Cotswolds Ring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest
 The spine of the Cotswolds runs southwest to northeast through six counties, particularly Gloucestershire, west Oxfordshire and southwestern Warwickshire. The northern and western edges of the Cotswolds are marked by steep
The spine of the Cotswolds runs southwest to northeast through six counties, particularly Gloucestershire, west Oxfordshire and southwestern Warwickshire. The northern and western edges of the Cotswolds are marked by steep
 A 2017 report on employment within the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, stated that the main sources of income were real estate, renting and business activities, manufacturing and wholesale & retail trade repairs. Some 44% of residents were employed in these sectors. Agriculture is also important. Some 86% of the land in the AONB is used for this purpose. The primary crops include barley, beans, rape seed oil and wheat, while the raising of sheep is also important; cows and pigs are also reared. The livestock sector has been declining since 2002, however.
According to the 2011 Census data for the Cotswolds, the wholesale and retail trade was the largest employer (15.8% of the workforce), followed by education (9.7%) and health and social work (9.3%). The report also indicates that a relatively higher proportion of residents were working in agriculture, forestry and fishing, accommodation and food services as well as in professional, scientific and technical activities.
Unemployment in the Cotswold District was among the lowest in the country. A report in August 2017 showed only 315 unemployed persons, a slight decrease of five from a year earlier.
A 2017 report on employment within the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, stated that the main sources of income were real estate, renting and business activities, manufacturing and wholesale & retail trade repairs. Some 44% of residents were employed in these sectors. Agriculture is also important. Some 86% of the land in the AONB is used for this purpose. The primary crops include barley, beans, rape seed oil and wheat, while the raising of sheep is also important; cows and pigs are also reared. The livestock sector has been declining since 2002, however.
According to the 2011 Census data for the Cotswolds, the wholesale and retail trade was the largest employer (15.8% of the workforce), followed by education (9.7%) and health and social work (9.3%). The report also indicates that a relatively higher proportion of residents were working in agriculture, forestry and fishing, accommodation and food services as well as in professional, scientific and technical activities.
Unemployment in the Cotswold District was among the lowest in the country. A report in August 2017 showed only 315 unemployed persons, a slight decrease of five from a year earlier.
 Cotswold stone is a yellow oolitic
Cotswold stone is a yellow oolitic  The rock outcrops at places on the Cotswold Edge; small quarries are common. The exposures are rarely sufficiently compact to be good for
The rock outcrops at places on the Cotswold Edge; small quarries are common. The exposures are rarely sufficiently compact to be good for
 Pictured is the Garden of
Pictured is the Garden of
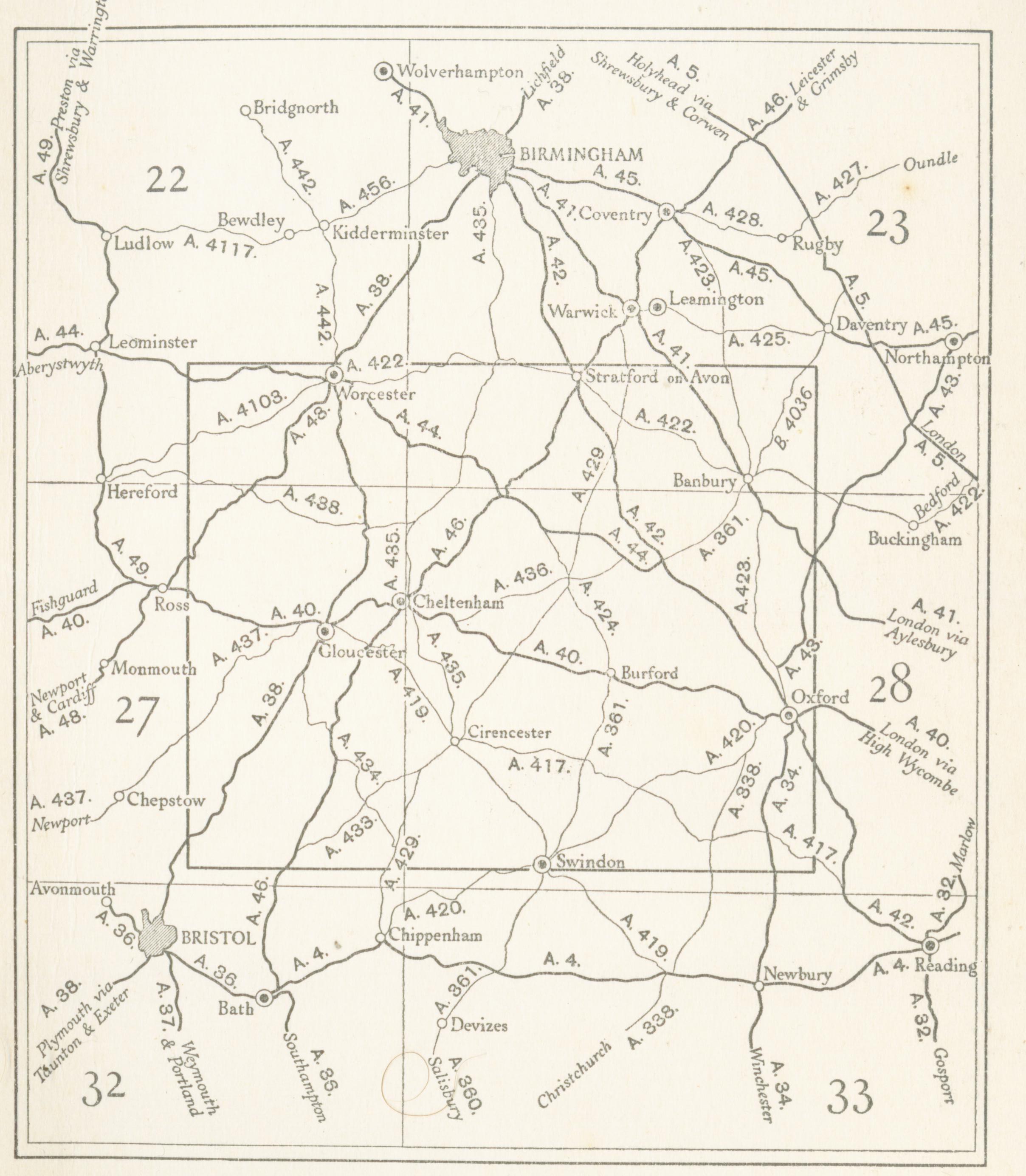 The Cotswolds lie between the M5, M40 and
The Cotswolds lie between the M5, M40 and
National Character Area profile
– Natural England
Cotswolds Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
– Cotswolds Conservation Board
Cotswolds Tourism Partnership
* Independent tourist guides: *
cotswolds.org
*
thecotswolds.com
*
icotswolds.com
*
Explore Gloucestershire
{{Authority control Hills of Gloucestershire Hills of Oxfordshire Hills of Somerset Hills of Warwickshire Hills of Wiltshire Hills of Worcestershire Protected areas of Gloucestershire Protected areas of Oxfordshire Protected areas of Somerset Protected areas of Warwickshire Protected areas of Wiltshire Protected areas of Worcestershire Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England Natural regions of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
to an escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
above the Severn Valley and Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, Cheltenham and Stratford-upon-Avon. It lies within the Vale of Evesha ...
Vale.
The area is defined by the bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
of Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
that creates a type of grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
habitat rare in the UK and that is quarried for the golden-coloured Cotswold stone. The predominantly rural landscape contains stone-built villages, towns, and stately homes and gardens featuring the local stone.
Designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in 1966, the Cotswolds covers making it the largest AONB. It is the third largest protected landscape in England after the Lake District and Yorkshire Dales national parks. Its boundaries are roughly across and long, stretching southwest from just south of Stratford-upon-Avon
Stratford-upon-Avon (), commonly known as just Stratford, is a market town and civil parish in the Stratford-on-Avon district, in the county of Warwickshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It is situated on the River Avon, north-we ...
to just south of Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
near Radstock
Radstock is a town and civil parish on the northern slope of the Mendip Hills in Somerset, England, about south-west of Bath and north-west of Frome. It is within the area of the unitary authority of Bath and North East Somerset. The Radstoc ...
. It lies across the boundaries of several English counties; mainly Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
and Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily ...
, and parts of Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
, Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
, Worcestershire
Worcestershire ( , ; written abbreviation: Worcs) is a county in the West Midlands of England. The area that is now Worcestershire was absorbed into the unified Kingdom of England in 927, at which time it was constituted as a county (see His ...
, and Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, and the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare at Stratford-upon-Avon an ...
. The highest point of the region is Cleeve Hill at , just east of Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
.
The hills give their name to the Cotswold
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale.
The area is defined by the bedrock of Juras ...
local government district, formed on 1 April 1974, which is within the county of Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
. Its main town is Cirencester, where the Cotswold District Council offices are located. The population of the District was about 83,000 in 2011. The much larger area referred to as the Cotswolds encompasses nearly , over five counties: Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire, Warwickshire, Wiltshire, and Worcestershire. The population of the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty was 139,000 in 2016.
History
The largest excavation ofJurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
-era echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea ...
fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s, including of rare and previously unknown species, occurred at a quarry in the Cotswolds in 2021. There is evidence of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
settlement from burial chambers on Cotswold Edge, and there are remains of Bronze and Iron Age forts. Later the Romans built villas, such as at Chedworth
Chedworth is a village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, southwest England, in the Cotswolds. It is known as the location of Chedworth Roman Villa, administered since 1924 by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beaut ...
, settlements such as Gloucester, and paved the Celtic path later known as Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bath), Corini ...
.
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, thanks to the breed of sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
known as the Cotswold Lion, the Cotswolds became prosperous from the wool trade with the continent, with much of the money made from wool directed towards the building of churches. The most successful era for the wool trade was 1250–1350; much of the wool at that time was sold to Italian merchants. The area still preserves numerous large, handsome Cotswold Stone "wool churches". The affluent area in the 21st century has attracted wealthy Londoners and others who own second homes there or have chosen to retire to the Cotswolds.
Etymology
The name ''Cotswold'' is popularly attributed the meaning "sheep enclosure in rolling hillsides", incorporating the term, '' wold'', meaning hills. Compare also the Weald from the Saxon/German word ''Wald'' meaning 'forest'. However, the English Place-Name Society has for many years accepted that the term ''Cotswold'' is derived from ''Codesuualt'' of the 12th century or other variations on this form, the etymology of which was given, 'Cod's-wold', which is 'Cod's high open land'. ''Cod'' was interpreted as an Old English personal name, which may be recognised in further names:Cutsdean
Cutsdean is a rural village in the Cotswolds and smaller than average sized parish, a few miles east north-east of Cheltenham, Gloucestershire and the same distance south-southeast of Evesham. The River Windrush runs through the village.
It c ...
, Codeswellan, and Codesbyrig, some of which date back to the eighth century AD. It has subsequently been noticed that "Cod" could derive philologically from a Brittonic female cognate ''"Cuda"'', a hypothetical mother goddess
A mother goddess is a goddess who represents a personified deification of motherhood, fertility goddess, fertility, creation, destruction, or the earth goddess who embodies the bounty of the earth or nature. When equated with the earth or th ...
in Celtic mythology
Celtic mythology is the body of myths belonging to the Celtic peoples.Cunliffe, Barry, (1997) ''The Ancient Celts''. Oxford, Oxford University Press , pp. 183 (religion), 202, 204–8. Like other Iron Age Europeans, Celtic peoples followed a ...
postulated to have been worshipped in the Cotswold region.
Geography
 The spine of the Cotswolds runs southwest to northeast through six counties, particularly Gloucestershire, west Oxfordshire and southwestern Warwickshire. The northern and western edges of the Cotswolds are marked by steep
The spine of the Cotswolds runs southwest to northeast through six counties, particularly Gloucestershire, west Oxfordshire and southwestern Warwickshire. The northern and western edges of the Cotswolds are marked by steep escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
s down to the Severn valley and the Warwickshire Avon. This feature, known as the Cotswold escarpment, or sometimes the Cotswold Edge, is a result of the uplifting (tilting) of the limestone layer, exposing its broken edge. This is a cuesta, in geological terms. The dip slope is to the southeast.
On the eastern boundary lies the city of Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
and on the west is Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
. To the southeast, the upper reaches of the Thames Valley and towns such as Lechlade, Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parish inside the Cotswold district in England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxon monastery was founded, probably by Ine of Wessex, in 681. The population of the parish was 5,250 in ...
, and Fairford
Fairford is a town in Gloucestershire, England. The town lies in the Cotswold hills on the River Coln, east of Cirencester, west of Lechlade and north of Swindon. Nearby are RAF Fairford and the Cotswold Water Park.
History
Evidence of se ...
are often considered to mark the limit of this region. To the south the Cotswolds, with the characteristic uplift of the Cotswold Edge, reach beyond Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, and towns such as Chipping Sodbury
Chipping Sodbury is a market town and former civil parish, now in the parish of Sodbury, in the unitary authority area of South Gloucestershire, in the ceremonial county of Gloucestershire, England. It was founded in the 12th century by William ...
and Marshfield share elements of Cotswold character.
The area is characterised by attractive small towns and villages built of the underlying Cotswold stone (a yellow oolitic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
). This limestone is rich in fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s, particularly of fossilised sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
s. Cotswold towns include Bourton-on-the-Water, Broadway, Burford
Burford () is a town on the River Windrush, in the Cotswolds, Cotswold hills, in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England. It is often referred to as the 'gateway' to the Cotswolds. Burford is located west of Oxford and southeas ...
, Chalford, Chipping Campden, Chipping Norton
Chipping Norton is a market town and civil parish in the Cotswold Hills in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England, about south-west of Banbury and north-west of Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the civil parish population as ...
, Cricklade, Dursley
Dursley is a market town and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in southern Gloucestershire, England, almost equidistant from the cities of Bristol and Gloucester. It is under the northeast flank of Stinchcombe#Stinchcombe Hill, Stinchco ...
, Malmesbury, Minchinhampton
Minchinhampton is an ancient Cotswolds market town in the Stroud District in Gloucestershire, South West England. The town is located on a hilltop, south-east of Stroud. The common offers wide views over the Severn Estuary into Wales and furth ...
, Moreton-in-Marsh, Nailsworth, Northleach, Painswick, Stow-on-the-Wold, Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
, Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parish inside the Cotswold district in England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxon monastery was founded, probably by Ine of Wessex, in 681. The population of the parish was 5,250 in ...
, Witney
Witney is a market town on the River Windrush in West Oxfordshire in the county of Oxfordshire, England. It is west of Oxford. The place-name "Witney" is derived from the Old English for "Witta's island". The earliest known record of it is as ...
, Winchcombe
Winchcombe () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Tewkesbury in the county of Gloucestershire, England, it is 6 miles north-east of Cheltenham. The population was recorded as 4,538 in the 2011 census and estimated at 5,347 in ...
and Wotton-under-Edge. In addition, much of Box
A box (plural: boxes) is a container used for the storage or transportation of its contents. Most boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides. Boxes can be very small (like a matchbox) or very large (like a shipping box for furniture), and can ...
lies in the Cotswolds. Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
, Cirencester, Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
, Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
, and Swindon
Swindon () is a town and unitary authority with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Wiltshire, England. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Swindon was 201,669, making it the largest town in the county. The Swindon un ...
are larger urban centres that border on, or are virtually surrounded by, the Cotswold AONB.
The town of Chipping Campden is notable for being the home of the Arts and Crafts movement, founded by William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was a British textile designer, poet, artist, novelist, architectural conservationist, printer, translator and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He ...
at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries. William Morris lived occasionally in Broadway Tower
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
, a folly, now part of a country park. Chipping Campden is also known for the annual Cotswold Olimpick Games
The Cotswold Olimpick Games is an annual public celebration of games and sports now held on the Friday after Spring Bank Holiday near Chipping Campden, in the Cotswolds of England. The games likely began in 1612 and ran (through a period of disc ...
, a celebration of sports and games dating back to the early 17th century.
Of the nearly of the Cotswolds, roughly eighty percent is farmland. There are over of footpaths and bridleways. There are also of historic stone walls.
Economy
 A 2017 report on employment within the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, stated that the main sources of income were real estate, renting and business activities, manufacturing and wholesale & retail trade repairs. Some 44% of residents were employed in these sectors. Agriculture is also important. Some 86% of the land in the AONB is used for this purpose. The primary crops include barley, beans, rape seed oil and wheat, while the raising of sheep is also important; cows and pigs are also reared. The livestock sector has been declining since 2002, however.
According to the 2011 Census data for the Cotswolds, the wholesale and retail trade was the largest employer (15.8% of the workforce), followed by education (9.7%) and health and social work (9.3%). The report also indicates that a relatively higher proportion of residents were working in agriculture, forestry and fishing, accommodation and food services as well as in professional, scientific and technical activities.
Unemployment in the Cotswold District was among the lowest in the country. A report in August 2017 showed only 315 unemployed persons, a slight decrease of five from a year earlier.
A 2017 report on employment within the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, stated that the main sources of income were real estate, renting and business activities, manufacturing and wholesale & retail trade repairs. Some 44% of residents were employed in these sectors. Agriculture is also important. Some 86% of the land in the AONB is used for this purpose. The primary crops include barley, beans, rape seed oil and wheat, while the raising of sheep is also important; cows and pigs are also reared. The livestock sector has been declining since 2002, however.
According to the 2011 Census data for the Cotswolds, the wholesale and retail trade was the largest employer (15.8% of the workforce), followed by education (9.7%) and health and social work (9.3%). The report also indicates that a relatively higher proportion of residents were working in agriculture, forestry and fishing, accommodation and food services as well as in professional, scientific and technical activities.
Unemployment in the Cotswold District was among the lowest in the country. A report in August 2017 showed only 315 unemployed persons, a slight decrease of five from a year earlier.
Tourism
Tourism is a significant part of the economy. The Cotswold District area alone gained over £373 million from visitor spending on accommodation, £157 million on local attractions and entertainments, and about £100m on travel in 2016. In the larger Cotswolds Tourism area, including Stroud, Cheltenham, Gloucester and Tewkesbury, tourism generated about £1 billion in 2016, providing 200,000 jobs. Some 38 million day visits were made to the Cotswold Tourism area that year. Many travel guides direct tourists to Chipping Campden, Stow-on-the-Wold, Bourton-on-the-Water, Broadway, Bibury, and Stanton. Some of these locations can be very crowded at times. Roughly 300,000 people visit Bourton per year, for example, with about half staying for a day or less. The area also has numerous public walking trails and footpaths that attract visitors, including theCotswold Way
The Cotswold Way is a long-distance footpath, running along the Cotswold Edge escarpment of the Cotswold Hills in England. It was officially inaugurated as a National Trail on 24 May 2007 and several new rights of way have been created.
His ...
(part of the National Trails System) from Bath to Chipping Campden.
Housing development
In August 2018, the final decision was made for a Local Plan that would lead to the building of nearly 7,000 additional homes by 2031, in addition to over 3,000 already built. Areas for development include Cirencester, Bourton-on-the-Water, Down Ampney, Fairford, Kemble, Lechlade, Northleach, South Cerney, Stow-on-the-Wold, Tetbury and Moreton-in-Marsh. Some of the money received from developers will be earmarked for new infrastructure to support the increasing population.Cotswold stone
 Cotswold stone is a yellow oolitic
Cotswold stone is a yellow oolitic Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
. This limestone is rich in fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s, particularly of fossilised sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
s. When weathered, the colour of buildings made or faced with this stone is often described as honey or golden.
The stone varies in colour from north to south, being honey-coloured in the north and north east of the region, as shown in Cotswold villages such as Stanton and Broadway; golden-coloured in the central and southern areas, as shown in Dursley
Dursley is a market town and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in southern Gloucestershire, England, almost equidistant from the cities of Bristol and Gloucester. It is under the northeast flank of Stinchcombe#Stinchcombe Hill, Stinchco ...
and Cirencester; and pearly white in Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
.
 The rock outcrops at places on the Cotswold Edge; small quarries are common. The exposures are rarely sufficiently compact to be good for
The rock outcrops at places on the Cotswold Edge; small quarries are common. The exposures are rarely sufficiently compact to be good for rock-climbing
Rock climbing is a sport in which participants climb up, across, or down natural rock formations. The goal is to reach the summit of a formation or the endpoint of a usually pre-defined route without falling. Rock climbing is a physically and ...
, but an exception is Castle Rock, on Cleeve Hill, near Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
. Because of the rapid expansion of the Cotswolds in order for nearby areas to capitalize on increased house prices, well-known ironstone villages, such as Hook Norton
Hook Norton is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, England. It lies northeast of Chipping Norton, close to the Cotswold Hills. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 2,117. The village is formed of four neighbourhoods: Ea ...
, have even been claimed by some to be in the Cotswolds despite lacking key features of Cotswolds villages such as Cotswold stone, and are instead built using a deep red/orange ironstone, known locally as Hornton Stone.
In his 1934 book ''English Journey
''English Journey'' is an account by J. B. Priestley of his travels in England which was published in 1934.
Commissioned by publisher Victor Gollancz to write a study of contemporary England, Priestley recounts his travels around England in 1933 ...
'', J. B. Priestley made this comment about Cotswold buildings made of the local stone.
The truth is that it has no colour that can be described. Even when the sun is obscured and the light is cold, these walls are still faintly warm and luminous, as if they knew the trick of keeping the lost sunlight of centuries glimmering about them
Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
The Cotswolds were designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in 1966, with an expansion on 21 December 1990 to . In 1991, all AONBs were measured again using modern methods, and the official area of the Cotswolds AONB was increased to . In 2000, the government confirmed that AONBs have the same landscape quality and status asNational Parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual ...
.
The Cotswolds AONB, which is the largest in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is Eng ...
, stretches from the border regions of South Warwickshire and Worcestershire, through West Oxfordshire and Gloucestershire, and takes in parts of Wiltshire and of Bath and North East Somerset
Bath and North East Somerset (B&NES) is a unitary authority district in England. Bath and North East Somerset Council was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the county of Avon. It is part of the ceremonial county of Somerset.
Th ...
in the south. Gloucestershire County Council is responsible for sixty-three percent of the AONB.
The Cotswolds Conservation Board has the task of conserving and enhancing the AONB. Established under statute in 2004 as an independent public body, the Board carries out a range of work from securing funding for 'on the ground' conservation projects, to providing a strategic overview of the area for key decision makers, such as planning officials. The Board is funded by Natural England and the seventeen local authorities that are covered by the AONB. The Cotswolds AONB Management Plan 2018–2023 was adopted by the Board in September 2018.
The landscape of the AONB is varied, including escarpment outliers, escarpments, rolling hills and valleys, enclosed limestone valleys, settled valleys, ironstone hills and valleys, high wolds and high wold valleys, high wold dip-slopes, dip-slope lowland and valleys, a Low limestone plateau, cornbrash lowlands, farmed slopes, a broad floodplain valley, a large pastoral lowland vale, a settled unwooded vale, and an unwooded vale.
While the beauty of the Cotswolds AONB is intertwined with that of the villages that seem almost to grow out of the landscape, the Cotswolds were primarily designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty for the rare limestone grassland habitats as well as the old growth beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
woodlands that typify the area. These habitat areas are also the last refuge for many other flora and fauna, with some so endangered that they are protected under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981
The Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom implemented to comply with European Council Directive 79/409/EEC on the conservation of wild birds. In short, the act gives protection to native species (especia ...
. Cleeve Hill, and its associated commons, is a fine example of a limestone grassland and it is one of the few locations where the Duke of Burgundy butterfly
''Hamearis lucina'', the Duke of Burgundy, the only member of the genus ''Hamearis'', is a European butterfly in the family Riodinidae. For many years, it was known as the "Duke of Burgundy fritillary", because the adult's chequered pattern is s ...
may still be found in abundance.
A June 2018 report stated that the AONB receives "23 million visitors a year, the third largest of any protected landscape". Earlier that year, Environment secretary Michael Gove
Michael Andrew Gove (; born Graeme Andrew Logan, 26 August 1967) is a British politician serving as Secretary of State for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities and Minister for Intergovernmental Relations since 2021. He has been Member of Parli ...
announced that a panel would be formed to consider making some of the AONBs into National Parks. The review will file its report in 2019. In April 2018, the Cotswolds Conservation Board had written to Natural England "requesting that consideration be given to making the Cotswolds a National Park", according to Liz Eyre, Chairman. This has led to some concern as stated by one member of the Cotswold District Council, "National Park designation is a significant step further and raises the prospect of key decision making powers being taken away from democratically elected councillors". In other words, Cotswold District Council would no longer have the authority to grant and refuse housing applications.
The uniqueness and value of the Cotswolds is shown in the fact that five European Special Areas of Conservation, three national nature reserves and more than 80 Sites of Special Scientific Interest are within the Cotswolds AONB.
The Cotswold Voluntary Wardens Service was established in 1968 to help conserve and enhance the area, and now has more than 300 wardens.
The Cotswold Way
The Cotswold Way is a long-distance footpath, running along the Cotswold Edge escarpment of the Cotswold Hills in England. It was officially inaugurated as a National Trail on 24 May 2007 and several new rights of way have been created.
His ...
is a long-distance footpath, just over long, running the length of the AONB, mainly on the edge of the Cotswold escarpment with views over the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, Cheltenham and Stratford-upon-Avon. It lies within the Vale of Evesha ...
.
In September 2020, the Cotswolds AONB rebranded itself as the "Cotswolds National Landscape", using a proposed name replacement for "Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty".
Places of interest
 Pictured is the Garden of
Pictured is the Garden of Sudeley Castle
Sudeley Castle is a Grade I listed castle in the parish of Sudeley, in the Cotswolds, near to the medieval market town of Winchcombe, Gloucestershire, England. The castle has 10 notable gardens covering some 15 acres within a 1,200-acre estate ...
at Winchcombe
Winchcombe () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Tewkesbury in the county of Gloucestershire, England, it is 6 miles north-east of Cheltenham. The population was recorded as 4,538 in the 2011 census and estimated at 5,347 in ...
. The present structure was built in the 15th century and may be on the site of a 12th-century castle. It is north of the spa town
A spa town is a resort town based on a mineral spa (a developed mineral spring). Patrons visit spas to "take the waters" for their purported health benefits.
Thomas Guidott set up a medical practice in the English town of Bath in 1668. H ...
of Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
which has much Georgian architecture of some merit. Further south, towards Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parish inside the Cotswold district in England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxon monastery was founded, probably by Ine of Wessex, in 681. The population of the parish was 5,250 in ...
, is the ancient fortress known as Beverston Castle, founded in 1229 by Maurice de Gaunt. In the same area is Calcot Manor
Calcot Manor is a historic building in Calcot, three and a half miles west of Tetbury on A 4135 in Gloucestershire, England, near the junction of roads A46 and A4135 (National Grid Reference ST 841180 94891). The original building was establish ...
, a manor house with origins in about 1300 as a tithe barn.
Tetbury Market House was built in 1655. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, Tetbury became an important market for Cotswold wool and yarn. Chavenage House
Chavenage House, Beverston, Gloucestershire is a country house dating from the late 16th century. The house was built in 1576 and is constructed of Cotswold stone, with a Cotswold stone tiled roof. David Verey and Alan Brooks, in their Gloucester ...
is an Elizabethan-era manor house northwest of Tetbury. Chedworth Roman Villa, where several mosaic floors are on display, is near the Roman road known as the Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bath), Corini ...
, north of the important town of Corinium Dobunnorum (Cirencester). Cirencester Abbey
Cirencester Abbey or St Mary's Abbey, Cirencester in Gloucestershire was founded as an Augustinian monastery in 1117 on the site of an earlier church, the oldest-known Saxon church in England, which had itself been built on the site of a Roman stru ...
was founded as an Augustinian monastery in 1117 and Malmesbury Abbey
Malmesbury Abbey, at Malmesbury in Wiltshire, England, is a religious house dedicated to Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul. It was one of the few English houses with a continuous history from the 7th century through to the dissolution ...
was one of the few English houses with a continual history from the 7th century through to the Dissolution of the Monasteries.
An unusual house in this area is Quarwood, a Victorian Gothic house in Stow-on-the-Wold. The grounds, covering , include parkland, fish ponds, paddocks, garages, woodlands and seven cottages. Another is Woodchester Mansion
Woodchester Mansion is an unfinished, Gothic revival mansion house in Nympsfield, Gloucestershire, England. It is on the site of an earlier house known as Spring Park. The mansion is a Grade I listed building.
The mansion was abandoned by its b ...
, an unfinished, Gothic revival mansion house in Woodchester Park near Nympsfield. Newark Park
Newark Park is a Grade I listed country house of Tudor origins located near the village of Ozleworth, Wotton-under-Edge, Gloucestershire. The house sits in an estate of at the southern end of the Cotswold escarpment with views down the Severn ...
is a Grade I listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
country house of Tudor origins near the village of Ozleworth, Wotton-under-Edge. The house sits in an estate of at the southern end of the Cotswold escarpment.
Another of the many manor houses in the area, Owlpen Manor
Owlpen Manor is a Tudor Grade I listed manor house of the Mander family, situated in the village of Owlpen in the Stroud district in Gloucestershire, England. There is an associated estate set in a valley within the Cotswold Area of Outstandi ...
in the village of Owlpen in the Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
district, is also Tudor and also Grade I listed. Further north, Broadway Tower
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
is a folly on Broadway Hill, near the village of Broadway, Worcestershire. To the south of the Cotswolds is Corsham Court, a country house
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a town house. This allowed them to spend time in the country and in the city—hence, for these peopl ...
in a park designed by Capability Brown
Lancelot Brown (born c. 1715–16, baptised 30 August 1716 – 6 February 1783), more commonly known as Capability Brown, was an English gardener and landscape architect, who remains the most famous figure in the history of the English la ...
in the town of Corsham, west of Chippenham, Wiltshire.
Top attractions
According to users of the worldwide TripAdvisor travel site, in 2018 the following were among the best attractions in the Cotswolds: *Walks With Hawks, Cheltenham *Cotswolds Distillery, Stourton *Cotswold Falconry Centre, Moreton-in-Marsh *Mechanical Music Museum, Northleach *Chavenage House
Chavenage House, Beverston, Gloucestershire is a country house dating from the late 16th century. The house was built in 1576 and is constructed of Cotswold stone, with a Cotswold stone tiled roof. David Verey and Alan Brooks, in their Gloucester ...
, Tetbury
* Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury
*Gloucestershire Warwickshire Steam Railway
The Gloucestershire Warwickshire Steam Railway (GWR, GWSR or Gloucs-Warks Steam Railway) is a volunteer-run heritage railway which runs along the Gloucestershire/Worcestershire border of the Cotswolds, England.
The GWSR has restored and reope ...
, Cheltenham
*Gloucester Cathedral
Gloucester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity, in Gloucester, England, stands in the north of the city near the River Severn. It originated with the establishment of a minster dedicated to S ...
, Gloucester
*The Royal Gardens at Highgrove, Tetbury
*Jet Age Museum
The Jet Age Museum is the trading name of the Gloucestershire Aviation Collection, an all-volunteer, charitable organisation dedicated to the preservation of Gloucestershire's aviation heritage. The aviation museum is located on the north side ...
, Gloucester
*Cotswold Wildlife Park
The Cotswold Wildlife Park & Gardens exhibits over 260 different species of animals. The park is set in of landscaped parkland and gardens 2 miles south of Burford, on the A361, Oxfordshire, England. Around 350,000 people visited the park in 20 ...
, Burford
Burford () is a town on the River Windrush, in the Cotswolds, Cotswold hills, in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England. It is often referred to as the 'gateway' to the Cotswolds. Burford is located west of Oxford and southeas ...
*Hook Norton Brewery
Hook Norton Brewery is a regional brewery in Hook Norton, Oxfordshire, England, several miles outside the Cotswold Hills. Founded in 1849, the brewing plant is a traditional Victorian 'tower' brewery in which all the stages of the brewing pr ...
, Hook Norton
Hook Norton is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, England. It lies northeast of Chipping Norton, close to the Cotswold Hills. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 2,117. The village is formed of four neighbourhoods: Ea ...
Transport
 The Cotswolds lie between the M5, M40 and
The Cotswolds lie between the M5, M40 and M4 motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is a motorway in the United Kingdom running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh element was largely ...
s. The main A-roads through the area are:
* the A46: Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
– Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
– Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
– Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, Cheltenham and Stratford-upon-Avon. It lies within the Vale of Evesha ...
;
* the A419
The A419 road is a primary route between Chiseldon near Swindon at junction 15 of the M4 with the A346 road, and Whitminster in Gloucestershire, England near the M5 motorway. The A419 is managed and maintained by a private company, Road Manag ...
: Swindon
Swindon () is a town and unitary authority with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Wiltshire, England. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Swindon was 201,669, making it the largest town in the county. The Swindon un ...
– Cirencester – Stroud;
* the A417
The A417 is a main road in England running from Streatley, Berkshire to Hope under Dinmore, Herefordshire. It is best known for its section between Cirencester and Gloucester where it has primary status and forms part of the link between the m ...
: Lechlade – Cirencester – Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
;
* the A429
A4 most often refers to:
*A4 paper, a paper size defined by the ISO 216 standard, measuring 210 × 297 mm
A4 and variants may also refer to:
Science and mathematics
* British NVC community A4 (''Hydrocharis morsus-ranae - Stratiotes aloide ...
: Malmesbury – Cirencester – Stow-on-the-Wold – Moreton-in-Marsh;
* the A44 A44 may refer to :
* A44 road (Great Britain), a road connecting Oxford, England and Aberystwyth, Wales
* A44 motorway (Germany), a road connecting Aachen at the German-Belgian border and Kassel
* A44 motorway (Netherlands), a motorway in the Nethe ...
: Chipping Norton
Chipping Norton is a market town and civil parish in the Cotswold Hills in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England, about south-west of Banbury and north-west of Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the civil parish population as ...
– Moreton-in-Marsh – Evesham;
* the A40: Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
– Burford
Burford () is a town on the River Windrush, in the Cotswolds, Cotswold hills, in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England. It is often referred to as the 'gateway' to the Cotswolds. Burford is located west of Oxford and southeas ...
– Cheltenham – Gloucester.
These all roughly follow the routes of ancient roads, some laid down by the Romans, such as Ermin Way and the Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bath), Corini ...
.
There are local bus services across the area, but some are infrequent.
The River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
flows from the Cotswolds and is navigable from Inglesham
Inglesham is a small village and civil parish in the Borough of Swindon, Wiltshire, England, notable for the Grade-I listed St John the Baptist Church. The village is just off the A361 road about south-west of Lechlade in Gloucestershire. Mos ...
and Lechlade-on-Thames
Lechlade () is a town at the southern edge of the Cotswolds in Gloucestershire, England, south of Birmingham and west of London. It is the highest point at which the River Thames is navigable, although there is a right of navigation that contin ...
downstream to Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
. West of Inglesham. the Thames and Severn Canal
The Thames and Severn Canal is a canal in Gloucestershire in the south-west of England, which was completed in 1789. It was conceived as part of a cargo route from Bristol and the Midlands to London, linking England's two largest rivers for bett ...
and the Stroudwater Navigation connected the Thames to the River Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
; this route is mostly disused nowadays but several parts are in the process of being restored.
Railways
The area is bounded by two major rail routes: in the south by the main Bristol–Bath–London line (including the South Wales main line) and in the west by the Bristol–Birmingham main line. In addition, the Cotswold line runs through the Cotswolds fromOxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
to Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Englan ...
, and the Golden Valley line runs across the hills from Swindon via Stroud
Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.
Below the western escarpment of the Cotswold Hills, at the meeting point of the Five ...
to Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
, carrying fast and local services.
Mainline rail services to the big cities run from railway stations such as Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Swindon
Swindon () is a town and unitary authority with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Wiltshire, England. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Swindon was 201,669, making it the largest town in the county. The Swindon un ...
, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
, and Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Englan ...
. Mainline trains run by Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
to London Paddington
Paddington, also known as London Paddington, is a London station group, Central London railway terminus and London Underground station complex, located on Praed Street in the Paddington area. The site has been the London terminus of services pro ...
also are available from Kemble station near Cirencester, Kingham station near Stow-on-the-Wold, Charlbury station, and Moreton-in-Marsh station.
Additionally, there is the Gloucestershire Warwickshire Railway, a steam heritage railway over part of the closed Stratford–Cheltenham line, running from Cheltenham Racecourse
Cheltenham Racecourse at Prestbury Park, near Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England, hosts National Hunt horse racing. Its most prestigious meeting is the Cheltenham Festival, held in March, which features several Grade I races including the Chel ...
through Gotherington
Gotherington is a small village north of Bishops Cleeve in Gloucestershire, England. It is surrounded on the north by the villages of Woolstone and Oxenton, and to the south by Woodmancote and Bishop's Cleeve, a very large urban village. Got ...
, Winchcombe
Winchcombe () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Tewkesbury in the county of Gloucestershire, England, it is 6 miles north-east of Cheltenham. The population was recorded as 4,538 in the 2011 census and estimated at 5,347 in ...
, and Hayles Abbey Halt to Toddington Toddington could be
*Toddington, Bedfordshire
**Toddington services, M1 motorway
*Toddington, Gloucestershire
**Toddington railway station
Toddington railway station serves the village of Toddington in Gloucestershire, England. Since 1984 it h ...
and Laverton. The preserved line has been extended to Broadway.
In culture
The Cotswold region has inspired several notable English composers. In the early 1900s,Herbert Howells
Herbert Norman Howells (17 October 1892 – 23 February 1983) was an English composer, organist, and teacher, most famous for his large output of Anglican church music.
Life
Background and early education
Howells was born in Lydney, Gloucest ...
and Ivor Gurney used to take long walks together over the hills, and Gurney urged Howells to make the landscape, including the nearby Malvern Hills, the inspiration for his future work. In 1916, Howells wrote his first major piece, the ''Piano Quartet in A minor,'' inspired by the magnificent view of the Malverns; he dedicated it to "the hill at Chosen (Churchdown
Churchdown is a large village in Gloucestershire, England, situated between Gloucester and Cheltenham in the south of the Tewkesbury Borough.
The village has two centres. The older (Brookfield or "village") centre is in Church Road near St A ...
) and Ivor Gurney who knows it". Another contemporary of theirs, Gerald Finzi
Gerald Raphael Finzi (14 July 1901 – 27 September 1956) was a British composer. Finzi is best known as a choral composer, but also wrote in other genres. Large-scale compositions by Finzi include the cantata '' Dies natalis'' for solo voice and ...
, lived in nearby Painswick.
Gustav Holst, who was born in Cheltenham, spent much of his early years playing the organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
in Cotswold village churches, including at Cranham, after which village he titled his tune for In the Bleak Midwinter
"In the Bleak Midwinter" is a poem by the English poet Christina Rossetti, commonly performed as a Christmas carol. The poem was published, under the title "A Christmas Carol", in the January 1872 issue of ''Scribner's Monthly,'' and was first c ...
. He also called his Symphony in F major, Op. 8 H47 ''The Cotswolds''.
Holst’s friend, the composer Ralph Vaughan Williams
Ralph Vaughan Williams, (; 12 October 1872– 26 August 1958) was an English composer. His works include operas, ballets, chamber music, secular and religious vocal pieces and orchestral compositions including nine symphonies, written over ...
, was born at Down Ampney in the Cotswolds and, though he moved to Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
as a boy, he gave the name of his native village to the tune for Come Down, O Love Divine
"Come Down, O Love Divine" is a Christian hymn usually sung for the festival of Pentecost. It makes reference to the descent of the Holy Spirit as an invocation to God to come to into the soul of the believer. It is a popular piece of Anglican chu ...
. He also composed his opera Hugh the Drover
''Hugh the Drover'' (or ''Love in the Stocks'') is an opera in two acts by Ralph Vaughan Williams to an original English libretto by Harold Child. The work has set numbers with recitatives. It has been described as a modern example of a ballad ...
from 1913 to 1924, which depicts life in a Cotswold village and incorporates local folk melodies. In 1988, the 6th symphony (Op. 109) of composer Derek Bourgeois was titled ''"A Cotswold Symphony"''.
The Cotswolds are a popular location for filming scenes for movies and television programmes. The film '' Better Things'' (2008), directed by Duane Hopkins, is set in a small Cotswold village. The fictional detective Agatha Raisin
Agatha Raisin is a fictional detective in a series of humorous mystery novels, originally written by Marion Chesney using the pseudonym M. C. Beaton. Chesney's friend Rod W. Green took over as writer with ''Hot to Trot''. The books are published ...
lives in the fictional village of Carsely in the Cotswolds.
Other movies filmed in the Cotswolds or nearby, at least in part, include some of the Harry Potter series
''Harry Potter'' is a series of seven fantasy novels written by British author J. K. Rowling. The novels chronicle the lives of a young wizard, Harry Potter, and his friends Hermione Granger and Ron Weasley, all of whom are students at Hog ...
(Gloucester Cathedral), ''Bridget Jones's Diary
''Bridget Jones's Diary'' is a 2001 romantic comedy film directed by Sharon Maguire and written by Richard Curtis, Andrew Davies (writer), Andrew Davies, and Helen Fielding. A co-production of the United Kingdom, United States and France, it is ...
'' (Snowshill
Snowshill ( , ) is a small Cotswolds village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England, located near Broadway, Worcestershire. The population taken at the 2011 census was 164.
Prehistoric history
An important early Bronze Age hoard was fo ...
), ''Pride and Prejudice
''Pride and Prejudice'' is an 1813 novel of manners by Jane Austen. The novel follows the character development of Elizabeth Bennet, the dynamic protagonist of the book who learns about the repercussions of hasty judgments and comes to appreci ...
'' (Cheltenham Town Hall), and ''Braveheart
''Braveheart'' is a 1995 American historical drama film directed and produced by, and starring Mel Gibson. Gibson portrays Sir William Wallace, a late-13th century Scottish warrior who led the Scots in the First War of Scottish Independence ag ...
'' (Cotswold Farm Park). In 2014, some scenes of the 2016 movie Alice Through the Looking Glass were filmed at the Gloucester Docks just outside the Cotswold District; some scenes for the 2006 movie Amazing Grace were also filmed at the Docks.
The television series ''Father Brown
Father Brown is a fictional Roman Catholic priest and amateur detective who is featured in 53 short stories published between 1910 and 1936 written by English author G. K. Chesterton. Father Brown solves mysteries and crimes using his intuiti ...
'' was almost entirely filmed in the Cotswolds. Scenes and buildings in Sudeley Castle
Sudeley Castle is a Grade I listed castle in the parish of Sudeley, in the Cotswolds, near to the medieval market town of Winchcombe, Gloucestershire, England. The castle has 10 notable gardens covering some 15 acres within a 1,200-acre estate ...
was often featured in the series. The vicarage in Blockley
Blockley is a village, civil parish and ecclesiastical parish in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England, about northwest of Moreton-in-Marsh. Until 1931 Blockley was an exclave of Worcestershire.
The civil and ecclesiastical parish ...
was used for the main character's residence and the Anglican St Peter and St Paul church was the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
St Mary's in the series. Other filming locations included Guiting Power
Guiting Power is a village and civil parish in the Cotswolds, in Gloucestershire, England. The population of the parish at the 2011 census was 296.
Guiting Power stands on the slopes of a small valley formed by a tributary of the River Windrush ...
, the former hospital in Moreton-in-Marsh, the Winchcombe
Winchcombe () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Tewkesbury in the county of Gloucestershire, England, it is 6 miles north-east of Cheltenham. The population was recorded as 4,538 in the 2011 census and estimated at 5,347 in ...
railway station, Lower Slaughter
Lower Slaughter is a village in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England, south west of Stow-on-the-Wold.
The village is built on both banks of the River Eye, a slow-moving stream crossed by two footbridges, which also flows through ...
, and St Peter's Church in Upper Slaughter.
In the 2010s, BBC TV series '' Poldark'', the location for Ross Poldark's family home "Trenwith" is Chavenage House
Chavenage House, Beverston, Gloucestershire is a country house dating from the late 16th century. The house was built in 1576 and is constructed of Cotswold stone, with a Cotswold stone tiled roof. David Verey and Alan Brooks, in their Gloucester ...
, Tetbury, which is open to the public.
Many exterior shots of village life in the '' Downton Abbey'' TV series were filmed in Bampton, Oxfordshire
Bampton, also called Bampton-in-the-Bush, is a settlement and civil parish in the Thames Valley about southwest of Witney in Oxfordshire. The parish includes the hamlet of Weald. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 2,564. Bam ...
. Other filming locations in that county included Swinbrook, Cogges, and Shilton.
The city of Bath hosted crews that filmed parts of the movies '' Vanity Fair'', ''Persuasion
Persuasion or persuasion arts is an umbrella term for Social influence, influence. Persuasion can influence a person's Belief, beliefs, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, Intention, intentions, Motivation, motivations, or Behavior, behaviours.
...
'', ''Dracula'', and '' The Duchess''. Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
and other places in Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
, some within the Area of Natural Beauty, have been a popular location for filming period films and television programmes over the years. Gloucester Cathedral
Gloucester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity, in Gloucester, England, stands in the north of the city near the River Severn. It originated with the establishment of a minster dedicated to S ...
has been particularly popular.
The sighting of peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
s in the landscape of the Cotswolds is mentioned in ''The Peregrine'' by John Alec Baker.
The television documentary agriculture-themed series Clarkson's Farm
''Clarkson's Farm'' is a British television documentary series about Jeremy Clarkson and his farm in the Cotswolds. It was first broadcast by Amazon Prime Video on 11 June 2021. The series documents Clarkson's attempts at running a farm in th ...
were filmed at various locations around Chipping Norton
Chipping Norton is a market town and civil parish in the Cotswold Hills in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England, about south-west of Banbury and north-west of Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the civil parish population as ...
.
See also
* Chilterns *Cotswold architecture
The Cotswold style of architecture is a style based on houses from the Cotswold region of England, and is sometimes called the ''storybook style''. Cotswold houses often have a prominent chimney, often near the front door of the house. Other nota ...
* Geology of Great Britain
The geology of Great Britain is renowned for its diversity. As a result of its eventful geological history, Great Britain shows a rich variety of landscapes across the constituent countries of England, Wales and Scotland. Rocks of almost all geolo ...
References
Further reading
* Brace, Catherine. "Looking back: the Cotswolds and English national identity, c. 1890–1950." ''Journal of Historical Geography'' 25.4 (1999): 502-516. * Brace, Catherine. "A pleasure ground for the noisy herds? Incompatible encounters with the Cotswolds and England, 1900–1950." ''Rural History'' 11.1 (2000): 75-94. * Briggs, Katharine Mary. ''The folklore of the Cotswolds'' (BT Batsford Limited, 1974). * Hilton, R. H. "The Cotswolds and Regional History." ''History Today'' (July 1953) 3#7 pp 490–499. * Verey, David Cecil Wynter. ''The buildings of England: Gloucestershire. I. The Cotswolds'' (Penguin Books, 1979).External links
National Character Area profile
– Natural England
Cotswolds Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
– Cotswolds Conservation Board
Cotswolds Tourism Partnership
* Independent tourist guides: *
cotswolds.org
*
thecotswolds.com
*
icotswolds.com
*
Explore Gloucestershire
{{Authority control Hills of Gloucestershire Hills of Oxfordshire Hills of Somerset Hills of Warwickshire Hills of Wiltshire Hills of Worcestershire Protected areas of Gloucestershire Protected areas of Oxfordshire Protected areas of Somerset Protected areas of Warwickshire Protected areas of Wiltshire Protected areas of Worcestershire Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England Natural regions of England