The genocide of indigenous peoples, colonial genocide, or settler genocide is elimination of entire communities of
indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
as part of
colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
. Genocide of the native population is especially likely in cases of
settler colonialism
Settler colonialism is a structure that perpetuates the elimination of Indigenous people and cultures to replace them with a settler society. Some, but not all, scholars argue that settler colonialism is inherently genocidal. It may be enacted ...
,
with some scholars arguing that settler colonialism is inherently genocidal.
While the concept of
genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
was formulated by
Raphael Lemkin
Raphael Lemkin ( pl, Rafał Lemkin; 24 June 1900 – 28 August 1959) was a Polish lawyer who is best known for coining the term ''genocide'' and initiating the Genocide Convention, an interest spurred on after learning about the Armenian genocid ...
in the mid-20th century, the expansion of various European colonial powers such as the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
empires and the subsequent establishment of
colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
on indigenous territories frequently involved acts of genocidal violence against indigenous groups in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
,
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
,
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. According to Lemkin,
colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
was in itself "intrinsically genocidal". He saw this genocide as a two-stage process, the first being the destruction of the indigenous population's way of life. In the second stage, the newcomers impose their way of life on the indigenous group. According to
David Maybury-Lewis
David Henry Peter Maybury-Lewis (5 May 1929 – 2 December 2007) was a British anthropologist, ethnologist of lowland South America, activist for indigenous peoples' human rights, and professor emeritus of Harvard University.
Born in Hyderaba ...
, imperial and colonial forms of genocide are enacted in two main ways, either through the deliberate clearing of territories of their original inhabitants in order to make them exploitable for purposes of resource extraction or colonial settlements, or through enlisting indigenous peoples as
forced laborers
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
in colonial or imperialist projects of resource extraction. The designation of specific events as genocidal is often controversial.
Some scholars, among them Lemkin, have argued that
cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
, sometimes called
ethnocide
Ethnocide is the extermination of cultures.
Reviewing the legal and the academic history of the usage of the terms genocide and ethnocide, Bartolomé Clavero differentiates them by stating that "Genocide kills people while ethnocide kills social ...
, should also be recognized. A people group may continue to exist, but if it is prevented from perpetuating its group identity by prohibitions of its cultural and religious practices, practices which are the basis of its group identity, this may also be considered a form of genocide. Examples that can be considered this form of genocide include the treatment of
Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live ...
and
Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
by the
Government of China
The Government of the People's Republic of China () is an Authoritarianism, authoritarian political system in the China, People's Republic of China under the exclusive political leadership of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It consists of Leg ...
, the treatment of
Native Americans by citizens of the United States and/or agents of the United States government, and the treatment of
First Nations peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
by the Canadian government.
Genocide debate
The concept of genocide was coined in 1944 by
Raphael Lemkin
Raphael Lemkin ( pl, Rafał Lemkin; 24 June 1900 – 28 August 1959) was a Polish lawyer who is best known for coining the term ''genocide'' and initiating the Genocide Convention, an interest spurred on after learning about the Armenian genocid ...
:
After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, this concept of genocide was adopted by the United Nations in 1948. For Lemkin, genocide was broadly defined and included all attempts to destroy a specific ethnic group, whether strictly physical through mass killings, or cultural or psychological through oppression and destruction of indigenous ways of life.
The UN definition, which is used in
international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
, is narrower than Lemkin's, and states that genocide is:
"any of the following acts committed with
intent to destroy
''Intent to Destroy: Death, Denial, & Depiction'' is a 2017 documentary film directed by Joe Berlinger about the Armenian genocide.
Production
Berlinger embedded in the filming crew of '' The Promise'' to shoot ''Intent to Destroy''. The film p ...
,
in whole or in part, a national, ethnic, racial or religious group," as such:
:(a) "Killing members of the group;"
:(b) "Causing serious bodily or mental harm to members of the group;"
:(c) "Deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part;"
:(d) "Imposing measures intended to prevent births within the group;"
:(e) "Forcibly transferring children of the group to another group."
The determination of whether a historical event should or should not be considered a genocide can be a matter of scholarly debate. Historians often draw on broader definitions such as Lemkin's, which sees colonialist violence against indigenous peoples as inherently genocidal. For example, in the case of the
colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short ter ...
, where the
indigenous people of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Ame ...
declined by up to 90% in the first centuries of European colonization, how much of the population decline is attributable to genocide is debatable because disease is considered the main cause of this decline due to the fact that the introduction of disease was partially unintentional.
Some genocide scholars separate the population declines which are due to
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
from the genocidal aggression of one group towards another. Some scholars argue that an intent to commit a genocide is not needed, because a genocide may be the cumulative result of minor conflicts in which settlers, colonial agents or state agents perpetrate violent acts against minority groups. Others argue that the dire consequences of
European diseases among many New World populations were exacerbated by different forms of genocidal violence, and they also argue that intentional deaths and unintentional deaths cannot easily be separated from each other. Some scholars regard the colonization of the Americas as genocide, since they argue it was largely achieved through systematically exploiting, removing and destroying specific ethnic groups, which would create environments and conditions for such disease to proliferate.
According to a 2020 study by Tai S Edwards and Paul Kelton, recent scholarship shows "that colonizers bear responsibility for creating conditions that made natives vulnerable to infection, increased mortality, and hindered population recovery. This responsibility intersected with more intentional and direct forms of violence to depopulate the Americas... germs can no longer serve as the basis for denying American genocides."
Indigenous peoples of the Americas (pre-1948)
It is estimated that during the initial
Spanish conquest of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions of ...
, up to eight million indigenous people died, primarily through the spread of
Afro-Eurasian diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that ar ...
.
Simultaneously, wars and atrocities waged by Europeans against Native Americans also resulted in deaths. Mistreatment and killing of Native Americans continued for centuries, in every area of the Americas, including the areas that would become Canada, the United States, Mexico, Brazil, and the Southern Cone countries such as Paraguay, Chile, and Argentina. In the United States, some scholars (examples listed below) state that the
American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
and the doctrine of
manifest destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
contributed to the genocide, with one major event cited being the
Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
.
Categorization as a genocide
Historians and scholars whose work has examined this history in the context of genocide have included historian Jeffrey Ostler,
historian
David Stannard
David Edward Stannard (born 1941) is an American historian and Professor of American Studies at the University of Hawaii. He is particularly known for his book '' American Holocaust'' (Oxford University Press, 1992), in which he argues that Europea ...
, anthropological demographer
Russell Thornton, Indigenous Studies scholar
Vine Deloria, Jr., as well as scholar-activists such as
Russell Means
Russell Charles Means (November 10, 1939 – October 22, 2012) was an Oglala Lakota activist for the rights of Native Americans, libertarian political activist, actor, musician, and writer. He became a prominent member of the American Ind ...
and
Ward Churchill
Ward LeRoy Churchill (born 1947) is an American author and political activist. He was a professor of ethnic studies at the University of Colorado Boulder from 1990 until 2007. . In his book ''
American Holocaust'' Stannard compares the events of colonization in the Americas to the definition of genocide which is written in the
1948 UN convention, and he writes that,
In light of the U.N. language—even putting aside some of its looser constructions—it is impossible to know what transpired in the Americas during the sixteenth, seventeenth, eighteenth, and nineteenth centuries and not conclude that it was genocide.
Thornton describes the direct consequences of
war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
fare,
violence
Violence is the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy. Other definitions are also used, such as the World Health Organization's definition of violence as "the intentional use of physical force or Power (social and p ...
and
massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
s as genocides, many of which had the effect of wiping out entire
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
s. Political scientist
Guenter Lewy
Guenter Lewy (born 22 August 1923) is a German-born American author and political scientist who is a professor emeritus of political science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. His works span several topics, but he is most often associat ...
states that "even if up to 90 percent of the reduction in Indian population was the result of disease, that leaves a sizable death toll caused by mistreatment and violence."
Native American studies professor
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (born September 10, 1938) is an American historian, writer, and activist, known for her 2014 book ''An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States''.
Early life and education
Born in San Antonio, Texas, in 1938 to ...
states,
Proponents of the default position emphasize attrition by disease despite other causes equally deadly, if not more so. In doing so they refuse to accept that the colonization of America was genocidal by plan, not simply the tragic fate of populations lacking immunity to disease.
By 1900, the indigenous population in the Americas declined by more than 80%, and by as much as 98% in some areas. The effects of diseases such as
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
,
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
and
cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
during the first century of colonialism contributed greatly to the death toll, while violence, displacement and warfare against the Indians by colonizers contributed to the death toll in subsequent centuries.
As detailed in ''American Philosophy: From Wounded Knee to the Present'' (2015),
It is also apparent that the shared history of the hemisphere is one which is framed by the dual tragedies of genocide and slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, both of which are part of the legacy of the European invasions of the past 500 years. Indigenous people both north and south were displaced, died of disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
, and were killed by Europeans through slavery, rape, and war. In 1491, about 145 million people lived in the western hemisphere. By 1691, the population of indigenous Americans had declined by 90–95 percent, or by around 130 million people.
According to geographers from
University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
, the colonization of the Americas by Europeans killed so many people it resulted in
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
and
global cooling
Global cooling was a conjecture, especially during the 1970s, of imminent cooling of the Earth culminating in a period of extensive glaciation, due to the cooling effects of aerosols or orbital forcing.
Some press reports in the 1970s specul ...
. UCL Geography Professor Mark Maslin, one of the co-authors of the study, states that the large death toll also boosted the economies of Europe: "the depopulation of the Americas may have inadvertently allowed the Europeans to dominate the world. It also allowed for the Industrial Revolution and for Europeans to continue that domination."
Spanish colonization of the Americas

It is estimated that during the initial
Spanish conquest of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions of ...
up to eight million indigenous people died, primarily through the spread of
Afro-Eurasian diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that ar ...
,
in a series of events that have been described as the first large-scale act of genocide of the modern era. Acts of brutality and systematic annihilation against the
Taíno People
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
of the
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
prompted
Dominican friar
Bartolomé de las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar ...
to write ('
A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name ...
') in 1542—an account that had a wide impact throughout the western world as well as contributing to the
abolition of indigenous slavery in all Spanish territories the same year it was written. Las Casas wrote that the native population on the Spanish colony of
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
had been reduced from 400,000 to 200 in a few decades. His writings were among those that gave rise to ''
Spanish Black Legend
The Black Legend ( es, Leyenda negra) or the Spanish Black Legend ( es, Leyenda negra española, link=no) is a theorised historiographical tendency which consists of anti-Spanish and anti-Catholic propaganda. Its proponents argue that its ro ...
'', which
Charles Gibson
Charles deWolf Gibson (born March 9, 1943) is an American broadcast television anchor, journalist and podcaster. Gibson was a host of ''Good Morning America'' from 1987 to 1998 and again from 1999 to 2006, and the anchor of ''World News with Char ...
describes as "the accumulated tradition of propaganda and Hispanophobia according to which the Spanish Empire is regarded as cruel, bigoted, degenerate, exploitative and self-righteous in excess of reality".
Historian
Andrés Reséndez at the
University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university near Davis, California. Named a Public Ivy, it is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The institut ...
asserts that even though disease was a factor, the indigenous population of Hispaniola would have rebounded the same way Europeans did following the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
if it were not for the constant enslavement they were subject to.
He says that "among these human factors, slavery was the major killer" of Hispaniola's population, and that "between 1492 and 1550, a nexus of slavery, overwork and famine killed more natives in the Caribbean than smallpox, influenza or malaria." Noble David Cook, writing about the
Black Legend conquest of the Americas wrote, "There were too few Spaniards to have killed the millions who were reported to have died in the first century after Old and New World contact." He instead estimates that the death toll was caused by diseases like
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
,
which according to some estimates had an 80–90% fatality rate in Native American populations.
[ ] However, historian Jeffrey Ostler has argued that Spanish colonization created conditions for disease to spread, for example, "careful studies have revealed that it is highly unlikely that members" of Hernando de Soto's 1539 expedition in the American South "had smallpox or measles. Instead, the disruptions caused by the expedition increased vulnerability of Native people to diseases including syphilis and dysentery, already present in the Americas, and malaria, a disease recently introduced from the eastern hemisphere."
With the initial conquest of the Americas completed, the Spanish implemented the
encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
system in 1503. In theory, the ''encomienda'' placed groups of indigenous peoples under Spanish oversight to foster cultural assimilation and
conversion to Catholicism
Catholicisation refers mainly to the conversion of adherents of other religions into Catholicism, and the system of expanding Catholic influence in politics. Catholicisation was a policy of the Holy See through the Papal States, Holy Roman Empi ...
, but in practice led to the legally sanctioned forced labor and resource extraction under brutal conditions with a high death rate. Though the Spaniards did not set out to exterminate the indigenous peoples, believing their numbers to be inexhaustible, their actions led to the annihilation of entire tribes such as the
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater ...
. Many Arawaks died from lethal forced labor in the mines, in which a third of workers died every six months.
According to historian
David Stannard
David Edward Stannard (born 1941) is an American historian and Professor of American Studies at the University of Hawaii. He is particularly known for his book '' American Holocaust'' (Oxford University Press, 1992), in which he argues that Europea ...
, the ''encomienda'' was a genocidal system which "had driven many millions of native peoples in Central and South America to early and agonizing deaths.".
According to Doctor
Clifford Trafzer Clifford may refer to:
People
*Clifford (name), an English given name and surname, includes a list of people with that name
*William Kingdon Clifford
*Baron Clifford
*Baron Clifford of Chudleigh
*Baron de Clifford
*Clifford baronets
*Clifford fami ...
, Professor at
UC Riverside
The University of California, Riverside (UCR or UC Riverside) is a public land-grant research university in Riverside, California. It is one of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The main campus sits on in a suburban distr ...
, in the 1760s, an expedition dispatched to fortify California, led by
Gaspar de Portolà
Gaspar is a given and/or surname of French, German, Portuguese, and Spanish origin, cognate to Casper (given name) or Casper (surname).
It is a name of biblical origin, per Saint Gaspar, one of the wise men mentioned in the Bible.
Notable peo ...
and
Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size ...
, was marked by slavery,
forced conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which ...
s, and genocide through the introduction of disease.
British colonization of the Americas
Beaver Wars
During the
Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
of the seventeenth century, the
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
effectively destroyed several large tribal confederacies, including the
Mohicans
The Mohican ( or , alternate spelling: Mahican) are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, who ...
, Huron (
Wyandot
Wyandot may refer to:
Native American ethnography
* Wyandot people, also known as the Huron
* Wyandot language
* Wyandot religion
Places
* Wyandot, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Wyandot County, Ohio
* Camp Wyandot, a Camp Fire Boys and ...
),
Neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
,
Erie
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 a ...
,
Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
(Conestoga), and northern
Algonquins
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely related to the Odawa, Potawatomi, ...
, with the extreme brutality and exterminatory nature of the mode of warfare practised by the Iroquois causing some historians to label these wars as acts of genocide committed by the Iroquois Confederacy.
Kalinago genocide, 1626
The Kalinago genocide was the
massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
of some 2,000
Island Carib
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language ...
s by
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
settlers in 1628 in
St. Kitts.
The Carib Chief
Tegremond became uneasy with the increasing number of English and French settlers occupying St. Kitts. This led to confrontations, which led him to plot the settlers' elimination with the aid of other Island Caribs. However, his scheme was betrayed by an Indian woman called Barbe, to
Thomas Warner and
Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc
Pierre Belain, sieur d'Esnambuc (; 1585–1636) was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635.
Biography Youth
Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc wa ...
. Taking action, the English and French settlers invited the Caribs to a party where they became intoxicated. When the Caribs returned to their village, 120 were killed in their sleep, including Chief Tegremond. The following day, the remaining 2,000–4,000 Caribs were forced into the area of
Bloody Point and
Bloody River, where over 2,000 were massacred, though 100 settlers were also killed. One Frenchman went mad after being struck by a
manchineel
The manchineel tree (''Hippomane mancinella'') is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae). Its native range stretches from tropical southern North America to northern South America.
The name "manchineel" (sometimes spel ...
-
poisoned arrow
Arrow poisons are used to poison arrow heads or darts for the purposes of hunting and warfare. They have been used by indigenous peoples worldwide and are still in use in areas of South America, Africa and Asia. Notable examples are the poisons se ...
. The remaining Caribs fled, but by 1640, those not already enslaved were removed to
Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
.
Attempted extermination of the Pequot, 1636–1638
The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place between 1636 and 1638 in New England between the
Pequot
The Pequot () are a Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut including the Eastern Pequot Tribal Nation, or th ...
tribe and an alliance of the
colonists
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
of the
Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its ...
,
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
, and
Saybrook colonies and their allies from the
Narragansett and
Mohegan
The Mohegan are an Algonquian Native American tribe historically based in present-day Connecticut. Today the majority of the people are associated with the Mohegan Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe living on a reservation in the easte ...
tribes. The war concluded with the decisive defeat of the Pequots. The
Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
and
colonies offered bounties for the heads of killed hostile Indians, and later for just their scalps, during the
Pequot War
The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place between 1636 and 1638 in New England between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Narragans ...
in the 1630s;
Connecticut specifically reimbursed
Mohegan
The Mohegan are an Algonquian Native American tribe historically based in present-day Connecticut. Today the majority of the people are associated with the Mohegan Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe living on a reservation in the easte ...
s for slaying the
Pequot
The Pequot () are a Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut including the Eastern Pequot Tribal Nation, or th ...
in 1637.
At the end, about 700 Pequots had been killed or taken into captivity. Hundreds of prisoners were sold into slavery to the West Indies; other survivors were dispersed as captives to the victorious tribes. The result was the elimination of the Pequot tribe as a viable polity in
Southern New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces of ...
, and the colonial authorities classified them as extinct. However, members of the Pequot tribe still live today as a federally recognized tribe.
Massacre of the Narragansett people, 1675
The Great Swamp Massacre was committed during
King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England coloni ...
by colonial militia of
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
on the
Narragansett tribe
The Narragansett people are an Algonquian American Indian tribe from Rhode Island. Today, Narragansett people are enrolled in the federally recognized Narragansett Indian Tribe. They gained federal recognition in 1983.
The tribe was nearly lan ...
in December 1675. On 15 December of that year, Narraganset warriors attacked the
Jireh Bull Blockhouse
The Jireh Bull Blockhouse (RI-926, also known as the Jireh Bull Garrison House or Jireh Bull Block House) is an historic archaeological site on Middlebridge Road in South Kingstown, Rhode Island. In 1657 a blockhouse was built on the site by Jire ...
and killed at least 15 people. Four days later, the colonial militia from
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the British America, first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the pa ...
,
Connecticut Colony
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
, and
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
were led to the main Narragansett town in South Kingstown, Rhode Island. The settlement was burned, its inhabitants (including women and children) killed or evicted, and most of the tribe's winter stores destroyed. It is believed that at least 97 Narragansett warriors and 300 to 1,000 non-combatants were killed, though exact figures are unknown.
[Gott, Richard (2004). ''Cuba: A new history''. Yale University Press. p. 32.] The massacre was a critical blow to the Narragansett tribe during the period directly following the massacre. However, much like the Pequot, the Narragansett people continue to live today as a federally recognized tribe.
French and Indian War and Pontiac's War, 1754–1763
On 12 June 1755, during the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, Massachusetts governor
William Shirley
William Shirley (2 December 1694 – 24 March 1771) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of the British American colonies of Massachusetts Bay and the Bahamas. He is best known for his role in organi ...
issued a bounty of £40 for a male Indian scalp, and £20 for scalps of Indian females or of children under 12 years old.
[ In 1756, Pennsylvania lieutenant-governor ]Robert Hunter Morris
Robert Hunter Morris ( – 27 January 1764), was a prominent governmental figure in Colonial Pennsylvania, serving as governor of Pennsylvania and Chief Justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court.
Early life and education
Morris was born in ...
, in his declaration of war against the Lenni Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
(Delaware) people, offered "130 Pieces of Eight
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
, for the Scalp of Every Male Indian Enemy, above the Age of Twelve Years", and "50 Pieces of Eight for the Scalp of Every Indian Woman, produced as evidence of their being killed."Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
, Colonel Henry Bouquet
Henry Bouquet (born Henri Louis Bouquet; 1719 – 2 September 1765) was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American ...
conspired with his superior, Sir Jeffrey Amherst, to infect hostile Native Americans through biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an act of war. Bio ...
with smallpox blanket
The siege of Fort Pitt took place during June and July 1763 in what is now the city of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The siege was a part of Pontiac's War, an effort by Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to remov ...
s.
Canada
 On 13 April 1709, New France
On 13 April 1709, New France intendant
An intendant (; pt, intendente ; es, intendente ) was, and sometimes still is, a public official, especially in France, Spain, Portugal, and Latin America. The intendancy system was a centralizing administrative system developed in France. In ...
Jacques Raudot
Jacques Raudot (1638 - 20 February 1728, Paris) was the co-Intendant of New France between 1705 and 1710 with his son Antoine-Denis Raudot.
In 1709 Raudot issued an ordinance to clarify whether individuals could legally own slaves, in New Franc ...
passed the ''Ordinance
Ordinance may refer to:
Law
* Ordinance (Belgium), a law adopted by the Brussels Parliament or the Common Community Commission
* Ordinance (India), a temporary law promulgated by the President of India on recommendation of the Union Cabinet
* ...
Rendered on the Subject of the Negroes and the Savages Called Panis
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern p ...
'', legalizing the purchase and possession of indigenous slaves in New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
. When Raudot pronounced indigenous slavery to be legal in New France, the practice had already been well established in the Native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
alliances throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. After the 1709 Ordinance came into effect, slavery in the colony grew exponentially. Natives flooded the slave market in the course of intense diplomacy with the French to prevent colonial encroachment of Native land. Therefore, the flood of Native slaves in the St. Lawrence largely came from their Western counterparts. According to Rushforth, "by narrowing the target to a specific set of victims known as the 'Panis nation,' Raudot and his successors created a North American counterpart to the African kingdom of Nigritie: a distant and populous nation at war with more proximate allies, poorly understood but clearly identified as legally and morally enslavable". Effectively, this meant Western Natives were strengthening future adversaries in the east, with their own slaves, in a struggle to preserve their land.
Although not without conflict, French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
' early interactions with Canada's indigenous populations were relatively peaceful in comparison to the expansionist and aggressive policies of British North America. First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
and Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives ...
peoples played a critical part in the development of French colonies in Canada, particularly for their role in assisting French coureur des bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; plural: coureurs de(s) bois) was an independent entrepreneurial French-Canadian trader who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with First Nations peoples by e ...
and voyageurs
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ' ...
in the exploration of the continent during the North American fur trade
The North American fur trade is the commercial trade in furs in North America. Various Indigenous peoples of the Americas traded furs with other tribes during the pre-Columbian era. Europeans started their participation in the North American fur ...
.Shanawdithit
Shanawdithit (ca. 1801 – June 6, 1829), also noted as Shawnadithititis, Shawnawdithit, Nancy April and Nancy Shanawdithit, was the last known living member of the Beothuk people, who inhabited Newfoundland, Canada. Remembered for her contr ...
, the Beothuk
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of indigenous people who lived on the island of Newfoundland.
Beginning around AD 1500, the Beothuk culture formed. This appeared to be the most recent cultural manifestation of peoples w ...
people, the indigenous people of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
were officially declared extinct after suffering epidemics, starvation, loss of access to food sources, and displacement by English and French fishermen and traders. Scholars disagree in their definition of genocide in relation to the Beothuk, and the parties have differing political agendas. While some scholars believe that the Beothuk died out due to the elements noted above, another theory is that Europeans conducted a sustained campaign of genocide against them.
More recent understandings of the concept of "cultural genocide" and its relation to settler colonialism have led modern scholars to a renewed discussion of the genocidal aspects of the Canadian states' role in producing and legitimating the process of physical and cultural destruction of Indigenous people. In the 1990s some scholars began pushing for Canada to recognize the ''Canadian Indian residential school system
In Canada, the Indian residential school system was a network of boarding schools for Indigenous peoples. The network was funded by the Canadian government's Department of Indian Affairs and administered by Christian churches. The school sy ...
'' as a genocidal process rooted in colonialism. This public debate led to the formation of the Canadian Truth and Reconciliation Commission which was formed in 2008.Canadian Indian residential school system
In Canada, the Indian residential school system was a network of boarding schools for Indigenous peoples. The network was funded by the Canadian government's Department of Indian Affairs and administered by Christian churches. The school sy ...
'' was established following the passage of the Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' (, long name ''An Act to amend and consolidate the laws respecting Indians'') is a Canadian act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still ...
in 1876. The system was designed to remove children from the influence of their families and culture with the aim of assimilating them into the dominant Canadian culture.cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
: "killing the Indian in the child".Sixties Scoop
The Sixties Scoop was a period in which a series of policies were enacted in Canada that enabled child welfare authorities to take, or "scoop up," Indigenous children from their families and communities for placement in foster homes, from which th ...
, was investigated and the child seizures deemed genocidal by Judge Edwin Kimelman, who wrote: "You took a child from his or her specific culture and you placed him into a foreign culture without any ounsellingassistance to the family which had the child. There is something dramatically and basically wrong with that." another aspect of the residential school systems was its use of forced sterilization of Indigenous women who chose not to follow the schools advice of marrying non-Indigenous men. Indigenous women made up only 2.5% of the Canadian population, but 25% of those who were sterilized under the Canadian eugenics laws (such as the ''Sexual Sterilization Act
In 1928, the Legislative Assembly of Alberta, Canada, enacted the ''Sexual Sterilization Act''. The Act, drafted to protect the gene pool, allowed for sterilization of mentally disabled people in order to prevent the transmission of traits to ...
'' of Alberta) – many without their knowledge or consent.
The Executive Summary of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission found that the state pursued a policy of cultural genocide through forced assimilation.[MacDonald, D. B. (2015). Canada's history wars: indigenous genocide and public memory in the United States, Australia, and Canada. Journal of Genocide Research, 17(4), 411–431.]scalping
Scalping is the act of cutting or tearing a part of the human scalp, with hair attached, from the head, and generally occurred in warfare with the scalp being a trophy. Scalp-taking is considered part of the broader cultural practice of the tak ...
bounties offered by the governor of Nova Scotia, Edward Cornwallis
Edward Cornwallis ( – 14 January 1776) was a British career military officer and was a member of the aristocratic Cornwallis family, who reached the rank of Lieutenant General. After Cornwallis fought in Scotland, putting down the Jacobi ...
.
Secondly, as affirmed by the Truth and Reconciliation Commission, the residential school system was a clear example of (b) and (e) and similar acts continue to this day through the Millennium Scoop, as Indigenous children are disproportionately removed from their families and placed into the care of others who are often of different cultures through the Canadian child welfare system. Once again this repeats the separation of Indigenous children from their traditional ways of life. Moreover, children living on-reserve are subject to inadequate funding for social services which has led to filing of a ninth non-compliance order in early 2021 the Canadian Human Rights Tribunal
The Canadian Human Rights Tribunal (french: Tribunal canadien des droits de la personne, link=no) is an administrative tribunal established in 1977 through the ''Canadian Human Rights Act''. It is directly funded by the Parliament of Canada and i ...
in attempts to hold the Canadian government accountable.
Subsection (c) of the UN definition: "deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part" is an act of genocide that has historic legacies, such as the near and full extrapolation of caribou
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
and bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
that contributed to mass famines in Indigenous communities, how on reserve conditions infringe on the quality of life of Indigenous peoples as their social services are underfunded and inaccessible, and hold the bleakest water qualities in the first world country. Canada also situates precarious and lethal ecological toxicities that pose threats to the land, water, air and peoples themselves near or on Indigenous territories.
Indigenous people continue to report (d), the "imposing measures intended to prevent births within the group," within more recent years. Specifically through the avoidance of informed consent
Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics and medical law, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatme ...
surrounding sterilization procedures with Indigenous people like the case of D.D.S. represented by lawyer Alisa Lombard from 2018 in Moose Jaw, Saskatchewan
Moose Jaw is the fourth largest city in Saskatchewan, Canada. Lying on the Moose Jaw River in the south-central part of the province, it is situated on the Trans-Canada Highway, west of Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. Residents of Moose Jaw are k ...
. Examples such as the ones listed above have led to widespread physical and virtual action across the country to protest the historical and current genocidal harms faced by Indigenous peoples.
On July 28, 2022, during the visit by Pope Francis to Canada
Pope Francis visited Canada from July 24 to 29, 2022, with stops in the provinces of Alberta and Quebec and the territory of Nunavut. The trip mainly focused on apologizing for the Catholic Church's role in the Canadian Indian residential school ...
, at the Notre-Dame de Québec Cathedral
Notre Dame, French for "Our Lady", a title of Mary, mother of Jesus, most commonly refers to:
* Notre-Dame de Paris, a cathedral in Paris, France
* University of Notre Dame, a university in Indiana, United States
** Notre Dame Fighting Irish, the ...
the Francis
Francis may refer to:
People
*Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome
*Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
*Francis (surname)
Places
* Rural M ...
stated: "And thinking about the process of healing and reconciliation with our indigenous brothers and sisters, never again can the Christian community allow itself to be infected by the idea that one culture is superior to others, or that it is legitimate to employ ways of coercing others. " Pope Francis on his return flight to Rome on July 30, 2022, after a week-long trip to Canada, responded to a question from a journalist: "It's true, I didn't use the word because it didn't occur to me, but I described the genocide and asked for pardon, forgiveness for this work that is genocidal. For example, I condemned this too: Taking away children and changing culture, changing mentalities, changing traditions, changing a race, let's say, a whole culture. Yes, it's a technical word, genocide, but I didn't use it because it didn't come to mind, but I described it. It is true; yes, it's genocide. Yes, you all, be calm. You can say that I said that, yes, that it was genocide."
Mexico
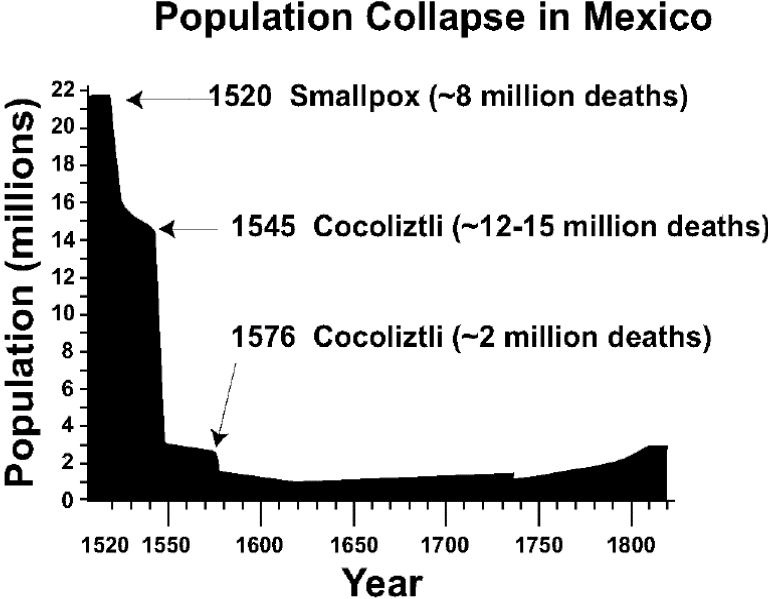
Apaches
In 1835, the government of the Mexican state of Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is d ...
put a bounty on the Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño an ...
which, over time, evolved into a payment by the government of 100 pesos for each scalp of a male 14 or more years old.Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
*Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mun ...
also offered a bounty on Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño an ...
scalps, 100 pesos per warrior, 50 pesos per woman, and 25 pesos per child.
Mayas
The Caste War of Yucatán
The Caste War of Yucatán (1847–1915) began with the revolt of Native Maya people of the Yucatán Peninsula against Hispanic populations, called ''Yucatecos''. The latter had long held political and economic control of the region. A lengthy w ...
was caused by encroachment of colonizers on communal land of Mayas
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical reg ...
in Southeast Mexico. According to political scientist Adam Jones: "This ferocious race war featured genocidal atrocities on both sides, with up to 200,000 killed."
Yaquis
The Mexican government's response to the various uprisings of the Yaqui
The Yaqui, Hiaki, or Yoeme, are a Native American people of the southwest, who speak a Uto-Aztecan language. Their homelands include the Río Yaqui valley in Sonora, Mexico, and the area below the Gila River in Arizona, Southwestern United Stat ...
tribe have been likened to genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
particularly under Porfirio Diaz Porfirio is a given name in Spanish, derived from the Greek Porphyry (''porphyrios'' "purple-clad").
It can refer to:
* Porfirio Salinas – Mexican-American artist
* Porfirio Armando Betancourt – Honduran football player
* Porfirio Barba-Jac ...
. Due to slavery and massacre, the population of the Yaqui
The Yaqui, Hiaki, or Yoeme, are a Native American people of the southwest, who speak a Uto-Aztecan language. Their homelands include the Río Yaqui valley in Sonora, Mexico, and the area below the Gila River in Arizona, Southwestern United Stat ...
tribe in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
was reduced from 30,000 to 7,000 under Diaz's rule. One source estimates at least 20,000 out of these Yaquis were victims of state murders in Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is d ...
. Mexican president Andrés Manuel López Obrador
Andrés Manuel López Obrador (; born 13 November 1953), also known by his initials AMLO, is a Mexican politician who has been serving as the 65th president of Mexico since 1 December 2018. He previously served as Head of Government of Mexico ...
said he'd be willing to offer apologies for the abuses in 2019.
Southern Cone
Both Argentina and Chile launched campaigns of territorial expansion in the second half of the 19th century, at the expenses of indigenous peoples and neighbor states. The so-called Pacification of the Araucania by the Chilean army dispossessed the up-to-then independent Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sha ...
people between the 1860s and the 1880s, as did Argentina with the Conquest of the Desert. In southern Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ...
, both states occupied indigenous lands and waters, and facilitated the genocide implemented by sheep-farmers and the businessmen in Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla G ...
. Argentina also expanded northward, dispossessing a number of Chaco peoples through a policy that may be considered as genocidal.
Paraguay
The War of the Triple Alliance
The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadlies ...
(1865-1870) was launched by the Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom Pe ...
, in alliance with the Argentine government of Bartolomé Mitre
Bartolomé Mitre Martínez (26 June 1821 – 19 January 1906) was an Argentine statesman, soldier and author. He was President of Argentina from 1862 to 1868 and the first president of unified Argentina.
Mitre is known as the most versatile ...
and the Uruguayan government of Venancio Flores
Venancio Flores Barrios (18 May 1808 – 19 February 1868) was a Uruguayan political leader and general. Flores was President of Uruguay from 1854 to 1855 (interim) and from 1865 to 1868.
Background and early career
In 1839, he was made politi ...
, against Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
. The governments of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay signed a secret treaty in which the "high contracting parties" solemnly bind themselves to overthrow the government of Paraguay. In the 5 years of war, the Paraguayan population was reduced, including, civilians, women, children, and the elderly. Julio José Chiavenato in his book ''American Genocide'' affirms that it was "a war of total extermination that only ended when there were no more Paraguayans to kill" and concludes that 99.5% of the adult male population of Paraguay died during the war. Of a population of approximately 420,000 before the war, only 14,000 men and 180,000 women remained.
Author Steven Pinker
Steven Arthur Pinker (born September 18, 1954) is a Canadian-American cognitive psychologist, psycholinguist, popular science author, and public intellectual. He is an advocate of evolutionary psychology and the computational theory of mind.
P ...
wrote:
Chile
First during the ''Arauco War
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities and force Mapuche ...
'' and then during the ''Occupation of Araucanía
The Occupation of Araucanía or Pacification of Araucanía (1861–1883) was a series of military campaigns, agreements and penetrations by the Chilean army and settlers into Mapuche territory which led to the incorporation of Araucanía into Ch ...
'' there was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sha ...
people, mostly fought in the Araucanía.
Argentina
The so-called ''Conquest of the Desert
The Conquest of the Desert ( es, Conquista del desierto) was an Argentine military campaign directed mainly by General Julio Argentino Roca in the 1870s with the intention of establishing dominance over the Patagonian Desert, inhabited primari ...
'' ( es, Conquista del desierto) was an Argentine military
The Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, in es, Fuerzas Armadas de la República Argentina, are controlled by the Commander-in-Chief (the President) and a civilian Minister of Defense. In addition to the Army, Navy and Air Force, there are ...
campaign with the intention of establishing dominance over the Patagonian Desert
The Patagonian Desert, also known as the Patagonian Steppe, is the largest desert in Argentina and is the 8th largest desert in the world by area, occupying 673,000 square kilometers (260,000 mi2). It is located primarily in Argentina and ...
, inhabited primarily by indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
. Argentine troops killed and displaced Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sha ...
from their traditional lands.
United States colonization of indigenous territories
Stacie Martin states that the United States has not been legally admonished by the international community for genocidal acts against its indigenous population, but many historians and academics describe events such as the Mystic massacre
The Mystic massacrealso known as the Pequot massacre and the Battle of Mystic Forttook place on May 26, 1637 during the Pequot War, when Connecticut colonizers under Captain John Mason and their Narragansett and Mohegan allies set fire to the ...
, the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
, the Sand Creek massacre and the Mendocino War
The Mendocino War was a conflict between the Yuki (mainly Yuki tribes) and white settlers in Mendocino County, California between July 1859 and January 18, 1860. It was caused by settler intrusion and slave raids on native lands and subsequent ...
as genocidal in nature. Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (born September 10, 1938) is an American historian, writer, and activist, known for her 2014 book ''An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States''.
Early life and education
Born in San Antonio, Texas, in 1938 to ...
states that U.S. history, as well as inherited Indigenous trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
, cannot be understood without dealing with the genocide that the United States committed against Indigenous peoples. From the colonial period through the founding of the United States and continuing in the twentieth century, this has entailed torture, terror, sexual abuse, massacres, systematic military occupations, removals of Indigenous peoples from their ancestral territories via Indian removal policies, forced removal of Native American children to military-like boarding schools, allotment, and a policy of termination. The letters exchanged between Bouquet and Amherst during Pontiac's War, in which Amherst wrote to Bouquet stating that "You will Do well to try to Inoculate the Indians by means of Blanketts, as well as to try Every other method that can serve to Extirpate this Execreble Race", has been seen by historians as evidence of genocidal intent on Amherst's part as well as part of a broader genocidal attitude that was frequently displayed to Native Americans during the colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short ter ...
.smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
swept the northern plains of the U.S. in 1837, the U.S. Secretary of War Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was an American military officer, politician, and statesman. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He w ...
ordered that no Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still res ...
(along with the Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011) , the Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
, and the Blackfeet
The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a federally recognized tribe of Siksikaitsitapi people with an Indian reservation in Monta ...
) be given smallpox vaccinations, which were provided to other tribes in other areas.
The United States has to-date not undertaken any truth commission
A truth commission, also known as a truth and reconciliation commission or truth and justice commission, is an official body tasked with discovering and revealing past wrongdoing by a government (or, depending on the circumstances, non-state act ...
nor built a memorial
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of a ...
for the genocide of indigenous people.Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
do not dedicate a section to the genocide.National Congress of American Indians
The National Congress of American Indians (NCAI) is an American Indian and Alaska Native rights organization. It was founded in 1944 to represent the tribes and resist federal government pressure for termination of tribal rights and assimilati ...
passed a resolution to create a space for the National American Indian Holocaust Museum inside the Smithsonian, but it was ignored by the latter.
Sterilization of natives
The Family Planning Services and Population Research Act
The Title X Family Planning Program is the only federal grant program dedicated to providing individuals with comprehensive family planning and related preventive health services. It was enacted under President Richard Nixon in 1970 as part of th ...
of 1970 caused the sterilization of an estimated 25% of fertile Native American women within 6 years.Marie Sanchez
Marie Elena Brady Sanchez (born Juanita Marie Brady, ''Cheyenne'': ''Otseohtse’e''; April 30, 1939 - August 9, 2019), was an American Cheyenne, Chief Judge of the Northern Cheyenne Tribe, a human rights activist for indigenous people and a ling ...
, chief tribal judge on the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation
The Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation ( chy, Tsėhéstáno; formerly named the Tongue River) is the federally recognized Northern Cheyenne tribe. Located in southeastern Montana, the reservation is approximately ...
told the United Nations Convention on Indigenous Rights in Geneva, that Native American women suffered involuntary sterilization which she equated with modern genocide.
Indian Removal and the Trail of Tears
Following the Indian Removal Act of 1830
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
the American government began forcibly relocating East Coast tribes across the Mississippi. The removal included many members of the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, Muscogee (Creek)
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands[Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, an ...]
, Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as ...
, and Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
nations, among others in the United States, from their homelands to Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
in eastern sections of the present-day state of Oklahoma. About 2,500–6,000 died along the Trail of Tears. Chalk and Jonassohn assert that the deportation of the Cherokee tribe along the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
would almost certainly be considered an act of genocide today. The Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
of 1830 led to the exodus. About 17,000 Cherokees, along with approximately 2,000 Cherokee-owned black slaves, were removed from their homes. The number of people who died as a result of the Trail of Tears has been variously estimated. American doctor and missionary Elizur Butler, who made the journey with one party, estimated 4,000 deaths.
Historians such as David Stannard and Barbara Mann have noted that the army deliberately routed the march of the Cherokee to pass through areas of a known cholera epidemic, such as Vicksburg. Stannard estimates that during the forced removal from their homelands, following the Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
signed into law by President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
in 1830, 8,000 Cherokee died, about half the total population.
American Indian Wars
 During the American Indian Wars, the American Army carried out a number of massacres and forced relocations of Indigenous peoples that are sometimes considered genocide. The 1864 Sand Creek Massacre, which caused outrage in its own time, has been called genocide. Colonel
During the American Indian Wars, the American Army carried out a number of massacres and forced relocations of Indigenous peoples that are sometimes considered genocide. The 1864 Sand Creek Massacre, which caused outrage in its own time, has been called genocide. Colonel John Chivington
John Milton Chivington (January 27, 1821 – October 4, 1894) was an American Methodist pastor and Mason who served as a colonel in the United States Volunteers during the New Mexico Campaign of the American Civil War. He led a rear action ...
led a 700-man force of Colorado Territory
The Territory of Colorado was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from February 28, 1861, until August 1, 1876, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Colorado.
The territory was organized in the w ...
militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
in a massacre of 70–163 peaceful Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
and Arapaho
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota.
By the 1850s, Arapaho band ...
, about two-thirds of whom were women, children, and infants. Chivington and his men took scalps and other body parts as trophies, including human fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal deve ...
es and male and female genitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
.[United States Congress Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War, 1865 (testimonies and report)] In defense of his actions Chivington stated,
United States acquisition of California
The U.S. colonization of California started in earnest in 1845, with the Mexican–American War. With the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, giving the United States authority over 525,000 square miles of new territory. In addition to Gold Rush slaughter, there was also a large number of state-subsidized massacres by colonists against Native Americans in the territory, causing several entire ethnic groups to be wiped out. In one such series of conflicts, the so-called Mendocino War
The Mendocino War was a conflict between the Yuki (mainly Yuki tribes) and white settlers in Mendocino County, California between July 1859 and January 18, 1860. It was caused by settler intrusion and slave raids on native lands and subsequent ...
and the subsequent Round Valley War The Round Valley War was an 1887 conflict between American Colonists and Yuki Indians on the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation
The Round Valley Indian Reservation is a federally recognized Indian reservation lying primari ...
, the entirety of the Yuki people
The Yuki (also known as Yukiah) are an indigenous people of California, whose traditional territory is around Round Valley, Mendocino County. Today they are enrolled members of the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation. Before ...
was brought to the brink of extinction, from a previous population of some 3,500 people to fewer than 100. According to Russell Thornton, estimates of the pre-Columbian population of California may have been as high as 300,000. By 1849, due to a number of epidemics, the number had decreased to 150,000. But from 1849 and up until 1890 the Indigenous population of California had fallen below 20,000, primarily because of the killings. At least 4,500 California Indians were killed between 1849 and 1870, while many more perished due to disease and starvation. 10,000 Indians were also kidnapped and sold as slaves. In a speech before representatives of Native American peoples in June 2019, California governor Gavin Newsom
Gavin Christopher Newsom (born October 10, 1967) is an American politician and businessman who has been the 40th governor of California since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 49th lieutenant governor of California fr ...
apologized for the genocide. Newsom said, "That's what it was, a genocide. No other way to describe it. And that's the way it needs to be described in the history books."
One California law made it legal to declare any jobless Indian a vagrant, then auction his services off for up to four months. It also permitted whites to force Indian children to work for them until they were eighteen, provided that they obtained permission from what the law referred to as a 'friend' was obtained first. Whites hunted down adult Indians in the mountains, kidnapped their children, and sold them as apprentices for as little as $50. Indians could not complain in court because of another California statute that stated 'no Indian or Black or Mulatto person was permitted to give evidence in favor of or against a white person'. One contemporary wrote "The minor are sometimes guilty of the most brutal acts with the Indians... such incidents have fallen under my notice that would make humanity weep and men disown their race". The towns of Marysville and Honey Lake paid bounties for Indian scalps. Shasta City offered $5 for every Indian head brought to City Hall; California's State Treasury reimbursed many of the local governments for their expenses.
March across Samar
During the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
, on September 28, 1901, Filipino forces defeated and nearly wiped out a US company in the Battle of Balangiga
The Battle of Balangiga ( es, Batalla de Balangíga; tl, Labanan sa Balangiga; war, Gubat ha Balangiga), also known as the Balangiga Encounter, Balangiga Incident, or Balangiga Conflict, was a battle that occurred during the Philippine–Amer ...
. In response, US forces carried out widespread atrocities during the March across Samar
The march across Samar, or Waller's March across the island of Samar, was a failed attempt made in 1901 by a U.S. Marine unit commanded by Major Littleton W. T. Waller to traverse the Philippine island of Samar from Lanang (now Llorente, Easter ...
, which lasted from December, 1901 to February, 1902. US forces killed between 2,000 and 2,500 Filipino civilians, according to most sources, and carried out an extensive scorched-earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, communi ...
policy, which included burning down villages. Some Filipino historians have called these killings genocidal. U.S. Brigadier General Jacob H. Smith
General Jacob Hurd Smith (January 29, 1840 – March 1, 1918) was a U.S. Army officer notorious for ordering indiscriminate retaliation on the island of Samar in response to what is called the Balangiga massacre during the Philippine–Amer ...
instructed his soldiers to "kill everyone over ten years old", including children who were capable of bearing arms, and to take no prisoners, however Major Littleton Waller
Littleton Tazewell "Tony" Waller (September 26, 1856 – July 13, 1926) was a career officer in the United States Marine Corps, who served in the Spanish–American War, the Caribbean and Asia. He was court martialled and acquitted for acti ...
, commanding officer of a battalion of 315 US Marines, refused to follow the order. Some Filipino historians estimate higher at 5,000 killed during the campaign, while other estimates are as high as 50,000.
Politics of modern Brazil
Over 80 indigenous tribes disappeared between 1900 and 1957, and of a population of over one million during this period 80% had been killed through deculturalization
Deculturalization is the process by which an ethnic group is forced to abandon its language, culture, and customs. It is the destruction of the culture of a dominated group and its replacement by the culture of the dominating group. Deculturalizat ...
, disease, or murder. It has also been argued that genocide has occurred during the modern era with the ongoing destruction of the Jivaro, Yanomami
The Yanomami, also spelled Yąnomamö or Yanomama, are a group of approximately 35,000 indigenous people who live in some 200–250 villages in the Amazon rainforest on the border between Venezuela and Brazil.
Etymology
The ethnonym ''Yanomami ...
and other tribes.
Indigenous peoples of Africa (pre-1948)
French colonization of Africa
Algeria
Over the course of the French conquest of Algeria
The French invasion of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Deylik of Algiers, and the French consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France inva ...
and immediately after it, a series of demographic catastrophes which were due to a variety of factors occurred in Algeria between 1830 and 1871. Because the demographic crisis was so severe, Dr. René Ricoux, head of demographic and medical statistics at the statistical office of the General Government of Algeria, foresaw the simple disappearance of Algerian "natives as a whole". Algerian demographic change can be divided into three phases: an almost constant decline during the conquest period, up until its heaviest drop from an estimated 2.7 million in 1861 to 2.1 million in 1871, and finally moving into a gradual increase to a level of three million inhabitants by 1890. Causes range from a series of famines, diseases, emigration; to the violent methods used by the French army during their Pacification of Algeria
The Pacification of Algeria was a series of military operations after the French conquest of the Regency of Algiers that aimed to put an end to various tribal rebellions, razzias and massacres of French settlers that were sporadically held in ...
which historians argue constitute acts of genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
.
Congo Free State
Under Leopold II of Belgium
* german: link=no, Leopold Ludwig Philipp Maria Viktor
, house = Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
, father = Leopold I of Belgium
, mother = Louise of Orléans
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Brussels, Belgium
, death_date = ...
the population loss in the Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leopo ...
is estimated at sixty percent where up to 15 million people were killed. Congo Free State was especially hard hit by sleeping sickness
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. It is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two typ ...
and smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
epidemics.
Genocide in German South West Africa
Atrocities against the indigenous African population by the German colonial empire
The German colonial empire (german: Deutsches Kolonialreich) constituted the overseas colonies, dependencies and territories of the German Empire. Unified in the early 1870s, the chancellor of this time period was Otto von Bismarck. Short-li ...
can be dated to the earliest German settlements on the continent. The German colonial authorities carried out genocide in German South-West Africa
German South West Africa (german: Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of ...
(GSWA) and the survivors were incarcerated in concentration camps. It was also reported that, between 1885 and 1918, the indigenous population of Togo, German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
(GEA) and the Cameroons suffered from various human rights abuses including starvation from scorched earth tactics and forced relocation for use as labour. The German Empire's action in GSWA against the Herero tribe is considered by Howard Ball to be the first genocide of the 20th century. After the Herero
Herero may refer to:
* Herero people, a people belonging to the Bantu group, with about 240,000 members alive today
* Herero language, a language of the Bantu family (Niger-Congo group)
* Herero and Namaqua Genocide
* Herero chat, a species of b ...
, Namaqua and Damara began an uprising against the colonial government, General Lothar von Trotha
General Adrian Dietrich Lothar von Trotha (3 July 1848 – 31 March 1920) was a German military commander during the European new colonial era. As a brigade commander of the East Asian Expedition Corps, he was involved in suppressing the Boxe ...
, appointed as head of the German forces in GSWA by Emperor Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empi ...
in 1904, gave the order for the German forces to push them into the desert where they would die. In 2004, the German state apologised for the genocide.
While many argue that the military campaign in Tanzania to suppress the Maji Maji Rebellion
The Maji Maji Rebellion (german: Maji-Maji-Aufstand, sw, Vita vya Maji Maji), was an armed rebellion of Islamic and animist Africans against German colonial rule in German East Africa (modern-day Tanzania). The war was triggered by German Colon ...
in GEA between 1905 and 1907 was not an act of genocide, as the military did not have as an intentional goal the deaths of hundreds of thousands of Africans, according to Dominik J. Schaller, the statement
released at the time by Governor Gustav Adolf von Götzen
Gustav Adolf Graf von Götzen (12 May 1866 – 2 December 1910) was a German colonizer and Governor of German East Africa. He came to Rwanda in 1894 becoming the second European to enter the territory, since Oscar Baumann’s brief expedition in ...
did not exculpate him from the charge of genocide, but was proof that the German administration knew that their scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, communi ...
methods would result in famine. It is estimated that 200,000 Africans died from famine with some areas completely and permanently devoid of human life.
Indigenous peoples of Asia (pre-1948)
Tsardom of Russia's conquest of Siberia
 The
The Russian conquest of Siberia
The Russian conquest of Siberia took place in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, when the Khanate of Sibir became a loose political structure of vassalages that were being undermined by the activities of Russian explorers. Although outnumber ...
was accompanied by massacres due to indigenous resistance to colonization by the Russian Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s, who savagely crushed the natives. At the hands of people like Vasilii Poyarkov in 1645 and Yerofei Khabarov
Yerofey Pavlovich Khabarov or Svyatitsky (russian: Ерофе́й Па́влович Хаба́ров (Святи́тский), ; the first name is often spelled Ярофей (Yarofey) in contemporary accounts; 1603 – after 1671), was a Russia ...
in 1650 some peoples like the Daur were slaughtered by the Russians to the extent that it is considered genocide. 8,000 out of a previously 20,000 strong population in Kamchatka remained after being subjected to half a century of Cossack slaughter.
In the 1640s the Yakuts
The Yakuts, or the Sakha ( sah, саха, ; , ), are a Turkic ethnic group who mainly live in the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation, with some extending to the Amur, Magadan, Sakhalin regions, and the Taymyr and Evenk Districts ...
were subjected to massacres during the Russian advance into their land near the Lena River, and on Kamchatka in the 1690s the Koryak, Kamchadals
The Kamchadals (russian: камчадалы) inhabit Kamchatka, Russia. The name "Kamchadal" was applied to the descendants of the local Siberians and aboriginal peoples (the Itelmens, Ainu, Koryaks and Chuvans) who assimilated with the Russ ...
, and Chukchi were also subjected to massacres by the Russians. When the Russians did not obtain the demanded amount of yasak
''Yasak'' or ''yasaq'', sometimes ''iasak'', (russian: ясак; akin to Yassa) is a Turkic languages, Turkic word for "tribute" that was used in Imperial Russia to designate fur tribute exacted from the indigenous peoples of Siberia.
Origin
The ...
from the natives, the Governor of Yakutsk
Yakutsk (russian: Якутск, p=jɪˈkutsk; sah, Дьокуускай, translit=Djokuuskay, ) is the capital city of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located about south of the Arctic Circle. Fueled by the mining industry, Yakutsk has become one of ...
, Peter Golovin, who was a Cossack, used meat hooks to hang the native men. In the Lena basin, 70% of the Yakut population died within 40 years, and rape and enslavement were used against native women and children in order to force the natives to pay the Yasak.Itelmens
The Itelmens (Itelmen: Итәнмән, russian: Ительмены) are an indigenous ethnic group of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The Itelmen language is distantly related to Chukchi and Koryak, forming the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language ...
uprisings against their rule in 1706, 1731, and 1741. The first time the Itelmen were armed with stone weapons and were badly unprepared and equipped but they used gunpowder weapons the second time. The Russians faced tougher resistance when from 1745 to 1756 they tried to exterminate the gun and bow equipped Koraks until their victory. The Russian Cossacks also faced fierce resistance and were forced to give up when trying unsuccessfully to wipe out the Chukchi through genocide in 1729, 1730–1731, and 1744–1747. After the Russian defeat in 1729 at Chukchi hands, the Russian commander Major Pavlutskiy was responsible for the Russian war against the Chukchi and the mass slaughters and enslavement of Chukchi women and children in 1730–1731, but his cruelty only made the Chukchis fight more fiercely. A genocide of the Chukchis and Koraks was ordered by Empress Elizabeth
Elizabeth Petrovna (russian: Елизаве́та (Елисаве́та) Петро́вна) (), also known as Yelisaveta or Elizaveta, reigned as Empress of Russia from 1741 until her death in 1762. She remains one of the most popular Russian ...
in 1742 to totally expel them from their native lands and erase their culture through war. The command was that the natives be "totally extirpated" with Pavlutskiy leading again in this war from 1744 to 1747 in which he led to the Cossacks "with the help of Almighty God and to the good fortune of Her Imperial Highness", to slaughter the Chukchi men and enslave their women and children as booty. However the Chukchi ended this campaign and forced them to give up by killing Pavlitskiy and decapitating his head.
The Russians were also launching wars and slaughters against the Koraks in 1744 and 1753–1754. After the Russians tried to force the natives to convert to Christianity, the different native peoples like the Koraks, Chukchis, Itelmens, and Yukagirs all united to drive the Russians out of their land in the 1740s, culminating in the assault on Nizhnekamchatsk fort in 1746. Kamchatka today is European in demographics and culture with only 2.5% of it being native, around 10,000 from a previous number of 150,000, due to the mass slaughters by the Cossacks after its annexation in 1697 of the Itelmen and Koryaks throughout the first decades of Russian rule. The genocide by the Russian Cossacks devastated the native peoples of Kamchatka and exterminated much of their population. In addition to committing genocide the Cossacks also devastated the wildlife by slaughtering massive numbers of animals for fur. 90% of the Kamchadals
The Kamchadals (russian: камчадалы) inhabit Kamchatka, Russia. The name "Kamchadal" was applied to the descendants of the local Siberians and aboriginal peoples (the Itelmens, Ainu, Koryaks and Chuvans) who assimilated with the Russ ...
and half of the Vogules were killed from the eighteenth to nineteenth centuries and the rapid genocide of the indigenous population led to entire ethnic groups being entirely wiped out, with around 12 exterminated groups which could be named by Nikolai Iadrintsev as of 1882. Much of the slaughter was brought on by the fur trade.
The Aleuts
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the U ...
in the Aleutians
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large vo ...
were subjected to genocide and slavery by the Russians for the first 20 years of Russian rule, with the Aleut women and children captured by the Russians and Aleut men slaughtered.
The Russian colonization of Siberia and treatment of the resident indigenous peoples has been compared to European colonization of the Americas, with similar negative impacts on the indigenous Siberians as upon the indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
. One of these commonalities is the appropriation of indigenous peoples' land.
Japanese Empire
Colonization of Hokkaido
The Ainu are an indigenous people in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
(Hokkaidō
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
).Kuril islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
and the southern half of Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: ...
, and that Japan and Russia both invaded. In 2004, the small Ainu community living in Russia in Kamchatka Krai wrote a letter to Vladimir Putin, urging him to reconsider any move to award the Southern Kuril islands to Japan. In the letter they blamed the Japanese, the Tsarist Russians and the Soviets for crimes against the Ainu such as killings and assimilation, and also urged him to recognize the Japanese genocide against the Ainu people, which was turned down by Putin.
Colonization of Okinawa
Okinawans are an indigenous people to the islands to the west of Japan, originally known as the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yonaguni ...
.World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
); The UN has encouraged that Okinawan history, and language be mandatorily taught in schools in Okinawa. Nothing has yet to be done.
Genocide of Oroqen and Hezhen
During the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Th ...
(1937–1945), the Japanese performed "bacterial experiments" on the Oroqen people
The Oroqen people (; Mongolian: ; also spelt ''Orochen'' or ''Orochon'') are an ethnic group in northern China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The Oroqen people are largely concent ...
and introduced them to opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
which contributed to their deaths and caused their population to decline until only 1,000 of them remained alive at the end of the war. The Japanese banned the Oroqen from communicating with members of other ethnicities, and they also forced them to hunt animals for them in exchange for starvation rations and unsuitable clothing which caused them to die from exposure to the inclement weather. The Japanese also forced Oroqen adults who were older than 18 to take opium. After 2 Japanese troops were killed in Alihe by an Oroqen hunter, the Japanese poisoned 40 Oroqen to death.Hezhen
The Nanai people are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Jurchens of northernmost Manch ...
population declined by 90% due to deaths from forced opium use, slave labor and relocation by the Japanese.
Vietnamese conquest of Champa
The Cham and Vietnamese had a long history of conflict, with many wars ending due to economic exhaustion. It was common that the antagonists of the wars would rebuild their economies simply to go to war again. In 1471, Champa was particularly weakened prior to the Vietnamese invasion by a series of civil wars. The Vietnamese conquered Champa
Champa (Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd cen ...
and settled its territory with Vietnamese migrants during the march to the south after fighting repeated wars with Champa, shattering Champa in the invasion of Champa in 1471 and finally completing the conquest in 1832 under Emperor Minh Mang
{{Orphan, date=December 2021
Minh (Chữ Nôm: 明) is a popular unisex given name of Vietnamese origin, written using the Chinese character (明) meaning "bright", and is also popular among other East Asian names. The Chinese name Ming has the sa ...
. 100,000 Cham soldiers besieged a Vietnamese garrison which led to anger from Vietnam and orders to attack Champa. 30,000 Chams were captured and over 40,000 were killed.
Qing dynasty
Dzungar genocide
 Some scholars estimate that about 80% of the
Some scholars estimate that about 80% of the Dzungar
Dzungar may refer to:
*Dzungar people, Oirat tribes in the Dzungar Khanate
*Dzungar Khanate, a historical empire
* Jungar Banner, an administrative division of China
*Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in ...
(Western Mongol) population (600,000 or more) was destroyed by a combination of warfare and disease in the Dzungar genocide
The Dzungar genocide () was the mass extermination of the Mongol Dzungar people by the Qing dynasty. The Qianlong Emperor ordered the genocide due to the rebellion in 1755 by Dzungar leader Amursana against Qing rule, after the dynasty first co ...
which was perpetrated during the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
conquest of the Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate, also written as the Zunghar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyzstan in the south, and from t ...
in 1755–1757, in which Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
Bannermen
Bannerman is a name of Scottish origin (see Clan Bannerman) and may refer to
Places
;Canada
* Bannerman, Edmonton, a neighbourhood in Edmonton, Canada
;United States
* Bannerman, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community
* Bannerman's Castle, an a ...
and Khalkha Mongols
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin khans ...
exterminated the Dzungar Oirat Mongols. Mark Levene, a historian whose recent research interests focus on genocide, has stated that the extermination of the Dzungars was "arguably the eighteenth-century genocide par excellence".
Anti-Zunghar Uyghur rebels from the Turfan and Hami oases had submitted to Qing rule as vassals and requested Qing help for overthrowing Zunghar rule. Uyghur leaders like Emin Khoja
Emin may refer to:
As a name
* Emin (given name)
* Emin (surname)
Places
* Emin County, county in Xinjiang, China
* Emin Minaret, the tallest minaret in China
* Emin Valley, on the borders of China and Kazakhstan
* Emin or Emil River, in Emi ...
were granted titles within the Qing nobility, and these Uyghurs helped supply the Qing military forces during the anti-Zunghar campaign. The Qing employed Khoja Emin in its campaign against the Dzungars and used him as an intermediary with Muslims from the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
to inform them that the Qing were only aiming to kill Oirats (Zunghars) and that they would leave the Muslims alone, and also to convince them to kill the Oirats (Dzungars) themselves and side with the Qing since the Qing noted the Muslims' resentment of their former experience under Zunghar rule at the hands of Tsewang Araptan.
British Empire (pre-1945)
 In places like the
In places like the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, settler colonialism
Settler colonialism is a structure that perpetuates the elimination of Indigenous people and cultures to replace them with a settler society. Some, but not all, scholars argue that settler colonialism is inherently genocidal. It may be enacted ...
was carried out by the British. Foreign land viewed as attractive for settlement was declared as terra nullius
''Terra nullius'' (, plural ''terrae nullius'') is a Latin expression meaning " nobody's land".
It was a principle sometimes used in international law to justify claims that territory may be acquired by a state's occupation of it.
:
:
...
or "nobody's land". The indigenous inhabitants were therefore denied any sovereignty or property rights in the eyes of the British. This justified invasion and the violent seizure of native land to create colonies populated by British settlers. Colonization like this usually caused a large decrease in the indigenous population from war, newly introduced diseases, massacre by colonists and attempts at forced assimilation
Forced assimilation is an involuntary process of cultural assimilation of religious or ethnic minority groups during which they are forced to adopt language, identity, norms, mores, customs, traditions, values, mentality, perceptions, way of lif ...
. The settlers from Britain and Europe grew rapidly in number and created entirely new societies. The indigenous population became an oppressed minority in their own country. The gradual violent expansion of colonies into indigenous land could last for centuries, as it did in the Australian frontier wars and American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
.
Widespread population decline occurred following conquest principally from introduction of infectious disease. The number of Australian Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands ...
declined by 84% after British colonization. The Maori population of New Zealand suffered a 57% drop from its highest point. In Canada, the indigenous first nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
population of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
decreased by 75%. Surviving indigenous groups continued to suffer from severe racially motivated discrimination from their new colonial societies. Aboriginal children, the Stolen Generations
The Stolen Generations (also known as Stolen Children) were the children of Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander descent who were removed from their families by the Australian federal and state government agencies and church miss ...
, were confiscated by the Australian government and subject to forced assimilation and child abuse
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child or children, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to a ...
for most of the 20th century. Aboriginal Australians were only granted the right to vote in some states in 1962.
Similarly, the Canadian government has apologized for its historical "attitudes of racial and cultural superiority" and "suppression" of the first nations, including its role in residential schools where first nation children were confined and abused. Canada has been accused of genocide for its historical compulsory sterilization of indigenous peoples in Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
during the fears of jobs being stolen by immigrants and living lives of poverty provoked by the great depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
.
It has proven a controversial question whether the drastic population decline can be considered an example of genocide, and scholars have argued whether the process as a whole or specific periods and local processes qualify under the legal definition. Raphael Lemkin
Raphael Lemkin ( pl, Rafał Lemkin; 24 June 1900 – 28 August 1959) was a Polish lawyer who is best known for coining the term ''genocide'' and initiating the Genocide Convention, an interest spurred on after learning about the Armenian genocid ...
, the originator of the term "genocide", considered the colonial replacement of Native Americans by English and later British colonists to be one of the historical examples of genocide. Historian has referred to the case in Tasmania as "an event that truly merits the now overused term 'genocide'", and mentions Ireland and North America as areas that suffered ethnic cleansing at the hands of the British. According to Patrick Wolfe in the Journal of Genocide Research, the "frontier massacring of indigenous peoples" by the British constitutes a genocide.
The numerous massacres and widespread starvation that accompanied the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland (1649–1653) has led to it being called a genocide; hundreds of thousands of Irish civilians died, and about 50,000 Irish were sold into indentured servitude. As one author put it, "A loss of more than 40 per cent of the population might, however, suggest a conscious plan of elimination based on racial and religious hatred, which in other circumstances and times would rightly be called genocide. Cromwell's murderous campaign in Ireland was fuelled by a pathological hatred of Irish Catholics, which he himself clearly expressed."
The Plantations of Ireland were attempts to expel the native Irish from the best land of the island, and settle it with loyal British Protestants; they too have been described as genocidal. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine (1845–1850) has also been blamed on British policy and called genocidal. Writing in ''Indian Country Today'', Christina Rose drew parallels between the Irish and Native American experience of dispossession and genocide; Katie Kane has compared the Sand Creek massacre with the Drogheda massacre. R. Barry O'Brien compared the Irish Rebellion of 1641 with the Indian Wars, writing "The warfare which ensued… resembled that waged by the early settlers in America with the native tribes. No mercy whatever was shown to the natives, no act of treachery was considered dishonourable, no personal tortures and indignities were spared to the captives. The slaughter of Irishmen was looked upon as literally the slaughter of wild beasts. Not only the men, but even the women and children who fell into the hands of the English were deliberately and systematically butchered. Year after year, over a great part of all Ireland, all means of human subsistence was destroyed, no quarter was given to prisoners who surrendered, and the whole population was skillfully and steadily starved to death." Similar to the European Colonization of The Americas, the death toll under the British Empire is estimated to be as high as 150 million.
Colonization of Australia
The so-called extinction of the Aboriginal Tasmanians is regarded as a classic case of near genocide by Lemkin, most comparative scholars of genocide, and many general historians, including Robert Hughes (critic), Robert Hughes, Ward Churchill
Ward LeRoy Churchill (born 1947) is an American author and political activist. He was a professor of ethnic studies at the University of Colorado Boulder from 1990 until 2007. , Leo Kuper and Jared Diamond, who base their analysis on previously published histories. Between 1824 and 1908 White settlers and Australian native police, Native Mounted Police in Queensland, according to Raymond Evans, killed more than 10,000 Aboriginal people, who were regarded as vermin and sometimes even hunted for sport.
Prior to the arrival of the First Fleet in 1788, which marked the beginning of History of Australia (1788–1850), Britain's colonization of Australia, the Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal population had been estimated by historians to be around roughly 500,000 people; by 1900, that number had plummeted to fewer than 50,000. While most died due to the introduction of infectious diseases which accompanied colonization, up to 20,000 were killed during the Australian frontier wars by British settlers and colonial authorities through Massacres of Indigenous Australians, massacres, Mass poisonings of Aboriginal Australians, mass poisonings and other actions. Ben Kiernan, an Australian historian of genocide, treats the Australian evidence over the first century of colonization as an example of genocide in his 2007 history of the concept and practice, Blood and Soil (book), ''Blood and Soil: A World History of Genocide and Extermination from Sparta to Darfur''. The Australian practice of removing the children of Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders, Torres Strait Islander descent from their families, has been described as genocidal. The 1997 report ''Bringing Them Home'', which examined the fate of the "stolen generations" concluded that the forced separation of Aboriginal children from their family constituted an act of genocide. In the 1990s a number of Australian state institutions, including the state of Queensland, apologized for its policies regarding forcible separation of Aboriginal children. Another allegation against the Australian state is the use of medical services to Aboriginal people to administer contraceptive therapy to Aboriginal women without their knowledge or consent, including the use of Depo Provera, as well as tubal ligations. Both forced adoption and forced contraception would fall under the provisions of the UN genocide convention. Some Australian scholars, including historians Geoffrey Blainey and Keith Windschuttle and political scientist Ken Minogue, reject the view that Australian Aboriginal policy was genocidal.
Famines in British India
Late Victorian Holocausts: El Niño Famines and the Making of the Third World is a book by Mike Davis (scholar), Mike Davis about the connection between political economy and global climate patterns, particularly El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). By comparing ENSO episodes in different time periods and across countries, Davis explores the impact of colonialism and the introduction of capitalism, and the relation with famine in particular. Davis argues that "Millions died, not outside the 'modern world system', but in the very process of being forcibly incorporated into its economic and political structures. They died in the golden age of Liberal Capitalism; indeed, many were murdered ... by the theological application of the sacred principles of Smith, Bentham and Mill."
Davis characterizes the Timeline of major famines in India during British rule, Indian famines under the British Raj as "colonial genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
". Some scholars, including , have disputed this judgment, while others, including Adam Jones, have affirmed it.
Rubber Boom in Congo and Putumayo
 From 1879 to 1912, the world experienced a rubber boom. Rubber prices skyrocketed, and it became increasingly profitable to extract rubber from rainforest zones in South America and Central Africa. Rubber extraction was labor-intensive, and the need for a large workforce had a significant negative effect on the indigenous population across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia and in the Congo. The owners of the plantations or rubber barons were rich, but those who collected the rubber made very little, as a large amount of rubber was needed to be profitable. Rubber barons rounded up all the Indians and forced them to tap rubber out of the trees. Slavery and gross human rights abuses were widespread, and in some areas, 90% of the Indian population was wiped out. One plantation started with 50,000 Indians and when the killings were discovered, only 8,000 were still alive. These rubber plantations were part of the Brazilian rubber market which declined as rubber plantations in Southeast Asia became more effective.
Roger Casement, an Irishman travelling the Putumayo region of Peru as a British consul during 1910–1911, documented the abuse, slavery, murder, and use of stocks for torture against the native Indians: "The crimes charged against many men now in the employ of the Peruvian Amazon Company are of the most atrocious kind, including murder, violation, and constant flogging."
From 1879 to 1912, the world experienced a rubber boom. Rubber prices skyrocketed, and it became increasingly profitable to extract rubber from rainforest zones in South America and Central Africa. Rubber extraction was labor-intensive, and the need for a large workforce had a significant negative effect on the indigenous population across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia and in the Congo. The owners of the plantations or rubber barons were rich, but those who collected the rubber made very little, as a large amount of rubber was needed to be profitable. Rubber barons rounded up all the Indians and forced them to tap rubber out of the trees. Slavery and gross human rights abuses were widespread, and in some areas, 90% of the Indian population was wiped out. One plantation started with 50,000 Indians and when the killings were discovered, only 8,000 were still alive. These rubber plantations were part of the Brazilian rubber market which declined as rubber plantations in Southeast Asia became more effective.
Roger Casement, an Irishman travelling the Putumayo region of Peru as a British consul during 1910–1911, documented the abuse, slavery, murder, and use of stocks for torture against the native Indians: "The crimes charged against many men now in the employ of the Peruvian Amazon Company are of the most atrocious kind, including murder, violation, and constant flogging."
Contemporary examples
The genocide of indigenous tribes is still an ongoing feature in the modern world, with the ongoing depopulation of the Jivaro, Yanomami
The Yanomami, also spelled Yąnomamö or Yanomama, are a group of approximately 35,000 indigenous people who live in some 200–250 villages in the Amazon rainforest on the border between Venezuela and Brazil.
Etymology
The ethnonym ''Yanomami ...
and other tribes in Brazil having been described as genocide. Multiple incidents of rioting against the minority communities in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Myanmar
Assam, India
Bengali speaking minority people of Assam were targeted based on racial hatred in the region by native people of Assam in 1983, leading to 2000 - 10,000 deaths in that year alone. This was part of the larger Assam Movement and longstanding hatred of Bengali speaking people in the region and has been described as genocidal in nature. Although the people of Assam claims the Bengali speaking people are immigrants, there has been no proof to support the claim and Anti-Bengali sentiment in India, discrimination against Bengali speaking people in the region continues until present day. The Detention centres in Assam, Matia (Goalpara) Detention Centre was established in 2018 to capture and captivate alleged Bengali speaking immigrdants in Assam.
Bangladesh
According to Amnesty International and Reference Services Review, the indigenous Chakma people of the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Chittagong hill tracts have allegedly been subjected to genocidal violence for decades. Their population had been dwindling since the military rule launched by dictator Major General Ziaur Rahman who took control of the country after a military coup in 1975 and reigned from 1975 to 1981. and later his successor Lieutenant General HM Ershad who reigned from 1982 to 1990. In response the indigenous Chakma rebels led by Manabendra Narayan Larma, M.N. Larma (who would be killed in 1983) started an Chittagong Hill Tracts conflict, insurgency in the region in 1977. The Bangladeshi government had settled hundreds of thousands of Bengali people in the region who now constitute the majority of the population there. On 11 September 1996 the indigenous rebels reportedly abducted and killed 28 to 30 Bengali woodcutters. After democracy was reestablished in the country, fresh rounds of talks began in 1996 with the newly elected prime minister Sheikh Hasina Wajed of the Awami League, the daughter of the late Father of the Nation Sheikh Mujibur Rahman and the representatives of the indigenous rebels.
Brazil
From the late 1950s until 1968, the state of Brazil submitted their indigenous peoples of Brazil to violent attempts to integrate, pacify and acculturate their communities. In 1967 public prosecutor Jader de Figueiredo Correia, submitted the Figueiredo Report to the Brazilian military government, dictatorship which was then ruling the country, the report which ran to seven thousand pages was not released until 2013. The report documents genocidal crimes against the indigenous peoples of Brazil, including mass murder, torture and bacteriological and chemical warfare, reported slavery, and sexual abuse. The rediscovered documents are being examined by the National Truth Commission who have been tasked with the investigations of human rights violations which occurred in the periods 1947 through to 1988. The report reveals that the IPS had enslaved indigenous people, tortured children and stolen land. The Truth Commission is of the opinion that entire tribes in Maranhão were completely eradicated and in Mato Grosso, an attack on thirty Cinta Larga people, Cinturão Largo left only two survivors. The report also states that landowners and members of the IPS had entered isolated villages and deliberately introduced smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
. Of the one hundred and thirty-four people accused in the report the state has as yet not tried a single one, since the Amnesty Law passed in the end of the dictatorship does not allow trials for the abuses which happened in such period. The report also detailed instances of mass killings, rapes, and torture, Figueiredo stated that the actions of the IPS had left the indigenous peoples near extinction. The state abolished the IPS following the release of the report. The Red Cross launched an investigation after further allegations of ethnic cleansing were made after the IPS had been replaced.
China
The Government of China, Chinese government has committed a series of Human rights, human rights abuses against the native Uyghurs, Uyghur people and other ethnic and religious minorities both in and around the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR) of the China, People's Republic of China that have often been characterized as genocide.Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
) in secretive Xinjiang internment camps, internment camps without any legal processWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Critics of the policy have described it as the Sinicization of Xinjiang and they have also called it an ethnocide
Ethnocide is the extermination of cultures.
Reviewing the legal and the academic history of the usage of the terms genocide and ethnocide, Bartolomé Clavero differentiates them by stating that "Genocide kills people while ethnocide kills social ...
or a cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
, while some governments, activists, independent NGOs, human rights experts, academics, government officials, independent researchers, and the East Turkistan Government-in-Exile have called it a genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
. In particular, critics have highlighted the concentration of Uyghurs in state-sponsored internment camps, the suppression of Uyghur Islam in China, religious practices, political indoctrination,
Colombia
In the protracted conflict in Colombia, indigenous groups such as the Awá, Wayuu, Pijao and Paez people have become subjected to intense violence by right-wing paramilitaries, leftist guerrillas, and the Colombian army. Drug cartels, international resource extraction companies and the military have also used violence to force the indigenous groups out of their territories. The National Indigenous Organization of Colombia argues that the violence is genocidal in nature, but others question whether there is a "genocidal intent" as required in international law.
Congo (DRC)
In the Democratic Republic of Congo genocidal violence against the indigenous Mbuti, Lese and Ituri peoples has reportedly been endemic for decades. During the Second Congo War, Congo Civil War (1998–2003), Pygmies were hunted down and eaten by both sides in the conflict, who regarded them as subhuman. Sinafasi Makelo, a representative of Mbuti pygmies, has asked the UN Security Council to recognize cannibalism as a crime against humanity and also as an act of genocide. According to a report by Minority Rights Group International there is evidence of mass killings, cannibalism and rape. The report, which labeled these events as a campaign of extermination, linked much of the violence to beliefs about special powers held by the Bambuti. In Ituri district, rebel forces ran an operation code-named "Effacer le Tableau" (to wipe the slate clean). The aim of the operation, according to witnesses, was to rid the forest of pygmies.
East Timor
Indonesia Indonesian invasion of East Timor, invaded East Timor or Timor-Leste, which had previously been a Portuguese Timor, Portuguese colony, in 1975. Following the invasion, the Indonesian government implemented East Timor genocide, repressive military policies in an attempt to quell ethnic protests and armed resistance in the area and it also encouraged people who lived in other parts of Indonesia to settle in the region. The violence which occurred between 1975 and 1993 claimed between 120,000 and 200,000 lives. The repression entered the international spotlight in 1991 when a protest in Dili was disrupted by Indonesian forces which killed over 250 people and disappeared hundreds of others. The Santa Cruz massacre, as the event became known, drew a significant amount of international attention to the issue (it was highlighted when the 1996 Nobel Peace Prize was awarded to Catholic Bishop Carlos Filipe Ximenes Belo, Carlos Belo and resistance leader José Ramos-Horta). Following the international outcry, the Indonesian government began to organize a host of paramilitary groups which continued to harass and kill pro-independence activists in East Timor. At the same time, the Indonesian government significantly increased its population resettlement efforts in the area and it also intensified the destruction of the infrastructure and the environment which were both being used by East Timorese communities. In response to this policy, an International Force for East Timor, international intervention force was eventually deployed to East Timor in order to monitor a vote for the independence of East Timor by its population in 1999. The vote was significantly in favor of independence and the Indonesian forces withdrew, but paramilitaries continued to carry out reprisal attacks for a few years. A UN Report on the Indonesian occupation identified starvation, defoliant and napalm use, torture, rape, sexual slavery, disappearances, public executions, and extrajudicial killings as sanctioned by the Indonesian government and the entire colflict resulting in reducing the population to a third of its 1975 level.
Guatemala
During the Guatemalan Civil War (1960–1996), the state forces carried out Guatemalan genocide, violent atrocities against the Maya peoples, Maya. The government considered the Maya to be aligned with the communist insurgents, which they sometimes were but often were not. Guatemalan armed forces carried out three campaigns that have been described as genocidal.
The first was a scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, communi ...
policy which was also accompanied by mass killing, including the forced conscription of Mayan boys into the military where they were sometimes forced to participate in massacres against their own home villages. The second was to hunt down and exterminate those who had survived and evaded the army and the third was the forced relocation of survivors to "reeducation centers" and the continued pursuit of those who had fled into the mountains.
The armed forces used genocidal rape of women and children as a deliberate tactic. Children were bludgeoned to death by beating them against walls or thrown alive into mass graves where they would be crushed by the weight of the adult dead thrown atop them. An estimated 200,000 people, most of them Maya, disappeared during the Guatemalan Civil War.
After the 1996 peace accords, a legal process was begun to determine the legal responsibility of the atrocities, and to locate and identify the disappeared. In 2013 former president Efraín Ríos Montt was convicted of genocide and crimes against humanity, and was sentenced to 80 years imprisonment.
Yazidi genocide in Iraq
The Yazidis are an indigenous minority group in the Middle East and its members practice their own monotheistic religion, and as a result, they have frequently been stigmatized and targeted for violence by Islamic extremism, Islamist extremists in Iraq (most recently by Genocide of Yazidis by the islamic State, ISIL, but other Islamist groups also perpetrated acts of violence against Yazidis in the past), with multiple studies concluding that acts of genocide have been perpetrated against the Yazidi community in Iraq, including Mass murder, mass killings and rape. While acts of violence against Yazidis have been documented for centuries, recent acts of violence against Yazidis include deadly terrorist attacks which targeted the Yazidi community, including the 2007 Yazidi communities bombings and the Sinjar massacre, August 2014 Sinjar massacre. Yazidi women and girls have frequently been kept as Sexual slavery, sex slaves and they have also been subjected to slave trading by Islamic State, ISIL terrorists during the most recent events of the genocide of Yazidis by ISIL, which resulted in the forcible displacement of over 500,000 Yazidis from Iraq. In 2014 alone, 5000 Yazidis were killed, but long before that year, the genocide was already being committed against the Yazidis and at present, it is still going on. In February 2021, the remains of 104 Yazidis killed by ISIL were found and laid to rest.
Indonesia
From the time of its independence until the late 1960s, the Indonesian government sought control of Western New Guinea, the western half of the island of New Guinea, which had remained under the control of the Netherlands. When it finally achieved internationally recognized control of the area, a number of clashes occurred between the Indonesian government and the Free Papua Movement. The government of Indonesia began a series of measures aimed to suppress the organization in the 1970s and the suppression reached high levels in the mid-1980s.
The resulting human rights abuses included extrajudicial killings, torture, disappearances, rape, and harassment of indigenous people throughout the province. A 2004 report by the Allard K. Lowenstein International Human Rights Clinic at Yale Law School identified both the mass violence and the Transmigration program, transmigration policies which encouraged mostly Balinese and Javanese families to relocate to the area as strong evidence "that the Indonesian government has committed proscribed acts with the intent to destroy the West Papuans as such, in violation of the 1948 Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide."
Genocide against indigenous people in the region were key claims made in the U.S. case of Beanal v. Freeport, one of the first lawsuits where indigenous people outside the U.S. petitioned to get a ruling against a multinational corporation for environmental destruction outside of the U.S. While the petitioner, an indigenous leader, claimed that the mining company Freeport-McMoRan had committed genocide through environmental destruction which "resulted in the purposeful, deliberate, contrived and planned demise of a culture of indigenous people," the court found that genocide pertains only to destruction of indigenous people and did not apply to the destruction of the culture of indigenous people; however, the court did leave open the opportunity for the petitioners to amend their filings with additional claim.
Myanmar/Burma
In Myanmar (Burma), the long-running civil war between the Military Junta and the insurgents has resulted in widespread atrocities against the indigenous Karen people, some of whom are allied with the insurgents. These atrocities have been described as genocidal. Burmese General Maung Hla stated that one day the Karen will only exist "in a museum" The government has deployed 50 battalions in the Northern sector systematically attacking Karen villages with mortar and machine gun fire, and landmines. At least 446,000 Karen have been displaced from their homes by the military. The Karen are also reported to have been subjected to forced labor, genocidal rape, child labor and the conscription of child soldiers. The Rohingya people have also been subjected to Persecution of Muslims in Myanmar, persecution mass killings, genocidal mass rapes and forced displacement. The Myanmar army burned their villages and forced them to flee the country. Mass graves which contain the remains of many victims of genocide were discovered. By 2017 over 700,000 Rohingya people fled to Bangladesh, whose government was praised for giving shelter to them.
Paraguay
There are 17 indigenous tribes which primarily live in the Chaco region of Paraguay. In 2002, their numbers were estimated to be 86,000. During the period between 1954 and 1989, when the military dictatorship of General Alfredo Stroessner ruled Paraguay, the indigenous population of the country suffered from more loss of territory and human rights abuses than at any other time in the nation's history. In early 1970, international groups claimed that the state was complicit in the genocide of the Aché people, Aché, with charges ranging from kidnapping and the sale of children, withholding medicines and food, slavery and torture. During the 1960s and 1970s, 85% of the Aché people were killed, often hacked to death with machetes, in order to make room for the timber industry, mining, farming and ranchers. According to Jérémie Gilbert, the situation in Paraguay has proven that it is difficult to provide the proof required to show "specific intent", in support of a claim that genocide had occurred. The Aché, whose cultural group is now seen as extinct, fell victim to development by the state who had promoted the exploration of their territories by transnational companies for natural resources. Gilbert concludes that although a planned and voluntary destruction had occurred, it is argued by the state that there was no intent to destroy the Aché, as what had happened was due to development and was not a deliberate action.
Sri Lanka
The crack down on the Sri Lankan Tamils during the 1958 anti-Tamil pogrom and the Sri Lankan Civil War have been described as genocidal in nature by the United Nations. Sri Lankan mobs brutally butchered thousands of Tamil people in 1958 initiating the genocides that eventually led to a civil war beginning in 1983. Since the end of the civil war in 2009, the Sri Lankan state has been subject to much global criticism for violating human rights as a result of committing war crimes through bombing civilian targets, usage of heavy weaponry, the abduction and massacres of Sri Lankan Tamils and sexual violence.
Tibet
On 5 June 1959, Shri Purshottam Trikamdas, the Senior Advocate, Supreme Court of India, presented a report on Tibet to the International Commission of Jurists (an non-governmental organisation, NGO):
According to the Tibet Society of the UK, "In all, over one million Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live ...
, a fifth of the population, had died as a result of the Incorporation of Tibet into the People's Republic of China, Chinese occupation right up until the end of the Cultural Revolution."
See also
* Colonialism and genocide
* List of films featuring colonialism
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{genocide topics
Genocide of indigenous peoples,
Anti-indigenous racism
Genocide
Truth and reconciliation commissions
Truth and reconciliation reports
Settler colonialism
 On 13 April 1709, New France
On 13 April 1709, New France 
 During the American Indian Wars, the American Army carried out a number of massacres and forced relocations of Indigenous peoples that are sometimes considered genocide. The 1864 Sand Creek Massacre, which caused outrage in its own time, has been called genocide. Colonel
During the American Indian Wars, the American Army carried out a number of massacres and forced relocations of Indigenous peoples that are sometimes considered genocide. The 1864 Sand Creek Massacre, which caused outrage in its own time, has been called genocide. Colonel  The
The  Some scholars estimate that about 80% of the
Some scholars estimate that about 80% of the  In places like the
In places like the  From 1879 to 1912, the world experienced a rubber boom. Rubber prices skyrocketed, and it became increasingly profitable to extract rubber from rainforest zones in South America and Central Africa. Rubber extraction was labor-intensive, and the need for a large workforce had a significant negative effect on the indigenous population across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia and in the Congo. The owners of the plantations or rubber barons were rich, but those who collected the rubber made very little, as a large amount of rubber was needed to be profitable. Rubber barons rounded up all the Indians and forced them to tap rubber out of the trees. Slavery and gross human rights abuses were widespread, and in some areas, 90% of the Indian population was wiped out. One plantation started with 50,000 Indians and when the killings were discovered, only 8,000 were still alive. These rubber plantations were part of the Brazilian rubber market which declined as rubber plantations in Southeast Asia became more effective.
Roger Casement, an Irishman travelling the Putumayo region of Peru as a British consul during 1910–1911, documented the abuse, slavery, murder, and use of stocks for torture against the native Indians: "The crimes charged against many men now in the employ of the Peruvian Amazon Company are of the most atrocious kind, including murder, violation, and constant flogging."
From 1879 to 1912, the world experienced a rubber boom. Rubber prices skyrocketed, and it became increasingly profitable to extract rubber from rainforest zones in South America and Central Africa. Rubber extraction was labor-intensive, and the need for a large workforce had a significant negative effect on the indigenous population across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia and in the Congo. The owners of the plantations or rubber barons were rich, but those who collected the rubber made very little, as a large amount of rubber was needed to be profitable. Rubber barons rounded up all the Indians and forced them to tap rubber out of the trees. Slavery and gross human rights abuses were widespread, and in some areas, 90% of the Indian population was wiped out. One plantation started with 50,000 Indians and when the killings were discovered, only 8,000 were still alive. These rubber plantations were part of the Brazilian rubber market which declined as rubber plantations in Southeast Asia became more effective.
Roger Casement, an Irishman travelling the Putumayo region of Peru as a British consul during 1910–1911, documented the abuse, slavery, murder, and use of stocks for torture against the native Indians: "The crimes charged against many men now in the employ of the Peruvian Amazon Company are of the most atrocious kind, including murder, violation, and constant flogging."