French Revolutionary wars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the
 While the revolutionary government frantically raised fresh troops and reorganized its armies, a mostly Prussian Allied army under
While the revolutionary government frantically raised fresh troops and reorganized its armies, a mostly Prussian Allied army under
 Spain and Portugal entered the anti-French coalition in January 1793. Britain began military preparations in late 1792 and declared that war was inevitable unless France gave up its conquests, notwithstanding French assurances they would not attack Holland or annex the Low Countries. Britain expelled the French ambassador following the execution of
Spain and Portugal entered the anti-French coalition in January 1793. Britain began military preparations in late 1792 and declared that war was inevitable unless France gave up its conquests, notwithstanding French assurances they would not attack Holland or annex the Low Countries. Britain expelled the French ambassador following the execution of
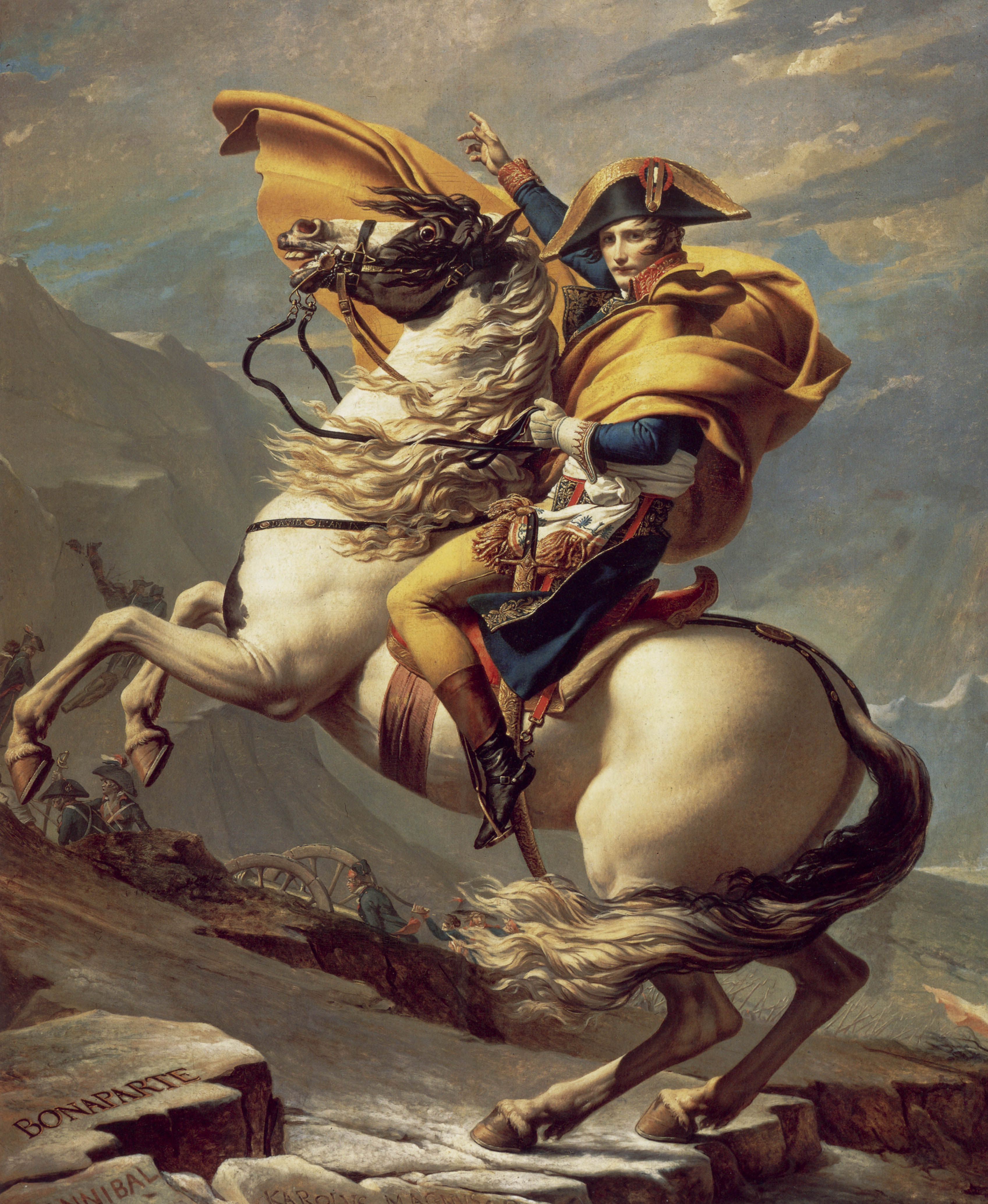
 The year 1794 brought increased success to the French armies. On the Alpine frontier, there was little change, with the French invasion of
The year 1794 brought increased success to the French armies. On the Alpine frontier, there was little change, with the French invasion of

 The year opened with French forces in the process of attacking the
The year opened with French forces in the process of attacking the
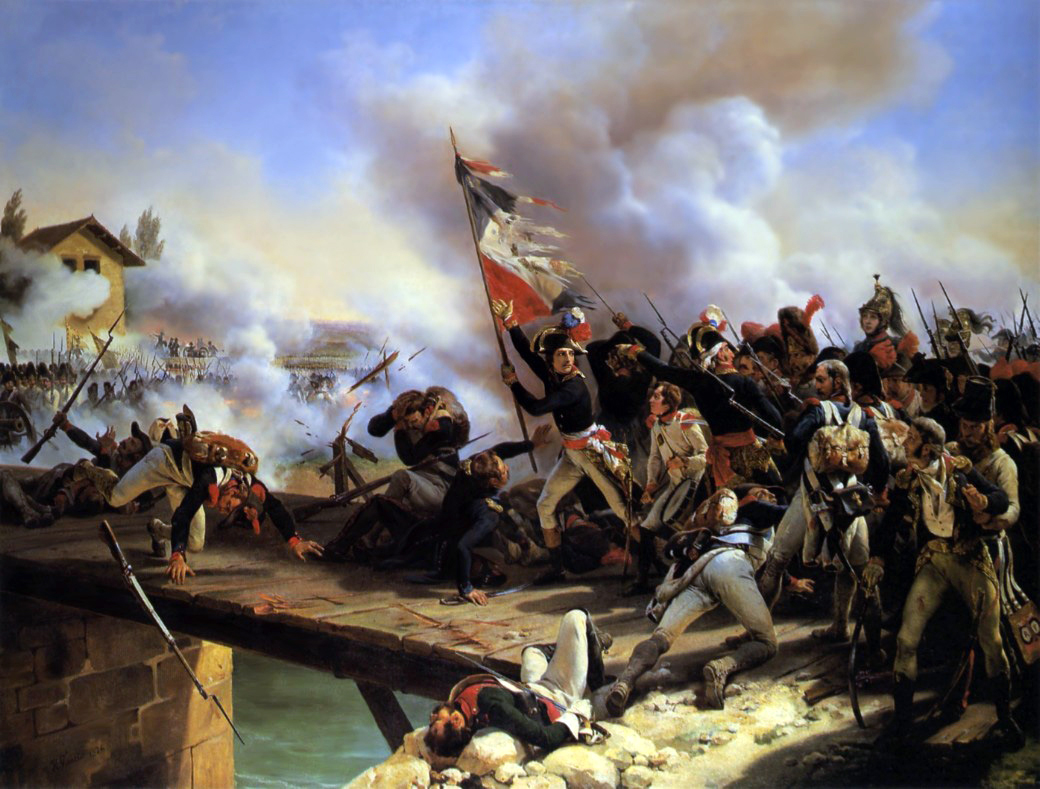

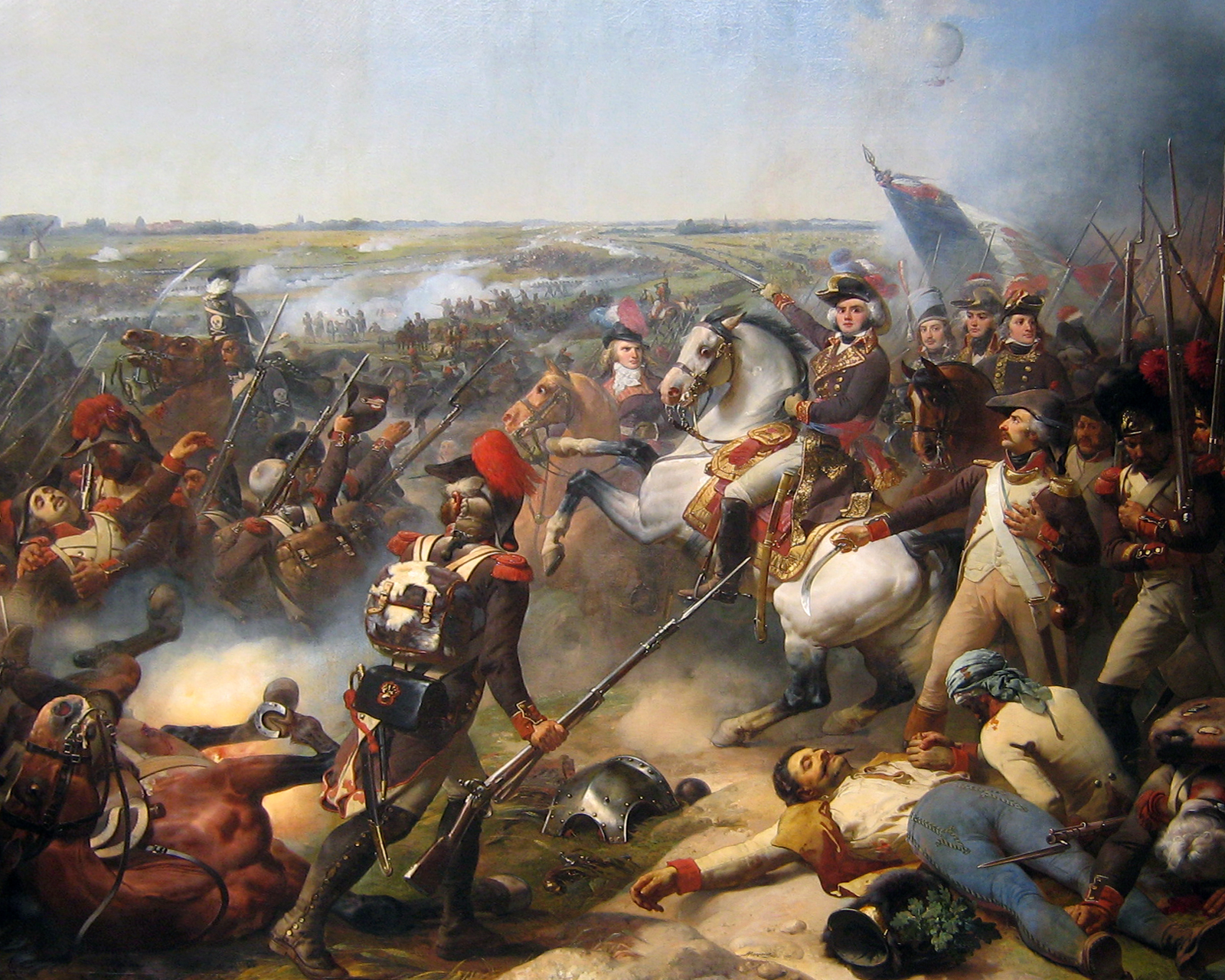
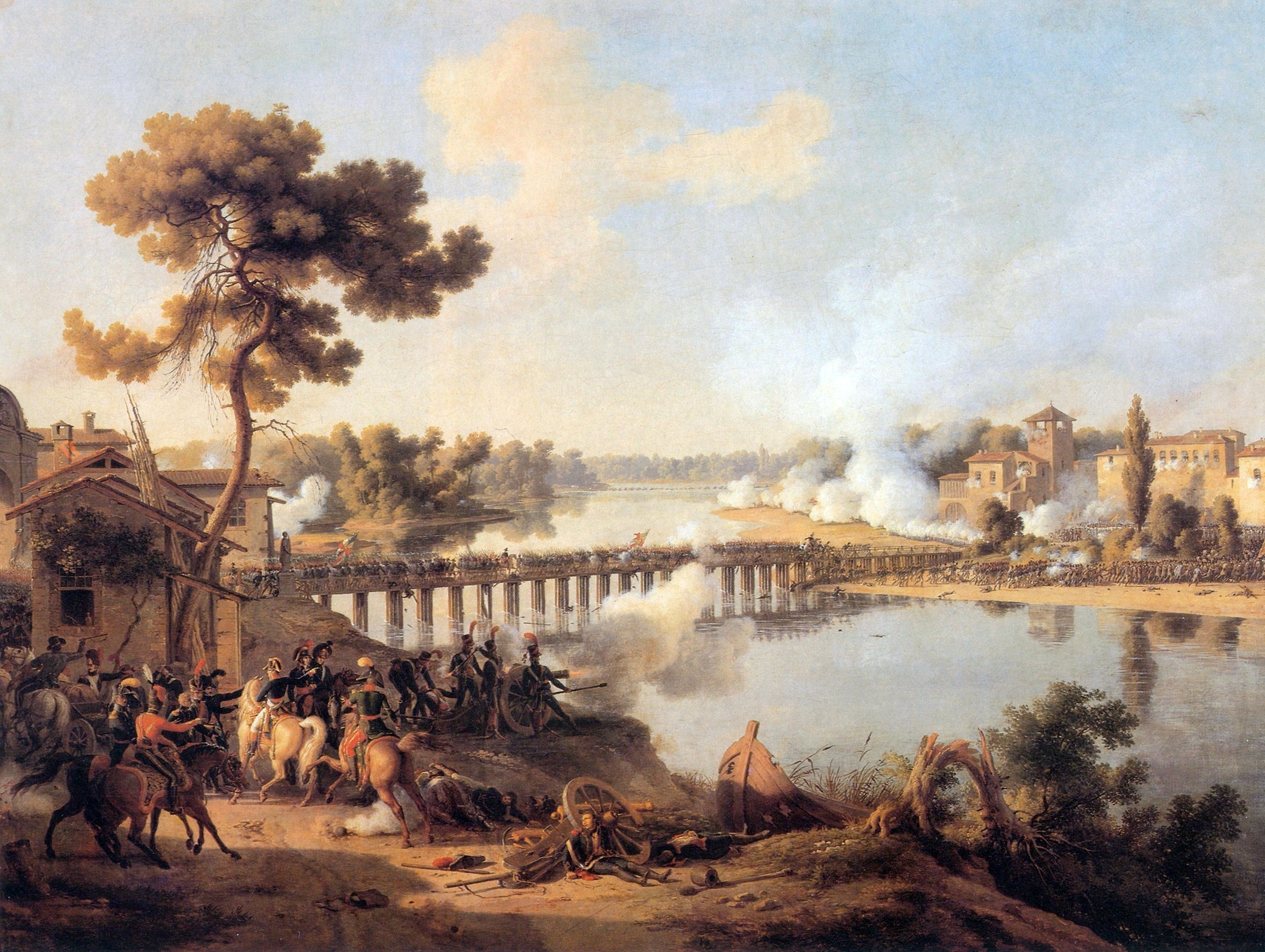 The French prepared a great advance on three fronts, with Jourdan and
The French prepared a great advance on three fronts, with Jourdan and
 On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer.
On 22 February French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the '' La Legion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists,
On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer.
On 22 February French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the '' La Legion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists,
 With only Britain left to fight and not enough of a navy to fight a direct war, Napoleon conceived of an invasion of Egypt in 1798, which satisfied his personal desire for glory and the Directory's desire to have him far from Paris. The military objective of the expedition is not entirely clear, but may have been to threaten British dominance in India.
Napoleon sailed from
With only Britain left to fight and not enough of a navy to fight a direct war, Napoleon conceived of an invasion of Egypt in 1798, which satisfied his personal desire for glory and the Directory's desire to have him far from Paris. The military objective of the expedition is not entirely clear, but may have been to threaten British dominance in India.
Napoleon sailed from

 In Egypt, Napoleon had consolidated his control of the country for the time being. Soon after the beginning of the year, he mounted an invasion of Syria, capturing El Arish and Jaffa. On 17 March, he laid siege to Acre, and defeated an Ottoman effort to relieve the city at the Battle of Mount Tabor on 17 April. However, his repeated assaults on Acre were driven back by Ottoman and British forces under the command of
In Egypt, Napoleon had consolidated his control of the country for the time being. Soon after the beginning of the year, he mounted an invasion of Syria, capturing El Arish and Jaffa. On 17 March, he laid siege to Acre, and defeated an Ottoman effort to relieve the city at the Battle of Mount Tabor on 17 April. However, his repeated assaults on Acre were driven back by Ottoman and British forces under the command of  The Army was reorganized, and a portion placed under the command of André Masséna and merged with the Army of Helvetia. Following the reorganization and change in command, the Army participated in several skirmishes and actions on the eastern part of the Swiss Plateau, including the Battle of Winterthur. After this action, three forces of the imperial army united north of Zürich, completing a partial encirclement of Massena's combined Army of the Danube and Army of Switzerland. A few days later, at the First Battle of Zurich, Massena was forced west, across the Limmat. In late summer, 1799, Charles was ordered to support imperial activities in the middle Rhineland; he withdrew north across the Rhine, and marched toward
The Army was reorganized, and a portion placed under the command of André Masséna and merged with the Army of Helvetia. Following the reorganization and change in command, the Army participated in several skirmishes and actions on the eastern part of the Swiss Plateau, including the Battle of Winterthur. After this action, three forces of the imperial army united north of Zürich, completing a partial encirclement of Massena's combined Army of the Danube and Army of Switzerland. A few days later, at the First Battle of Zurich, Massena was forced west, across the Limmat. In late summer, 1799, Charles was ordered to support imperial activities in the middle Rhineland; he withdrew north across the Rhine, and marched toward
 In Italy, the Austrians under General Melas attacked first, and by the third week in April had advanced to the Var, with Massena and half his army in
In Italy, the Austrians under General Melas attacked first, and by the third week in April had advanced to the Var, with Massena and half his army in  General of Division Jean Victor Marie Moreau commanded a modestly-equipped army of 137,000 French troops. Of these, 108,000 troops were available for field operations while the other 29,000 watched the Swiss border and held the Rhine fortresses. First Consul
General of Division Jean Victor Marie Moreau commanded a modestly-equipped army of 137,000 French troops. Of these, 108,000 troops were available for field operations while the other 29,000 watched the Swiss border and held the Rhine fortresses. First Consul
 By 9 February, the Austrians had signed the
By 9 February, the Austrians had signed the
 The
The
excerpt and text search
* Bryant, Arthur. ''Years of Endurance 1793–1802'' (1942); on Britain * Bryant, Arthur. ''Years of victory, 1802–1812'' (1942); on Britain * Clausewitz, Carl von (2018). ''Napoleon's 1796 Italian Campaign.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Clausewitz, Carl von (2020). ''Napoleon Absent, Coalition Ascendant: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 1.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Clausewitz, Carl von (2021). ''The Coalition Crumbles, Napoleon Returns: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 2.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Connelly, Owen. ''The wars of the French Revolution and Napoleon, 1792–1815'' (2006) * Crawley, C. W., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 9: War and Peace in an Age of Upheaval, 1793–1830'' (1965), comprehensive global coverage by experts * Doughty, Robert, and
excerpt and text search
ch 1 * Forrest, Alan. ''Soldiers of the French Revolution'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. "French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802)" in Gordon Martel, ed. ''The Encyclopedia of War'' (2012). * Forrest, Alan. ''Conscripts and Deserters: The Army and French Society During the Revolution and Empire'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. ''Napoleon's Men: The Soldiers of the Revolution and Empire'' (2002) * Fremont-Barnes, Gregory. ''The French Revolutionary Wars'' (Essential Histories) (2013
excerpt and text search
* Fremont-Barnes, Gregory, ed. ''The Encyclopedia of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars: A Political, Social, and Military History'' (3 vol. 2006) * Gardiner, Robert. ''Fleet Battle And Blockade: The French Revolutionary War 1793–1797'' (2006), nava
excerpt and text search
*
excerpt and text search
military topics, but not a battle history * Knight, Roger. ''Britain Against Napoleon: The Organisation of Victory, 1793–1815'' (2013) * Lavery, Brian. '' Nelson's Navy, Revised and Updated: The Ships, Men, and Organization, 1793–1815'' (2nd ed. 2012) * Lefebvre, Georges. ''The French Revolution Volume II: from 1793 to 1799'' (1964). * Lynn, John A. ''The Bayonets of the Republic: Motivation And Tactics in the Army of Revolutionary France, 1791–94'' (1984) * Roberts, Andrew. ''Napoleon'' (2014), a major biography * Rodger, A.B. ''The War of the Second Coalition: 1798 to 1801, a strategic commentary'' (1964) * Ross, Steven T. '' Quest for Victory; French Military Strategy, 1792–1799'' (1973) * Ross, Steven T. ''European Diplomatic History, 1789–1815: France Against Europe'' (1969) * * Rothenberg, Gunther E. "The Origins, Causes, and Extension of the Wars of the French Revolution and Napoleon," ''Journal of Interdisciplinary History'' (1988) 18#4 pp. 771–9
in JSTOR
* Schroeder, Paul W. ''The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848'' (Oxford University Press, 1996); advanced diplomatic history; pp. 100–230 * Schneid, Frederick C.
''The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars''
European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011. Retrieved 29 June 2011. * Scott, Samuel F. ''From Yorktown to Valmy: The Transformation of the French Army in an Age of Revolution'' (University Press of Colorado, 1998)
online
* Simms, Brendan. "Britain and Napoleon," ''Historical Journal'' (1998) 41#3 pp. 885–9
in JSTOR
The French Revolution
'
(2015). {{authority control French Revolutionary Wars, 1790s conflicts Global conflicts 1790s in France 1800s in France Wars involving Baden Wars involving the Holy Roman Empire Wars involving Ireland Wars involving Italy Wars involving Monaco Wars involving the Kingdom of Naples Wars involving the Netherlands Wars involving Norway Wars involving the Ottoman Empire Wars involving the Papal States Wars involving Poland Wars involving Portugal Wars involving the Russian Empire Wars involving the United Kingdom Wars involving the United States Wars involving the Republic of Venice Conflicts in 1801 Conflicts in 1802 Conflicts in 1800 als:Koalitionskriege
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
. They pitted France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
against Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and the Rhineland in Europe and abandoned Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a U.S. state, state in the Deep South and South Central United States, South Central regions of the United States. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-smal ...
in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.
As early as 1791, the other monarchies of Europe looked with outrage at the revolution and its upheavals; and they considered whether they should intervene, either in support of King Louis XVI, to prevent the spread of revolution, or to take advantage of the chaos in France. Austria stationed significant troops on its French border and together with Prussia, issued the Declaration of Pillnitz, which threatened severe consequences should anything happen to King Louis XVI and Queen Marie-Antoinette. After Austria refused to recall its troops from the French border and to back down on the perceived threat of using force, France declared war on Austria and Prussia in the spring of 1792; both countries responded with a coordinated invasion that was eventually turned back at the Battle of Valmy
The Battle of Valmy, also known as the Cannonade of Valmy, was the first major victory by the army of France during the Revolutionary Wars that followed the French Revolution. The battle took place on 20 September 1792 as Prussian troops com ...
in September. This victory emboldened the National Convention
The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National ...
to abolish the monarchy. A series of victories by the new French armies abruptly ended with defeat at Neerwinden in the spring of 1793. The French suffered additional defeats in the remainder of the year and these difficult times allowed the Jacobins to rise to power and impose the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First French Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public Capital punishment, executions took pl ...
to unify the nation.
In 1794, the situation improved dramatically for the French as huge victories at Fleurus
Fleurus (; wa, Fleuru) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It has been the site of four major battles.
The municipality consists of the following districts: Brye, Heppignies, Fleurus, Lambusart, ...
against the Austrians and at the Black Mountain
Black Mountain may refer to:
Places Australia
* Black Mountain (Australian Capital Territory), a mountain in Canberra
* Black Mountain, New South Wales, a village in Armidale Regional Council, New South Wales
* Black Mountain, Queensland, a loca ...
against the Spanish signaled the start of a new stage in the wars. By 1795, the French had captured the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
. The French also put Spain and Prussia out of the war with the Peace of Basel
The Peace of Basel of 1795 consists of three peace treaties involving France during the French Revolution (represented by François de Barthélemy).
*The first was with Prussia (represented by Karl August von Hardenberg) on 5 April;
*The sec ...
. A hitherto unknown general named Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
began his first campaign in Italy in April 1796. In less than a year, French armies under Napoleon decimated the Habsburg forces and evicted them from the Italian peninsula, winning almost every battle and capturing 150,000 prisoners. With French forces marching toward Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, the Austrians sued for peace and agreed to the Treaty of Campo Formio, ending the First Coalition against the Republic.
The War of the Second Coalition began in 1798 with the French invasion of Egypt
The French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801) was Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in the Ottoman territories of Egypt and Syria, proclaimed to defend French trade interests, to establish scientific enterprise in the region. It was the p ...
, headed by Napoleon. The Allies took the opportunity presented by the French effort in the Middle East to regain territories lost from the First Coalition. The war began well for the Allies in Europe, where they gradually pushed the French out of Italy and invaded Switzerland – racking up victories at Magnano, Cassano and Novi along the way. However, their efforts largely unraveled with the French victory at Zurich in September 1799, which caused Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
to drop out of the war. Meanwhile, Napoleon's forces annihilated a series of Egyptian and Ottoman armies at the battles of the Pyramids
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
, Mount Tabor
Mount Tabor ( he, הר תבור) (Har Tavor) is located in Lower Galilee, Israel, at the eastern end of the Jezreel Valley, west of the Sea of Galilee.
In the Hebrew Bible (Joshua, Judges), Mount Tabor is the site of the Battle of Mount T ...
and Abukir
Abu Qir ( ar, ابو قير, ''Abu Qīr'', or , ), formerly also spelled Abukir or Aboukir, is a town on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt, near the ruins of ancient Canopus and northeast of Alexandria by rail. It is located on Abu Qir Penin ...
. These victories in Egypt further enhanced Napoleon's popularity back in France, and he returned in triumph in the autumn of 1799, although the Egyptian Campaign ultimately ended in failure. Furthermore, the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
had won the Battle of the Nile in 1798, further strengthening British control of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
and weakening the French Navy.
Napoleon's arrival from Egypt led to the fall of the Directory in the Coup of 18 Brumaire, with Napoleon installing himself as Consul. Napoleon then reorganized the French army and launched a new assault against the Austrians in Italy during the spring of 1800. This brought a decisive French victory at the Battle of Marengo in June 1800, after which the Austrians withdrew from the peninsula once again. Another crushing French triumph at Hohenlinden in Bavaria forced the Austrians to seek peace for a second time, leading to the Treaty of Lunéville
The Treaty of Lunéville (or Peace of Lunéville) was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville on 9 February 1801. The signatory parties were the French Republic and Emperor Francis II, who signed on his own behalf as ruler of the hereditary do ...
in 1801. With Austria and Russia out of the war, Britain found itself increasingly isolated and agreed to the Treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it s ...
with Napoleon's government in 1802, concluding the Revolutionary Wars. However, the lingering tensions proved too difficult to contain, and the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
began over a year later with the formation of the Third Coalition, continuing the series of Coalition Wars.
War of the First Coalition
1791–1792
The key figure in initial foreign reaction to the revolution was Holy Roman Emperor Leopold II, brother of Louis XVI's QueenMarie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette Josèphe Jeanne (; ; née Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last queen of France before the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria, and was the penultimate child ...
. Leopold had initially looked on the Revolution with equanimity, but became more and more disturbed as the Revolution became more radical, although he still hoped to avoid war. On 27 August 1791, Leopold and King Frederick William II of Prussia
Frederick William II (german: Friedrich Wilhelm II.; 25 September 1744 – 16 November 1797) was King of Prussia from 1786 until his death in 1797. He was in personal union the Prince-elector of Brandenburg and (via the Orange-Nassau inherita ...
, in consultation with emigrant French nobles, issued the Declaration of Pillnitz, which declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe in the well-being of Louis and his family, and threatened vague but severe consequences if anything should befall them. Although Leopold saw the Pillnitz Declaration as a non-committal gesture to placate the sentiments of French monarchists and nobles, it was seen in France as a serious threat and was denounced by the revolutionary leaders.Georges Lefebvre, ''The French Revolution Volume II: from 1793 to 1799'' (1964) ch. 1.
France eventually issued an ultimatum demanding that the Habsburg monarchy of Austria under Leopold II, who was also Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, renounce any hostile alliances and withdraw its troops from the French border. The reply was evasive, and the French Assembly
Assembly may refer to:
Organisations and meetings
* Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions
* General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa ...
voted for war on 20 April 1792 against Francis II (who succeeded Leopold II), after a long list of grievances presented by foreign minister Charles François Dumouriez. Dumouriez prepared an immediate invasion of the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
, where he expected the local population to rise against Austrian rule as they had earlier in 1790. However, the revolution had thoroughly disorganized the army, and the forces raised were insufficient for the invasion. Following the declaration of war, French soldiers deserted ''en masse'' and in one case murdered their general, Théobald Dillon.
 While the revolutionary government frantically raised fresh troops and reorganized its armies, a mostly Prussian Allied army under
While the revolutionary government frantically raised fresh troops and reorganized its armies, a mostly Prussian Allied army under Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick
Charles William Ferdinand (german: Karl Wilhelm Ferdinand; 9 October 1735 – 10 November 1806) was the Prince of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and a military leader. His titles are usually shortened to Duke of Brunswi ...
assembled at Koblenz
Koblenz (; Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz''), spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman military post by Drusus around 8 B.C. Its na ...
on the Rhine. The duke then issued a proclamation called the Brunswick Manifesto (July 1792), written by the French king's cousin, Louis Joseph de Bourbon, Prince de Condé, the leader of an émigré corps within the Allied army, which declared the Allies' intent to restore the king to his full powers and to treat any person or town who opposed them as rebels to be condemned to death by martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
. This, however, had the effect of strengthening the resolve of the revolutionary army and government to oppose them by any means necessary.
On 10 August, a crowd stormed the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, fr ...
, seizing the king and his family. On 19 August 1792, the invasion by Brunswick's army commenced, with Brunswick's army easily taking the fortresses of Longwy
Longwy (; older german: Langich, ; lb, label= Luxemburgish, Lonkech) is a commune in the French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle, Lorraine, administrative region of Grand Est, northeastern France.
The inhabitants are known as ''Longovicien ...
and Verdun
Verdun (, , , ; official name before 1970 ''Verdun-sur-Meuse'') is a large city in the Meuse department in Grand Est, northeastern France. It is an arrondissement of the department.
Verdun is the biggest city in Meuse, although the capital ...
. The invasion continued, but at Valmy on 20 September, the invaders came to a stalemate against Dumouriez and Kellermann in which the highly professional French artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieg ...
distinguished itself. Although the battle was a tactical draw, it gave a great boost to French morale. Further, the Prussians, finding that the campaign had been longer and more costly than predicted, decided that the cost and risk of continued fighting was too great and, with winter approaching, they decided to retreat from France to preserve their army. The next day, the monarchy was formally abolished as the First Republic was declared (21 September 1792).
Meanwhile, the French had been successful on several other fronts, occupying Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
...
and Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
, which were parts of the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
, while General Custine invaded Germany, occupying several German towns along the Rhine and reaching as far as Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its ...
. Dumouriez went on the offensive in the Austrian Netherlands once again, winning a great victory over the Austrians at the Battle of Jemappes
The Battle of Jemappes (6 November 1792) took place near the town of Jemappes in Hainaut, Austrian Netherlands (now Belgium), near Mons during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. One of the first major offe ...
on 6 November and occupying the entire country by the beginning of winter.
1793
 Spain and Portugal entered the anti-French coalition in January 1793. Britain began military preparations in late 1792 and declared that war was inevitable unless France gave up its conquests, notwithstanding French assurances they would not attack Holland or annex the Low Countries. Britain expelled the French ambassador following the execution of
Spain and Portugal entered the anti-French coalition in January 1793. Britain began military preparations in late 1792 and declared that war was inevitable unless France gave up its conquests, notwithstanding French assurances they would not attack Holland or annex the Low Countries. Britain expelled the French ambassador following the execution of Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was e ...
and on 1 February, France responded by declaring war on Great Britain and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
.
France drafted hundreds of thousands of men, beginning a policy of using mass conscription to deploy more of its manpower than the autocratic states could manage to do (first stage, with a decree of 24 February 1793 ordering the draft of 300,000 men, followed by the general mobilization of all the young men able to be drafted, through the famous decree of 23 August 1793). Nonetheless, the Coalition allies launched a determined drive to invade France during the Flanders Campaign
The Flanders Campaign (or Campaign in the Low Countries) was conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. A coalition of states representing the Ancien Régime in Western Europe – Au ...
.
France suffered severe reverses at first. They were driven out of the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
, and serious revolts flared in the west and south of France. One of these, at Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
, was the first serious taste of action for an unknown young artillery officer Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
. He contributed to the siege of the city and its harbour by planning an effective assault with well-placed artillery batteries raining projectiles down on rebel positions. This performance helped make his reputation as a capable tactician, and it fueled his meteoric rise to military and political power. Once the city was occupied, he participated in pacifying the rebelling citizens of Toulon with the same artillery that he first used to conquer the city.
By the end of the year, large new armies had turned back foreign invaders, and the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First French Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public Capital punishment, executions took pl ...
, a fierce policy of repression, had suppressed internal revolts. The French military was in the ascendant. Lazare Carnot
Lazare Nicolas Marguerite, Count Carnot (; 13 May 1753 – 2 August 1823) was a French mathematician, physicist and politician. He was known as the "Organizer of Victory" in the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars.
Education and early ...
, a scientist and prominent member of the Committee of Public Safety
The Committee of Public Safety (french: link=no, Comité de salut public) was a committee of the National Convention which formed the provisional government and war cabinet during the Reign of Terror, a violent phase of the French Revolution ...
, organized the fourteen armies of the Republic, and was then nicknamed the Organizer of the Victory.
1794
Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
failing. On the Spanish border, the French under General Dugommier rallied from their defensive positions at Bayonne
Bayonne (; eu, Baiona ; oc, label= Gascon, Baiona ; es, Bayona) is a city in Southwestern France near the Spanish border. It is a commune and one of two subprefectures in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine ...
and Perpignan
Perpignan (, , ; ca, Perpinyà ; es, Perpiñán ; it, Perpignano ) is the prefecture of the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France, in the heart of the plain of Roussillon, at the foot of the Pyrenees a few kilometres from the ...
, driving the Spanish out of Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of th ...
and invading Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
. Dugommier was killed in the Battle of the Black Mountain in November.
On the northern front in the Flanders Campaign
The Flanders Campaign (or Campaign in the Low Countries) was conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. A coalition of states representing the Ancien Régime in Western Europe – Au ...
, the Austrians and French both prepared offensives in Belgium, with the Austrians besieging Landrecies and advancing towards Mons
Mons (; German and nl, Bergen, ; Walloon and pcd, Mont) is a city and municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the province of Hainaut, Belgium.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. ...
and Maubeuge. The French prepared an offensive on multiple fronts, with two armies in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
under Pichegru and Moreau
Moreau may refer to:
People
*Moreau (surname)
Places
*Moreau, New York
*Moreau River (disambiguation)
Music
*An alternate name for the band Cousteau, used for the album ''Nova Scotia'' in the United States for legal reasons
In fiction
*Dr. Mo ...
, and Jourdan attacking from the German border. The French withstood several damaging but inconclusive actions before regaining the initiative at the battles of Tourcoing
Tourcoing (; nl, Toerkonje ; vls, Terkoeje; pcd, Tourco) is a city in northern France on the Belgian border. It is designated municipally as a commune within the department of Nord. Located to the north-northeast of Lille, adjacent to Rouba ...
and Fleurus
Fleurus (; wa, Fleuru) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It has been the site of four major battles.
The municipality consists of the following districts: Brye, Heppignies, Fleurus, Lambusart, ...
in June. The French armies drove the Austrians, British, and Dutch beyond the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
, occupying Belgium, the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhineland ...
, and the south of the Netherlands.
On the middle Rhine front in July, General Michaud's Army of the Rhine attempted two offensives in July in the Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single ...
, the second of which was successful but not followed up, allowing for a Prussian counter-attack in September. Otherwise this sector of the front was largely quiet over the course of the year.
At sea, the French Atlantic Fleet succeeded in holding off a British attempt to interdict a vital cereal convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be use ...
from the United States on the Glorious First of June, though at the cost of one quarter of its strength. In the Caribbean, the British fleet landed in Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
in February, taking the whole island by 24 March and holding it until the Treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it s ...
, and in Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
in April, where they captured the island briefly but were driven out by Victor Hugues later in the year. In the Mediterranean, following the British evacuation of Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
, the Corsican leader Pasquale Paoli agreed with admiral Samuel Hood to place Corsica under British protection in return for assistance capturing French garrisons at Saint-Florent, Bastia
Bastia (, , , ; co, Bastìa ) is a communes of France, commune in the Departments of France, department of Haute-Corse, Corsica, France. It is located in the northeast of the island of Corsica at the base of Cap Corse. It also has the second-hi ...
, and Calvi, creating the short-lived Anglo-Corsican Kingdom.
By the end of the year French armies had won victories on all fronts, and as the year closed they began advancing into the Netherlands.
1795

 The year opened with French forces in the process of attacking the
The year opened with French forces in the process of attacking the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
in the middle of winter. The Dutch people rallied to the French call and started the Batavian Revolution
The Batavian Revolution ( nl, De Bataafse Revolutie) was a time of political, social and cultural turmoil at the end of the 18th century that marked the end of the Dutch Republic and saw the proclamation of the Batavian Republic. The period of ...
. City after city was occupied by the French. The Dutch fleet was captured, and the stadtholder William V William V may refer to:
* William V, Duke of Aquitaine (969–1030)
* William V of Montpellier (1075–1121)
* William V, Marquess of Montferrat (1191)
*William V, Count of Nevers
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcast ...
fled to be replaced by a popular Batavian Republic, a sister republic which supported the revolutionary cause and signed a treaty with the French, ceding the territories of North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to th ...
and Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
to France on 16 May.
With the Netherlands falling, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
also decided to leave the coalition, signing the Peace of Basel
The Peace of Basel of 1795 consists of three peace treaties involving France during the French Revolution (represented by François de Barthélemy).
*The first was with Prussia (represented by Karl August von Hardenberg) on 5 April;
*The sec ...
on 6 April, ceding the west bank of the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
to France. This freed Prussia to finish the occupation of Poland.
The French army in Spain advanced in Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
while taking Bilbao
)
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize = 275 px
, map_caption = Interactive map outlining Bilbao
, pushpin_map = Spain Basque Country#Spain#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption ...
and Vitoria and marching toward Castile. By 10 July, Spain also decided to make peace, recognizing the revolutionary government and ceding the territory of Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
, but returning to the pre-war borders in Europe. This left the armies on the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
free to march east and reinforce the armies on the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, and the combined army overran Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
.
Meanwhile in Asia and Africa, Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was inco ...
and Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
were invaded by the British.
Meanwhile, Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
's attempt to reinforce the rebels in the Vendée by landing troops at Quiberon failed, and a conspiracy to overthrow the republican government from within ended when Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's garrison used cannon to fire grapeshot into the attacking mob (which led to the establishment of the Directory).
On the Rhine frontier, General Pichegru, negotiating with the exiled Royalists, betrayed his army and forced the evacuation of Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's ...
and the failure of the siege of Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
by Jourdan. This was a moderate setback to the position of the French.
In northern Italy, victory at the Battle of Loano in November gave France access to the Italian peninsula.
1796

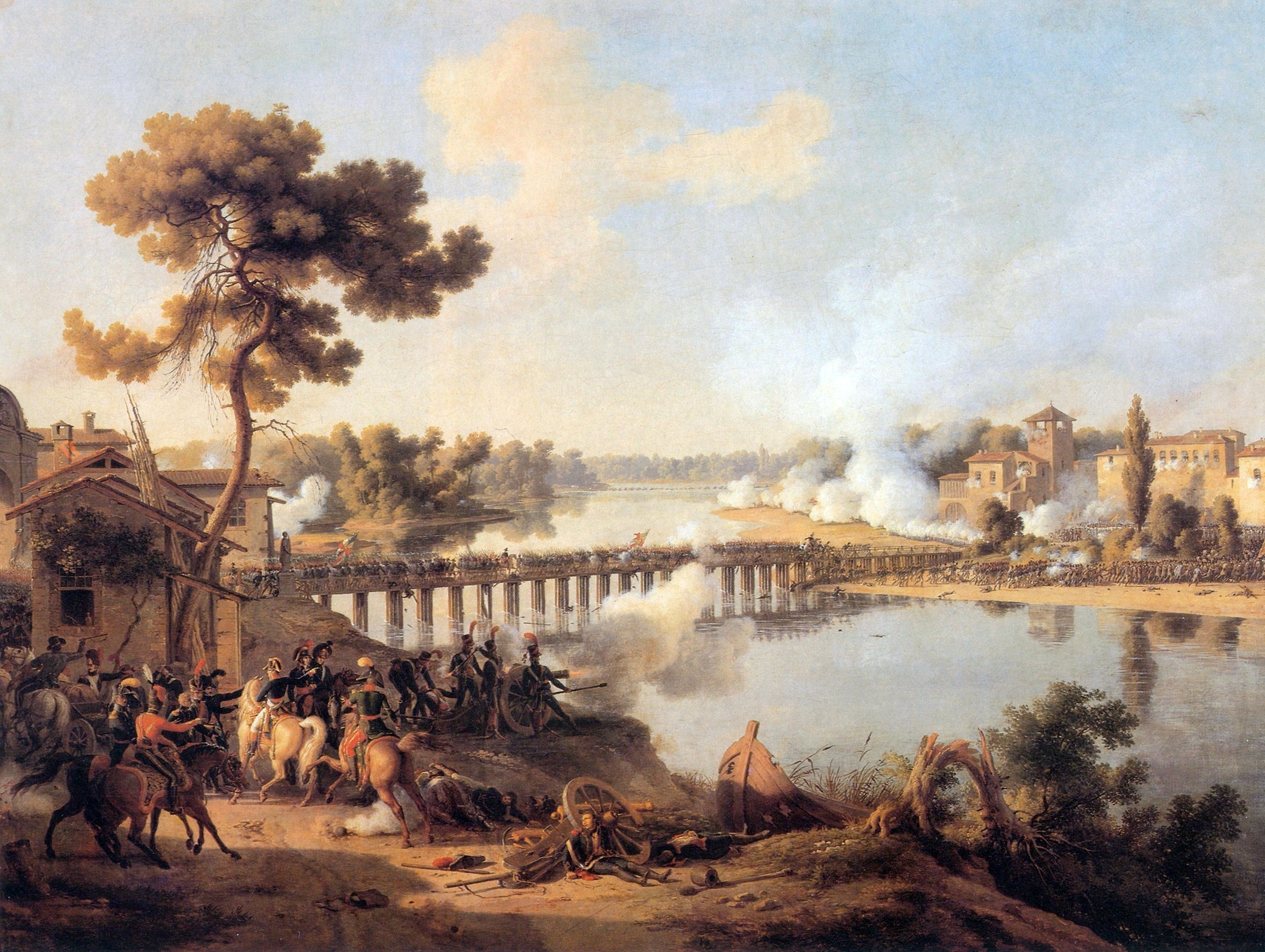 The French prepared a great advance on three fronts, with Jourdan and
The French prepared a great advance on three fronts, with Jourdan and Moreau
Moreau may refer to:
People
*Moreau (surname)
Places
*Moreau, New York
*Moreau River (disambiguation)
Music
*An alternate name for the band Cousteau, used for the album ''Nova Scotia'' in the United States for legal reasons
In fiction
*Dr. Mo ...
on the Rhine, and Bonaparte in Italy. The three armies were to link up in Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and march on Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. Jourdan and Moreau advanced rapidly into Germany, and Moreau had reached Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
and the edge of Tyrol by September, but Jourdan was defeated by Archduke Charles, and both armies were forced to retreat back across the Rhine.
Napoleon, on the other hand, was completely successful in a daring invasion of Italy. He left Paris on 11 March for Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
to take over the weak and poorly supplied Army of Italy, arriving on 26 March. The army was already being reorganised and supplied when he arrived, and he found that the situation was rapidly improving. He was soon able to carry out the plan for the invasion of Italy that he had been advocating for years, which provided for an advance over the Apennines near Altare to attack the enemy position of Ceva
Ceva, the ancient Ceba, is a small Italian town in the province of Cuneo, region of Piedmont, east of Cuneo. It lies on the right bank of the Tanaro on a wedge of land between that river and the Cevetta stream.
History
In the pre-Roman period ...
.
The Montenotte Campaign opened after Johann Beaulieu's Austrian forces attacked the extreme French eastern flank near Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of t ...
on 10 April. Bonaparte countered by attacking and crushing the isolated right wing of the allied armies at the Battle of Montenotte on 12 April. The next day he defeated an Austro-Sardinian force at the Battle of Millesimo
The Battle of Millesimo, fought on 13 and 14 April 1796, was the name that Napoleon Bonaparte gave in his correspondence to one of a series of small battles that were fought in Liguria, Northern Italy between the armies of France and the alli ...
. He then won a victory at the Second Battle of Dego, driving the Austrians northeast, away from their Piedmontese allies. Satisfied that the Austrians were temporarily inert, Bonaparte harried Michelangelo Colli's Piedmontese at Ceva
Ceva, the ancient Ceba, is a small Italian town in the province of Cuneo, region of Piedmont, east of Cuneo. It lies on the right bank of the Tanaro on a wedge of land between that river and the Cevetta stream.
History
In the pre-Roman period ...
and San Michele Mondovi before whipping them at the Battle of Mondovì. A week later, on 28 April, the Piedmontese signed an armistice at Cherasco, withdrawing from the hostilities. On 18 May they signed a peace treaty at Paris, ceding Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
...
and Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
and allowing the French bases to be used against Austria.
After a short pause, Napoleon carried out a brilliant flanking manoeuvre, and crossed the Po at Piacenza
Piacenza (; egl, label= Piacentino, Piaṡëinsa ; ) is a city and in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy, and the capital of the eponymous province. As of 2022, Piacenza is the ninth largest city in the region by population, with over ...
, nearly cutting the Austrian line of retreat. The Austrians escaped after the Battle of Fombio, but had their rear-guard mauled at Lodi on 10 May, after which the French took Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 ...
. Bonaparte then advanced eastwards again, drove off the Austrians in the Battle of Borghetto and in June began the Siege of Mantua. Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard language, Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture ...
was the strongest Austrian base in Italy. Meanwhile, the Austrians retreated north into the foothills of the Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
.
During July and August, Austria sent a fresh army into Italy under Dagobert Wurmser
Dagobert or Taginbert is a Germanic male given name, possibly from Old Frankish ''Dag'' "day" and ''beraht'' "bright".
Alternatively, it has been identified as Gaulish ''dago'' "good" ''berxto'' "bright".
Animals
* Roi Dagobert (born 1964), t ...
. Wurmser attacked toward Mantua along the east side of Lake Garda
Lake Garda ( it, Lago di Garda or ; lmo, label= Eastern Lombard, Lach de Garda; vec, Ƚago de Garda; la, Benacus; grc, Βήνακος) is the largest lake in Italy.
It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, about halfway between ...
, sending Peter Quasdanovich down the west side in an effort to envelop Bonaparte. Bonaparte exploited the Austrian mistake of dividing their forces to defeat them in detail, but in so doing, he abandoned the siege of Mantua, which held out for another six months (Carl von Clauswitz mentioned in On War
''Vom Kriege'' () is a book on war and military strategy by Prussian general Carl von Clausewitz (1780–1831), written mostly after the Napoleonic wars, between 1816 and 1830, and published posthumously by his wife Marie von Brühl in 1832. ...
that the siege might have been able to be kept up if Bonaparte had circumvallated the city). Quasdanovich was overcome at Lonato
Lonato del Garda (before 1 July 2007 simply Lonato; lmo, label= Eastern Lombard, Lonad, ) is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy, northern Italy. Lonato is located about halfway between Milan and Venice, on the sout ...
on 3 August and Wurmser at Castiglione on 5 August. Wurmser retreated to the Tyrol, and Bonaparte resumed the siege.
In September, Bonaparte marched north against Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th cen ...
in Tyrol, but Wurmser had already marched toward Mantua by the Brenta valley, leaving Paul Davidovich
Baron Paul Davidovich or Pavle Davidović ( sr-cyr, Павле Давидовић) (1737, Buda – 18 February 1814, Komárom) became a general of the Austrian Empire and a Knight of the Military Order of Maria Theresa. He played a major ro ...
's force to hold off the French. Bonaparte overran the holding force at the Battle of Rovereto. Then he followed Wurmser down the Brenta valley, to fall upon and defeat the Austrians at the Battle of Bassano on 8 September. Wurmser elected to march for Mantua with a large portion of his surviving troops. The Austrians evaded Bonaparte's attempts to intercept them but were driven into the city after a pitched battle on 15 September. This left nearly 30,000 Austrians trapped in the fortress. This number rapidly diminished due to disease, combat losses, and hunger.
The Austrians sent yet another army under József Alvinczi against Bonaparte in November. Again the Austrians divided their effort, sending Davidovich's corps from the north while Alvinczi's main body attacked from the east. At first they proved victorious over the French at Bassano, Calliano, and Caldiero. But Bonaparte ultimately defeated Alvinczi in the Battle of Arcole
The Battle of Arcole or Battle of Arcola (15–17 November 1796) was fought between French and Austrian forces southeast of Verona during the War of the First Coalition, a part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The battle saw a bold maneuver b ...
southeast of Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
. The French then turned on Davidovich in great strength and chased him into the Tyrol. Wurmser's only sortie was late and ineffectual.
The rebellion in the Vendée was also finally crushed in 1796 by Hoche, but Hoche's attempt to land a large invasion force in Ireland was unsuccessful.
1797
 On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer.
On 22 February French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the '' La Legion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists,
On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer.
On 22 February French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the '' La Legion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists, militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non- professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
and sailors under the command of John Campbell, 1st Baron Cawdor. After brief clashes with the local civilian population and Lord Cawdor's forces on 23 February, Tate was forced into an unconditional surrender
An unconditional surrender is a surrender in which no guarantees are given to the surrendering party. It is often demanded with the threat of complete destruction, extermination or annihilation.
In modern times, unconditional surrenders most oft ...
by 24 February.
In Italy, Napoleon's armies were laying siege to Mantua at the beginning of the year, and a second attempt by Austrians under Joseph Alvinczy
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the m ...
to raise the siege was driven off at the Battle of Rivoli, where the French scored a decisive victory. Finally, on 2 February, Wurmser surrendered Mantua and 18,000 troops. The Papal forces sued for peace, which was granted at Tolentino on 19 February. Napoleon was now free to attack the Austrian heartland. He advanced directly toward Austria over the Julian Alps
The Julian Alps ( sl, Julijske Alpe, it, Alpi Giulie, , ) are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps that stretch from northeastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2,864 m at Mount Triglav, the highest peak in Slovenia. A large p ...
, sending Barthélemy Joubert to invade the Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
.
Archduke Charles of Austria hurried from the German front to defend Austria, but he was defeated at the Tagliamento
The Tagliamento () is a braided river in north-east Italy, flowing from the Alps to the Adriatic Sea at a point between Trieste and Venice.
The Tagliamento river is considered as the last morphologically intact river in the Alps. (Its c ...
on 16 March, and Napoleon proceeded into Austria, occupying Klagenfurt
Klagenfurt am WörtherseeLandesgesetzblatt 2008 vom 16. Jänner 2008, Stück 1, Nr. 1: ''Gesetz vom 25. Oktober 2007, mit dem die Kärntner Landesverfassung und das Klagenfurter Stadtrecht 1998 geändert werden.'/ref> (; ; sl, Celovec), usually ...
and preparing for a rendezvous with Joubert in front of Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. In Germany, the armies of Hoche and Moreau
Moreau may refer to:
People
*Moreau (surname)
Places
*Moreau, New York
*Moreau River (disambiguation)
Music
*An alternate name for the band Cousteau, used for the album ''Nova Scotia'' in the United States for legal reasons
In fiction
*Dr. Mo ...
crossed the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
again in April after the previous year's failure. The victories of Napoleon had frightened the Austrians into making peace, and they concluded the Peace of Leoben in April, ending hostilities. However, his absence from Italy had allowed the outbreak of the revolt known as the Veronese Easters on 17 April, which was put down eight days later.
Although Britain remained at war with France, this effectively ended the First Coalition. Austria later signed the Treaty of Campo Formio, ceding the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
to France and recognizing the French border at the Rhine. Austria and France also partitioned Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
between them.
1798
 With only Britain left to fight and not enough of a navy to fight a direct war, Napoleon conceived of an invasion of Egypt in 1798, which satisfied his personal desire for glory and the Directory's desire to have him far from Paris. The military objective of the expedition is not entirely clear, but may have been to threaten British dominance in India.
Napoleon sailed from
With only Britain left to fight and not enough of a navy to fight a direct war, Napoleon conceived of an invasion of Egypt in 1798, which satisfied his personal desire for glory and the Directory's desire to have him far from Paris. The military objective of the expedition is not entirely clear, but may have been to threaten British dominance in India.
Napoleon sailed from Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label=Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the ...
to Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandr ...
, taking Malta on the way, and landing in June. Marching to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
, he won a great victory at the Battle of the Pyramids; however, his fleet was sunk by Nelson at the Battle of the Nile, stranding him in Egypt. Napoleon spent the remainder of the year consolidating his position in Egypt.
The French government also took advantage of internal strife in Switzerland to invade
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing c ...
, establishing the Helvetic Republic and annexing Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situ ...
. French troops also deposed Pope Pius VI
Pope Pius VI ( it, Pio VI; born Count Giovanni Angelo Braschi, 25 December 171729 August 1799) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 15 February 1775 to his death in August 1799.
Pius VI condemned the French Revoluti ...
, establishing a republic in Rome.
An expeditionary force was sent to County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the yew trees") is a county in Ireland. In the West of Ireland, in the province of Connacht, it is named after the village of Mayo, now generally known as Mayo Abbey. Mayo County Coun ...
, in Ireland, when it was part of the Republic of Connacht, to assist in the rebellion against Britain in the summer of 1798. It had some success against British forces, most notably at Castlebar, but was ultimately routed while trying to reach Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
. French ships sent to assist them were captured by the Royal Navy off County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconn ...
.
The French were also under pressure in the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
and Luxembourg where the local people revolted against conscription and anti-religious violence ( Peasants' War). The French had taken this territory in 1794, but it was officially theirs in 1797 due to a treaty with Austria. The French forces easily handled the Peasants' rebellion in the Southern Netherlands, and were able to put down the revolting forces in under 2 months.
The French in 1798 fought an undeclared war at sea against the United States, that was known variously as the "Quasi-War
The Quasi-War (french: Quasi-guerre) was an undeclared naval war fought from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and the French First Republic, primarily in the Caribbean and off the East Coast of the United States. The ability of Con ...
", the "Half War" and the "Pirate Wars". It was resolved peaceably with the Convention of 1800.
War of the Second Coalition
Britain and Austria organized a new coalition against France in 1798, including for the first time theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
, although no action occurred until 1799 except against the kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
1799

 In Egypt, Napoleon had consolidated his control of the country for the time being. Soon after the beginning of the year, he mounted an invasion of Syria, capturing El Arish and Jaffa. On 17 March, he laid siege to Acre, and defeated an Ottoman effort to relieve the city at the Battle of Mount Tabor on 17 April. However, his repeated assaults on Acre were driven back by Ottoman and British forces under the command of
In Egypt, Napoleon had consolidated his control of the country for the time being. Soon after the beginning of the year, he mounted an invasion of Syria, capturing El Arish and Jaffa. On 17 March, he laid siege to Acre, and defeated an Ottoman effort to relieve the city at the Battle of Mount Tabor on 17 April. However, his repeated assaults on Acre were driven back by Ottoman and British forces under the command of Jezzar Pasha
Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar ( ar, أحمد باشا الجزّار; ota, جزّار أحمد پاشا; ca. 1720–30s7 May 1804) was the Acre-based Ottoman governor of Sidon Eyalet from 1776 until his death in 1804 and the simultaneous governor of Da ...
and Sir Sidney Smith. By May, with plague rampant in his army and no sign of success against the city, Napoleon was forced to retreat into Egypt. In July, Turkey, with the help of the British navy, mounted an invasion by sea from Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. Napoleon attacked the Turkish beachheads and scored a crushing victory at the Battle of Abukir, capturing and killing the entire enemy army. In August, Napoleon decided to return to Europe, hearing of the political and military crisis in France. Leaving his army behind with Kléber in command, he sailed through the British blockade to return to Paris and resolved to take control of the government there in a coup.
In Europe, the French Army of Observation, organized with 30,000 men in four divisions, crossed the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
at Kehl and Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
in March 1799. The following day, it was renamed the Army of the Danube. Under command of Jourdan, the army advanced in four columns through the Black Forest. First Division, the right wing, assembled at Hüningen, crossed at Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
and advanced eastward along the north shore of the Rhine toward Lake Constance. Masséna, commanding the Army of Switzerland, sent a Demi-brigade
A ''demi-brigade'' ( en, Half-brigade) is a military formation used by the French Army since the French Revolutionary Wars. The ''Demi-brigade'' amalgamated the various infantry organizations of the French Revolutionary infantry into a single ...
to secure the Swiss town of Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimat ...
, on the north shore of the Rhine, which guaranteed communications between the two forces. The Advanced Guard crossed at Kehl, and Vandamme led it north-east through the mountains via Freudenstadt. This column eventually became the left flank. It was followed across the Rhine, also at Kehl, by the II. Division. The Third Division and the Reserve also crossed at Kehl, and then divided into two columns, III. Division traveling through the Black Forest via Oberkirch, and the Reserve, with most of the artillery and horse, by the valley at Freiburg im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as o ...
, where they would find more forage, and then over the mountains past the Titisee to Löffingen and Hüfingen.
The major part of the imperial army, under command of the Archduke Charles, had wintered immediately east of the Lech, which Jourdan knew, because he had sent agents into Germany with instructions to identify the location and strength of his enemy. This was less than distant; any passage over the Lech was facilitated by available bridges, both of permanent construction and temporary pontoons and a traverse through friendly territory.
In March 1799, the Army of the Danube engaged in two major battles, both in the southwestern German theater. At the intensely fought Battle of Ostrach, 21–2 March 1799, the first battle of the War of the Second Coalition, Austrian forces, under the command of Archduke Charles, defeated Jourdan's Army of the Danube. The French suffered significant losses and were forced to retreat from the region, taking up new positions to the west at Meßkirch (Messkirch, Mößkirch), and then at Stockach and Engen. At the second battle, in Stockach, on 27 March 1799, the Austrian army achieved a decisive victory over the French forces, and again pushed the French army west. Jourdan instructed his generals to take up positions in the Black Forest, and he himself established a base at Hornberg. From there, General Jourdan relegated command of the army to his chief of staff, Jean Augustin Ernouf, and traveled to Paris to ask for more and better troops and, ultimately, to request a medical leave.Young, pp. 230–345; Gallagher, p. 70–79; Jourdan, pp. 190–204.
 The Army was reorganized, and a portion placed under the command of André Masséna and merged with the Army of Helvetia. Following the reorganization and change in command, the Army participated in several skirmishes and actions on the eastern part of the Swiss Plateau, including the Battle of Winterthur. After this action, three forces of the imperial army united north of Zürich, completing a partial encirclement of Massena's combined Army of the Danube and Army of Switzerland. A few days later, at the First Battle of Zurich, Massena was forced west, across the Limmat. In late summer, 1799, Charles was ordered to support imperial activities in the middle Rhineland; he withdrew north across the Rhine, and marched toward
The Army was reorganized, and a portion placed under the command of André Masséna and merged with the Army of Helvetia. Following the reorganization and change in command, the Army participated in several skirmishes and actions on the eastern part of the Swiss Plateau, including the Battle of Winterthur. After this action, three forces of the imperial army united north of Zürich, completing a partial encirclement of Massena's combined Army of the Danube and Army of Switzerland. A few days later, at the First Battle of Zurich, Massena was forced west, across the Limmat. In late summer, 1799, Charles was ordered to support imperial activities in the middle Rhineland; he withdrew north across the Rhine, and marched toward Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's ...
, leaving Zürich and northern Switzerland in the hands of the inexperienced Alexander Korsakov
Alexander Mikhailovich Rimsky-Korsakov (russian: Алекса́ндр Миха́йлович Ри́мский-Ко́рсаков) (August 24, 1753May 25, 1840) was a Russian general remembered as an unlucky assistant to Alexander Suvorov during ...
and 25,000 Russian troops. Although the highly capable Friedrich Freiherr von Hotze
Friedrich Freiherr (Baron) von Hotze (20 April 1739 – 25 September 1799), was a Swiss-born general in the Austrian army during the French Revolutionary Wars. He campaigned in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition and in Switzer ...
remained in support, his 15,000 men were not able to counter Korsakov's poor defensive arrangements. Three weeks later, at the Second Battle of Zurich, the Russian force was annihilated, and Hotze was killed south of Zürich. This left Massena in control of northern Switzerland, and forced Suvorov into an arduous three-week march into the Vorarlberg, where his troops arrived, starving and exhausted, in mid-October.
Napoleon himself invaded Syria from Egypt, but after a failed siege of Acre retreated to Egypt, repelling a British-Turkish invasion. Alerted to the political and military crisis in France, he returned, leaving his army behind, and used his popularity and army support to mount a coup that made him First Consul
The Consulate (french: Le Consulat) was the top-level Government of France from the fall of the Directory in the coup of 18 Brumaire on 10 November 1799 until the start of the Napoleonic Empire on 18 May 1804. By extension, the term ''The ...
, the head of the French government.
1800
 In Italy, the Austrians under General Melas attacked first, and by the third week in April had advanced to the Var, with Massena and half his army in
In Italy, the Austrians under General Melas attacked first, and by the third week in April had advanced to the Var, with Massena and half his army in Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of t ...
besieged by land, by the Austrians and under tight blockade by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
. In response Berthier moved – not to the threatened frontier, but to Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situ ...
– and Massena was instructed to hold Genoa until 4 June. The Army of the Reserve was joined by Napoleon, and in mid-May set out to cross the Alps to attack the Austrian rear. The bulk of the army crossed by the Great St Bernard Pass, still under snow, and by 24 May 40,000 troops were in the valley of the Po. Artillery was man-hauled over with great effort and ingenuity; however an Austrian-held fort on the Italian side (although bypassed by infantry and cavalry) prevented most of the artillery reaching the plains of Northern Italy until the start of June.
Once over the Alps, Napoleon did not proceed directly to the relief of Genoa. Instead, he advanced on Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 ...
, to improve his lines of communication (via the Simplon and St Gotthard passes) and to threaten Melas's lines of communication with Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard language, Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture ...
and Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, in the belief that this would cause Melas to raise the siege of Genoa. He entered Milan on 2 June and by crossing to the South bank of the Po completely cut Melas's communications. Taking up a strong defensive position at Stradella, he confidently awaited an attempt by the Austrian Army to fight its way out.
However, Melas had not raised the siege of Genoa, and on 4 June, Masséna had duly capitulated. Napoleon then faced the possibility that, thanks to the British command of the Mediterranean, far from falling back, the Austrians could instead take Genoa as their new base and be supplied by sea. His defensive posture would not prevent this; he had to find and attack the Austrians before they could regroup. He therefore advanced from Stradella towards Alessandria, where Melas was, apparently doing nothing. Convinced that Melas was about to retreat, Napoleon sent strong detachments to block Melas's routes northwards to the Po, and southwards to Genoa. At this point, Melas attacked, and for all the brilliance of the previous campaign, Napoleon found himself at a significant disadvantage in the consequent Battle of Marengo (14 June). Napoleon and the French came under huge pressure in the early hours of the battle. Melas believed he had already won and turned over delivery of the final blow to a subordinate. Suddenly, the prompt return of a detached French force under Desaix Desaix may refer to:
*Louis Desaix
Louis Charles Antoine Desaix () (17 August 176814 June 1800) was a French general and military leader during the French Revolutionary Wars. According to the usage of the time, he took the name ''Louis Charles An ...
and a vigorous French counter-attack converted the battle into a decisive French victory. The Austrians lost half of their army, but Desaix was one of the French victims.
Melas promptly entered into negotiations, which led to the Austrians evacuating Northern Italy west of the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and suspending military operations in Italy. Napoleon returned to Paris after the victory, leaving Brune
Guillaume Marie-Anne Brune, 1st Count Brune (, 13 March 1764 – 2 August 1815) was a French military commander, Marshal of the Empire, and political figure who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
Early life
Bru ...
to consolidate in Italy and begin a march toward Austria.
In the German theater, the armies of France and Austria faced each other across the Rhine at the beginning of 1800. Feldzeugmeister Pál Kray led approximately 120,000 troops. In addition to his Austrian regulars, his force included 12,000 men from the Electorate of Bavaria
The Electorate of Bavaria (german: Kurfürstentum Bayern) was an independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy ...
, 6,000 troops from the Duchy of Württemberg, 5,000 soldiers of low quality from the Archbishopric of Mainz
The Electorate of Mainz (german: Kurfürstentum Mainz or ', la, Electoratus Moguntinus), previously known in English as Mentz and by its French name Mayence, was one of the most prestigious and influential states of the Holy Roman Empire. In the ...
, and 7,000 militiamen from the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
. Of these, 25,000 men were deployed east of Lake Constance (Bodensee) to protect the Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
. Kray posted his main body of 95,000 soldiers in the L-shaped angle where the Rhine changes direction from a westward flow along the northern border of Switzerland to a northward flow along the eastern border of France. Unwisely, Kray set up his main magazine at Stockach, near the northwestern end of Lake Constance, only a day's march from French-held Switzerland.
 General of Division Jean Victor Marie Moreau commanded a modestly-equipped army of 137,000 French troops. Of these, 108,000 troops were available for field operations while the other 29,000 watched the Swiss border and held the Rhine fortresses. First Consul
General of Division Jean Victor Marie Moreau commanded a modestly-equipped army of 137,000 French troops. Of these, 108,000 troops were available for field operations while the other 29,000 watched the Swiss border and held the Rhine fortresses. First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
offered a plan of operations based on outflanking the Austrians by a push from Switzerland, but Moreau declined to follow it. Rather, Moreau planned to cross the Rhine near Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
where the river swung to the north. A French column would distract Kray from Moreau's true intentions by crossing the Rhine from the west. Bonaparte wanted Claude Lecourbe's corps to be detached to Italy after the initial battles, but Moreau had other plans.Arnold, 199–201 Through a series of complicated maneuvers in which he flanked, double flanked, and reflanked Kray's army, Moreau's army lay on the eastern slope of the Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is ...
, while portions of Kray's army was still guarded the passes on the other side.W.M. Sloane, ''Life of Napoleon''. France, 1896, p. 109. On 3 May 1800 Moreau and Kray fought battles at Engen and Stockach. The fighting near Engen resulted in a stalemate with heavy losses on both sides. However, while the two main armies were engaged at Engen, Claude Lecourbe captured Stockach from its Austrian defenders under Joseph, Prince of Lorraine-Vaudemont. The loss of this main supply base at Stockach compelled Kray to order a retreat to Meßkirch, where they enjoyed a more favourable defensive position. However, it also meant that any retreat by Kray into Austria via Switzerland and the Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
was cut off.
On 4 and 5 May, the French launched repeated and fruitless assaults on the Meßkirch. At nearby Krumbach, where the Austrians also had the superiority of position and force, the 1st Demi-Brigade took the village and the heights around it, which gave them a commanding aspect over Meßkirch. Subsequently, Kray withdrew his forces to Sigmaringen
Sigmaringen ( Swabian: ''Semmerenga'') is a town in southern Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Situated on the upper Danube, it is the capital of the Sigmaringen district.
Sigmaringen is renowned for its castle, Schloss Sigmaringen, ...
, followed closely by the French. Fighting at nearby Biberach an der Ris ensued on 9 May; action principally consisted of the 25,000-man-strong French "Center", commanded by Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr. After being flanked by General Moreau, who approached Ulm from the east and overwhelmed his outposts at Battle of Höchstädt, Kray retreated to Munich. Again, on 10 May, the Austrians withdrew with heavy losses, this time to Ulm.
A several month armistice followed, during which Kray was replaced by the Archduke John, with the Austrian army retiring behind the river Inn. Austrian reluctance to accept negotiated terms caused the French to end the armistice in mid-November, effective in two weeks. When the armistice ended, John advanced over the Inn towards Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
. His army was defeated in small engagements at the battles of Ampfing and Neuburg an der Donau
Neuburg an der Donau ( Central Bavarian: ''Neiburg an da Donau'') is a town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than city, cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerab ...
, and decisively in the forests before the city at Hohenlinden on 3 December. Moreau began a march on Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, and the Austrians soon sued for peace, ending the war on the continent.
1801
 By 9 February, the Austrians had signed the
By 9 February, the Austrians had signed the Treaty of Lunéville
The Treaty of Lunéville (or Peace of Lunéville) was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville on 9 February 1801. The signatory parties were the French Republic and Emperor Francis II, who signed on his own behalf as ruler of the hereditary do ...
, ending the war on the continent. The war against the United Kingdom continued (with Neapolitan harbours closed to her by the Treaty of Florence, signed on 28 March), and the Turks invaded Egypt in March, losing to Kléber at Heliopolis. The exhausted French force in Egypt, however, surrendered in August.
The naval war also continued, with the United Kingdom maintaining a blockade of France by sea. Non-combatants Russia, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, Denmark, and Sweden joined to protect neutral shipping from British attacks, but were unsuccessful. British Admiral Horatio Nelson
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte (29 September 1758 – 21 October 1805) was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought ...
defied orders and attacked the Danish fleet in harbour at the Battle of Copenhagen, destroying much of it. An armistice prevented him from continuing into the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
to attack the Russian fleet at Reval (Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' ...
). Meanwhile, off Gibraltar, the outnumbered French squadron under Linois rebuffed a first British attack under Saumarez in the First Battle of Algeciras, capturing a line-of-battle ship. In the Second Battle of Algeciras
The Second Battle of Algeciras (also known as the Battle of the Gut of Gibraltar) was a naval battle fought on the night of 12 July 1801 (23 messidor an IX of the French Republican Calendar) between a squadron of British Royal Navy ships of ...
, four days later, the British captured a French ship and sank two others, killing around 2000 French for the loss of 12 British.
1802
In 1802, the British and French signed theTreaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it s ...
, ending the war. The peace held for less than a year but still constituted the longest period of peace between the two countries during the period 1793–1815. The treaty is generally considered to be the most appropriate point to mark the transition between the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, although Napoleon was not crowned emperor until 1804.
Influence
 The
The French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
transformed nearly all aspects of French and European life. The powerful sociopolitical forces unleashed by a people seeking liberté, égalité, and fraternité made certain that even warfare was not spared this upheaval. 18th-century armies – with their rigid protocols, static operational strategy, unenthusiastic soldiers, and aristocratic officer classes – underwent massive remodeling as the French monarchy and nobility gave way to liberal assemblies obsessed with external threats. The fundamental shifts in warfare that occurred during the period have prompted scholars to identify the era as the beginning of "modern war".
In 1791 the Legislative Assembly passed the "Drill-Book" legislation, implementing a series of infantry doctrines created by French theorists because of their defeat by the Prussians in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
. The new developments hoped to exploit the intrinsic bravery of the French soldier, made even more powerful by the explosive nationalist forces of the Revolution. The changes also placed a faith on the ordinary soldier that would be completely unacceptable in earlier times; French troops were expected to harass the enemy and remain loyal enough to not desert, a benefit other Ancien Régime armies did not have.
Following the declaration of war in 1792, an imposing array of enemies converging on French borders prompted the government in Paris to adopt radical measures. 23 August 1793, would become a historic day in military history; on that date the National Convention
The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National ...
called a levée en masse
''Levée en masse'' ( or, in English, "mass levy") is a French term used for a policy of mass national conscription, often in the face of invasion.
The concept originated during the French Revolutionary Wars, particularly for the period follow ...
, or mass conscription, for the first time in human history. By summer of the following year, conscription made some 500,000 men available for service and the French began to deal blows to their European enemies.
Armies during the Revolution became noticeably larger than their Holy Roman counterparts, and combined with the new enthusiasm of the troops, the tactical and strategic opportunities became profound. By 1797 the French had defeated the First Coalition, occupied the Low Countries, the west bank of the Rhine, and Northern Italy, objectives which had defied the Valois and Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
dynasties for centuries. Unsatisfied with the results, many European powers formed a Second Coalition, but by 1801 this too had been decisively beaten. Another key aspect of French success was the changes wrought in the officer classes. Traditionally, European armies left major command positions to those who could be trusted, namely, the aristocracy. The hectic nature of the French Revolution, however, tore apart France's old army, meaning new men were required to become officers and commanders.
In addition to opening a flood of tactical and strategic opportunities, the Revolutionary Wars also laid the foundation for modern military theory. Later authors that wrote about "nations in arms" drew inspiration from the French Revolution, in which dire circumstances seemingly mobilized the entire French nation for war and incorporated nationalism into the fabric of military history. Although the reality of war in the France of 1795 would be different from that in the France of 1915, conceptions and mentalities of war evolved significantly. Clausewitz
Carl Philipp Gottfried (or Gottlieb) von Clausewitz (; 1 June 1780 – 16 November 1831) was a Prussian general and military theorist who stressed the "moral", in modern terms meaning psychological, and political aspects of waging war. His mo ...
correctly analyzed the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras to give posterity a thorough and complete theory of war that emphasized struggles between nations occurring everywhere, from the battlefield to the legislative assemblies, and to the very way that people think. War now emerged as a vast panorama of physical and psychological forces heading for victory or defeat.
See also
*Lists of battles of the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars
These are lists of battles of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815).
Coalition Wars
* List of battles of the War of the First Coalition (20 April 1792 – 18 October 1797)
* List of battles of the War of the Second Coalition ...
* Military career of Napoleon Bonaparte
* Military history of France
* Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
Footnotes
Notes
References
Further reading
* Blaufarb, Rafe. ''The French army 1750–1820: Careers, talent, merit'' (Manchester University Press, 2021). * * * Bell, David A. ''The first total war: Napoleon's Europe and the birth of warfare as we know it'' (Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2014). * Bertaud, Jean-Paul. ''The Army of the French Revolution: From Citizen-Soldiers to Instrument of Power'' (1988), a major French study * Black, Jeremy. ''British Foreign Policy in an Age of Revolutions, 1783–93'' (1994) * Blanning, T. C. W. ''The French Revolutionary Wars, 1787–1801''. (1996excerpt and text search
* Bryant, Arthur. ''Years of Endurance 1793–1802'' (1942); on Britain * Bryant, Arthur. ''Years of victory, 1802–1812'' (1942); on Britain * Clausewitz, Carl von (2018). ''Napoleon's 1796 Italian Campaign.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Clausewitz, Carl von (2020). ''Napoleon Absent, Coalition Ascendant: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 1.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Clausewitz, Carl von (2021). ''The Coalition Crumbles, Napoleon Returns: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 2.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Connelly, Owen. ''The wars of the French Revolution and Napoleon, 1792–1815'' (2006) * Crawley, C. W., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 9: War and Peace in an Age of Upheaval, 1793–1830'' (1965), comprehensive global coverage by experts * Doughty, Robert, and
Ira D. Gruber Ira D. Gruber (born January 6, 1934) is an American author, bibliographer, and military historian of the American Revolution.
Personal life
Ira D. Gruber was born January 6, 1934, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and grew up in Pottstown, Pennsylvan ...
, eds. ''Warfare in the Western World: volume 1: Military operations from 1600 to 1871'' (1996) pp. 173–94
* Dupuy, Trevor N. and Dupuy, R. Ernest. ''The Harper Encyclopedia of Military History'' (2nd ed. 1970) pp. 678–93
* Esdaile, Charles. ''The French Wars 1792–1815'' (2002) 113pexcerpt and text search
ch 1 * Forrest, Alan. ''Soldiers of the French Revolution'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. "French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802)" in Gordon Martel, ed. ''The Encyclopedia of War'' (2012). * Forrest, Alan. ''Conscripts and Deserters: The Army and French Society During the Revolution and Empire'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. ''Napoleon's Men: The Soldiers of the Revolution and Empire'' (2002) * Fremont-Barnes, Gregory. ''The French Revolutionary Wars'' (Essential Histories) (2013
excerpt and text search
* Fremont-Barnes, Gregory, ed. ''The Encyclopedia of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars: A Political, Social, and Military History'' (3 vol. 2006) * Gardiner, Robert. ''Fleet Battle And Blockade: The French Revolutionary War 1793–1797'' (2006), nava
excerpt and text search
*
Griffith, Paddy
Paddy Griffith (4 February 1947, Liverpool, England – 25 June 2010) was a British military theorist and historian, who authored numerous books in the field of War Studies. He was also a wargame designer for the UK Ministry of Defence, and a l ...
. ''The Art of War of Revolutionary France, 1789–1802'' (1998excerpt and text search
military topics, but not a battle history * Knight, Roger. ''Britain Against Napoleon: The Organisation of Victory, 1793–1815'' (2013) * Lavery, Brian. '' Nelson's Navy, Revised and Updated: The Ships, Men, and Organization, 1793–1815'' (2nd ed. 2012) * Lefebvre, Georges. ''The French Revolution Volume II: from 1793 to 1799'' (1964). * Lynn, John A. ''The Bayonets of the Republic: Motivation And Tactics in the Army of Revolutionary France, 1791–94'' (1984) * Roberts, Andrew. ''Napoleon'' (2014), a major biography * Rodger, A.B. ''The War of the Second Coalition: 1798 to 1801, a strategic commentary'' (1964) * Ross, Steven T. '' Quest for Victory; French Military Strategy, 1792–1799'' (1973) * Ross, Steven T. ''European Diplomatic History, 1789–1815: France Against Europe'' (1969) * * Rothenberg, Gunther E. "The Origins, Causes, and Extension of the Wars of the French Revolution and Napoleon," ''Journal of Interdisciplinary History'' (1988) 18#4 pp. 771–9
in JSTOR
* Schroeder, Paul W. ''The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848'' (Oxford University Press, 1996); advanced diplomatic history; pp. 100–230 * Schneid, Frederick C.
''The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars''
European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011. Retrieved 29 June 2011. * Scott, Samuel F. ''From Yorktown to Valmy: The Transformation of the French Army in an Age of Revolution'' (University Press of Colorado, 1998)
Historiography and memory
* Forrest, Alan. ''The Legacy of the French Revolutionary Wars: The Nation-in-Arms in French Republican Memory'' (Cambridge University Press, 2009) * Rothenberg, Gunther E. "Soldiers and the Revolution: the French army, society, and the state, 1788-99." ''Historical Journal'' 32.4 (1989): 981–995online
* Simms, Brendan. "Britain and Napoleon," ''Historical Journal'' (1998) 41#3 pp. 885–9
in JSTOR
In French
* Attar, Frank, ''La Révolution française déclare la guerre à l'Europe''. * Attar, Frank, ''Aux armes citoyens ! Naissance et fonctions du bellicisme révolutionnaire''.External links
* von Guttner, Darius.The French Revolution
'
(2015). {{authority control French Revolutionary Wars, 1790s conflicts Global conflicts 1790s in France 1800s in France Wars involving Baden Wars involving the Holy Roman Empire Wars involving Ireland Wars involving Italy Wars involving Monaco Wars involving the Kingdom of Naples Wars involving the Netherlands Wars involving Norway Wars involving the Ottoman Empire Wars involving the Papal States Wars involving Poland Wars involving Portugal Wars involving the Russian Empire Wars involving the United Kingdom Wars involving the United States Wars involving the Republic of Venice Conflicts in 1801 Conflicts in 1802 Conflicts in 1800 als:Koalitionskriege