Early Warfare on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ancient warfare is
 Manned crews for these massive warships would have been quite impressive, but accounts vary in actual numbers of men from source to source.
Manned crews for these massive warships would have been quite impressive, but accounts vary in actual numbers of men from source to source.
 Siege warfare of the
Siege warfare of the
 Historical records of the
Historical records of the
Evolution of Sling Weapons
war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
that was conducted from the beginning of recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
to the end of the ancient period. The difference between prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
and ancient warfare is more organization oriented than technology oriented. The development of first city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s, and then empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
s, allowed warfare to change dramatically. Beginning in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, states produced sufficient agricultural surplus. This allowed full-time ruling elites and military commanders to emerge. While the bulk of military forces were still farmers, the society could portion off each year. Thus, organized armies developed for the first time. These new armies were able to help states grow in size and become increasingly centralized.
In Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
, the end of antiquity is often equated with the Fall of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
in 476 AD, the wars of the Eastern Roman Empire on its Southwestern Asian and North African borders, and the beginnings of the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
in the 7th century. In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, it can also be seen as ending of the growing role of mounted warriors needed to counter the ever-growing threat from the north in the 5th century and the beginning of the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
in 618 AD. In India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, the ancient period ends with the decline of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
(6th century) and the beginning of the Muslim conquests there from the 8th century. In Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, the ancient period is considered to end with the rise of feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
in the Kamakura period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle bet ...
in the 12–13th century.
Early ancient armies continued to primarily use bows and spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
s, the same weapons that had been developed in prehistoric times for hunting. The findings at the site of Nataruk
Nataruk in Turkana County, Kenya, is the site of an archaeological investigation which uncovered the 10,000-year-old remains of 27 people. The remains have garnered wide media attention for possible bioarchaeological evidence of interpersonal vio ...
in Turkana, Kenya, have been interpreted as evidence of inter-group conflict and warfare in antiquity, but this interpretation has been challenged. Early armies in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and China followed a similar pattern of using massed infantry armed with bows and spears.
Infantry at this time was the dominant form of war, partially due to the camel saddle and the stirrup not being invented yet. The infantries at this time would be divided into ranged and shock, with shock infantry either charging to cause penetration of the enemy line or hold their own. These forces would ideally be combined, thus presenting the opponent with a dilemma: group the forces and leave them vulnerable to ranged, or spread them out and make them vulnerable to shock. This balance would eventually change as technology allowed for chariots, cavalry, and artillery to play an active role on the field.
No clear line can be drawn between ancient and medieval warfare
Medieval warfare is the warfare of the Middle Ages. Technological, cultural, and social advancements had forced a severe transformation in the character of warfare from antiquity, changing military tactics and the role of cavalry and artillery ( ...
. The characteristic properties of medieval warfare, notably heavy cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a Military reserve, tactical reserve; they are also often termed ''shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the re ...
and siege engines
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while other ...
such as the trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weigh ...
were first introduced in Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
. The main division within the ancient period is at the beginning Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
with the introduction of cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
(resulting in the decline of chariot warfare), of naval warfare
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
(Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
), and the development of an industry based on ferrous metallurgy
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
which allowed for the mass production of metal weapons and thus the equipment of large standing armies.
The first military power to profit from these innovations was the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
, which achieved a hitherto unseen extent of centralized control, the first "world power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
" to extend over the entire Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
(Mesopotamia, the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
).
Chariots
As states grew in size, the speed of mobilization became crucial because central power could not hold if rebellions could not be suppressed rapidly. The first solution to this was thechariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nbs ...
, which was initially used in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
from around 1800 BC. First pulled by oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
and donkeys, they allowed rapid traversing of the relatively flat lands of the Middle East. The chariots were light enough that they could easily be floated across rivers. Improvements in the ability to train horses soon allowed them to be used to pull chariots, possibly as early as 2100 BC, and their greater speed and power made chariots even more efficient. The major limitation of the use of chariots was terrain; while very mobile on flat, hard, open ground, it was very difficult to traverse more difficult terrain, such as rough ground, even sparse trees or bushes, small ravines or streams, or marsh. In such terrain, chariots were less maneuverable than common foot soldiers, and later cavalry.
The chariot was so powerful for transportation and warfare that it became the key weapon in the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
in the 2nd millennium BC. The typical chariot was worked by two men: one would be a bowman who would fire at enemy forces, while the other would control the vehicle. Over time, chariots were developed to carry up to five warriors. In China, chariots
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 ...
became the central weapon of the Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
, allowing them to unify a great area.
Although chariots have been compared to modern-day tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
s in the role they played on the battlefield, i.e. shock attack
Shock tactics, shock tactic or shock attack is the name of an offensive maneuver which attempts to place the enemy under psychological pressure by a rapid and fully-committed advance with the aim of causing their combatants to retreat. The accep ...
s, this is disputed, with scholars pointing out that chariots were vulnerable and fragile, and required a level terrain while tanks are all-terrain vehicles; thus chariots were unsuitable for use like modern tanks as a physical shock force. The chief advantage of the chariot was the tactical mobility they provided to bowmen. Tightly packed infantry was the formation of choice, in order for ancient generals to maintain command and control
Command and control (abbr. C2) is a "set of organizational and technical attributes and processes ... hatemploys human, physical, and information resources to solve problems and accomplish missions" to achieve the goals of an organization or en ...
during the battle as well as for mutual protection. But a force of chariots could stand off at long range and rain arrows down on the infantrymen's heads. Because of their speed, any attempts to charge the chariots could be easily evaded. If, on the other hand, an infantry unit spread out to minimize the damage from arrows, they would lose the benefit of mutual protection and the charioteers could easily overrun them.
Thus any force facing chariots was in a tactical dilemma, making chariots indispensable to armies of those times. But they were complicated equipment that required specialized craftsmen to maintain them. This made chariots expensive to own. When chariots were owned by individuals within a society, it tended to give rise to a warrior class of specialists and a feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
(an example of which can be seen in Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's The Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Ody ...
). Where chariots were publicly owned, they helped in the maintenance and establishment of a strong central government, e.g. the New Egyptian Kingdom
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioca ...
. Chariot usage peaked in the Battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the New Kingdom of Egypt under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the mod ...
in 1274 BC, which was probably the largest chariot battle ever fought, involving perhaps 5,000 chariots.
Naval warfare
Naval warfare in the ancient world can be traced back to theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
in the third millennium BC, from evidence of paintings in the Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The nam ...
and models of ships which were made across the Aegean. Ships were used for civilian transport and trade, as well as for military purposes. They were propelled by both rowing and sailing, but since the Mediterranean is known for its inconsistent weather patterns, rowing was probably the primary means of propulsion.
The first documented, physical evidence of a naval battle is found in a relief painting located in the temple of Medinet Habu, near Luxor
Luxor ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palaces) is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of ''Thebes''.
Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open-a ...
, Egypt. It shows the victory of Ramses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great mona ...
over the 'Sea-Peoples' in the Nile river delta in the early twelfth century BC. These 'Sea-Peoples' were originally believed to be of Philistine and Phoenician descent, while there is speculation that there could be some Greek influence in their seafaring. Even before this relief painting, there are earlier records of the practice of sea battles as early as 2550 BC under the Egyptian Pharaoh Sahue, who reportedly used transport vessels to escort his armies to foreign shores. There is even further evidence from earlier sources that illustrate seafaring and military action around the Nile Delta during the early dynastic period in Egypt, following into the reign of Ramses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded as t ...
Before that victory of Ramses III, the state of Egypt had no access to the kind of timber needed to build seafaring vessels and warships on a large scale. Instead of importing large quantities of timber to build warships, Egyptian naval architects and early engineers began to convert the common Egyptian riverboats. They reconfigured the size of the ship and added heavy trees for longitudinal support of the hull on the open sea. The warships constructed in this way contributed to that victory. The relief painting shows in great detail how fighting was conducted in a naval battle. It shows Egyptian warships with over twenty rows of oarsmen along with infantry troops and archers fighting in apparent hand-to-hand combat with the opposing naval force. This raises a question to the theory that there was no actual naval weaponry developed at this time but rather a reliance upon maneuvering tactics and strategy in order to engage with infantry troops.
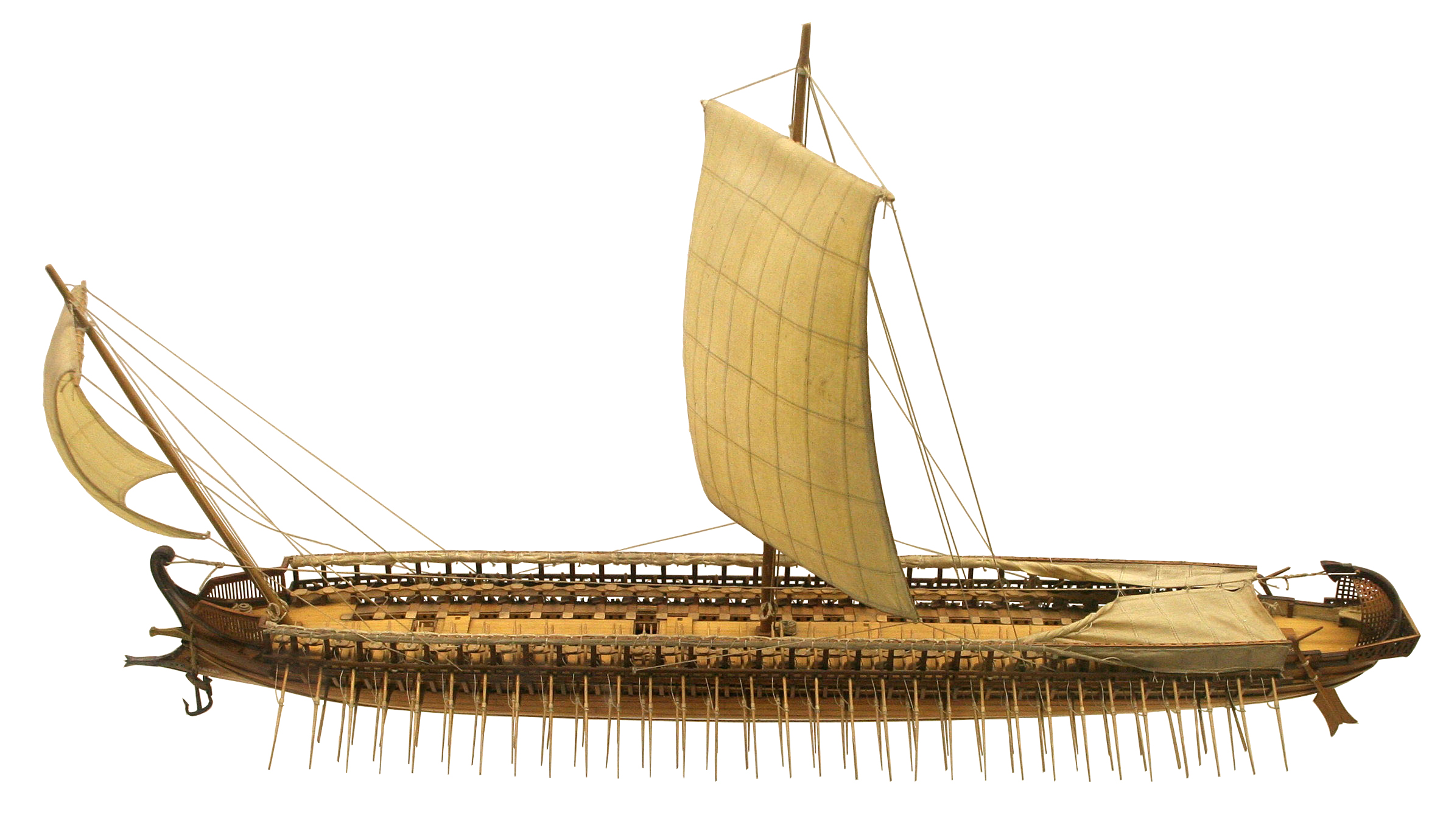
The trireme
Among the great innovations of naval warfare in the ancient world there are few that can surpass the Trireme style warship in terms of efficiency, strategy, and overall effectiveness. The first depiction of this 'longship' style vessel can be found in Homer's ''The Iliad'' as a means of transport of armed men and supplies to areas of conflict across the seas. These ships were said to have consisted of two separate levels that could have held up to 60 men per level, all operating oars in unison to propel the ship. The upper level of oarsmen would sit in single-file fashion, pulling their oars through what is called a top wale or some sort of oar-port; while the men in the lower rows would sit in the ships' hold also rowing through lower oar-ports. It is also said that each oar throughout the ship would be made in length proportionate to the physique of an average Greek man. Manned crews for these massive warships would have been quite impressive, but accounts vary in actual numbers of men from source to source.
Manned crews for these massive warships would have been quite impressive, but accounts vary in actual numbers of men from source to source. Herodotus of Halicarnassus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known for having ...
was a Greek historian in the fourth century BC who, through his accounts, said that these Triremes would consist of at least two-hundred men manning all positions. With these massive crews, these ships were able to work at maximum capacity and efficiency in regards to speed, navigation, and transport. While these ships were built for maximum efficiency, there is room for debate about the conditions and space aboard the ship itself. It is estimated that out of the 200 man crew, around 170 of those men would have been oarsmen with respective positions below deck. These oarsmen below deck would sit on thwarts and kept their personal storage items beneath them, reassuring the theory that these ships would be very crowded with little room for anything other than operational functions.
What exactly these Greek triremes were capable of in battle is debated. There are various different accounts that lay down foundations of what equipment was used and how these ships engaged in combat. The main military applications of Greek Triremes, besides the transport of troops and supplies, would be the advantages of ramming tactics. Developments and innovations of the Greek Trireme evolved over time, especially in respect to ramming tactics. Naval architects during this time saw fit to bring about full effectiveness and damaging power to these ships. By doing this, the amount of manpower would stay consistent, i.e., keeping the same amount of rowing power but shortening the length of the ship to condense the ramming power while keeping speed and agility consistent. This new ideology of warfare and naval tactics would prove to be prudent to the overall military applications of the Trireme, and soon would become the principal combative strategy of the Greek navy and other navies alike.
The Greek Trireme, soon after its appearance in the Aegean, would become the standard warship throughout the Mediterranean as sovereign states such as Egypt and even the Persian Empire would adopt the design of these ships and apply them to their own military applications. One major attraction of the Greek design was not only its efficient ramming capability but also its ability to travel long distances at fair speeds. One account from the Athenian soldier and historian Xenophon describes the voyage of the Athenian fleet commander Iphicrates through unfriendly waters and the strategy he used combined with the sheer sailing power of the Trireme. This primary source account can be interpreted as functional and efficient use of the Greek trireme. Maximizing its speed through rugged and unfriendly seas while also utilizing specific military strategy in order to ensure the most prudent and effective outcome was what led to the success of the trireme across all kinds of empires and civilizations throughout the Mediterranean. The trireme would later become a vital piece of naval weaponry throughout the Persian Wars, for both the Greeks and the Persian Empire, as well as the base standard for the formation of the Roman Navy.
The Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
were the first to feature large-scale naval operations: not only sophisticated fleet engagements with dozens of trireme
A trireme( ; derived from Latin: ''trirēmis'' "with three banks of oars"; cf. Greek ''triērēs'', literally "three-rower") was an ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean S ...
s on each side, but also combined land-sea operations. Ships in the ancient world could operate only on the relatively quiet waters of seas and rivers; the oceans were off-limits. Navies were almost always used as auxiliaries to land forces, often essential to bringing them supplies. They would rarely strike out on their own. With only limited-range weapons, naval galleys would often attempt to ram their opponents with their reinforced bow to cause damage or sink the enemy warships which often caused the two ships to become joined, and initiated a boarding battle. Only occasionally was a decisive naval battle fought, such as the Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade ( grc, Ναυμαχία τῆς Λάδης, translit=Naumachia tēs Ladēs) was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities (joined by the Lesbi ...
in which a Persian navy destroyed the Greek navy.
Tactics and weapons
Strategy
Ancient strategy focused broadly on the twin goals of convincing the enemy that continued war was more costly than submitting, and of making the most gain possible from war. Forcing the enemy to submit generally consisted of defeating their army in the field. Once the enemy force was routed, the threat of siege, civilian deaths, and the like often forced the enemy to the bargaining table. However, this goal could be accomplished by other means. Burning enemy fields would force the choice of surrendering or fighting apitched battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A ...
. Waiting an enemy out until their army had to disband due to the beginning of the harvest season or running out of payment for mercenaries presented an enemy with a similar choice. The exceptional conflicts of the ancient world were when these rules of warfare were violated. The Spartan and Athenian refusal to accept surrender after many years of war and near bankruptcy in the Peloponnesian War is one such exceptional example, as is the Roman refusal to surrender after the Battle of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae () was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by ...
.
A more personal goal in war was simple profit. This profit was often monetary, as was the case with the raiding culture of the Gallic tribes. But the profit could be political, as great leaders in war were often rewarded with government office after their success. These strategies often contradict modern common sense as they conflict with what would be best for the states involved in the war.
Tactics
Effective tactics varied greatly, depending on: # The army's size # Unit types # Terrain # The weather # Positional advantage # Skill level # Individual battle experience # Individual morale # Armament (quantity and quality)Weapons
Ancient weapons included the spear, theatlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store ene ...
with light javelin or similar projectile, the bow and arrow, the sling; polearm
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, thereby extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantl ...
s such as the spear, falx
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.
Etymology
''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' b ...
and javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
; hand-to-hand weapons such as sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
s, spears, clubs
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands and enterprises
...
, maces, axe
An axe ( sometimes ax in American English; see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for millennia to shape, split and cut wood, to harvest timber, as a weapon, and as a ceremonial or heraldic symbol. The axe has ma ...
s, and knives
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced ...
. Catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored p ...
s, siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s, and battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient history, ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, hea ...
s were used during siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
s.
The Ancient Greeks left behind many examples of their weapons though their burial practices. In ''Arms and Armour of the Greeks'', the rapier-like swords found within Mycenean tombs tended to be brittle due to their length and slim designs. During the Bronze Age, two new types of swords made a debut: the horned and cruciform varieties. The horned sword was named after the horn-like appearance of the handguard and was the preferred weapon for cutting strikes. The cruciform sword was derived from the Minoan dagger's flanged hilt and rounded handguards set at right angles. Spears continued to remain the preferred means for thrusting attacks, but the Palace Period saw the addition of a socketed base to the weapon. This new period also saw a shift in the role of the bow and arrow from hunting implements to full-fledged weapons. As Greek civilization progressed, the need for weapons changed and by the Late Period of Mycenae, weapons had become shorter and more suited for use in work environments rather than battles.
Macedon was known more traditionally for having a strong cavalry rather than infantry. During Alexander's reign, the Sarissophori came into being and this was unique to Alexander's time in power. While the cavalry was more prominent, the Macedon infantry, made up of the poor and peasant classes, formed into a new and unique branch of the military that was different from the hoplite. These warriors were armed with a huge pike weapon called a sarissa as well as the army being equipped with slings, which used almond-shaped bronze bullets that were engraved with either Philip's or his generals' name. For siege warfare, the Macedonians used an arrow-firing catapult. For armor, they were equipped with a metal helmet, greaves, and a shield covered with bronze.
In ''The Archaeology of Weapons'', a broader account of ancient weaponry is taken into account through the investigation of European weapons. Oakeshott believes that at some point between 1500 and 100 BC that the sword developed from the knife in both Minoan Crete and Celtic Britain and strongly resembles the rapiers. During the Bronze Age in the same general region, several other swords were developed: the Hallstatt first appeared during this Age but did not become widely used until the Iron Age, the Carps Tongues, and the Rhone Valley swords. The Hallstatt swords gained prominence during the Iron Age and were a long sword with a rather curious point that was one of three shapes: rounded, a square shape, or similar to a fishtail, and were the preferred weapon for use in a chariot. The Carps Tongues blade were also rather large swords with the edges running parallel for two-thirds of the blade before narrowing to the usually point. The last sword is that of the Rhone Valley and is generally considered more of small sword or an overly large dagger with each hilt uniquely cast in bronze. The pommel of this type of dagger has the ends drawn out into two thin points that curve in towards the blade. Along with Hallstatt swords, there were found to be spears, similar to the spearheads found in Mycenae they were quite large at fifteen inches and having a hollow socket however they were unique in that they had a small collar of bronze near where they attached to the shaft.
Within India's long history there are several different regimes that produced unique weapons. The list of weapons primarily used in India are the battle axe, the bow and arrow, spears, spike, barbed dart, the sword, iron club, javelin, iron arrow, and the scimitar. One sword type is the katar blade, these are equipped with sword breaking bars and both the shape and size would depend on whether the bearer was cavalry or an infantryman. A curved sword such as the talwar or shamsheer was ideal for a cutting motion delivered from horseback. There were three early iron sword types being the leaf-shaped, spoon-shaped and the parallel sword each ideal for thrusting and jabbing as opposed to a striking or cutting motion. The Rajputs, Gurkhas, Nagas, and Coorg and Malabar each developed a weapon unique to themselves. The Rajputs wielded the khanda which is a broad and straight sword with a wider point. The Gurkhas had two swords that they preferred to use the kukri, a short sword that angled towards a wide tip, and the kora, their historical war sword which was around 60 centimeters with a single edge that was rather narrow near the handler and curving towards the front. The daos had a blade equal to two feet in length that had a wide and square-like tip and the handle was made of either wood or ivory, these were the weapons that came to popularity for the Nagas. The Ayudha katti
Odi katti (also written ayda katti or aydha katti or आयुध कटि) is an indigenous weapon of war and tools to the Kodava people of Kodagu, in the state of Karnataka, India. The ayudha katti is developed from an implement used to cut thro ...
was a single-edged blade also near two feet long but with no handle and wield by the Coorg and Malabar. In Southern India, the Borobudur and the Veragal, either shaped like a hook or a wavy design, were the swords in use. A rather unique weapon used in India is the Baghnakh, which is similar to a knuckle duster and was used to slit the opponent's throat or belly.
Armor in India can be found dating back to 500 BC and Vedic literature; there are several different types: leather and fabric, scale, brigandine, lamellar, mail, plate, and a combination of mail and plate. In ''Arms and Armour: Traditional Weapons of India'' it is read that the wrastrana, a breastplate, has been in use since prehistoric times though the most popular is the char-aina meaning four mirrors is a coat of mail overlaid with four elaborately designed plates. The helmets consisted of a sliding nose guard with a piece of chainmail hanging from it designed to protect the neck and shoulders. Armor was not just limited to human soldiers but extended to their horses and elephants as well. The horse armor was made up of mail and plates or lamellae which covered the neck, chest, and hindquarters underneath which was some form of padding to keep it in place while a faceplate protected the animal's face. The elephants, used as a battering ram or to break and trample enemy lines, were also donned in armor for battle. The elephant's head was covered by a steel mask and covered half of the trunk while the throat and sides were protected by lamellae armor while the tusks were tipped with sharp metal.
Sieges
 Siege warfare of the
Siege warfare of the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
took place behind walls built of mud bricks, stone, wood or a combination of these materials depending on local availability. The earliest representations of siege warfare date to the Protodynastic Period of Egypt
Naqada III is the last phase of the Naqada culture of ancient Egyptian prehistory, dating from approximately 3200 to 3000 BC. It is the period during which the process of state formation, which began in Naqada II, became highly visible, ...
, c. 3000 BC, while the first siege equipment is known from Egyptian tomb reliefs of the 24th century BC showing wheeled siege ladders. Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n palace reliefs of the 9th to 7th centuries BC display sieges of several Near Eastern cities. Though a simple battering ram had come into use in the previous millennium, the Assyrians improved siege warfare. The most common practice of siege warfare was, however, to lay siege and wait for the surrender of the enemies inside. Due to the problem of logistics, long-lasting sieges involving anything but a minor force could seldom be maintained.
Ancient siege warfare varied from each civilization and how each city was defended differently and had to approach with different tactics. One way to ensure an army used all its troops in its siege is shown when its explained how a chariot can be used in a siege, saying that, "During the sieges, the chariots, and mostly in the Neo-Assyrian armies, were surely employed to patrol and protect the flanks and the rear of the besiegers' lines and camp." (UF 41 p. 5).
This shows that generals had to find new tactics to incorporate parts of their army that wouldn't work in the siege, as shown with the chariots on patrol duty and ensuring the army was safe from a flank attack from the enemy army. This strategy ensures that all forces are used and contributing to the battle effort and helping gain victory for them and all pulling their weight as well.
By culture
Ancient Near East
Mesopotamia
Egypt
Throughout most of its history, ancient Egypt was unified under one government. The main military concern for the nation was to keep enemies out. The arid plains and deserts surrounding Egypt were inhabited by nomadic tribes who occasionally tried to raid or settle in the fertileNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
river valley. The Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
built fortresses and outposts along the borders east and west of the Nile Delta, in the Eastern Desert, and in Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
to the south. Small garrisons could prevent minor incursions, but if a large force was detected a message was sent for the main army corps. Most Egyptian cities lacked city walls and other defenses.
The first Egyptian soldiers carried a simple armament consisting of a spear with a copper spearhead and a large wooden shield covered by leather hides. A stone mace was also carried in the Archaic period, though later this weapon was probably only in ceremonial use, and was replaced with the bronze battle axe. The spearmen were supported by archers carrying a composite bow and arrows with arrowheads made of flint or copper. No armour was used during the 3rd and early 2nd Millennium BC. As the dynasties expanded and grew upon the last that fell to gain new territory and control new people for the empire of Egypt. One of the ways the dynasties were different were the new technologies used in the later dynasties against the enemy. One example is the armies of Ramesses' II faced off against the Hittites in the Battle of Qadesh. Both armies have cavalry units supporting their infantry and scouts to get updates on the movements. These advances differ from two groups attacking head-on for control of an area and facing losses on both sides
The major advance in weapons technology and warfare began around 1600 BC when the Egyptians fought and defeated the Hyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC).
T ...
people, who ruled Lower Egypt at the time. It was during this period the horse and chariot were introduced into Egypt. Other new technologies included the sickle sword
The ''khopesh'' ('; also vocalized khepesh) is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that evolved from battle axes.
Description
A typical ''khopesh'' is 50–60 cm (20–24 inches) in length, though smaller examples also exist. The inside c ...
, body armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
and improved bronze casting. In the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
, the Egyptian military changed from levy troops into a firm organization of professional soldiers. Conquests of foreign territories, like Nubia, required a permanent force to be garrisoned abroad. The Egyptians were mostly used to slowly defeating a much weaker enemy, town-by-town until beaten into submission. The preferred tactic was to subdue a weaker city or kingdom one at a time resulting in the surrender of each fraction until complete domination was achieved. The encounter with other powerful Near Eastern kingdoms like Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in ...
, the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centra ...
, and later the Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
ns and Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
, made it necessary for the Egyptians to conduct campaigns far from home. The next leap forwards came in the Late Period (712–332 BC), when mounted troops and weapons made of iron came into use. After the conquest by Alexander the Great, Egypt was heavily Hellenized and the main military force became the infantry phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly use ...
. The ancient Egyptians were not great innovators in weapons technology, and most weapons technology innovation came from Western Asia and the Greek world.
These soldiers were paid with a plot of land for the provision of their families. After fulfillment of their service, the veterans were allowed retirement to these estates. Generals could become quite influential at the court, but unlike other feudal states, the Egyptian military was completely controlled by the king. Foreign mercenaries were also recruited; first Nubians (Medjay
Medjay (also ''Medjai'', ''Mazoi'', ''Madjai'', ''Mejay'', Egyptian ''mḏꜣ.j'', a nisba of ''mḏꜣ'',) was a demonym used in various ways throughout ancient Egyptian history to refer initially to a nomadic group from Nubia and later as a gen ...
), and later also Libyans and Sherdens in the New Kingdom. By the Persian period, Greek mercenaries entered service into the armies of the rebellious pharaohs. The Jewish mercenaries at Elephantine
Elephantine ( ; ; arz, جزيرة الفنتين; el, Ἐλεφαντίνη ''Elephantíne''; , ) is an island on the Nile, forming part of the city of Aswan in Upper Egypt. The archaeological sites on the island were inscribed on the UNESCO ...
served the Persian overlords of Egypt in the 5th century BC. Although, they might also have served the Egyptian Pharaohs of the 6th century BC.
As far as had been seen from the royal propaganda of the time, the king or the crown prince personally headed the Egyptian troops into battle. The army could number tens of thousands of soldiers, so the smaller battalions consisting of 250 men, led by an officer, may have been the key of command. The tactics involved a massive strike by archery followed by infantry and/or chariotry attacking the broken enemy lines. The enemies could, however, try to surprise the large Egyptian force with ambushes and by blocking the road as the Egyptian campaign records informs us.
Within the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
valley itself, ships and barges were important military elements. Ships were vital for providing supplies for the troops. The Nile river had no fords so barges had to be used for river crossings. Dominating the river often proved necessary for prosecuting sieges, like the Egyptian conquest of the Hyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC).
T ...
capital Avaris
Avaris (; Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; grc, Αὔαρις, Auaris; el, Άβαρις, Ávaris; ar, حوّارة, Hawwara) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern r ...
. Egypt had no navy to fight naval battles at sea before the Late Period. However, a battle involving ships took place at the Egyptian coast in the 12th century BC between Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monar ...
and seafaring raiders.
Persia
Ancient Persia first emerged as a major military power underCyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
. Its form of warfare was based on massed infantry in light armor to pin the enemy force whilst cavalry dealt the killing blow. Cavalry was used in huge numbers but it is not known whether they were heavily armored or not. Most Greek sources claim the Persians wore no armor, but we do have an example from Herodotus which claims that an unhorsed cavalry Officer wore a gold cuirass under his red robes. Chariots were used in the early days but during the later days of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
they were surpassed by horsemen. During the Persian Empire's height, they even possessed war elephants
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
from North Africa and distant India. The elite of the Persian Army were the famous Persian Immortals
Immortals ( grc, Ἀθάνατοι, Athánatoi) or Persian Immortals was the name given by Herodotus to an elite heavy infantry unit of 10,000 soldiers in the army of the Achaemenid Empire. The unit served in a dual capacity through its role as i ...
, a 10,000 strong unit of professional soldiers armed with a spear, a sword and a bow. Archers also formed a major component of the Persian Army.
Persian tactics primarily had four stages involving archers, infantry and cavalry. The archers, who wielded longbows, would fire waves of arrows before the battle, attempting to cut the enemy numbers down prior battle. The cavalry would then attempt to run into the enemy and sever communications between generals and soldiers. Infantry would then proceed to attack the disoriented soldiers, subsequently weakened from the previous attacks.
Nubia
TheKerma culture
The Kerma culture or Kerma kingdom was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia" (in parts of present ...
was the first Nubian kingdom to unify much of the region. The Classic Kerma Culture, named for its royal capital at Kerma
Kerma was the capital city of the Kerma culture, which was located in present-day Sudan at least 5,500 years ago. Kerma is one of the largest archaeological sites in ancient Nubia. It has produced decades of extensive excavations and research, in ...
, was one of the earliest urban centers in the Nile region
Kerma culture was militaristic. This is attested by the many bronze daggers
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use def ...
or sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
s as well as archer
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In mo ...
burials found in their graves. The Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian language, Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Akkadian language, Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, ce ...
began to emerge around 1000 BC, 500 years after the end of the Kingdom of Kerma.
The first period of the kingdom's history, the 'Napata
Napata (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; grc, Νάπατα and Ναπάται) was a city of ancient Kingdom of Kush, Kush at the fourth cataract of the Nile. It is located approximately 1.5 kilometers from ...
n', was succeeded by the ' Meroitic period', when the royal cemeteries relocated to Meroë around 300 BC.
Bowmen were the most important force components throughout Kushite military history.Jim Hamm. 2000. The Traditional Bowyer's Bible, Volume 3, pp. 138-152 Archaeology has also revealed the use of the crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fi ...
in Kush. Siege engines
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while other ...
were deployed in Kushite siege warfare; for instance, during Piye
Piye (once transliterated as Pankhy or Piankhi; d. 714 BC) was an ancient Kushite king and founder of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled Egypt from 744–714 BC. He ruled from the city of Napata, located deep in Nubia, modern-day Sudan. ...
's invasion of Ashmunein
Hermopolis ( grc, Ἑρμούπολις ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', egy, ḫmnw , Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; cop, Ϣⲙⲟⲩⲛ ''Shmun''; ar, الأشموني ...
in the 8th Century BC. Other Kushite weapons included War Elephants
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
, chariots
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 ...
, armor
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
. At its peak, the kingdom of Kush stretched all the way from Nubia to the Near East.
India
During theVedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
( fl. 1500–500 BC), the ''Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
'' and other associated texts contain references to warfare. The earliest allusions to a specific battle are those to the Battle of the Ten Kings
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, दाशराज्ञ युद्ध, translit=Dāśarājñá yuddhá) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulte ...
in Mandala 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to ''Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are addi ...
of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
.
The two great ancient epics of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, ''Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
'' and ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
'' (–500 BC) are centered on conflicts and refer to military formations, theories of warfare and esoteric weaponry. Valmiki
Valmiki (; Sanskrit: वाल्मीकि, ) is celebrated as the wikt:harbinger, harbinger-poet in Sanskrit literature. The epic ''Ramayana'', dated variously from the 5th century BCE to first century BCE, is attributed to him, based on ...
's ''Ramayana'' describes Ayodhya
Ayodhya (; ) is a city situated on the banks of holy river Saryu in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.
Ayodhya, also known as Sāketa, Saketa, is an ancient city of India, the birthplace of Rama and ...
's military as defensive rather than aggressive. The city, it says, was strongly fortified and was surrounded by a deep moat. ''Ramayana'' describes Ayodhya in the following words: "The city abounded in warriors undefeated in battle, fearless and chinskilled in the use of arms, resembling lions guarding their mountain caves". ''Mahabharata'' describes various military techniques, including the '' Chakravyuha''.
The world's first recorded military application of war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant ...
s is in the Mahabharatha. From India, war elephants were brought to the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
where they were used in several campaigns. The Persian king Darius III
Darius III ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; c. 380 – 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC.
Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Dar ...
employed about 50 Indian elephants in the Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, Γαυγάμηλα, translit=Gaugámela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, Ἄρβηλα, translit=Árbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great a ...
(331 BC) fought against Alexander the Great. In the Battle of the Hydaspes River, the Indian king Porus
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only ment ...
, who ruled in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, with his smaller army of 200 war elephants, 2,000 cavalry and 20,000 infantry, presented great difficulty for Alexander the Great's larger army of 4,000 cavalry and 50,000 infantry, though Porus was eventually defeated. At this time, the Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
further east in northern and eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
India had an army of 6000 war elephants, 80,000 cavalry, 200,000 infantry and 8,000 armed chariots.
Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya o ...
(–275 BC) was a professor of political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
at Takshashila University, and later the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
of emperor Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empi ...
, the founder of the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
. Chanakya wrote the ''Arthashastra
The ''Arthashastra'' ( sa, अर्थशास्त्रम्, ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, political science, economic policy and military strategy. Kautilya, also identified as Vishnugupta and Chanakya, is ...
'', which covered various topics on ancient Indian warfare in great detail, including various techniques and strategies relating to war. These included the earliest uses of espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tangibl ...
and assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
s. These techniques and strategies were employed by Chandragupta Maurya, who was a student of Chanakya, and later by Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
(304–232 BC).
Chandragupta Maurya conquered the Magadha Empire and expanded to all of northern India, establishing the Maurya Empire, which extended from the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
to the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
. In 305 BC, Chandragupta defeated Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
, who ruled the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
and controlled most of the territories conquered by Alexander the Great. Seleucus eventually lost his territories in Southern Asia, including southern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, to Chandragupta. Seleucus exchanged territory west of the Indus for 500 war elephants and offered his daughter to Chandragupta. In this matrimonial alliance, the enmity turned into friendship, and Seleucus' dispatched an ambassador, Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has ...
, to the Mauryan court at Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the ...
. As a result of this treaty, the Maurya Empire was recognized as a great power by the Hellenistic World
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
, and the kings of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
sent their own ambassadors to his court. According to Megasthenes, Chandragupta Maurya built an army consisting of 30,000 cavalry, 9000 war elephants, and 600,000 infantry, which was the largest army known in the ancient world. Ashoka went on to expand the Maurya Empire to almost all of South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
, along with much of Afghanistan and parts of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Ashoka eventually gave up on warfare after converting to Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
.
The Cholas
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
were the first rulers of the Indian subcontinent to maintain a navy and use it to expand their dominion overseas. Vijayalaya Chola
Vijayalaya Chola (Tamil: விஜயாலய சோழன்) was a king of South India () who founded the imperial Chola Empire. He ruled over the region to the north of the river Kaveri.
Dark age of Cholas
The ancient Chola kingdom once ...
defeated the Pallavas and captured Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is the 11th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of South Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the Gr ...
. In the early 10th century the Chola king Parantaka I
Parantaka Chola I (Tamil : பராந்தக சோழன் I) (873 CE–955 CE) was a Chola emperor who ruled for forty-eight years, annexing Pandya by defeating Rajasimhan II. The best part of his reign was marked by increasing success ...
defeated the Pandyan king Maravarman Rajasimha II
Maravarman Rajasimha II (''r. c.'' 900–915 AD) was the last major king of the early medieval Pandya kingdom (6th–10th century AD) of south India. He was the son and successor of Parantaka Viranarayana (''r. c.'' 880–900 AD).Sastri, K. A. ...
and invaded Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. The Rashtrakuta
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
ruler Krishna III
Krishna III whose Kannada name was Kannara (r. 939 – 967 C.E.) was the last great warrior and able monarch of the Rashtrakuta dynasty of Manyakheta. He was a shrewd administrator and skillful military campaigner. He waged many wars to bring b ...
defeated and killed Parantaka I's son Rajaditya
Rajaditya Chola (''fl.'' mid-10th century AD) was a Chola prince, son of king Parantaka I (r. 907–955) and a Chera/Kerala princess ( the Ko Kizhan AdigalNarayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 96- ...
in about 949.
Uttama Chola
Uttama was a Chola Emperor who ruled from 973 CE to 985 CE in present-day Tamil Nadu, India. According to Tiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola, Madurantaka Uttama Chola's reign is placed after Aditya II. The latter may have been a co-regent ...
reigned 970–85. Inscriptions tell that at least from his time, Chola warriors wore waist coats of armour. Hence, one regiment was called ''Niyayam-Uttama-Chola-tterinda-andalakattalar''. Paluvettaraiyar Maravan Kandanar served as a general under Uttama and his predecessor, Sundara.
Rajaraja Chola
Rajaraja I (947 CE – 1014 CE), born Arunmozhi Varman or Arulmozhi Varman and often described as Raja Raja the Great or Raja Raja Chozhan was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He was the most powerful Tamil king in South ...
began his military career with the conquest of the Cheras in the Kandalur War
The battle of Kandalur salai (c. 988 CE), also spelled Kanthaloor salai, was a naval engagement of the Cholas under Rajaraja I (985—1014 CE) against the "salai" at Kandalur in Trivandrum Kerala.Noburu Karashmia (ed.), ''A Concise History of ...
. He captured the Pandya ruler Amara Bhujanga, the town of Vizhinjam
Vizhinjam is a region located in the city of Thiruvananthapuram, the capital of the state of Kerala in India. It is located 16 km south west from the city centre and 17 km south of Trivandrum International Airport along NH66. Adani Por ...
, and a part of Sri Lanka. In the 14th year of his reign (998–999) he conquered the Gangas
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
of Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, the Nolambas The Nolamba dynasty the area they held sway over is referred to as ''Nolambasa-37'' of Henjeru (Hemavathi), ''Nolambalige'' (''Nolambavadi''-32000), etc. R. Narasimhacharya states that the Nolambas were a native Kannada dynasty.
Officers and kings ...
of Bellary
Bellary, officially Ballari, in the eponymous Bellary district, is a city in the state of Karnataka, India.
History
Bellary was a part of Rayalaseema (Ceded Districts) which was part of Madras Presidency till 1 November 1956.
The Ball ...
and Eastern Mysore, Tadigaipadi, Vengi
Vengi (or Venginadu) is a delta region spread over the Krishna and Godavari River, (also called Godavari and Krishna districts), the region is also known as Godavari Delta, that used to house world famous diamond mines in the Medieval period. The ...
, Coorg
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
, the Pandyas and the Chalukyas of the Deccan. During the next three years, he subdued Quilon
Kollam (), also known by its former name Quilon , is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The city i ...
and the northern kingdom of Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
with the help of his son Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra Chola I (; Middle Tamil: Rājēntira Cōḻaṉ; Classical Sanskrit: Rājēndradēva Cōla; Old Malay: ''Raja Suran''; c. 971 CE – 1044 CE), often referred to as Rajendra the Great, and also known as Gangaikonda Chola (Middle Tami ...
. Rajendra later completed the conquest of Sri Lanka, crossed the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
, and marched across Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
to Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. He sent out a great naval expedition that occupied parts of Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
, Malaya, and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
. The Cholas were brought down by the Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
from the west and Pandyas from the south.
China
Ancient China during theShang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
was a Bronze Age society based on chariot armies. An archaeological study of Shang sites at Anyang
Anyang (; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan province, China. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively.
It had a ...
have revealed extensive examples of chariots and bronze weapons. The overthrow of the Shang by the Zhou saw the creation of a feudal social order, resting militarily on a class of aristocratic chariot warriors (士).
In the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
, warfare increased. ''Zuo zhuan'' describes the wars and battles among the feudal lords during the period. Warfare continued to be stylised and ceremonial even as it grew more violent and decisive. The concept of military hegemon (霸) and his "way of force" (霸道) came to dominate Chinese society. Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu ( ; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) was a Chinese military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period of 771 to 256 BCE. Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the author of ''The ...
created a book that still applies to today's modern armies, The Art of War
''The Art of War'' () is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the Late Spring and Autumn Period (roughly 5th century BC). The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu ("Master Sun"), is com ...
.
Formations of the army can be clearly seen from the Terracotta Army of Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor ( ...
, the first Emperor in the history of China to be successful in the unification of different warring states. Light infantry acting as shock troops lead the army, followed by heavy infantry as the main body of the army. Wide usage of cavalry and chariots behind the heavy infantry also gave the Qin army an edge in battles against the other warring states.
Warfare became more intense, ruthless and much more decisive during the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
, in which great social and political change was accompanied by the end of the system of chariot warfare and the adoption of mass infantry armies. Cavalry was also introduced from the northern frontier, despite the cultural challenge it posed for robe-wearing Chinese men. Chinese river valley civilizations would adopt nomadic "pants
Trousers (British English), slacks, or pants are an item of clothing worn from the waist to anywhere between the knees and the ankles, covering both legs separately (rather than with cloth extending across both legs as in robes, skirts, and dr ...
" for their cavalry units and soldiers.
Ancient Greece
In general, most features of the hoplite panoply of classical Greek antiquity, were already known during the Late Bronze Age byMycenaean Greeks
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
(–1100 BC). Mycenaean Greek society invested in the development of military infrastructure, while military production and logistics were supervised directly from the palatial centers.
Infantry did almost all of the fighting in Greek battles. The Greeks did not have any notable cavalry tradition except the Thessalians. Hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The fo ...
, Greek infantry, fought with a long spear and a large shield, the aspis
An aspis ( grc, ἀσπίς, plural ''aspides'', ), or porpax shield, sometimes mistakenly referred to as a hoplon ( el, ὅπλον) (a term actually referring to the whole equipment of a hoplite), was the heavy wooden shield used by the infa ...
. Light infantry (psiloi) peltasts
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis distin ...
, served as skirmishers.
Despite the fact that most Greek cities were well fortified (with the notable exception of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
) and Greek siege technology was not up to the task of breaching these fortifications by force, most land battles were pitched ones fought on flat-open ground. This was because of the limited period of service Greek soldiers could offer before they needed to return to their farms; hence, a decisive battle was needed to settle matters at hand. To draw out a city's defenders, its fields would be threatened with destruction, threatening the defenders with starvation in the winter if they did not surrender or accept battle.
This pattern of warfare was broken during the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
, when Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
' command of the sea allowed the city to ignore the destruction of the Athenian crops by Sparta and her allies by shipping grain into the city from the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. This led to a warfare style in which both sides were forced to engage in repeated raids over several years without reaching a settlement. It also made sea battle a vital part of warfare. Greek naval battles were fought between triremes
A trireme( ; derived from Latin: ''trirēmis'' "with three banks of oars"; cf. Greek ''triērēs'', literally "three-rower") was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizat ...
– long and speedy rowing ships which engaged the enemy by ramming and boarding actions.
Hellenistic Era
During the time ofPhilip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
and Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, the Macedonians were regarded as the most complete well co-ordinated military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
force in the known world. Although they are best known for the achievements of Alexander the Great, his father Philip II of Macedon created and designed the fighting force Alexander used in his conquests. Before this time and for centuries their military prowess was nowhere near that the sarissa phalanx offered.
However, prior to the improvements made by Philip II of Macedon armies fought in the traditional manner of the Greeks; that of the hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
phalanx.
Philip provided his Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
ian soldiers in the phalanx with sarissa
The sarisa or sarissa ( el, σάρισα) was a long spear or pike about in length. It was introduced by Philip II of Macedon and was used in his Macedonian phalanxes as a replacement for the earlier dory, which was considerably shorter. Thes ...
, a spear which was 4–6 meters in length. The sarissa, when held upright by the rear rank
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as:
Level or position in a hierarchical organization
* Academic rank
* Diplomatic rank
* Hierarchy
* H ...
s of the phalanx (there were usually eight ranks), helped hide maneuvers behind the phalanx from the view of the enemy. When held horizontal by the front ranks of the phalanx, enemies could be run through from far away. The hoplite type troops were not abandoned,Macedonian Warrior Alexander's elite infantryman, p. 41,,2006 but were no longer the core of the army.
In 358 BC he met the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
in battle with his reorganized Macedonian phalanx and utterly defeated them. The Illyrians fled in panic, leaving the majority of their 9,000-strong army dead. The Macedonian army invaded Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
and conquered the southern Illyrian tribes.
After the defeat of the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
, Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
's policy became increasingly aggressive. Paeonia was already forcefully integrated into Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
under Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
's rule. In 357 BC Philip broke the treaty with Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
and attacked Amphipolis
Amphipolis ( ell, Αμφίπολη, translit=Amfipoli; grc, Ἀμφίπολις, translit=Amphipolis) is a municipality in the Serres (regional unit), Serres regional unit, Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, Greece. The seat of the municipality is ...
which promised to surrender to the Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
in exchange for the fortified town of Pydna
Pydna (in Greek: Πύδνα, older transliteration: Pýdna) was a Greek city in ancient Macedon, the most important in Pieria. Modern Pydna is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern part of Pieria regional unit, Greece. Sinc ...
, a promise he didn't keep. The city fell back in the hands of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
ia after an intense siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
. Then he secured possession over the gold mines
Gold mining is the extraction of gold resources by mining. Historically, mining gold from alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. However, with the expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface, ...
of nearby Mount Pangaeus, which would enable him to finance his future wars.
In 356 the Macedonian army advanced further eastward and captured the town of Crenides (near modern Drama
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance: a play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has been ...
) which was in the hands of the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
, and which Philip renamed after himself to Philippi
Philippi (; grc-gre, Φίλιπποι, ''Philippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides ( grc-gre, Κρηνῖδες, ''Krenides'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colon ...
. The Macedonian eastern border with Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
was now secured at the river Nestus
Nestos ( ), Mesta ( ), or formerly the Mesta Karasu in Turkish (Karasu meaning "black river"), is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. It rises in the Rila Mountains and flows into the Aegean Sea near the island of Thasos. It plunges down towering c ...
(Mesta).
Philip next marched against his southern enemies. In Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
he defeated his enemies and by 352, he was firmly in control of this region. The Macedonian army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
advanced as far as the pass of Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
which divides Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
in two parts, but it did not attempt to take it because it was strongly guarded by a joint force of Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
, Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns, and Achaeans.
Having secured the bordering regions of Macedon, Philip assembled a large Macedonian army and marched deep into Thrace for a long conquering campaign. By 339 after defeating the Thracians in series of battles, most of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
was firmly in Macedonian hands save the most eastern Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
coastal cities of Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
and Perinthus
Perinthus or Perinthos ( grc, ἡ Πέρινθος) was a great and flourishing town of ancient Thrace, situated on the Propontis. According to John Tzetzes, it bore at an early period the name of Mygdonia (Μυγδονία). It lay 22 miles west ...
who successfully withstood the long and difficult sieges. But both Byzantium and Perinthus would have surely fallen had it not been for the help they received from the various Greek city-states, and the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
king himself, who now viewed the rise of Macedonia and its eastern expansion with concern. Ironically, the Greeks invited and sided with the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
against the Macedonians, although Persia had been the nation hated the most by Greece for more than a century. The memory of the Persian invasion of Greece some 150 years ago was still alive, but the current politics for the Macedonians had put it aside.
Much greater would be the conquests of his son, Alexander the Great, who would add to the phalanx a powerful cavalry, led by his elite Companions, and flexible, innovative formations and tactics. He advanced Greek style of combat, and was able to muster large bodies of men for long periods of time for his campaigns against Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
Iron Age Europe
Roman Empire
TheRoman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
was the world's first professional army. It had its origins in the citizen army of the Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
, which was staffed by citizens serving mandatory duty for Rome. The reforms of Marius around 100 BC turned the army into a professional structure, still largely filled by citizens, but citizens who served continuously for 20 years before being discharged.
The Romans were also noted for making use of auxiliary troops, non-Romans who served with the legions and filled roles that the traditional Roman military could not fill effectively, such as light skirmish troops and heavy cavalry. Later in the Empire, these auxiliary troops, along with foreign mercenaries, became the core of the Roman military. By the late Empire, tribes such as the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
were bribed to serve as mercenaries.
The Roman navy was traditionally considered less important, although it remained vital for the transportation of supplies and troops, also during the great purge of pirates from the Mediterranean sea by Pompey the Great in the 1st century BC. Most of Rome's battles occurred on land, especially when the Empire was at its height and all the land around the Mediterranean was controlled by Rome.
But there were notable exceptions. The First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
, a pivotal war between Rome and Carthage in the 3rd century BC, was largely a naval conflict. And the naval Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, nea ...
established the Roman empire under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
.
Balkans
The Illyrian kingBardyllis
Bardylis (also Bardyllis ; grc, Βάρδυλις; 448 – c. 358 BC) was an Illyrian king, and the founder of the first attested Illyrian dynasty. During his reign, Bardylis aimed to made Illyria a regional power interfering with Macedon. He ...
turned part of south Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
into a formidable local power in the 4th century BC. He managed to become king of the Dardanians Dardania, Dardanian or Dardanians may refer to ancient peoples or locations.
People
* Dardani, an ancient tribe in the Balkans
* Dardanians (Trojan) (''Dardanoi''), a people closely related to the Trojans and believed to be related to the Dardani
...
and include other tribes under his rule. However, their power was weakened by bitter rivalries and jealousy. The army was composed by peltast
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis disting ...
s with a variety of weapons.
The Thracians fought as peltasts using javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
and crescent or round wicker shields. Missile weapons were favored but close combat weaponry was carried by the Thracians as well. These close combat weapons varied from the dreaded Rhomphaia
The rhomphaia ( grc, ῥομφαία) was a close-combat bladed weapon used by the Thracians as early as 350-400 BC. Rhomphaias were weapons with a straight or slightly curved single-edged blade attached to a pole, which in most cases was conside ...
& Falx
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.
Etymology
''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' b ...
to spears and swords. Thracians shunned armor and greaves and fought as light as possible favoring mobility above all other traits and had excellent horsemen.
The Dacian tribes, located on modern-day Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The List of states ...
were part of the greater Thracian family of peoples. They established a highly militarized
Militarism is the belief or the desire of a government or a people that a state should maintain a strong military capability and to use it aggressively to expand national interests and/or values. It may also imply the glorification of the mili ...
society and, during the periods when the tribes were united under one king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
(82–44 BC, 86–106) posed a major threat to the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
s of Lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
. Dacia was conquered and transformed into a Roman province in 106 after a long, hard war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
.
Celtic
Tribal warfare
__NOTOC__
Ritual warfare (sometimes called endemic warfare) is a state of continual or frequent warfare, such as is found in some tribal societies (but is not limited to tribal societies).
Description
Ritual fighting (or ritual battle or ritual ...
appears to have been a regular feature of Celtic societies. While epic literature depicts this as more of a sport focused on raids and hunting rather than organised territorial conquest, the historical record is more of tribes using warfare to exert political control and harass rivals, for economic advantage, and in some instances to conquer territory.
The Celts were described by classical writers such as Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditiona ...
, Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
, and Florus as fighting like "wild beasts", and as hordes. Dionysius said that their "manner of fighting, being in large measure that of wild beasts and frenzied, was an erratic procedure, quite lacking in military science
Military science is the study of military processes, institutions, and behavior, along with the study of warfare, and the theory and application of organized coercive force. It is mainly focused on theory, method, and practice of producing mil ...
. Thus, at one moment they would raise their swords aloft and smite after the manner of wild boars
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is n ...
, throwing the whole weight of their bodies into the blow like hewers of wood or men digging with mattocks, and again they would deliver crosswise blows aimed at no target as if they intended to cut to pieces the entire bodies of their adversaries, protective armour and all". Such descriptions have been challenged by contemporary historians. Caesar himself describes the Gauls as forming phalanxes (likely similar to the medieval shieldwall) and testudos in battle, and using spears as their main weapon, as opposed to swords.
Germanic
 Historical records of the
Historical records of the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
in Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north- ...
east of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
and west of the Danube do not begin until quite late in the ancient period, so only the period after 100 BC can be examined. What is clear is that the Germanic idea of warfare was quite different from the pitched battles fought by Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and Greece. Instead, the Germanic tribes focused on raids.
The purpose of these was generally not to gain territory, but rather to capture resources and secure prestige. These raids were conducted by irregular troops, often formed along family or village lines. Leaders of unusual personal magnetism could gather more soldiers for longer periods, but there was no systematic method of gathering and training men, so the death of a charismatic leader could mean the destruction of an army. Armies also often consisted of more than 50 percent noncombatants, as displaced people would travel with large groups of soldiers, the elderly, women, and children.
Though often defeated by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, the Germanic tribes were remembered in Roman records as fierce combatants, whose main downfall was that they failed to unite successfully into one fighting force, under one command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
.Tacitus, The Annals 2.45 After the three Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
s were ambushed and destroyed by an alliance of Germanic tribes headed by Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of ge ...
at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Ancient Rome, Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius ...
in 9 AD, the Roman Empire made no further concentrated attempts at conquering Germania beyond the Rhine. Prolonged warfare against the Romans accustomed the Germanic tribes to improved tactics such as the use of reserves, military discipline and centralised command. Germanic tribes would eventually overwhelm and conquer the ancient world, giving rise to modern Europe and medieval warfare. For an analysis of Germanic tactics versus the Roman empire see tactical problems in facing the Gauls and the Germanic tribes
Japanese
Horses and bows were very important in Japan and were used in warfare from very early times, as shown in statues and artifacts found in tombs of early chieftains. Samurai eventually became very skilled in using the horse. Because their main weapon at this time was the bow and arrow, early samurai exploits were spoken of in Japanese war tales as the "Way of the Horse and Bow." Horse and bow combined was a battlefield advantage to the early samurai. A bunch of arrows made of mainly wood with poison-tipped points was worn on a warrior's right side so he could quickly knock and release an arrow mid-gallop. Although they weren't as important as the bow, swords of various sizes and types were also part of an early samurai's armory. They were mostly for close-quarters engagements. Many different kinds of spears were also used. One, thenaginata
The ''naginata'' (, ) is a pole weapon and one of several varieties of traditionally made Japanese blades (''nihontō''). ''Naginata'' were originally used by the samurai class of feudal Japan, as well as by ashigaru (foot soldiers) and sōhei ( ...
, was a curved blade fixed to the end of a pole several feet long. This was known as a 'woman's spear' because samurai girls were taught to use it from an early age. A device called the kumade, which resembled a long-handled garden rake, was used to catch the clothing or helmet of enemy horsemen and unseat them.
Common samurai archers had armor made of lamellae pieces laced together with colorful cords. The lightweight armor allowed for greater freedom of movement, faster speed, and reduced fatigue for horse and rider.
The early Yamato period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province.
While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710, including both the Kofun period (–538) and the Asuka ...
had seen a continual engagement in the Korean Peninsula until Japan finally withdrew, along with the remaining forces of the Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder Jum ...
Kingdom. Several battles occurred in these periods as the Emperor's succession gained importance. By the Nara period
The of the history of Japan covers the years from CE 710 to 794. Empress Genmei established the capital of Heijō-kyō (present-day Nara). Except for a five-year period (740–745), when the capital was briefly moved again, it remained the cap ...
, Honshū
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separa ...
was completely under the control of the Yamato
was originally the area around today's Sakurai City in Nara Prefecture of Japan, which became Yamato Province and by extension a name for the whole of Japan.
Yamato is also the dynastic name of the ruling Imperial House of Japan.
Japanese his ...
clan. Near the end of the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. ...
, samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They h ...
became a powerful political force, thus starting the feudal period.
Notable ancient wars
*Medo-Babylonian war against Assyrian Empire
The Medo-Babylonian conquest of the Assyrian Empire was the last war fought by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, between 626 and 609 BC. Succeeding his brother Ashur-etil-ilani (631–627 BC), the new king of Assyria, Sinsharishkun (627–612 BC), immedi ...
* Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfac ...
:The Ionian Revolt was a series of conflicts between the Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...
and the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
that began 499 BC and lasted until 493 BC. The revolt begins because of Athens's offensive attack to the city of Sardis and massacring the Persian citizens by burning down the city. This revolt had a major role in starting the Greco-Persian wars.
* Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
:The Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Greek City-States
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
and the Persian Empire that began around 500 BC and lasted until 448 BC.
* Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
:The Peloponnesian War was begun in 431 BC between the Athenian Empire
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plat ...
and the Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC ...
which included Sparta and Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
. The war was documented by Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientifi ...
, an Athenian general, in his work ''The History of The Peloponnesian War''. The war lasted 27 years, with a brief truce in the middle.
* Wars of Alexander the Great
The wars of Alexander the Great were a series of conquests that were carried out by Alexander III of Macedon from 336 BC to 323 BC. They began with battles against the Achaemenid Persian Empire, then under the rule of Darius III of Persia. ...
:King Alexander the III of Macedonia throughout his entire reign from 336 to 321 B.C embarked on a campaign of conquest of the Persian Empire. Starting from modern-day Western Turkey Alexander the Great conquered the entirety of Egypt, the Middle East, Iran and parts of India and Central Asia. Never losing a battle Alexander expanded the boundaries of the known world to the Greek World
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as sig ...
at the time. With an untimely death, his successors fought over the territories they had conquered. However, due to Alexander the Great Greek culture and technology spread into Asia for centuries to come.
* Kalinga War (265–264 BC) was a war fought between the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
under Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
and the state of Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
, a feudal republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
located on the coast of the present-day India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n state of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
. Ashoka's response to the Kalinga War is recorded in the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who reigned from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the expres ...
. According to some of these (Rock Edict XIII and Minor Rock Edict I), the Kalinga War prompted Ashoka, already a non-engaged Buddhist, to devote the rest of his life to Ahimsa
Ahimsa (, IAST: ''ahiṃsā'', ) is the ancient Indian principle of nonviolence which applies to all living beings. It is a key virtue in most Indian religions: Jainism, Buddhism, and Hinduism.Bajpai, Shiva (2011). The History of India � ...
(non-violence) and to Dhamma-Vijaya (victory through Dhamma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ''d ...
).
*Qin's wars of unification
Qin's wars of unification were a series of military campaigns launched in the late 3rd century BC by the Qin state against the other six major Chinese states — Han, Zhao, Yan, Wei, Chu and Qi.
Between 247 BC and 221 BC, Qin had emerged as ...
:Qin's wars of unification were a series of military campaigns launched in the late 3rd century BC by the Qin state
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted ex ...
against the other six major states – Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
, Zhao, Yan
Yan may refer to:
Chinese states
* Yan (state) (11th century – 222 BC), a major state in northern China during the Zhou dynasty
* Yan (Han dynasty kingdom), first appearing in 206 BC
* Yan (Three Kingdoms kingdom), officially claimed indepe ...
, Wei, Chu and Qi – within the territories that formed modern China. By the end of the wars in 221 BC, Qin had unified most of the states and occupied some lands south of the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
. The territories conquered by Qin served as the foundation of the Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), ...
.
* Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
:The Punic Wars were a series of three wars fought between Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and the city of Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
(a Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n descendant). They are known as the "Punic" Wars because Rome's name for Carthaginians was ''Punici'' (older ''Poeni'', due to their Phoenician ancestry). They determined that the Romans would control the Mediterranean Sea and led to the eventual rise of the greater Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
across Europe, Asia and Africa.
# The First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
was primarily a naval war fought between 264 BC and 241 BC.
# The Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
is famous for Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
's crossing of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
and was fought between 218 BC and 202 BC.
# The Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
resulted in the destruction of Carthage and was fought between 149 BC and 146 BC.
* Roman-Persian Wars
:The Roman–Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between states of the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
and two successive Iranian empires: the Parthian and the Sassanid. Battles between the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
and the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
began in 92 BC; wars began under the late Republic, and continued through the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and Sassanid empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
s. They were ended by the Arab Muslim invasions, which devastated the Sassanid and Byzantine East Roman empires shortly after the end of the last war between them.
*Han–Xiongnu War
The Han–Xiongnu War,. also known as the Sino–Xiongnu War, was a series of military battles fought between the Han Empire and the nomadic Xiongnu confederation from 133 BC to 89 AD.
Starting from Emperor Wu's reign (r. 141–87 BC), the Han ...
:The Han–Xiongnu War,. also known as the Sino-Xiongnu War, was a series of military battles fought between the Chinese Han empire
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
and the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
confederated state located in modern day Mongolia from 133 BC to 89 AD. The final wars resulted in the final destruction of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
as a political entity in Siberia. China would temporally enjoy peace on its northern frontier before new peoples such as the Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the ...
took the role of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
.
* Roman-Germanic Wars
This is a chronology of warfare between the Romans and various Germanic peoples between 113 BC and 476. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings and later Germanic invasions of the Western Roman ...
:The Germanic Wars is a name given to a large series of military engagements between the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and various Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
between 113 BC and AD 596. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings and later Germanic invasions in the Roman Empire that started in the late 2nd century. The series of conflicts which began in the 5th century, under the Western Roman Emperor Honorius
Honorius (9 September 384 – 15 August 423) was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius, Honorius ruled the western half of the empire while ...
, led (along with internal strife) to the ultimate downfall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
.
Notable ancient battles
Unit types
*Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine i ...
** Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
** Slingman
** Peltast
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis disting ...
** Hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
** Persian Immortal
** Phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly use ...
*** Macedonian phalanx
The Macedonian phalanx ( gr, Μακεδονική φάλαγξ) was an infantry formation developed by Philip II from the classical Greek phalanx, of which the main innovation was the use of the sarissa, a 6 meter pike. It was famously commanded b ...
** Legion
Legion may refer to:
Military
* Roman legion, the basic military unit of the ancient Roman army
* Spanish Legion, an elite military unit within the Spanish Army
* Legion of the United States, a reorganization of the United States Army from 179 ...
*** Legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republi ...
* Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
** Cataphract
A cataphract was a form of armored heavy cavalryman that originated in Persia and was fielded in ancient warfare throughout Eurasia and Northern Africa.
The English word derives from the Greek ' (plural: '), literally meaning "armored" or "co ...
** Clibanarii
The Clibanarii or Klibanophoroi ( el, κλιβανοφόροι, meaning "camp oven-bearers" from the Greek word meaning "camp oven" or "metallic furnace"), in Persian Grivpanvar, were a Sasanian Persian, late Roman and Byzantine military unit of ...
** Horse archer
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, f ...
** Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nbs ...
** War elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant ...
* Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
and siege engines
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while other ...
** Catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored p ...
** Onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
** Ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ta ...
** Scorpio
** Siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
** Battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient history, ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, hea ...
See also
*Ancient Mediterranean piracy
Piracy in the ancient Mediterranean dates back at least as far as the Bronze Age. The roots of the word "piracy" come from the ancient Greek πειράομαι, or ''peiráomai'', meaning "attempt" (i.e., of something illegal for personal gain). ...
* History of physical training and fitness
Physical training has been present in human societies throughout history. Usually, it was performed for the purposes of preparing for physical competition or display, improving physical, emotional and mental health, and looking attractive. It ...
* Horses in warfare
The first evidence of horses in warfare dates from Eurasia between 4000 and 3000 BC. A Sumerian illustration of warfare from 2500 BC depicts some type of equine pulling wagons. By 1600 BC, improved harness and chariot designs ...
* Women in warfare
References
Sources
*Literature
# Anglim, Simon, and Phyllis G. Jestice. ''Fighting Techniques of the Ancient World (3000 B.C. to 500 A.D.): Equipment, Combat Skills, and Tactics''. Dunne Books: 2003. . # # Bradford, Alfred S. ''With Arrow, Sword, and Spear: A History of Warfare in the Ancient World.'' Praeger Publishing: 2001. . # Connolly, Peter. ''Greece and Rome at War''. Greenhill Books: 1998. . # Gabriel, Richard A. ''The Great Armies of Antiquity''. Praeger Publishing: 2002. # Gichon, Mordechai, and Chaim Herzog. ''Battles of the Bible''. Greenhill Books: 2002. . # Goldsworthy, Adrian. ''The Complete Roman Army''. Thames & Hudson: 2003. . # Keegan, John. ''A History of Warfare
''A History of Warfare'' is a book by military historian John Keegan, which was published in 1993 by Random House.
Summary
Keegan discusses early warfare, the proliferation of Bronze Age warfare and then Iron Age warfare (Greek hoplites and pha ...
''. Vintage: 1993. .
# Kern, Paul Bentley. ''Ancient Siege Warfare''. Indiana University Press: 1999. .
# Leblanc, Steven A. ''Prehistoric Warfare in the American Southwest''. University of Utah Press: 1999. .
# Mayor, Adrienne. ''Greek Fire, Poison Arrows & Scorpion Bombs: Biological and Chemical Warfare in the Ancient World''. Overlook Press: 2003. .
# Peers, Chris J. ''Ancient Chinese Armies 1500–200 BC''. Osprey Publishing
Osprey Publishing is a British, Oxford-based, publishing company specializing in military history. Predominantly an illustrated publisher, many of their books contain full-colour artwork plates, maps and photographs, and the company produces ov ...
: 1990. .
# Peers, Chris J., and Michael Perry. ''Imperial Chinese Armies : 200 BC–589 AD''. Osprey Publishing
Osprey Publishing is a British, Oxford-based, publishing company specializing in military history. Predominantly an illustrated publisher, many of their books contain full-colour artwork plates, maps and photographs, and the company produces ov ...
: 1995. .
# Sabin, Philip. ''Lost Battles: Reconstructing The Great Clashes of the Ancient World''. Hambledon Continuum
Continuum International Publishing Group was an academic publisher of books with editorial offices in London and New York City. It was purchased by Nova Capital Management in 2005. In July 2011, it was taken over by Bloomsbury Publishing. , all ...
: 2007. .
# Van Creveld, Martin. "Technology and War: From 2000 B.C. to the Present". Free Press: 1991. {{ISBN, 0-02-933153-6.
# Warry, John Gibson, and John Warry. ''Warfare in the Classical World: An Illustrated Encyclopedia of Weapons, Warriors and Warfare in the Ancient Civilisations of Greece and Rome''. University of Oklahoma Press: 1999.
External links
Evolution of Sling Weapons