Cosmos Jupiter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bristol Jupiter was a British nine-cylinder single-row piston
 ;Bristol Jupiter IV
:(1926) ; fitted with variable valve timing and a Bristol Triplex carburettor.
;Bristol Jupiter V
:(1925) .
;Bristol Jupiter VI
:(1927) ; produced in both high- (6.3:1) and low- (5.3:1)
;Bristol Jupiter IV
:(1926) ; fitted with variable valve timing and a Bristol Triplex carburettor.
;Bristol Jupiter V
:(1925) .
;Bristol Jupiter VI
:(1927) ; produced in both high- (6.3:1) and low- (5.3:1) 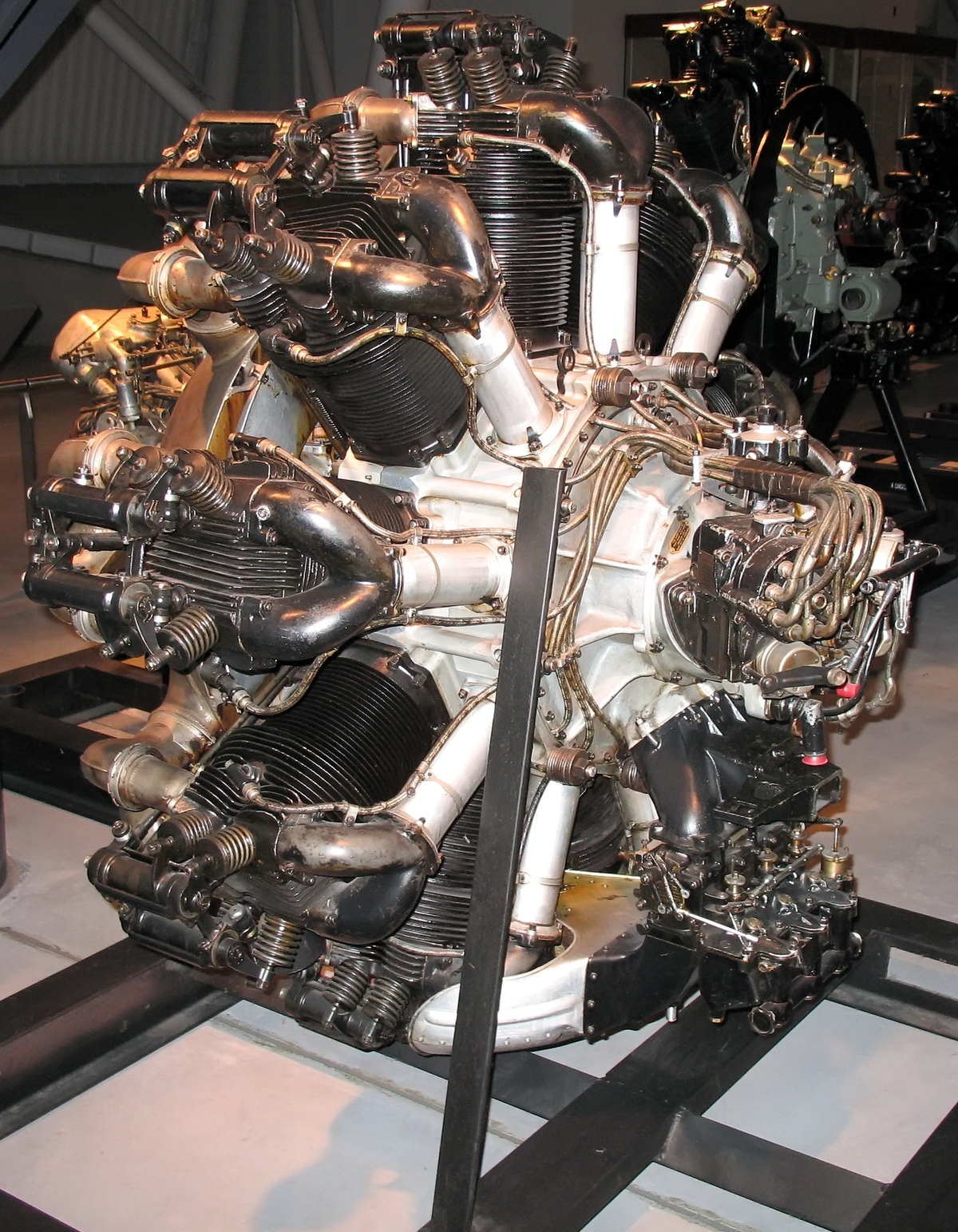 ;Bristol Jupiter VIIFP
:(1930) ; version of Jupiter VII with pressure feed lubrication to wrist-pins.
;Bristol Jupiter VIII
:(1929) ; first version with propeller reduction gearing; compression ratio 6.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIF
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with forged cylinder heads and lowered compression ratio (5.8:1).
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIFP
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with pressure feed lubrication (
;Bristol Jupiter VIIFP
:(1930) ; version of Jupiter VII with pressure feed lubrication to wrist-pins.
;Bristol Jupiter VIII
:(1929) ; first version with propeller reduction gearing; compression ratio 6.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIF
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with forged cylinder heads and lowered compression ratio (5.8:1).
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIFP
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with pressure feed lubrication (
page 870
and a short technical description is o
{{Walter aeroengines Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines
radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is ca ...
built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company
The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable a ...
. Originally designed late in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and known as the Cosmos Jupiter, a lengthy series of upgrades and developments turned it into one of the finest engines of its era.
The Jupiter was widely used on many aircraft designs during the 1920s and 1930s. Thousands of Jupiters of all versions were produced, both by Bristol and abroad under licence.
A turbo-supercharged version of the Jupiter known as the Orion suffered development problems and only a small number were produced. The "Orion" name was later re-used by Bristol for an unrelated turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel ...
engine.
Design and development
The Jupiter was designed duringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
by Roy Fedden
Sir Alfred Hubert Roy Fedden MBE, FRAeS (6 June 1885 – 21 November 1973) was an engineer who designed most of Bristol Engine Company's successful piston aircraft engine designs.
Early life
Fedden was born in the Bristol area to fairly wealthy ...
of Brazil Straker
Straker-Squire (also known as Brazil Straker) was a British automobile manufacturer based in Bristol, and later Edmonton in North London.
The company was formed in 1893 at St Philips, Bristol, as Brazil, Straker & Co by the Irish engineer J.P. ...
and later Cosmos Engineering
Cosmos Engineering was a company that manufactured aero-engines in a factory in Fishponds, Bristol during World War I. Sir Roy Fedden, the company's principal designer, developed the 14-cylinder radial Mercury engine during this period. The co ...
. The first Jupiter was completed by Brazil Straker in 1918 and featured three carburettors, each one feeding three of the engine's nine cylinders via a spiral deflector housed inside the induction chamber. During the rapid downscaling of military spending after the war, Cosmos Engineering became bankrupt
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debt ...
in 1920, and was eventually purchased by the Bristol Aeroplane Company
The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable a ...
on the strengths of the Jupiter design and the encouragement of the Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State ...
. The engine matured into one of the most reliable on the market. It was the first air-cooled engine to pass the Air Ministry full-throttle test, the first to be equipped with automatic boost control, and the first to be fitted to airliners.
The Jupiter was fairly standard in design, but featured four valves per cylinder, which was uncommon at the time. The cylinders
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
were machined from steel forgings, and the cast cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern ov ...
s were later replaced with aluminium alloy following studies by the Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), bef ...
. In 1927, a change was made to move to a forged head design due to the rejection rate of the castings. The Jupiter VII introduced a mechanically-driven supercharger to the design, and the Jupiter VIII was the first to be fitted with reduction gears.
In 1925, Fedden started designing a replacement for the Jupiter. Using a shorter stroke to increase the revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
(rpm), and including a supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induct ...
for added power, resulted in the Bristol Mercury
The Bristol Mercury is a British nine-cylinder, air-cooled, single-row, piston radial engine. Designed by Roy Fedden of the Bristol Aeroplane Company it was used to power both civil and military aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s. Developed from ...
of 1927. Applying the same techniques to the original Jupiter-sized engine in 1927 resulted in the Bristol Pegasus
The Bristol Pegasus is a British nine-cylinder, single-row, air-cooled radial aero engine. Designed by Roy Fedden of the Bristol Aeroplane Company, it was used to power both civil and military aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s. Developed from t ...
. Neither engine would fully replace the Jupiter for a few years.
In 1926 a Jupiter-engined Bristol Bloodhound
The Bristol Bloodhound is a British ramjet powered surface-to-air missile developed during the 1950s. It served as the UK's main air defence weapon into the 1990s and was in large-scale service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the forces of f ...
with the registration
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), th ...
G-EBGG completed an endurance flight of , during which the Jupiter ran for a total of 225 hours and 54 minutes without part failure or replacement.
Licensed production
The Jupiter saw widespread use in licensed versions, with fourteen countries eventually producing the engine. In France, Gnome-Rhone produced a version known as the Gnome-Rhône 9 Jupiter that was used in several local civilian designs, as well as achieving some export success.Siemens-Halske
Siemens & Halske AG (or Siemens-Halske) was a German electrical engineering company that later became part of Siemens.
It was founded on 12 October 1847 as ''Telegraphen-Bauanstalt von Siemens & Halske'' by Werner von Siemens and Johann Geo ...
took out a licence in Germany and produced several versions of increasing power, eventually resulting in the Bramo 323
The Bramo 323 ''Fafnir'' is a nine-cylinder radial aircraft engine of the World War II era. Based heavily on Siemens/Bramo's earlier experience producing the Bristol Jupiter under licence, the Bramo 323 saw limited use.
Design and development
...
Fafnir, which saw use in German wartime aircraft.
In Japan, the Jupiter was license-built from 1924 by Nakajima, forming the basis of its own subsequent radial aero-engine design, the Nakajima Ha-1 Kotobuki. It was produced in Poland as the PZL Bristol Jupiter, in Italy as the Alfa Romeo 126-RC35, and in Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
by Walter Engines
Walter Aircraft Engines is an aircraft engine manufacturer and former automotive manufacturer. Its notable products include the Walter M601, M601 turboprop. The company is based in Prague, Czech Republic. It has been a subsidiary of GE Aviation ...
. The most produced version was in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, where its Shvetsov
UEC-Aviadvigatel JSC (Russian: АО "ОДК-Авиадвигатель", lit. Aeroengine) is a Russian developer and builder of aircraft engines, most notably jet engines for commercial aircraft. Based at the Perm Engine Plant, its products power ...
M-22 version powered the initial Type 4 version of the Polikarpov I-16
The Polikarpov I-16 (russian: Поликарпов И-16) is a Soviet single-engine single-seat fighter aircraft of revolutionary design; it was the world's first low-wing cantilever monoplane fighter with retractable landing gear to attain ope ...
(55 units produced). Type 4 Polikarpovs can be identified by their lack of exhaust stubs, rounded NACA cowling and lack of cowling shutters, features which were introduced on the Shvetsov M-25
The Shvetsov M-25 was an aircraft radial engine produced in the Soviet Union (USSR) in the 1930s and 1940s, a licensed production variant of the Wright R-1820-F3.
Design and development
The first M-25s were produced from kits imported from the ...
powered Type 5 and later variants (total production 4,500+ units). Production started in 1918 and ceased in 1930.
Variants
The Jupiter was produced in many variants, one of which was the Bristol Orion of 1926.Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
problems with this turbo-supercharged engine caused the project to be abandoned after only nine engines had been built.
;Brazil Straker (Cosmos) Jupiter I
:(1918) ; only two engines assembled.
;Cosmos Jupiter II
:(1918) ; a single engine assembled.
;Bristol Jupiter II
:(1923) .
;Bristol Jupiter III
:(1923) .
compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
versions.
;Bristol Jupiter VIA
:(1927) ; civil version of Jupiter VI.
;Bristol Jupiter VIFH
:(1932) ; version of Jupiter VI equipped with gas starter motor.
;Bristol Jupiter VIFL
:(1932) ; version of Jupiter VI with compression ratio of 5.15:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIFM
:(1932) ; version of Jupiter VI with compression ratio of 5.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIFS
:(1932) ; version of Jupiter VI with compression ratio of 6.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VII
:(1928) ; fitted with supercharger, with compression ratio of 5.3:1; also manufactured by Gnome-Rhone as the 9ASB.
;Bristol Jupiter VIIF
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VII with forged cylinder heads.
 ;Bristol Jupiter VIIFP
:(1930) ; version of Jupiter VII with pressure feed lubrication to wrist-pins.
;Bristol Jupiter VIII
:(1929) ; first version with propeller reduction gearing; compression ratio 6.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIF
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with forged cylinder heads and lowered compression ratio (5.8:1).
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIFP
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with pressure feed lubrication (
;Bristol Jupiter VIIFP
:(1930) ; version of Jupiter VII with pressure feed lubrication to wrist-pins.
;Bristol Jupiter VIII
:(1929) ; first version with propeller reduction gearing; compression ratio 6.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIF
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with forged cylinder heads and lowered compression ratio (5.8:1).
;Bristol Jupiter VIIIFP
:(1929) ; version of Jupiter VIII with pressure feed lubrication (time between overhauls
Time between overhauls (abbreviated as TBO or TBOH) is the manufacturer's recommended number of running hours or calendar time before an aircraft engine or other component requires overhaul.
On rotorcraft, many components have recommended or man ...
at this stage in development was only 150 hours due to multiple failures).
;Bristol Jupiter IX
: ; compression ratio 5.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter IXF
: ; version of Jupiter IX with forged cylinder heads
;Bristol Jupiter X
: ; compression ratio 5.3:1.
;Bristol Jupiter XF
: ; version of Jupiter X with forged cylinder heads
;Bristol Jupiter XFA
:
;Bristol Jupiter XFAM
:
;Bristol Jupiter XFBM
:
;Bristol Jupiter XFS
:Fully supercharged.
;Bristol Jupiter XI
:Compression ratio 5.15:1.
;Bristol Jupiter XIF
: ; compression ratio 5.15:1.
;Bristol Jupiter XIFA
: ; version of Jupiter XIF with 0.656:1 propeller gear reduction ratio
;Bristol Jupiter XIFP
: ; version of Jupiter XIF with pressure feed lubrication.
;Bristol Orion I
:(1926) Jupiter III, turbo-supercharged, abandoned programme.
;Gnome-Rhône 9A Jupiter:French licence production primarily of 9A, 9Aa, 9Ab, 9Ac, 9Akx and 9Ad variants.
;Siemens-Halske Sh20, Sh21 and Sh22
The Siemens-Halske Sh 22 (also known as SAM 22) was a nine-cylinder aircraft radial engine manufactured by Siemens & Halske in Germany in the 1930s. Following the reorganization of its manufacturer and change in military nomenclature, the engine b ...
: Siemens-Halske took out a licence in Germany and produced several versions of increasing power, eventually resulting in the Bramo 323 Fafnir, which saw use in wartime models.
; Nakajima Ha-1 Kotobuki: In Japan, the Jupiter was licence-built from 1924 by Nakajima.
;PZL Bristol Jupiter: Polish production.
;Alfa Romeo Jupiter
Alfa Romeo built/designed a range of aircraft engines based on the Bristol Jupiter and Bristol Pegasus designs, designated Alfa 125, Alfa 126, Alfa 127, Alfa 128, Alfa 129 and Alfa 131. All these essentially similar engines were mainly fitted ...
: Italian licence production, .
; Alfa 126 R.C.35: Alfa Romeo developed variant
;Walter Jupiter: Licence production in Czechoslovakia by Walter Engines
;Shvetsov M-22: The most produced version; manufactured in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
.
;IAM 9AD Jupiter: Licence production of the Gnome-Rhône 9A in Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
;SABCA Jupiter: license production in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
by SABCA
SABCA (Sociétés Anonyme Belge de Constructions Aéronautiques) is a Belgian aerospace company. Its main sectors of activity are civil aviation, space and defence.
SABCA was established during 1920. Presently, it is owned by the French aircraf ...
(''Société Anonyme Belge de Constructions Aéronautiques'')
;Piaggio-Jupiter: License production by Piaggio
Applications
The Jupiter is probably best known for powering theHandley Page H.P.42
The Handley Page H.P.42 and H.P.45 were four-engine biplane airliners designed and manufactured by British aviation company Handley Page, based in Radlett, Hertfordshire. It held the distinction of being the largest airliner in regular use in ...
airliners, which flew the London-Paris route in the 1930s. Other civilian uses included the de Havilland Giant Moth
The de Havilland DH.61 Giant Moth was a 1920s British large single-engined biplane transport built by de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome, Edgware. Intended primarily for use in Australia, a number were also shipped to Canada.
Design
Follow ...
and de Havilland Hercules
The de Havilland DH.66 Hercules was a 1920s British seven-passenger, three-engined airliner built by de Havilland Aircraft Company at Stag Lane Aerodrome. As a more modern replacement for the Airco DH.10 Amiens used on the RAF's airmail se ...
, the Junkers G 31
The Junkers G 31 was an advanced tri-motor airliner produced in small numbers in Germany in the 1920s. Like other Junkers types, it was an all-metal, low-wing cantilever monoplane. In the mid-1920s, the all-metal construction and an aerodynamical ...
and the huge Dornier Do X
The Dornier Do X was the largest, heaviest, and most powerful flying boat in the world when it was produced by the Dornier company of Germany in 1929. First conceived by Claude Dornier in 1924, planning started in late 1925 and after over 240 ...
flying boat, which used no less than twelve engines.
Military uses were less common, but included the parent company's Bristol Bulldog
The Bristol Bulldog is a British Royal Air Force single-seat biplane fighter designed during the 1920s by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. More than 400 Bulldogs were produced for the RAF and overseas customers, and it was one of the most fa ...
, as well as the Gloster Gamecock
The Gloster Gamecock was a biplane fighter designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Gloster.
The Gamecock was a development of the earlier Grebe Mk III, an early interwar fighter procured by the Royal Air Force (RAF). Wor ...
and Boulton Paul Sidestrand
The Boulton Paul P.29 Sidestrand was a twin-engine biplane medium bomber of the Royal Air Force. Designed for daylight operations, it was manoeuvrable and provided with three defensive gun positions. Named after a village on the Norfolk coast n ...
. It was also found in prototypes around the world, from Japan to Sweden.
By 1929 the Bristol Jupiter had flown in 262 different aircraft types,
''Note:''
Cosmos Jupiter
*Bristol Badger
The Bristol Badger was designed to meet a British need for a two-seat fighter-reconnaissance aeroplane at the end of the First World War. Three Badgers were delivered to the Air Board to develop air-cooled radial engines, particularly that ...
* Bristol Bullet
The Bristol Type 32 Bullet was a British biplane racing aircraft. It was designed in 1919 by Frank Barnwell as a high-speed testbed for the Jupiter engine being developed in Bristol by Roy Fedden for the Cosmos Engineering company, and also to ...
* Sopwith Schneider
The Sopwith Tabloid and Sopwith Schneider (floatplane) were British biplanes, originally designed as sports aircraft and later adapted for military use. They were among the first successful types to be built by the Sopwith Aviation Company. The ...
* Westland Limousine
The Westland Limousine was a 1920s British single-engined four-seat light transport aircraft built by Westland Aircraft.
History
At the end of World War I, the prospect of an expanding aviation market led Westland Aircraft to design a light ...
Bristol Jupiter
*Aero A.32
The Aero A.32 was a biplane built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1920s for army co-operation duties including reconnaissance and tactical bombing. While the design took the Aero A.11 as its starting point (and was originally designated A.11J), ...
* Airco DH.9
* Arado Ar 64
* Avia BH-25
* Avia BH-33E
* Bernard 190
The Bernard 190 or Bernard-Hubert 190 was a French airliner of 1928. It was a high-wing cantilever monoplane of conventional configuration, based on the Bernard 18. Compared with its predecessor, it kept the same basic design but featured rede ...
* Blériot-SPAD 51
* Blériot-SPAD S.56
The Blériot-SPAD S.56 was a family of France, French airliners developed in the 1920s as various refinements of the Blériot-SPAD S.33, S.33 design. All S.56 versions shared two new features: the first was a newly designed, all-metal wing, repl ...
* Boulton & Paul Bugle
The Boulton & Paul Bugle was a heavy bomber designed and produced by the British manufacturing group Boulton & Paul.
There were two variants; the Bugle I with 400 hp (298 kW) Bristol Jupiter II radial engines (five built) and the N ...
* Boulton Paul P.32
The sole Boulton & Paul P.32 was a British three-engined biplane built to an Air Ministry specification for a long range night bomber. A lack of engine availability slowed construction and by the time it went for tests the thinking on bomber ty ...
* Boulton Paul Partridge
* Boulton Paul Sidestrand
The Boulton Paul P.29 Sidestrand was a twin-engine biplane medium bomber of the Royal Air Force. Designed for daylight operations, it was manoeuvrable and provided with three defensive gun positions. Named after a village on the Norfolk coast n ...
* Blackburn Beagle
The Blackburn B.T.1 Beagle was a British single-engine, two-seat biplane bomber/torpedo aircraft from 1928. Designed to Air Ministry specifications which led to no contracts for any manufacturer, only one Beagle was built.
Development
The B.T. ...
* Blackburn Nile
* Blackburn Ripon
The Blackburn T.5 Ripon was a carrier-based torpedo bomber and reconnaissance biplane designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Blackburn Aircraft. It was the basis for both the license-produced Mitsubishi B2M and the improved ...
* Bristol Badger
The Bristol Badger was designed to meet a British need for a two-seat fighter-reconnaissance aeroplane at the end of the First World War. Three Badgers were delivered to the Air Board to develop air-cooled radial engines, particularly that ...
* Bristol Badminton
__NOTOC__
The Bristol Type 99 Badminton was a 1920s British single-seat racing biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and designed by F.S. Barnwell.Jackson 1973, page 308
Design and development
The Badminton was a single-seat single- ...
* Bristol Bagshot
The Bristol Bagshot, also known as the Type 95, was a prototype heavily armed British fighter built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and first flown in 1927. Flight testing revealed serious problems, and the project was abandoned.
Developme ...
* Bristol Beaver
* Bristol Bloodhound
The Bristol Bloodhound is a British ramjet powered surface-to-air missile developed during the 1950s. It served as the UK's main air defence weapon into the 1990s and was in large-scale service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the forces of f ...
* Bristol Boarhound
The Bristol Boarhound was a British army cooperation and liaison aircraft of the 1920s. It was a two-seat biplane with wings of equal span, of steel frame construction with fabric covering.
Design and development
The Boarhound was built as a ...
* Bristol Brandon
* Bristol Bulldog
The Bristol Bulldog is a British Royal Air Force single-seat biplane fighter designed during the 1920s by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. More than 400 Bulldogs were produced for the RAF and overseas customers, and it was one of the most fa ...
* Bristol Bullfinch
The Bristol Bullfinch was an experimental British military aircraft first flown in 1922. Variants were built as both parasol wing monoplanes and biplanes, but both versions proved unsuccessful, and only the three prototypes were built.
Develop ...
* Bristol Jupiter Fighter
The Bristol Type 76 Jupiter Fighter and Type 89 Trainer were derivatives of the British fighter of the First World War (the F.2 Fighter), powered by Bristol Jupiter radial engines. While unsuccessful as a fighter, it was used as an advanced tr ...
* Bristol Seely
The Bristol Seely was entered into an Air Ministry competition for safe civil aeroplanes held in 1920. It was a single-engine biplane with accommodation for one passenger. After the competition, the single Seely was used as a testbed for the Br ...
* Bristol Type 72
* Bristol Type 75
* Bristol Type 76
* Bristol Type 89
* Bristol Type 92
The Bristol Type 92, sometimes known as the Laboratory biplane, was an aircraft built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company to address the differences between wind tunnel cowling models and full scale cowling for radial engines and was designed as a ...
* Bristol Type 118
The Bristol Type 118 was a general-purpose military aircraft, a two-seat biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in the early 1930s, powered by a Bristol Mercury radial engine and aimed at overseas markets. The Type 120 was a Bristol Peg ...
* de Havilland Dingo
* de Havilland DH.72
The de Havilland DH.72 was a large British three-engined biplane bomber, designed as a Vickers Virginia replacement. It did not go into production.
Development
Air Ministry specification B.22/27 was for a Vickers Virginia night bomber replac ...
* de Havilland DH.50
The de Havilland DH.50 was a 1920s British large single-engined biplane transport built by de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome, Edgware, and licence-built in Australia, Belgium, and Czechoslovakia.
History
In the early 1920s, Geoffrey de Havi ...
* de Havilland Dormouse
The de Havilland DH.42 Dormouse and its two variants the de Havilland DH.42A Dingo I and II were two-seat single-engined biplanes designed for fighter-reconnaissance and army cooperation roles. They did not achieve production.
Development
Apa ...
* de Havilland Hercules
The de Havilland DH.66 Hercules was a 1920s British seven-passenger, three-engined airliner built by de Havilland Aircraft Company at Stag Lane Aerodrome. As a more modern replacement for the Airco DH.10 Amiens used on the RAF's airmail se ...
* de Havilland Hound
The de Havilland DH.65 Hound was a 1920s British two-seat day bomber built by de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome.
History
The Hound was designed as a two-seat general purpose biplane, a private venture to meet Air Ministry Specification 1 ...
* de Havilland Giant Moth
The de Havilland DH.61 Giant Moth was a 1920s British large single-engined biplane transport built by de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome, Edgware. Intended primarily for use in Australia, a number were also shipped to Canada.
Design
Follow ...
* de Havilland Survey
* Dornier Do 11
The Dornier Do 11 was a Nazi Germany, German heavy bomber, developed in secret in the early 1930s. It was originally called the Dornier F before being renamed by the ''Reich Air Ministry, Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) in 1933, and was consid ...
* Dornier Do J
The Dornier Do J ''Wal'' ("whale") is a twin-engine German flying boat of the 1920s designed by '' Dornier Flugzeugwerke''. The Do J was designated the Do 16 by the Reich Air Ministry (''RLM'') under its aircraft designation system of 1933.
...
* Dornier Do X
The Dornier Do X was the largest, heaviest, and most powerful flying boat in the world when it was produced by the Dornier company of Germany in 1929. First conceived by Claude Dornier in 1924, planning started in late 1925 and after over 240 ...
* Fairey III
The Fairey Aviation Company Fairey III was a family of British reconnaissance biplanes that enjoyed a very long production and service history in both landplane and seaplane variants. First flying on 14 September 1917, examples were still in us ...
F
* Fairey Ferret
The Fairey Ferret was a 1930s British general-purpose biplane designed and built by the Fairey Aviation Company. It performed well in trials but was not ordered into production.
Development
The Ferret was designed to meet a Fleet Air Arm requi ...
* Fairey Flycatcher
The Fairey Flycatcher was a British single-seat biplane carrier-borne fighter aircraft made by Fairey Aviation Company which served from 1923 to 1934. It was produced with a conventional undercarriage for carrier use, although this could be exc ...
* Fairey Hendon
The Fairey Hendon was a British monoplane, heavy bomber of the Royal Air Force, designed by Fairey Aviation in the late 1920s. The aircraft served in small numbers with one squadron of the RAF between 1936 and 1939. It was the first all-metal lo ...
* Fokker C.V
The Fokker C.V was a Dutch light reconnaissance and bomber biplane aircraft manufactured by Fokker. It was designed by Anthony Fokker and the series manufacture began in 1924 at Fokker in Amsterdam.
Development
The C.V was constructed in the earl ...
* Fokker F.VII
The Fokker F.VII, also known as the Fokker Trimotor, was an airliner produced in the 1920s by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker, Fokker's American subsidiary Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, and other companies under licence.
Design and d ...
A
* Fokker F.VIII
The Fokker F.VIII (or F.8) was a large twin-engined airliner designed and produced by the Netherlands, Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker in the 1920s.
It was similar overall to the Fokker F.VII which was trimotor, but the F.VIII was not a trimoto ...
* Fokker F.IX
The Fokker F.IX was an airliner developed in the Netherlands in the late 1920s, intended to provide KLM with an aircraft suitable for regular services to the Dutch East Indies. When the onset of the Great Depression forced the postponement of t ...
* Gloster Gambet
* Gloster Gamecock
The Gloster Gamecock was a biplane fighter designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Gloster.
The Gamecock was a development of the earlier Grebe Mk III, an early interwar fighter procured by the Royal Air Force (RAF). Wor ...
* Gloster Gnatsnapper
The Gloster SS.35 Gnatsnapper was a British naval biplane fighter design of the late 1920s. Two prototypes were built but the type did not enter production.
Design and development
The Gnatsnapper was a submission to Air Ministry specification ...
* Gloster Goldfinch
* Gloster Goral
The Gloster Goral was a single-engined two-seat biplane built to an Air Ministry contract for a general-purpose military aircraft in the late 1920s. It did not win the contest and only one was built.
Development
In 1927, driven by conflicting p ...
* Gloster Goring
The Gloster Goring was a single-engined two-seat biplane designed to meet 1926 Air Ministry specifications for a day/torpedo bomber. It was not put into production and the one aircraft built served later as an engine testbed.
Development
Early ...
* Gloster Grebe
The Gloster Grebe was developed by the Gloster Aircraft Company from the Gloster Grouse (an experimental aircraft later developed as a trainer), and was the Royal Air Force's first post-First World War fighter aircraft, entering service in 1923 ...
* Gloster Mars
The Nieuport Nighthawk was a British fighter aircraft developed by the Nieuport & General Aircraft company for the Royal Air Force towards the end of the First World War. Although ordered into production before the aircraft first flew, it did n ...
* Gloster Survey
The Gloster A.S.31 Survey was a 1920s British photo-survey biplane developed by the Gloster Aircraft Company from the de Havilland DH.67 design project.
Background
In 1926, the Aircraft Operating Company, an official contractor to the British ...
* Gourdou-Leseurre LGL.32
* Handley Page Clive
* Handley Page Hampstead
* Handley Page Hare
__NOTOC__
The Handley Page HP.34 Hare was a British two-seat high-altitude day bomber designed and built at Cricklewood by Handley Page. It was designed by Harold Boultbee to meet the requirements of List Of Air Ministry Specifications#1920-192 ...
* Handley Page Hinaidi
The Handley Page Hinaidi was one of two twin-engine bombers built by Handley Page that served with the Royal Air Force between 1925 and 1935. The aircraft was developed from the Handley Page Hyderabad and named after Hinaidi, an RAF station in ...
* Handley Page HP.12
* Handley Page H.P.42
The Handley Page H.P.42 and H.P.45 were four-engine biplane airliners designed and manufactured by British aviation company Handley Page, based in Radlett, Hertfordshire. It held the distinction of being the largest airliner in regular use in ...
* Hawker Duiker
The Hawker Duiker was an unusual and unsuccessful aircraft. It was the first design at Hawker Aircraft, Hawker under a new chief designer, Captain Thomson, in 1922. Much of the equipment and parts were proprietary and made by another aircraft com ...
* Hawker Harrier
The Hawker Harrier was an experimental biplane torpedo bomber aircraft built by Hawker Aircraft to a specification issued in the 1920s for the RAF.
Development
In 1925, the British Air Ministry laid down specifications for a high altitude b ...
* Hawker Hart
The Hawker Hart is a British two-seater biplane light bomber aircraft that saw service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was designed during the 1920s by Sydney Camm and manufactured by Hawker Aircraft. The Hart was a prominent British aircraf ...
* Hawker Hawfinch
The Hawker Hawfinch was a British single-engined biplane fighter of the 1920s. It was unsuccessful, with the Bristol Bulldog being selected instead.
Development
The Hawker Hawfinch fighter aircraft was designed in 1925 as a replacement for both ...
* Hawker Hedgehog
The Hawker Hedgehog was a three-seat reconnaissance biplane, to be used for naval scouting, produced to meet List of Air Ministry specifications, Air Ministry Specification 37/22.
It was designed in 1923, and had its first flight the next year, ...
* Hawker Heron
The Hawker Heron was the first fighter aircraft designed at Hawker Aircraft with a basically metal structure. Sydney Camm was the chief designer that introduced what became the typical structure for all Hawker aircraft until the introduction of ...
* Hawker Woodcock
The Hawker Woodcock was a British single-seat fighter built by the Hawker Engineering Company as the first fighter to be produced by Hawker Engineering (the successor to Sopwith Aviation). It was used by the RAF as a night fighter in the 1920 ...
* Junkers F.13
The Junkers F 13 was the world's first all-metal transport aircraft, developed in Weimar Republic, Germany at the end of World War I. It was an advanced Cantilever#Aircraft, cantilever-wing monoplane, with enclosed accommodation for four passenge ...
* Junkers G 31
The Junkers G 31 was an advanced tri-motor airliner produced in small numbers in Germany in the 1920s. Like other Junkers types, it was an all-metal, low-wing cantilever monoplane. In the mid-1920s, the all-metal construction and an aerodynamical ...
* Junkers W 34
The Junkers W 34 was a German-built, single-engine, passenger and transport aircraft. Developed in the 1920s, it was taken into service in 1926. The passenger version could take a pilot and five passengers. The aircraft was developed from the J ...
* Parnall Plover
The Parnall Plover was a British single-seat naval fighter aircraft of the 1920s. Designed and built by George Parnall & Co. for use on Royal Navy aircraft carriers, it was ordered into small-scale production but after extensive evaluation, t ...
* PZL P.7
The PZLP.7 was a Polish gull wing monoplane fighter aircraft designed in the early 1930s at the PZL factory in Warsaw. It was the main fighter of the Polish Air Force between 1933 and 1935. The PZLP.7 was replaced in Polish service by its follow-u ...
* Saunders Medina
__NOTOC__
The Saunders A.4 Medina was a British flying boat built by S.E. Saunders at East Cowes, Isle of Wight.
Development
The Medina was built for the Air Council between 1925 and 1926 and was a plywood-covered wooden flying boat powered b ...
* Saunders Severn
The Saunders Severn was a three-engined biplane flying boat intended for maritime patrol duties. It performed well but was fragile and unreliable. Only one was built.
Design and development
The Saunders A.7 Severn was the last flying boat des ...
* Short Calcutta
The Short Calcutta or S.8 was a civilian biplane airliner flying boat made by Short Brothers.
Design and development
The Calcutta biplane flying boat originated from an Imperial Airways requirement to service the Mediterranean legs of its servi ...
* Short Chamois
* Short Gurnard
The Short Gurnard was a single-engined two-seat biplane naval fighter, built in the United Kingdom to an Air Ministry specification in 1929. It failed to win production orders and only two flew.
Design and development
The duralumin-framed S ...
* Short Kent
The Short S.17 Kent was a British four-engined 15-seat biplane luxury flying boat airliner, designed and built by Short Brothers, Shorts to meet a requirement from Imperial Airways for an aircraft with greater range than the Short Calcutta.
The ...
* Short Rangoon
* Short Scylla
The Short L.17 Scylla was a British four-engined 39-seat biplane airliner designed and built by Short Brothers at the request of Imperial Airways to supplement the Handley Page H.P.42 fleet already in service after Handley Page quoted an excessi ...
* Short Springbok
The Short Springbok was a two-seat, all-metal reconnaissance biplane produced for the British Air Ministry in the 1920s. All together six aircraft of the Springbok design were built but none entered service with the armed forces.
Design
The Sp ...
* Short S.6 Sturgeon
* Short Valetta
The Short S.11 Valetta was a 1930s United Kingdom, British passenger monoplane designed and built by Short Brothers at Rochester.
Development
The Valetta was designed and built for the Air Ministry to enable comparisons between a floatplane/l ...
* Supermarine Seagull
* Supermarine Solent
* Supermarine Southampton
The Supermarine Southampton was a flying boat of the interwar period designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Supermarine. It was one of the most successful flying boats of the era.
The Southampton was derived from the experime ...
* Svenska Aero Jaktfalken
Svenska Aero Jaktfalken ("Gyrfalcon") was a Swedish biplane fighter aircraft, constructed in the late 1920s. The aircraft was first manufactured by Svenska Aero and later by AB Svenska Järnvägsverkstädernas Aeroplanavdelning (ASJA).
Histor ...
* Tupolev I-4
The Tupolev I-4 was a Soviet sesquiplane single-seat fighter. It was conceived in 1927 by Pavel Sukhoi as his first aircraft design for the Tupolev design bureau, and was the first Soviet all-metal fighter.
Design and development
After the first ...
* Vickers F.21/26
* Vickers F.29/27
* Vickers Jockey
The Vickers Type 151 Jockey was an experimental low-wing monoplane interceptor fighter powered by a radial engine. It was later modified into the Type 171 Jockey II, which had a more powerful engine and detail improvements. Only one was built; ...
* Vickers Type 143
The Vickers Type 143 or Bolivian Scout was a British single-seat fighter biplane designed and built by Vickers in 1929-1930. Six were built for Bolivia in 1930, which used the survivors in the Chaco War against Paraguay.
Design and developm ...
* Vickers Type 150
* Vickers Valiant
The Vickers Valiant was a British high-altitude jet bomber designed to carry nuclear weapons, and in the 1950s and 1960s was part of the Royal Air Force's "V bomber" strategic deterrent force. It was developed by Vickers-Armstrongs in response ...
* Vickers Vellore
The Vickers Vellore was a large biplane designed as a freight and mail carrier, in single-engined and twin-engined versions, which saw limited use as freighters and long-range experimental aircraft. A final variant with a broader fuselage, the ...
* Vickers Vellox
* Vickers Vespa
The Vickers Vespa was a British army cooperation biplane designed and built by Vickers Limited in the 1920s. While not adopted by Britain's Royal Air Force, small numbers were bought by the Irish Free State and Bolivia, the latter of which used ...
* Vickers Viastra
* Vickers Victoria
The Vickers Type 56 Victoria was a British biplane Cargo aircraft, freighter and troop transport aircraft used by the Royal Air Force. The Victoria flew for the first time in 1922 and was selected for production over the Armstrong Whitworth Awan ...
* Vickers Vildebeest
The Vickers Vildebeest and the similar Vickers Vincent were two very large two- to three-seat single-engined British biplanes designed and built by Vickers and used as light bombers, torpedo bombers and in army cooperation roles. First flown i ...
* Vickers Vimy
The Vickers Vimy was a British heavy bomber aircraft developed and manufactured by Vickers Limited. Developed during the latter stages of the First World War to equip the Royal Flying Corps (RFC), the Vimy was designed by Reginald Kirshaw "Rex" ...
* Vickers Vimy Trainer
* Vickers Wibault Scout
* Villiers 26
The Villiers 26 was a French naval seaplane which used Handley Page slats to provide the wide speed range required for escort and patrol duties. It was tested, behaved satisfactorily but received no production order.
Design
The 1928 Villiers X ...
* Westland Interceptor
The Westland Interceptor was a fighter developed by the British company Westland Aircraft to Air Ministry Specification ''F.20/27''. When tested in 1929 and 1930, it showed unsatisfactory handling characteristics and was rejected by the RAF in ...
* Westland Wapiti
The Westland Wapiti was a British two-seat general-purpose military single-engined biplane of the 1920s. It was designed and built by Westland Aircraft Works to replace the Airco DH.9A in Royal Air Force service.
First flying in 1927, the Wa ...
* Westland Westbury
The Westland Westbury was a British twin-engined fighter prototype of 1926. Designed by Westland Aircraft it never entered service but played a useful role in the testing of the COW 37 mm gun. Only the two prototypes were completed.
Developmen ...
* Westland Witch
The Westland Witch was an unsuccessful British bomber prototype, first flown in 1928. Only a single aircraft of this type was built.
Development
The Witch was developed to List of Air Ministry specifications, specification 23/25 for a single-e ...
* Westland-Houston PV.3
Gnome-Rhône Jupiter
* Bernard SIMB AB 12 *Blanchard BB-1
__NOTOC__
The Blanchard BB-1 was a 1920s French racing flying-boat designed and built by Société des Avions Blanchard to compete in Schneider Trophy
The Coupe d'Aviation Maritime Jacques Schneider, also known as the Schneider Trophy, Schneid ...
* Breguet 19 Breguet or Bréguet may refer to:
* Breguet (watch), watch manufacturer
**Abraham-Louis Breguet (1747–1823), Swiss watchmaker
**Louis-François-Clement Breguet (1804–1883), French physicist, watchmaker, electrical and telegraph work
* Bréguet ...
* Fizir F1M-Jupiter
* Latécoère 6
The Latécoère 6 was a French four-engined biplane bomber of the early 1920s. It was of advanced all-metal construction and probably the first aircraft to use geodetic construction. Only one was built.
Design and development
In October 1920 Lat ...
* Lioré et Olivier LeO H-15
The Lioré et Olivier Leo H-15 was a French twelve-seat civil flying boat, flown in a national contest in 1926. It did not win but set two load carrying records, one a world record.
Design and development
In 1926 the French government offered ...
* Potez 29/4
* Wibault Wib.220
* Denhaut Hy.479
The Denhaut Hy.479 was a French flying boat flown in 1926 and intended to be suitable for commercial or military applications. Only one, in military configuration, was built and was sometimes known as the France-Aviation Denhaut.
Design and deve ...
Shvetsov M-22
*Kalinin K-5
The Kalinin K-5 was an airliner produced in the Soviet Union in the 1930s, built in larger quantities than any other Soviet airliner of its time, with some 260 aircraft constructed. It was a conventional, high-wing, strut-braced monoplane with a ...
* Kalinin K-12
The Kalinin K-12 was a proof-of-concept aircraft developed by the Kalinin Design Bureau in the 1930s.
Design and development
The K-12 was intended as a tailless bomber aircraft. Also called the Kalinin BS-2 or the ''Zhar-Ptitsa'' ("Firebird"), it ...
* Polikarpov I-5
The Polikarpov I-5 was a single-seat biplane which became the primary Soviet fighter between its introduction in 1931 through 1936, after which it became the standard advanced trainer. Following Operation Barbarossa, which destroyed much of the ...
* Polikarpov I-15
The Polikarpov I-15 (russian: И-15) was a Soviet biplane fighter aircraft of the 1930s. Nicknamed ''Chaika'' (''russian: Чайка'', "Seagull") because of its gulled upper wings,Gunston 1995, p. 299.Green and Swanborough 1979, p. 10. it was o ...
* Polikarpov I-16
The Polikarpov I-16 (russian: Поликарпов И-16) is a Soviet single-engine single-seat fighter aircraft of revolutionary design; it was the world's first low-wing cantilever monoplane fighter with retractable landing gear to attain ope ...
* Tupolev I-4
The Tupolev I-4 was a Soviet sesquiplane single-seat fighter. It was conceived in 1927 by Pavel Sukhoi as his first aircraft design for the Tupolev design bureau, and was the first Soviet all-metal fighter.
Design and development
After the first ...
* Yakovlev AIR-7
Engines on display
* A Bristol Jupiter VI is on static display atAerospace Bristol
Aerospace Bristol is an aerospace museum at Filton, to the north of Bristol, England, U.K. The project is run by the Bristol Aero Collection Trust and houses a varied collection of exhibits, including Concorde ''Alpha Foxtrot'', the final Conco ...
in the former Bristol Aeroplane Company factory complex in Filton, a suburb of Bristol, United Kingdom.
* A Bristol Jupiter VIIF is on static display at the Shuttleworth Collection
The Shuttleworth Collection is a working aeronautical and automotive collection located at the Old Warden Aerodrome, Old Warden in Bedfordshire, England. It is the oldest in the world and one of the most prestigious, due to the variety of old a ...
in Old Warden, United Kingdom.
* A Bristol Jupiter VIIIF is on static display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center
The Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, also called the Udvar-Hazy Center, is the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum (NASM)'s annex at Washington Dulles International Airport in the Chantilly area of Fairfax County, Virginia. It holds numerous ...
of the National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the Nat ...
at Washington Dulles International Airport in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States.
* A Bristol Bulldog
The Bristol Bulldog is a British Royal Air Force single-seat biplane fighter designed during the 1920s by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. More than 400 Bulldogs were produced for the RAF and overseas customers, and it was one of the most fa ...
complete with a Jupiter VIIFP engine is on static display at the Royal Air Force Museum London
The Royal Air Force Museum London (also commonly known as the RAF Museum) is located on the former Hendon Aerodrome. It includes five buildings and hangars showing the history of aviation and the Royal Air Force. It is part of the Royal Air Forc ...
in Hendon, United Kingdom.
Specifications (Jupiter XFA)
See also
References
Bibliography
* * Bridgman, L. (ed.) ''Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II''. New York: Crescent Books, 1998. * Lumsden, Alec. ''British Piston Engines and their Aircraft''. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. . * Gunston, Bill. ''Development of Piston Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 2006. * Gunston, Bill. ''World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 1989.Further reading
* Gunston, Bill. ''By Jupiter! The Life of Sir Roy Fedden''. The Johns Hopkins University Press.External links
* Contemporary article on Cosmos Engineering's air-cooled radial engines. Photos of the Cosmos Jupiter are opage 870
and a short technical description is o
{{Walter aeroengines Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
1910s aircraft piston engines