|
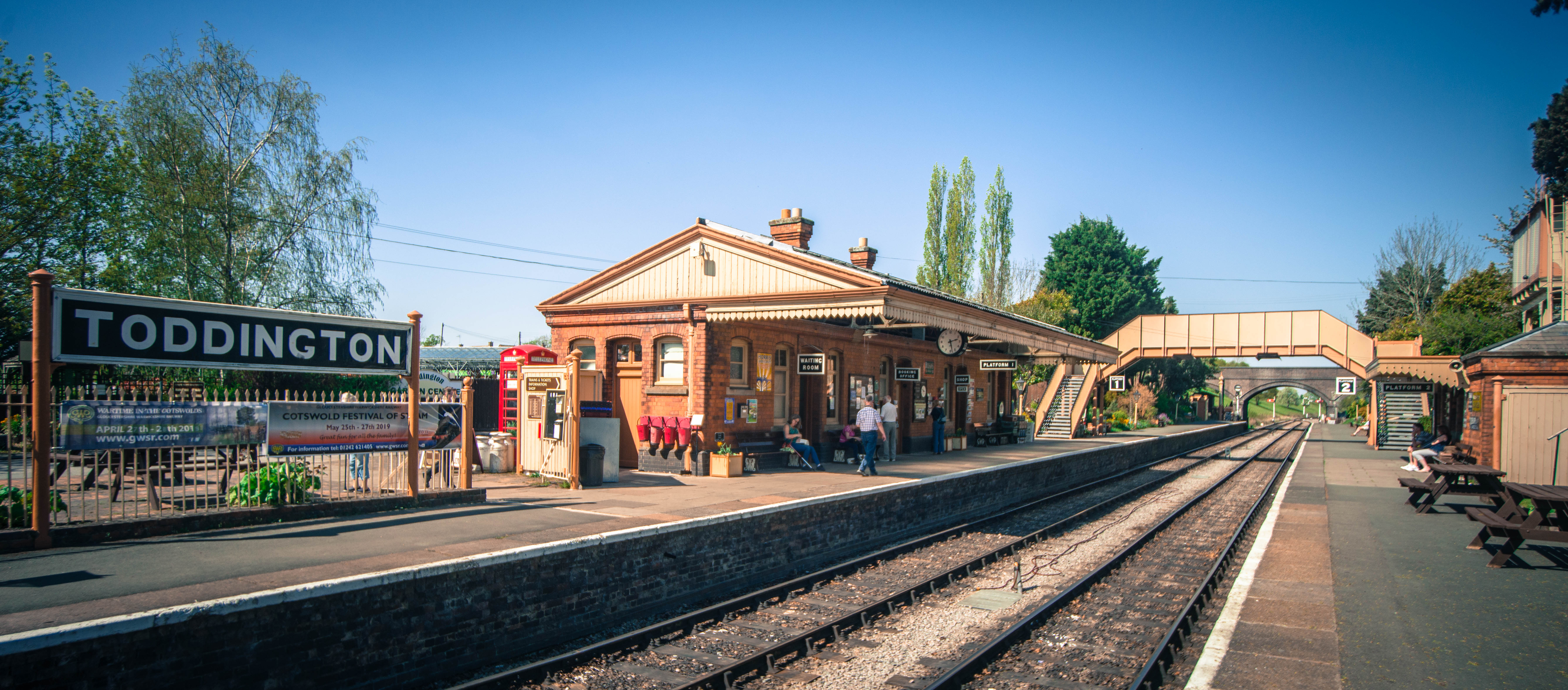
Toddington Railway Station
Toddington railway station serves the village of Toddington in Gloucestershire, England. Since 1984 it has been the main base of operations for the heritage Gloucestershire Warwickshire Railway. The station is located on the Honeybourne Line which linked Cheltenham and and which was opened by the Great Western Railway in 1906. The station was a centre of fruit and milk traffic, but receipts dwindled after a railwaymen's strike in 1955. The station closed to passengers in 1960, although the line itself remained open for freight and diversionary use until 1976; the track was lifted in 1979-80. History On 9 July 1859, the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway opened a line from to . The OW&W became the West Midland Railway in 1860 and was acquired by Great Western Railway in 1883 with a view to combining it with the Birmingham to Stratford Line to create a high-speed route from the Midlands to the South West. The GWR obtained authorisation in 1899 for the construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage Railway
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) in the history of rail transport. Definition The British Office of Rail and Road defines heritage railways as follows:...'lines of local interest', museum railways or tourist railways that have retained or assumed the character and appearance and operating practices of railways of former times. Several lines that operate in isolation provide genuine transport facilities, providing community links. Most lines constitute tourist or educational attractions in their own right. Much of the rolling stock and other equipment used on these systems is original and is of historic value in its own right. Many systems aim to replicate both the look and operating practices of historic former railways companies. Infrastructure Heritage railway lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and large towns in the region include Bath, Somerset, Bath, Bristol, Bournemouth, Cheltenham, Exeter, Gloucester, Plymouth and Swindon. It is geographically the largest of the nine regions of England covering , but the third-least populous, with approximately five million residents. The region includes the West Country and much of the ancient kingdom of Wessex. It includes two entire national parks of England and Wales, national parks, Dartmoor and Exmoor (a small part of the New Forest is also within the region); and four List of World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom, World Heritage Sites: Stonehenge, the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape, the Jurassic Coast and the Bath, Somerset, City of Bath. The northern part of Gloucestershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanway House
Stanway House is a Jacobean manor house, located near the village of Stanway in Gloucestershire, England. The manor of Stanway was owned by Tewkesbury Abbey for 800 years then for 500 years by the Tracy family and their descendants, the Earls of Wemyss and March. Stanway House, originally constructed in the late 16th and early 17th century for the Tracy family, is a Grade I listed building. The principal rooms are in a long south-facing range forming an L-shape with the hall, unlike the usual Tudor house plan of a central hall. The north-east wing, remodelled in 1913 by Detmar Blow, was demolished in 1948. The kitchen court was designed by William Burn in 1859. The Gatehouse was built in about 1630. The construction includes Guiting Yellow stone and some Jacobean mullions and gables. The then Lord Neidpath, now the 13th Earl of Wemyss and March, has pursued a programme of restoration for a number of years. The house and grounds are open to the public on a limited basis e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Warwickshire Line
The North Warwickshire Line (also known as the Shakespeare Line) is a suburban railway line in the West Midlands region of the United Kingdom. It runs from Birmingham to Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire, now the southern terminus of the line, although until 1976 the line continued to Cheltenham as part of the Great Western Railway route from Birmingham to Bristol. The line is one of the Snow Hill lines. It is not electrified and is operated by West Midlands Trains using Class 172 diesel multiple units. The northern part of the line is suburban in nature, and has a regular and busy commuter service into central Birmingham. The southern part (south of ) is rural in nature, and has a less frequent service, with a number of rural request stops. Despite the name, the line does not pass through the area commonly known as North Warwickshire, instead, the name of the line was believed to be derived from that of the local hunt. History Early history The original plans for the line w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
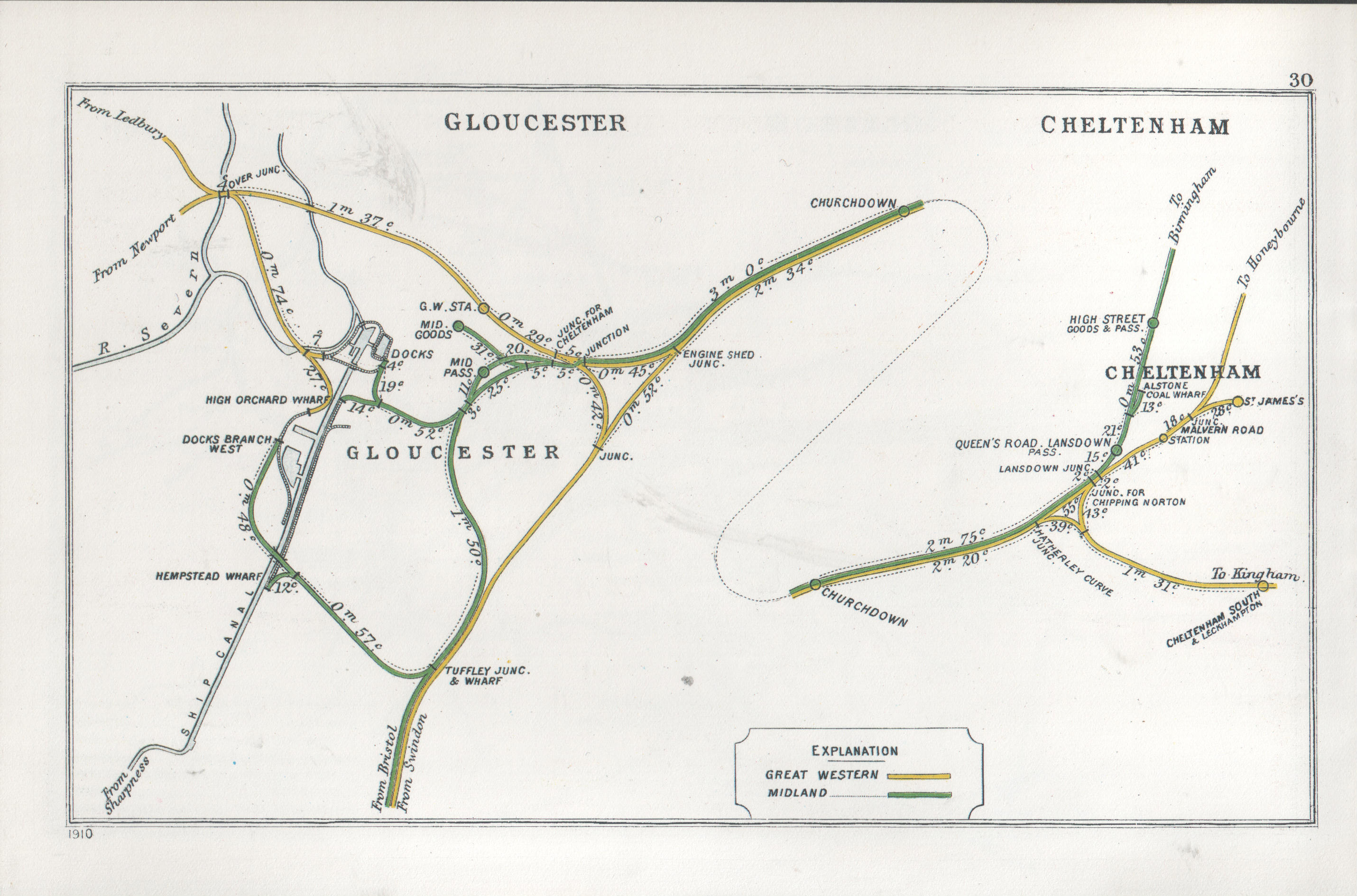
Cheltenham Spa Railway Station
Cheltenham Spa railway station is a railway station serving Cheltenham in Gloucestershire, England. Situated on the Bristol-Birmingham main line, it is managed by Great Western Railway (despite most services being operated by CrossCountry, which does not manage any stations) and is about one mile from the town centre. The official name of the town is simply ''Cheltenham'', but, when the station was renamed in 1925, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway chose to add ''Spa'' to the station name. The station is a key regional interchange and is the fifth busiest rail station in South West England. History The first railway to Cheltenham was the broad-gauge Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway (C&GWUR), authorised by Act of Parliament in 1836, and opened between Cheltenham and Gloucester in 1840. In the same year, the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) opened its line between Cheltenham and Bromsgrove, whence trains ran on mixed-gauge tracks to Gloucester. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of Ca C2. Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide. The pure material is colorless, while pieces of technical-grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of about 80–85% of CaC2 (the rest is CaO (calcium oxide), Ca3P2 (calcium phosphide), CaS (calcium sulfide), Ca3N2 (calcium nitride), SiC (silicon carbide), etc.). In the presence of trace moisture, technical-grade calcium carbide emits an unpleasant odor reminiscent of garlic. Applications of calcium carbide include manufacture of acetylene gas, generation of acetylene in carbide lamps, manufacture of chemicals for fertilizer, and steelmaking. Production Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately . This is an endothermic reaction requiring per mole and high temperatures to drive off the carbon monoxide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbide Lamp
Carbide lamps, or acetylene gas lamps, are simple lamps that produce and burn acetylene (C2H2) which is created by the reaction of calcium carbide (CaC2) with water (H2O). Acetylene gas lamps were used to illuminate buildings, as lighthouse beacons, and as headlights on motor-cars and bicycles. Portable acetylene gas lamps, worn on the hat or carried by hand, were widely used in mining in the early twentieth century. They are still employed by cavers, hunters, and cataphiles. Small carbide lamps called "carbide candles" or "smokers" are used for blackening rifle sights to reduce glare. They are sometimes referred to as "smokers" because of the sooty flame produced by acetylene. Mechanism A mining or caving lamp has calcium carbide placed in a lower chamber, the generator. The upper reservoir is then filled with water. A threaded valve or other mechanism is used to control the rate at which the water is allowed to drip into the chamber containing the calcium carbide. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Tank
A water tank is a container for storing water. Water tanks are used to provide storage of water for use in many applications, drinking water, irrigation agriculture, fire suppression, agricultural farming, both for plants and livestock, chemical manufacturing, food preparation as well as many other uses. Water tank parameters include the general design of the tank, and choice of construction materials, linings. Various materials are used for making a water tank: plastics (polyethylene, polypropylene), fiberglass, concrete, stone, steel (welded or bolted, carbon, or stainless). Earthen pots, such as matki used in South Asia, can also be used for water storage. Water tanks are an efficient way to help developing countries to store clean water. History Throughout history, wood, ceramic and stone tanks have been used as water tanks. These containers were all naturally occurring and some man made and a few of these tanks are still in service. The Indus Valley civilization (30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Box
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toddington Railway Station9
Toddington could be *Toddington, Bedfordshire **Toddington services, M1 motorway *Toddington, Gloucestershire **Toddington railway station Toddington railway station serves the village of Toddington in Gloucestershire, England. Since 1984 it has been the main base of operations for the heritage Gloucestershire Warwickshire Railway. The station is located on the Honeybourne Line w ... * Toddington, West Sussex {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Siding
A siding, in rail terminology, is a low-speed track section distinct from a running line or through route such as a main line, branch line, or spur. It may connect to through track or to other sidings at either end. Sidings often have lighter rails, meant for lower speed or less heavy traffic, and few, if any, signals. Sidings connected at both ends to a running line are commonly known as loops; those not so connected may be referred to as single-ended or dead-end sidings, or (if short) stubs. Functions Sidings may be used for marshalling (classifying), stabling, storing, loading, and unloading vehicles. Common sidings store stationary rolling stock, especially for loading and unloading. Industrial sidings (also known as spurs) go to factories, mines, quarries, wharves, warehouses, some of them are essentially links to industrial railways. Such sidings can sometimes be found at stations for public use; in American usage these are referred to as team tracks (after the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crane (railroad)
A railroad crane (North America: crane car or wrecker; UK: breakdown crane) is a type of crane used on a railroad for one of three primary purposes: freight handling in goods yards, permanent way (PW) maintenance, and accident recovery work. Although the design differs according to the type of work, the basic configuration is similar in all cases: a rotating crane body is mounted on a sturdy chassis fitted with flanged wheels. The body supports the jib (UK; North America: boom) and provides all the lifting and operating mechanisms; on larger cranes, an operator's cabin is usually provided. The chassis is fitted with buffing (UK) and/or coupling gear to allow the crane to be moved by a locomotive, although many are also self-propelled to allow limited movement about a work site. For cranes with a jib that extends beyond the length of the chassis, an idler car (also known as a 'jib carrier' (UK) or 'boom car' (North America)) is provided to protect the jib and to allow the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
