|
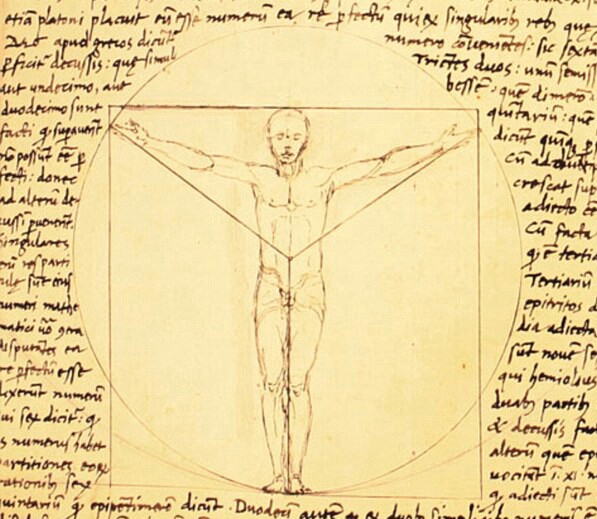
Vitruvian Man
The ''Vitruvian Man'' (; ) is a drawing by the Italian Renaissance artist and scientist Leonardo da Vinci, dated to . Inspired by the writings of the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius, the drawing depicts a nude man in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and inscribed in both a circle and square. It was described by the art historian Carmen C. Bambach as "justly ranked among the all-time iconic images of Western civilization". Although not the only known drawing of a man inspired by the writings of Vitruvius, the work is a unique synthesis of artistic and scientific ideals and often considered an archetypal representation of the High Renaissance. The drawing represents Leonardo's conception of ideal body proportions, originally derived from Vitruvius but influenced by his own measurements, the drawings of his contemporaries, and the '' De pictura'' treatise by Leon Battista Alberti. Leonardo produced the ''Vitruvian Man'' in Milan and the work was probably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is spoken by about 68 million people, including 64 million native speakers as of 2024. Italian is an official language in Languages of Italy, Italy, Languages of San Marino, San Marino, Languages of Switzerland, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), and Languages of Vatican City, Vatican City; it has official Minority language, minority status in Minority languages of Croatia, Croatia, Slovene Istria, Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the municipalities of Santa Teresa, Espírito Santo, Santa Tereza, Encantado, Rio Grande do Sul, Encantado, and Venda Nova do Imigrante in Languages of Brazil#Language co-officialization, Brazil. Italian is also spoken by large Italian diaspora, immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
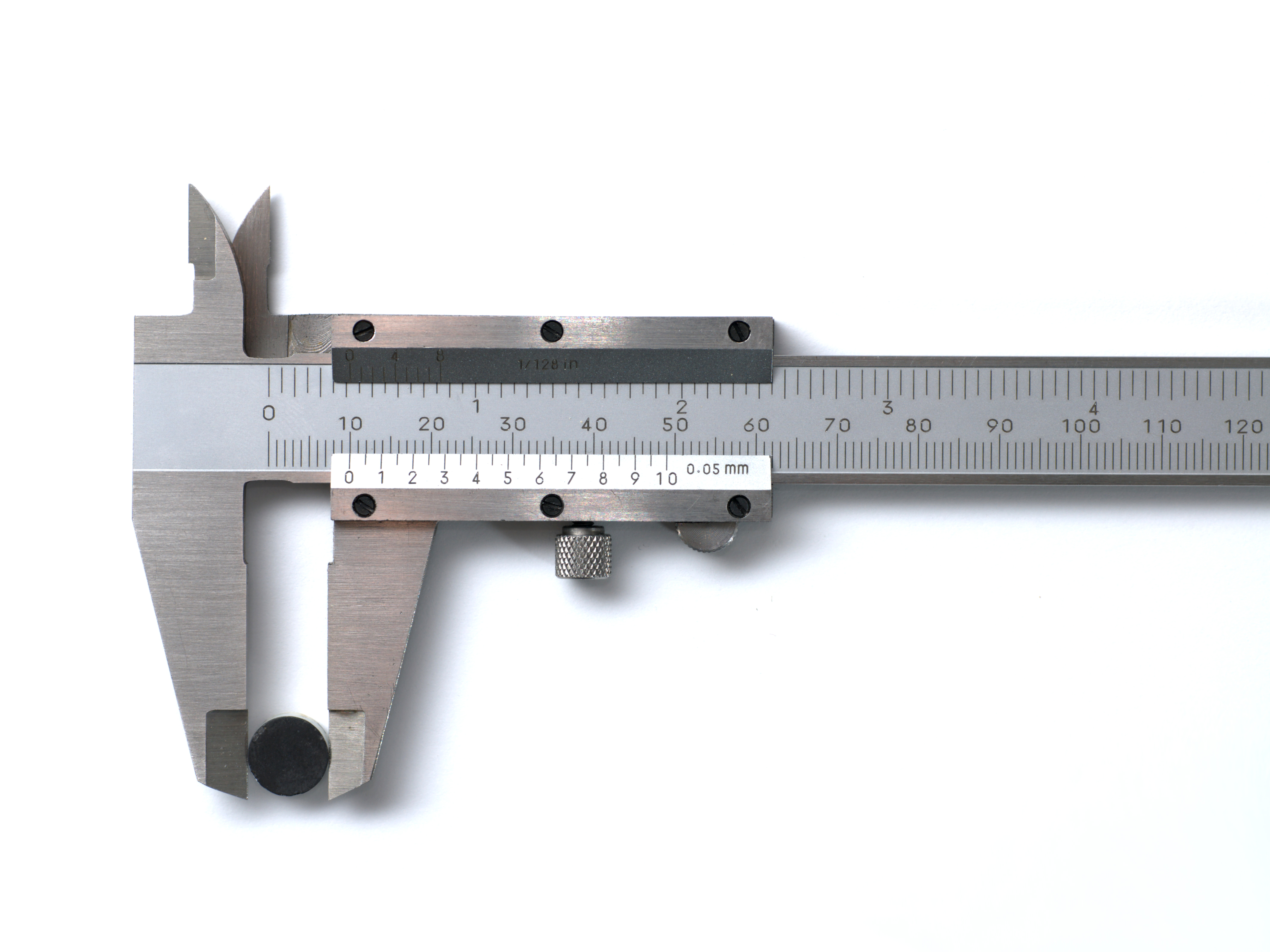
Calipers
Calipers or callipers are an instrument used to measure the linear dimensions of an object or hole; namely, the length, width, thickness, diameter or depth of an object or hole. The word "caliper" comes from a corrupt form of caliber. Many types of calipers permit reading out a measurement on a ruled scale, a dial, or an electronic digital display. A common association is to calipers using a sliding vernier scale. Some calipers can be as simple as a compass with inward or outward-facing points, but with no scale (measurement indication). The tips of the caliper are adjusted to fit across the points to be measured, and then kept at that span while moved to separate measuring device, such as a ruler. Calipers are used in many fields such as mechanical engineering, metalworking, forestry, woodworking, science and medicine. Terminology ''Caliper'' is the American spelling, while ''calliper'' (double "L") is the British spelling. A single tool might be referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
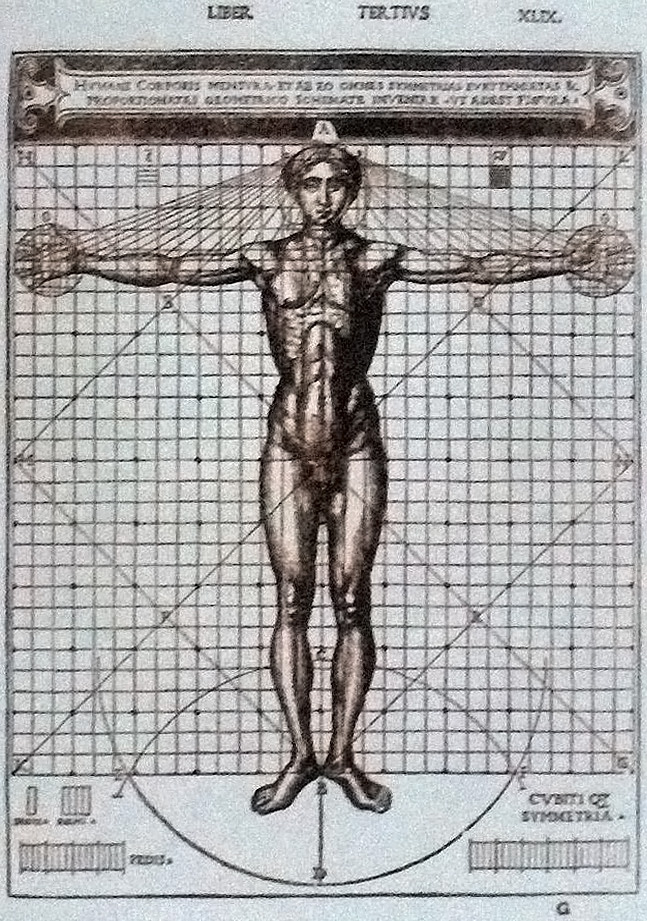
Cesare Cesariano
240px, The 1521 Italian edition of Vitruvius' , translated and illustrated by Cesare Cesariano. Cesare di Lorenzo Cesariano (December 10, 1475 – March 30, 1543) was an Italian painter, architect and architectural theorist. He authored the first Italian-language version of Vitruvius' . Biography Cesariano was born in Milan. Information about his life is scarce. In 1496 he lived for a period at Reggio Emilia; in the early 1500s he worked at Parma, where he painted the sacristy of San Giovanni Evangelista. In 1507 he was in Rome, where he met Perugino, Pinturicchio and Luca Signorelli. However, most of his activity was in Milan, where he returned in 1512-1513 as military engineer at Maximilian Sforza's court. He worked at Santa Maria presso San Celso and to part of the renovation of the Sforza Castle; he collaborated in the painting decoration of Milan Cathedral (Duomo), in the ''Sala dei Deputati'', which was demolished in the 19th century. Giorgio Vasari wrote in Bram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Architectura
(''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on architecture written by the Ancient Rome, Roman architect and military engineer Vitruvius, Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for Caesar Augustus#Building projects, building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It contains a variety of information on Greek and Roman buildings, as well as prescriptions for the planning and design of military camps, cities, and structures both large (aqueducts, buildings, baths, harbours) and small (machines, measuring devices, instruments). Since Vitruvius wrote early in the Roman architectural revolution that saw the full development of cross vaulting, domes, Roman concrete, concrete, and other innovations associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giacomo Andrea
Giacomo Andrea da Ferrara (also known as Iacomo Andrea; died May 12, 1500) was an architect from Ferrara and the author on a commentary on Vitruvius. Very little is known about him; his name did not appear on any buildings in Milan. Luca Pacioli wrote that Giacomo Andrea was almost like a brother to Leonardo da Vinci. Giacomo Andrea, active by the 1480s, drew a prototypical ''Vitruvian Man'' which may have served as the basis for Leonardo's drawing, or have been conceived alongside it as a collaborative effort. Giacomo Andrea was very loyal to the Sforza family. After the occupation of Milan by the French, he is said to have plotted against the French. He was put on trial and sentenced to death. Archbishop Pallavicini attempted to plead for his innocence. Giacomo Andrea was publicly beheaded Decapitation is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and all vertebrate animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Di Giorgio Martini
Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439–1501) was an Italian architect, engineer, painter, sculptor, and writer. As a painter, he belonged to the Sienese School. He was considered a visionary architectural theorist—in Nikolaus Pevsner's terms: "one of the most interesting later Quattrocento architects". As a military engineer, he executed architectural designs and sculptural projects and built almost seventy fortifications for the Federico da Montefeltro, Count (later Duke) of Urbino, building city walls and early examples of star-shaped fortifications. Born in Siena, he apprenticed as a painter with Vecchietta. In panels painted for '' cassoni'' he departed from the traditional representations of joyful wedding processions in frieze-like formulas to express visions of ideal, symmetrical, vast and all but empty urban spaces rendered in perspective. He composed an architectural treatis''Trattato di architettura, ingegneria e arte militare'' the third of the Quattrocento, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Rerum Natura
(; ''On the Nature of Things'') is a first-century BC Didacticism, didactic poem by the Roman Republic, Roman poet and philosopher Lucretius () with the goal of explaining Epicureanism, Epicurean philosophy to a Roman audience. The poem, written in some 7,400 dactylic hexameters, is divided into six untitled books, and explores Epicurean physics through poetic language and metaphors.#Greenblatt1, Greenblatt (2011). Namely, Lucretius explores the principles of atomism; the nature of the mind and soul; explanations of Sense, sensation and thought; the development of the world and its phenomena; and explains a variety of Celestial sphere, celestial and Earth, terrestrial phenomena. The universe described in the poem operates according to these physical principles, guided by ''fortuna'' ("chance"), and not the divine intervention of the Religion in ancient Rome, traditional Roman deities. Background To the Greek philosopher Epicurus, the unhappiness and degradation of humans arose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poggio Bracciolini
Gian Francesco Poggio Bracciolini (; 11 February 1380 – 30 October 1459), usually referred to simply as Poggio Bracciolini, was an Italian scholar and an early Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. He is noted for rediscovering and recovering many Classics, classical Latin manuscripts, mostly decaying and forgotten in German, Swiss, and French monastery, monastic libraries. His most celebrated finds are ''De rerum natura'', the only surviving work by Lucretius, ''De architectura'' by Vitruvius, lost orations by Cicero such as ''Pro Roscio Amerino, Pro Sexto Roscio'', Quintilian's ''Institutio Oratoria'', Statius' ''Silvae'', Ammianus Marcellinus' ''Res Gestae'' (''Rerum gestarum Libri XXXI''), and Silius Italicus's ''Punica (poem), Punica'', as well as works by several minor authors such as Frontinus' ''De aquaeductu'', Nonius Marcellus, Marcus Valerius Probus, Probus, Flavius Caper, and Eutyches. Birth and education Poggio di Guccio (the surname Bracciolini added during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Architectura
(''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on architecture written by the Ancient Rome, Roman architect and military engineer Vitruvius, Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for Caesar Augustus#Building projects, building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It contains a variety of information on Greek and Roman buildings, as well as prescriptions for the planning and design of military camps, cities, and structures both large (aqueducts, buildings, baths, harbours) and small (machines, measuring devices, instruments). Since Vitruvius wrote early in the Roman architectural revolution that saw the full development of cross vaulting, domes, Roman concrete, concrete, and other innovations associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annunciation (Leonardo)
The ''Annunciation'' is a painting by the Italian Renaissance artist Leonardo da Vinci, dated to . Leonardo's earliest extant major work, it was completed in Florence while he was an apprentice in the studio of Andrea del Verrocchio. The painting was made using oil and tempera on a large poplar panel and depicts the Annunciation, a popular biblical subject in 15th-century Florence. Since 1867 it has been housed in the Uffizi in Florence, the city where it was created. Though the work has been criticized for inaccuracies in its composition, it is among the best-known portrayals of the Annunciation in Christian art. Description The subject matter of the work is drawn from Luke 1.26–39. It depicts the angel Gabriel announcing to Mary that she would conceive miraculously and give birth to a son to be named Jesus and called "the Son of God", whose reign would never end. The subject of the annunciation was very popular for contemporaneous artworks painted in Christian countries s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |