Duisburg Hauptbahnhof on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Duisburg Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the city of Duisburg in western Germany. It is situated at the meeting point of many important national and international railway lines in the Northwestern Ruhr valley.


 Trams and buses call at the northern concourse (not connected to the main hall). There is another bus station at the eastern end of the main concourse, but not all lines serving the station call there. Taxis are available at both ends of the main concourse. The station is directly connected to the motorway A59, which runs under the plaza in front of the main entrance. Long-distance coaches depart from a small bus station at the city end of the station (behind the taxi ranks, to the left).
Trams and buses call at the northern concourse (not connected to the main hall). There is another bus station at the eastern end of the main concourse, but not all lines serving the station call there. Taxis are available at both ends of the main concourse. The station is directly connected to the motorway A59, which runs under the plaza in front of the main entrance. Long-distance coaches depart from a small bus station at the city end of the station (behind the taxi ranks, to the left).
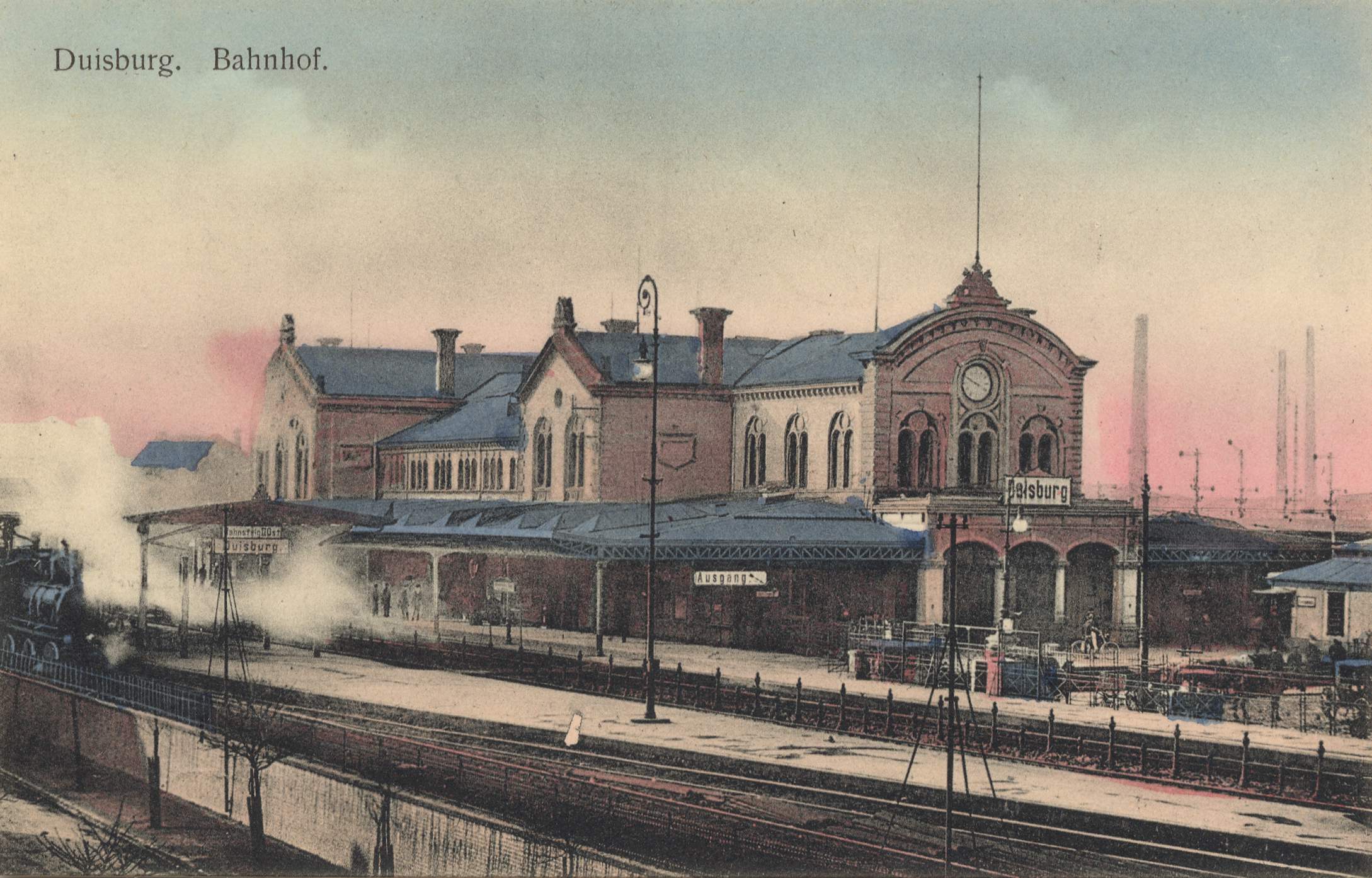

 On 12 December 2008 Deutsche Bahn and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia announced that much-needed renovation work would begin in mid of 2009. The total cost was estimated at €60 million. The first phase includes the renovation of the lobby and the underpass. Among other things, the false ceilings would be removed and the building returned to its original state. Renovation work on the monumental facade is planned. The cost for the first phase is estimated at €10.1 million.
On 24 July 2009, the first phase of renovation work began and the major renovations in the entrance hall were completed on 22 December 2009. From January 2010 work started on the renovation of the pedestrian tunnel. In a second, much more expensive construction phase, the railway platforms, railway tracks and the dilapidated roof were due to be rehabilitated in 2011. However work on the roof and platforms only commenced in August 2022, with the first two platforms to be completed during 2023
On 12 December 2008 Deutsche Bahn and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia announced that much-needed renovation work would begin in mid of 2009. The total cost was estimated at €60 million. The first phase includes the renovation of the lobby and the underpass. Among other things, the false ceilings would be removed and the building returned to its original state. Renovation work on the monumental facade is planned. The cost for the first phase is estimated at €10.1 million.
On 24 July 2009, the first phase of renovation work began and the major renovations in the entrance hall were completed on 22 December 2009. From January 2010 work started on the renovation of the pedestrian tunnel. In a second, much more expensive construction phase, the railway platforms, railway tracks and the dilapidated roof were due to be rehabilitated in 2011. However work on the roof and platforms only commenced in August 2022, with the first two platforms to be completed during 2023
Timetables for Duisburg Hbf station
/ref>
Lines
The station is situated at the northern end of the relatively straight Duisburg to Düsseldorf railway line which has to cope with one of the highest daily loads in continental Europe. This line is slated to be widened to six tracks in the near future. Currently it has four—and in some places five—tracks. The line to Krefeld and Mönchengladbach runs to the south. This crosses theRiver Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sourc ...
and then splits into the main line and a branch to Moers and Xanten at Rheinhausen. North of the station, seven tracks run to the River Ruhr crossing (which is a sight on the ''Route der Industriekultur
The Industrial Heritage Trail (german: Route der Industriekultur) links tourist attractions related to the industrial heritage in the Ruhr area in Germany. It is a part of the European Route of Industrial Heritage. The series of routes were devel ...
'' (Route of industrial heritage) due to a maze of girder bridges) where a three track line split for Oberhausen
Oberhausen (, ) is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen ( ). The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Rout ...
and on to Arnhem and the other line runs to Dortmund
Dortmund (; Westphalian nds, Düörpm ; la, Tremonia) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the eighth-largest city of Germany, with a population of 588,250 inhabitants as of 2021. It is the la ...
via Gelsenkirchen
Gelsenkirchen (, , ; wep, Gelsenkiärken) is the 25th most populous city of Germany and the 11th most populous in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia with 262,528 (2016) inhabitants. On the Emscher River (a tributary of the Rhine), it lies ...
. The four-tracked main line turns east and runs via Essen
Essen (; Latin: ''Assindia'') is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and D ...
and Bochum
Bochum ( , also , ; wep, Baukem) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia. With a population of 364,920 (2016), is the sixth largest city (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund, Essen and Duisburg) of the most populous Germany, German federal state o ...
to Dortmund
Dortmund (; Westphalian nds, Düörpm ; la, Tremonia) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the eighth-largest city of Germany, with a population of 588,250 inhabitants as of 2021. It is the la ...
.
Operational usage


Railway
The station is an important hub forInterCityExpress
The Intercity Express (commonly known as ICE ()) is a system of high-speed trains predominantly running in Germany. It also serves some destinations in Austria, Denmark (ceased in 2017 but planned to resume in 2022), France, Belgium, Switzerla ...
, InterCity and EuroCity
EuroCity, abbreviated as EC, is a cross-border train category within the European inter-city rail network. In contrast to trains allocated to the lower-level "IC" (InterCity) category, EC trains are international services that meet 20 criteri ...
trains from and to the Netherlands, Berlin, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Munich, Frankfurt and Cologne. It also is an important connection point for RegionalExpress
In Germany, Luxembourg and Austria, the Regional-Express (RE, or in Austria: REX) is a type of regional train. It is similar to a semi-fast train, with average speed at about 70–90 km/h (top speed often 160 km/h) as it calls at f ...
and RegionalBahn lines and has two S-Bahn lines of the Rhein-Ruhr S-Bahn calling at the station. A nearby Stadtbahn station offers local connections as well as trams to Mülheim an der Ruhr
Mülheim, officially Mülheim an der Ruhr () and also described as ''"City on the River"'', is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It is located in the Ruhr Area between Duisburg, Essen, Oberhausen and Ratingen. It is home to many compan ...
and Düsseldorf.
Local travel
 Trams and buses call at the northern concourse (not connected to the main hall). There is another bus station at the eastern end of the main concourse, but not all lines serving the station call there. Taxis are available at both ends of the main concourse. The station is directly connected to the motorway A59, which runs under the plaza in front of the main entrance. Long-distance coaches depart from a small bus station at the city end of the station (behind the taxi ranks, to the left).
Trams and buses call at the northern concourse (not connected to the main hall). There is another bus station at the eastern end of the main concourse, but not all lines serving the station call there. Taxis are available at both ends of the main concourse. The station is directly connected to the motorway A59, which runs under the plaza in front of the main entrance. Long-distance coaches depart from a small bus station at the city end of the station (behind the taxi ranks, to the left).
Architecture
The current station building dates from the 1930s and was modelled after the station in Königsberg. After WW2 it was extensively rebuilt and many features (such as murals in the main concourse) were lost. Its 6 platforms are covered by a train shed at their southern ends and modern canopies to the north where there is a second concourse housing the bus and tram stops. The station today has a rather drab feeling with the train shed in need of repair as there are quite a number of holes in the roof. Work to replace the roof and platforms commenced in August 2022, starting with tracks 12 and 13. This work is expected to take several yearsAmenities
As is usual with station of its size, Duisburg Hbf has a number of shops on its concourse and in the main hall. These include a book shop, a barber shop, several telecommunication accessories dealers, 2 bars, a small gambling arcade and several bakers and fast food stalls. The booking hall is located in the main hall (city exit), and lockers are provided at the beginning of the concourse to the right, next to the toilets. In the station building outside the concourse there is a hotel and local newspaper offices, and there used to be a fairly large night club which closed in early 2006 and has remained empty since.History


Former private railways
Duisburg station was opened in Duisburg on 9 February 1846 by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (''Cöln-Mindener Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', CME) along with the second section of its trunk line from Cologne-Deutz toMinden
Minden () is a middle-sized town in the very north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, the greatest town between Bielefeld and Hanover. It is the capital of the district (''Kreis'') of Minden-Lübbecke, which is part of the region of Detm ...
. On 15 May 1847 the line was extended to Hamm
Hamm (, Latin: ''Hammona'') is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northeastern part of the Ruhr area. As of 2016 its population was 179,397. The city is situated between the A1 motorway and A2 motorway. Hamm railwa ...
and Duisburg station became a through station on the line from Düsseldorf to Oberhausen
Oberhausen (, ) is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen ( ). The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Rout ...
.
Fifteen years later, in 1862, the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (''Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', BME), opened its east–west route through the Ruhr region from Dortmund
Dortmund (; Westphalian nds, Düörpm ; la, Tremonia) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the eighth-largest city of Germany, with a population of 588,250 inhabitants as of 2021. It is the la ...
and Witten to Duisburg. Its station was built close to the existing station, but it was a terminal station that was approached only from the northeast, not a through station.
Finally, on 15 February 1870, a three kilometre long branch line was opened by the Rhenish Railway Company (''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RHE) from the Rheinhausen–Hochfeld train ferry to Duisburg, which became the starting point of its new route to Quakenbrück, completed in 1879. It built a through station next to other stations in Duisburg.
Prussian state railways
The station buildings of the three railway companies survived until after their nationalisation when they became part of the Prussian state railways. In the 1880s the three stations were demolished and a joint station building was built on an island between the platforms of the various lines. The entrance to this building was to the north on Mülheimer Straße, which the lines crossed at that time over level crossings. It was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that all tracks had been raised above street level.Deutsche Reichsbahn
At the beginning of the 1930s, the station, which had been taken over by Deutsche Reichsbahn in 1920 when it absorbed the Prussian State Railway, was extended and rebuilt to its present size. The buildings have since been replaced. The still-existing entrance building of the station at Portsmouthplatz was built from 1931 to 1934 under the direction of the government architect Johannes Ziertmann (an architect at therailway division
In Germany and Austria, the running of railway services for a railway administration or the regional network of a large railway company was devolved to railway divisions, variously known as ''Eisenbahndirektionen (ED), Bundesbahndirektionen (BD)'' ...
of Essen) and was considered one of the most modern station buildings of its time. It is comparable with the entrance buildings in Düsseldorf, Königsberg (Pr.) and Oberhausen, built in the same period. The two sculptures at the front of a steel frame structure built for the ticket hall are by the Essen sculptor Joseph Enseling. The platform canopies were built with Vierendeel trusses
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assembla ...
and are structurally similar to the canopies at Düsseldorf Hauptbahnhof, which were scrapped in the 1980s, and follow the conceptually similar canopies of Darmstadt Hauptbahnhof built before the First World War. The Duisburg platform canopies were the first all-welded steel construction of this size.
During the Second World War the station was heavily damaged in a heavy bombing attack on Duisburg by allied forces.
Deutsche Bundesbahn
The station has been rebuilt several times since the war. In 1992, as part of the inauguration of theDuisburg Stadtbahn
The Duisburg Stadtbahn is a light rail (german: Stadtbahn) network forming part of the larger Rhine-Ruhr Stadtbahn system. It is the centrepiece of the public transport system in Duisburg, a city in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, ...
(light rail), the new northern connecting hall (''Verknüpfungshalle'') was opened, all six platforms were lengthened to several hundred metres over the former road underpass connecting Mühlheimerstraße and Königstraße and provided with simple platform roofs, which are easily distinguished from the old station hall.
Deutsche Bahn
 On 12 December 2008 Deutsche Bahn and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia announced that much-needed renovation work would begin in mid of 2009. The total cost was estimated at €60 million. The first phase includes the renovation of the lobby and the underpass. Among other things, the false ceilings would be removed and the building returned to its original state. Renovation work on the monumental facade is planned. The cost for the first phase is estimated at €10.1 million.
On 24 July 2009, the first phase of renovation work began and the major renovations in the entrance hall were completed on 22 December 2009. From January 2010 work started on the renovation of the pedestrian tunnel. In a second, much more expensive construction phase, the railway platforms, railway tracks and the dilapidated roof were due to be rehabilitated in 2011. However work on the roof and platforms only commenced in August 2022, with the first two platforms to be completed during 2023
On 12 December 2008 Deutsche Bahn and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia announced that much-needed renovation work would begin in mid of 2009. The total cost was estimated at €60 million. The first phase includes the renovation of the lobby and the underpass. Among other things, the false ceilings would be removed and the building returned to its original state. Renovation work on the monumental facade is planned. The cost for the first phase is estimated at €10.1 million.
On 24 July 2009, the first phase of renovation work began and the major renovations in the entrance hall were completed on 22 December 2009. From January 2010 work started on the renovation of the pedestrian tunnel. In a second, much more expensive construction phase, the railway platforms, railway tracks and the dilapidated roof were due to be rehabilitated in 2011. However work on the roof and platforms only commenced in August 2022, with the first two platforms to be completed during 2023
Train services
The station is served by the following services:/ref>
Long distance
Regional
*Regional services NRW-Express ''Aachen - Cologne - Düsseldorf - Duisburg - Essen - Dortmund - Hamm'' *Regional services Rhein-Haard-Express ''Münster - Dülmen - Recklinghausen - Essen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf'' *Regional servicesRhein-Emscher-Express
The Rhein-Emscher-Express (RE 3) is a Regional-Express service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW), running from Düsseldorf via Duisburg, Gelsenkirchen and Dortmund to Hamm. It connects with the rest of the regional rail networ ...
''Hamm - Dortmund - Gelsenkirchen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf''
*Regional services Rhein-Express ''Wesel - Oberhausen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf - Cologne - Bonn - Koblenz''
*Regional services Rhein-Weser-Express ''Minden - Bielefeld - Hamm - Dortmund - Essen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf - Neuss - Cologne - Cologne/Bonn Airport''
*Regional services Rhein-Hellweg-Express ''Kassel - Paderborn - Hamm - Dortmund - Essen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf''
*Regional services Rhein-IJssel-Express ''Arnhem - Emmerich - Wesel - Oberhausen - Duisburg - Düsseldorf''
*Regional services Niers-Haard-Express ''Münster - Dülmen - Recklinghausen - Essen - Duisburg - Krefeld - Mönchengladbach''
*Regional services Fossa-Emscher-Express: ''Moers – Rheinhausen – Duisburg – Oberhausen – Bottrop''
*Local services Niederrheinstrecke ''Xanten – Moers – Duisburg''
*Local services Rhein-Emscher-Bahn ''Dortmund - Gelsenkirchen - Wanne-Eickel - Duisburg''
*Local services Rhein-Niers-Bahn ''Essen – Duisburg - Krefeld - Mönchengladbach - Aachen''
*Local services Emscher-Niederrhein-Bahn
The Emscher-Niederrhein-Bahn (RB 35) is a Regionalbahn service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It runs hourly between Gelsenkirchen and Duisburg with Mönchengladbach. Its name refers to the Emscher river (which runs near Dui ...
''Gelsenkirchen - Oberhausen - Duisburg - Krefeld - Mönchengladbach''
*Rhein-Ruhr S-Bahn services ''Solingen - Düsseldorf - Duisburg - Essen - Dortmund''
Notes
External links
* * * * * * {{Authority control Railway stations in North Rhine-Westphalia S1 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn) S2 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn) Buildings and structures in Duisburg Transport in Duisburg Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn stations Railway stations in Germany opened in 1846 1846 establishments in Prussia