|
Typhoon Pamela (1976)
Typhoon Pamela was a powerful typhoon that struck the U.S. territory of Guam in May 1976, causing about $500 million in damage (USD). The sixth named storm and third typhoon of the 1976 Pacific typhoon season, Pamela developed on May 14 from a trough in the Federated States of Micronesia in the area of the Nomoi Islands. It executed a counterclockwise loop and slowly intensified, bringing heavy rains to the islands in the region. Ten people died on Chuuk due to a landslide. After beginning a steady northwest motion toward Guam, Pamela attained its peak winds of 240 km/h (150 mph). On May 21, the large eye of the typhoon crossed Guam, producing typhoon-force winds (greater than 118 km/h or 73 mph) for a period of 18 hours. An estimated 80% of the buildings on the island were damaged to some degree, including 3,300 houses that were destroyed. Pamela's slow motion produced 856 mm (33.7 in) of rainfall, making May 1976 the wett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
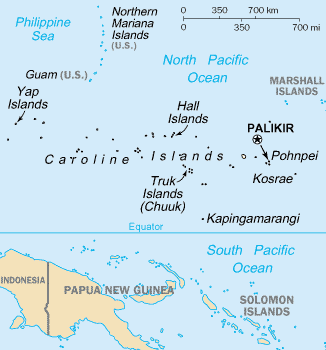
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately 3,540 kilometers (2,200 miles), from the westernmost island, Tobi (island), Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a Administrative divisions of the Federated States of Micronesia, state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
54th Weather Reconnaissance Squadron
54 may refer to: * 54 (number) * one of the years 54 BC, AD 54, 1954, 2054 * ''54'' (novel), a 2002 novel by Wu Ming * Studio 54, a New York City nightclub from 1977 until 1981 * ''54'' (film), a 1998 American drama film about the club * ''54'' (album), a 2010 album by Metropole Orkest * "Fifty Four", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Arch Stanton'', 2014 * 54th Division (other) * 54th Regiment of Foot (other) 54th Regiment of Foot The 54th Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1755. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 39th (Dorsetshire) Regiment of Foot to form the Dorsetshire Regiment in 1881. Histor ... * 54th Infantry (other) {{number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Warnings And Watches
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local population and civil authorities to make appropriate preparation for the cyclone, including evacuation of vulnerable areas where necessary. It is important that interests throughout the area of an alert make preparations to protect life and property, and do not disregard it on the strength of the detailed forecast track. Western hemisphere New tropical cyclone position and forecast information is available at least every twelve hours in the Southern Hemisphere and at least every six hours in the Northern Hemisphere from Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers. In conjunction with the National Hurricane Center, the national meteorological and hydrological services of Central America, the northern Atlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelf, continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named for Vitus Bering, a Denmark, Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean. The Bering Sea is separated from the Gulf of Alaska by the Alaska Peninsula. It covers over and is bordered on the east and northeast by Alaska, on the west by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula, on the south by the Alaska Peninsula and the Aleutian Islands and on the far north by the Bering Strait, which connects the Bering Sea to the Arctic Ocean's Chukchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a high-pressure area at the divergence of trade winds and the westerlies. Origin of the term A likely and documented explanation is that the term is derived from the "dead horse" ritual of seamen (see Flogging a dead horse#Earlier meaning, Beating a dead horse). In this practice, the seaman paraded a straw-stuffed effigy of a horse around the deck before throwing it overboard. Seamen were paid partly in advance before a long voyage, and they frequently spent their pay all at once, resulting in a period of time without income. If they got advances from the ship's paymaster, they would incur debt. This period was called the "dead horse" time, and it usually lasted a month or two. The seaman's ceremony was to celebrate having worked off the "d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyewall Replacement Cycle
In meteorology, eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones, generally with winds greater than , or major hurricanes ( Category 3 or above). When tropical cyclones reach this intensity, and the eyewall contracts or is already sufficiently small, some of the outer rainbands may strengthen and organize into a ring of thunderstorms—a new, outer eyewall—that slowly moves inward and robs the original, inner eyewall of its needed moisture and angular momentum. Since the strongest winds are in a tropical cyclone's eyewall, the storm usually weakens during this phase, as the inner wall is "choked" by the outer wall. Eventually the outer eyewall replaces the inner one completely, and the storm may re-intensify. The discovery of this process was partially responsible for the end of the U.S. government's hurricane modification experiment Project Stormfury. This project set out to seed clouds outside the eyewall, apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Sustained Wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are determined via their sampling and averaging the sampled results over a period of time. Wind measuring has been standardized globally to reflect the winds at above the Earth's surface, and the maximum sustained wind represents the highest average wind over either a one-minute (US) or ten-minute time span (see the definition, below), anywhere within the tropical cyclone. Surface winds are highly variable due to friction between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, as well as near hills and mountains over land. Over the ocean, satellite imagery determines the value of the maximum sustained winds within a tropical cyclone. Land, ship, aircraft reconnaissance observations, and radar imagery can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





