|
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed). In serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to muscarinic receptors in the glands, leading to increased salivation. The fourth pair of salivary glands, the tubarial glands discovered in 2020, are named for their location, being positioned in front and over the torus tubarius. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
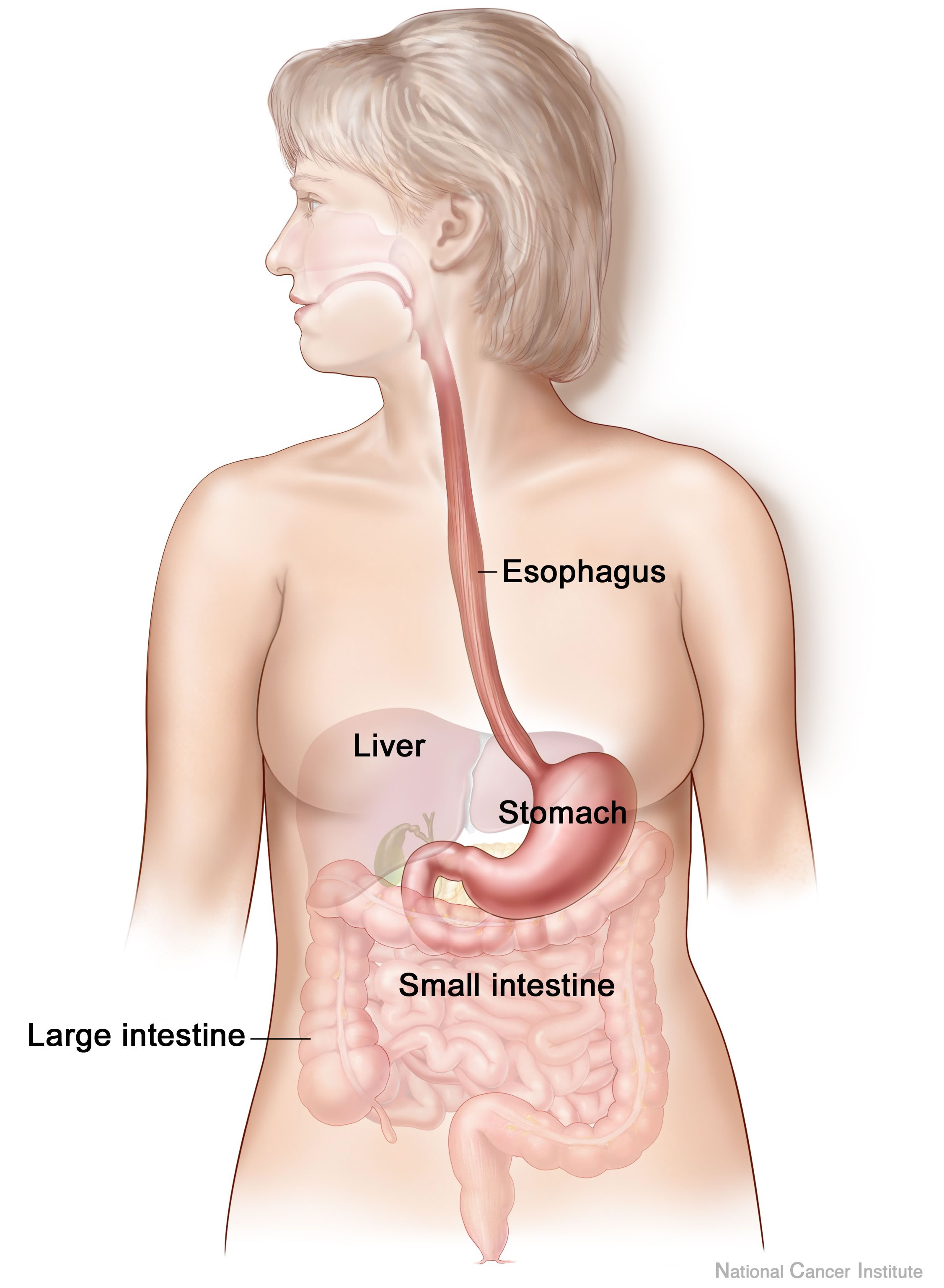
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a slightly sweet taste as they are chewed because amylase degrades some of their starch into sugar. The pancreas and salivary gland make amylase ( alpha amylase) to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. Specific amylase proteins are designated by different Greek letters. All amylases are glycoside hydrolases and act on α-1,4- glycosidic bonds. Classification α-Amylase The α-amylases () (CAS 9014-71-5) (alternative names: 1,4-α-D-glucan glucanohydrolase; glycogenase) are calcium metalloenzymes. By acting at ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material (such as food, drink, or medicine) goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex. The portion of food, drink, or other material that will move through the neck in one swallow is called a bolus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting, where the word gulping is more adequate. In humans Swallowing comes so easily to most people that the process rarely prompts much thought. However, from the viewpoints of physiology, of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastication
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, the food is positioned by the cheek and tongue between the teeth for grinding. The muscles of mastication move the jaws to bring the teeth into intermittent contact, repeatedly occluding and opening. As chewing continues, the food is made softer and warmer, and the enzymes in saliva begin to break down carbohydrates in the food. After chewing, the food (now called a bolus) is swallowed. It enters the esophagus and via peristalsis continues on to the stomach, where the next step of digestion occurs. Increasing the number of chews per bite increases relevant gut hormones. Studies suggest that chewing may decrease self-reported hunger and food intake. Chewing gum has been around for many centuries; there is evidence that northern Europeans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from '' mandere'' "to chew" and ''-bula'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotid Gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands. Etymology The word ''parotid'' literally means "beside the ear". From Greek παρωτίς (stem παρωτιδ-) : (gland) behind the ear < παρά - pará : in front, and οὖς - ous (stem ὠτ-, ōt-) : ear. Structure The parotid glands are a pair of mainly serous salivary gland ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus Tubarius
The base of the cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube (auditory tube) lies directly under the mucous membrane A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ... of the nasal part of the pharynx, where it forms an elevation or cushion, the torus tubarius or torus of the auditory tube, behind the pharyngeal orifice of the tube. The torus tubarius is very close to the tubal tonsil, which is sometimes also called the ''tonsil of (the) torus tubarius''. Two folds run posteriorly and anteriorly: *posteriorly, the vertical fold of mucous membrane, the salpingopharyngeal fold, stretches from the lower part of the torus tubarius; it contains the Salpingopharyngeus muscle which originates from the superior border of the medial lamina of the cartilage of the auditory tube, and pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1, is a muscarinic receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CHRM1'' gene. It is localized to 11q13. This receptor is found mediating slow EPSP at the ganglion in the postganglionic nerve, is common in exocrine glands and in the CNS. It is predominantly found bound to G proteins of class Gq that use upregulation of phospholipase C and, therefore, inositol trisphosphate and intracellular calcium as a signalling pathway. A receptor so bound would not be susceptible to CTX or PTX. However, Gi (causing a downstream decrease in cAMP) and Gs (causing an increase in cAMP) have also been shown to be involved in interactions in certain tissues, and so would be susceptible to PTX and CTX respectively. Effects * EPSP in autonomic ganglia * Secretion from salivary glands * Gastric acid secretion from stomach * In CNS (memory?) * Vagally-induced bronchoconstriction * Mediating olfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Substances that increase or decrease the overall activity of the cholinergic system are called cholinergics and anticholinergics, respectively. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction—in other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for the sympathetic nervous system and as the final product released by the para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |