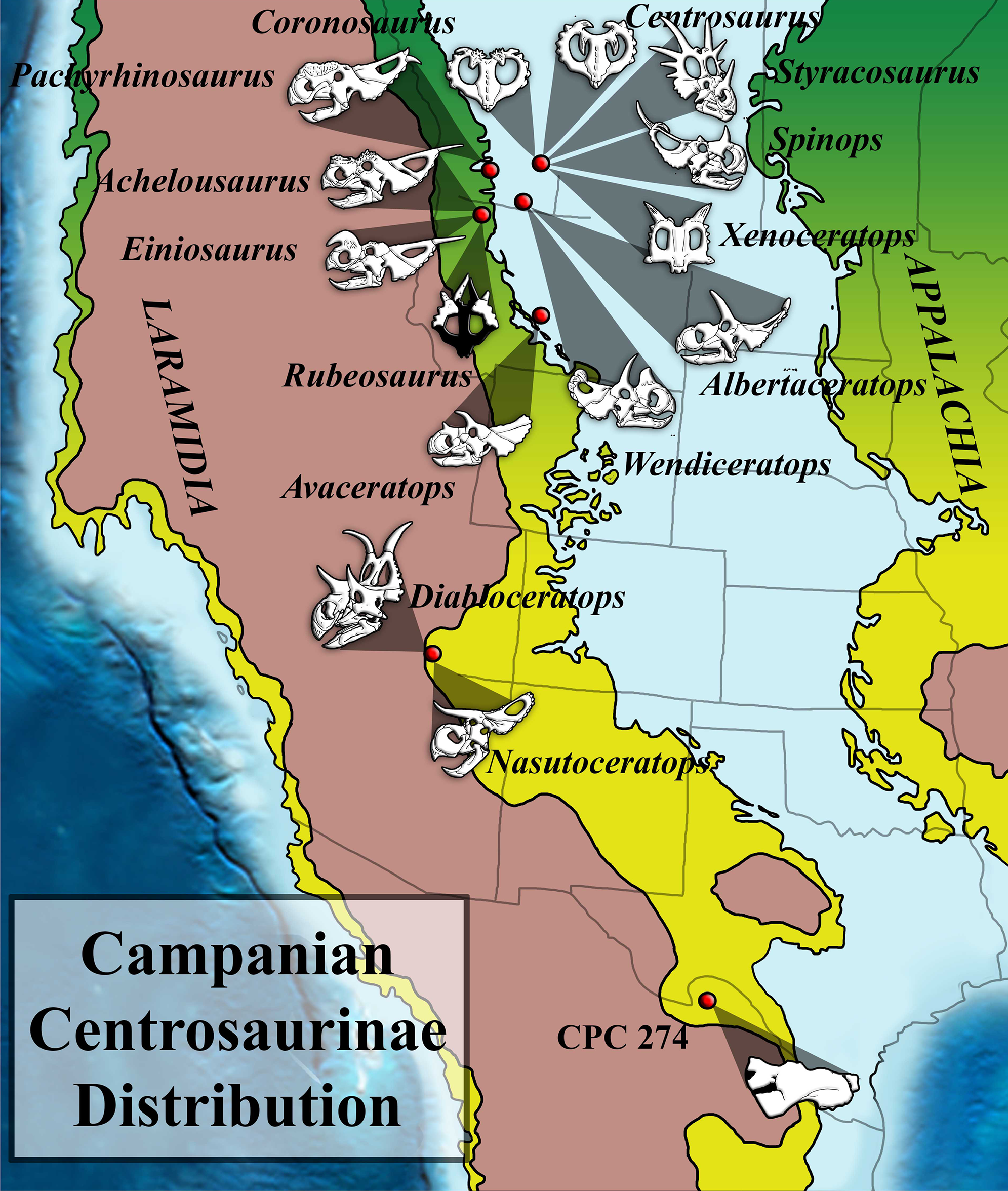
Coronosaurus Brinkmani on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Coronosaurus'' is a
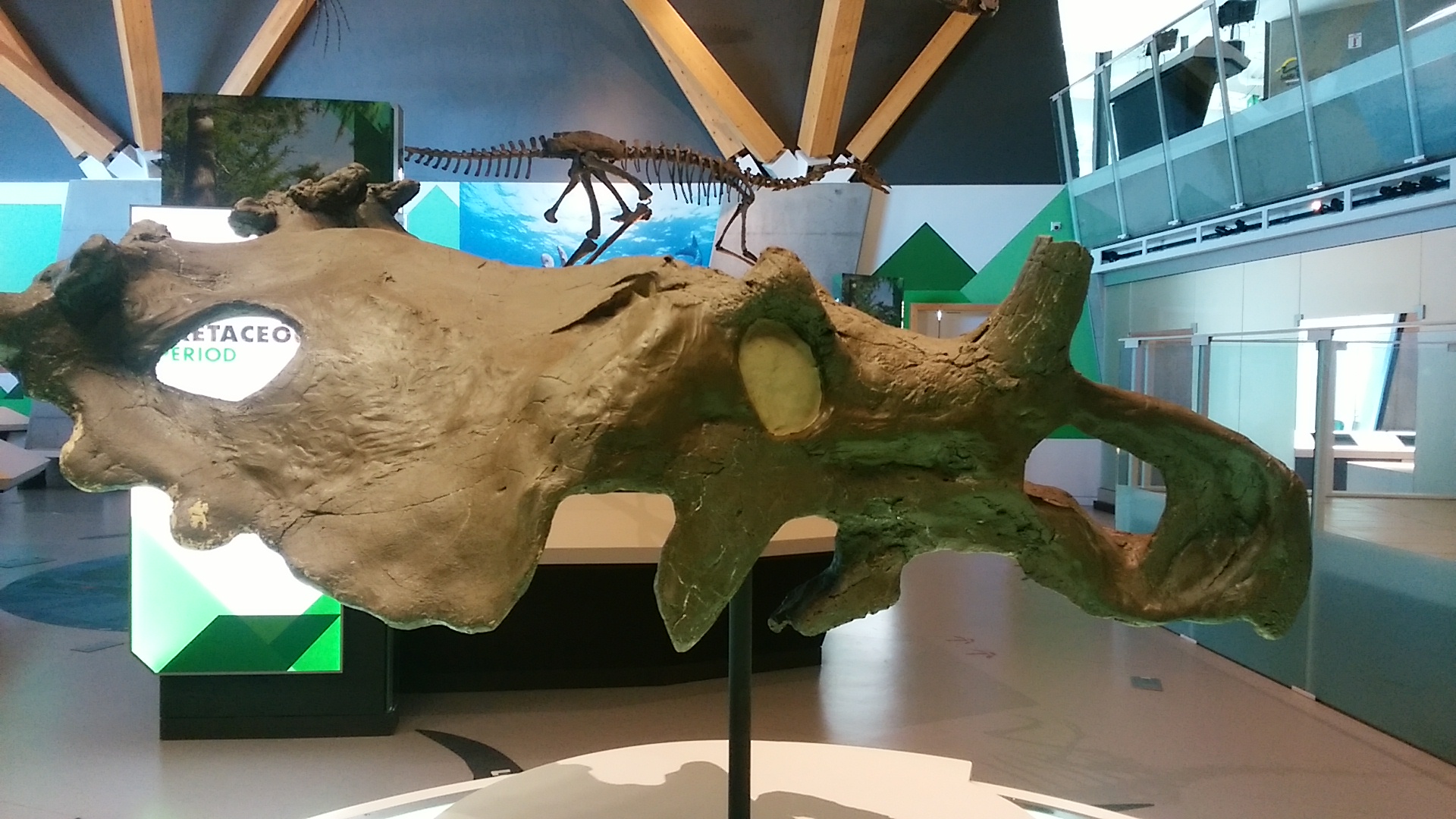 ''Coronosaurus'' is known from two
''Coronosaurus'' is known from two
 ''Coronosaurus'' is a medium-sized
''Coronosaurus'' is a medium-sized
 Studies suggest that the
Studies suggest that the
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of centrosaurine
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Al ...
ceratopsian
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s which lived in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
, in the middle Campanian stage. Its remains, two bone beds
A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. ...
, were discovered by Phillip J. Currie in the Oldman Formation of Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, and its type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
and only species, ''Coronosaurus brinkmani'', was first described in 2005, as a new species within the genus '' Centrosaurus''. Later studies questioned the presence of a direct relationship, and in 2012 it was named as a separate genus. ''Coronosaurus'' means "crowned lizard", coming from "''corona''", Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for crown, and "''sauros''", Greek for lizard; this name refers to the unique, crown-like shape of the horns on the top of its frill.
Like other ceratopsids
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are k ...
, ''Coronosaurus'' had a large frill and horns on its head. These include a small pair of brow horns over its eyes, a large nasal horn on its snout, and, unique among ceratopsians, irregular, spiky bone masses on its frill. Growing up to around long and in weight, it was mid-sized for its kind. The genus is classified as a member of the Centrosaurini, a group of derived centrosaurines which has also been found include taxa such as ''Styracosaurus
''Styracosaurus'' ( ; meaning "spiked lizard" from the Ancient Greek / "spike at the butt-end of a spear-shaft" and / "lizard") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period (Campanian stage), about 75.5 to 74.5&nbs ...
'', '' Spinops'', ''Rubeosaurus
''Styracosaurus'' ( ; meaning "spiked lizard" from the Ancient Greek / "spike at the butt-end of a spear-shaft" and / "lizard") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period (Campanian stage), about 75.5 to 74.5 ...
'', and '' Centrosaurus'', the genus it was originally placed within.
Discovery and naming
 ''Coronosaurus'' is known from two
''Coronosaurus'' is known from two bone bed
A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. ...
s, BB 138 and MRR BB, located in the upper unit of the Oldman Formation, of the Belly River Group, excavated by Philip Currie between 1996 and 2000.M.J. Ryan and A.P. Russell, 2003, "New centrosaurine ceratopsids from the late Campanian of Alberta and Montana and a review of contemporaneous and regional patterns of centrosaurine evolution", ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' 23(3): 91A Most of the ceratopsid material, if not all, from BB 138 in Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, and the MRR BB near Warner, Alberta
Warner is a village in Alberta, Canada. It is surrounded by the County of Warner No. 5, approximately south of Lethbridge. Warner is a farming community. Warner is situated at the intersection of Highway 4 and Highway 36, about 38 km nor ...
, was referred to ''C. brinkmani''. Bone bed 138 is located approximately from Brooks, Alberta
Brooks is a city in southeast Alberta, Canada that is surrounded by the County of Newell. It is located on Highway 1 (Trans-Canada Highway) and the Canadian Pacific Railway, approximately southeast of Calgary, and northwest of Medicine Hat. Th ...
, in the Oldman Formation and below the contact with the Dinosaur Park Formation. The MRR BB located approximately southwest of BB 138, is also from the Oldman Formation. These bone beds date to the middle Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
period. Both the specimens and the precise localities are archived at the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology
The Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology (RTMP, and often referred to as the Royal Tyrrell Museum) is a palaeontology museum and research facility in Drumheller, Alberta, Canada. The museum was named in honour of Joseph Burr Tyrrell, and is situ ...
, in Drumheller, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
.
Michael J. Ryan and Anthony P. Russell described and named the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
, then as '' Centrosaurus brinkmani'', in 2005
File:2005 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: Hurricane Katrina in the Gulf of Mexico; the Funeral of Pope John Paul II is held in Vatican City; "Me at the zoo", the first video ever to be uploaded to YouTube; Eris was discovered in ...
. Later studies, however, did not recover a monophyletic clade with the genus' type species ''Centrosaurus apertus'' in phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analyses. Due to this, Ryan, David C. Evans
David Cannon Evans (February 24, 1924 – October 3, 1998) was the founder of the computer science department at the University of Utah and co-founder (with Ivan Sutherland) of Evans & Sutherland, a pioneering firm in computer graphics hardwar ...
and Kieran M. Shepherd erected the genus ''Coronosaurus'' for the species in 2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gather ...
. The generic name is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''corona'', meaning "crown" in reference to the multiple occurrences of extra epiparietals that cover the posterior margin of its parietal, giving it a crown-like appearance, and ''saurus'' (Latinized from Greek ''sauros''), meaning "lizard". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
''brinkmani'' honors Donald Brinkman, for his research in palaeoecology
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
of the Late Cretaceous environments of Alberta. In 2020, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
, Ryan was asked about the naming of the dinosaur, and stated he came up with it because its frill ornamentation made him think of the corona of the sun. He also stated his fellow students at the time had jokingly called it ‘broccoli-ceratops’.
The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
of ''Coronosaurus'' is TMP TMP can refer to any of the following:
Chemistry
* 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine, an organic chemistry reagent
* Thymidine monophosphate, a nucleotide
* Trimethoprim, an antibiotic
* Trimethyl phosphate, a solvent
* Trimethylolpropane, a precurso ...
2002.68.1. It is a large adult-sized parietal with an almost complete midline bar and a partial posterior bar with left P1–P3 processes and the partially eroded right P1-P2. The specimen lacks the extreme anterior margin of the midline bar that forms the posterior wall of the frontal fontanelle and the paper-thin lateral margins that define the medial margins of the supraorbital foramina. Other significant specimens according to Ryan & Russell (2005) include TMP 2002.68.3 (a parietal), TMP 2002.68.10 (a postorbital), and TMP 2002.68.5 ( supraorbitals).
Description
 ''Coronosaurus'' is a medium-sized
''Coronosaurus'' is a medium-sized centrosaurine
Centrosaurinae (from the Greek, meaning "pointed lizards") is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs, a group of large quadrupedal ornithischians. Centrosaurine fossil remains are known primarily from the northern region of Laramidia (modern day Al ...
ceratopsid. Gregory S. Paul in 2010 estimated its body length at and its weight at .Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 260 It had as an adult inflated supraorbital horncores — the "brow horns" above the eye sockets — but not elongated as in ''Zuniceratops
''Zuniceratops'' ('Zuni-horned face') was a ceratopsian dinosaur from the mid Turonian of the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now New Mexico, United States. It lived about 10 million years earlier than the more familiar horned Ceratopsidae ...
'', chasmosaurine
Chasmosaurinae is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs. They were one of the most successful groups of herbivores of their time. Chasmosaurines appeared in the early Campanian, and became extinct, along with all other non-avian dinosaurs, during t ...
s, and more basal centrosaurines (like ''Albertaceratops
''Albertaceratops'' (meaning "Alberta horned face") was a genus of centrosaurine horned dinosaur from the middle Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Oldman Formation of Alberta, Canada.
Description
''Albertaceratops'' is unusual in combining long ...
'' and '' Diabloceratops''), that project laterally (to the sides) over the orbit. As a sub-adult its postorbital horncores are pyramidal in shape with a slight lateral inflection of the distal, upper, one half.
Uniquely among ceratopsians, ''Coronosaurus'' possesses a number of accessory epiparietal ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
s rear parietal frill of the skull that fuse to the posterior and dorsal frill surface. They develop through ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the stu ...
, the growth of the individual, as short spines that may fuse along their adjacent margins into larger, irregular bone masses. They are located close to the midline of the frill in a closely packed bunch above the base of the first epiparietal (P1), the bone spur that at each side growths downwards over the large opening in each frill half. They contribute to the substance of P1 and, through fusion, form a composite epiparietal, that is equivalent to the second epiparietal (P2) normally formed in a more lateral position. The P1 bases can thus be considered the growth positions of the second epiparietals, the P2 loci. ''Coronosaurus'' has also a uniquely shaped P3 epiparietal. It is variably developed as a short tongue-like hook or tapered spike that is oriented dorsolaterally, following the curve of the frill.
Otherwise, as far as is known ''Coronosaurus'' resembles its relatives '' Centrosaurus'' and ''Styracosaurus
''Styracosaurus'' ( ; meaning "spiked lizard" from the Ancient Greek / "spike at the butt-end of a spear-shaft" and / "lizard") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period (Campanian stage), about 75.5 to 74.5&nbs ...
'' in its morphology. For example, the nasal
Nasal is an adjective referring to the nose, part of human or animal anatomy. It may also be shorthand for the following uses in combination:
* With reference to the human nose:
** Nasal administration, a method of pharmaceutical drug delivery
** ...
of ''Coronosaurus'' closely resembles that of ''Centrosaurus apertus'' in its unfused juvenile or subadult and fused adult forms and appears to have undergone a similar ontogenetic changes. Its erect, laterally compressed nasal horn core has a blunt tip that is formed from the fusion of the opposing nasals. It sits over the posterior portion of the external nares, as it does in all centrosaurines. All juvenile and most adult specimens have gently recurved anterior and posterior margins resulting in most horns having an apex that is oriented at least slightly caudally (backwards).
Classification
In its original description, Ryan & Russell (2005) considered ''Coronosaurus'' to represent a newspecies
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of ''Centrosaurus'' on the basis of a small phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analysis. It included seventeen characters and nine taxa. ''Coronosaurus'' (as ''Centrosaurus brinkmani'') and ''C. apertus'' grouped at the base of the Centrosaurinae, while ''Styracosaurus'' was found to be more closely related to ''Pachyrhinosaurus
''Pachyrhinosaurus'' (meaning in Greek "thick-nosed lizard", from ' (), thick; ' (), nose; and (), lizard) is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discove ...
'', and other derived centrosaurines, than to ''Centrosaurus''. In 2011, Anthony R. Fiorillo and Ronald S. Tykoski modified the analysis of Currie ''et al.'' (2008), with 54 characters, to include more taxa, such as ''C. brinkmani''. They found ''C. brinkmani'' to be the sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
of the clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
of ''Styracosaurus'' and ''C. apertus'', while ''Pachyrhinosaurus
''Pachyrhinosaurus'' (meaning in Greek "thick-nosed lizard", from ' (), thick; ' (), nose; and (), lizard) is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discove ...
'' and other derived centrosaurines were in a separate lineage. Thus, this analysis found no support for the monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic grou ...
of ''Centrosaurus''.
Later, Farke ''et al.'' (2011) used 97 morphological characters to assess the phylogenetic position of a new taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
which they named '' Spinops''. ''Spinops'' was found to be in a polytomy with ''Centrosaurus apertus'', ''C. brinkmani'' and ''Styracosaurus'', and therefore ''C. brinkmani'' was excluded from the analysis to increase the resolution. Finally, Ryan, Evans & Shepherd (2012) used the data matrix of Farke ''et al.'' (2011) to assess the phylogenetic position of ''Xenoceratops
''Xenoceratops'' (meaning "alien horned face") is a genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian stage), and is known to have lived in what is currently Alberta, Canada. The genus has one known speci ...
''. Their revised analysis had significantly better resolution than that presented by Farke ''et al.'' (2011), due in part to the additional scoring of missing characters for some taxa based on direct observation of their specimens. For example, five additional characters were scored for ''C. brinkmani''. In the resultant tree, it was found to be in more advanced position than ''Spinops'' and ''C. apertus'', as the sister taxon of ''Styracosaurus''. Thus the new generic name, ''Coronosaurus'', was given to it. The cladogram presented below follows a phylogenetic analysis by Chiba ''et al.'' (2017):

Paleoecology
 Studies suggest that the
Studies suggest that the paleoenvironment
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
of the Oldman Formation was an ancient coastal plain.Eberth, D.A., and Hamblin, A.P., 1993 , Tectonic, stratigraphic, and sedimentologic significance of a regional discontinuity in the upper Judith River Group (Belly River wedge) of southern Alberta, Saskatchewan, and northern Montana : Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 30, 174‒200. In addition to remains of ''Coronosaurus'', this formation has produced the remains of the theropods ''Saurornitholestes
''Saurornitholestes'' ("lizard-bird thief") is a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Canada (Alberta) and the United States (Montana, New Mexico, Alabama, North Carolina, and South Carolina).
Two spec ...
'', ''Daspletosaurus
''Daspletosaurus'' ( ; meaning "frightful lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Laramidia between about 79.5 and 74 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus ''Daspletosaurus'' contains three species ...
'', '' Troodon'', ''Dromaeosaurus
''Dromaeosaurus'' (, "running lizard") is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous period (middle late Campanian and Maastrichtian), sometime between 80 and 69 million years ago, in Alberta, Canada and the ...
'' and ''Hesperonychus
''Hesperonychus'' (meaning "western claw") was a small, carnivorous dinosaur. It was a member of the family Dromaeosauridae, along with its larger relatives ''Deinonychus'' and ''Velociraptor''. There is one described species, ''Hesperonychus eli ...
'', the ceratopsids ''Albertaceratops
''Albertaceratops'' (meaning "Alberta horned face") was a genus of centrosaurine horned dinosaur from the middle Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Oldman Formation of Alberta, Canada.
Description
''Albertaceratops'' is unusual in combining long ...
'', ''Chasmosaurus
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' ...
'', and ''Anchiceratops
''Anchiceratops'' ( ) is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Alberta, Canada.
''Anchiceratops'' was a medium-size ...
'', the hadrosaurids '' Brachylophosaurus'', ''Gryposaurus
''Gryposaurus'' (meaning "hooked-nosed (Ancient Greek, Greek ''grypos'') lizard"; sometimes incorrectly translated as "griffin (Latin ''gryphus'') lizard") was a genus of hadrosaur, duckbilled dinosaur that lived about 80 to 75 million years ...
'', ''Parasaurolophus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, abou ...
'', and ''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived fr ...
'', the thescelosaurid '' Albertadromeus'' and the ankylosaurid '' Scolosaurus''.
See also
* Timeline of ceratopsian researchReferences
{{Taxonbar, from=Q135802 Fossils of Canada Centrosaurines Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Fossil taxa described in 2012 Monotypic dinosaur genera Oldman fauna Paleontology in Alberta Campanian genus first appearances Campanian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera