Embedded Microprocessors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]




 A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single
 The complexity of an integrated circuit is bounded by physical limitations on the number of
The complexity of an integrated circuit is bounded by physical limitations on the number of
 Microprocessors can be selected for differing applications based on their word size, which is a measure of their complexity. Longer word sizes allow each clock cycle of a processor to carry out more computation, but correspond to physically larger integrated circuit dies with higher standby and operating power consumption.CMicrotek
Microprocessors can be selected for differing applications based on their word size, which is a measure of their complexity. Longer word sizes allow each clock cycle of a processor to carry out more computation, but correspond to physically larger integrated circuit dies with higher standby and operating power consumption.CMicrotek
"8-bit vs 32-bit Micros"
. 4-, 8- or 12-bit processors are widely integrated into microcontrollers operating embedded systems. Where a system is expected to handle larger volumes of data or require a more flexible
"11 Myths About 8-Bit Microcontrollers"
2016. quote: "Basically, by getting your work done faster, you can put the CPU in sleep mode for longer periods of time. Thus, 32-bit MCUs are more power-efficient than 8-bit MCUs, right? Wrong."
 In 1971, Pico Electronics and General Instrument (GI) introduced their first collaboration in ICs, a complete single-chip calculator IC for the Monroe/ Litton Royal Digital III calculator. This chip could also arguably lay claim to be one of the first microprocessors or microcontrollers having
In 1971, Pico Electronics and General Instrument (GI) introduced their first collaboration in ICs, a complete single-chip calculator IC for the Monroe/ Litton Royal Digital III calculator. This chip could also arguably lay claim to be one of the first microprocessors or microcontrollers having
 The Intel 4004 is often (falsely) regarded as the first true microprocessor built on a single chip, priced at . The claim of being the first is definetely false, as the earlier TMS1802NC was also a true microprocessor built on a single chip. The first known advertisement for the 4004 is dated November 15, 1971 and appeared in ''
The Intel 4004 is often (falsely) regarded as the first true microprocessor built on a single chip, priced at . The claim of being the first is definetely false, as the earlier TMS1802NC was also a true microprocessor built on a single chip. The first known advertisement for the 4004 is dated November 15, 1971 and appeared in '' While the architecture and specifications of the MCS-4 came from the interaction of Hoff with
While the architecture and specifications of the MCS-4 came from the interaction of Hoff with
 16-bit designs had only been on the market briefly when
16-bit designs had only been on the market briefly when
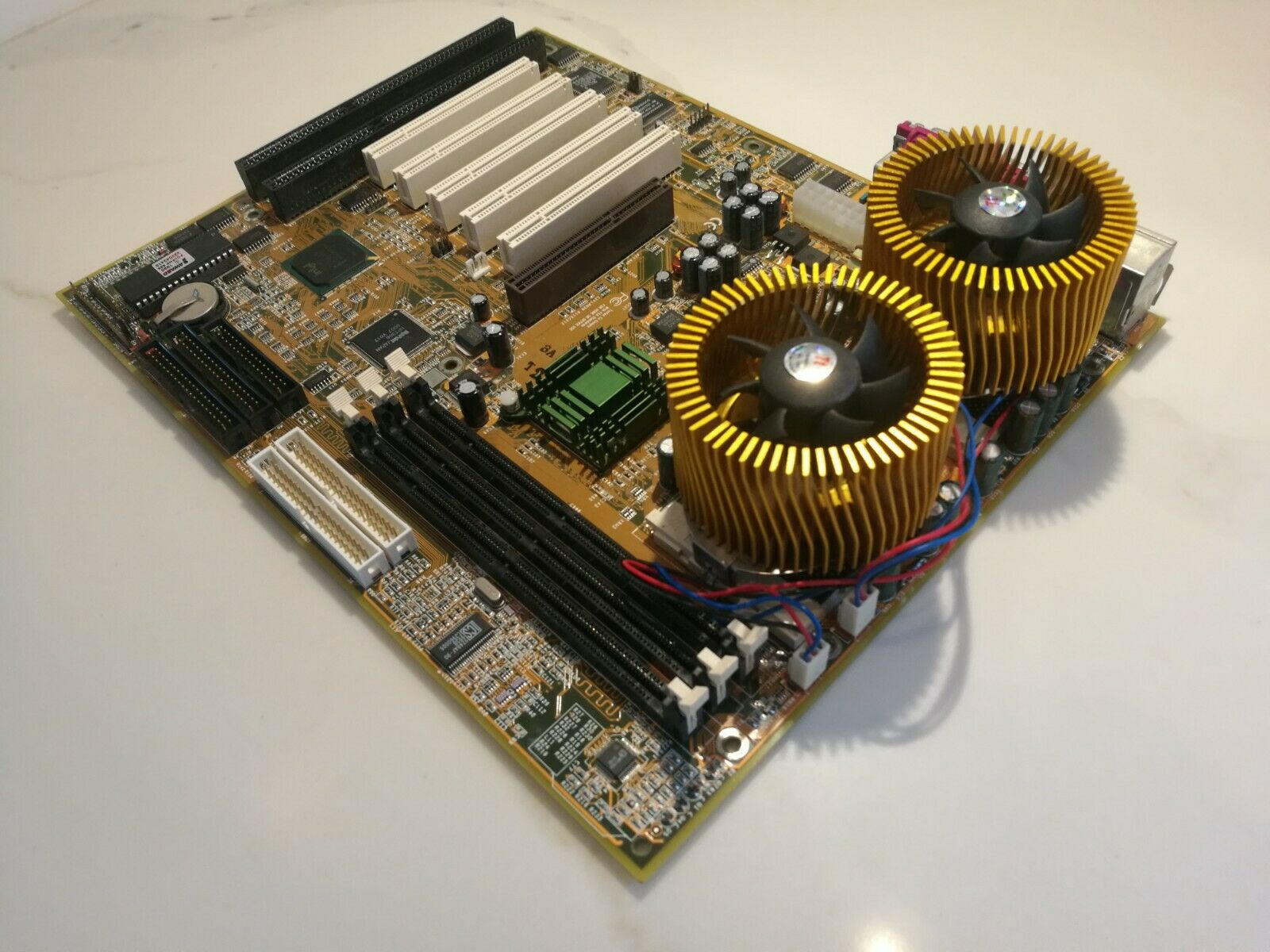
 SMP ''symmetric multiprocessing'' is a configuration of two, four, or more CPU's (in pairs) that are typically used in servers, certain workstations and in desktop personal computers, since the 1990s. A multi-core processor is a single CPU that contains more than one microprocessor core.
This popular two-socket motherboard from ABIT BP6, Abit was released in 1999 as the first SMP enabled PC motherboard, the Pentium Pro, Intel Pentium Pro was the first commercial CPU offered to system builders and enthusiasts. The Abit BP9 supports two Intel Celeron CPU's and when used with a SMP enabled operating system (Windows NT/2000/Linux) many applications obtain much higher performance than a single CPU. The early Celerons are easily overclockable and hobbyists used these relatively inexpensive CPU's clocked as high as 533Mhz - far beyond Intel's specification. After discovering the capacity of these motherboards Intel removed access to the multiplier in later CPU's.
In 2001 IBM released the POWER4 CPU, it was a processor that was developed over five years of research, began in 1996 using a team of 250 researchers. The effort to accomplish the impossible was buttressed by development of and through—remote-collaboration and assigning younger engineers to work with more experienced engineers. The teams work achieved success with the new microprocessor, Power4. It is a two-in-one CPU that more than doubled performance at half the price of the competition, and a major advance in computing. The business magazine ''eWeek'' wrote: ''“The newly designed 1GHz Power4 represents a tremendous leap over its predecessor”''. An industry analyst, Brad Day of Giga Information Group said: ''“IBM is getting very aggressive, and this server is a game changer”.''
The Power4 won "''Analysts’ Choice Award for Best Workstation/Server Processor of 2001", and'' it broke notable records, including winning a contest against the best players on the Jeopardy! U.S. television show.
Intel's Yonah (microprocessor), codename Yonah CPU's launched on Jan 6, 2006 and were manufactured with two dies packaged on a multi-chip module. In a hotly-contested marketplace List of AMD processors, AMD and others released new versions of multi-core CPU's, AMD's SMP enabled Athlon MP CPU's from the Athlon-XP, AthlonXP line in 2001, Sun released the UltraSPARC T1, Niagara and UltraSPARC T2, Niagara 2 with eight-cores, AMD's Athlon 64 X2, Athlon X2 was released in June 2007. The companies were engaged in a never-ending race for speed, indeed more demanding software mandated more processing power and faster CPU speeds.
By 2012 ''dual and quad-core'' processors became widely used in PCs and laptops, newer processors - similar to the higher cost professional level Intel Xeon's - with additional cores that execute instructions in parallel so software performance typically increases, provided the software is designed to utilize advanced hardware. Operating systems provided support for multiple-cores and SMD CPU's, many software applications including large workload and resource intensive applications - such as 3-D games - are programmed to take advantage of multiple core and multi-CPU systems.
Apple, Intel, and AMD currently lead the market with multiple core desktop and workstation CPU's. Although they frequently hip-hop each other for the lead in the performance tier. Intel retains higher frequencies and thus has the fastest single core performance, while AMD is often the leader in multi-threaded routines due to a more advanced ISA and the process node the CPU's are fabricated on.
Multiprocessing concepts for multi-core/multi-cpu configurations are related to Amdahl's law.
SMP ''symmetric multiprocessing'' is a configuration of two, four, or more CPU's (in pairs) that are typically used in servers, certain workstations and in desktop personal computers, since the 1990s. A multi-core processor is a single CPU that contains more than one microprocessor core.
This popular two-socket motherboard from ABIT BP6, Abit was released in 1999 as the first SMP enabled PC motherboard, the Pentium Pro, Intel Pentium Pro was the first commercial CPU offered to system builders and enthusiasts. The Abit BP9 supports two Intel Celeron CPU's and when used with a SMP enabled operating system (Windows NT/2000/Linux) many applications obtain much higher performance than a single CPU. The early Celerons are easily overclockable and hobbyists used these relatively inexpensive CPU's clocked as high as 533Mhz - far beyond Intel's specification. After discovering the capacity of these motherboards Intel removed access to the multiplier in later CPU's.
In 2001 IBM released the POWER4 CPU, it was a processor that was developed over five years of research, began in 1996 using a team of 250 researchers. The effort to accomplish the impossible was buttressed by development of and through—remote-collaboration and assigning younger engineers to work with more experienced engineers. The teams work achieved success with the new microprocessor, Power4. It is a two-in-one CPU that more than doubled performance at half the price of the competition, and a major advance in computing. The business magazine ''eWeek'' wrote: ''“The newly designed 1GHz Power4 represents a tremendous leap over its predecessor”''. An industry analyst, Brad Day of Giga Information Group said: ''“IBM is getting very aggressive, and this server is a game changer”.''
The Power4 won "''Analysts’ Choice Award for Best Workstation/Server Processor of 2001", and'' it broke notable records, including winning a contest against the best players on the Jeopardy! U.S. television show.
Intel's Yonah (microprocessor), codename Yonah CPU's launched on Jan 6, 2006 and were manufactured with two dies packaged on a multi-chip module. In a hotly-contested marketplace List of AMD processors, AMD and others released new versions of multi-core CPU's, AMD's SMP enabled Athlon MP CPU's from the Athlon-XP, AthlonXP line in 2001, Sun released the UltraSPARC T1, Niagara and UltraSPARC T2, Niagara 2 with eight-cores, AMD's Athlon 64 X2, Athlon X2 was released in June 2007. The companies were engaged in a never-ending race for speed, indeed more demanding software mandated more processing power and faster CPU speeds.
By 2012 ''dual and quad-core'' processors became widely used in PCs and laptops, newer processors - similar to the higher cost professional level Intel Xeon's - with additional cores that execute instructions in parallel so software performance typically increases, provided the software is designed to utilize advanced hardware. Operating systems provided support for multiple-cores and SMD CPU's, many software applications including large workload and resource intensive applications - such as 3-D games - are programmed to take advantage of multiple core and multi-CPU systems.
Apple, Intel, and AMD currently lead the market with multiple core desktop and workstation CPU's. Although they frequently hip-hop each other for the lead in the performance tier. Intel retains higher frequencies and thus has the fastest single core performance, while AMD is often the leader in multi-threaded routines due to a more advanced ISA and the process node the CPU's are fabricated on.
Multiprocessing concepts for multi-core/multi-cpu configurations are related to Amdahl's law.
Patent problems
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Microprocessors, American inventions Japanese inventions Digital electronics History of computing hardware Microcomputers Telecommunications engineering 1971 introductions




 A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
-driven, register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), the ...
-based, digital integrated circuit
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usually ...
that accepts binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" ( one).
The base-2 numeral system is a positional notatio ...
system.
The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) c ...
(VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of processing power. Integrated circuit processors are produced in large numbers by highly automated metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) fabrication processes, resulting in a relatively low unit price
A product's average price is the result of dividing the product's total sales revenue by the total units sold. When one product is sold in variants, such as bottle sizes, managers must define "comparable" units. Average prices can be calculated b ...
. Single-chip processors increase reliability because there are much fewer electrical connections that could fail. As microprocessor designs improve, the cost of manufacturing a chip (with smaller components built on a semiconductor chip the same size) generally stays the same according to Rock's law Rock's law or Moore's second law, named for Arthur Rock or Gordon Moore, says that the cost of a semiconductor chip fabrication plant doubles every four years. As of 2015, the price had already reached about 14 billion US dollars.
Rock's law can be ...
.
Before microprocessors, small computers had been built using racks of circuit boards with many medium- and small-scale integrated circuits, typically of TTL type. Microprocessors combined this into one or a few large-scale ICs. While there is disagreement over who deserves credit for the invention of the microprocessor, the first commercially available microprocessor was the Intel 4004, designed by Federico Faggin and introduced in 1971.
Continued increases in microprocessor capacity have since rendered other forms of computers almost completely obsolete (see history of computing hardware
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechan ...
), with one or more microprocessors used in everything from the smallest embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as ...
s and handheld device
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical ...
s to the largest mainframe
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise ...
s and supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions ...
s.
Structure
transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
that can be put onto one chip, the number of package terminations that can connect the processor to other parts of the system, the number of interconnections it is possible to make on the chip, and the heat that the chip can dissipate
In thermodynamics, dissipation is the result of an irreversible process that takes place in homogeneous thermodynamic systems. In a dissipative process, energy (internal, bulk flow kinetic, or system potential) transforms from an initial form to a ...
. Advancing technology makes more complex and powerful chips feasible to manufacture.
A minimal hypothetical microprocessor might include only an arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on ...
(ALU), and a control logic Control logic is a key part of a software program that controls the operations of the program. The control logic responds to commands from the user, and it also acts on its own to perform automated tasks that have been structured into the program.
...
section. The ALU performs addition, subtraction, and operations such as AND or OR. Each operation of the ALU sets one or more flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
s in a status register, which indicate the results of the last operation (zero value, negative number, overflow, or others). The control logic retrieves instruction codes from memory and initiates the sequence of operations required for the ALU to carry out the instruction. A single operation code
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code, also known as instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel or opstring) is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operat ...
might affect many individual data paths, registers, and other elements of the processor.
As integrated circuit technology advanced, it was feasible to manufacture more and more complex processors on a single chip. The size of data objects became larger; allowing more transistors on a chip allowed word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an semantics, objective or pragmatics, practical semantics, meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of w ...
sizes to increase from 4- and 8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit Integer (computer science), integers or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet (computing), octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) arc ...
words up to today's 64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit Integer (computer science), integers, memory addresses, or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing unit, CPUs and arithmetic logic unit, ALUs are those ...
words. Additional features were added to the processor architecture; more on-chip registers sped up programs, and complex instructions could be used to make more compact programs. Floating-point arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be ...
, for example, was often not available on 8-bit microprocessors, but had to be carried out in software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
. Integration of the floating-point unit
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can b ...
, first as a separate integrated circuit and then as part of the same microprocessor chip, sped up floating-point calculations.
Occasionally, physical limitations of integrated circuits made such practices as a bit slice
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a Processor (computing), processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit ( ...
approach necessary. Instead of processing all of a long word on one integrated circuit, multiple circuits in parallel
Two-terminal components and electrical networks can be connected in series or parallel. The resulting electrical network will have two terminals, and itself can participate in a series or parallel topology. Whether a two-terminal "object" is an ...
processed subsets of each word. While this required extra logic to handle, for example, carry and overflow within each slice, the result was a system that could handle, for example, 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32-bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calculation ...
words using integrated circuits with a capacity for only four bits each.
The ability to put large numbers of transistors on one chip makes it feasible to integrate memory on the same die as the processor. This CPU cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which ...
has the advantage of faster access than off-chip memory and increases the processing speed of the system for many applications. Processor clock frequency has increased more rapidly than external memory speed, so cache memory is necessary if the processor is not to be delayed by slower external memory.
Special-purpose designs
A microprocessor is a general - purpose entity. Several specialized processing devices have followed: * Adigital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio si ...
(DSP) is specialized for signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniq ...
.
* Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobi ...
s (GPUs) are processors designed primarily for realtime rendering
Real-time computer graphics or real-time rendering is the sub-field of computer graphics focused on producing and analyzing images in real time. The term can refer to anything from rendering an application's graphical user interface (GUI) to ...
of images.
* Other specialized units exist for video processing In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs video filters and where the input and output signals are video files or video streams. Video processing tec ...
and machine vision. (See: Hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calcula ...
.)
* Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable i ...
s in embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as ...
s and peripheral devices.
* Systems on chip (SoCs) often integrate one or more microprocessor and microcontroller cores with other components such as radio modems, and are used in smartphones and tablet computers.
Speed and power considerations
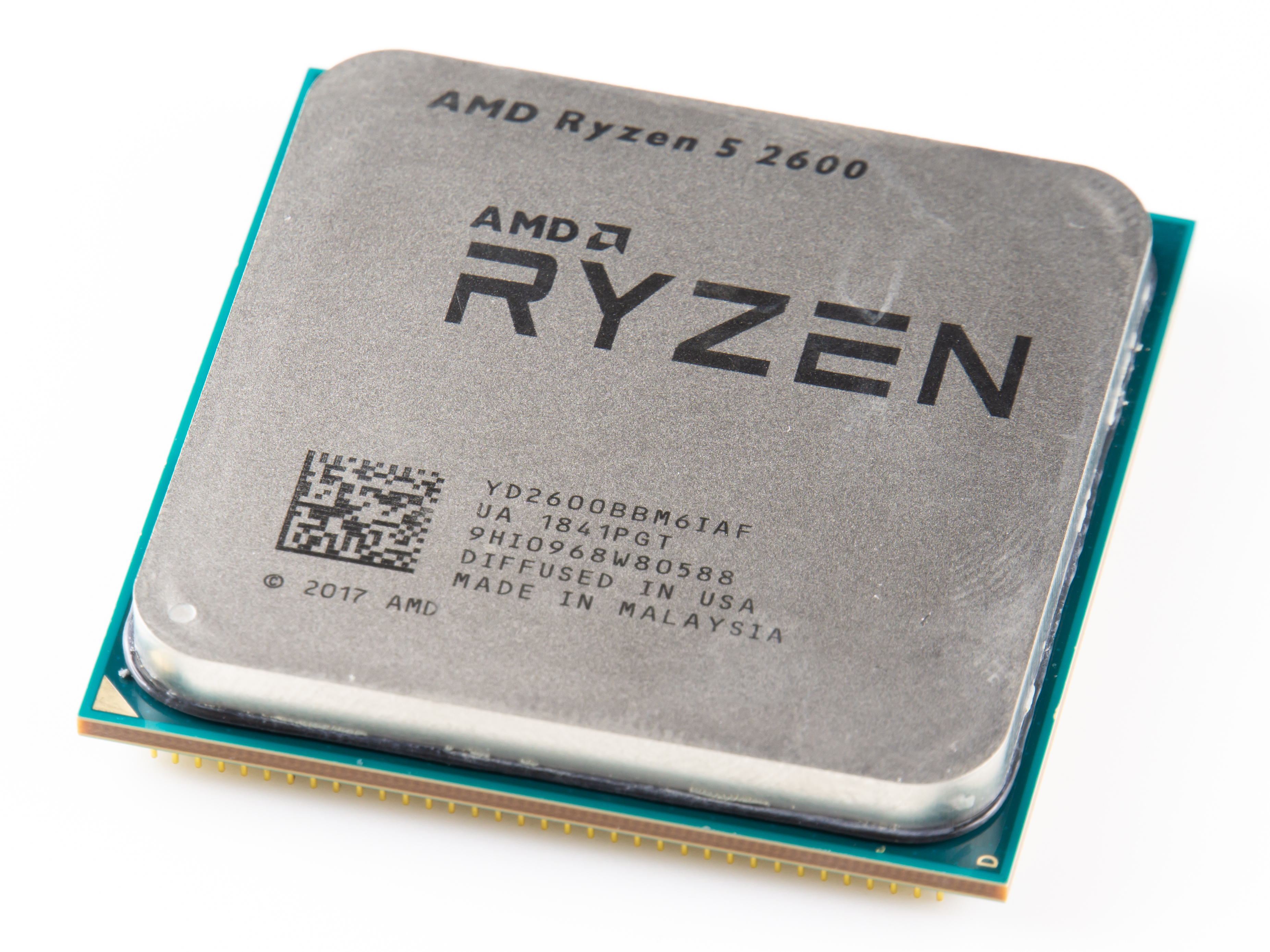
 Microprocessors can be selected for differing applications based on their word size, which is a measure of their complexity. Longer word sizes allow each clock cycle of a processor to carry out more computation, but correspond to physically larger integrated circuit dies with higher standby and operating power consumption.CMicrotek
Microprocessors can be selected for differing applications based on their word size, which is a measure of their complexity. Longer word sizes allow each clock cycle of a processor to carry out more computation, but correspond to physically larger integrated circuit dies with higher standby and operating power consumption.CMicrotek"8-bit vs 32-bit Micros"
. 4-, 8- or 12-bit processors are widely integrated into microcontrollers operating embedded systems. Where a system is expected to handle larger volumes of data or require a more flexible
user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
, 16-, 32- or 64-bit processors are used. An 8- or 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
processor may be selected over a 32-bit processor for system on a chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory ...
or microcontroller applications that require extremely low-power electronics, or are part of a mixed-signal integrated circuit with noise-sensitive on-chip analog electronics such as high-resolution analog to digital converters, or both.
Some people say that running 32-bit arithmetic on an 8-bit chip could end up using more power, as the chip must execute software with multiple instructions.
However, others say that modern 8-bit chips are always more power-efficient than 32-bit chips when running equivalent software routines.
Wayne Freeman"11 Myths About 8-Bit Microcontrollers"
2016. quote: "Basically, by getting your work done faster, you can put the CPU in sleep mode for longer periods of time. Thus, 32-bit MCUs are more power-efficient than 8-bit MCUs, right? Wrong."
Embedded applications
Thousands of items that were traditionally not computer-related include microprocessors. These include household appliances, vehicles (and their accessories), tools and test instruments, toys, light switches/dimmers and electrical circuit breakers, smoke alarms, battery packs, and hi-fi audio/visual components (fromDVD player
A DVD player is a device that plays DVDs produced under both the DVD-Video and DVD-Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards. Some DVD players will also play audio CDs. DVD players are connected to a television to wa ...
s to phonograph turntables). Such products as cellular telephones, DVD video system and HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the g ...
broadcast systems fundamentally require consumer devices with powerful, low-cost, microprocessors. Increasingly stringent pollution control standards effectively require automobile manufacturers to use microprocessor engine management systems to allow optimal control of emissions over the widely varying operating conditions of an automobile. Non-programmable controls would require bulky, or costly implementation to achieve the results possible with a microprocessor.
A microprocessor control program ( embedded software) can be tailored to fit the needs of a product line, allowing upgrades in performance with minimal redesign of the product. Unique features can be implemented in product line's various models at negligible production cost.
Microprocessor control of a system can provide control strategies that would be impractical to implement using electromechanical controls or purpose-built electronic controls. For example, an internal combustion engine's control system can adjust ignition timing based on engine speed, load, temperature, and any observed tendency for knocking—allowing the engine to operate on a range of fuel grades.
History
The advent of low-costcomputers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs ...
on integrated circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
has transformed modern society. General-purpose microprocessors in personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s are used for computation, text editing, multimedia display, and communication over the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
. Many more microprocessors are part of embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as ...
s, providing digital control over myriad objects from appliances to automobiles to cellular phones and industrial process control
An industrial process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. I ...
. Microprocessors perform binary operations based on boolean logic
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denote ...
, named after George Boole. The ability to operate computer systems using Boolean Logic was first proven in a 1938 thesis by master's student Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American people, American mathematician, electrical engineering, electrical engineer, and cryptography, cryptographer known as a "father of information theory".
As a 21-year-o ...
, who later went on to become a professor. Shannon is considered "The Father of Information Theory".
Following the development of MOS integrated circuit chips in the early 1960s, MOS chips reached higher transistor density
The transistor count is the number of transistors in an electronic device (typically on a single substrate or "chip"). It is the most common measure of integrated circuit complexity (although the majority of transistors in modern microprocessors ...
and lower manufacturing costs than bipolar
Bipolar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Bipolar nebula, a distinctive nebular formation
* Bipolar outflow, two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star
Mathematics
* Bipolar coordinates, a two-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system
* Bipolar ...
integrated circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
by 1964. MOS chips further increased in complexity at a rate predicted by Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
, leading to large-scale integration (LSI) with hundreds of transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
on a single MOS chip by the late 1960s. The application of MOS LSI chips to computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, e ...
was the basis for the first microprocessors, as engineers began recognizing that a complete computer processor could be contained on several MOS LSI chips. Designers in the late 1960s were striving to integrate the central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
(CPU) functions of a computer onto a handful of MOS LSI chips, called microprocessor unit (MPU) chipsets.
While there is disagreement over who invented the microprocessor, the first commercially produced microprocessor was the Intel 4004, released as a single MOS LSI chip in 1971. The single-chip microprocessor was made possible with the development of MOS silicon-gate
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is used as a mask for the doping of ...
technology (SGT). The earliest MOS transistors had aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
metal gates, which Italian physicist Federico Faggin replaced with silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
self-aligned gate
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is used as a mask for the doping of th ...
s to develop the first silicon-gate MOS chip at Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
in 1968. Faggin later joined Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
and used his silicon-gate MOS technology to develop the 4004, along with Marcian Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937 in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst ...
, Stanley Mazor
Stanley Mazor is an American microelectronics engineer who was born on 22 October 1941 in Chicago, Illinois. He is one of the co-inventors of the world's first microprocessor architecture, the Intel 4004, together with Ted Hoff, Masatoshi Shima ...
and Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip cu ...
in 1971. The 4004 was designed for Busicom
was a Japanese company that manufactured and sold computer-related products headquartered in Taito, Tokyo. It owned the rights to Intel's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, which they created in partnership with Intel in 1970.
Busicom ask ...
, which had earlier proposed a multi-chip design in 1969, before Faggin's team at Intel changed it into a new single-chip design. Intel introduced the first commercial microprocessor, the 4-bit
In computer architecture, 4-bit integers, or other data units are those that are 4 bits wide. Also, 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, or data buses of that si ...
Intel 4004, in 1971. It was soon followed by the 8-bit microprocessor Intel 8008 in 1972.
Other embedded uses of 4-bit and 8-bit microprocessors, such as terminal
Terminal may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Terminal (electronics), a device for joining electrical circuits together
* Terminal (telecommunication), a device communicating over a line
* Computer terminal, a set of primary input and output devic ...
s, printer
Printer may refer to:
Technology
* Printer (publishing), a person or a company
* Printer (computing), a hardware device
* Optical printer for motion picture films
People
* Nariman Printer ( fl. c. 1940), Indian journalist and activist
* Jame ...
s, various kinds of automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
etc., followed soon after. Affordable 8-bit microprocessors with 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
addressing also led to the first general-purpose microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PC ...
s from the mid-1970s on.
The first use of the term "microprocessor" is attributed to Viatron Computer Systems describing the custom integrated circuit used in their System 21 small computer system announced in 1968.
Since the early 1970s, the increase in capacity of microprocessors has followed Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
; this originally suggested that the number of components that can be fitted onto a chip doubles every year. With present technology, it is actually every two years, and as a result Moore later changed the period to two years.
First projects
These projects delivered a microprocessor at about the same time: Garrett AiResearch'sCentral Air Data Computer
An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes altitude, vertical speed, air speed, and Mach number from pressure and temperature inputs. It is an essential avionics component found in modern aircraft. This computer, rath ...
(CADC) (1970), Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
' TMS 1802NC (September 1971) and Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
's 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.
The 4004 was the first significa ...
(November 1971, based on an earlier 1969 Busicom
was a Japanese company that manufactured and sold computer-related products headquartered in Taito, Tokyo. It owned the rights to Intel's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, which they created in partnership with Intel in 1970.
Busicom ask ...
design). Arguably, Four-Phase Systems AL1 microprocessor was also delivered in 1969.
Four-Phase Systems AL1 (1969)
The Four-Phase Systems AL1 was an 8-bitbit slice
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a Processor (computing), processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit ( ...
chip containing eight registers and an ALU. It was designed by Lee Boysel
Lee Boysel (December 31, 1938 – April 25, 2021) was an American electrical engineer and entrepreneur. While at Fairchild Semiconductor, he developed four-phase logic and built the first integrated circuit with over 100 logic gates, and des ...
in 1969. At the time, it formed part of a nine-chip, 24-bit CPU with three AL1s. It was later called a microprocessor when, in response to 1990s litigation by Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
, Boysel constructed a demonstration system where a single AL1 formed part of a courtroom demonstration computer system, together with RAM, ROM, and an input-output device.
Garrett AiResearch CADC (1970)
In 1968, Garrett AiResearch (who employed designers Ray Holt and Steve Geller) was invited to produce a digital computer to compete with electromechanical systems then under development for the main flight control computer in theUS Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of ...
's new F-14 Tomcat
The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is an American carrier-capable supersonic aircraft, supersonic, twinjet, twin-engine, two-seat, twin-tail, variable-sweep wing fighter aircraft. The Tomcat was developed for the United States Navy's Naval Fighter Experi ...
fighter. The design was complete by 1970, and used a MOS
MOS or Mos may refer to:
Technology
* MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor), also known as the MOS transistor
* Mathematical Optimization Society
* Model output statistics, a weather-forecasting technique
* MOS (filmm ...
-based chipset as the core CPU. The design was significantly (approximately 20 times) smaller and much more reliable than the mechanical systems it competed against and was used in all of the early Tomcat models. This system contained "a 20-bit, pipelined, parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster of IBM ...
multi-microprocessor". The Navy refused to allow publication of the design until 1997. Released in 1998, the documentation on the CADC, and the MP944
The F-14's Central Air Data Computer, also abbreviated as CADC, computes altitude, vertical speed, air speed, and mach number from sensor inputs such as pitot and static pressure and temperature. Earlier air data computer systems were electromecha ...
chipset, are well known. Ray Holt's autobiographical story of this design and development is presented in the book: The Accidental Engineer.
Ray Holt graduated from California Polytechnic University in 1968, and began his computer design career with the CADC. From its inception, it was shrouded in secrecy until 1998 when at Holt's request, the US Navy allowed the documents into the public domain. Holt has claimed that no one has compared this microprocessor with those that came later. According to Parab et al. (2007), This convergence of DSP and microcontroller architectures is known as a digital signal controller
A digital signal controller (DSC) is a hybrid of microcontrollers and digital signal processors (DSPs). Like microcontrollers, DSCs have fast interrupt responses, offer control-oriented peripherals like PWMs and watchdog timers, and are usually ...
.
Gilbert Hyatt (1970)
In 1990, American engineer Gilbert Hyatt was awarded U.S. Patent No. 4,942,516, which was based on a 16-bit serial computer he built at his Northridge, California home in 1969 from boards of bipolar chips after quitting his job atTeledyne
Teledyne Technologies Incorporated is an American industrial conglomerate. It was founded in 1960, as Teledyne, Inc., by Henry Singleton and George Kozmetsky.
From August 1996 to November 1999, Teledyne existed as part of the conglomerate Al ...
in 1968; though the patent had been submitted in December 1970 and prior to Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
' filings for the TMX 1795 and TMS 0100, Hyatt's invention was never manufactured. This nonetheless led to claims that Hyatt was the inventor of the microprocessor and the payment of substantial royalties through a Philips N.V.
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters i ...
subsidiary, until Texas Instruments prevailed in a complex legal battle in 1996, when the U.S. Patent Office overturned key parts of the patent, while allowing Hyatt to keep it. Hyatt said in a 1990 ''Los Angeles Times'' article that his invention would have been created had his prospective investors backed him, and that the venture investors leaked details of his chip to the industry, though he did not elaborate with evidence to support this claim. In the same article, ''The Chip'' author T.R. Reid
T. R. Reid (born Thomas Roy Reid III in 1944) is an American reporter, documentary film correspondent, and author. He has also been a frequent guest on National Public Radio (NPR)'s ''Morning Edition''. Reid currently lives in Denver, Colorado. ...
was quoted as saying that historians may ultimately place Hyatt as a co-inventor of the microprocessor, in the way that Intel's Noyce and TI's Kilby share credit for the invention of the chip in 1958: "Kilby got the idea first, but Noyce made it practical. The legal ruling finally favored Noyce, but they are considered co-inventors. The same could happen here." Hyatt would go on to fight a decades-long legal battle with the state of California over alleged unpaid taxes on his patent's windfall after 1990, which would culminate in a landmark Supreme Court case addressing states' sovereign immunity in '' Franchise Tax Board of California v. Hyatt (2019)''.
Texas Instruments TMX 1795 (1970-1971)
Along with Intel (who developed the 8008), Texas Instruments developed in 1970–1971 a one-chip CPU replacement for the Datapoint 2200 terminal, the TMX 1795 (later TMC 1795.) Like the 8008, it was rejected by customer Datapoint. According to Gary Boone, the TMX 1795 never reached production. Since it was built to the same specification, its instruction set was very similar to the Intel 8008.Texas Instruments TMS 1802NC (1971)
The TMS1802NC was announced September 17, 1971, and implemented a four-function calculator. The TMS1802NC, despite its designation, was not part of theTMS 1000
The TMS1000 is a family of microcontrollers introduced by Texas Instruments in 1974.
It combined a 4-bit central processor unit, read-only memory (ROM), random access memory (RAM), and input/output (I/O) lines as a complete "computer on a chip". ...
series; it was later redesignated as part of the TMS 0100 series, which was used in the TI Datamath calculator. Although marketed as a calculator-on-a-chip, the TMS1802NC was fully programmable, including on the chip a CPU with an 11-bit instruction word, 3520 bits (320 instructions) of ROM and 182 bits of RAM.
Pico/General Instrument (1971)
 In 1971, Pico Electronics and General Instrument (GI) introduced their first collaboration in ICs, a complete single-chip calculator IC for the Monroe/ Litton Royal Digital III calculator. This chip could also arguably lay claim to be one of the first microprocessors or microcontrollers having
In 1971, Pico Electronics and General Instrument (GI) introduced their first collaboration in ICs, a complete single-chip calculator IC for the Monroe/ Litton Royal Digital III calculator. This chip could also arguably lay claim to be one of the first microprocessors or microcontrollers having ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* R ...
, RAM and a RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set comput ...
instruction set on-chip. The layout for the four layers of the PMOS process was hand drawn at x500 scale on mylar film, a significant task at the time given the complexity of the chip.
Pico was a spinout by five GI design engineers whose vision was to create single-chip calculator ICs. They had significant previous design experience on multiple calculator chipsets with both GI and Marconi-Elliott. The key team members had originally been tasked by Elliott Automation
Elliott Brothers (London) Ltd was an early computer company of the 1950s–60s in the United Kingdom. It traced its descent from a firm of instrument makers founded by William Elliott (1780 or 1781-1853) in London around 1804. The research ...
to create an 8-bit computer in MOS and had helped establish a MOS Research Laboratory in Glenrothes, Scotland in 1967.
Calculators were becoming the largest single market for semiconductors so Pico and GI went on to have significant success in this burgeoning market. GI continued to innovate in microprocessors and microcontrollers with products including the CP1600, IOB1680 and PIC1650. In 1987, the GI Microelectronics business was spun out into the Microchip
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny M ...
PIC microcontroller business.
Intel 4004 (1971)
 The Intel 4004 is often (falsely) regarded as the first true microprocessor built on a single chip, priced at . The claim of being the first is definetely false, as the earlier TMS1802NC was also a true microprocessor built on a single chip. The first known advertisement for the 4004 is dated November 15, 1971 and appeared in ''
The Intel 4004 is often (falsely) regarded as the first true microprocessor built on a single chip, priced at . The claim of being the first is definetely false, as the earlier TMS1802NC was also a true microprocessor built on a single chip. The first known advertisement for the 4004 is dated November 15, 1971 and appeared in ''Electronic News
''Electronic News'' was a publication that covered the electronics industry, from semiconductor equipment and materials to military/aerospace electronics to supercomputers. It was originally a weekly trade newspaper, which covered all aspects of ...
''. The microprocessor was designed by a team consisting of Italian engineer Federico Faggin, American engineers Marcian Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937 in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst ...
and Stanley Mazor
Stanley Mazor is an American microelectronics engineer who was born on 22 October 1941 in Chicago, Illinois. He is one of the co-inventors of the world's first microprocessor architecture, the Intel 4004, together with Ted Hoff, Masatoshi Shima ...
, and Japanese engineer Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip cu ...
.
The project that produced the 4004 originated in 1969, when Busicom
was a Japanese company that manufactured and sold computer-related products headquartered in Taito, Tokyo. It owned the rights to Intel's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, which they created in partnership with Intel in 1970.
Busicom ask ...
, a Japanese calculator manufacturer, asked Intel to build a chipset for high-performance desktop calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized d ...
s. Busicom's original design called for a programmable chip set consisting of seven different chips. Three of the chips were to make a special-purpose CPU with its program stored in ROM and its data stored in shift register read-write memory. Ted Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937 in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Ins ...
, the Intel engineer assigned to evaluate the project, believed the Busicom design could be simplified by using dynamic RAM storage for data, rather than shift register memory, and a more traditional general-purpose CPU architecture. Hoff came up with a four-chip architectural proposal: a ROM chip for storing the programs, a dynamic RAM chip for storing data, a simple I/O device, and a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU). Although not a chip designer, he felt the CPU could be integrated into a single chip, but as he lacked the technical know-how the idea remained just a wish for the time being.
 While the architecture and specifications of the MCS-4 came from the interaction of Hoff with
While the architecture and specifications of the MCS-4 came from the interaction of Hoff with Stanley Mazor
Stanley Mazor is an American microelectronics engineer who was born on 22 October 1941 in Chicago, Illinois. He is one of the co-inventors of the world's first microprocessor architecture, the Intel 4004, together with Ted Hoff, Masatoshi Shima ...
, a software engineer reporting to him, and with Busicom engineer Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip cu ...
, during 1969, Mazor and Hoff moved on to other projects. In April 1970, Intel hired Italian engineer Federico Faggin as project leader, a move that ultimately made the single-chip CPU final design a reality (Shima meanwhile designed the Busicom calculator firmware and assisted Faggin during the first six months of the implementation). Faggin, who originally developed the silicon gate technology (SGT) in 1968 at Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
and designed the world's first commercial integrated circuit using SGT, the Fairchild 3708, had the correct background to lead the project into what would become the first commercial general purpose microprocessor. Since SGT was his very own invention, Faggin also used it to create his new methodology for random logic Random logic is a semiconductor circuit design technique that translates high-level logic descriptions directly into hardware features such as AND and OR gates. The name derives from the fact that few easily discernible patterns are evident in the a ...
design that made it possible to implement a single-chip CPU with the proper speed, power dissipation and cost. The manager of Intel's MOS Design Department was Leslie L. Vadász
Leslie L. Vadász (born Vadász László; born September 12, 1936 in Budapest, Hungary) is a Hungarian-Americans, American engineer and Management, manager, one of the founding members of Intel Corporation.
Early life and education
In his homet ...
at the time of the MCS-4 development but Vadász's attention was completely focused on the mainstream business of semiconductor memories so he left the leadership and the management of the MCS-4 project to Faggin, who was ultimately responsible for leading the 4004 project to its realization. Production units of the 4004 were first delivered to Busicom in March 1971 and shipped to other customers in late 1971.
8-bit designs
The Intel 4004 was followed in 1972 by the Intel 8008, the world's first8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit Integer (computer science), integers or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet (computing), octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) arc ...
microprocessor. The 8008 was not, however, an extension of the 4004 design, but instead the culmination of a separate design project at Intel, arising from a contract with Computer Terminals Corporation, of San Antonio TX, for a chip for a terminal they were designing, the Datapoint 2200—fundamental aspects of the design came not from Intel but from CTC. In 1968, CTC's Vic Poor and Harry Pyle developed the original design for the instruction set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ' ...
and operation of the processor. In 1969, CTC contracted two companies, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
and Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
, to make a single-chip implementation, known as the CTC 1201. In late 1970 or early 1971, TI dropped out being unable to make a reliable part. In 1970, with Intel yet to deliver the part, CTC opted to use their own implementation in the Datapoint 2200, using traditional TTL logic instead (thus the first machine to run "8008 code" was not in fact a microprocessor at all and was delivered a year earlier). Intel's version of the 1201 microprocessor arrived in late 1971, but was too late, slow, and required a number of additional support chips. CTC had no interest in using it. CTC had originally contracted Intel for the chip, and would have owed them for their design work. To avoid paying for a chip they did not want (and could not use), CTC released Intel from their contract and allowed them free use of the design. Intel marketed it as the 8008 in April, 1972, as the world's first 8-bit microprocessor. It was the basis for the famous "Mark-8
The Mark-8 is a microcomputer design from 1974, based on the Intel 8008 CPU (which was the world's first 8-bit microprocessor). The Mark-8 was designed by Jonathan Titus, a Virginia Tech graduate student in Chemistry. After building the machine ...
" computer kit advertised in the magazine ''Radio-Electronics
''Radio-Electronics'' was an American electronics magazine that was published under various titles from 1929 to 2003. Hugo Gernsback, sometimes called the father of science fiction, started it as ''Radio-Craft'' in July 1929. The title was changed ...
'' in 1974. This processor had an 8-bit data bus and a 14-bit address bus.
The 8008 was the precursor to the successful Intel 8080 (1974), which offered improved performance over the 8008 and required fewer support chips. Federico Faggin conceived and designed it using high voltage N channel MOS. The Zilog Z80 (1976) was also a Faggin design, using low voltage N channel with depletion load and derivative Intel 8-bit processors: all designed with the methodology Faggin created for the 4004. Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, United States. After having lost $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009, the company split into two independent p ...
released the competing 6800 in August 1974, and the similar MOS Technology 6502 was released in 1975 (both designed largely by the same people). The 6502 family rivaled the Z80 in popularity during the 1980s.
A low overall cost, little packaging, simple computer bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This ex ...
requirements, and sometimes the integration of extra circuitry (e.g. the Z80's built-in memory refresh circuitry) allowed the home computer "revolution" to accelerate sharply in the early 1980s. This delivered such inexpensive machines as the Sinclair ZX81
The ZX81 is a home computer that was produced by Sinclair Research and manufactured in Dundee, Scotland, by Timex Corporation. It was launched in the United Kingdom in March 1981 as the successor to Sinclair's ZX80 and designed to be a low-cost ...
, which sold for . A variation of the 6502, the MOS Technology 6510 was used in the Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in the Guinness ...
and yet another variant, the 8502, powered the Commodore 128
The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128,The "C=" represents the graphical part of the logo. is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the ...
.
The Western Design Center, Inc (WDC) introduced the CMOS WDC 65C02 in 1982 and licensed the design to several firms. It was used as the CPU in the Apple IIe and IIc personal computers as well as in medical implantable grade pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart eith ...
s and defibrillators, automotive, industrial and consumer devices. WDC pioneered the licensing of microprocessor designs, later followed by ARM (company), ARM (32-bit) and other microprocessor intellectual property (IP) providers in the 1990s.
Motorola introduced the Motorola 6809, MC6809 in 1978. It was an ambitious and well thought-through 8-bit design that was source-code compatibility, source compatible with the 6800, and implemented using purely electrical wiring, hard-wired logic (subsequent 16-bit microprocessors typically used microcode to some extent, as complex instruction set computer, CISC design requirements were becoming too complex for pure hard-wired logic).
Another early 8-bit microprocessor was the Signetics 2650, which enjoyed a brief surge of interest due to its innovative and powerful instruction set architecture.
A seminal microprocessor in the world of spaceflight was Radio Corporation of America, RCA's RCA 1802 (aka CDP1802, RCA COSMAC) (introduced in 1976), which was used on board the ''Galileo (spacecraft), Galileo'' probe to Jupiter (launched 1989, arrived 1995). RCA COSMAC was the first to implement CMOS technology. The CDP1802 was used because it could be run at very low-power electronics, low power, and because a variant was available fabricated using a special production process, silicon on sapphire (SOS), which provided much better protection against cosmic radiation and electrostatic discharge than that of any other processor of the era. Thus, the SOS version of the 1802 was said to be the first radiation-hardened microprocessor.
The RCA 1802 had a static logic (digital logic), static design, meaning that the clock frequency could be made arbitrarily low, or even stopped. This let the Galileo (spacecraft), ''Galileo'' spacecraft use minimum electric power for long uneventful stretches of a voyage. Timers or sensors would awaken the processor in time for important tasks, such as navigation updates, attitude control, data acquisition, and radio communication. Current versions of the Western Design Center 65C02 and 65C816 also have static cores, and thus retain data even when the clock is completely halted.
12-bit designs
The Intersil 6100 family consisted of a 12-bit computing, 12-bit microprocessor (the 6100) and a range of peripheral support and memory ICs. The microprocessor recognised the DEC PDP-8 minicomputer instruction set. As such it was sometimes referred to as the CMOS-PDP8. Since it was also produced by Harris Corporation, it was also known as the Harris HM-6100. By virtue of its CMOS technology and associated benefits, the 6100 was being incorporated into some military designs until the early 1980s.16-bit designs
The first multi-chip16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
microprocessor was the National Semiconductor IMP-16, introduced in early 1973. An 8-bit version of the chipset was introduced in 1974 as the IMP-8.
Other early multi-chip 16-bit microprocessors include the MCP-1600 that Digital Equipment Corporation, Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) used in the LSI-11 OEM board set and the packaged PDP-11, PDP-11/03 minicomputer—and the Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
MicroFlame 9440, both introduced in 1975–76. In late 1974, National introduced the first 16-bit single-chip microprocessor, the National Semiconductor PACE, which was later followed by an NMOS logic, NMOS version, the INS8900.
Next in list is the General Instrument CP1600, released in February 1975, which was used mainly in the Intellivision console.
Another early single-chip 16-bit microprocessor was TI's Texas Instruments TMS9900, TMS 9900, which was also compatible with their TI-990 line of minicomputers. The 9900 was used in the TI 990/4 minicomputer, the TI-99/4A home computer, and the TM990 line of OEM microcomputer boards. The chip was packaged in a large ceramic 64-pin Dual in-line package, DIP package, while most 8-bit microprocessors such as the Intel 8080 used the more common, smaller, and less expensive plastic 40-pin DIP. A follow-on chip, the TMS 9980, was designed to compete with the Intel 8080, had the full TI 990 16-bit instruction set, used a plastic 40-pin package, moved data 8 bits at a time, but could only address 16 Kilobyte, KB. A third chip, the TMS 9995, was a new design. The family later expanded to include the 99105 and 99110.
The Western Design Center (WDC) introduced the CMOS WDC 65816/65802, 65816 16-bit upgrade of the WDC CMOS WDC 65C02, 65C02 in 1984. The 65816 16-bit microprocessor was the core of the Apple IIGS and later the Super Nintendo Entertainment System, making it one of the most popular 16-bit designs of all time.
Intel "upsized" their 8080 design into the 16-bit Intel 8086, the first member of the x86 family, which powers most modern IBM PC compatible, PC type computers. Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
introduced the 8086 as a cost-effective way of porting software from the 8080 lines, and succeeded in winning much business on that premise. The Intel 8088, 8088, a version of the 8086 that used an 8-bit external data bus, was the microprocessor in the first IBM PC. Intel then released the Intel 80186, 80186 and Intel 80188, 80188, the Intel 80286, 80286 and, in 1985, the 32-bit Intel 80386, 80386, cementing their PC market dominance with the processor family's backwards compatibility. The 80186 and 80188 were essentially versions of the 8086 and 8088, enhanced with some onboard peripherals and a few new instructions. Although Intel's 80186 and 80188 were not used in IBM PC type designs, second source versions from NEC, the NEC V20, V20 and V30 frequently were. The 8086 and successors had an innovative but limited method of memory segmentation, while the 80286 introduced a full-featured segmented memory management unit (MMU). The 80386 introduced a flat 32-bit memory model with paged memory management.
The 16-bit Intel x86 processors up to and including the 80386 do not include Floating-point unit, floating-point units (FPUs). Intel introduced the Intel 8087, 8087, Intel 80187, 80187, Intel 80287, 80287 and Intel 80387, 80387 math coprocessors to add hardware floating-point and transcendental function capabilities to the 8086 through 80386 CPUs. The 8087 works with the 8086/8088 and 80186/80188, the 80187 works with the 80186 but not the 80188, the 80287 works with the 80286 and the 80387 works with the 80386. The combination of an x86 CPU and an x87 coprocessor forms a single multi-chip microprocessor; the two chips are programmed as a unit using a single integrated instruction set. The 8087 and 80187 coprocessors are connected in parallel with the data and address buses of their parent processor and directly execute instructions intended for them. The 80287 and 80387 coprocessors are interfaced to the CPU through I/O ports in the CPU's address space, this is transparent to the program, which does not need to know about or access these I/O ports directly; the program accesses the coprocessor and its registers through normal instruction opcodes.
32-bit designs
 16-bit designs had only been on the market briefly when
16-bit designs had only been on the market briefly when 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32-bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calculation ...
implementations started to appear.
The most significant of the 32-bit designs is the Motorola 68000, Motorola MC68000, introduced in 1979. The 68k, as it was widely known, had 32-bit registers in its programming model but used 16-bit internal data paths, three 16-bit Arithmetic Logic Units, and a 16-bit external data bus (to reduce pin count), and externally supported only 24-bit addresses (internally it worked with full 32 bit addresses). In PC-based IBM-compatible mainframes the MC68000 internal microcode was modified to emulate the 32-bit System/370 IBM mainframe. Motorola generally described it as a 16-bit processor. The combination of high performance, large (16 megabytes or 224 bytes) memory space and fairly low cost made it the most popular CPU design of its class. The Apple Lisa and Apple Macintosh, Macintosh designs made use of the 68000, as did a host of other designs in the mid-1980s, including the Atari ST and Commodore Amiga.
The world's first single-chip fully 32-bit microprocessor, with 32-bit data paths, 32-bit buses, and 32-bit addresses, was the AT&T Corporation, AT&T Bell Labs Bellmac 32, BELLMAC-32A, with first samples in 1980, and general production in 1982. After the Bell System divestiture, divestiture of AT&T in 1984, it was renamed the WE 32000 (WE for Western Electric), and had two follow-on generations, the WE 32100 and WE 32200. These microprocessors were used in the AT&T 3B5 and 3B15 minicomputers; in the 3B2, the world's first desktop super microcomputer; in the "Companion", the world's first 32-bit laptop computer; and in "Alexander", the world's first book-sized super microcomputer, featuring ROM-pack memory cartridges similar to today's gaming consoles. All these systems ran the UNIX System V operating system.
The first commercial, single chip, fully 32-bit microprocessor available on the market was the HP FOCUS.
Intel's first 32-bit microprocessor was the Intel iAPX 432, iAPX 432, which was introduced in 1981, but was not a commercial success. It had an advanced Capability-based security, capability-based Object (computer science), object-oriented architecture, but poor performance compared to contemporary architectures such as Intel's own 80286 (introduced 1982), which was almost four times as fast on typical benchmark tests. However, the results for the iAPX432 was partly due to a rushed and therefore suboptimal Ada (programming language), Ada compiler.
Motorola's success with the 68000 led to the Motorola 68010, MC68010, which added virtual memory support. The Motorola 68020, MC68020, introduced in 1984 added full 32-bit data and address buses. The 68020 became hugely popular in the Unix supermicrocomputer market, and many small companies (e.g., Altos Computer Systems, Altos, UNOS (operating system), Charles River Data Systems, Cromemco) produced desktop-size systems. The Motorola 68030, MC68030 was introduced next, improving upon the previous design by integrating the MMU into the chip. The continued success led to the Motorola 68040, MC68040, which included an floating-point unit, FPU for better math performance. The 68050 failed to achieve its performance goals and was not released, and the follow-up Motorola 68060, MC68060 was released into a market saturated by much faster RISC designs. The 68k family faded from use in the early 1990s.
Other large companies designed the 68020 and follow-ons into embedded equipment. At one point, there were more 68020s in embedded equipment than there were Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
Pentiums in PCs. The Motorola ColdFire, ColdFire processor cores are derivatives of the 68020.
During this time (early to mid-1980s), National Semiconductor introduced a very similar 16-bit pinout, 32-bit internal microprocessor called the NS 16032 (later renamed 32016), the full 32-bit version named the NS320xx, NS 32032. Later, National Semiconductor produced the NS320xx, NS 32132, which allowed two CPUs to reside on the same memory bus with built in arbitration. The NS32016/32 outperformed the MC68000/10, but the NS32332—which arrived at approximately the same time as the MC68020—did not have enough performance. The third generation chip, the NS32532, was different. It had about double the performance of the MC68030, which was released around the same time. The appearance of RISC processors like the AM29000 and MC88000 (now both dead) influenced the architecture of the final core, the NS32764. Technically advanced—with a superscalar RISC core, 64-bit bus, and internally overclocked—it could still execute Series 32000 instructions through real-time translation.
When National Semiconductor decided to leave the Unix market, the chip was redesigned into the Swordfish Embedded processor with a set of on-chip peripherals. The chip turned out to be too expensive for the laser printer market and was killed. The design team went to Intel and there designed the Pentium processor, which is very similar to the NS32764 core internally. The big success of the Series 32000 was in the laser printer market, where the NS32CG16 with microcoded BitBlt instructions had very good price/performance and was adopted by large companies like Canon. By the mid-1980s, Sequent Computer Systems, Sequent introduced the first SMP server-class computer using the NS 32032. This was one of the design's few wins, and it disappeared in the late 1980s. The MIPS architecture, MIPS R2000 (microprocessor), R2000 (1984) and R3000 (1989) were highly successful 32-bit RISC microprocessors. They were used in high-end workstations and servers by Silicon Graphics, SGI, among others. Other designs included the Zilog Z80000, which arrived too late to market to stand a chance and disappeared quickly.
The ARM architecture family, ARM first appeared in 1985. This is a RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set comput ...
processor design, which has since come to dominate the 32-bit embedded systems processor space due in large part to its power efficiency, its licensing model, and its wide selection of system development tools. Semiconductor manufacturers generally license cores and integrate them into their own system on a chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory ...
products; only a few such vendors such as Apple are licensed to modify the ARM cores or create their own. Most cell phones include an ARM processor, as do a wide variety of other products. There are microcontroller-oriented ARM cores without virtual memory support, as well as symmetric multiprocessor system, symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) applications processors with virtual memory.
From 1993 to 2003, the 32-bit x86 architectures became increasingly dominant in desktop computer, desktop, laptop, and server markets, and these microprocessors became faster and more capable. Intel had licensed early versions of the architecture to other companies, but declined to license the Pentium, so AMD and Cyrix built later versions of the architecture based on their own designs. During this span, these processors increased in complexity (transistor count) and capability (instructions/second) by at least three orders of magnitude. Intel's Pentium line is probably the most famous and recognizable 32-bit processor model, at least with the public at broad.
64-bit designs in personal computers
While64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit Integer (computer science), integers, memory addresses, or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing unit, CPUs and arithmetic logic unit, ALUs are those ...
microprocessor designs have been in use in several markets since the early 1990s (including the Nintendo 64 gaming console in 1996), the early 2000s saw the introduction of 64-bit microprocessors targeted at the PC market.
With AMD's introduction of a 64-bit architecture backwards-compatible with x86, x86-64 (also called AMD64), in September 2003, followed by Intel's near fully compatible 64-bit extensions (first called IA-32e or EM64T, later renamed Intel 64), the 64-bit desktop era began. Both versions can run 32-bit legacy applications without any performance penalty as well as new 64-bit software. With operating systems Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, Windows XP x64, Windows Vista x64, Windows 7 x64, Linux, BSD, and macOS that run 64-bit natively, the software is also geared to fully utilize the capabilities of such processors. The move to 64 bits is more than just an increase in register size from the IA-32 as it also doubles the number of general-purpose registers.
The move to 64 bits by PowerPC had been intended since the architecture's design in the early 90s and was not a major cause of incompatibility. Existing integer registers are extended as are all related data pathways, but, as was the case with IA-32, both floating-point and vector units had been operating at or above 64 bits for several years. Unlike what happened when IA-32 was extended to x86-64, no new general purpose registers were added in 64-bit PowerPC, so any performance gained when using the 64-bit mode for applications making no use of the larger address space is minimal.
In 2011, ARM introduced the new 64-bit ARM architecture.
RISC
In the mid-1980s to early 1990s, a crop of new high-performance reduced instruction set computer (RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set comput ...
) microprocessors appeared, influenced by discrete RISC-like CPU designs such as the IBM 801 and others. RISC microprocessors were initially used in special-purpose machines and Unix workstations, but then gained wide acceptance in other roles.
The first commercial RISC microprocessor design was released in 1984, by MIPS Computer Systems, the 32-bit R2000 (microprocessor), R2000 (the R1000 was not released). In 1986, HP released its first system with a PA-RISC CPU. In 1987, in the non-Unix Acorn computers' 32-bit, then cache-less, ARM2-based Acorn Archimedes became the first commercial success using the ARM architecture family, ARM architecture, then known as Acorn RISC Machine (ARM); first silicon ARM1 in 1985. The R3000 made the design truly practical, and the R4000 introduced the world's first commercially available 64-bit RISC microprocessor. Competing projects would result in the IBM IBM POWER Instruction Set Architecture, POWER and Sun Microsystems, Sun SPARC architectures. Soon every major vendor was releasing a RISC design, including the AT&T CRISP, AMD 29000, Intel i860 and Intel i960, Motorola 88000, DEC Alpha.
In the late 1990s, only two 64-bit RISC architectures were still produced in volume for non-embedded applications: SPARC and Power ISA, but as ARM has become increasingly powerful, in the early 2010s, it became the third RISC architecture in the general computing segment.
SMP and multi-core design

 SMP ''symmetric multiprocessing'' is a configuration of two, four, or more CPU's (in pairs) that are typically used in servers, certain workstations and in desktop personal computers, since the 1990s. A multi-core processor is a single CPU that contains more than one microprocessor core.
This popular two-socket motherboard from ABIT BP6, Abit was released in 1999 as the first SMP enabled PC motherboard, the Pentium Pro, Intel Pentium Pro was the first commercial CPU offered to system builders and enthusiasts. The Abit BP9 supports two Intel Celeron CPU's and when used with a SMP enabled operating system (Windows NT/2000/Linux) many applications obtain much higher performance than a single CPU. The early Celerons are easily overclockable and hobbyists used these relatively inexpensive CPU's clocked as high as 533Mhz - far beyond Intel's specification. After discovering the capacity of these motherboards Intel removed access to the multiplier in later CPU's.
In 2001 IBM released the POWER4 CPU, it was a processor that was developed over five years of research, began in 1996 using a team of 250 researchers. The effort to accomplish the impossible was buttressed by development of and through—remote-collaboration and assigning younger engineers to work with more experienced engineers. The teams work achieved success with the new microprocessor, Power4. It is a two-in-one CPU that more than doubled performance at half the price of the competition, and a major advance in computing. The business magazine ''eWeek'' wrote: ''“The newly designed 1GHz Power4 represents a tremendous leap over its predecessor”''. An industry analyst, Brad Day of Giga Information Group said: ''“IBM is getting very aggressive, and this server is a game changer”.''
The Power4 won "''Analysts’ Choice Award for Best Workstation/Server Processor of 2001", and'' it broke notable records, including winning a contest against the best players on the Jeopardy! U.S. television show.
Intel's Yonah (microprocessor), codename Yonah CPU's launched on Jan 6, 2006 and were manufactured with two dies packaged on a multi-chip module. In a hotly-contested marketplace List of AMD processors, AMD and others released new versions of multi-core CPU's, AMD's SMP enabled Athlon MP CPU's from the Athlon-XP, AthlonXP line in 2001, Sun released the UltraSPARC T1, Niagara and UltraSPARC T2, Niagara 2 with eight-cores, AMD's Athlon 64 X2, Athlon X2 was released in June 2007. The companies were engaged in a never-ending race for speed, indeed more demanding software mandated more processing power and faster CPU speeds.
By 2012 ''dual and quad-core'' processors became widely used in PCs and laptops, newer processors - similar to the higher cost professional level Intel Xeon's - with additional cores that execute instructions in parallel so software performance typically increases, provided the software is designed to utilize advanced hardware. Operating systems provided support for multiple-cores and SMD CPU's, many software applications including large workload and resource intensive applications - such as 3-D games - are programmed to take advantage of multiple core and multi-CPU systems.
Apple, Intel, and AMD currently lead the market with multiple core desktop and workstation CPU's. Although they frequently hip-hop each other for the lead in the performance tier. Intel retains higher frequencies and thus has the fastest single core performance, while AMD is often the leader in multi-threaded routines due to a more advanced ISA and the process node the CPU's are fabricated on.
Multiprocessing concepts for multi-core/multi-cpu configurations are related to Amdahl's law.
SMP ''symmetric multiprocessing'' is a configuration of two, four, or more CPU's (in pairs) that are typically used in servers, certain workstations and in desktop personal computers, since the 1990s. A multi-core processor is a single CPU that contains more than one microprocessor core.
This popular two-socket motherboard from ABIT BP6, Abit was released in 1999 as the first SMP enabled PC motherboard, the Pentium Pro, Intel Pentium Pro was the first commercial CPU offered to system builders and enthusiasts. The Abit BP9 supports two Intel Celeron CPU's and when used with a SMP enabled operating system (Windows NT/2000/Linux) many applications obtain much higher performance than a single CPU. The early Celerons are easily overclockable and hobbyists used these relatively inexpensive CPU's clocked as high as 533Mhz - far beyond Intel's specification. After discovering the capacity of these motherboards Intel removed access to the multiplier in later CPU's.
In 2001 IBM released the POWER4 CPU, it was a processor that was developed over five years of research, began in 1996 using a team of 250 researchers. The effort to accomplish the impossible was buttressed by development of and through—remote-collaboration and assigning younger engineers to work with more experienced engineers. The teams work achieved success with the new microprocessor, Power4. It is a two-in-one CPU that more than doubled performance at half the price of the competition, and a major advance in computing. The business magazine ''eWeek'' wrote: ''“The newly designed 1GHz Power4 represents a tremendous leap over its predecessor”''. An industry analyst, Brad Day of Giga Information Group said: ''“IBM is getting very aggressive, and this server is a game changer”.''
The Power4 won "''Analysts’ Choice Award for Best Workstation/Server Processor of 2001", and'' it broke notable records, including winning a contest against the best players on the Jeopardy! U.S. television show.
Intel's Yonah (microprocessor), codename Yonah CPU's launched on Jan 6, 2006 and were manufactured with two dies packaged on a multi-chip module. In a hotly-contested marketplace List of AMD processors, AMD and others released new versions of multi-core CPU's, AMD's SMP enabled Athlon MP CPU's from the Athlon-XP, AthlonXP line in 2001, Sun released the UltraSPARC T1, Niagara and UltraSPARC T2, Niagara 2 with eight-cores, AMD's Athlon 64 X2, Athlon X2 was released in June 2007. The companies were engaged in a never-ending race for speed, indeed more demanding software mandated more processing power and faster CPU speeds.
By 2012 ''dual and quad-core'' processors became widely used in PCs and laptops, newer processors - similar to the higher cost professional level Intel Xeon's - with additional cores that execute instructions in parallel so software performance typically increases, provided the software is designed to utilize advanced hardware. Operating systems provided support for multiple-cores and SMD CPU's, many software applications including large workload and resource intensive applications - such as 3-D games - are programmed to take advantage of multiple core and multi-CPU systems.
Apple, Intel, and AMD currently lead the market with multiple core desktop and workstation CPU's. Although they frequently hip-hop each other for the lead in the performance tier. Intel retains higher frequencies and thus has the fastest single core performance, while AMD is often the leader in multi-threaded routines due to a more advanced ISA and the process node the CPU's are fabricated on.
Multiprocessing concepts for multi-core/multi-cpu configurations are related to Amdahl's law.
Market statistics
In 1997, about 55% of all central processing unit, CPUs sold in the world were 8-bit microcontrollers, of which over 2 billion were sold. In 2002, less than 10% of all the CPUs sold in the world were 32-bit or more. Of all the 32-bit CPUs sold, about 2% are used in desktop or laptop personal computers. Most microprocessors are used in embedded control applications such as household appliances, automobiles, and computer peripherals. Taken as a whole, the average price for a microprocessor, microcontroller, or digital signal processor, DSP is just over . In 2003, about $44 billion (equivalent to about $ billion in ) worth of microprocessors were manufactured and sold. Although about half of that money was spent on CPUs used in desktop or laptoppersonal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s, those count for only about 2% of all CPUs sold. The quality-adjusted price of laptop microprocessors improved −25% to −35% per year in 2004–2010, and the rate of improvement slowed to −15% to −25% per year in 2010–2013.
About 10 billion CPUs were manufactured in 2008. Most new CPUs produced each year are embedded.
See also
* Comparison of instruction set architectures * Computer architecture * Computer engineering * List of microprocessors * Microarchitecture * Microprocessor chronologyNotes
References
*External links
Patent problems
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Microprocessors, American inventions Japanese inventions Digital electronics History of computing hardware Microcomputers Telecommunications engineering 1971 introductions