|
Beothuk
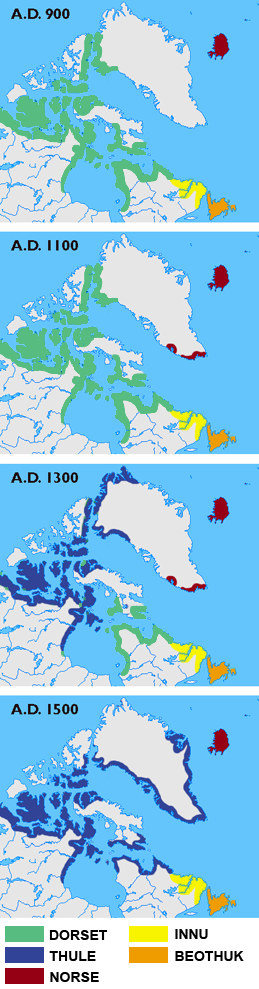
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of indigenous people who lived on the island of Newfoundland. Beginning around AD 1500, the Beothuk culture formed. This appeared to be the most recent cultural manifestation of peoples who first migrated from Labrador to present-day Newfoundland around AD 1. The ancestors of this group had three earlier cultural phases, each lasting approximately 500 years. Description The Beothuk lived throughout the island of Newfoundland, mostly in the Notre Dame and Bonavista Bay areas. Estimates vary as to the number of Beothuk at the time of contact with Europeans. Beothuk researcher Ingeborg Marshall has argued that a valid understanding of Beothuk history and culture is directly impacted by how and by whom historical records were created, pointing to the ethnocentric nature of European accounts as inherently unreliable. Scholars of the 19th and early 20th century estimated about 2,000 individuals at the time of European contact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beothuk Language Map
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of indigenous people Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ... who lived on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland. Beginning around AD 1500, the Beothuk culture formed. This appeared to be the most recent cultural manifestation of peoples who first migrated from Labrador to present-day Newfoundland around AD 1. The ancestors of this group had three earlier cultural phases, each lasting approximately 500 years. Description The Beothuk lived throughout the island of Newfoundland, mostly in the Notre Dame Bay, Notre Dame and Bonavista Bay areas. Estimates vary as to the number of Beothuk at the time of contact with Europeans. Beothuk researcher Ingeborg Marshall has argued that a valid understanding of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanawdithit
Shanawdithit (ca. 1801 – June 6, 1829), also noted as Shawnadithititis, Shawnawdithit, Nancy April and Nancy Shanawdithit, was the last known living member of the Beothuk people, who inhabited Newfoundland, Canada. Remembered for her contributions to the historical understanding of Beothuk culture, including drawings depicting interactions with European settlers, Shanawdithit died of tuberculosis in St. John's, Newfoundland on June 6, 1829. Early life with the Beothuk Shanawdithit was born near a large lake on the island of Newfoundland in about 1801. At the time the Beothuk population was dwindling, their traditional way of life becoming increasingly unsustainable in the face of encroachment from both European colonial settlements and other Indigenous peoples, as well as infectious diseases from Europe such as smallpox against which they had little or no immunity. The Beothuks were also slowly being cut off from the sea, one of their food sources. During this period, mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newfoundland (island)
Newfoundland (, ; french: link=no, Terre-Neuve, ; ) is a large island off the east coast of the North American mainland and the most populous part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It has 29 percent of the province's land area. The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula by the Strait of Belle Isle and from Cape Breton Island by the Cabot Strait. It blocks the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, creating the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the world's largest estuary. Newfoundland's nearest neighbour is the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. With an area of , Newfoundland is the world's 16th-largest island, Canada's fourth-largest island, and the largest Canadian island outside the North. The provincial capital, St. John's, is located on the southeastern coast of the island; Cape Spear, just south of the capital, is the easternmost point of North America, excluding Greenland. It is common to consider all directly neighbouring i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Indian Lake
Beothuk Lake, formerly Red Indian Lake, is located in the interior of central Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The lake drains into the Exploits River which flows through the interior of Newfoundland and exits into the Atlantic Ocean through the Bay of Exploits. Lloyds River, the Victoria River and Star River feed into the lake. History The Beothuk, also known as 'Red Indians,' inhabited several campsites on the shore of the lake. An expedition into the interior by John Cartwright and brother George Cartwright in search of the Beothuk found only abandoned campsites. At the time of their discovery of the lake they named it ''Lieutenant's Lake'' and they had assumed that the lake was part of the same system as ''Lake Mickmack'', known today as Grand Lake. In January 1811, an expedition led by David Buchan travelled up the Exploits River in an attempt to establish friendly relations with the Beothuk; Buchan found them, but the encounter went badl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Buchan
David Buchan (1780 – after 8 December 1838) was a Scottish naval officer and Arctic explorer. Family In 1802 or 1803, he married Maria Adye. They had at least three children. Exploration In 1806, Buchan was appointed as a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, and from about 1808 to 1817 he operated in and around Newfoundland. In 1810 he was captain of HMS ''Adonis''. In autumn 1810 he conducted an expedition to the River of Exploits. From there he and his men marched inland for 130 miles to establish contact with the dwindling native Beothuk population, one of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas in the region. The expedition resulted in the death and decapitation of two marines at their hands.William James Mills, ''Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia'', ABC-CLIO, 2003; In 1813, ''Adonis'' and the frigate escorted the Newfoundland fishing fleet back to Britain. The voyage was stormy and the vessels separated near the English Channel. ''Adonis'' regained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. * Yellow ochre, , is a hydrated iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre. * Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite, which is an anhydrous iron oxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Guy (governor)
John Guy (25 December 1568 – February 1629) was an English merchant adventurer, colonist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1621 to 1624. He was the first proprietary governor of Newfoundland Colony, the first attempt to establish a colony on Newfoundland. Early life Guy was the eldest son and second child of Thomas Guy, a cordwainer (shoemaker) of Bristol. He was born on 25 December 1568, and baptized a week later on 1 January 1569 at St Mary le Port Church, Bristol. He spent his youth growing up amongst his siblings, and was well educated for his times, he managed in later life to write poetry in Latin. He was apprenticed to a yeoman farmer, and on his parents' deaths, he inherited the family shoemaking business, he had various farming interests, and served as a factor representing the interests of the Bristol merchant community overseas for a period in Spain, where he mastered the art of navigation. Guy became a merchant and was admitted to the corporati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Cartwright (trader)
George Cartwright (12 February 1739/40 – 19 May 1819) was an English army officer and a trader and explorer in Newfoundland and Labrador. His name is borne by Cartwright, a settlement at the entrance to Sandwich Bay. Early life and family George Cartwright was born at Marnham in Nottinghamshire, England, an elder brother of Edmund Cartwright, clergyman and inventor of the power loom, and of John Cartwright, naval officer and English parliamentary reformer. Army career Cartwright became a gentleman cadet in the Royal Military Academy at Woolwich, London, when he was fifteen. He served in India as ensign in the 39th Foot. In 1759, he was promoted lieutenant while in Ireland. In 1760 he was aide-de-camp to the Marquess of Granby in Germany and a staff officer under Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick. He was brevetted captain in 1762, returned to England and went on half pay from 1762 to 1766. In 1766, Cartwright was commissioned Captain in the 37th Foot, and went to Minorca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skræling
''Skræling'' (Old Norse and Icelandic: ''skrælingi'', plural ''skrælingjar'') is the name the Norse Greenlanders used for the peoples they encountered in North America (Canada and Greenland). In surviving sources, it is first applied to the Thule people, the proto-Inuit group with whom the Norse coexisted in Greenland after about the 13th century. In the sagas, it is also used for the peoples of the region known as Vinland whom the Norse encountered and fought during their expeditions there in the early 11th century. Etymology The word is most likely related to the Old Norse word , meaning "dried skin", in reference to the animal pelts worn by the Inuit. William Thalbitzer (1932: 14) speculated that might have been derived from the Old Norse verb , meaning "bawl, shout, or yell". In modern Icelandic, means "barbarian", whereas the Danish descendant, , means "weakling". The term is thought to have first been used by in his work , also called ''The Book of the Icelanders' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auk
The great auk (''Pinguinus impennis'') is a species of flightless alcid that became extinct in the mid-19th century. It was the only modern species in the genus ''Pinguinus''. It is not closely related to the birds now known as penguins, which were discovered later by Europeans and so named by sailors because of their physical resemblance to the great auk. It bred on rocky, remote islands with easy access to the ocean and a plentiful food supply, a rarity in nature that provided only a few breeding sites for the great auks. When not breeding, they spent their time foraging in the waters of the North Atlantic, ranging as far south as northern Spain and along the coastlines of Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Norway, Ireland, and Great Britain. The bird was tall and weighed about , making it the largest alcid to survive into the modern era, and the second-largest member of the alcid family overall (the prehistoric ''Miomancalla'' was larger). It had a black ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples In Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and ''Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. ''Aboriginal peoples'' as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', though in most Indigenous circles ''Aboriginal'' has also fallen into disfavour. Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are some of the earliest known sites of human habitation in Canada. The Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indian Clovis culture, Clovis, Plano cultures, Plano and Pre-Dorset cultures pre-date the current Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Projectile point tools, spears, pottery, bangles, chisels and Scraper (archaeology), scrapers mark archaeological sites, thus distinguishing cultural periods, traditions, and lithic reduction styles. The characteristics of Indigenous culture in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)