new infectious diseases, it proved damaging to the Hawaiians.
Kingdom of Hawaii
House of Kamehameha

During the 1780s, and 1790s, chiefs often fought for power. After a series of battles that ended in 1795, all inhabited islands were subjugated under a single ruler, who became known as
King Kamehameha the Great
Kamehameha I (; Kalani Paiea Wohi o Kaleikini Kealiikui Kamehameha o Iolani i Kaiwikapu kaui Ka Liholiho K┼½nui─ükea; ŌĆō May 8 or 14, 1819), also known as Kamehameha the Great, was the conqueror and first ruler of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kin ...
. He established the
House of Kamehameha
The House of Kamehameha ''(Hale O Kamehameha)'', or the Kamehameha dynasty, was the reigning Royal Family of the Kingdom of Hawaii, beginning with its founding by Kamehameha I in 1795 and ending with the death of Kamehameha V in 1872 and Lunalilo ...
, a dynasty that ruled the kingdom until 1872.
After
Kamehameha II
Kamehameha II (November 1797 ŌĆō July 14, 1824) was the second king of the Kingdom of Hawaii. His birth name was Liholiho and full name was Kalaninui kua Liholiho i ke kapu ╩╗Iolani. It was lengthened to Kalani Kalei╩╗aimoku o Kaiwikapu o La╩╗ ...
inherited the throne in 1819, American Protestant missionaries to Hawaii converted many Hawaiians to Christianity. Scholars have argued that one function of missionary work was to "civilize" and "purify" perceived heathenism in the New World. This carried into Hawaii.
According to research by historical archaeologist James L. Flexner, "missionaries provided the moral means to rationalize conquest and wholesale conversion to Christianity".
However, rather than abandoning traditional beliefs entirely, most native Hawaiians merged their
Indigenous religion
Indigenous religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the religious belief systems of communities described as being "indigenous". This category is often juxtaposed against others such as the "world religions" and "new re ...
with Christianity.
Missionaries used their influence to end many traditional practices of the people, including the ''
kapu Kapu may refer to:
* Kapu (Hawaiian culture), a Hawaiian code of conduct
* Kapu (caste), a social group of India
* Kapu, Karnataka, a town in Karnataka, India
** Kapu Assembly constituency
* Kapu, Arunachal Pradesh, a settlement in Tirap district, A ...
'' system, the prevailing legal system before European contact, and ''heiau'', or 'temples' to religious figures.
''Kapu'', which typically translates to "the sacred", refers to social regulations (like gender and class restrictions) that were based upon spiritual beliefs. Under the guidance of missionaries, laws against gambling, consuming alcohol, dancing the ''
hula
Hula () is a Hawaiian dance form accompanied by chant (oli) or song (Mele (Hawaiian language), mele). It was developed in the Hawaiian Islands by the Native Hawaiians who originally settled there. The hula dramatizes or portrays the words of t ...
'', breaking the Sabbath, and polygamy were enacted.
Without the ''kapu'' system, many temples and priestly statuses were jeopardized, idols were burned, and participation in Christianity increased.
When King
Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 ŌĆō December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name is Keaweaweula K─½wala┼Ź Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula K─ ...
inherited the throne at twelve years old, he was pressured by his advisors to merge Christianity with traditional Hawaiian ways. Under the guidance of his ''kuhina nui'' (his mother and coregent
Elizabeth Kaahumanu) and British allies, Hawai╩╗i turned into a Christian monarchy with the signing of the
1840 Constitution.
Hiram Bingham I
Hiram Bingham, formally Hiram Bingham I (October 30, 1789 ŌĆō November 11, 1869), was leader of the first group of American Protestant missionary, missionaries to introduce Christianity to the Hawaiian islands. Like most of the missionaries, he w ...
, a prominent Protestant missionary, was a trusted adviser to the monarchy during this period. Other missionaries and their descendants became active in commercial and political affairs, leading to conflicts between the monarchy and its restive American subjects. Catholic and Mormon missionaries were also active in the kingdom, but they converted a minority of the Native Hawaiian population. Missionaries from each major group administered to the leper colony at Kalaupapa on Molokai, which was established in 1866 and operated well into the 20th century. The best known were
Father Damien
Father Damien or Saint Damien of Molokai, SS.CC. or Saint Damien De Veuster ( nl, Pater Damiaan or '; 3 January 1840 ŌĆō 15 April 1889), born Jozef De Veuster, was a Roman Catholic priest from Belgium and member of the Congregation of the Sacr ...
and
Mother Marianne Cope
Marianne Cope, also known as Saint Marianne of Molokai, (January 23, 1838 ŌĆō August 9, 1918) was a German-born American religious sister who was a member of the Sisters of St Francis of Syracuse, New York, and founding leader of its St. Jose ...
, both of whom were canonized in the early 21st century as Roman
Catholic saints
This is an incomplete list of people and angels whom the Catholic Church has Canonization, canonized as saints. According to Catholic theology, all saints enjoy the beatific vision. Many of the Calendar of saints, saints listed here are to be f ...
.
The death of the bachelor
King Kamehameha V
Kamehameha V (Lota Kapu─üiwa Kalanimakua Ali╩╗i┼Źlani Kalanikupuapa╩╗─½kalaninui; December 11, 1830 ŌĆō December 11, 1872), reigned as the fifth monarch of the Kingdom of Hawai╩╗i from 1863 to 1872. His motto was "Onipa╩╗a": immovable, firm, s ...
ŌĆöwho did not name an heirŌĆöresulted in the popular election of
Lunalilo
Lunalilo (William Charles Lunalilo; January 31, 1835 ŌĆō February 3, 1874) was the sixth monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaii from his election on January 8, 1873, until his death a year later.
Born to Kek─üuluohi and High Chief Charles Kana╩╗ina, ...
over
Kal─ükaua
Kal─ükaua (David La╩╗amea Kamananakapu Mahinulani Naloiaehuokalani Lumialani Kal─ükaua; November 16, 1836 ŌĆō January 20, 1891), sometimes called The Merrie Monarch, was the last king and penultimate monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kin ...
. Lunalilo died the next year, also without naming an heir. In 1874, the election was contested within the legislature between Kal─ükaua and
Emma, Queen Consort of Kamehameha IV. After riots broke out, the United States and Britain landed troops on the islands to restore order.
King Kal─ükaua
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the ti ...
was chosen as monarch by the
Legislative Assembly by a vote of 39 to6 on February 12, 1874.
1887 Constitution and overthrow preparations
In 1887, Kal─ükaua was forced to sign the
1887 Constitution of the Kingdom of Hawaii. Drafted by white businessmen and lawyers, the document stripped the king of much of his authority. It established a property qualification for voting that effectively disenfranchised most Hawaiians and immigrant laborers and favored the wealthier, white elite. Resident whites were allowed to vote but resident Asians were not. As the 1887 Constitution was signed under threat of violence, it is known as the Bayonet Constitution. King Kal─ükaua, reduced to a figurehead, reigned until his death in 1891. His sister, Queen
Liliuokalani, succeeded him; she was the last monarch of Hawaii.
In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani announced plans for a new constitution to proclaim herself an absolute monarch. On January 14, 1893, a group of mostly Euro-American business leaders and residents formed the
Committee of Safety to stage a
coup d'├®tat
A coup d'├®tat (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
against the kingdom and seek annexation by the United States. United States Government Minister
John L. Stevens
John Leavitt Stevens (August 1, 1820 – February 8, 1895) was the United States Minister to the Hawaiian Kingdom in 1893 when he was accused of conspiring to overthrow Queen Liliuokalani in association with the Committee of Safety, led by ...
, responding to a request from the Committee of Safety, summoned a company of U.S. Marines. The Queen's soldiers did not resist. According to historian William Russ, the monarchy was unable to protect itself.
In ''Hawaiian Autonomy'', Queen Liliuokalani states:
If we did not by force resist their final outrage, it was because we could not do so without striking at the military force of the United States. Whatever constraint the executive of this great country may be under to recognize the present government at Honolulu has been forced upon it by no act of ours, but by the unlawful acts of its own agents. Attempts to repudiate those acts are vain.
In a message to Sanford B. Dole, Queen Liliuokalani states:
Now to avoid any collision of armed forces and perhaps the loss of life, I do under this protest, and impelled by said force, yield my authority until such time as the Government of the United States shall, upon the facts being presented to it, undo the action of its representatives and reinstate me in the authority which I claim as the constitutional sovereign of the Hawaiian Islands.
Overthrow of 1893 ŌĆō Republic of Hawaii (1894ŌĆō1898)
The treason trials of 1892 brought together the main players in the 1893 overthrow. American Minister John L. Stevens voiced support for Native Hawaiian revolutionaries, William R. Castle, a Committee of Safety member, served as a defense counsel in the treason trials, Alfred Stedman Hartwell, the 1893 annexation commissioner, led the defense effort, and Sanford B. Dole ruled as a supreme court justice against acts of conspiracy and treason.

On January 17, 1893, a small group of sugar and pineapple-growing businessmen, aided by the American minister to Hawaii and backed by heavily armed U.S. soldiers and marines, deposed Queen Liliuokalani and was replaced by a provisional government composed of members of the Committee of Safety.
According to scholar Lydia Kualapai and Hawaii State Representative Roy Takumi, this was a committee formed against the will of Indigenous Hawaiian voters, who constituted the majority of voters at the time, and consisted of "thirteen white men" according to scholar J Kehaulani Kauanui.
The United States Minister to the
Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawai╩╗i ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawai╩╗i Pae ╩╗─Ćina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island ...
(
John L. Stevens
John Leavitt Stevens (August 1, 1820 – February 8, 1895) was the United States Minister to the Hawaiian Kingdom in 1893 when he was accused of conspiring to overthrow Queen Liliuokalani in association with the Committee of Safety, led by ...
) conspired with U.S. citizens to overthrow the monarchy.
After the overthrow, Lawyer
Sanford B. Dole
Sanford Ballard Dole (April 23, 1844 ŌĆō June 9, 1926) was a lawyer and jurist from the Hawaiian Islands. He lived through the periods when Hawaii was a kingdom, protectorate, republic, and territory. A descendant of the American missionary ...
, a citizen of Hawaii and cousin to James Dole, owner of Hawaiian Fruit Company, a company that benefited from the annexation of Hawaii, became President of the Republic when the
Provisional Government of Hawaii
The Provisional Government of Hawaii (abbr.: P.G.; Hawaiian: ''Aupuni Kūikawā o Hawaiʻi'') was proclaimed after the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on January 17, 1893, by the 13-member Committee of Safety under the leadership of its ch ...
ended on July 4, 1894.
Controversy ensued in the following years as the Queen tried to regain her throne. Scholar Lydia Kualapai writes that Queen Liliuokalani had "yielded under protest not to the counterfeit Provisional Government of Hawaii but to the superior force of the United States of America" and wrote letters of protest to the President requesting a recognizance of allyship and a reinstatement of her sovereignty against the recent actions of the Provisional Government of Hawaii.
Following the January 1893 coup that deposed Queen Liliuokalani, a significant number of royalists were preparing to overthrow the white-led Republic of Hawaii oligarchy. Hundreds of rifles were covertly shipped to Hawaii and hidden in caves nearby. As armed men were coming and going, the rebel group was discovered by a Republic of Hawaii patrol. On January 6, 1895, gunfire began on both sides and later the rebels were surrounded and captured. Throughout the following 10 days several skirmishes occurred, until the last armed opposition surrendered or were captured. The Republic of Hawaii took 123 men into custody as Prisoners of War. The mass arrest of nearly 300 more men and women as political prisoners including Queen Liliuokalani was intended to incapacitate the political resistance against the ruling oligarchy. In March 1895, a military tribunal convicted 170 prisoners with treason and 6 men to be "hung by the neck" until dead, according to historian Ronald Williams Jr. The other prisoners were sentenced from 5ŌĆō35 years imprisonment at hard labor, while those convicted of lesser charges received sentences from 6 months to 6 years imprisonment at hard labor.
The queen was sentenced to 5 years in prison, but she spent 8 months under house arrest until she was released on parole. The total number of arrests related to the 1895 Kaua Kūloko was 406 people on a summary list of statistics, published by the government of the Republic of Hawaii.
The administration of President
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
commissioned the
Blount Report
The Blount Report is the popular name given to the part of the 1893 United States House of Representatives Foreign Relations Committee Report regarding the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii. The report was conducted by U.S. Commissioner James H ...
, which concluded that the removal of Liliuokalani had been illegal. Commissioner Blount found the United States and its Minister guilty on all counts including the overthrow, the landing of the marines, and the recognition of the provisional government.
In a message to Congress, President Grover Cleveland wrote:
And finally, but for the lawless occupation of Honolulu under false pretexts by the United States forces, and but for Minister Stevens' recognition of the provisional government when the United States forces were its sole support and constituted its only military strength, the Queen and her Government would never have yielded to the provisional government, even for a time and for the sole purpose of submitting her case to the enlightened justice of the United States."
The U.S. government first demanded that Queen Liliuokalani be reinstated, but the Provisional Government refused. On December 23, 1893, the response from the Provisional Government of Hawaii, authored by President Sanford B. Dole, was received by President Grover Cleveland's representative ŌĆō Minister Albert S. Willis ŌĆō and emphasized that the Provisional Government of Hawaii "unhesitatingly" rejected the demand from the Cleveland Administration.
Congress conducted an independent investigation, and on February 26, 1894, submitted the
Morgan Report
The Morgan Report was an 1894 report concluding an official U.S. Congressional investigation into the events surrounding the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom, including the alleged role of U.S. military troops (both bluejackets and marines) in the ...
, which found all parties, including Minister StevensŌĆöwith the exception of the QueenŌĆö"not guilty" and not responsible for the coup. Partisans on both sides of the debate questioned the accuracy and impartiality of both the Blount and Morgan reports over the events of 1893.
In 1993, the US Congress passed a joint
Apology Resolution
United States Public Law 103-150, informally known as the Apology Resolution, is a Joint Resolution of the U.S. Congress adopted in 1993 that "acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of age ...
regarding the overthrow; it was signed by President
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( n├® Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
. The resolution apologized and said that the overthrow was illegal in the following phrase: "The CongressŌĆöon the occasion of the 100th anniversary of the illegal overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii on January 17, 1893, acknowledges the historical significance of this event which resulted in the suppression of the inherent sovereignty of the Native Hawaiian people."
The Apology Resolution also "acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and further acknowledges that the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the Kingdom of Hawaii or through a plebiscite or referendum".
Annexation ŌĆō Territory of Hawaii (1898ŌĆō1959)

After
William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. As a politician he led a realignment that made his Republican Party largely dominant in ...
won the 1896 U.S. presidential election, advocates pressed to annex the Republic of Hawaii. The previous president, Grover Cleveland, was a friend of Queen Liliuokalani. McKinley was open to persuasion by U.S. expansionists and by annexationists from Hawaii. He met with three non-native annexationists:
Lorrin A. Thurston
Lorrin Andrews Thurston (July 31, 1858 ŌĆō May 11, 1931) was an American lawyer, politician, and businessman born and raised in the Kingdom of Hawaii. Thurston played a prominent role in the Overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom that replaced Q ...
, Francis March Hatch and
William Ansel Kinney
William Ansel Kinney (1860ŌĆō1930) was a lawyer and politician in the Kingdom of Hawaii, through the Republic of Hawaii and into the Territory of Hawaii.
Family
William Ansel Kinney was born October 16, 1860, in Honolulu, Hawaii.
His father was ...
. After negotiations in June 1897, Secretary of State
John Sherman
John Sherman (May 10, 1823October 22, 1900) was an American politician from Ohio throughout the Civil War and into the late nineteenth century. A member of the Republican Party, he served in both houses of the U.S. Congress. He also served as ...
agreed to a treaty of annexation with these representatives of the Republic of Hawaii. The
U.S. Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
never ratified the treaty. Despite the opposition of most native Hawaiians, the
Newlands Resolution
The Newlands Resolution was a joint resolution passed on July 7, 1898, by the United States Congress to annex the independent Republic of Hawaii. In 1900, Congress created the Territory of Hawaii.
The resolution was drafted by Representative Fra ...
was used to annex the Republic to the U.S.; it became the
Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory ( Hawaiian: ''Panalāʻau o Hawaiʻi'') was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900, until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding ...
. The Newlands Resolution was passed by the House on June 15, 1898, by 209 votes in favor to 91 against, and by the Senate on July 6, 1898, by a vote of 42 to 21.
A majority of Native Hawaiians opposed annexation, voiced chiefly by Queen Liliuokalani, who Hawaiian
Haunani-Kay Trask
Haunani-Kay Trask (October 3, 1949 ŌĆō July 3, 2021) was a Native Hawaiian activist, educator, author, and poet. She served as leader of the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and was professor emeritus at the University of Hawai╩╗i at M─ünoa. She w ...
described as beloved and respected by her people. Liliuokalani wrote that "it had not entered into our hearts to believe that these friends and allies from the United States ... would ever go so far as to absolutely overthrow our form of government, seize our nation by the throat, and pass it over to an alien power" in her retelling of the overthrow of her government. According to Trask, newspapers at the time argued Hawaiians would suffer "virtual enslavement under annexation", including further loss of lands and liberties, in particular to sugar plantation owners.
These plantations were protected by the U.S. Navy as economic interests, justifying a continued military presence in the islands.
In 1900, Hawaii was granted self-governance and retained
Iolani Palace Iolani is a masculine Hawaiian name meaning "royal ''hawk''." It comes from the Hawaiian words ''╩╗io'', meaning "Hawaiian hawk," and ''lani'', meaning "royal."
It may refer to:
*╩╗Iolani School, a private school located in Hawaii
*╩╗Iolani Palac ...
as the territorial capitol building. Despite several attempts to become a state, Hawaii remained a territory for 60 years. Plantation owners and capitalists, who maintained control through financial institutions such as the
Big Five, found territorial status convenient because they remained able to import cheap, foreign labor. Such immigration and labor practices were prohibited in many states.

Puerto Rican immigration to Hawaii
Puerto Rican migration to Hawaii began when Puerto Rico's sugar industry was devastated by two hurricanes in 1899. The devastation caused a worldwide shortage in sugar and a huge demand for the product from Hawaii. Consequently, Hawaiian sugarcane ...
began in 1899, when Puerto Rico's sugar industry was devastated by
a hurricane, causing a worldwide shortage of sugar and a huge demand for sugar from Hawaii. Hawaiian
sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2ŌĆō6 m (6ŌĆō20 ft) tall with ...
plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
owners began to recruit experienced, unemployed laborers in Puerto Rico. Two waves of
Korean immigration to Hawaii
Korean immigration to Hawaii has been constant since the early 20th century. There have been two distinct points at which immigration has peaked: the first wave from 1903 to 1949, the second wave from 1950 to 1964. On January 13, 2003, George W. ...
occurred in the 20th century. The first wave arrived between 1903 and 1924; the second wave began in 1965 after President
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
signed the
Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, also known as the HartŌĆōCeller Act and more recently as the 1965 Immigration Act, is a federal law passed by the 89th United States Congress and signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. The l ...
, which removed racial and national barriers and resulted in significantly altering the demographic mix in the U.S.
Oahu was the target of a surprise
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
by
Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
on December 7, 1941. The attack on Pearl Harbor and other military and naval installations, carried out by
aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
and by
midget submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, ...
s, brought the United States into
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
.
Political changes of 1954 ŌĆō State of Hawaii (1959ŌĆōpresent)
In the 1950s, the power of the plantation owners was broken by the descendants of immigrant laborers, who were born in Hawaii and were U.S. citizens. They voted against the
Hawaii Republican Party
The Hawaii Republican Party ( haw, ╩╗Ao╩╗ao Lepupalika o Hawai╩╗i) is the affiliate of the Republican Party (GOP) in Hawaii, headquartered in Honolulu. The party was initially strong during Hawaii's territorial days, but following statehood the ...
, strongly supported by plantation owners. The new majority voted for the
Democratic Party of Hawaii
The Democratic Party of Hawaii ( haw, ╩╗Ao╩╗ao Demokalaka o Hawai╩╗i) is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the state of Hawaii.
The party is a centralized organization established to promote the party platform as drafted in convention b ...
, which dominated territorial and state politics for more than 40 years. Eager to gain full representation in Congress and the Electoral College, residents actively campaigned for statehood. In Washington there was talk that Hawaii would be a Republican Party stronghold so it was matched with the admission of Alaska, seen as a Democratic Party stronghold. These predictions turned out to be inaccurate; today, Hawaii votes Democratic predominantly, while Alaska votes Republican.
In March 1959, Congress passed the
Hawaii Admissions Act, which U.S. President
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 ŌĆō March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
signed into law. The act excluded
Palmyra Atoll
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Line Islands, Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef and north of Kiribati). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way bet ...
from statehood; it had been part of the Kingdom and Territory of Hawaii. On June 27, 1959, a referendum asked residents of Hawaii to vote on the statehood bill; 94.3% voted in favor of statehood and 5.7% opposed it.
The referendum asked voters to choose between accepting the Act and remaining a U.S. territory. The United Nations'
Special Committee on Decolonization
The United Nations Special Committee on the Situation with Regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples, or the Special Committee on Decolonization (C-24), is a committee of ...
later removed Hawaii from
its list of non-self-governing territories.
After attaining statehood, Hawaii quickly modernized through construction and a rapidly growing tourism economy. Later, state programs promoted Hawaiian culture. The
Hawaii State Constitutional Convention of 1978 created institutions such as the
Office of Hawaiian Affairs
The Office of Hawaiian Affairs (OHA) is a self-governing corporate body of the State of Hawaii created by the 1978 Hawaii State Constitutional Convention.
Background
In 1893, pro-American elements in Hawaii overthrew the monarchy and formed the ...
to promote indigenous language and culture.
Legacy of annexation on Hawaiian land
In 1897, over 21,000 Natives, representing the overwhelming majority of adult Hawaiians, signed anti-annexation petitions in one of the first examples of protest against the overthrow of Queen Liliuokalanis government. Nearly 100 years later, in 1993, 17,000 Hawaiians marched to demand access and control over Hawaiian trust lands and as part of the modern Hawaiian sovereignty movement.
Hawaiian trust land ownership and use is still widely contested as a consequence of annexation. According to scholar Winona LaDuke, as of 2015, 95% of Hawaiis land was owned or controlled by just 82 landholders, including over 50% by federal and state governments, as well as the established sugar and pineapple companies.
is planned to be built on Hawaiian trust land, but has faced resistance as the project interferes with Kanaka indigeneity.
Demographics
Population
After Europeans and mainland Americans first arrived during the
Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawai╩╗i ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawai╩╗i Pae ╩╗─Ćina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island ...
period, the overall population of HawaiiŌĆöwhich until that time composed solely of Indigenous HawaiiansŌĆöfell dramatically. Many people of the Indigenous Hawaiian population died to foreign diseases, declining from 300,000 in the 1770s, to 60,000 in the 1850s, to 24,000 in 1920. Other estimates for the pre-contact population range from 150,000 to 1.5 million.
In 1923, 42% of the population was of Japanese descent, 9% was of Chinese descent, and 16% was native descent. The population of Hawaii began to finally increase after an influx of primarily Asian settlers that arrived as migrant laborers at the end of the 19thcentury.
The unmixed indigenous Hawaiian population has still not restored itself to its 300,000 pre-contact level. , only 156,000 persons declared themselves to be of Native Hawaiian-only ancestry, just over half the pre-contact level Native Hawaiian population, although an additional 371,000 persons declared themselves to possess Native Hawaiian ancestry in combination with one or more other races (including other Polynesian groups, but mostly Asian and/or Caucasian).
, the
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
estimates the population of Hawaii at 1,420,491, a decrease of 7,047 from the previous year and an increase of 60,190 (4.42%) since 2010. This includes a natural increase of 48,111 (96,028 births minus 47,917 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 16,956 people into the state. Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 30,068; migration within the country produced a net loss of 13,112 people.
The center of population of Hawaii is located on the island of
O'ahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''O╩╗ahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million peopleŌĆöover two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of OŌĆÖ ...
. Large numbers of Native Hawaiians have moved to
Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
, which has been called the "ninth island" of Hawaii.
Hawaii has a ''de facto'' population of over 1.4million, due in part to a large number of military personnel and tourist residents.
O'ahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''O╩╗ahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million peopleŌĆöover two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of OŌĆÖ ...
is the most populous island; it has the highest population density with a resident population of just under one million in , approximately 1,650 people per square mile. Hawaii's 1.4million residents, spread across of land, result in an average population density of 188.6 persons per square mile. The state has a lower population density than
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
and
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
.
The average projected lifespan of people born in Hawaii in 2000 is 79.8 years; 77.1 years if male, 82.5 if femaleŌĆölonger than the average lifespan of any other U.S. state. the U.S. military reported it had 42,371 personnel on the islands.
Ancestry

According to the 2020 United States Census, Hawaii had a population of 1,455,271. The state's population identified as 37.2%
Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
; 25.3%
Multiracial
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
; 22.9%
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
; 10.8%
Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, K─ünaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, k─ünaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawaii ...
and
other Pacific Islanders; 9.5%
Hispanic and Latinos of any race; 1.6%
Black or African American; 1.8% from some other race; and 0.3%
Native American and Alaskan Native.
Hawaii has the highest percentage of Asian Americans and multiracial Americans and the lowest percentage of White Americans of any state. It is the only state where people who identify as Asian Americans are the largest ethnic group. In 2012, 14.5% of the resident population under age 1 was non-Hispanic white. Hawaii's Asian population consists mainly of 198,000 (14.6%) Filipino Americans, 185,000 (13.6%) Japanese Americans, roughly 55,000 (4.0%) Chinese Americans, and 24,000 (1.8%)
Korean American
Korean Americans are Americans of Korean ancestry (mostly from South Korea). In 2015, the Korean-American community constituted about 0.56% of the United States population, or about 1.82 million people, and was the fifth-largest Asian Americans ...
s.
There are more than 80,000 Indigenous HawaiiansŌĆö5.9% of the population.
Including those with partial ancestry, Samoan Americans constitute 2.8% of Hawaii's population, and Tongan Americans constitute 0.6%.
Over 120,000 (8.8%) Hispanic and Latino Americans live in Hawaii. Mexican Americans number over 35,000 (2.6%); Puerto Ricans exceed 44,000 (3.2%). Multiracial Americans constitute almost 25% of Hawaii's population, exceeding 320,000 people. Hawaii is the only state to have a tri-racial group as its largest multiracial group, one that includes white, Asian and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander (22% of all mutiracial population). The non-Hispanic White population numbers around 310,000ŌĆöjust over 20% of the population. The multi-racial population outnumbers the non-Hispanic white population by about 10,000 people.
In 1970, the Census Bureau reported Hawaii's population was 38.8% white and 57.7% Asian and Pacific Islander.
The five largest European ancestries in Hawaii are German (7.4%), Irish (5.2%), English (4.6%), Portuguese (4.3%) and Italian (2.7%). About 82.2% of the state's residents were born in the United States. Roughly 75% of foreign-born residents originate in Asia. Hawaii is a
majority-minority state
A majority-minority or minority-majority area is a term used to refer to a subdivision in which one or more racial, ethnic, and/or religious minorities (relative to the whole country's population) make up a majority of the local population.
Ter ...
. It was expected to be one of three states that would not have a non-Hispanic white plurality in 2014; the other two are California and
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
.

The third group of foreigners to arrive in Hawaii were from China. Chinese workers on Western trading ships settled in Hawaii starting in 1789. In 1820, the first American missionaries arrived to preach Christianity and teach the Hawaiians Western ways.
, a large proportion of Hawaii's population have Asian ancestryŌĆöespecially Filipino, Japanese and Chinese. Many are descendants of immigrants brought to work on the sugarcane plantations in the mid-to-late 19th century. The first 153 Japanese immigrants arrived in Hawaii on June 19, 1868. They were not approved by the then-current Japanese government because the contract was between a broker and the
Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese ÕŠ│ÕĘØÕ╣ĢÕ║£ ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr├®d├®ric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
ŌĆöby then replaced by the
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
. The first Japanese current-government-approved immigrants arrived on February 9, 1885, after Kal─ükaua's petition to
Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
when Kal─ükaua visited Japan in 1881.
Almost 13,000 Portuguese migrants had arrived by 1899; they also worked on the sugarcane plantations.
[ See pp. 332ŌĆō33.] By 1901, more than 5,000 Puerto Ricans were living in Hawaii.
Languages

English and
Hawaiian are listed as Hawaii's official languages in the state's 1978 constitution, in Article XV, Section 4. However, the use of Hawaiian is limited because the constitution specifies that "Hawaiian shall be required for public acts and transactions only as provided by law".
Hawai╩╗i Creole English, locally referred to as "Pidgin", is the native language of many native residents and is a second language for many others.
As of the 2000 Census, 73.4% of Hawaii residents age5 and older exclusively speak English at home.
According to the 2008 American Community Survey, 74.6% of Hawaii's residents older than5 speak only English at home.
In their homes, 21.0% of state residents speak an additional
Asian language, 2.6% speak Spanish, 1.6% speak other
Indo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
s and 0.2% speak another language.
After English, other languages popularly spoken in the state are
Tagalog, Japanese and
Ilocano. Significant numbers of European immigrants and their descendants also speak their native languages; the most numerous are German, Portuguese, Italian and French. 5.4% of residents speak Tagalog, which includes non-native speakers of
Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
, a Tagalog-based national and co-official language of the Philippines; 5.0% speak Japanese and 4.0% speak Ilocano; 1.2% speak Chinese, 1.7% speak Hawaiian; 1.7% speak Spanish; 1.6% speak
Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chos┼Ån'g┼Łl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
; and 1.0% speak
Samoan.
Hawaiian
The Hawaiian language has about 2,000 native speakers, about 0.15% of the total population.
According to the
United States Census, there were more than 24,000 total speakers of the language in Hawaii in 2006ŌĆō2008.
Hawaiian is a Polynesian member of the
Austronesian language family.
It is closely related to other
Polynesian languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austron ...
, such as
Marquesan
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
,
Tahitian,
M─üori
M─üori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the M─üori people
* M─üori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* M─üori language, the language of the M─üori people of New Zealand
* M─üori culture
* Cook Islanders, the M─üori people of the C ...
,
Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
(the language of
Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
), and less closely to
Samoan and
Tongan.
According to Sch├╝tz, the Marquesans colonized the archipelago in roughly 300 CE and were later followed by waves of seafarers from the
Society Islands
The Society Islands (french: ├Äles de la Soci├®t├®, officially ''Archipel de la Soci├®t├®;'' ty, T┼Źtaiete m─ü) are an archipelago located in the South Pacific Ocean. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the F ...
,
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, S─ümoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono an ...
and
Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Pule╩╗anga Fakatu╩╗i ╩╗o Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands ŌĆō of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
. These Polynesians remained in the islands; they eventually became the Hawaiian people and
their languages evolved into the Hawaiian language. Kimura and Wilson say, "
nguists agree that Hawaiian is closely related to Eastern Polynesian, with a particularly strong link in the Southern Marquesas, and a secondary link in Tahiti, which may be explained by voyaging between the Hawaiian and Society Islands".
Before the arrival of Captain James Cook, the Hawaiian language had no written form. That form was developed mainly by American Protestant missionaries between 1820 and 1826 who assigned to the Hawaiian phonemes letters from the Latin alphabet. Interest in Hawaiian increased significantly in the late 20th century. With the help of the Office of Hawaiian Affairs, specially designated immersion schools in which all subjects would be taught in Hawaiian were established. The
University of Hawaii
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
developed a Hawaiian language graduate studies program. Municipal codes were altered to favor Hawaiian place and street names for new civic developments.
Hawaiian distinguishes between
long and short vowel sounds. In modern practice, vowel length is indicated with a
macron (''
kahak┼Ź
A macron () is a diacritical mark: it is a straight bar placed above a letter, usually a vowel. Its name derives from Ancient Greek (''makr├│n'') "long", since it was originally used to mark long or heavy syllables in Greco-Roman metrics. ...
''). Hawaiian-language newspapers (''n┼½pepa'') published from 1834 to 1948 and traditional native speakers of Hawaiian generally omit the marks in their own writing. The ╩╗okina and kahak┼Ź are intended to capture the proper pronunciation of Hawaiian words. The Hawaiian language uses the
glottal stop
The glottal plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents thi ...
(''
╩╗Okina'') as a consonant. It is written as a symbol similar to the apostrophe or left-hanging (opening) single quotation mark.
The keyboard layout used for Hawaiian is
QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created f ...
.
Hawaiian Pidgin

Some residents of Hawaii speak
Hawai╩╗i Creole English (HCE), endonymically called ''pidgin'' or ''pidgin English''. The lexicon of HCE derives mainly from English but also uses words that have derived from Hawaiian, Chinese, Japanese, Portuguese, Ilocano and Tagalog. During the 19th century, the increase in immigrationŌĆömainly from China, Japan, PortugalŌĆöespecially from the
Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
and
Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
, and SpainŌĆöcatalyzed the development of a hybrid variant of English known to its speakers as ''pidgin''. By the early 20th century, pidgin speakers had children who acquired it as their first language. HCE speakers use some Hawaiian words without those words being considered archaic. Most place names are retained from Hawaiian, as are some names for plants and animals. For example, tuna fish is often called by its Hawaiian name, ''ahi''.
HCE speakers have modified the meanings of some English words. For example, "aunty" and "uncle" may either refer to any adult who is a friend or be used to show respect to an elder.
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
and
grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraint ...
follow distinctive rules different from those of General American English. For example, instead of "it is hot today, isn't it?", an HCE speaker would say simply "stay hot, eh?" The term ''
da kine
Da kine () is an expression in Hawaiian Pidgin (Hawaii Creole English), probably derived from "that kind", that usually functions grammatically as a placeholder name (compare to English "whatsit" and "whatchamacallit"). It can also take the role ...
'' is used as a
filler; a substitute for virtually any word or phrase. During the
surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitabl ...
boom in Hawaii, HCE was influenced by surfer slang. Some HCE expressions, such as ''brah'' and ''da kine'', have found their ways elsewhere through surfing communities.
Hawai╩╗i Sign Language
Hawai╩╗i Sign Language
Hawai╩╗i Sign Language (HSL; Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Hoailona ╩╗┼īlelo o Hawai╩╗i''), also known as Hoailona ╩╗┼īlelo and Old Hawai╩╗i Sign Language, is an indigenous sign language native to Hawaii, Hawai╩╗i. Historical records document i ...
, a
sign language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign l ...
for the Deaf based on the Hawaiian language, has been in use in the islands since the early 1800s. It is dwindling in numbers due to
American Sign Language
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canadians, Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual lang ...
supplanting HSL through schooling and various other domains.
Religion
Hawaii is among the most religiously diverse states in the U.S., with one in ten residents practicing a non-Christian faith. Native Hawaiians continue to engage in traditional religious and spiritual practices today, often adhering to Christian and traditional beliefs at the same time.
Christianity remains the majority religion, mainly represented by various
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
groups and
Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The second largest religion is
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, which is concentrated in the Japanese community, and comprises a larger proportion of the population than any other state. The unaffiliated and nonreligious account for roughly half the population, making Hawaii one of the most secular states.
The
Cathedral Church of Saint Andrew in Honolulu was formally the seat of the
Hawaiian Reformed Catholic Church, a province of the
Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
that had been the state church of the Kingdom of Hawaii; it subsequently merged into the
Episcopal Church in the 1890s following the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii, becoming the seat of the
Episcopal Diocese of Hawaii
The Episcopal Diocese of Hawai'i is the ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Episcopal Church of the Anglican Communion in the United States encompassing the state of Hawaii. It is led by the Episcopal Bishop of Hawaii pastoring the Hawaii ...
. The
Cathedral Basilica of Our Lady of Peace
The Cathedral Basilica of Our Lady of Peace (French: ''Cath├®drale de Notre Dame de la Paix''; Portuguese: ''Catedral de Nossa Senhora da Paz''; Hawaiian: ''Malia o ka Malu Hale Pule Nui''; Latin: ''Basilic├” cathedralis Sanct├” Mari├” de Pa ...
and the
Co-Cathedral of Saint Theresa of the Child Jesus
The Co-Cathedral of Saint Theresa of the Child Jesus is a co-cathedral of the Roman Catholic Church and its Diocese of Honolulu. Located in the outskirts of downtown Honolulu, Hawaii. The principal cathedral of the diocese remains the Cathedral ...
serve as seats of the
Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu
The Catholic Diocese of Honolulu ( la, Di┼ōcesis Honoluluensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church that comprises the entire U.S. state, state of Hawaii, Hawaii and the unincorporated Hawaiian Islands.
T ...
. The Eastern Orthodox community is centered around the
Saints Constantine and Helen Greek Orthodox Cathedral of the Pacific.
The largest denominations by membership were the Roman Catholic Church with 249,619 adherents in 2010;
the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
with 68,128 adherents in 2009; the
United Church of Christ
The United Church of Christ (UCC) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination based in the United States, with historical and confessional roots in the Congregational, Calvinist, Lutheran, and Anabaptist traditions, and with approximately 4 ...
with 115 congregations and 20,000 members; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 108 congregations and 18,000 members. All non-denominational churches have 128 congregations and 32,000 members.
According to data provided by religious establishments, religion in Hawaii in 2000 was distributed as follows:
* Christianity: 351,000 (29%)
* Buddhism: 110,000 (9%)
* Judaism: 10,000 (1%)
* Other: 100,000 (10%)
* Unaffiliated: 650,000 (51%)
A
Pew
A pew () is a long bench (furniture), bench seat or enclosed box, used for seating Member (local church), members of a Church (congregation), congregation or choir in a Church (building), church, synagogue or sometimes a courtroom.
Overview
...
poll found that the religious composition was as follows:
Birth data
''Note: Births in this table do not add up, because Hispanic peoples are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
:1) Until 2016, data for births of Asian origin, included also births of the Pacific Islander group.
:2) Since 2016, data for births of
White Hispanic
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
LGBTQIA+
Hawaii has had a long history of
LGBTQIA+
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term is an ...
identities. ''
Māhū
' ('in the middle') in Native Hawaiian and Tahitian cultures are third gender people with traditional spiritual and social roles within the culture, similar to Tongan ' and Samoan '. Historically māhū were assigned male at birth (AMAB), but in ...
'' ("in the middle") were a precolonial
third gender
Third gender is a concept in which individuals are categorized, either by themselves or by society, as neither man nor woman. It is also a social category present in societies that recognize three or more genders. The term ''third'' is usually ...
with traditional spiritual and social roles, widely respected as healers. Homosexual relationships known as ''
aik─üne'' were widespread and normal in ancient Hawaiian society.
Among men, ''aik─üne'' relationships often began as teens and continued throughout their adult lives, even if they also maintained heterosexual partners.
While ''aik─üne'' usually refers to male homosexuality, some stories also refer to women, implying that women may have been involved in ''aik─üne'' relationships as well.
Journals written by
Captain Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October ŌĆō 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
's crew record that many ''
ali╩╗i
The ali╩╗i were the traditional nobility of the Hawaiian islands. They were part of a hereditary line of rulers, the ''noho ali╩╗i''.
The word ''ali╩╗i'' has a similar meaning in the Samoan language and other Polynesian languages, and in M─üori ...
'' (hereditary nobles) also engaged in ''aik─üne'' relationships, and
Kamehameha the Great
Kamehameha I (; Kalani Paiea Wohi o Kaleikini Kealiikui Kamehameha o Iolani i Kaiwikapu kaui Ka Liholiho K┼½nui─ükea; ŌĆō May 8 or 14, 1819), also known as Kamehameha the Great, was the conqueror and first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii. T ...
, the founder and first ruler of the
Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawai╩╗i ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawai╩╗i Pae ╩╗─Ćina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island ...
, was also known to participate. Cook's second lieutenant and co-astronomer
James King observed that "all the chiefs had them", and recounts that Cook was actually asked by one chief to leave King behind, considering the role a great honor.
Hawaiian scholar
Lilikal─ü Kame╩╗eleihiwa
Lilikalā K. Kameʻeleihiwa is a Hawaiian historian, filmmaker, and senior professor at the University of Hawaii's Kamakakūokalani Center for Hawaiian Studies. Her earliest work was published under the name of Lilikalā L. Dorton.
With a PhD. ...
notes that ''aik─üne'' served a practical purpose of building mutual trust and cohesion; "If you didn't sleep with a man, how could you trust him when you went into battle? How would you know if he was going to be the warrior that would protect you at all costs, if he wasn't your lover?"
As Western colonial influences intensified in the late 19th and early 20th century, the word ''aik─üne'' was
expurgated of its original sexual meaning, and in print simply meant "friend". Nonetheless, in Hawaiian language publications its metaphorical meaning can still mean either "friend" or "lover" without stigmatization.
A 2012 Gallup poll found that Hawaii had the largest proportion of LGBTQIA+ adults in the U.S., at 5.1%, an estimated 53,966 individuals. The number of same-sex couple households in 2010 was 3,239, representing a 35.5% increase from a decade earlier. In 2013, Hawaii became the fifteenth U.S. state to legalize same-sex marriage; this reportedly boosted tourism by $217million.
Economy

The history of Hawaii's economy can be traced through a succession of dominant industries:
sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for us ...
,
whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industry ...
, sugarcane,
pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, the military, tourism and education. By the 1840s, sugar plantations had gained a strong foothold in the Hawaiian economy, due to a high demand of sugar in the United States and rapid transport via steamships.
Sugarcane plantations were tightly controlled by American missionary families and businessmen known as "
the Big Five", who monopolized control of the sugar industry's profits.
By the time Hawaiian annexation was being considered in 1898, sugarcane producers turned to cultivating tropical fruits like pineapple, which became the principal export for Hawai╩╗i's plantation economy.
Since statehood in 1959, tourism has been the largest industry, contributing 24.3% of the gross state product (GSP) in 1997, despite efforts to diversify. The state's gross output for 2003 was billion; per capita income for Hawaii residents in 2014 was . Hawaiian exports include food and clothing. These industries play a small role in the Hawaiian economy, due to the shipping distance to viable markets, such as the
West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
. The state's food exports include coffee, macadamia nuts, pineapple, livestock, sugarcane and honey.
By weight, honey bees may be the state's most valuable export. According to the Hawaii Agricultural Statistics Service, agricultural sales were million from diversified agriculture, million from pineapple, and million from sugarcane. Hawaii's relatively consistent climate has attracted the seed industry, which is able to test three generations of crops per year on the islands, compared with one or two on the mainland. Seeds yielded million in 2012, supporting 1,400 workers.
, the state's unemployment rate was 3.2%. In 2009, the United States military spent billion in Hawaii, accounting for 18% of spending in the state for that year. 75,000 United States Department of Defense personnel live in Hawaii. According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, Hawaii had the fourth-largest number of millionaires per capita in the United States, with a ratio of 7.2%.
Taxation
Tax is collected by the Hawaii Department of Taxation. Most government revenue comes from
personal income taxes and a
general excise tax (GET) levied primarily on businesses; there is no statewide tax on sales, personal property, or stock transfers, while the effective property tax rate is among the lowest in the country. The high rate of tourism means that millions of visitors generate public revenue through GET and the hotel room tax.
However, Hawaii residents generally pay among the most state taxes per person in the U.S.
The Tax Foundation of Hawaii considers the state's tax burden too high, claiming that it contributes to higher prices and the perception of an unfriendly business climate.
The nonprofit Tax Foundation ranks Hawaii third in income tax burden and second in its overall tax burden, though notes that a significant portion of taxes are borne by tourists. Former Hawaii Senate, State Senator Sam Slom attributed Hawaii's comparatively high tax rate to the fact that the state government is responsible for education, health care, and social services that are usually handled at a county or municipal level in most other states.
Cost of living
The cost of living in Hawaii, specifically Honolulu, is high compared to that of most major U.S. cities, although it is 6.7% lower than in New York City and 3.6% lower than in San Francisco. These numbers may not take into account some costs, such as increased travel costs for flights, additional shipping fees, and the loss of promotional participation opportunities for customers outside the contiguous U.S. While some online stores offer free shipping on orders to Hawaii, many merchants exclude Hawaii, Alaska, Puerto Rico and certain other U.S. territories.
Hawaiian Electric Industries, a privately owned company, provides 95% of the state's population with electricity, mostly from fossil-fuel power stations. Average electricity prices in October 2014 () were nearly three times the national average () and 80% higher than the second-highest state, Connecticut.
The median home value in Hawaii in the 2000 U.S. Census was , while the national median home value was . Hawaii home values were the highest of all states, including California with a median home value of . Research from the National Association of Realtors places the 2010 median sale price of a single family home in Honolulu, Hawaii, at and the U.S. median sales price at . The sale price of single family homes in Hawaii was the highest of any U.S. city in 2010, just above that of the Silicon Valley area of California ().
Hawaii's very high cost of living is the result of several interwoven factors of the global economy in addition to domestic U.S. government trade policy. Like other regions with desirable weather year-round, such as California, Arizona and Florida, Hawaii's residents can be considered to be subject to a "sunshine tax". This situation is further exacerbated by the natural factors of geography and world distribution that lead to higher prices for goods due to increased shipping costs, a problem which many island country, island states and territories suffer from as well.
The higher costs to ship goods across an ocean may be further increased by the requirements of the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, Jones Act, which generally requires that goods be transported between places within the U.S., including between the mainland U.S. west coast and Hawaii, using only U.S.-owned, built, and crewed ships. Jones Act-compliant vessels are often more expensive to build and operate than foreign equivalents, which can drive up shipping costs. While the Jones Act does not affect transportation of goods to Hawaii directly from Asia, this type of trade is nonetheless not common; this is a result of other primarily economic reasons including additional costs associated with stopping over in Hawaii (e.g. pilot and port fees), the market size of Hawaii, and the economics of using ever-larger ships that cannot be handled in Hawaii for transoceanic voyages. Therefore, Hawaii relies on receiving most inbound goods on Jones Act-qualified vessels originating from the U.S. west coast, which may contribute to the increased cost of some consumer goods and therefore the overall cost of living.
Critics of the Jones Act contend that Hawaii consumers ultimately bear the expense of transporting goods imposed by the Jones Act.
Culture
The aboriginal culture of Hawaii is Polynesian. Hawaii represents the northernmost extension of the vast Polynesian Triangle of the south and central Pacific Ocean. While traditional Hawaiian culture remains as vestiges in modern Hawaiian society, there are re-enactments of the ceremonies and traditions throughout the islands. Some of these cultural influences, including the popularity (in greatly modified form) of ''luau, lūau'' and ''
hula
Hula () is a Hawaiian dance form accompanied by chant (oli) or song (Mele (Hawaiian language), mele). It was developed in the Hawaiian Islands by the Native Hawaiians who originally settled there. The hula dramatizes or portrays the words of t ...
'', are strong enough to affect the wider United States.
Cuisine
The cuisine of Hawaii is a fusion of many foods brought by immigrants to the Hawaiian Islands, including the earliest Polynesians and Native Hawaiian cuisine, and Cuisine of the United States, American, Chinese cuisine, Chinese, Philippine cuisine, Filipino, Japanese cuisine, Japanese, Korean cuisine, Korean, Polynesian cuisine, Polynesian, Puerto Rican cuisine, Puerto Rican, and Portuguese cuisine, Portuguese origins. Plant and animal food sources are imported from around the world for agricultural use in Hawaii. ''Poi (food), Poi'', a starch made by pounding taro, is one of the traditional foods of the islands. Many local restaurants serve the ubiquitous plate lunch, which features two scoops of rice, a simplified version of American macaroni salad and a variety of toppings including hamburger patties, a fried egg, and gravy of a ''loco moco'', Japanese style ''tonkatsu'' or the traditional lūau favorites, including ''kalua, kālua'' pork and ''laulau''. ''Spam musubi'' is an example of the fusion of ethnic cuisine that developed on the islands among the mix of immigrant groups and military personnel. In the 1990s, a group of chefs developed Hawaii regional cuisine as a contemporary fusion cuisine.
Customs and etiquette
Some key customs and etiquette in Hawaii are as follows: when visiting a home, it is considered good manners to bring a small gift for one's host (for example, a dessert). Thus, parties are usually in the form of potlucks. Most locals take their shoes off before entering a home. It is customary for Hawaiian families, regardless of ethnicity, to hold a luau to celebrate a child's first birthday. It is also customary at Hawaiian weddings, especially at Filipino weddings, for the bride and groom to do a money dance (also called the pandanggo). Print media and local residents recommend that one refer to non-Hawaiians as "locals of Hawaii" or "people of Hawaii".
Hawaiian mythology

Hawaiian mythology includes the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient Hawaiian people. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian mythology that developed a unique character for several centuries before ''circa'' 1800. It is associated with the Hawaiian religion, which was officially suppressed in the 19th century but was kept alive by some practitioners to the modern day. Prominent figures and terms include Aumakua, the spirit of an ancestor or family god and K─üne, the highest of the four major Hawaiian deities.
Polynesian mythology

Polynesian mythology is the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia, a grouping of Central and South Pacific Ocean island
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
s in the Polynesian triangle together with the scattered cultures known as the Polynesian outliers. Polynesians speak languages that descend from a language reconstructed as
Proto-Polynesian
Proto-Polynesian (abbreviated PPn) is the hypothetical proto-language from which all the modern Polynesian languages descend. It is a daughter language of the Proto-Austronesian language. Historical linguists have reconstructed the language using ...
that was probably spoken in the area around
Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Pule╩╗anga Fakatu╩╗i ╩╗o Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands ŌĆō of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
and
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, S─ümoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono an ...
in around 1000 BC.
Prior to the 15th century, Polynesian culture, Polynesian people migrated east to the Cook Islands, and from there to other island groups such as Tahiti and the Marquesas. Their descendants later discovered the islands
Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austr ...
, Rapa Nui, and later the Hawaiian Islands and New Zealand.
The Polynesian languages are part of the Austronesian language family. Many are close enough in terms of vocabulary and grammar to be mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. There are also substantial cultural similarities between the various groups, especially in terms of social organization, childrearing, horticulture, building and textile technologies. Their mythologies in particular demonstrate local reworkings of commonly shared tales. The Polynesian cultures each have distinct but related oral traditions; legends or myths are traditionally considered to recount ancient history (the time of "p┼Ź") and the adventures of gods ("atua") and deified ancestors.
List of state parks
There are list of Hawaiian state parks, many Hawaiian state parks.
* The Hawaii (island), Island of Hawaii has state parks, recreation areas, and historical parks.
*
Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Ni╩╗ihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island ...
has the Ahukini State Recreation Pier, six state parks, and the Russian Fort Elizabeth State Historical Park.
*
Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which ...
has two state monuments, several state parks, and the Polipoli Spring State Recreation Area. Moloka'i has the Pala'au State Park.
*
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''O╩╗ahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of O╩╗ahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million peopleŌĆöover t ...
has several state parks, a number of state recreation areas, and a number of monuments, including the Ulu P┼Ź Heiau State Monument.
Literature
The literature of Hawaii is diverse and includes authors Kiana Davenport, Lois-Ann Yamanaka, and Kaui Hart Hemmings. Hawaiian magazines include ''Hana Hou!'', ''Hawaii Business'' and ''Honolulu (magazine), Honolulu'', among others.
Music


The music of Hawaii includes traditional and popular styles, ranging from native Hawaiian folk music to modern rock and hip hop music, hip hop. Hawaii's musical contributions to the music of the United States are out of proportion to the state's small size.
Styles such as slack-key guitar are well known worldwide, while Hawaiian-tinged music is a frequent part of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood soundtracks. Hawaii also made a major contribution to country music with the introduction of the steel guitar.
Traditional Hawaiian folk music is a major part of the state's musical heritage. The Hawaiian people have inhabited the islands for centuries and have retained much of their traditional musical knowledge. Their music is largely religious in nature, and includes chanting and dance music.
Hawaiian music has had an enormous impact on the Polynesian music, music of other Polynesian islands; according to Peter Manuel, the influence of Hawaiian music is a "unifying factor in the development of modern Pacific musics".
Native Hawaiian musician and Hawaiian sovereignty activist Israel Kamakawiwo╩╗ole, famous for his medley of "Somewhere Over the Rainbow/What a Wonderful World", was named "The Voice of Hawaii" by NPR in 2010 in its 50 great voices series.
Sports
Due to its distance from the continental United States, team sports in Hawaii are characterised by youth, collegial and amateur teams over professional teams, although some professional teams sports teams have at one time played in the state. Notable professional teams include The Hawaiians (WFL), The Hawaiians, which played at the World Football League in 1974 and 1975; the Hawaii Islanders, a Triple-A minor league baseball team that played at the Pacific Coast League from 1961 to 1987; and Team Hawaii, a North American Soccer League (1968ŌĆō84), North American Soccer League team that played in 1977.
Notable college sports events in Hawaii include the Maui Invitational Tournament, Diamond Head Classic (basketball) and Hawaii Bowl (football). The only NCAA Division I team in Hawaii is the Hawaii Rainbow Warriors and Rainbow Wahine, which competes at the Big West Conference (major sports), Mountain West Conference (football) and Mountain Pacific Sports Federation (minor sports). There are three teams in NCAA Division II: Chaminade Silverswords, Hawaii Pacific Sharks and Hawaii-Hilo Vulcans, all of which compete at the Pacific West Conference.
Surfing has been a central part of Polynesian culture for centuries. Since the late 19th century, Hawaii has become a major site for surfists from around the world. Notable competitions include the Triple Crown of Surfing and The Eddie. Likewise, Hawaii has produced elite-level swimmers, including five-time Olympic medalist Duke Kahanamoku and Buster Crabbe, who set 16 swimming
world records.
Hawaii has hosted the Sony Open in Hawaii golf tournament since 1965, the Tournament of Champions (golf), Tournament of Champions golf tournament since 1999, the Lotte Championship golf tournament since 2012, the Honolulu Marathon since 1973, the Ironman World Championship triathlon race since 1978, the Ultraman (endurance challenge), Ultraman triathlon since 1983, the National Football League's Pro Bowl from 1980 to 2016, the 2000 FINA World Open Water Swimming Championships, and the 2008 Pan-Pacific Championship and 2012 Hawaiian Islands Invitational soccer tournaments.
Hawaii has produced a number of notable Mixed Martial Arts fighters, such as former UFC Lightweight Champion and UFC Welterweight Champion B.J. Penn, and former UFC Featherweight Champion Max Holloway. Other notable Hawaiian Martial Artists include Travis Browne, K. J. Noons, Brad Tavares and Wesley Correira.
Hawaiians have found success in the world of sumo wrestling. Takamiyama Daigor┼Ź was the first foreigner to ever win a sumo title in Japan, while his protege Akebono Tar┼Ź became a top-level sumo wrestler in Japan during the 1990s before transitioning into a successful professional wrestling career in the 2000s. Akebono was the first foreign-born Sumo to reach Yokozuna in history and helped fuel a boom in interest in Sumo during his career.
Tourism

Tourism is an important part of the Hawaiian economy as it represents ┬╝ of the economy. According to the Hawaii Tourism: 2019 Annual Visitor Research Report, a total of 10,386,673 visitors arrived in 2019 which increased 5% from the previous year, with expenditures of almost $18 billion. In 2019, tourism provided over 216,000 jobs statewide and contributed more than $2 billion in tax revenue. Due to mild year-round weather, tourist travel is popular throughout the year. Tourists across the globe visited Hawaii in 2019 with over 1 million tourists from the U.S. East, almost 2 million Japanese tourists, and almost 500,000 Canadian tourists.
It was with statehood in 1959 that the Hawaii tourism industry began to grow.
According to Hawaiian scholar
Haunani-Kay Trask
Haunani-Kay Trask (October 3, 1949 ŌĆō July 3, 2021) was a Native Hawaiian activist, educator, author, and poet. She served as leader of the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and was professor emeritus at the University of Hawai╩╗i at M─ünoa. She w ...
, tourism in Hawaii has led to the commodification and exploitation of Hawaiian culture resulting in insidious forms of "cultural prostitution". Hawaii has been used to fuel ideas of escapism yet tourism in Hawaii ignores the harm Kanaka and locals experience.
Cultural traditions such as the hula have been made "ornamental ... a form of exotica" for tourists as a way for large corporations and land owners to gain profit over the exploitation of Hawaiian people and culture.
[
Tourism in Hawaii has been considered as an escape from reality resulting in the dismissal of violence faced by Native Hawaiians and locals living on the land. According to scholar ]Winona LaDuke
Winona LaDuke (born August 18, 1959) is an American economist, environmentalist, writer and industrial hemp grower, known for her work on tribal land claims and preservation, as well as sustainable development.
In 1996 and 2000, she ran for Vice ...
, native Hawaiians have been forced to gather "shrimp and fish from ponds sitting on resort property". Tourism has also had damaging effects on the environment such as water shortages, overcrowding, sea level rising, elevated sea surface temperatures and micro plastics on beaches.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, tourism in Hawaii came to a halt, which the land, water, and animals began to heal. Fish like the baby akule and big ulua have returned after years of not being around the bay. The coral reefs, fish, water growth, and Limu (algae), limu (algae) growth was able to flourish without the heavy toll of tourism.
There has been pushback against tourism by Native Hawaiians, urging people to not visit the islands. A survey by the Hawaii Tourism Authority indicated over Ōģö of Hawaiians did not want tourists to return to Hawaii. Tourism had "become extractive and hurtful, with tourists coming here and taking, taking, taking, taking, without any reciprocation with locals".
Hawaii hosts numerous cultural events. The annual Merrie Monarch Festival is an international Hula competition. The Hawaii International Film Festival is the premier film festival for Pacific rim cinema.
Health
, Hawaii's health care system insures 92% of residents. Under the state's plan, businesses are required to provide insurance to employees who work more than twenty hours per week. Heavy regulation of insurance companies helps reduce the cost to employers. Due in part to heavy emphasis on preventive care, Hawaiians require hospital treatment less frequently than the rest of the United States, while total health care expenses measured as a percentage of state GDP are substantially lower. Proponents of universal health care elsewhere in the U.S. sometimes use Hawaii as a model for proposed federal and state health care plans.
Education
Public schools
 Hawaii has the only school system within the U.S. that is unified statewide. Policy decisions are made by the fourteen-member state Hawaii Board of Education, Board of Education, which sets policy and hires the superintendent of schools, who oversees the Hawaii Department of Education. The Department of Education is divided into seven districts; four on Oahu and one for each of the other three counties.
Public elementary, middle and high school test scores in Hawaii are below national averages on tests mandated under the No Child Left Behind Act. The Hawaii Board of Education requires all eligible students to take these tests and report all student test scores. This may have unbalanced the results that reported in August 2005 that of 282 schools across the state, 185 failed to reach federal minimum performance standards in mathematics and reading. The ACT (examination), ACT college placement tests show that in 2005, seniors scored slightly above the national average (21.9 compared with 20.9), but in the widely accepted SAT examinations, Hawaii's college-bound seniors tend to score below the national average in all categories except mathematics.
The first native controlled public charter school was the Kanu O Ka Aina New Century Charter School.
Hawaii has the only school system within the U.S. that is unified statewide. Policy decisions are made by the fourteen-member state Hawaii Board of Education, Board of Education, which sets policy and hires the superintendent of schools, who oversees the Hawaii Department of Education. The Department of Education is divided into seven districts; four on Oahu and one for each of the other three counties.
Public elementary, middle and high school test scores in Hawaii are below national averages on tests mandated under the No Child Left Behind Act. The Hawaii Board of Education requires all eligible students to take these tests and report all student test scores. This may have unbalanced the results that reported in August 2005 that of 282 schools across the state, 185 failed to reach federal minimum performance standards in mathematics and reading. The ACT (examination), ACT college placement tests show that in 2005, seniors scored slightly above the national average (21.9 compared with 20.9), but in the widely accepted SAT examinations, Hawaii's college-bound seniors tend to score below the national average in all categories except mathematics.
The first native controlled public charter school was the Kanu O Ka Aina New Century Charter School.
Private schools
Hawaii has the highest rates of private school attendance in the nation. During the 2011ŌĆō2012 school year, Hawaii public and charter schools had an enrollment of 181,213,
Colleges and universities
 The largest institution of higher learning in Hawaii is the University of Hawaii System, which consists of the research university at University of Hawaii at Manoa, M─ünoa, two comprehensive campuses at University of Hawaii at Hilo, Hilo and University of Hawaii-West Oahu, West Oahu, and seven community colleges. Private universities include Brigham Young UniversityŌĆōHawaii, Chaminade University of Honolulu, Hawaii Pacific University, and Wayland Baptist University. Saint Stephen Diocesan Seminary, Honolulu, Saint Stephen Diocesan Center is a seminary of the
The largest institution of higher learning in Hawaii is the University of Hawaii System, which consists of the research university at University of Hawaii at Manoa, M─ünoa, two comprehensive campuses at University of Hawaii at Hilo, Hilo and University of Hawaii-West Oahu, West Oahu, and seven community colleges. Private universities include Brigham Young UniversityŌĆōHawaii, Chaminade University of Honolulu, Hawaii Pacific University, and Wayland Baptist University. Saint Stephen Diocesan Seminary, Honolulu, Saint Stephen Diocesan Center is a seminary of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu
The Catholic Diocese of Honolulu ( la, Di┼ōcesis Honoluluensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church that comprises the entire U.S. state, state of Hawaii, Hawaii and the unincorporated Hawaiian Islands.
T ...
. Kona hosts the University of the Nations, which is not an educational accreditation, accredited university.
Transportation
 A List of Hawaii state highways, system of state highways encircles each main island. Only Oahu has federal highways, and is the only area outside the contiguous 48 states to have signed Interstate Highway System, Interstate highways. Narrow, winding roads and congestion in populated places can slow traffic. Each major island has a public bus system.
Honolulu International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA:HNL), which shares runways with the adjacent Hickam Field (IATA:HIK), is the major commercial aviation hub of Hawaii. The commercial aviation airport offers intercontinental service to North America, Asia, Australia and Oceania. Hawaiian Airlines and Mokulele Airlines use jets to provide services between the large airports in Honolulu, L─½hue, Kahului, Kona and Hilo. These airlines also provide air freight services between the islands. On May 30, 2017, the airport was officially renamed as the Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (HNL), after U.S. Senator Daniel Inouye, Daniel K. Inouye.
Until air passenger services began in the 1920s,
A List of Hawaii state highways, system of state highways encircles each main island. Only Oahu has federal highways, and is the only area outside the contiguous 48 states to have signed Interstate Highway System, Interstate highways. Narrow, winding roads and congestion in populated places can slow traffic. Each major island has a public bus system.
Honolulu International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA:HNL), which shares runways with the adjacent Hickam Field (IATA:HIK), is the major commercial aviation hub of Hawaii. The commercial aviation airport offers intercontinental service to North America, Asia, Australia and Oceania. Hawaiian Airlines and Mokulele Airlines use jets to provide services between the large airports in Honolulu, L─½hue, Kahului, Kona and Hilo. These airlines also provide air freight services between the islands. On May 30, 2017, the airport was officially renamed as the Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (HNL), after U.S. Senator Daniel Inouye, Daniel K. Inouye.
Until air passenger services began in the 1920s,
Rail
At one time Hawaii had a network of railroads on each of the larger islands that transported farm commodities and passengers. Most were narrow gauge systems but there were some gauge on some of the smaller islands. The standard gauge in the U.S. is . By far the largest railroad was the Oahu Railway and Land Company (OR&L) that ran lines from Honolulu across the western and northern part of Oahu.
Governance
Political subdivisions and local government
The movement of the Hawaiian royal family from Hawaii Island to Maui, and subsequently to Oahu, explains the modern-day distribution of population centers. Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 ŌĆō December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name is Keaweaweula K─½wala┼Ź Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula K─ ...
chose the largest city, Honolulu, as his capital because of its natural harborŌĆöthe present-day Honolulu Harbor. Now the state capital, Honolulu is located along the southeast coast of Oahu. The previous capital was Lahaina, Hawaii, Lahaina, Maui, and before that Kailua-Kona, Hawaii. Some major towns are Hilo, Hawaii, Hilo; Kaneohe, Hawaii, Kaneohe; Kailua, Honolulu County, Hawaii, Kailua; Pearl City, Hawaii, Pearl City; Waipahu, Hawaii, Waipahu; Kahului, Hawaii, Kahului; Kailua-Kona
Kailua-Kona is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Hawaii County, Hawaii, United States. It is also known as Kailua (a name it shares with a community located on the windward side of Oahu), as Kona (a name it shares ...
. Kihei, Hawaii, K─½hei; and Lihue, Hawaii, L─½hue.
Hawaii has five counties: the Honolulu County, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii County, Hawaii, Hawaii County, Maui County, Hawaii, Maui County, Kauai County, Hawaii, Kauai County, and Kalawao County, Hawaii, Kalawao County.
Hawaii has the fewest local governments among U.S. states.
State government
 The state government of Hawaii is modeled after the federal government with adaptations originating from the kingdom era of Hawaiian history. As codified in the Constitution of Hawaii, there are three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch is led by the Governor of Hawaii, who is assisted by the Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii, both of whom are elected on the same ticket. The governor is the only state public official elected statewide; all others are appointed by the governor. The lieutenant governor acts as the Secretary of State of Hawaii, Secretary of State. The governor and lieutenant governor oversee twenty agencies and departments from offices in the Hawaii State Capitol, State Capitol. The official residence of the governor is Washington Place.
The legislative branch consists of the Bicameralism, bicameral Hawaii State Legislature, which is composed of the 51-member Hawaii House of Representatives led by the Speaker (politics), Speaker of the House, and the 25-member Hawaii Senate led by the President of the Senate. The Legislature meets at the State Capitol. The unified judicial branch of Hawaii is the Hawaii State Judiciary. The State supreme court, state's highest court is the Supreme Court of Hawaii, which uses Aliiolani Hale, Alii┼Źlani Hale as its chambers.
The state government of Hawaii is modeled after the federal government with adaptations originating from the kingdom era of Hawaiian history. As codified in the Constitution of Hawaii, there are three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch is led by the Governor of Hawaii, who is assisted by the Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii, both of whom are elected on the same ticket. The governor is the only state public official elected statewide; all others are appointed by the governor. The lieutenant governor acts as the Secretary of State of Hawaii, Secretary of State. The governor and lieutenant governor oversee twenty agencies and departments from offices in the Hawaii State Capitol, State Capitol. The official residence of the governor is Washington Place.
The legislative branch consists of the Bicameralism, bicameral Hawaii State Legislature, which is composed of the 51-member Hawaii House of Representatives led by the Speaker (politics), Speaker of the House, and the 25-member Hawaii Senate led by the President of the Senate. The Legislature meets at the State Capitol. The unified judicial branch of Hawaii is the Hawaii State Judiciary. The State supreme court, state's highest court is the Supreme Court of Hawaii, which uses Aliiolani Hale, Alii┼Źlani Hale as its chambers.
Federal government
Brian Schatz, official portrait, 113th Congress 2.jpg, Senator Brian Schatz
Mazie Hirono, official portrait, 113th Congress.jpg, Senator Mazie Hirono
Ed Case, Official Portrait, 116th Congress 2.jpg, Representative Ed Case (Hawaii's 1st congressional district, )
Kai_Kahele_117th_U.S_Congress.jpg, Representative Kai Kahele (Hawaii's 2nd congressional district, HI-2)
Hawaii is represented in the United States Congress by two senators and two United States House of Representatives, representatives. , all four seats are held by Democrats. Former representative Ed Case was elected in 2018 to the Hawaii's 1st congressional district, 1st congressional district. Kai Kahele represents the Hawaii's 2nd congressional district, 2nd congressional district, representing the rest of the state, which is largely rural and semi-rural.
Brian Schatz is the senior United States senator from Hawaii. He was appointed to the office on December 26, 2012, by Governor Neil Abercrombie, following the death of former senator Daniel Inouye. The state's junior senator is Mazie Hirono, the former representative from the second congressional district. Hirono is the first female Asian American senator and the first Buddhist senator. Hawaii incurred the biggest Seniority in the United States Senate, seniority shift between the 112th United States Congress, 112th and 113th United States Congress, 113th Congresses. The state went from a delegation consisting of senators who were first and twenty-first in seniority to their respective replacements, relative newcomers Schatz and Hirono.
Federal officials in Hawaii are based at the Prince Kuhio Federal Building, Prince K┼½hi┼Ź Federal Building near the Aloha Tower and Honolulu Harbor. The Federal Bureau of Investigation, Internal Revenue Service and the United States Secret Service, Secret Service maintain their offices there; the building is also the site of the United States federal courts, federal United States District Court for the District of Hawaii, District Court for the District of Hawaii and the United States Attorney for the District of Hawaii.
Politics
 Since gaining statehood and participating in its first election in 1960 United States presidential election, 1960, Hawaii has supported Democrats in all but two presidential elections: 1972 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1972 and 1984 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1984, both of which were landslide reelection victories for Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan respectively. In Hawaii's statehood tenure, only Minnesota has supported Republican candidates fewer times in presidential elections. The 2016 Cook Partisan Voting Index ranks Hawaii as the most heavily Democratic state in the nation.
Hawaii has not elected a Republican to represent the state in the U.S. Senate since Hiram Fong in 1970; since 1977, both of the state's U.S. Senators have been Democrats.
In 2004 United States presidential election, 2004, John Kerry won the state's four electoral votes by a margin of nine percentage points with 54% of the vote. Every county supported the Democratic candidate. In 1964, favorite son candidate senator Hiram Fong of Hawaii sought the Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential nomination, while Patsy Mink ran in the Oregon primary in 1972.
Honolulu-born Barack Obama, then serving as a United States senator from
Since gaining statehood and participating in its first election in 1960 United States presidential election, 1960, Hawaii has supported Democrats in all but two presidential elections: 1972 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1972 and 1984 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1984, both of which were landslide reelection victories for Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan respectively. In Hawaii's statehood tenure, only Minnesota has supported Republican candidates fewer times in presidential elections. The 2016 Cook Partisan Voting Index ranks Hawaii as the most heavily Democratic state in the nation.
Hawaii has not elected a Republican to represent the state in the U.S. Senate since Hiram Fong in 1970; since 1977, both of the state's U.S. Senators have been Democrats.
In 2004 United States presidential election, 2004, John Kerry won the state's four electoral votes by a margin of nine percentage points with 54% of the vote. Every county supported the Democratic candidate. In 1964, favorite son candidate senator Hiram Fong of Hawaii sought the Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential nomination, while Patsy Mink ran in the Oregon primary in 1972.
Honolulu-born Barack Obama, then serving as a United States senator from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, was elected the List of presidents of the United States, 44th president of the United States on 2008 United States presidential election, November 4, 2008, and was re-elected for a second term on 2012 United States presidential election, November 6, 2012. Obama had won the Hawaii Democratic caucus on February 19, 2008, with 76% of the vote. He was the third Hawaii-born candidate to seek the nomination of a major party, the first presidential nominee and first president from Hawaii.
In a 2020 study, Hawaii was ranked as the 6th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Law enforcement
Hawaii has a statewide sheriff department under its Hawaii Department of Public Safety, Department of Public Safety that provides law enforcement protection to government buildings and Daniel K. Inouye International Airport as well as correction services to all correctional facilities owned by the state.
Counties have their own respective police departments with their own jurisdictions:
* Kauai County Police Department for the island of Kauai
* Honolulu Police Department for Oahu
* Maui County Police Department for Molokai, Maui and Lanai
* Hawaii County Police Department for the Big Island
Forensic services for all agencies in the state are provided by the Honolulu Police Department.
Hawaiian sovereignty movement
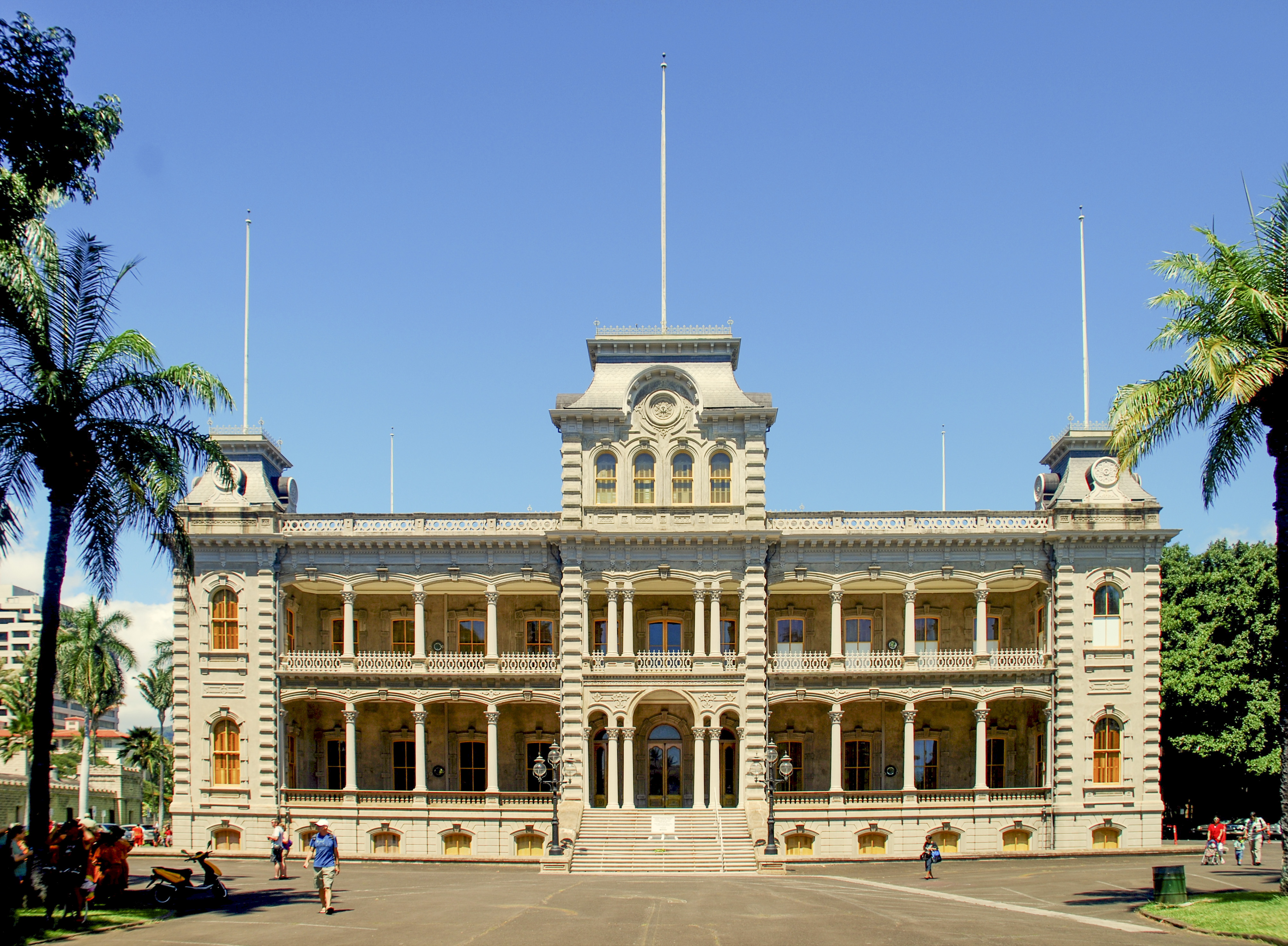 While Hawaii is internationally recognized as a state of the United States while also being broadly accepted as such in mainstream understanding, the Legal status of Hawaii, legality of this status has been questioned in U.S. District Court,
While Hawaii is internationally recognized as a state of the United States while also being broadly accepted as such in mainstream understanding, the Legal status of Hawaii, legality of this status has been questioned in U.S. District Court,[ the U.N., and other international forums.][ Domestically, the debate is a topic covered in the Kamehameha Schools curriculum,][ and in classes at the University of Hawai╩╗i at M─ünoa.
Political organizations seeking some form of sovereignty for Hawaii have been active since the late 19th century. Generally, their focus is on self-determination and self-governance, either for Hawaii as an independent nation (in many proposals, for "Hawaiian nationals" descended from subjects of the Hawaiian Kingdom or declaring themselves as such by choice), or for people of whole or part native Hawaiian ancestry in an indigenous "''nation to nation''" relationship akin to tribal sovereignty with US federal recognition of Native Hawaiians. The pro-federal recognition Akaka Bill drew substantial opposition among Hawaiian residents in the 2000s.]Hawaiian sovereignty movement
The Hawaiian sovereignty movement ( haw, ke ea Hawai╩╗i), is a grassroots political and cultural campaign to re-establish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom of Hawaii due to desire for sovereignty, self-determination, and self-gove ...
views the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii in 1893 as illegal, and views the subsequent Newlands Resolution, annexation of Hawaii by the United States as illegal as well; the movement seeks some form of greater autonomy for Hawaii, such as associated state, free association or independence from the United States.Apology Resolution
United States Public Law 103-150, informally known as the Apology Resolution, is a Joint Resolution of the U.S. Congress adopted in 1993 that "acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of age ...
passed by US Congress in 1993 is cited as a major impetus by the movement for Hawaiian sovereignty.
International sister relationships
* Ehime Prefecture, Ehime, Japan
* Fukuoka Prefecture, Fukuoka, Japan
* Hiroshima Prefecture, Hiroshima, Japan
* Hokkaido, Japan
* Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa, Japan
See also
* Index of Hawaii-related articles
* Outline of Hawaii
References
Informational notes
Citations
Bibliography
* Beechert, Edward D. ''Working in Hawaii: A Labor History'' (University of Hawaii Press, 1985).
*
* Kuykendall, Ralph S. ''A History of Hawaii'' (Macmillan, 1926
online
* Russ Jr., William Adam (1961) ''The Hawaiian Republic (1894ŌĆō98) and Its Struggle to Win Annexation''. Selinsgrove, Pennsylvania: Susquehanna University Press.
* Schmitt, Robert C. ''Historical Statistics of Hawaii''. (University Press of Hawaii, 1977).
* Schmitt, Robert C. "Religious statistics of Hawaii, 1825-1972". '' Hawaiian Journal of History'' (1973), vol. 7, pp 41ŌĆō47.
* Schmitt, Robert C. ''Demographic Statistics of Hawaii''. (University of Hawaii Press, 2021).
* Tabrah, Ruth M. ''Hawaii: a history'' (WW Norton & Company, 1984).
Guides
* Cooperm, Jeanne, and Natalie Schack. '' Frommer's Hawaii'' (2022
excerpt
* Doughty, Andrew. ''Hawaii the Big Island Revealed: The Ultimate Guidebook'' (2021
excerpt
* FODOR. ''Fodor's Essential Hawaii'' (2020
excerpt
External links
*
Hawaii State Guide from the Library of Congress
*
Hawaii State Fact Sheet
from the U.S. Department of Agriculture
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Hawaii
Energy Data & Statistics for Hawaii
Satellite image of Hawaiian Islands
at NASA's Earth Observatory
Documents relating to Hawaii Statehood, Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library
by ''The New York Times''
"Hawaii Then and Now"
Ćöslideshow by ''Life (magazine), Life'' magazine (Archived fro
the original
on November 3, 2010)
*
From th
Rare Book and Special Collections Division at the Library of Congress
{{coord, 21.5, N, 158.0, W, region:US-HI_type:adm1st, name=State of Hawai{{okinai, display=title
Hawaii,
1959 establishments in the United States
Geography of Polynesia
States and territories established in 1959
States of the United States
Western United States
Islands of Oceania
Articles containing video clips
 The Hawaiian
The Hawaiian  The Hawaiian islands were formed by volcanic activity initiated at an undersea
The Hawaiian islands were formed by volcanic activity initiated at an undersea  The islands of Hawaii are distant from other land habitats, and life is thought to have arrived there by wind, waves (i.e., by ocean currents), and wings (i.e., birds, insects, and any seeds that they may have carried on their feathers). Hawaii has more endangered species and has lost a higher percentage of its endemic species than any other U.S. state. The endemic plant ''
The islands of Hawaii are distant from other land habitats, and life is thought to have arrived there by wind, waves (i.e., by ocean currents), and wings (i.e., birds, insects, and any seeds that they may have carried on their feathers). Hawaii has more endangered species and has lost a higher percentage of its endemic species than any other U.S. state. The endemic plant '' Several areas in Hawaii are under the protection of the
Several areas in Hawaii are under the protection of the  Hawaii has a tropical climate. Temperatures and humidity tend to be less extreme because of near-constant
Hawaii has a tropical climate. Temperatures and humidity tend to be less extreme because of near-constant  Despite such contested claims, Cook is generally credited as being the first European to land at Hawaii, having visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as "firewood", and a minor chief and his men stole a boat from his ship. Cook abducted the King of Hawaii Island, Kalani┼Źpuu, and held him for ransom aboard his ship to gain return of Cook's boat, as this tactic had previously worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, the supporters of Kalani┼Źpuu attacked, killing Cook and four sailors as Cook's party retreated along the beach to their ship. The ship departed without retrieving the stolen boat.
After Cook's visit and the publication of several books relating his voyages, the Hawaiian Islands attracted many European and American visitors: explorers, traders, and eventually whalers, who found the islands to be a convenient harbor and source of supplies. These visitors introduced diseases to the once-isolated islands, causing the Hawaiian population to drop precipitously. Native Hawaiians had no resistance to Eurasian diseases, such as
Despite such contested claims, Cook is generally credited as being the first European to land at Hawaii, having visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as "firewood", and a minor chief and his men stole a boat from his ship. Cook abducted the King of Hawaii Island, Kalani┼Źpuu, and held him for ransom aboard his ship to gain return of Cook's boat, as this tactic had previously worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, the supporters of Kalani┼Źpuu attacked, killing Cook and four sailors as Cook's party retreated along the beach to their ship. The ship departed without retrieving the stolen boat.
After Cook's visit and the publication of several books relating his voyages, the Hawaiian Islands attracted many European and American visitors: explorers, traders, and eventually whalers, who found the islands to be a convenient harbor and source of supplies. These visitors introduced diseases to the once-isolated islands, causing the Hawaiian population to drop precipitously. Native Hawaiians had no resistance to Eurasian diseases, such as  During the 1780s, and 1790s, chiefs often fought for power. After a series of battles that ended in 1795, all inhabited islands were subjugated under a single ruler, who became known as
During the 1780s, and 1790s, chiefs often fought for power. After a series of battles that ended in 1795, all inhabited islands were subjugated under a single ruler, who became known as  On January 17, 1893, a small group of sugar and pineapple-growing businessmen, aided by the American minister to Hawaii and backed by heavily armed U.S. soldiers and marines, deposed Queen Liliuokalani and was replaced by a provisional government composed of members of the Committee of Safety. According to scholar Lydia Kualapai and Hawaii State Representative Roy Takumi, this was a committee formed against the will of Indigenous Hawaiian voters, who constituted the majority of voters at the time, and consisted of "thirteen white men" according to scholar J Kehaulani Kauanui. The United States Minister to the
On January 17, 1893, a small group of sugar and pineapple-growing businessmen, aided by the American minister to Hawaii and backed by heavily armed U.S. soldiers and marines, deposed Queen Liliuokalani and was replaced by a provisional government composed of members of the Committee of Safety. According to scholar Lydia Kualapai and Hawaii State Representative Roy Takumi, this was a committee formed against the will of Indigenous Hawaiian voters, who constituted the majority of voters at the time, and consisted of "thirteen white men" according to scholar J Kehaulani Kauanui. The United States Minister to the  After
After 
 After Europeans and mainland Americans first arrived during the
After Europeans and mainland Americans first arrived during the  According to the 2020 United States Census, Hawaii had a population of 1,455,271. The state's population identified as 37.2%
According to the 2020 United States Census, Hawaii had a population of 1,455,271. The state's population identified as 37.2%  English and Hawaiian are listed as Hawaii's official languages in the state's 1978 constitution, in Article XV, Section 4. However, the use of Hawaiian is limited because the constitution specifies that "Hawaiian shall be required for public acts and transactions only as provided by law". Hawai╩╗i Creole English, locally referred to as "Pidgin", is the native language of many native residents and is a second language for many others.
As of the 2000 Census, 73.4% of Hawaii residents age5 and older exclusively speak English at home. According to the 2008 American Community Survey, 74.6% of Hawaii's residents older than5 speak only English at home. In their homes, 21.0% of state residents speak an additional Asian language, 2.6% speak Spanish, 1.6% speak other
English and Hawaiian are listed as Hawaii's official languages in the state's 1978 constitution, in Article XV, Section 4. However, the use of Hawaiian is limited because the constitution specifies that "Hawaiian shall be required for public acts and transactions only as provided by law". Hawai╩╗i Creole English, locally referred to as "Pidgin", is the native language of many native residents and is a second language for many others.
As of the 2000 Census, 73.4% of Hawaii residents age5 and older exclusively speak English at home. According to the 2008 American Community Survey, 74.6% of Hawaii's residents older than5 speak only English at home. In their homes, 21.0% of state residents speak an additional Asian language, 2.6% speak Spanish, 1.6% speak other  Some residents of Hawaii speak Hawai╩╗i Creole English (HCE), endonymically called ''pidgin'' or ''pidgin English''. The lexicon of HCE derives mainly from English but also uses words that have derived from Hawaiian, Chinese, Japanese, Portuguese, Ilocano and Tagalog. During the 19th century, the increase in immigrationŌĆömainly from China, Japan, PortugalŌĆöespecially from the
Some residents of Hawaii speak Hawai╩╗i Creole English (HCE), endonymically called ''pidgin'' or ''pidgin English''. The lexicon of HCE derives mainly from English but also uses words that have derived from Hawaiian, Chinese, Japanese, Portuguese, Ilocano and Tagalog. During the 19th century, the increase in immigrationŌĆömainly from China, Japan, PortugalŌĆöespecially from the  The history of Hawaii's economy can be traced through a succession of dominant industries:
The history of Hawaii's economy can be traced through a succession of dominant industries:  Hawaiian mythology includes the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient Hawaiian people. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian mythology that developed a unique character for several centuries before ''circa'' 1800. It is associated with the Hawaiian religion, which was officially suppressed in the 19th century but was kept alive by some practitioners to the modern day. Prominent figures and terms include Aumakua, the spirit of an ancestor or family god and K─üne, the highest of the four major Hawaiian deities.
Hawaiian mythology includes the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient Hawaiian people. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian mythology that developed a unique character for several centuries before ''circa'' 1800. It is associated with the Hawaiian religion, which was officially suppressed in the 19th century but was kept alive by some practitioners to the modern day. Prominent figures and terms include Aumakua, the spirit of an ancestor or family god and K─üne, the highest of the four major Hawaiian deities.
 Polynesian mythology is the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia, a grouping of Central and South Pacific Ocean island
Polynesian mythology is the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia, a grouping of Central and South Pacific Ocean island 
 The music of Hawaii includes traditional and popular styles, ranging from native Hawaiian folk music to modern rock and hip hop music, hip hop. Hawaii's musical contributions to the music of the United States are out of proportion to the state's small size.
Styles such as slack-key guitar are well known worldwide, while Hawaiian-tinged music is a frequent part of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood soundtracks. Hawaii also made a major contribution to country music with the introduction of the steel guitar.
Traditional Hawaiian folk music is a major part of the state's musical heritage. The Hawaiian people have inhabited the islands for centuries and have retained much of their traditional musical knowledge. Their music is largely religious in nature, and includes chanting and dance music.
Hawaiian music has had an enormous impact on the Polynesian music, music of other Polynesian islands; according to Peter Manuel, the influence of Hawaiian music is a "unifying factor in the development of modern Pacific musics". Native Hawaiian musician and Hawaiian sovereignty activist Israel Kamakawiwo╩╗ole, famous for his medley of "Somewhere Over the Rainbow/What a Wonderful World", was named "The Voice of Hawaii" by NPR in 2010 in its 50 great voices series.
The music of Hawaii includes traditional and popular styles, ranging from native Hawaiian folk music to modern rock and hip hop music, hip hop. Hawaii's musical contributions to the music of the United States are out of proportion to the state's small size.
Styles such as slack-key guitar are well known worldwide, while Hawaiian-tinged music is a frequent part of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood soundtracks. Hawaii also made a major contribution to country music with the introduction of the steel guitar.
Traditional Hawaiian folk music is a major part of the state's musical heritage. The Hawaiian people have inhabited the islands for centuries and have retained much of their traditional musical knowledge. Their music is largely religious in nature, and includes chanting and dance music.
Hawaiian music has had an enormous impact on the Polynesian music, music of other Polynesian islands; according to Peter Manuel, the influence of Hawaiian music is a "unifying factor in the development of modern Pacific musics". Native Hawaiian musician and Hawaiian sovereignty activist Israel Kamakawiwo╩╗ole, famous for his medley of "Somewhere Over the Rainbow/What a Wonderful World", was named "The Voice of Hawaii" by NPR in 2010 in its 50 great voices series.
 Tourism is an important part of the Hawaiian economy as it represents ┬╝ of the economy. According to the Hawaii Tourism: 2019 Annual Visitor Research Report, a total of 10,386,673 visitors arrived in 2019 which increased 5% from the previous year, with expenditures of almost $18 billion. In 2019, tourism provided over 216,000 jobs statewide and contributed more than $2 billion in tax revenue. Due to mild year-round weather, tourist travel is popular throughout the year. Tourists across the globe visited Hawaii in 2019 with over 1 million tourists from the U.S. East, almost 2 million Japanese tourists, and almost 500,000 Canadian tourists.
It was with statehood in 1959 that the Hawaii tourism industry began to grow.
According to Hawaiian scholar
Tourism is an important part of the Hawaiian economy as it represents ┬╝ of the economy. According to the Hawaii Tourism: 2019 Annual Visitor Research Report, a total of 10,386,673 visitors arrived in 2019 which increased 5% from the previous year, with expenditures of almost $18 billion. In 2019, tourism provided over 216,000 jobs statewide and contributed more than $2 billion in tax revenue. Due to mild year-round weather, tourist travel is popular throughout the year. Tourists across the globe visited Hawaii in 2019 with over 1 million tourists from the U.S. East, almost 2 million Japanese tourists, and almost 500,000 Canadian tourists.
It was with statehood in 1959 that the Hawaii tourism industry began to grow.
According to Hawaiian scholar  Hawaii has the only school system within the U.S. that is unified statewide. Policy decisions are made by the fourteen-member state Hawaii Board of Education, Board of Education, which sets policy and hires the superintendent of schools, who oversees the Hawaii Department of Education. The Department of Education is divided into seven districts; four on Oahu and one for each of the other three counties.
Public elementary, middle and high school test scores in Hawaii are below national averages on tests mandated under the No Child Left Behind Act. The Hawaii Board of Education requires all eligible students to take these tests and report all student test scores. This may have unbalanced the results that reported in August 2005 that of 282 schools across the state, 185 failed to reach federal minimum performance standards in mathematics and reading. The ACT (examination), ACT college placement tests show that in 2005, seniors scored slightly above the national average (21.9 compared with 20.9), but in the widely accepted SAT examinations, Hawaii's college-bound seniors tend to score below the national average in all categories except mathematics.
The first native controlled public charter school was the Kanu O Ka Aina New Century Charter School.
Hawaii has the only school system within the U.S. that is unified statewide. Policy decisions are made by the fourteen-member state Hawaii Board of Education, Board of Education, which sets policy and hires the superintendent of schools, who oversees the Hawaii Department of Education. The Department of Education is divided into seven districts; four on Oahu and one for each of the other three counties.
Public elementary, middle and high school test scores in Hawaii are below national averages on tests mandated under the No Child Left Behind Act. The Hawaii Board of Education requires all eligible students to take these tests and report all student test scores. This may have unbalanced the results that reported in August 2005 that of 282 schools across the state, 185 failed to reach federal minimum performance standards in mathematics and reading. The ACT (examination), ACT college placement tests show that in 2005, seniors scored slightly above the national average (21.9 compared with 20.9), but in the widely accepted SAT examinations, Hawaii's college-bound seniors tend to score below the national average in all categories except mathematics.
The first native controlled public charter school was the Kanu O Ka Aina New Century Charter School.
 The largest institution of higher learning in Hawaii is the University of Hawaii System, which consists of the research university at University of Hawaii at Manoa, M─ünoa, two comprehensive campuses at University of Hawaii at Hilo, Hilo and University of Hawaii-West Oahu, West Oahu, and seven community colleges. Private universities include Brigham Young UniversityŌĆōHawaii, Chaminade University of Honolulu, Hawaii Pacific University, and Wayland Baptist University. Saint Stephen Diocesan Seminary, Honolulu, Saint Stephen Diocesan Center is a seminary of the
The largest institution of higher learning in Hawaii is the University of Hawaii System, which consists of the research university at University of Hawaii at Manoa, M─ünoa, two comprehensive campuses at University of Hawaii at Hilo, Hilo and University of Hawaii-West Oahu, West Oahu, and seven community colleges. Private universities include Brigham Young UniversityŌĆōHawaii, Chaminade University of Honolulu, Hawaii Pacific University, and Wayland Baptist University. Saint Stephen Diocesan Seminary, Honolulu, Saint Stephen Diocesan Center is a seminary of the  A List of Hawaii state highways, system of state highways encircles each main island. Only Oahu has federal highways, and is the only area outside the contiguous 48 states to have signed Interstate Highway System, Interstate highways. Narrow, winding roads and congestion in populated places can slow traffic. Each major island has a public bus system.
Honolulu International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA:HNL), which shares runways with the adjacent Hickam Field (IATA:HIK), is the major commercial aviation hub of Hawaii. The commercial aviation airport offers intercontinental service to North America, Asia, Australia and Oceania. Hawaiian Airlines and Mokulele Airlines use jets to provide services between the large airports in Honolulu, L─½hue, Kahului, Kona and Hilo. These airlines also provide air freight services between the islands. On May 30, 2017, the airport was officially renamed as the Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (HNL), after U.S. Senator Daniel Inouye, Daniel K. Inouye.
Until air passenger services began in the 1920s, private boats were the sole means of traveling between the islands. Seaflite operated hydrofoils between the major islands in the mid-1970s.
The Hawaii Superferry operated between Oahu and Maui between December 2007 and March 2009, with additional routes planned for other islands. Protests and legal problems over environmental impact statements ended the service, though the company operating Superferry has expressed a wish to recommence ferry services in the future. Currently there is a passenger ferry service in Maui County between Lanai and Maui, which does not take vehicles; a passenger ferry to Molokai ended in 2016. Currently Norwegian Cruise Lines and Princess Cruises provide passenger cruise ship services between the larger islands.
A List of Hawaii state highways, system of state highways encircles each main island. Only Oahu has federal highways, and is the only area outside the contiguous 48 states to have signed Interstate Highway System, Interstate highways. Narrow, winding roads and congestion in populated places can slow traffic. Each major island has a public bus system.
Honolulu International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA:HNL), which shares runways with the adjacent Hickam Field (IATA:HIK), is the major commercial aviation hub of Hawaii. The commercial aviation airport offers intercontinental service to North America, Asia, Australia and Oceania. Hawaiian Airlines and Mokulele Airlines use jets to provide services between the large airports in Honolulu, L─½hue, Kahului, Kona and Hilo. These airlines also provide air freight services between the islands. On May 30, 2017, the airport was officially renamed as the Daniel K. Inouye International Airport (HNL), after U.S. Senator Daniel Inouye, Daniel K. Inouye.
Until air passenger services began in the 1920s, private boats were the sole means of traveling between the islands. Seaflite operated hydrofoils between the major islands in the mid-1970s.
The Hawaii Superferry operated between Oahu and Maui between December 2007 and March 2009, with additional routes planned for other islands. Protests and legal problems over environmental impact statements ended the service, though the company operating Superferry has expressed a wish to recommence ferry services in the future. Currently there is a passenger ferry service in Maui County between Lanai and Maui, which does not take vehicles; a passenger ferry to Molokai ended in 2016. Currently Norwegian Cruise Lines and Princess Cruises provide passenger cruise ship services between the larger islands.
 The state government of Hawaii is modeled after the federal government with adaptations originating from the kingdom era of Hawaiian history. As codified in the Constitution of Hawaii, there are three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch is led by the Governor of Hawaii, who is assisted by the Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii, both of whom are elected on the same ticket. The governor is the only state public official elected statewide; all others are appointed by the governor. The lieutenant governor acts as the Secretary of State of Hawaii, Secretary of State. The governor and lieutenant governor oversee twenty agencies and departments from offices in the Hawaii State Capitol, State Capitol. The official residence of the governor is Washington Place.
The legislative branch consists of the Bicameralism, bicameral Hawaii State Legislature, which is composed of the 51-member Hawaii House of Representatives led by the Speaker (politics), Speaker of the House, and the 25-member Hawaii Senate led by the President of the Senate. The Legislature meets at the State Capitol. The unified judicial branch of Hawaii is the Hawaii State Judiciary. The State supreme court, state's highest court is the Supreme Court of Hawaii, which uses Aliiolani Hale, Alii┼Źlani Hale as its chambers.
The state government of Hawaii is modeled after the federal government with adaptations originating from the kingdom era of Hawaiian history. As codified in the Constitution of Hawaii, there are three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch is led by the Governor of Hawaii, who is assisted by the Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii, both of whom are elected on the same ticket. The governor is the only state public official elected statewide; all others are appointed by the governor. The lieutenant governor acts as the Secretary of State of Hawaii, Secretary of State. The governor and lieutenant governor oversee twenty agencies and departments from offices in the Hawaii State Capitol, State Capitol. The official residence of the governor is Washington Place.
The legislative branch consists of the Bicameralism, bicameral Hawaii State Legislature, which is composed of the 51-member Hawaii House of Representatives led by the Speaker (politics), Speaker of the House, and the 25-member Hawaii Senate led by the President of the Senate. The Legislature meets at the State Capitol. The unified judicial branch of Hawaii is the Hawaii State Judiciary. The State supreme court, state's highest court is the Supreme Court of Hawaii, which uses Aliiolani Hale, Alii┼Źlani Hale as its chambers.
 Since gaining statehood and participating in its first election in 1960 United States presidential election, 1960, Hawaii has supported Democrats in all but two presidential elections: 1972 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1972 and 1984 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1984, both of which were landslide reelection victories for Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan respectively. In Hawaii's statehood tenure, only Minnesota has supported Republican candidates fewer times in presidential elections. The 2016 Cook Partisan Voting Index ranks Hawaii as the most heavily Democratic state in the nation.
Hawaii has not elected a Republican to represent the state in the U.S. Senate since Hiram Fong in 1970; since 1977, both of the state's U.S. Senators have been Democrats.
In 2004 United States presidential election, 2004, John Kerry won the state's four electoral votes by a margin of nine percentage points with 54% of the vote. Every county supported the Democratic candidate. In 1964, favorite son candidate senator Hiram Fong of Hawaii sought the Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential nomination, while Patsy Mink ran in the Oregon primary in 1972.
Honolulu-born Barack Obama, then serving as a United States senator from
Since gaining statehood and participating in its first election in 1960 United States presidential election, 1960, Hawaii has supported Democrats in all but two presidential elections: 1972 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1972 and 1984 United States presidential election in Hawaii, 1984, both of which were landslide reelection victories for Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan respectively. In Hawaii's statehood tenure, only Minnesota has supported Republican candidates fewer times in presidential elections. The 2016 Cook Partisan Voting Index ranks Hawaii as the most heavily Democratic state in the nation.
Hawaii has not elected a Republican to represent the state in the U.S. Senate since Hiram Fong in 1970; since 1977, both of the state's U.S. Senators have been Democrats.
In 2004 United States presidential election, 2004, John Kerry won the state's four electoral votes by a margin of nine percentage points with 54% of the vote. Every county supported the Democratic candidate. In 1964, favorite son candidate senator Hiram Fong of Hawaii sought the Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential nomination, while Patsy Mink ran in the Oregon primary in 1972.
Honolulu-born Barack Obama, then serving as a United States senator from