De Architectura on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 (''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on
(''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on
 Vitruvius sought to address the ethos of architecture, declaring that quality depends on the social relevance of the artist's work, not on the form or workmanship of the work itself. Perhaps the most famous declaration from is one still quoted by architects: "Well building hath three conditions: firmness, commodity, and delight". This quote is taken from Sir Henry Wotton's version of 1624, and accurately translates the passage in the work
Vitruvius sought to address the ethos of architecture, declaring that quality depends on the social relevance of the artist's work, not on the form or workmanship of the work itself. Perhaps the most famous declaration from is one still quoted by architects: "Well building hath three conditions: firmness, commodity, and delight". This quote is taken from Sir Henry Wotton's version of 1624, and accurately translates the passage in the work
(I.iii.2)
but English has changed since then, especially in regard to the word "

 is important for its descriptions of many different machines used for engineering structures, such as hoists,
is important for its descriptions of many different machines used for engineering structures, such as hoists,
 He advised that
He advised that
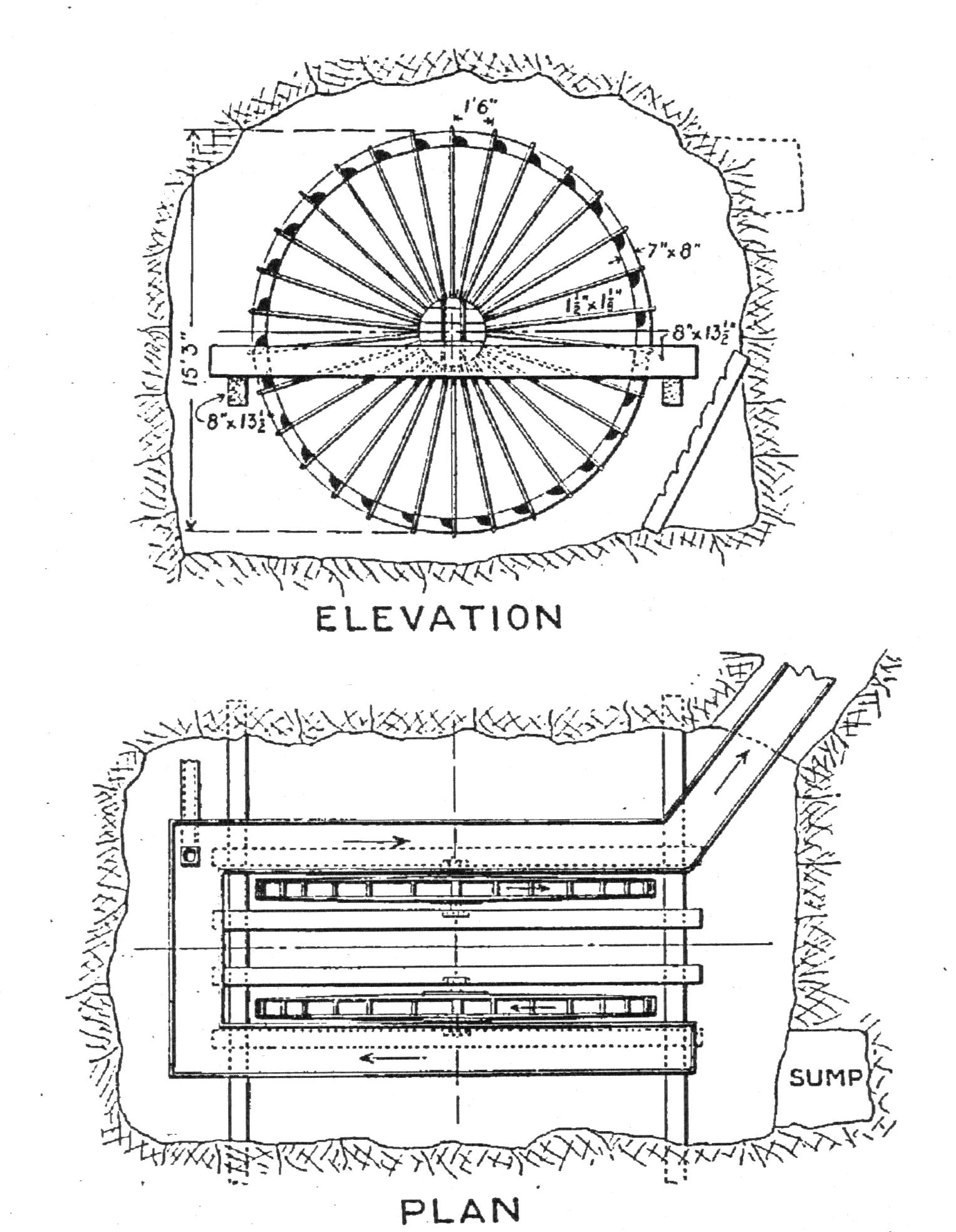
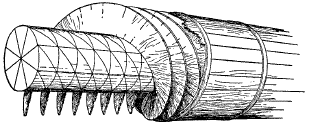
 Vitruvius described the construction of the Archimedes' screw in Chapter 10, although did not mention Archimedes by name. It was a device widely used for raising water to irrigate fields and dewater mines. Other lifting machines mentioned in include the endless chain of buckets and the reverse overshot water-wheel. Remains of the water wheels used for lifting water have been discovered in old mines such as those at Rio Tinto in Spain and Dolaucothi in west Wales. One of the wheels from Rio Tinto is now in the
Vitruvius described the construction of the Archimedes' screw in Chapter 10, although did not mention Archimedes by name. It was a device widely used for raising water to irrigate fields and dewater mines. Other lifting machines mentioned in include the endless chain of buckets and the reverse overshot water-wheel. Remains of the water wheels used for lifting water have been discovered in old mines such as those at Rio Tinto in Spain and Dolaucothi in west Wales. One of the wheels from Rio Tinto is now in the
 Vitruvius outlined the many innovations made in building design to improve the living conditions of the inhabitants. Foremost among them is the development of the
Vitruvius outlined the many innovations made in building design to improve the living conditions of the inhabitants. Foremost among them is the development of the
 Vitruvius's work was "rediscovered" in 1414 by the Florentine humanist
Vitruvius's work was "rediscovered" in 1414 by the Florentine humanist
 The rediscovery of Vitruvius's work had a profound influence on architects of the
The rediscovery of Vitruvius's work had a profound influence on architects of the
 The earliest evidence of use of the stereographic projection in a machine is in , which describes an anaphoric clock (it is presumed, a or
The earliest evidence of use of the stereographic projection in a machine is in , which describes an anaphoric clock (it is presumed, a or
The ''Ten Books of Architecture'' online: cross-linked Latin text and English translation
* (Morris Hicky Morgan translation with illustrations) *
Modern bibliography on line (15th-17th centuries)
* Vitruvii, M
Naples, c. 1480. A
Somni
{{Authority control Ancient Roman architecture Architectural treatises Latin prose texts Construction Military engineering Civil engineering Ancient Roman military technology Ancient Roman siege warfare Roman siege engines Latin military books 1st-century BC Latin books de:Vitruv#Werk

 (''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on
(''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
written by the Roman architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It contains a variety of information on Greek and Roman buildings, as well as prescriptions for the planning and design of military camps, cities, and structures both large (aqueducts, buildings, baths, harbours) and small (machines, measuring devices, instruments). Since Vitruvius published before the development of cross vaulting, domes, concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most ...
, and other innovations associated with Imperial Roman architecture, his ten books give no information on these hallmarks of Roman building design and technology.
Origin and contents
Probably written between 30-20 BCE, it combines the knowledge and views of many antique writers, Greek and Roman, on architecture, the arts, natural history and building technology. Vitruvius cites many authorities throughout the text, often praising Greek architects for their development of temple building and the orders ( Doric, Ionic and Corinthian), and providing key accounts of the origins of building in the primitive hut. Though often cited for his famous "triad" of characteristics associated with architecture – utilitas, firmitas and venustas (utility, strength and beauty) – the aesthetic principles that influenced later treatise writers were outlined in Book III. Derived partially from Latin rhetoric (through Cicero and Varro), Vitruvian terms for order, arrangement, proportion, and fitness for intended purposes have guided architects for centuries, and continue to do so. The Roman author gives advice on the qualifications of an architect (Book I) and on types of architectural drawing. The ten books or scrolls are organized as follows: – '' Ten Books on Architecture'' Roman architects were skilled in engineering, art, and craftsmanship combined. Vitruvius was very much of this type, a fact reflected in . He covered a wide variety of subjects he saw as touching on architecture. This included many aspects that may seem irrelevant to modern eyes, ranging from mathematics to astronomy, meteorology, and medicine. In the Roman conception, architecture needed to take into account everything touching on the physical and intellectual life of man and his surroundings. Vitruvius, thus, deals with many theoretical issues concerning architecture. For instance, in Book of , he advises architects working with bricks to familiarise themselves with pre-Socratic theories of matter so as to understand how their materials will behave. Book relates the abstractgeometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
of Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institutio ...
to the everyday work of the surveyor. Astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
is cited for its insights into the organisation of human life, while astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
is required for the understanding of sundial
A sundial is a horological device that tells the time of day (referred to as civil time in modern usage) when direct sunlight shines by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a fl ...
s. Likewise, Vitruvius cites Ctesibius of Alexandria and Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scienti ...
for their inventions, Aristoxenus
Aristoxenus of Tarentum ( el, Ἀριστόξενος ὁ Ταραντῖνος; born 375, fl. 335 BC) was a Greek Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have bee ...
(Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
's apprentice) for music, Agatharchus for theatre, and Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
for architecture.
Buildings
 Vitruvius sought to address the ethos of architecture, declaring that quality depends on the social relevance of the artist's work, not on the form or workmanship of the work itself. Perhaps the most famous declaration from is one still quoted by architects: "Well building hath three conditions: firmness, commodity, and delight". This quote is taken from Sir Henry Wotton's version of 1624, and accurately translates the passage in the work
Vitruvius sought to address the ethos of architecture, declaring that quality depends on the social relevance of the artist's work, not on the form or workmanship of the work itself. Perhaps the most famous declaration from is one still quoted by architects: "Well building hath three conditions: firmness, commodity, and delight". This quote is taken from Sir Henry Wotton's version of 1624, and accurately translates the passage in the work(I.iii.2)
but English has changed since then, especially in regard to the word "
commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
", and the tag may be misunderstood. In modern English it would read: "The ideal building has three elements; it is sturdy, useful, and beautiful."
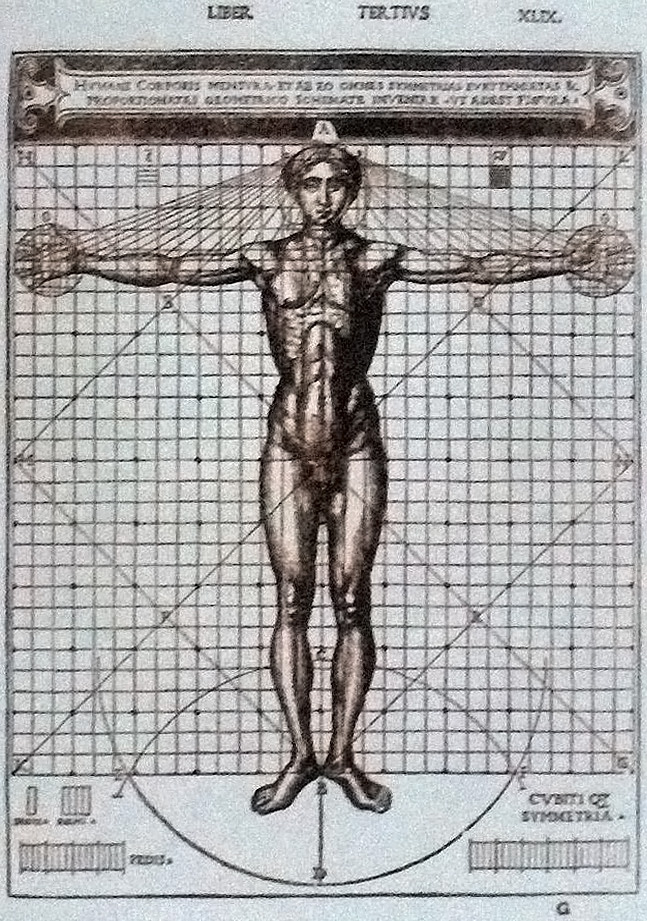
Vitruvius also studied human proportions (Book ) and this part of his ''canones'' were later adopted and adapted in the famous drawing (" Vitruvian Man") by Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
.
Domestic architecture
While Vitruvius is fulsome in his descriptions of religious buildings, infrastructure and machinery, he gives a mixed message on domestic architecture. Similar to Aristotle, Vitruvius offers admiration for householders who built their own homes without the involvement of an architect. His ambivalence on domestic architecture is most clearly read in the opening paragraph of the Introduction to Book 6. Book 6 focusses exclusively on residential architecture but as architectural theorist Simon Weir has explained, instead of writing the introduction on the virtues of residences or the family or some theme related directly to domestic life; Vitruvius writes an anecdote about the Greek ethical principle of xenia: showing kindness to strangers.Roman technology

 is important for its descriptions of many different machines used for engineering structures, such as hoists,
is important for its descriptions of many different machines used for engineering structures, such as hoists, crane
Crane or cranes may refer to:
Common meanings
* Crane (bird), a large, long-necked bird
* Crane (machine), industrial machinery for lifting
** Crane (rail), a crane suited for use on railroads
People and fictional characters
* Crane (surname) ...
s, and pulleys, as well as war machines such as catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of store ...
s, ballistae, and siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
s. Vitruvius also described the construction of sundials and water clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time- ...
s, and the use of an aeolipile (the first steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be ...
) as an experiment to demonstrate the nature of atmospheric air movements (wind).
Aqueducts and mills
Books , , and of form the basis of much of what is known about Roman technology, now augmented by archaeological studies of extant remains, such as the Pont du Gard in southern France. Numerous such massive structures occur across the former empire, a testament to the power ofRoman engineering
The ancient Romans were famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology inconceivable in Greece. The architecture ...
. Vitruvius's description of Roman aqueduct construction is short, but mentions key details especially for the way they were surveyed, and the careful choice of materials needed.
His book would have been of assistance to Frontinus, a general who was appointed in the late 1st century AD to administer the many aqueducts of Rome. Frontinus wrote , the definitive treatise on 1st-century Roman aqueducts, and discovered a discrepancy between the intake and supply of water caused by illegal pipes inserted into the channels to divert the water. The Roman Empire went far in exploiting water power, as the set of no fewer than 16 water mill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the productio ...
s at Barbegal in France demonstrates. The mills ground grain in a very efficient operation, and many other mills are now known, such as the much later Hierapolis sawmill.
Materials
Vitruvius described many different construction materials used for a wide variety of different structures, as well as such details asstucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
painting. Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel (aggregate) together. Cement m ...
, concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most ...
, and lime received in-depth descriptions, the longevity of many Roman structures being mute testimony to their skill in building materials and design.
 He advised that
He advised that lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
should not be used to conduct drinking water, clay pipes being preferred. He comes to this conclusion in Book of after empirical observation of the apparent laborer illnesses in the (lead pipe) foundries of his time. However, much of the water used by Rome and many other cities was very hard, minerals soon coated the inner surfaces of the pipes, so lead poisoning
Lead poisoning, also known as plumbism and saturnism, is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, inferti ...
was reduced.
Vitruvius related the famous story about Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scienti ...
and his detection of adulterated gold in a royal crown. When Archimedes realized the volume of the crown could be measured exactly by the displacement created in a bath of water, he ran into the street with the cry of " Eureka!", and the discovery enabled him to compare the density of the crown with pure gold. He showed the crown had been alloyed with silver, and the king was defrauded.
Dewatering machines

 Vitruvius described the construction of the Archimedes' screw in Chapter 10, although did not mention Archimedes by name. It was a device widely used for raising water to irrigate fields and dewater mines. Other lifting machines mentioned in include the endless chain of buckets and the reverse overshot water-wheel. Remains of the water wheels used for lifting water have been discovered in old mines such as those at Rio Tinto in Spain and Dolaucothi in west Wales. One of the wheels from Rio Tinto is now in the
Vitruvius described the construction of the Archimedes' screw in Chapter 10, although did not mention Archimedes by name. It was a device widely used for raising water to irrigate fields and dewater mines. Other lifting machines mentioned in include the endless chain of buckets and the reverse overshot water-wheel. Remains of the water wheels used for lifting water have been discovered in old mines such as those at Rio Tinto in Spain and Dolaucothi in west Wales. One of the wheels from Rio Tinto is now in the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
, and one from the latter in the National Museum of Wales. The remains were discovered when these mines were reopened in modern mining attempts. They would have been used in a vertical sequence, with 16 such mills capable of raising water at least above the water table. Each wheel would have been worked by a miner treading the device at the top of the wheel, by using cleats on the outer edge. That they were using such devices in mines clearly implies that they were entirely capable of using them as water wheels to develop power for a range of activities, not just for grinding wheat, but also probably for sawing timber, crushing ores, fulling
Fulling, also known as felting, tucking or walking (Scots: ''waukin'', hence often spelled waulking in Scottish English), is a step in woollen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of woven or knitted cloth (particularly wool) to elimin ...
, and so on.
Force pump
Ctesibius is credited with the invention of the force pump, which Vitruvius described as being built from bronze with valves to allow a head of water to be formed above the machine. The device is also described byHero of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἥρων ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς, ''Heron ho Alexandreus'', also known as Heron of Alexandria ; 60 AD) was a Greek mathematician and engineer who was active in his native city of Alexandria, Roman Egypt. He ...
in his . The machine is operated by hand in moving a lever up and down. He mentioned its use for supplying fountains above a reservoir, although a more mundane use might be as a simple fire engine. One was found at Calleva Atrebatum (Roman Silchester
Calleva Atrebatum ("Calleva of the Atrebates") was an Iron Age oppidum, the capital of the Atrebates tribe. It then became a walled town in the Roman province of Britannia, at a major crossroads of the roads of southern Britain.
The modern vill ...
) in England, and another is on display at the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
. Their functions are not described, but they are both made in bronze, just as Vitruvius specified.
Vitruvius also mentioned the several automaton
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton – Definition and More ...
s Ctesibius invented, and intended for amusement and pleasure rather than serving a useful function.
Central heating
 Vitruvius outlined the many innovations made in building design to improve the living conditions of the inhabitants. Foremost among them is the development of the
Vitruvius outlined the many innovations made in building design to improve the living conditions of the inhabitants. Foremost among them is the development of the hypocaust
A hypocaust ( la, hypocaustum) is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm th ...
, a type of central heating
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. It is a component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (short: HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
...
where hot air developed by a fire was channelled under the floor and inside the walls of public baths and villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
s. He gave explicit instructions on how to design such buildings so fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
is maximized; for example, the is next to the followed by the . He also advised using a type of regulator to control the heat in the hot rooms, a bronze disc set into the roof under a circular aperture, which could be raised or lowered by a pulley to adjust the ventilation. Although he did not suggest it himself, his dewatering devices such as the reverse overshot water-wheel likely were used in the larger baths to lift water to header tanks at the top of the larger , such as the Baths of Diocletian and the Baths of Caracalla.
Surveying instruments
That Vitruvius must have been well practised in surveying is shown by his descriptions of surveying instruments, especially the water level or , which he compared favourably with the , a device using plumb lines. They were essential in all building operations, but especially in aqueduct construction, where a uniform gradient was important to provision of a regular supply of water without damage to the walls of the channel. He described the , in essence a device for automatically measuring distances along roads, a machine essential for developing accurate itineraries, such as the Peutinger Table.Sea level change
In Book Chapter 1 Subsection 4 of is a description of 13Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
cities in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, "the land of Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the ...
", in present-day Turkey. These cities are given as: Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
, Miletus, Myus, Priene
Priene ( grc, Πριήνη, Priēnē; tr, Prien) was an ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called the ...
, Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a sepa ...
, Teos, Colophon, Chius, Erythrae, Phocaea, Clazomenae, Lebedos
Lebedus or Lebedos ( grc, Λέβεδος) was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League, located south of Smyrna, Klazomenai and neighboring Teos and before Ephesus, which is further south. It was on the coast, ninety stadia (16.65 km) t ...
, Mytilene, and later a 14th, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
eans. Myus, the third city, is described as being "long ago engulfed by the water, and its sacred rites and suffrage". This sentence indicates, at the time of Vitruvius's writing, it was known that sea-level change and/or land subsidence occurred. The layout of these cities is in general from south to north so that it appears that where Myrus should be located is inland. If this is the case, then since the writing of , the region has experienced either soil rebound
Soil consolidation refers to the mechanical process by which soil changes volume gradually in response to a change in pressure. This happens because soil is a two-phase material, comprising soil grains and pore fluid, usually groundwater. When ...
or a sea-level fall. Though not indicative of sea-level change, or speculation of such, during the later-empire many Roman ports suffered from what contemporary writers described as 'silting'. The constant need to dredge ports became a heavy burden on the treasury and some have speculated that this expense significantly contributed to the eventual collapse of the empire. Roman salt works in Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
, England, today are located at the five-metre contour, implying this was the coastline. These observations only indicate the extent of silting and soil rebound affecting coastline change since the writing of .
Survival and rediscovery
Vitruvius's work is one of many examples of Latin texts that owe their survival to the palace ofCharlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
in the early 9th century. (This activity of finding and recopying classical manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced ...
s is part of what is called the Carolingian Renaissance.) Many of Vitruvius's surviving works derive from an extant manuscript rewritten there, British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the Briti ...
manuscript Harley 2767.
These texts were not just copied, but also known at the court of Charlemagne, since his historian, bishop Einhard, asked the visiting English churchman Alcuin for explanations of some technical terms. In addition, a number of individuals are known to have read the text or have been indirectly influenced by it, including: Vussin, Hrabanus Maurus
Rabanus Maurus Magnentius ( 780 – 4 February 856), also known as Hrabanus or Rhabanus, was a Frankish Benedictine monk, theologian, poet, encyclopedist and military writer who became archbishop of Mainz in East Francia. He was the author of t ...
, Hermann of Reichenau
Blessed Hermann of Reichenau (18 July 1013– 24 September 1054), also known by other names, was an 11th-century Benedictine monk and scholar. He composed works on history, music theory, mathematics, and astronomy, as well as many hymns. H ...
, Hugo of St. Victor
Hugh of Saint Victor ( 1096 – 11 February 1141), was a Saxon canon regular and a leading theologian and writer on mystical theology.
Life
As with many medieval figures, little is known about Hugh's early life. He was probably born in the 1090s. ...
, Gervase of Melkey, William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a ...
, Theoderich of St. Trond, Petrus Diaconus, Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus (c. 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop. Later canonised as a Catholic saint, he was known during his li ...
, Filippo Villani, Jean de Montreuil
Jean de Montreuil (1354, Monthureux-le-Sec – 29 May 1418, Paris) was a French scholar of the late 14th and early 15th century and a friend of Laurent de Premierfait.
Life
He was among the first to invoke Salic Law as a reasoning against female ...
, Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credite ...
, Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was some ...
, Giovanni de Dondi, Domenico di Bandino, Niccolò Acciaioli bequeathed copy to the Basilica of San Lorenzo, Florence, Bernward of Hildesheim, and St. Thomas Aquinas. In 1244 the Dominican friar Vincent of Beauvais
Vincent of Beauvais ( la, Vincentius Bellovacensis or ''Vincentius Burgundus''; c. 1264) was a Dominican friar at the Cistercian monastery of Royaumont Abbey, France. He is known mostly for his '' Speculum Maius'' (''Great mirror''), a major wor ...
made a large number of references to in his compendium of all the knowledge of the Middle Ages
Many copies of , dating from the 8th to the 15th centuries, did exist in manuscript form during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and 92 are still available in public collections, but they appear to have received little attention, possibly due to the obsolescence of many specialized Latin terms used by Vitruvius and the loss of most of the original 10 illustrations thought by some to be helpful in understanding parts of the text.
 Vitruvius's work was "rediscovered" in 1414 by the Florentine humanist
Vitruvius's work was "rediscovered" in 1414 by the Florentine humanist Poggio Bracciolini
Gian Francesco Poggio Bracciolini (11 February 1380 – 30 October 1459), usually referred to simply as Poggio Bracciolini, was an Italian scholar and an early Renaissance humanist. He was responsible for rediscovering and recovering many class ...
, who found it in the Abbey library of Saint Gall, Switzerland. He publicized the manuscript to a receptive audience of Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
thinkers, just as interest in the classical cultural and scientific heritage was reviving.
The first printed edition (), an version, was published by the Veronese scholar Fra Giovanni Sulpitius Giovanni Sulpizio da Veroli or Johannes Sulpitius Verulanus or Verolensis (fl. c. 1470 – 1490) was an Italian Renaissance humanist and rhetorician. Known to Erasmus, he was the author of a work on epistolary art, the proper composition and ornamen ...
in 1486 (with a second edition in 1495 or 1496), but none were illustrated. The Dominican friar Fra Giovanni Giocondo produced the first version illustrated with woodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only t ...
s in Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
in 1511. It had a thorough philosophical approach and superb illustrations.
Translations into Italian were in circulation by the 1520s, the first in print being the translation with new illustrations by Cesare Cesariano, a Milanese friend of the architect Bramante
Donato Bramante ( , , ; 1444 – 11 April 1514), born as Donato di Pascuccio d'Antonio and also known as Bramante Lazzari, was an Italian architect and painter. He introduced Renaissance architecture to Milan and the High Renaissance styl ...
, printed in Como
Como (, ; lmo, Còmm, label=Comasco , or ; lat, Novum Comum; rm, Com; french: Côme) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy. It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como.
Its proximity to Lake Como and to the Alps has m ...
in 1521. It was rapidly translated into other European languagesthe first French version was published in 1547and the first German version followed in 1548. The first Spanish translation was published in 1582 by Miguel de Urrea and Juan Gracian. The most authoritative and influential edition was publicized in French in 1673 by Claude Perrault, commissioned by Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the countr ...
in 1664.
John Shute had drawn on the text as early as 1563 for his book ''The First and Chief Grounds of Architecture''. Sir Henry Wotton's 1624 work ''The Elements of Architecture'' amounts to a heavily-influenced adaptation, while a 1692 translation was much abridged. English-speakers had to wait until 1771 for a full translation of the first five volumes and 1791 for the whole thing. Thanks to the art of printing, Vitruvius's work had become a popular subject of hermeneutics
Hermeneutics () is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of Biblical hermeneutics, biblical texts, wisdom literature, and Philosophy, philosophical texts. Hermeneutics is more than interpretative principles ...
, with highly detailed and interpretive illustrations, and became widely dispersed.
Impact
 The rediscovery of Vitruvius's work had a profound influence on architects of the
The rediscovery of Vitruvius's work had a profound influence on architects of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
, prompting the rebirth of Classical architecture in subsequent centuries. Renaissance architects, such as Niccoli, Brunelleschi and Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. ...
, found in their rationale for raising their branch of knowledge to a scientific discipline as well as emphasising the skills of the artisan
An artisan (from french: artisan, it, artigiano) is a skilled craft worker who makes or creates material objects partly or entirely by hand. These objects may be functional or strictly decorative, for example furniture, decorative art, ...
. One of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
's best known drawings, the '' Vitruvian Man'', is based on the principles of body proportions
While there is significant variation in anatomical proportions between people, certain body proportions have become canonical in figurative art. The study of body proportions, as part of the study of artistic anatomy, explores the relation of t ...
developed by Vitruvius in the first chapter of Book III, ''On Symmetry: In Temples And In The Human Body''.
The English architect Inigo Jones
Inigo Jones (; 15 July 1573 – 21 June 1652) was the first significant Architecture of England, architect in England and Wales in the Early modern Europe, early modern period, and the first to employ Vitruvius, Vitruvian rules of proportion an ...
and the Frenchman Salomon de Caus were among the first to re-evaluate and implement those disciplines that Vitruvius considered a necessary element of architecture: arts and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
s based upon number and proportion. The 16th-century architect Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of ...
considered Vitruvius his master and guide, and made some drawings based on his work before conceiving his own architectural precepts.
Astrolabe
 The earliest evidence of use of the stereographic projection in a machine is in , which describes an anaphoric clock (it is presumed, a or
The earliest evidence of use of the stereographic projection in a machine is in , which describes an anaphoric clock (it is presumed, a or water clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time- ...
) in Alexandria. The clock had a rotating field of stars behind a wire frame indicating the hours of the day. The wire framework (the spider) and the star locations were constructed using the stereographic projection. Similar constructions dated from the 1st to 3rd centuries have been found in Salzburg and northeastern France, so such mechanisms were, it is presumed, fairly widespread among Romans.
Editions
* Translated in 1914 as ''Ten Books on Architecture'' byMorris H. Morgan
Morris Hicky Morgan (February 8, 1859 in Providence, Rhode IslandMORGAN, Morris Hick ...
, Ph.D, LL.D. Late Professor of Classical Philology in Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
. The full text of this translation is available from the ''Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
'', see external links, and from the Internet Archive.
See also
* by Leon Battista Alberti * * * * *References
Further reading
*B. Baldwin: ''The Date, Identity, and Career of Vitruvius''. In: Latomus 49 (1990), 425-34 *I. Rowland, T.N. Howe: ''Vitruvius. Ten Books on Architecture''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1999,External links
The ''Ten Books of Architecture'' online: cross-linked Latin text and English translation
* (Morris Hicky Morgan translation with illustrations) *
Modern bibliography on line (15th-17th centuries)
* Vitruvii, M
Naples, c. 1480. A
Somni
{{Authority control Ancient Roman architecture Architectural treatises Latin prose texts Construction Military engineering Civil engineering Ancient Roman military technology Ancient Roman siege warfare Roman siege engines Latin military books 1st-century BC Latin books de:Vitruv#Werk