|
Curare
Curare ( or ; or ) is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plant extracts. Used as a paralyzing agent by indigenous peoples in Central and South America for hunting and for therapeutic purposes, curare only becomes active when it contaminates a wound or is introduced directly to the bloodstream; it is not active when ingested orally. Curare is prepared by boiling the bark of one of the dozens of plant sources, leaving a dark, heavy paste that can be applied to arrow or dart heads. These poisons cause weakness of the skeletal muscles and, when administered in a sufficient dose, eventual death by asphyxiation due to paralysis of the diaphragm. In medicine, curare has been used as a treatment for tetanus and strychnine poisoning and as a paralyzing agent for surgical procedures. History The word 'curare' is derived from , from the Carib language of the Macusi of Guyana. It has its origins in the Carib phrase "mawa cure" meaning of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
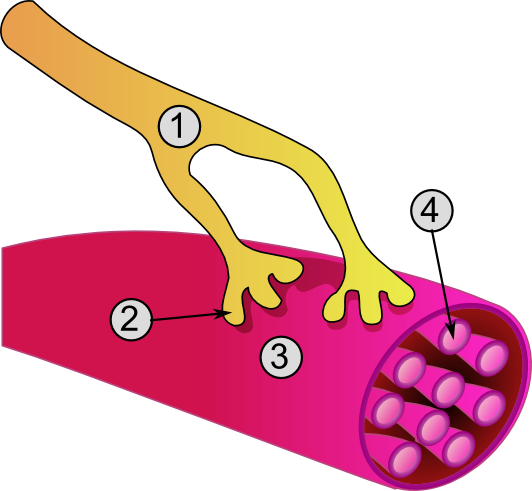
Neuromuscular-blocking Drug
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate Respiration (physiology), respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
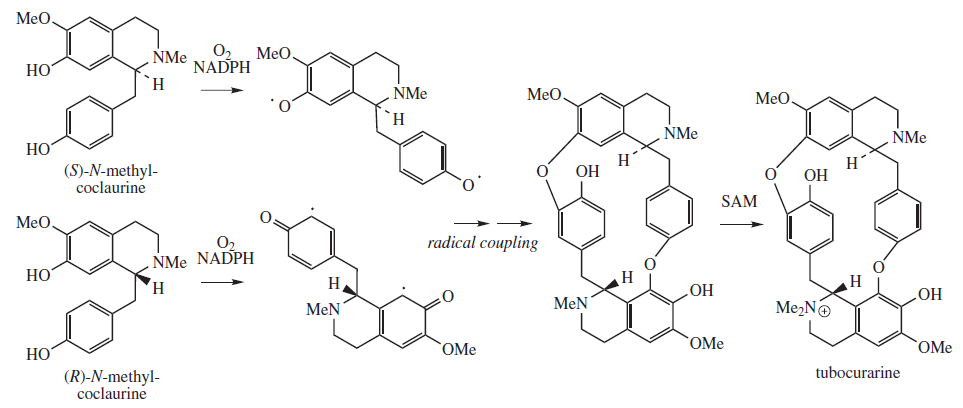
Tubocurarine Chloride
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. Safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, have largely replaced it as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia and it is now rarely used. The specific form used was tubocurarine chloride, its hydrated hydrochloride salt. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceous South American plant '' Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxiferine
Toxiferine, also known as c-toxiferine I, is one of the most toxic plant alkaloids known. It is derived from several plant species, including ''Strychnos toxifera. Historically, it has been used as an arrow poison by indigenous peoples in South America for its neuromuscular-blocking drug, neuromuscular blocking properties, allowing them to paralyze animals during hunting, but also possibly kill due to paralysis of the Muscles of respiration, respiratory muscles. Toxiferine functions as an acetylcholine receptor (AChR) Receptor antagonist, antagonist. The paralysis caused by toxiferine can in turn be antagonized by neostigmine. Toxiferine is the most important component in calabash curare. Curare poisons contain many different toxins with similar properties of toxiferine. The most well known component of curare is Tubocurarine chloride, tubocurarine. The paralysis caused by toxiferine is very similar to that caused by tubocurarine, however toxiferine is ~170 times as potent. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blowgun
A blowgun (also called a blowpipe or blow tube) is a simple ranged weapon consisting of a long narrow tube for shooting light projectiles such as darts. It operates by having the projectile placed inside the pipe and using the force created by forced exhalation ("blow") to pneumatically propel the projectile. The propulsive power is limited by the strength of the user's respiratory muscles and the vital capacity of their lungs. History Many cultures have used such a weapon, but various indigenous and aboriginal peoples of East Asia, Southeast Asia, Western Europe, North America, Central America (the Huehuetenango region of Guatemala), and South America (the Amazon Basin and the Guianas) are best known for its historical usage. Projectiles include seeds, clay pellets, and darts. Some cultures dip the tip of the darts in curare or other arrow poisons in order to paralyze the target. Blowguns were very rarely used by these tribes as anti-personnel weapons, but primarily to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Boehm
Rudolf Albert Martin Boehm (Böhm) (19 May 1844, in Nördlingen – 19 August 1926, in Bad Kohlgrub) was a German pharmacologist, known for his work in the field of experimental pharmacology. He studied medicine at the universities of University of Munich, Munich and University of Würzburg, Würzburg, and in 1868–70 served as an assistant to Franz von Rinecker at the Juliusspital in Würzburg. In 1871 he obtained his habilitation under Adolf Fick, then during the following year was named a professor of pharmacology, dietetics and history of medicine at the University of Dorpat. Later on, he worked as professor of pharmacology at the universities of University of Marburg, Marburg (from 1881) and University of Leipzig, Leipzig (from 1884), where on four separate occasions he was named dean to the medical faculty.Boehm, Rudolf Albert Martin [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow Poison
Arrow poisons are used to poison arrow heads or darts for the purposes of hunting and warfare. They have been used by indigenous peoples worldwide and are still in use in areas of South America, Africa and Asia. Notable examples are the poisons secreted from the skin of the poison dart frog, and curare (or 'ampi'), a general term for a range of plant-derived arrow poisons used by the indigenous peoples of South America. History Poisoned arrows have featured in mythology, notably the Greek story of Heracles slaying the centaur Nessus using arrows poisoned with the blood of the Lernaean Hydra. The Greek hero Odysseus poisons his arrows with hellebore in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Poisoned arrows also figure in Homer's epic about the Trojan War, the ''Iliad'', in which both Achaeans and Trojans used toxic arrows and spears. Poisoned arrows were known to be used by many ancient civilizations, including the Gauls, Scythians, and Svans. Ancient Greek and Roman historians describe recipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menispermaceae
Menispermaceae (botanical Latin: 'moonseed family' from Greek ''mene'' 'crescent moon' and ''sperma'' 'seed') is a family (biology), family of flowering plants. The alkaloid tubocurarine, a neuromuscular blocker and the active ingredient in the 'tube curare' form of the dart poison curare, is derived from the South American liana ''Chondrodendron tomentosum'', which belongs to this family. Several other South American genera belonging to the family have been used to prepare the 'pot' and 'calabash' forms of curare. The family contains 78 Genus, genera with some 440 species, which are distributed throughout low-lying tropical areas with some species present in temperate and arid regions. Description * Twining, ever-growing and woody climbing plants, winding anti-clockwise (''Stephania'' winds clockwise) and vines; rarely upright shrubs or small trees. Rarer still herbaceous plants or epiphytes (''Stephania cyanantha''), perennial or deciduous, with simple to uni-serrate hairs. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrodendron Tomentosum
''Chondrodendron tomentosum'' is one of six accepted species in the small genus Chondrodendron, belonging to the Moonseed family Menispermaceae. It is a large tropical liana native to Central and South America. It contains highly toxic alkaloids and is one of the sources of the arrow poison curare – specifically 'tube curare', the name of which is derived from the name of the medicinally valuable alkaloid tubocurarine Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxat .... __TOC__ Derivation of scientific name The generic name is a compound of Greek χόνδρος ( chondros ) 'cartilage' / 'lump' / 'grain' and δένδρον ( dendron ) 'tree' – hence 'lumpy / gristly tree', while the specific name consists of the Latin adjectival form ''tomentosum'' 'covered in matted hairs'. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strychnos Toxifera - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-267
''Strychnos'' is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae (sometimes Strychnaceae). The genus includes about 200 accepted species of trees and lianas. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare. Etymology The name ''strychnos'' was applied by Pliny the Elder in his ''Natural History'' to ''Solanum nigrum''. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek στρύχνον (''strúkhnon'') – "acrid", "bitter". The meaning of the word ''strychnos'' was not fixed in Ancient Greece, where it could designate a variety of different plants having in common the property of toxicity. Distribution The genus has a pantropical distribution. Taxonomy The genus is divided into 12 sections, though it is conceded that the sections do not reflect evolution of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek language, Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, Physical trauma, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Incidents th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanus
Tetanus (), also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'' and characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually lasts for a few minutes. Spasms occur frequently for three to four weeks. Some spasms may be severe enough to bone fracture, fracture bones. Other symptoms of tetanus may include fever, sweating, headache, dysphagia, trouble swallowing, hypertension, high blood pressure, and a tachycardia, fast heart rate. The onset of symptoms is typically 3 to 21 days following infection. Recovery may take months; about 10% of cases prove to be death, fatal. ''C. tetani'' is commonly found in soil, saliva, dust, and manure. The bacteria generally enter through a break in the skin, such as a cut or puncture wound caused by a contaminated object. They produce toxins that interfere with normal muscle contractions. Diagnosis is based on the presenting signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |