|
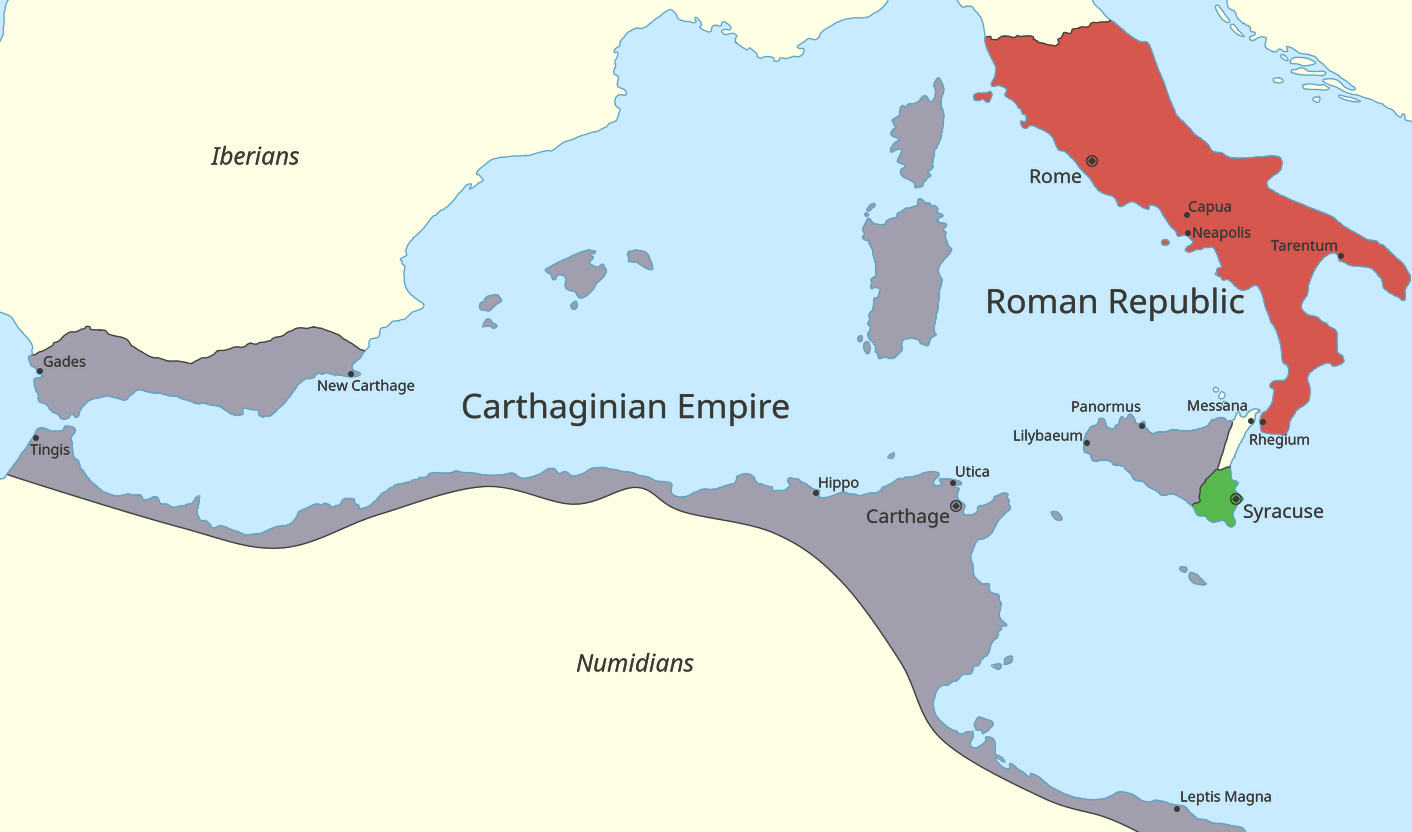
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians', and using novel tactics inflicted severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long Mercenary War, revolt against Carthage which started in 241BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides. The First Punic War broke out on the Mediterranean island of Sicily in 264BC as a result of Rome's expansionary attitude combined with Carthage's proprietary approach to the island. At the start of the war Carthage was the dominant power of the western Mediterranean, with an extensive Thalassocracy, maritime empire, while Rome was a rapidly expanding power in Roman Italy, Italy, with a strong Roman army of the mid-Republic, army but no navy. The fighting took place primarily on Sicily and its surroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Messana
The Battle of Messana in 264 BC was the first military clash between the Roman Republic and Carthage. It marked the start of the First Punic War. In that period, and after the recent successes in southern Italy, Sicily became of increasing strategic importance to Rome. Background The Greek historian Polybius states in Book One of '' The Histories'': "Even after long consideration, the (Roman) Senate did not approve the proposal to send help to Messana; they took the view that any advantage which would result from relieving the place would be counterbalanced by the inconsistency of such an action. However, the people who had suffered grievously from the wars that had just ended and were in dire need of rehabilitation of every kind, were inclined to listen to the consuls. These men, besides stressing the national advantages I have already mentioned which Rome could secure if she intervened, also dwelt on the great gains which would clearly accrue to every individual citizen fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Drepana
The naval Battle of Drepana (or Drepanum) took place in 249 BC during the First Punic War near Drepana (modern Trapani) in western Sicily, between a Carthaginian fleet under Adherbal and a Roman fleet commanded by Publius Claudius Pulcher. Pulcher was blockading the Carthaginian stronghold of Lilybaeum (modern Marsala) when he decided to attack their fleet, which was in the harbour of the nearby city of Drepana. The Roman fleet sailed by night to carry out a surprise attack but became scattered in the dark. Adherbal was able to lead his fleet out to sea before it was trapped in harbour; having gained sea room in which to manoeuvre he then counter-attacked. The Romans were pinned against the shore, and after a day of fighting were heavily defeated by the more manoeuvrable Carthaginian ships with their better-trained crews. It was Carthage's greatest naval victory of the war; they turned to the maritime offensive after Drepana and all but swept the Romans from the sea. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Panormus
The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal, son of Hanno. The Roman force of two legions defending the city of Panormus defeated the much larger Carthaginian army of 30,000 men and between 60 and 142 war elephants. The war had commenced in 264 BC with Carthage in control of much of Sicily, where most of the fighting took place. In 256–255 BC the Romans attempted to strike at the city of Carthage in North Africa, but suffered a heavy defeat by a Carthaginian army strong in cavalry and elephants. When the focus of the war returned to Sicily, the Romans captured the large and important city of Panormus in 254 BC. Thereafter they avoided battle for fear of the war elephants which the Carthaginians had shipped to Sicily. In late summer 250 BC Hasdrubal led out his army to devastate the crops of the cities of Rome's allies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. The city was founded in 734 BC by the Phoenicians as ("flower"). Palermo then became a possession of Carthage. Two ancient Greeks, Greek ancient Greek colonization, colonies were established, known collectively as ; the Carthaginians used this name on their coins after the 5th centuryBC. As , the town became part of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire, Empire for over a thousand years. From 831 to 1072 the city was under History of Islam in southern Italy, Arab ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cape Hermaeum
The Roman withdrawal from Africa was the attempt by the Roman Republic in 255 BC to rescue the survivors of their defeated expeditionary force to Carthaginian Africa during the First Punic War. A large fleet commanded by Servius Fulvius Paetinus Nobilior and Marcus Aemilius Paullus successfully evacuated the survivors after defeating an intercepting Carthaginian fleet, but was struck by a storm while returning, losing most of its ships. The Romans had invaded the Carthaginian homeland (in what is now north eastern Tunisia) in 256 BC. After initial successes, they had left a force of 15,500 men to hold their lodgement over the winter. This force, under Marcus Atilius Regulus, was decisively beaten at the Battle of Tunis in the spring of 255 BC and its commander, Marcus Atilius Regulus, captured. Two thousand survivors were besieged in the port of Aspis. The Roman fleet of 390 warships was sent to rescue and evacuate them. A Carthaginian fleet of 200 ships intercepted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Bagradas River (255 BC)
The Battle of the Bagradas River (the ancient name of the Medjerda), also known as the Battle of Tunis, was a victory by a Carthaginian army led by Xanthippus over a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus in the spring of 255 BC, nine years into the First Punic War. The previous year, the newly constructed Roman navy established naval superiority over Carthage. The Romans used this advantage to invade Carthage's homeland, which roughly aligned with modern-day Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter. Instead of holding his position, Regulus advanced towards the city of Carthage and defeated the Carthaginian army at the Battle of Adys. The Romans followed up and captured Tunis, only from Carthage. Despairing, the Carthaginians sued for peace, but Regulus's proposed terms were so harsh the Carthaginians de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suing For Peace
Suing for peace is an act by a warring party to initiate a peace process. Rationales "Suing for", in this older sense of the phrase, means "pleading or petitioning for". Suing for peace is usually initiated by the losing party in an attempt to stave off an unconditional surrender. The nation holding the upper hand may find, in the losing party's offer of making peace, an opportunity for relief from the necessity of having to continue to wage a costly war. Pressing for peace may sometimes, however, be started by the winning faction as a means to end the war for several reasons, such as if additional conflict would not be in the perceived best interest of the winning party. In that case, demands might be made, or both nations may agree to a "white peace", which is a return to the status quo ante bellum (the prewar situation). Examples The First Sino-Japanese War (1 August 1894 – 17 April 1895) was fought between the Qing Dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan, primarily over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largest Naval Battle In History
The "largest naval battle in history" is a disputed title between adherents of varying criteria which include the numbers of personnel and/or vessels involved in the naval battle, the total displacement of the vessels involved and sometimes the significance and/or implications of the battle. While battles fought in modern times are comparatively well-documented, the figures from those in pre-Renaissance era are generally believed by contemporary chroniclers to be exaggerated. Helmut Pemsel's evaluation In 1975, the Austrian historian Helmut Pemsel attempted to evaluate naval battles in history by a scoring system. He assigned a score to each of four aspects of a battle as follows: * Numbers involved (1–4) * Strategic significance (0–2) * Tactical execution (0–2) * Political significance (0–1) According to him, the largest naval battle ever is the Battle of Leyte Gulf, scoring 8 of a possible 9 points total, while six others tied for second at 7 points each: Salamis, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cape Ecnomus
The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos ( grc, Ἔκνομος) was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War (264–241 BC). It was the largest battle of the war and one of the largest naval battles in history. The Carthaginian fleet was commanded by Hanno and Hamilcar; the Roman fleet jointly by the consuls for the year, Marcus Atilius Regulus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. It resulted in a clear victory for the Romans. The Roman fleet of 330 warships plus an unknown number of transports had sailed from Ostia, the port of Rome, and had embarked approximately 26,000 picked legionaries shortly before the battle. They planned to cross to Africa and invade the Carthaginian homeland, in what is now Tunisia. The Carthaginians were aware of the Romans' intentions and mustered all available warships, 350, off the south coast of Sicily to intercept them. With a combined total of about 680 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Navy
The naval forces of the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman state ( la, Classis, lit=fleet) were instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean Basin, but it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions. Throughout their history, the Romans remained a primarily land-based people and relied partially on their more nautically inclined subjects, such as the Greeks and the Egyptians, to build their ships. Because of that, the navy was never completely embraced by the Roman state, and deemed somewhat "un-Roman". In antiquity, navies and trading fleets did not have the logistical autonomy that modern ships and fleets possess, and unlike modern naval forces, the Roman navy even at its height never existed as an autonomous service but operated as an adjunct to the Roman army. During the course of the First Punic War, the Roman navy was massively expanded and played a vital role in the Roman victory and the Roman Republic's eventual ascension to hegemony in the Mediterranean Sea. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Agrigentum
The Battle of Agrigentum (Sicily, 262 BC) was the first pitched battle of the First Punic War and the first large-scale military confrontation between Carthage and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought after a long siege which started in 262 BC and resulted both in a Roman victory and the beginning of Roman control of Sicily. The city Agrigentum is a city on the island of Sicily, from the southern coast. It is on a plateau, surrounded by steep slopes on all sides except the west. The city was protected by the Hypsas River (Drago) to the west and the Akragas River to the east. The natural barriers meant the only way to attack the city was from the west, making the city easily defensible. The city commanded a main route along the southern coast and also routes leading northwards and eastwards to other cities. The major status of Agrigentum meant that it was a target for invading forces, and in 262 BC the Romans attacked the city to prevent the Carthaginians from holding it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)