Hapalochlaena on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blue-ringed octopuses, comprising the genus ''Hapalochlaena'', are four highly venomous species of
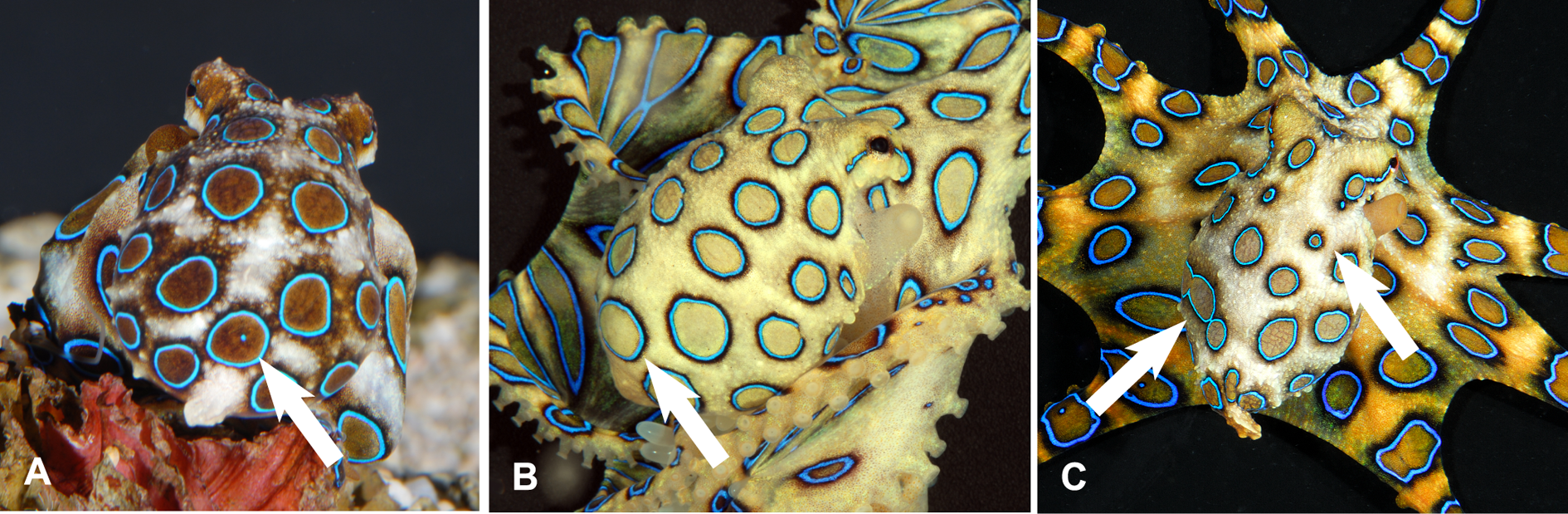 If they are provoked, they quickly change color, becoming bright yellow with each of the 50–60 rings flashing bright
If they are provoked, they quickly change color, becoming bright yellow with each of the 50–60 rings flashing bright
 The octopus produces venom containing tetrodotoxin, histamine, tryptamine, octopamine, taurine,
The octopus produces venom containing tetrodotoxin, histamine, tryptamine, octopamine, taurine,
CephBase: ''Hapalochlaena''
Life In The Fast Lane – Toxicology Conundrum #011
PBS Nature
* {{taxonbar, from=Q540649 Octopodidae Venomous molluscs
octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
that are found in tide pools and coral reefs in the Pacific and Indian oceans, from Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
to Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
. They can be identified by their yellowish skin and characteristic blue and black rings that change color dramatically when the animal is threatened. They eat small crustaceans, including crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, hermit crabs, shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
, and other small sea animals.
They are one of the world's most venomous marine animals. Despite their small size——and relatively docile nature, they are very dangerous to humans if provoked when handled because their venom contains the powerful neurotoxin tetrodotoxin.
The species tend to have a lifespan of approximately two to three years. This may vary depending on factors such as nutrition, temperature and the intensity of light within its habitat.
Classification
The genus was described by British zoologist Guy Coburn Robson in 1929. There are four confirmed species of ''Hapalochlaena'', and six possible but still undescribed species being researched: * Greater blue-ringed octopus (''Hapalochlaena lunulata'') *Southern blue-ringed octopus
The southern blue-ringed octopus (''Hapalochlaena maculosa'') is one of three (or perhaps four) highly venomous species of blue-ringed octopuses. It is most commonly found in tidal rock pools along the south coast of Australia. As an adult, it can ...
or lesser blue-ringed octopus (''Hapalochlaena maculosa'')
* Blue-lined octopus
The blue-lined octopus (''Hapalochlaena fasciata'') is one of four species of highly venomous blue-ringed octopuses. It can be found in Pacific Ocean waters that stretch from Australia to Japan. It is most commonly found around intertidal rocky s ...
(''Hapalochlaena fasciata'')
* ''Hapalochlaena nierstraszi'' was documented and described in 1938 from a single specimen found in the Bay of Bengal, with a second specimen caught and described in 2013.
Behavior
Blue-ringed octopuses spend most of their time hiding in crevices while displaying effective camouflage patterns with their dermal chromatophore cells. Like all octopuses, they can change shape easily, which helps them to squeeze into crevices much smaller than themselves. This, along with piling up rocks outside the entrance to its lair, helps safeguard the octopus from predators. If they are provoked, they quickly change color, becoming bright yellow with each of the 50–60 rings flashing bright
If they are provoked, they quickly change color, becoming bright yellow with each of the 50–60 rings flashing bright iridescent
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
blue within a third of a second as an aposematic warning display. In the greater blue-ringed octopus (''Hapalochlaena lunulata''), the rings contain multi-layer light reflectors called iridophores. These are arranged to reflect blue–green light in a wide viewing direction. Beneath and around each ring there are dark pigmented chromatophores which can be expanded within 1 second to enhance the contrast of the rings. There are no chromatophores above the ring, which is unusual for cephalopods as they typically use chromatophores to cover or spectrally modify iridescence. The fast flashes of the blue rings are achieved by using muscles which are under neural control. Under normal circumstances, each ring is hidden by contraction of muscles above the iridophores. When these relax and muscles outside the ring contract, the iridescence is exposed thereby revealing the blue color.
Similar to other Octopoda, the blue-ringed octopus swims by expelling water from a funnel in a form of jet propulsion.
Feeding
The blue-ringed octopus diet typically consists of small crustaceans such ascrab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s and shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
. They also tend to take advantage of small injured fish if they can catch them. The blue-ringed octopus pounces on its prey, seizing it with its arms and pulling it towards its mouth. It uses its horny beak to pierce through the tough crab or shrimp exoskeleton, releasing its venom. The venom paralyzes the muscles required for movement, which effectively kills the prey.
Reproduction
The mating ritual for the blue-ringed octopus begins when a male approaches a female and begins to caress her with his modified arm, the hectocotylus. A male mates with a female by grabbing her, which sometimes completely obscures the female's vision, then transferringsperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
packets by inserting his hectocotylus into her mantle cavity repeatedly. Mating continues until the female has had enough, and in at least one species the female has to remove the over-enthusiastic male by force. Males will attempt copulation with members of their own species regardless of sex or size, but interactions between males are most often shorter in duration and end with the mounting octopus withdrawing the hectocotylus without packet insertion or struggle.
Blue-ringed octopus females lay only one clutch of about 50 eggs in their lifetimes, towards the end of fall. Eggs are laid and then incubated underneath the female's arms for about six months, during this process the female does not eat. After the eggs hatch, the female dies, and the new offspring will reach maturity and be able to mate by the next year.
Mating behavior
In thesouthern blue-ringed octopus
The southern blue-ringed octopus (''Hapalochlaena maculosa'') is one of three (or perhaps four) highly venomous species of blue-ringed octopuses. It is most commonly found in tidal rock pools along the south coast of Australia. As an adult, it can ...
, body mass is observed to be the strongest factor that influence copulatory rates. Evidence of female preference of larger males is apparent, although no male preference of females is shown. In this species, it is suggested that males expend more effort than females to initiate copulation. Additionally, it is unlikely that males use odor cues to identify females with which to mate. Male-male mounting attempts are common in ''H. maculosa'', proposing that there is no discrimination between sex. Male blue-ringed octopus will adjust mating durations based on the female's recent mating history. Termination of copulation is not likely to happen with a female if she has not yet mated with another male. Duration length of mating is also found to be longer in these cases as well.
Toxicity
The blue-ringed octopus, despite its small size, carries enough venom to kill 26 adult humans within minutes. Their bites are tiny and often painless, with many victims not realizing they have been envenomated untilrespiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia ...
and paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
begins. No blue-ringed octopus antivenom is available.
Venom
 The octopus produces venom containing tetrodotoxin, histamine, tryptamine, octopamine, taurine,
The octopus produces venom containing tetrodotoxin, histamine, tryptamine, octopamine, taurine, acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Part ...
and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
. The venom can result in nausea, respiratory arrest
Respiratory arrest is a sickness caused by apnea (cessation of breathing) or respiratory dysfunction severe enough it will not sustain the body (such as agonal breathing). Prolonged apnea refers to a patient who has stopped breathing for a long p ...
, heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, severe and sometimes total paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
, blindness, and can lead to death within minutes if not treated. Death is usually from suffocation due to paralysis of the diaphragm.
The venom is produced in the posterior salivary gland of the octopus. The salivary glands possess a tubuloacinar exocrine structure and are located in the intestinal blood space.
The major neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature ner ...
component of the blue-ringed octopus is a compound that was originally known as maculotoxin but was later found to be identical to tetrodotoxin, a neurotoxin also found in pufferfish
Tetraodontidae is a family of primarily marine and estuarine fish of the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfis ...
, rough skinned newt
The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt (''Taricha granulosa'') is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.
Appearance
A stocky newt with rounded snout, it ranges from light brown to olive or brownish-black on ...
s and in some poison dart frog
Poison dart frog (also known as dart-poison frog, poison frog or formerly known as poison arrow frog) is the common name of a group of frogs in the family Dendrobatidae which are native to tropical Central and South America. These species are ...
s. Tetrodotoxin blocks sodium channels, causing motor paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
and respiratory arrest
Respiratory arrest is a sickness caused by apnea (cessation of breathing) or respiratory dysfunction severe enough it will not sustain the body (such as agonal breathing). Prolonged apnea refers to a patient who has stopped breathing for a long p ...
within minutes of exposure. The octopus's own sodium channels are adapted to be resistant to tetrodotoxin. The tetrodotoxin is produced by bacteria in the salivary glands of the octopus.
Direct contact is necessary to be envenomated. Faced with danger, the octopus's first instinct is to flee. If the threat persists, the octopus will go into a defensive stance, and display its blue rings. If the octopus is cornered and touched, it may bite and envenomate its attacker.
Estimates of the number of recorded fatalities caused by blue-ringed octopuses vary, ranging from seven to sixteen deaths; most scholars agree that there have been at least eleven.
Tetrodotoxin can be found in nearly every organ and gland of its body. Even sensitive areas such as the Needham's sac Needham's sac (also called a spermatophore sac) is the part of the reproductive tract of cephalopods in which spermatophores are stored. Spermatophores are complex structures consisting of ropes of sperm and in some species include an ejaculatory a ...
, branchial heart
Branchial hearts are accessory pumps that supplement the action of the systemic heart in a cephalopod's body. They are myogenic in nature. Branchial hearts are always in pairs located at the base of the gills. Each branchial heart consists of a ...
, nephridia, and gills, have been found to contain tetrodotoxin, and it has no effect on the octopus's normal functions. This may be possible through a unique blood transport. The mother will inject the neurotoxin into her eggs to make them generate their own venom before hatching.
Effects
Tetrodotoxin causes severe and often total body paralysis. Tetrodotoxin envenomation can result in victims being fully aware of their surroundings but unable to move. Because of the paralysis, they have no way of signaling for help or indicating distress. The victim remains conscious and alert in a manner similar to the effect of curare or pancuronium bromide. This effect is temporary and will fade over a period of hours as the tetrodotoxin is metabolized and excreted by the body. The symptoms vary in severity, with children being the most at risk because of their small body size.Treatment
First aid treatment is pressure on the wound andartificial respiration
Artificial ventilation (also called artificial respiration) is a means of assisting or stimulating respiration, a metabolic process referring to the overall exchange of gases in the body by pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, and interna ...
once the paralysis has disabled the victim's respiratory muscles, which often occurs within minutes of being bitten. Because the venom primarily kills through paralysis, victims are frequently saved if artificial respiration is started and maintained before marked cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
and hypotension develop. Respiratory support until medical assistance arrives will improve the victim's chances of survival. Definitive hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
treatment involves placing the patient on a ventilator until the toxin is removed by the body. Victims who survive the first 24 hours usually recover completely.
Conservation
Currently the blue-ringed octopus population information is listed as Least Concern according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, threats such as bioprospecting,habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological processes ...
, degradation, overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
, and human disturbance, as well as species collections for aquarium trade, may be threats to population numbers. It is possible that ''Hapalochlaena'' contribute to a variety of advantages to marine conservation. This genera of octopus provide stability of habitat biodiversity as well as expand the balance of marine food webs. Various species of blue-ringed octopus may help control populations of Asian date mussels. Additionally, future research of tetrodotoxins produced by the blue-ringed octopus may produce new medicinal discoveries.
In popular culture
In the 1983 James Bond film '' Octopussy'', the blue-ringed octopus is the prominent symbol of the secret order of female bandits and smugglers, appearing in an aquarium tank, on silk robes, and as a tattoo on women in the order. The animal was also featured in the book '' State of Fear'' byMichael Crichton
John Michael Crichton (; October 23, 1942 – November 4, 2008) was an American author and filmmaker. His books have sold over 200 million copies worldwide, and over a dozen have been adapted into films. His literary works heavily feature tech ...
, where a terrorist organization utilized the animal's venom as a favored murder weapon. '' The Adventure Zone'' featured a blue-ringed octopus in its "Petals to the Metal" series.
A video, originally posted on TikTok, of a tourist in Australia handling a blue-ringed octopus went viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
in January 2019.
References
External links
CephBase: ''Hapalochlaena''
Life In The Fast Lane – Toxicology Conundrum #011
PBS Nature
* {{taxonbar, from=Q540649 Octopodidae Venomous molluscs