Guam Men's International Footballers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the
 Guam, along with the other
Guam, along with the other
 During
During
Imperial Japan's World War Two, 1931–1945
'', Transaction Publishers, 2007 During the nearly three years of occupation approximately 1,100 Chamorros were killed, according to later US
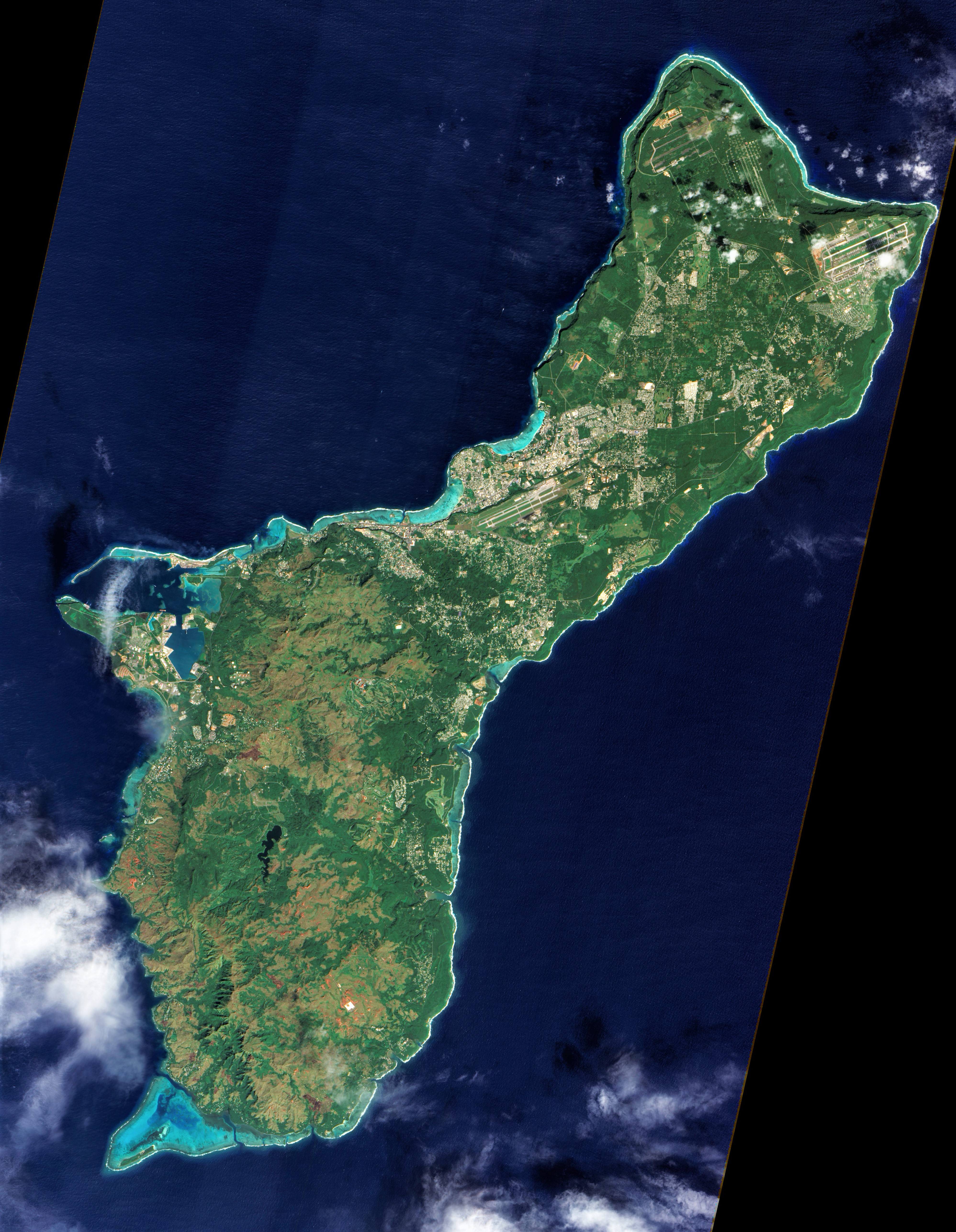 Guam is long and wide. It has an area of . It is the 32nd largest island of the United States. It is the southernmost and largest island in the
Guam is long and wide. It has an area of . It is the 32nd largest island of the United States. It is the southernmost and largest island in the
 Guam has a
Guam has a
Americans, Almost and Forgotten
, 107 California Law Review (2019)
 The tourism industry remains a cornerstone of Guam's economy, providing over 21,000 jobs, which constitute about one-third of the island's workforce. Major attractions contributing to the island's appeal include duty-free designer shopping outlets and American-style malls such as Micronesia Mall, Guam Premier Outlets, Agana Shopping Center, and the world's largest
The tourism industry remains a cornerstone of Guam's economy, providing over 21,000 jobs, which constitute about one-third of the island's workforce. Major attractions contributing to the island's appeal include duty-free designer shopping outlets and American-style malls such as Micronesia Mall, Guam Premier Outlets, Agana Shopping Center, and the world's largest
 Guam is governed by a popularly elected
Guam is governed by a popularly elected
 In the 1980s and early 1990s, there was a significant movement in favor of this U.S. territory becoming a
In the 1980s and early 1990s, there was a significant movement in favor of this U.S. territory becoming a
 Guam is divided into 19 municipal villages:
*
Guam is divided into 19 municipal villages:
*

''Guampedia''
– Guam's online Encyclopedia
"Guam Society of America"
fosters the Chamorro language, culture, and traditions
''The Insular Empire: America in the Mariana Islands''
PBS documentary film website.
Guam
''
U.S. Census Bureau: Island Areas Census 2000
from the U.S.
Guam Census
() {{coord, 13, 30, N, 144, 48, E, region:GU_type:isle_scale:250000, display=title 1898 establishments in Oceania Dependent territories in Micronesia Dependent territories in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Former Spanish colonies Insular areas of the United States Island countries Islands of Oceania Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Pacific islands of the United States Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1898 World War II sites
Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
subregion of the western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo
Dededo (; Spanish: ) is the most populated village in the United States territory of Guam. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Dededo's population was just under 45,000 in 2020. The village is located on the coral plateau of Northern Guam. The gr ...
. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States, as measured from the geographic center of the U.S. In Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
and the largest island in Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
. As of 2022, its population was 168,801. Chamorros are its largest ethnic group, but a minority on the multiethnic island. The territory spans and has a population density of .
Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Sout ...
peoples of the Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago is the archipelago between Mainland Southeast Asia and Australia, and is also called Insulindia or the Indo-Australian Archipelago. The name was taken from the 19th-century European concept of a Malay race, later based ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, and Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
. But unlike most of its neighbors, the Chamorro language
Chamorro (, ; orthern Mariana Islandsor uam) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken by about 58,000 people, numbering about 25,800 on Guam and about 32,200 in the Northern Mariana Islands and elsewhere.
It is the h ...
is not classified as a Micronesian or Polynesian language. Rather, like Palauan, it possibly constitutes an independent branch of the Malayo-Polynesian language family. The Chamorro people settled Guam and the Mariana islands approximately 3,500 years ago. Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fl ...
, while in the service of Spain, was the first European to visit and claim the island on March 6, 1521. Guam was fully colonized by Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
in 1668. Between the 17th and 19th centuries, Guam was an important stopover for Spanish Manila galleons
The Manila galleon (; ) refers to the Spanish trading ships that linked the Philippines in the Spanish East Indies to Mexico (New Spain), across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year between the ports of Man ...
. During the Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
, the United States captured Guam on June 21, 1898. Under the 1898 Treaty of Paris, Spain ceded Guam to the U.S. effective April 11, 1899.
Before World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Guam was one of five American jurisdictions in the Pacific Ocean, along with Wake Island
Wake Island (), also known as Wake Atoll, is a coral atoll in the Micronesia subregion of the Pacific Ocean. The atoll is composed of three islets – Wake, Wilkes, and Peale Islands – surrounding a lagoon encircled by a coral reef. The neare ...
in Micronesia, American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
in Polynesia, and the Philippines. On December 8, 1941, hours after the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
, Guam was captured by the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, who occupied the island for two and a half years before American forces recaptured it on July 21, 1944, which is commemorated there as Liberation Day
Liberation Day is a day, often a public holiday, that marks the liberation of a place, similar to an independence day, but differing from it because it does not involve the original creation of statehood. It commemorates the end of an occupation ...
. Since the 1960s, Guam's economy has been supported primarily by tourism and the U.S. military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. U.S. federal law names six armed forces: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and the Coast Guard. Since 1949, all of the armed forces, except th ...
, for which Guam is a major strategic asset. Its future political status has been a matter of significant discussion, with public opinion polls indicating a strong preference for American statehood.
Guam's '' de facto'' motto is "Where America's Day Begins", which refers to the island's proximity to the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is the line extending between the South and North Poles that is the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180.0° line of longitude and de ...
. Guam is among the 17 non-self-governing territories listed by the United Nations, and has been a member of the Pacific Community
The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories around the Pacific Ocean. The organisation's hea ...
since 1983.
Guam is called by Chamorro speakers, from the word , meaning 'to have'; its English gloss 'we have' references the island's providing everything needed to live.
History
Pre-Contact era
Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
, were the first islands settled by humans in Remote Oceania. It was also the first and the longest of the ocean-crossing voyages of the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melan ...
, and is separate from the later Polynesian settlement of the rest of Remote Oceania. They were first settled around 1500 to 1400 BC, by migrants departing from the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
which was followed by a second migration from the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the cen ...
in the first millennium AD. A third migration wave took place from Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Mari ...
, likely the Philippines or eastern Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, by 900 AD.
These original settlers of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
evolved into the Chamorro people
The Chamorro people (; also Chamoru) are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, Indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the Territories of the United States, United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Norther ...
, historically known as Chamorros after first contact with the Spaniards. The ancient Chamorro society had four classes: (chiefs), (upper class), (middle class), and (lower class). The were located in the coastal villages, which meant they had the best access to fishing grounds. The were located in the island's interior. and rarely communicated with each other. The often used as intermediaries.
There were also "" or "", shamans with magical powers and "'" or "", healers who used different kinds of plants and natural materials to make medicine. Belief in spirits of ancient Chamorros called "" still persists as a remnant of pre-European culture. It is believed that "" or "" are the only ones who can safely harvest plants and other natural materials from their homes or "" without incurring the wrath of the "." Their society was organized along matrilineal
Matrilineality, at times called matriliny, is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which people identify with their matriline, their mother's lineage, and which can involve the inheritan ...
clans.
The Chamorro people raised colonnades of megalithic capped pillars called upon which they built their homes. Latte stones are stone pillars that are found only in the Mariana Islands. They are a recent development in Pre-Contact Chamorro society. The latte-stone was used as a foundation on which thatched huts were built. Latte stones consist of a base shaped from limestone called the and with a capstone, or , made either from a large brain coral or limestone, placed on top. A possible source for these stones, the Rota Latte Stone Quarry, was discovered in 1925 on Rota.
Spanish era
The first European to travel to Guam was Portuguese navigatorFerdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fl ...
, sailing for the King of Spain
The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy () is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarch who reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country.
The Spanish ...
, when he sighted the island on March 6, 1521, during his fleet's circumnavigation of the globe. Despite Magellan's visit, Guam was not officially claimed by Spain until January 26, 1565, by Miguel López de Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as ''Adelantado, El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spanish conquistador who financed and led an expedition to conquer the Philippines, Philippine islan ...
. From 1565 to 1815, Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, the only Spanish outposts in the Pacific Ocean east of the Philippines, were reprovisioning stops for the Manila galleons
The Manila galleon (; ) refers to the Spanish trading ships that linked the Philippines in the Spanish East Indies to Mexico (New Spain), across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year between the ports of Man ...
, a fleet that covered the Pacific trade route between Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , ; ), is a city and Port of Acapulco, major seaport in the Political divisions of Mexico, state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Located on a deep, semicirc ...
and Manila
Manila, officially the City of Manila, is the Capital of the Philippines, capital and second-most populous city of the Philippines after Quezon City, with a population of 1,846,513 people in 2020. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay on ...
.
Spanish colonization commenced on June 15, 1668, with the arrival of a mission led by Diego Luis de San Vitores
Diego Luis de San Vitores, SJ (November 12, 1627 – April 2, 1672) was a Spanish Jesuit missionary who founded the first Catholic church on the island of Guam. He is responsible for establishing the Christian presence in the Mariana Islands. H ...
, who established the first Catholic church. The islands were part of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies were the colonies of the Spanish Empire in Asia-Pacific, Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1901, governed through the Captaincy General of the Philippines, captaincy general in Manila for the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish Crown, i ...
, and part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
, based in Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
. The Spanish-Chamorro Wars on Guam began in 1670 over growing tensions with the Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
mission, with the last large-scale uprising in 1683.
Intermittent warfare, plus the typhoons of 1671 and 1693, and in particular the smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
epidemic of 1688, reduced the Chamorro population from 50,000 to 10,000, and finally to less than 5,000. Up until the late 19th century, Guam was encountered by adventurers and pirates, including Thomas Cavendish, Olivier van Noort
Olivier van Noort (1558 – 22 February 1627) was a Dutch merchant captain and the first Dutchman to circumnavigate the world.Quanchi, ''Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Pacific Islands'', page 246
Olivier van Noort ...
, John Eaton John Eaton may refer to:
* John Eaton (divine) (born 1575), English divine
* John Eaton (pirate) (fl. 1683–1686), English buccaneer
*Sir John Craig Eaton (1876–1922), Canadian businessman
* John Craig Eaton II (born 1937), Canadian businessman ...
, William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavig ...
, Woodes Rogers
Woodes Rogers ( – 15 July 1732) was an English sea captain, privateer and colonial administrator who served as the List of governors of the Bahamas, governor of the Bahamas from 1718 to 1721 and again from 1728 to 1732. He is remembered ...
, John Clipperton, George Shelvocke
George Shelvocke (baptised 1 April 167530 November 1742) was an English Royal Navy officer and later privateer who in 1726 wrote the memoir ''A Voyage Round the World by Way of the Great South Sea'' based on his exploits. It includes an account o ...
and William "Bully" Hayes.
The island became a rest stop for whalers starting in 1823. A devastating typhoon struck the island on August 10, 1848, followed by a severe earthquake on January 25, 1849, which resulted in many refugees from the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the cen ...
, victims of a resultant tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
. This earthquake was much more powerful than the 8.2 one that occurred on August 8, 1993. After a smallpox epidemic killed 3,644 Guamanians in 1856, Carolinians and Japanese were permitted to settle in the Marianas.
American era
After almost four centuries as part of theKingdom of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, the United States occupied the island following Spain's defeat in the 1898 Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
, as part of the Treaty of Paris of 1898
The Treaty of Peace between the United States of America and the Kingdom of Spain, commonly known as the Treaty of Paris of 1898, was signed by Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States on December 10, 1898, and marked the end of the ...
. Guam was transferred to the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
control on December 23, 1898, by Executive Order 108-A from 25th President William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
.
The U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft ...
assumed administrative control, with Captain Richard P. Leary appointed as the first naval governor in 1899. This era marked the introduction of American governance structures and cultural influences to the island.
The naval administration prioritized the development of Guam's infrastructure to support its strategic military position in the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
. One notable project was the establishment of a coaling station to service naval vessels traveling between Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. Additionally, efforts were made to improve the island's roads, sanitation systems, and public health facilities. Educational reforms were also introduced, including the establishment of public schools with English as the medium of instruction, aiming to assimilate the local Chamorro population into American culture.
Despite these developments, the Chamorro people faced significant challenges under the naval administration. Civil liberties were limited, and the local population had minimal input in governmental decisions. Recognizing these constraints, Chamorro leaders petitioned for U.S. citizenship and greater political autonomy as early as 1901, though these efforts were largely unsuccessful during this period.
These advocacy efforts continued over the years, with Chamorro representatives seeking citizenship and self-governance. For instance, in 1936, delegates Baltazar J. Bordallo and Francisco B. Leon Guerrero traveled to Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, to personally petition for Chamorro citizenship. Despite these persistent efforts, substantial political reforms were not achieved during this period.
World War I
On December 10, 1914, the SMS ''Cormoran'', a German armedmerchant raider
Merchant raiders are armed commerce raiding ships that disguise themselves as non-combatant merchant vessels.
History
Germany used several merchant raiders early in World War I (1914–1918), and again early in World War II (1939–1945). The cap ...
, was forced to seek port at Apra Harbor
Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwat ...
on the U.S. territory of Guam after running short on coal as a result of being pursued by the Japanese. The United States, which was neutral at the time refused to supply provisions sufficient for the ''Cormoran'' to make a German port so the ship and her crew were interned until 1917.
On the morning of April 7, 1917, word reached Guam by telegraph cable that the U.S. Congress had declared war on Germany. The Naval Governor of Guam
The governor of Guam ( / ) is the head of government of Guam and the commander-in-chief of the Guam National Guard, whose responsibilities also include making the annual State of the Island (formerly the State of the Territory) addresses to t ...
, Roy Campbell Smith
Roy Campbell Smith (1858 – April 11, 1940) was an American naval officer and the Governor of Guam from 1916 to 1918.
Early life
On July 16, 1858, Smith was born in Fort Mason, Texas. Smith's father was Charles Henry Smith, an assistant surge ...
, sent two officers to inform the ''Cormoran'' that a state of war existed between the two countries, that the crew were now prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
, and that the ship must be surrendered. Meanwhile, the USS ''Supply'' blocked the entrance to Apra Harbor to prevent any attempt to flee. In a separate boat, the two officers were accompanied by a barge commanded by Lt. W.A. Hall, who was designated prize master, and had brought 18 sailors and 15 Marines from the barracks at Sumay.
Seeing a launch from ''Cormoran'' hauling a barge of supplies back shore, Hall ordered shots fired across the bow of the launch until it hove to. Meanwhile, the two officers reached ''Cormoran'' and informed Captain Adalbert Zuckschwerdt
Adalbert Zuckschwerdt (1 January 1874 – 1 July 1945) was captain (''Korvettenkapitän'') of the German raider SMS Cormoran, which sailed from the German Colony of Qingdao, China, until she was finally docked and interned at Guam by the America ...
of the situation. Zuckschwerdt agreed to surrender his crew but refused to turn over the ship. The U.S. officers informed Zuckschwerdt that the ''Cormoran'' would be treated as an enemy combatant and left to inform Governor Smith of the situation. Unbeknownst to the Americans, the Germans had secreted an explosive device in the ship's coal bunker. Minutes after the Americans left, an explosion aboard ''Cormoran'' hurled debris across the harbor and her crew began abandoning ship. The two American boats and USS ''Supply'' immediately began to recover German sailors from the water, saving all but seven of the roughly 370 ''Cormoran'' crew. This incident, including the warning shots against the launch, accounted for the first violent action of the United States in World War I
The United States became directly involved in World War I after declaring war on Germany on April 6, 1917. The declaration ended nearly three years of American neutrality in the war since the beginning, and the country's involvement in the conf ...
, first shots fired by the U.S. against Germany in World War I, the first German prisoners of war captured by the U.S., and the first Germans killed in action by the U.S. in World War I.
World War II
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
invaded and occupied Guam in the 1941 Battle of Guam on December 8, at the same time as the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
. The Japanese renamed Guam (Great Shrine Island). The Japanese occupation of Guam
The Japanese occupation of Guam was the period in the history of Guam between 1941 and 1944 when Imperial Japanese forces occupied Guam during World War II. The island was renamed Ōmiya-Jima ('Great Shrine Island').
Events leading to the occ ...
lasted about 31 months. During this period, the indigenous people of Guam were subjected to beatings, forced labor, family separation, concentration camps, massacres, beheadings and rape.Werner Gruhl, Imperial Japan's World War Two, 1931–1945
'', Transaction Publishers, 2007 During the nearly three years of occupation approximately 1,100 Chamorros were killed, according to later US
Congressional
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ad ...
committee testimony in 2004. Some historians estimate that war violence killed 10% of Guam's then 20,000 population. The United States returned and recaptured the island in the 1944 Battle of Guam from July 21 to August 10; July 21 became a territorial holiday, Liberation Day
Liberation Day is a day, often a public holiday, that marks the liberation of a place, similar to an independence day, but differing from it because it does not involve the original creation of statehood. It commemorates the end of an occupation ...
.
Post-war
After World War II, the Guam Organic Act of 1950 established Guam as an unincorporated organized territory of the United States, provided for the structure of the island's civilian government, and granted the people U.S. citizenship. The Governor of Guam was federally appointed until 1968 when the Guam Elective Governor Act provided for the office's popular election. Since Guam is not a U.S. state, U.S. citizens residing on Guam are not allowed to vote for president and their congressional representative is a non-voting member. They do, however, vote for party delegates in presidential primaries. In 1969, a referendum on unification with the Northern Mariana Islands was held and rejected. During the 1970s, Maryly Van Leer Peck started an engineering program, expandedUniversity of Guam
University of Guam () (U.O.G.) is a public university, public land-grant university in Mangilao, Guam. It is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges and offers thirty-four degree programs at the undergraduate level and ele ...
, and founded Guam Community College.Rottman, G. (2004) ''Guam 1941 & 1944: Loss and Reconquest''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, In the same period, Alby Mangels
Zwier Albertus "Alby" Mangels (born 16 November 1948) is an Australian adventurer and documentary film-maker widely remembered for his ''World Safari'' adventure travel films ('' World Safari'', '' World Safari II'', and '' World Safari III'').
...
, Australian adventurer and filmmaker of '' World Safari'' visited Guam during his six-year escapade on the leg of his voyage through the Pacific aboard the ''Klaraborg''.
The removal of Guam's security clearance by President John F. Kennedy in 1963 allowed for the development of a tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
industry. When the United States closed U.S. Naval Base Subic Bay and Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base in Luzon, located west of Angeles City, and about northwest of Metro Manila. It was previously operated by the U.S. Air Force and, before that, the U.S. Army, from 1903 to 1991. The base cov ...
bases in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
after the expiration of their leases in the early 1990s, many of the forces stationed there were relocated to Guam.
The 1997 Asian financial crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide eco ...
, which hit Japan particularly hard, severely affected Guam's tourism industry. Military cutbacks in the 1990s also disrupted the island's economy. Economic recovery was further hampered by devastation from super typhoons Paka in 1997 and Pongsona in 2002, as well as the effects of the September 11 terrorist attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
and the crash of Korean Air Flight 801
Korean Air Flight 801 (KE801, KAL801) was a scheduled international passenger flight operated by Korean Air, from Gimpo International Airport, Seoul to Antonio B. Won Pat International Airport, Guam. On August 6, 1997, the Boeing 747-300 operatin ...
on tourism.
Geography and environment
 Guam is long and wide. It has an area of . It is the 32nd largest island of the United States. It is the southernmost and largest island in the
Guam is long and wide. It has an area of . It is the 32nd largest island of the United States. It is the southernmost and largest island in the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
, as well as the largest in Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
. Guam's Point Udall is the westernmost point of the U.S., as measured from the geographic center of the United States.
The Mariana chain, of which Guam is a part, was created by collision of the Pacific and Philippine Sea tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
s. Guam is located on the micro Mariana Plate between the two. Guam is the closest land mass to the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deep sea, deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maxi ...
, the deep subduction zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
that runs east of the Marianas. Volcanic eruptions established the base of the island in the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
, roughly 56 to 33.9 million years ago. The north of Guam is a result of this base being covered with layers of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
, turning into limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, and then being thrust upward by tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
activity to create a plateau.
The rugged south of the island is a result of more recent volcanic activity. Cocos Island
Cocos Island () is a volcanic island in the Pacific Ocean administered by Costa Rica, approximately southwest of the Costa Rican mainland. It constitutes the 11th of the 15 districts of Puntarenas Canton of the Puntarenas Province, Province of ...
off the southern tip of Guam is the largest of the many small islet
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/ ...
s along the coastline. Guam's highest point is Mount Lamlam
Mount Lamlam (meaning ''lightning'' in Chamoru) is a peak on the United States island of Guam. It is located near the village of Agat ( north), in the south-west of the island.
Rising to above sea level, the distance from the peak to the botto ...
at above sea level."Geography of Guam". ''Official site of Guam'', April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 19, 2014, from . If its base is considered to be the nearby ''Challenger'' Deep, the deepest surveyed point in the Oceans
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and ...
, Mount Lamlam is the world's tallest mountain at .
Politically, Guam is divided into 19 villages. The majority of the population lives on the coralline limestone plateaus of the north, with political and economic activity concentrated in the central and northern regions. The rugged geography of the south largely limits settlement to rural coastal areas. The western coast is leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point o ...
of the trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere ...
and is the location of Apra Harbor
Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwat ...
, the capital Hagåtña, and the tourist center of Tumon
Tumon () is a district located on Tumon Bay along the northwest coast of the United States unincorporated territory of Guam. Located in the municipality of Tamuning, it is the center of Guam's tourist industry.
History
Tumon Bay or Agana Bay a ...
. The U.S. Defense Department
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, t ...
owns about 29% of the island, under the management of Joint Region Marianas
Joint Region Marianas' mission is to provide installation management support
to all Department of Defense components and tenants through assigned
regional installations on Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands in support
of training in the Marian ...
.Climate
 Guam has a
Guam has a tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southeast Florida, United States ...
on the Köppen scale (Köppen ''Af''). Its driest month of March almost qualifies as a tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate subtype that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ' ...
(Köppen ''Am''). The weather is generally hot and humid throughout the year with little seasonal temperature variation. Guam is known to have equable temperatures year-round. Trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere ...
are fairly constant throughout the year. There is often a weak westerly monsoon influence in the summer months.
Guam has two distinct seasons: Wet and dry season. The dry season runs from January through May. June is the transitional period. The wet season runs from July through November. Guam's average annual rainfall was between 1981 and 2010.
The wettest month on record at Guam Airport has been August 1997 with . The driest was February 2015 with . The wettest calendar year was 1976 with . The driest year was in 1998 with . The most rainfall in a single day occurred on October 15, 1953, when fell.
The mean high temperature is . The mean low is . Temperatures rarely exceed or fall below . The relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
commonly exceeds 84 percent at night throughout the year, but the average monthly humidity hovers near 66 percent.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Guam was on April 18, 1971, and April 1, 1990. A record low of was set on February 1, 2021. The lowest recorded temperature was 65 °F (18.3 °C), set on February 8, 1973.
Guam lies in the path of typhoon
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for a ...
s and it is common for the island to be threatened by tropical storms and possible typhoons during the wet season. The highest risk of typhoons is from August through November, where typhoons and tropical storms are most probable in the western Pacific. They can, however, occur year-round. Typhoons that have caused major damage on Guam in the American period include the Typhoon of 1900, Karen (1962), Pamela (1976), Paka (1997), Pongsona (2002), and Mawar (2023).
Since Typhoon Pamela in 1976, wooden structures have been largely replaced by concrete structures. During the 1980s, wooden utility poles began to be replaced by typhoon-resistant concrete and steel poles. After the local Government enforced stricter construction codes, many home and business owners have built their structures out of reinforced concrete with installed typhoon shutters.
Ecology
Guam is home to a diverse array of ecosystems, including coral reefs, deep seas, sea grasses, beach strand, mangroves, a variety of different limestone forest types, volcanic forests and grasslands, riparian systems, and caves. There are approximately 17 species of plant that are endemic only to the island of Guam, and many more that are endemic to the Mariana Islands. Numerous endemic insects have been described. There are approximately 29land snails
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have gastropod shell, shel ...
listed as endemic to the island of Guam, although many are now endangered or presumed extinct. Guam once hosted 14 kinds of terrestrial birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, 7 of which were endemic to Guam on the species or subspecies level, although all but one of the 14 are now extinct, extirpated, or endangered. Three locations on Guam (Guam National Wildlife Refuge
The Guam National Wildlife Refuge is composed of three units: the Andersen Air Force Base Overlay Unit (Air Force Overlay Unit), the Navy Overlay Unit, and the Ritidian Unit. The Ritidian Unit ( CHamoru: ''Puntan Litekyan'') is on the northernmo ...
, Cocos Island
Cocos Island () is a volcanic island in the Pacific Ocean administered by Costa Rica, approximately southwest of the Costa Rican mainland. It constitutes the 11th of the 15 districts of Puntarenas Canton of the Puntarenas Province, Province of ...
, and Mahlac Caves) have been identified as Important Bird Areas
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
(IBA) by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding i ...
because they support populations of Micronesian starlings, Mariana swiftlets, Mariana crows, and Guam rails. The Guam rail
The Guam rail (''Hypotaenidia owstoni''), known locally and in Chamorro as ''ko'ko, is a small, terrestrial bird endemic to Guam in the Rallidae family. They are one of the island's few remaining endemic bird species. The species became extinc ...
became the second bird species to ever be downlisted from Extinct in the wild
A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as only consisting of living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range ...
after a population was established on Cocos Island. Guam was home to three native bat species: the little Mariana fruit bat (''Pteropus tokudae''), now extinct; the endangered Pacific sheath-tailed bat
The Pacific sheath-tailed bat or Polynesian sheath-tailed bat (''Emballonura semicaudata'') is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae found in American Samoa, Fiji, Guam, Micronesia, Palau, Samoa (where it is called ''pe'a vai, ...
(''Emballonura semicaudata rotensis''); and the endangered Mariana fruit bat (''Pteropus mariannus mariannus'').
Guam has experienced severe effects of invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
upon the natural biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
of the island. These include the local extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
of endemic bird species after the introduction of the brown tree snake
The brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis''), also known as the brown catsnake, is an arboreal rear-fanged colubrid snake native to eastern and northern coastal Australia, eastern Indonesia (Sulawesi to Papua), Papua New Guinea, and many island ...
, an infestation of the coconut rhinoceros beetle destroying coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
palms, and the effect of introduced feral
A feral (; ) animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in som ...
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s and amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s.
Wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s plague the forested areas of Guam every dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
despite the island's humid climate. Most fires are caused by humans with 80% resulting from arson
Arson is the act of willfully and deliberately setting fire to or charring property. Although the act of arson typically involves buildings, the term can also refer to the intentional burning of other things, such as motor vehicles, watercr ...
. Poachers often start fires to attract deer to the new growth. Invasive grass species that rely on fire as part of their natural life cycle grow in many regularly burned areas. Grasslands and "barrens" have replaced previously forested areas leading to greater soil erosion.
During the rainy season, sediment is carried by the heavy rains into the Fena Lake Reservoir and Ugum River, leading to water quality problems for southern Guam. Eroded silt also destroys the marine life in reefs around the island. Soil stabilization efforts by volunteers and forestry workers (planting trees) have had little success in preserving natural habitats.
Efforts have been made to protect Guam's coral reef habitats from pollution, eroded silt and overfishing, problems that have led to decreased fish populations. This has both ecological and economic value, as Guam is a significant vacation spot for scuba divers, and one study found that Guam's reefs are worth US$
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
127 million per year. In recent years, the Department of Agriculture, Division of Aquatic and Wildlife Resources has established several new marine preserves where fish populations are monitored by biologists. These are located at Pati Point, Piti Bomb Holes, Sasa Bay
Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwat ...
, Achang Reef Flat, and Tumon Bay.
Before adopting U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
standards, portions of Tumon Bay were dredged by the hotel chains to provide a better experience for hotel guests. Tumon Bay has since been made into a preserve. A federal Guam National Wildlife Refuge
The Guam National Wildlife Refuge is composed of three units: the Andersen Air Force Base Overlay Unit (Air Force Overlay Unit), the Navy Overlay Unit, and the Ritidian Unit. The Ritidian Unit ( CHamoru: ''Puntan Litekyan'') is on the northernmo ...
in northern Guam protects the decimated sea turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerh ...
population in addition to a small colony of Mariana fruit bats.
Harvest of sea turtle eggs was a common occurrence on Guam before World War II. The green sea turtle
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exte ...
(''Chelonia mydas'') was harvested legally on Guam before August 1978, when it was listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The hawksbill sea turtle
The hawksbill sea turtle (''Eretmochelys imbricata'') is a critically endangered sea turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Eretmochelys''. The species has a global distribution that is largel ...
(''Eretmochelys imbricata'') has been on the endangered list since 1970. In an effort to ensure the protection of sea turtles on Guam, routine sightings are counted during aerial surveys and nest sites are recorded and monitored for hatchlings.
Demographics
In the 2020 United States census, the largest ethnic group were the nativeChamorros
The Chamorro people (; also Chamoru) are the Indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia, a commonweal ...
, accounting for 32.8% of the population. Asians
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term ...
, including Filipinos, Koreans, Chinese, and Japanese, accounted for 35.5% of the population. Other ethnic groups of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
, including those of Chuukese, Palauan, and Pohnpeians
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethno ...
, accounted for 13.2%. 10% of the population were multiracial
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races (human categorization), races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicity, ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used ...
, (two or more races). European Americans
European Americans are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes both people who descend from the first European settlers in the area of the present-day United States and people who descend from more recent European arrivals. Since th ...
made up 6.8% of the population; 1% are African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, and 3% are Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
; there are 1,740 Mexicans
Mexicans () are the citizens and nationals of the Mexico, United Mexican States. The Mexican people have varied origins with the most spoken language being Spanish language, Spanish, but many also speak languages from 68 different Languages o ...
in Guam, and there are other Hispanic ethnicities on the island. The estimated interracial marriage rate is over 40%.
The official languages of the island are English and Chamorro. Unlike most of its neighboring languages, Chamorro is not classified as Micronesian or Polynesian. Rather, like Palauan, it possibly constitutes an independent branch of the Malayo-Polynesian language family. Filipino is also commonly spoken across the island. Other Pacific and Asian languages are spoken in Guam as well. Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
, which was the language of administration for 300 years, influenced the Chamorro language
Chamorro (, ; orthern Mariana Islandsor uam) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken by about 58,000 people, numbering about 25,800 on Guam and about 32,200 in the Northern Mariana Islands and elsewhere.
It is the h ...
.
The predominant religion of Guam is Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. Three-quarters of the population adheres to Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, while most of the remainder belong to Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches. According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
, the religious demography of Guam in 2010 was as follows:
* Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
: 75%
* Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
: 17.7%
* Other religions: 1.6%
* Folk religions: 1.5%
* Other Christianity: 1.4%
* Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
: 1.1%
* Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
: <1%
* Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
: <1%
* Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
: <1%
* Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
: <1%
In 2020, the Vatican claimed that 87.72% of the population was Catholic, with 54 priests and 64 nuns across 27 parishes.
Culture
The culture of Guam is a reflection of traditional Chamorro customs, in combination with American, Spanish and Mexican traditions. Post-European-contact Chamorro Guamanian culture is a combination of American, Spanish, Filipino, other Micronesian Islander and Mexican traditions. Few indigenous pre-Hispanic customs remained following Spanish contact, but include plaiting and pottery. There has been a resurgence of interest among the Chamorro to preserve the language and culture. Hispanic influences are manifested in the local language, music, dance, sea navigation, cuisine, fishing, games (such as , , , and ), songs, and fashion. The island's original community are Chamorro natives, who have inhabited Guam for almost 4000 years. They had their own language related to the languages of Indonesia and southeast Asia. The Spanish later called them Chamorros. A derivative of the word, Chamorri, means "noble race". They began to grow rice on the island. Historically, the native people of Guam venerated the bones of their ancestors. They kept the skulls in their houses in small baskets, and practiced incantations before them when it was desired to attain certain objects. During Spanish rule (1668–1898) the majority of the population was converted toCatholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and religious festivities such as Easter and Christmas became widespread. Many Chamorros have Spanish surnames, although few of the inhabitants are themselves descended from the Spaniards. Instead, Spanish names and surnames became commonplace after their conversion to Catholicism and the imposition of the Catálogo alfabético de apellidos in Guam.
Historically, the diet of the native inhabitants of Guam consisted of fish, fowl, rice, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to have been selectively bred in Polynesia from the breadnut ('' Artocarpus camansi''). Breadfruit was spread into ...
, taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a ...
, yams, bananas, and coconuts used in a variety of dishes. Post-contact Chamorro cuisine is largely based on corn, and includes tortillas, tamales, atole, and chilaquiles, which are a clear influence from Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
, principally Mexico, from Spanish trade with Asia.
Due to foreign cultural influence from Spain, most aspects of the early indigenous culture have been lost, though there has been a resurgence in preserving any remaining pre-Hispanic culture in the last few decades. Some scholars have traveled throughout the Pacific Islands, conducting research to study what the original Chamorro cultural practices such as dance, language, and canoe building may have been like.
Sports
Guam's most popular sport isAmerican football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
, followed by basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
and baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
respectively. Soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
, Jiu Jitsu
Jujutsu ( , or ), also known as jiu-jitsu and ju-jitsu (both ), is a Japanese martial art and a system of close combat that can be used in a defensive or offensive manner to kill or subdue one or more weaponless or armed and armored opponent ...
, and Rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby union: 15 players per side
*** American flag rugby
*** Beach rugby
*** Mini rugby
*** Rugby sevens, 7 players per side
*** Rugby tens, 10 players per side
*** Snow rugby
*** Tou ...
are also somewhat popular. Guam hosted the Pacific Games
The Pacific Games (French: Jeux du Pacifique), is a continent, continental multi-sport event held every four years among athletes from Oceania. The inaugural Games took place in 1963 South Pacific Games, 1963 in Suva, Fiji, and most recently i ...
in 1975
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 – Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. ...
and 1999
1999 was designated as the International Year of Older Persons.
Events January
* January 1 – The euro currency is established and the European Central Bank assumes its full powers.
* January 3 – The Mars Polar Lander is launc ...
. At the 2007 Games, Guam finished 7th of 22 countries in the medal count, and 14th at the 2011 Games.
Guam men's national basketball team and the women's team are traditional powerhouses in the Oceania region, behind the Australia men's national basketball team
The Australia men's national basketball team, nicknamed the Boomers after the slang term for a male kangaroo, represents Australia in international basketball competition.
Since the late 1980s, Australia has placed among the world elite teams, ...
and the New Zealand national basketball team
The New Zealand men's national basketball team () represents New Zealand in international basketball competitions. The team is governed by Basketball New Zealand. The team's official nickname is the Tall Blacks ().
Over their history, New Zeal ...
. , the men's team is the reigning champion of the Pacific Games Basketball Tournament. Guam is home to various basketball organizations, including the Guam Basketball Association.
The Guam national football team
The Guam national football team represents Guam, an overseas territory of the United States, in international association football, football and is controlled by the Guam Football Association. They are affiliated with the Asian Football Confeder ...
was founded in 1975 and joined FIFA
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (), more commonly known by its acronym FIFA ( ), is the international self-regulatory governing body of association football, beach soccer, and futsal. It was founded on 21 May 1904 to o ...
in 1996. It was once considered one of FIFA's weakest teams, and experienced their first victory over a FIFA-registered side in 2009. Guam hosted qualifying games on the island for the first time in 2015 and, in 2018, clinched their first FIFA World Cup Qualifying win. The Guam national rugby union team played its first match in 2005 and has never qualified for a Rugby World Cup
The Men's Rugby World Cup is a rugby union tournament contested every four years between the top international teams, the winners of which are recognised as the World championship, world champions of the sport.
The tournament is administer ...
.
As an aspect of cultural revival, sling competitions are also being organized on Guam. As a national pastime of cultural import, the ovoid shape on Guamanian flag is that of a sling stone.
Economy
Guam's economy depends primarily on tourism, Department of Defense installations and locally owned businesses. Under the provisions of a special law byCongress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
, it is Guam's treasury rather than the U.S. treasury that receives the federal income taxes paid by local taxpayers, including military and civilian federal employees assigned to Guam.Lin, Tom C.W.Americans, Almost and Forgotten
, 107 California Law Review (2019)
Tourism
Guam, situated in the western Pacific, has long been a favored destination for tourists, particularly fromJapan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
. The island's tourism hub, Tumon
Tumon () is a district located on Tumon Bay along the northwest coast of the United States unincorporated territory of Guam. Located in the municipality of Tamuning, it is the center of Guam's tourist industry.
History
Tumon Bay or Agana Bay a ...
, boasts over 20 large hotels, the Duty Free Shoppers Galleria, the Pleasure Island district, an indoor aquarium, Sandcastle Las Vegas–styled shows, and various shopping and entertainment venues. Additionally, Guam offers seven public golf courses, catering to a diverse range of visitors.. visitguam.org
Historically, Japanese tourists comprised a significant portion of Guam's visitors. In 2019, approximately 685,000 Japanese travelers visited the island. However, this number declined to around 135,760 in 2023, reflecting broader shifts in travel patterns and external factors affecting global tourism. In recent years, South Korean tourists have become increasingly prominent. For instance, in May and June of 2024, South Korean visitors accounted for over 51% of Guam's total arrivals, while Japanese tourists comprised over 21%. Other significant visitor groups include travelers from the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
mainland, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
.
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
had a profound impact on Guam's tourism industry. In 2023, the island recorded approximately 656,000 visitor arrivals, a 50% decrease compared to 2013 figures. Despite these challenges, the industry has shown signs of recovery, with 775,000 passenger arrivals reported at the Guam International Airport during the 2024 fiscal year (October-July). While this indicated an upward trend, it remained below the pre-pandemic levels of 2019.
Kmart
Kmart ( ), formerly legally registered as Kmart Corporation, now operated by Transformco, is a department-store chain and online retailer in the United States and Territories of the United States, its territories. It operates four remaining Kma ...
.
Budget and unemployment
In 2003, Guam had a 14% unemployment rate, and the government suffered a $314 million budget shortfall. As of 2019 the unemployment rate had dropped to 6.1%. By September 2020, the unemployment rate had risen again to 17.9%. As of June 2023 the unemployment rate had fallen to 4.0%. The unemployment rate in Guam for September 2023 was 4.1%, an increase of 0.1 percentage points from the June 2023 figure of 4.0%, and a reduction of 0.3 percentage points from the September 2022 figure one year earlier of 4.4%.Pacific migration to Guam
The Compacts of Free Association (COFA) between the United States, theFederated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (, abbreviated FSM), or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Micronesia, a region of Oceania. The federation encompasses the majority of the Caroline Islands (excluding Palau) and consists of four Admin ...
, the Republic of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The territory consists of 29 c ...
, and the Republic of Palau
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands ...
accords the former entities of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994. The Imperial Japanese South Seas Mandate had been seized by the U.S. during the Pacifi ...
a political status of "free association" with the United States. The Compacts generally allow citizens of these island nations to reside in the 50 United States, and in US territories. Many people from other Pacific islands were attracted to Guam due to its proximity, environmental, and cultural familiarity.
Due to the impact of increased utilization of public assistance programs due to immigration, aid has been provided to the nations receiving immigrants. In 2003, the amended COFA was enacted, which provided 30 million dollars annually to Guam, Hawaii, American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
, as well as to forgive 157 million dollars of Guam's debt to the federal government to offset money already spent on public assistance programs. In 2024, the COFA was amended again to renew aid the freely associated nations as well as Guam and other U.S. Pacific territories.
Military bases
Joint Region Marianas
Joint Region Marianas' mission is to provide installation management support
to all Department of Defense components and tenants through assigned
regional installations on Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands in support
of training in the Marian ...
maintains jurisdiction over installations, which cover approximately , or 29% of the island's total land area. These include:
* U.S. Naval Base Guam
Naval Base Guam is a strategic U.S. naval base located on Apra Harbor and occupying the Orote Peninsula. In 2009, it was combined with Andersen Air Force Base to form Joint Region Marianas, which is a Navy-controlled joint base.
The Ship Rep ...
, U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft ...
(Santa Rita), comprising the Orote Peninsula
The Orote Peninsula is a four kilometer-long peninsula jutting from the west coast of the United States territory of Guam. A major geologic feature of the island, it forms the southern coast of Apra Harbor and the northern coast of Agat Bay. Its t ...
, additional lands, and with jurisdiction of the majority of Apra Harbor
Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwat ...
* Andersen Air Force Base
Andersen Air Force Base (Andersen AFB, AAFB) is a United States Air Force base located primarily within the village of Yigo in the United States territory of Guam. The host unit at Andersen AFB is the 36th Wing (36 WG), assigned to the Pacif ...
, U.S. Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its origins to 1 ...
(Yigo), including Northwest Field
Northwest Field (NWF; historically Northwest Guam Air Force Base) is a military airfield on the West Pacific island of Guam. Originally built during World War II, Northwest Field was closed as an airfield in 1949 but has been used for other mi ...
* Marine Corps Base Camp Blaz, U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionary ...
(Dededo)
* Ordnance Annex
Ordnance Annex is a US naval base in the United States territory of Guam. It used to be known as Naval Magazine, Guam. The base is on the south-central section of the island. It occupies an area of .
The entirety of the man-made Fena Lake, w ...
, U.S. Navy – South Central Highlands (formerly known as Naval Magazine)
* Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station Guam
Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station Guam (NCTS Guam) is a United States Navy communications facility on the U.S. territory of Guam. It is located on the Naval Base Guam North Finegayan Telecommunications Site along Guam Highway 3 in D ...
, U.S. Navy (Dededo), sometimes referred to "NCTS Finegayan"
* Naval Radio Station Barrigada (Barrigada), often referred to as "Radio Barrigada"
* Joint Region Marianas
Joint Region Marianas' mission is to provide installation management support
to all Department of Defense components and tenants through assigned
regional installations on Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands in support
of training in the Marian ...
Headquarters (Asan), at Nimitz Hill Annex
Nimitz Hill Annex is a community and census-designated place (CDP) in Asan-Maina, Guam. It contains the geographic feature of Nimitz Hill, and is located immediately northeast of the Nimitz Hill CDP in Piti. In normal conversation, the Nimitz Hil ...
* Naval Hospital Guam (Agana Heights)
* South Finegayan (Dededo), a military housing complex
* Andersen South (Yigo), formerly Marine Barracks Guam until its closure in 1992
* Fort Juan Muña, Guam National Guard (Tamuning)
In 2010, the U.S. military proposed building a new aircraft carrier berth on Guam and moving 8,600 Marines, and 9,000 of their dependents, to Guam from Okinawa
most commonly refers to:
* Okinawa Prefecture, Japan's southernmost prefecture
* Okinawa Island, the largest island of Okinawa Prefecture
* Okinawa Islands, an island group including Okinawa itself
* Okinawa (city), the second largest city in th ...
, Japan. Including the required construction workers, this buildup would increase Guam's population by a total of 79,000, a 49% increase over its 2010 population of 160,000. In a February 2010 letter, the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
sharply criticized these plans because of a water shortfall, sewage problems and the impact on coral reefs. As of 2022, the Marine Corps has decided to place 5,000 Marines on the island within the first half of the 2020s, with 1,300 already stationed on the base.
Government and politics
 Guam is governed by a popularly elected
Guam is governed by a popularly elected governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
and a unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature consisting of one house or assembly that legislates and votes as one. Unicameralism has become an increasingly common type of legislature, making up nearly ...
15-member legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
, whose members are known as senators. Its judiciary is overseen by the Supreme Court of Guam
The Supreme Court of Guam is the highest judicial body of the United States territory of Guam. The Court hears all appeals from the Superior Court of Guam and exercises original jurisdiction only in cases where a certified question is submitted ...
.
The District Court of Guam
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
is the court of United States federal jurisdiction in the territory. Guam elects one delegate to the United States House of Representatives, currently Republican James Moylan
James Camacho Moylan (born July 18, 1962) is an American politician and United States Army, Army veteran serving as the Non-voting members of the United States House of Representatives, delegate to the U.S. House of Representatives for Guam's a ...
. The delegate does not have a vote on the final passage of legislation, but is accorded a vote in committee, and the privilege to speak to the House.
U.S. citizens in Guam vote in a presidential straw poll for their choice in the U.S. presidential general election, but since Guam has no votes in the Electoral College
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliament ...
, the poll has no real effect. However, in sending delegates to the Republican and Democratic national conventions, Guam does have influence in the national presidential race. These delegates are elected by local party conventions.
Political status
 In the 1980s and early 1990s, there was a significant movement in favor of this U.S. territory becoming a
In the 1980s and early 1990s, there was a significant movement in favor of this U.S. territory becoming a commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
, which would give it a level of self-government similar to Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
. In a 1982 plebiscite
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a direct vote by the electorate (rather than their representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either binding (resulting in the adoption of a new policy) or adv ...
, voters indicated interest in seeking commonwealth status. However, the federal government rejected the version of a commonwealth that the government of Guam proposed, because its clauses were incompatible with the Territorial Clause
Article Four of the United States Constitution outlines the relationship between the various states, as well as the relationship between each state and the United States federal government. It also empowers Congress to admit new states and admini ...
(Art. IV, Sec. 3, cl. 2) of the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally including seven articles, the Constituti ...
. Other movements advocate U.S. statehood for Guam, union with the state of Hawaii, or union with the Northern Mariana Islands as a single territory, or independence.
The first Guam Constitutional Convention was funded by the 10th Guam Legislature and met from June 1, 1969, through June 29, 1970, with 43 elected delegates. The second Guam Constitutional Convention was convened on July 1, 1977, to create a constitution for Guam that would redefine the island's relationship with the US rather than merely modifying the existing relationship. The convention met periodically through October 31, 1977. Although approved at the federal level, the people of Guam overwhelmingly rejected the Constitution in a referendum held in August 1979, with 82% opposed. No new convention has been held pursuant to US congressional authority since 1979.
A Commission on Decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
was established in 1997 to educate the people of Guam about the various political status options in its relationship with the U.S.: statehood, free association, and independence. The island has been considering another non-binding plebiscite on decolonization since 1998. The group was dormant for some years. In 2013, the commission began seeking funding to start a public education campaign. There were few subsequent developments until late 2016. In early December 2016, the Commission scheduled a series of education sessions in various villages about the current status of Guam's relationship with the U.S. and the self-determination options that might be considered. The commission's current executive director is Edward Alvarez and there are ten members. The group is expected to release position papers on independence and statehood but the contents have not yet been completed.
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
is in favor of greater self-determination for Guam and other such territories. The UN's Special Committee on Decolonization
The United Nations Special Committee on the Situation with Regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples, or the Special Committee on Decolonization (C-24), is a committee of ...
has agreed to endorse the Governor's education plan. The commission's May 2016 report states: "With academics from the University of Guam, he Commissionwas working to create and approve educational materials. The Office of the Governor was collaborating closely with the Commission" in developing educational materials for the public.
The United States Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the management and conservation ...
approved a $300,000 grant for decolonization education, Edward Alvarez told the United Nations Pacific Regional Seminar in May 2016. "We are hopeful that this might indicate a shift in nited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
policy to its Non-Self-Governing Territories such as Guam, where they will be more willing to engage in discussions about our future and offer true support to help push us towards true self-governances and self-determination."
On July 31, 2020, the Government of Guam
The Government of Guam (GovGuam) is a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the president is the head of state and the governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory ...
joined the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) is an international organization established to facilitate the voices of unrepresented and marginalized nations and peoples worldwide. It was formed on 11 February 1991 at the Peace Pal ...
(UNPO).
Its future political status has been a matter of significant discussion, with public opinion polls indicating a strong preference of becoming a U.S state.
Villages
Agana Heights
Agana Heights () is one of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña (formerly Agana), in the central part of the island. United States Naval Hospital Guam is located in this lar ...
* Asan‑Maina
* Barrigada
Barrigada () is a village in the United States territory of Guam. A largely residential municipality, its main village is located south of the Antonio B. Won Pat International Airport near the intersections of Routes 8, 10, and 16. The communi ...
* Chalan Pago‑Ordot
* Dededo
Dededo (; Spanish: ) is the most populated village in the United States territory of Guam. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Dededo's population was just under 45,000 in 2020. The village is located on the coral plateau of Northern Guam. The gr ...
* Hågat
* Hagåtña
* Humåtak
* Inalåhan
* Malesso'
* Mangilao
Mangilao is a village on the eastern shore of the United States territory of Guam. The village's population has decreased slightly since the island's 2010 census.
Cliffs lie along much of the village's shoreline provide dramatic views, including ...
* Mongmong‑Toto‑Maite
* Piti
In relation to a mortgage, PITI (pronounced like the word "pity") is the sum of the monthly principal, interest, taxes, and insurance, the component costs that add up to the monthly mortgage payment in most mortgages. That is, PITI is the sum of th ...
* Sånta Rita-Sumai
* Sinajana
Sinajana () is the smallest of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam by area. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña (formerly Agana). The village's name may have come from the word "china-jan," cookware used to c ...
* Talo'fo'fo
* Tamuning
Tamuning, also known as Tamuning-Tumon-Harmon (), is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The village of Tamuning is the economic center of Guam, containing tourist center Tumon, Harmon Industrial Park, ...
* Yigo
Yigo, Guam (; ) is the northernmost village of the United States territory of Guam, and is the location of Andersen Air Force Base. The municipality of Yigo is the largest village on the island in terms of area. It contains a number of populated pl ...
* Yona
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gr ...
The entirety of Guam is treated as both a territory and a county equivalent
In the United States, a county or county equivalent is an administrative subdivision of a state or territory, typically with defined geographic boundaries and some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 states, whil ...
by the US Census
The United States census (plural censuses or census) is a census that is legally mandated by the Constitution of the United States. It takes place every ten years. The first census after the American Revolution was taken in 1790 under Secretar ...
, but the USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
counts the villages as county equivalents.
Transportation and communications
Most of the island has state-of-the-art mobile phone services and high-speed internet widely available through either cable orDSL
Digital subscriber line (DSL; originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric di ...
. Guam was added to the North American Numbering Plan
The North American Numbering Plan (NANP) is an integrated telephone numbering plan for twenty-five regions in twenty countries, primarily in North America and the Caribbean. This group is historically known as World Zone 1, World Numbering Zone ...
(NANP) in 1997. The country code 671 became NANP area code 671
The area code 671 is the local telephone area code of the United States territory of Guam. It was created with the beginning of permissive dialing on July 1, 1997, replacing Guam's previous International Telecommunication Union country code 671 at ...
. This removed the barrier of high-cost international long-distance calls to the continental U.S.
Guam is a major hub for submarine communications cables
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables were laid beginning in the 1850s and car ...
between the Western U.S., Hawaii, Australia and Asia. Guam currently serves twelve submarine cables, with most continuing to China. In 2012 ''Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
'' stated that the island has "tremendous bandwidth" and internet prices comparable to those of the U.S. Mainland due to being at the junction of undersea cables.
In 1899, the local postage stamps were overprinted "Guam" as was done for the other former Spanish colonies, but this was discontinued shortly thereafter and regular U.S. postage stamps have been used ever since. Guam is part of the U.S. Postal System ( postal abbreviation: GU, ZIP code range: 96910–96932). Mail to Guam from the U.S. mainland is considered domestic and no additional charges are required. Private shipping companies, such as FedEx, UPS, and DHL, however, have no obligation to do so, and do not regard Guam as domestic.
The speed of mail traveling between Guam and the states varies depending on size and time of year. Light, first-class items generally take less than a week to or from the mainland. Larger first-class or Priority items can take a week or two. Fourth-class mail, such as magazines, are transported by sea after reaching Hawaii. Most residents use post office boxes or private mail boxes, although residential delivery is becoming increasingly available.
The Port of Guam is the island's lifeline, because most products must be shipped into Guam for consumers. It receives the weekly calls of the Hawaii-based shipping line Matson, Inc. whose container ships connect Guam with Honolulu, Hawaii; Los Angeles, California; Oakland, California; and Seattle, Washington. The port is also the regional transhipment hub for over 500,000 customers throughout the Micronesian region. The port is the shipping and receiving point for containers designated for the island's U.S. Department of Defense installations, Andersen Air Force Base and Commander, Naval Forces Marianas and eventually the Third Marine Expeditionary Force.
Guam is served by the Antonio B. Won Pat International Airport. The island is outside the United States customs zone, so Guam is responsible for establishing and operating its own customs and quarantine agency and jurisdiction. Therefore, the U.S. Customs and Border Protection
United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is the largest federal law enforcement agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security. It is the country's primary border control organization, charged with regulating and facilita ...
only carries out immigration, but not customs functions. Since Guam is under federal immigration jurisdiction, passengers arriving directly from the United States skip immigration and proceed directly to Guam Customs and Quarantine.
Due to the Guam and CNMI visa waiver program for certain countries, an eligibility pre-clearance check is carried on Guam for flights to the States. For travel from the Northern Mariana Islands to Guam, a pre-flight passport and visa check is performed before boarding the flight to Guam. On flights from Guam to the Northern Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
, no immigration check is performed. Traveling between Guam and the States through a foreign point requires a passport.
Most residents travel within Guam using personally owned vehicles. The Guam Regional Transit Authority provides fixed route bus and paratransit services, and some commercial companies operate buses between tourist-frequented locations.
Education

Guam Public Library System
Guam Public Library System (Chamorro language, Chamoru: Sisteman Laibirihan Pupbleko Guåhan) is the public library system of the United States territory of Guam. The main library is the Nieves M. Flores Memorial Library at 254 Martyr Street in t ...
operates the Nieves M. Flores Memorial Library in Hagåtña and five branch libraries.
The Guam Department of Education
The Guam Department of Education (GDOE), formerly the Guam Public School System, is a school district that serves the United States territory of Guam. The school district can be thought of as analogous to the school districts of other cities a ...
serves the entire island of Guam. In 2000, 32,000 students attended Guam's public schools, including 26 elementary schools, eight middle schools, and six high schools and alternative schools. Guam Public Schools have struggled with problems such as high dropout rates and poor test scores.
Guam's educational system has always faced unique challenges as a small community located from the U.S. mainland with a very diverse student body including many students who come from backgrounds without traditional American education. An economic downturn in Guam since the mid-1990s has compounded the problems in schools.
Before September 1997, the U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, t ...
partnered with the Guam Board of Education. In September 1997, the Department of Defense Education Activity
The Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA) is a federal school system headquartered in Alexandria, Virginia, responsible for planning, directing, coordinating, and managing prekindergarten through 12th grade educational programs on beh ...
(DoDEA) opened its own schools for children of military personnel. DoDEA schools, which also serve children of some federal civilian employees, had an attendance of 2,500 in 2000. DoDEA Guam operates three elementary/middle schools and one high school.
The University of Guam
University of Guam () (U.O.G.) is a public university, public land-grant university in Mangilao, Guam. It is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges and offers thirty-four degree programs at the undergraduate level and ele ...
(UOG) and Guam Community College, both fully accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges
The Western Association of Schools and Colleges (WASC ( )) provided accreditation of public and private universities, colleges, secondary and elementary schools in California and Hawaii, the territories of Guam, American Samoa and Northern ...
, offer courses in higher education. UOG is a member of the exclusive group of only 106 land-grant institutions in the entire United States. Pacific Islands University is a small Christian liberal arts institution, nationally accredited by the Transnational Association of Christian Colleges and Schools
The Transnational Association of Christian Colleges and Schools (TRACS) is a U.S. based institutional accreditation organization that focuses on Christian colleges, universities, and seminaries seeking collegiate accreditation in the United Sta ...
.
Health care
The Government of Guam maintains the island's main health care facility,Guam Memorial Hospital
Guam Memorial Hospital is a rural general hospital located in Tamuning, Guam and is the only public hospital serving the island of Guam. The hospital has 161 licensed acute care beds, plus 40 beds at its off-site, long-term care Skilled Nursing F ...
, in Tamuning
Tamuning, also known as Tamuning-Tumon-Harmon (), is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The village of Tamuning is the economic center of Guam, containing tourist center Tumon, Harmon Industrial Park, ...
. U.S. board certified doctors and dentists practice in all specialties. The U.S. Naval Hospital in Agana Heights
Agana Heights () is one of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña (formerly Agana), in the central part of the island. United States Naval Hospital Guam is located in this lar ...
serves active-duty members and dependents of the military community.
There is one subscriber-based air ambulance
Air medical services are the use of aircraft, including both fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters to provide various kinds of urgent medical care, especially prehospital, emergency and critical care to patients during aeromedical evacuation an ...
located on the island, CareJet, which provides emergency patient transportation across Guam and surrounding islands. A private hospital, the Guam Regional Medical City, opened in early 2016. Medicaid is accepted in Guam.
See also
*51st state
"51st state" is a phrase used in the United States of America to refer to the idea of adding an additional state to the current 50-state Union. Proposals for a 51st state may include granting statehood to one of the U.S. territories or Washing ...
* Index of Guam-related articles
* Lists of hospitals in the United States#Insular areas
* List of people from Guam
* Outline of Guam
* Voting in Guam
Notes
References
Works cited
* * *Further reading
* * *External links
*''Guampedia''
– Guam's online Encyclopedia
"Guam Society of America"
fosters the Chamorro language, culture, and traditions
''The Insular Empire: America in the Mariana Islands''
PBS documentary film website.
Guam
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
.
U.S. Census Bureau: Island Areas Census 2000
from the U.S.
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
.
*
*
Guam Census
() {{coord, 13, 30, N, 144, 48, E, region:GU_type:isle_scale:250000, display=title 1898 establishments in Oceania Dependent territories in Micronesia Dependent territories in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Former Spanish colonies Insular areas of the United States Island countries Islands of Oceania Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Pacific islands of the United States Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1898 World War II sites