Confucius Qiqi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the
 It is thought that Confucius was born on September 28, 551 BCE, in Zou (, in modern
It is thought that Confucius was born on September 28, 551 BCE, in Zou (, in modern
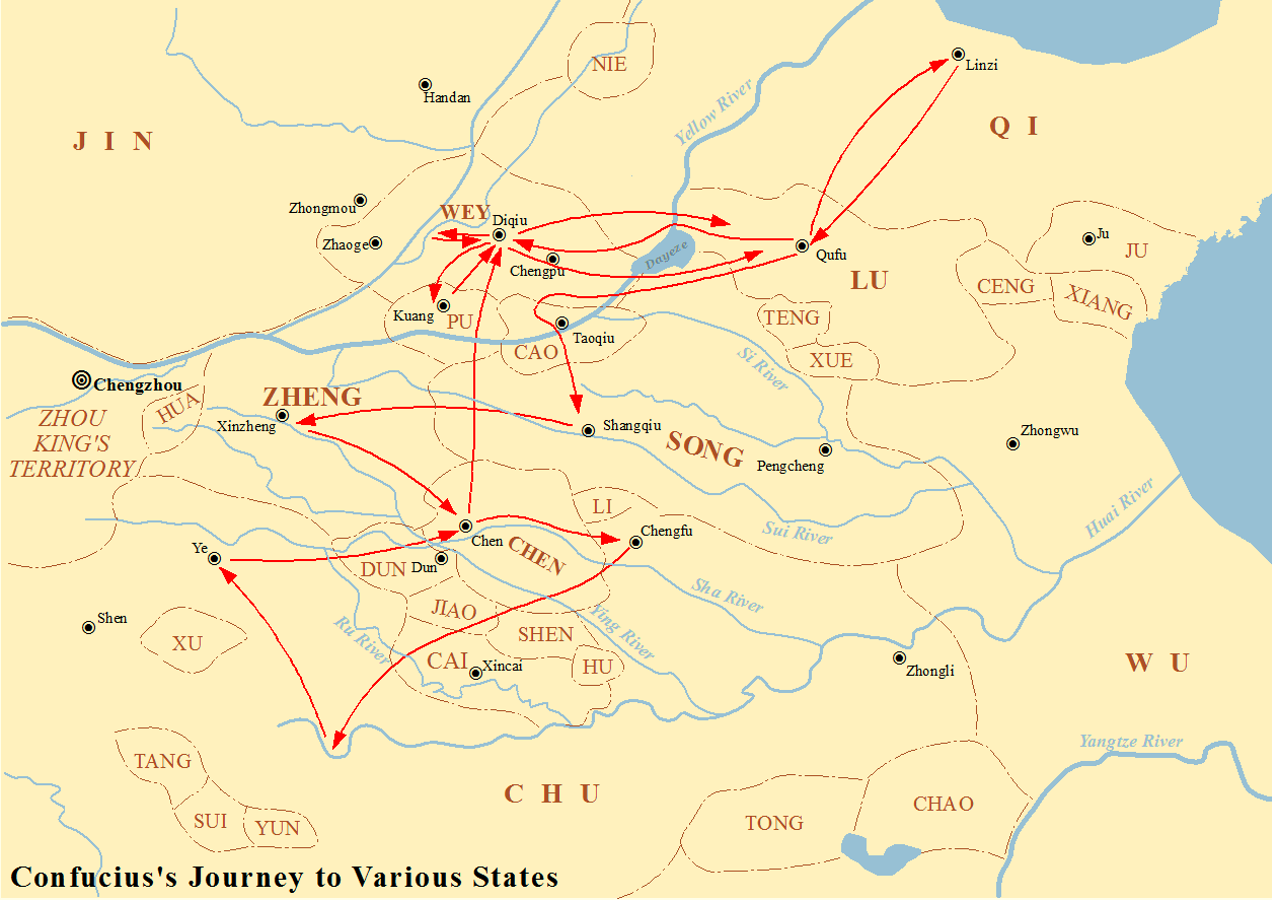 The '' Shiji'' stated that the neighboring Qi state was worried that Lu was becoming too powerful while Confucius was involved in the government of the Lu state. According to this account, Qi decided to sabotage Lu's reforms by sending 100 good horses and 80 beautiful dancing girls to the duke of Lu. The duke indulged himself in pleasure and did not attend to official duties for three days. Confucius was disappointed and resolved to leave Lu and seek better opportunities, yet to leave at once would expose the misbehavior of the duke and therefore bring public humiliation to the ruler Confucius was serving. Confucius therefore waited for the duke to make a lesser mistake. Soon after, the duke neglected to send to Confucius a portion of the sacrificial meat that was his due according to custom, and Confucius seized upon this pretext to leave both his post and the Lu state.
After Confucius's resignation, he began a long journey or set of journeys around the principality states of north-east and central China including
The '' Shiji'' stated that the neighboring Qi state was worried that Lu was becoming too powerful while Confucius was involved in the government of the Lu state. According to this account, Qi decided to sabotage Lu's reforms by sending 100 good horses and 80 beautiful dancing girls to the duke of Lu. The duke indulged himself in pleasure and did not attend to official duties for three days. Confucius was disappointed and resolved to leave Lu and seek better opportunities, yet to leave at once would expose the misbehavior of the duke and therefore bring public humiliation to the ruler Confucius was serving. Confucius therefore waited for the duke to make a lesser mistake. Soon after, the duke neglected to send to Confucius a portion of the sacrificial meat that was his due according to custom, and Confucius seized upon this pretext to leave both his post and the Lu state.
After Confucius's resignation, he began a long journey or set of journeys around the principality states of north-east and central China including
 According to the '' Zuozhuan'', Confucius returned home to his native Lu when he was 68, after he was invited to do so by Ji Kangzi, the chief minister of Lu. The ''Analects'' depict him spending his last years teaching 72 or 77
According to the '' Zuozhuan'', Confucius returned home to his native Lu when he was 68, after he was invited to do so by Ji Kangzi, the chief minister of Lu. The ''Analects'' depict him spending his last years teaching 72 or 77
 One of the deepest teachings of Confucius may have been the superiority of personal exemplification over explicit rules of behavior. His moral teachings emphasized self-cultivation, emulation of moral exemplars, and the attainment of skilled judgment rather than knowledge of rules. Confucian ethics may, therefore, be considered a type of virtue ethics. His teachings rarely rely on reasoned argument, and ethical ideals and methods are conveyed indirectly, through allusion, innuendo, and even tautology. His teachings require examination and context to be understood. A good example is found in this famous anecdote:
By not asking about the horses, Confucius demonstrates that the sage values human beings over property (which animals seem to represent in this example); readers are led to reflect on whether their response would follow Confucius's and to pursue self-improvement if it would not have.
One of his teachings was a variant of the Golden Rule, sometimes called the " Silver Rule" owing to its negative form:
Often overlooked in Confucian ethics are the virtues to the self: sincerity and the cultivation of knowledge. Virtuous action towards others begins with virtuous and sincere thought, which begins with knowledge. A virtuous disposition without knowledge is susceptible to corruption, and virtuous action without sincerity is not true righteousness. Cultivating knowledge and sincerity is also important for one's own sake; the superior person loves learning for the sake of learning and righteousness for the sake of righteousness.
The Confucian theory of ethics as exemplified in '' lǐ'' () is based on three important conceptual aspects of life: (a) ceremonies associated with sacrifice to ancestors and deities of various types, (b) social and political institutions, and (c) the etiquette of daily behavior. Some believed that ''lǐ'' originated from the heavens, but Confucius stressed the development of ''lǐ'' through the actions of sage leaders in human history. His discussions of ''lǐ'' seem to redefine the term to refer to all actions committed by a person to build the ideal society, rather than those conforming with canonical standards of ceremony.
In the early Confucian tradition, ''lǐ'' was doing the proper thing at the proper time; balancing between maintaining existing norms to perpetuate an ethical social fabric, and violating them in order to accomplish ethical good. Training in the ''lǐ'' of past sages, cultivates virtues in people that include ethical judgment about when ''lǐ'' must be adapted in light of situational contexts.
In Confucianism, the concept of ''li'' is closely related to ''yì'' (), which is based upon the idea of reciprocity. ''Yì'' can be translated as righteousness, though it may mean what is ethically best to do in a certain context. The term contrasts with action done out of self-interest. While pursuing one's own self-interest is not necessarily bad, one would be a better, more righteous person if one's life was based upon following a path designed to enhance the greater good. Thus an outcome of ''yì'' is doing the right thing for the right reason.
Just as action according to '' lǐ'' should be adapted to conform to the aspiration of adhering to ''yì'', so ''yì'' is linked to the core value of ''rén'' ().'' Rén'' consists of five basic virtues: seriousness, generosity, sincerity, diligence, and kindness.. ''Rén'' is the virtue of perfectly fulfilling one's responsibilities toward others, most often translated as "benevolence" or "humaneness"; translator Arthur Waley calls it "Goodness" (with a capital ''G''), and other translations that have been put forth include "authoritativeness" and "selflessness". Confucius's moral system was based upon empathy and understanding others, rather than divinely ordained rules. To develop one's spontaneous responses of ''rén'' so that these could guide action intuitively was even better than living by the rules of ''yì''. Confucius asserts that virtue is a mean between extremes. For example, the properly generous person gives the right amount – not too much and not too little.
One of the deepest teachings of Confucius may have been the superiority of personal exemplification over explicit rules of behavior. His moral teachings emphasized self-cultivation, emulation of moral exemplars, and the attainment of skilled judgment rather than knowledge of rules. Confucian ethics may, therefore, be considered a type of virtue ethics. His teachings rarely rely on reasoned argument, and ethical ideals and methods are conveyed indirectly, through allusion, innuendo, and even tautology. His teachings require examination and context to be understood. A good example is found in this famous anecdote:
By not asking about the horses, Confucius demonstrates that the sage values human beings over property (which animals seem to represent in this example); readers are led to reflect on whether their response would follow Confucius's and to pursue self-improvement if it would not have.
One of his teachings was a variant of the Golden Rule, sometimes called the " Silver Rule" owing to its negative form:
Often overlooked in Confucian ethics are the virtues to the self: sincerity and the cultivation of knowledge. Virtuous action towards others begins with virtuous and sincere thought, which begins with knowledge. A virtuous disposition without knowledge is susceptible to corruption, and virtuous action without sincerity is not true righteousness. Cultivating knowledge and sincerity is also important for one's own sake; the superior person loves learning for the sake of learning and righteousness for the sake of righteousness.
The Confucian theory of ethics as exemplified in '' lǐ'' () is based on three important conceptual aspects of life: (a) ceremonies associated with sacrifice to ancestors and deities of various types, (b) social and political institutions, and (c) the etiquette of daily behavior. Some believed that ''lǐ'' originated from the heavens, but Confucius stressed the development of ''lǐ'' through the actions of sage leaders in human history. His discussions of ''lǐ'' seem to redefine the term to refer to all actions committed by a person to build the ideal society, rather than those conforming with canonical standards of ceremony.
In the early Confucian tradition, ''lǐ'' was doing the proper thing at the proper time; balancing between maintaining existing norms to perpetuate an ethical social fabric, and violating them in order to accomplish ethical good. Training in the ''lǐ'' of past sages, cultivates virtues in people that include ethical judgment about when ''lǐ'' must be adapted in light of situational contexts.
In Confucianism, the concept of ''li'' is closely related to ''yì'' (), which is based upon the idea of reciprocity. ''Yì'' can be translated as righteousness, though it may mean what is ethically best to do in a certain context. The term contrasts with action done out of self-interest. While pursuing one's own self-interest is not necessarily bad, one would be a better, more righteous person if one's life was based upon following a path designed to enhance the greater good. Thus an outcome of ''yì'' is doing the right thing for the right reason.
Just as action according to '' lǐ'' should be adapted to conform to the aspiration of adhering to ''yì'', so ''yì'' is linked to the core value of ''rén'' ().'' Rén'' consists of five basic virtues: seriousness, generosity, sincerity, diligence, and kindness.. ''Rén'' is the virtue of perfectly fulfilling one's responsibilities toward others, most often translated as "benevolence" or "humaneness"; translator Arthur Waley calls it "Goodness" (with a capital ''G''), and other translations that have been put forth include "authoritativeness" and "selflessness". Confucius's moral system was based upon empathy and understanding others, rather than divinely ordained rules. To develop one's spontaneous responses of ''rén'' so that these could guide action intuitively was even better than living by the rules of ''yì''. Confucius asserts that virtue is a mean between extremes. For example, the properly generous person gives the right amount – not too much and not too little.
 Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar Li Zehou argued that Confucianism is based on the idea of rites. Rites serve as the starting point for each individual and that these sacred social functions allow each person's human nature to be harmonious with reality. Given this, Confucius believed that "music is the harmonization of heaven and earth; the rites is the order of heaven and earth". Thus the application of music in rites creates the order that makes it possible for society to prosper.
The Confucian approach to music was heavily inspired by the Shijing and the Classic of Music, which was said to be the sixth Confucian classic until it was lost during the Han Dynasty. The Shijing serves as one of the current Confucian classics and is a book on poetry that contains a diversified variety of poems as well as folk songs. Confucius is traditionally ascribed with compiling these classics within his school. In the Analects, Confucius described the importance of the art in the development of society:
Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar Li Zehou argued that Confucianism is based on the idea of rites. Rites serve as the starting point for each individual and that these sacred social functions allow each person's human nature to be harmonious with reality. Given this, Confucius believed that "music is the harmonization of heaven and earth; the rites is the order of heaven and earth". Thus the application of music in rites creates the order that makes it possible for society to prosper.
The Confucian approach to music was heavily inspired by the Shijing and the Classic of Music, which was said to be the sixth Confucian classic until it was lost during the Han Dynasty. The Shijing serves as one of the current Confucian classics and is a book on poetry that contains a diversified variety of poems as well as folk songs. Confucius is traditionally ascribed with compiling these classics within his school. In the Analects, Confucius described the importance of the art in the development of society:
 Confucius's teachings were later turned into an elaborate set of rules and practices by his numerous disciples and followers, who organized his teachings into the Analects. Confucius's disciples and his only grandson, Zisi, continued his philosophical school after his death. These efforts spread Confucian ideals to students who then became officials in many of the royal courts in China, thereby giving Confucianism the first wide-scale test of its dogma.
Two of Confucius's most famous later followers emphasized radically different aspects of his teachings. In the centuries after his death,
Confucius's teachings were later turned into an elaborate set of rules and practices by his numerous disciples and followers, who organized his teachings into the Analects. Confucius's disciples and his only grandson, Zisi, continued his philosophical school after his death. These efforts spread Confucian ideals to students who then became officials in many of the royal courts in China, thereby giving Confucianism the first wide-scale test of its dogma.
Two of Confucius's most famous later followers emphasized radically different aspects of his teachings. In the centuries after his death,  The works of Confucius were first translated into European languages by Jesuit missionaries in the 16th century during the late Ming dynasty. The first known effort was by Michele Ruggieri, who returned to Italy in 1588 and carried on his translations while residing in
The works of Confucius were first translated into European languages by Jesuit missionaries in the 16th century during the late Ming dynasty. The first known effort was by Michele Ruggieri, who returned to Italy in 1588 and carried on his translations while residing in
 No contemporary painting or sculpture of Confucius survives, and it was only during the Han Dynasty that he was portrayed visually. Carvings often depict his legendary meeting with
No contemporary painting or sculpture of Confucius survives, and it was only during the Han Dynasty that he was portrayed visually. Carvings often depict his legendary meeting with

 Soon after Confucius's death, Qufu, his home town, became a place of devotion and remembrance. The Han dynasty '' Records of the Grand Historian'' records that it had already become a place of pilgrimage for ministers. It is still a major destination for cultural tourism, and many people visit his grave and the surrounding temples. In Sinic cultures, there are many temples where representations of the Buddha,
Soon after Confucius's death, Qufu, his home town, became a place of devotion and remembrance. The Han dynasty '' Records of the Grand Historian'' records that it had already become a place of pilgrimage for ministers. It is still a major destination for cultural tourism, and many people visit his grave and the surrounding temples. In Sinic cultures, there are many temples where representations of the Buddha,
Multilingual web site on Confucius and the Analects
The Dao of Kongzi
introduction to the thought of Confucius. * * *
Confucian Analects
(Project Gutenberg release of James Legge's Translation)
in the ''Analects of Confucius''. {{Authority control 551 BC births 479 BC deaths 6th-century BC historians 6th-century BC Chinese philosophers 6th-century BC Chinese writers 5th-century BC historians 5th-century BC Chinese philosophers 5th-century BC Chinese writers Aphorists Chinese educational theorists Chinese ethicists Chinese logicians Chinese political philosophers Classical humanists Confucianism Cultural critics Deified Chinese people Education theory Educators from Shandong Epistemologists Founders of philosophical traditions Founders of religions Gong clan of Qufu Guqin players Historians from Shandong Moral philosophers People from Qufu Politicians from Jining Philosophers from Lu (state) Philosophers from Shandong Philosophers of culture Philosophers of education Philosophers of ethics and morality Philosophers of law Chinese social commentators Social critics Social philosophers Writers from Jining Zhou dynasty historians Zhou dynasty philosophers Zhou dynasty politicians 5th-century BC Chinese musicians 6th-century BC Chinese musicians 6th-century BC religious leaders 5th-century BC religious leaders
Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Confucius's teachings and philosophy underpin East Asian culture and society, remaining influential across China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and East Asia to this day.
Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, correctness of social relationships, justice, kindness, and sincerity. His followers competed with many other schools during the Hundred Schools of Thought era, only to be suppressed in favor of the Legalists during the Qin dynasty. After the collapse of Qin and the victory of Han over Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BC–223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BC–202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BC–70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
, Confucius's thoughts received official sanction in the new government. During the Tang and Song dynasties, Confucianism developed into a system known in the West as Neo-Confucianism, and later as New Confucianism. Confucianism was part of the Chinese social fabric and way of life; to Confucians, everyday life was the arena of religion.
Confucius is traditionally credited with having authored or edited many of the Chinese classic texts, including all of the Five Classics, but modern scholars are cautious of attributing specific assertions to Confucius himself. Aphorisms concerning his teachings were compiled in the ''Analects
The ''Analects'' (; ; Old Chinese: '' ŋ(r)aʔ''; meaning "Selected Sayings"), also known as the ''Analects of Confucius'', the ''Sayings of Confucius'', or the ''Lun Yu'', is an ancient Chinese book composed of a large collection of sayings a ...
'', but only many years after his death.
Confucius's principles have commonality with Chinese tradition and belief. With filial piety, he championed strong family loyalty, ancestor veneration
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of t ...
, and respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives, recommending family as a basis for ideal government. He espoused the Golden Rule, "Do not do unto others what you do not want done to yourself".
Name
The name "Confucius" is a Latinized form of the Mandarin Chinese (, "Master Kong"), and was coined in the late 16th century by the early Jesuit missionaries to China. Confucius's clan name was Kong () and his given name was Qiu (). His " courtesy name", a capping (''guan'': ) given at his coming of age ceremony, and by which he would have been known to all but his older family members, was Zhongni (), the "Zhòng" indicating that he was the second son in his family.Life
Early life
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
province). The area was notionally controlled by the kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
of Zhou but effectively independent under the local lords of Lu, who ruled from the nearby city of Qufu. His father Kong He
Kong He (), (622 BC–548 BC) also known as Shuliang He (), was a scholar and military officer of the State of Lu. He was the son of the Lu political figure Bo Xia and the father of Kong Pi and Confucius.
History
On the 69th day of the fourth lu ...
(or Shuliang He) was an elderly commandant of the local Lu garrison. His ancestry traced back through the dukes of Song to the Shang dynasty which had preceded the Zhou. Traditional accounts of Confucius's life relate that Kong He's grandfather had migrated the family from Song to Lu.
Kong He died when Confucius was three years old, and Confucius was raised by his mother Yan Zhengzai () in poverty. His mother later died at less than 40 years of age. At age 19 he married Lady Qiguan (), and a year later the couple had their first child, their son Kong Li
Kong may refer to:
Places
* Kong Empire (1710–1895), a former African state covering north-eastern Côte d'Ivoire and much of Burkina Faso
* Kong, Iran, a city on the Persian Gulf
* Kong, Shandong (), a town in Laoling, Shandong, China
* Kong, I ...
(). Qiguan and Confucius later had two daughters together, one of whom is thought to have died as a child and one was named Kong Jiao ().
Confucius was educated at schools for commoners, where he studied and learned the Six Arts.
Confucius was born into the class of '' shi'' (), between the aristocracy and the common people. He is said to have worked in various government jobs during his early 20s, and as a bookkeeper and a caretaker of sheep and horses, using the proceeds to give his mother a proper burial. When his mother died, Confucius (aged 23) is said to have mourned for three years, as was the tradition.
Political career
In Confucius's time, the state of Lu was headed by a ruling ducal house. Under the duke were three aristocratic families, whose heads bore the title of viscount and held hereditary positions in the Lu bureaucracy. The Ji family held the position "Minister over the Masses", who was also the "Prime Minister"; the Meng family held the position "Minister of Works"; and the Shu family held the position "Minister of War". In the winter of , Yang Hu—a retainer of the Ji family—rose up in rebellion and seized power from the Ji family. However, by the summer of , the three hereditary families had succeeded in expelling Yang Hu from Lu. By then, Confucius had built up a considerable reputation through his teachings, while the families came to see the value of proper conduct and righteousness, so they could achieve loyalty to a legitimate government. Thus, that year (), Confucius came to be appointed to the minor position of governor of a town. Eventually, he rose to the position of Minister of Crime. Confucius desired to return the authority of the state to the duke by dismantling the fortifications of the city—strongholds belonging to the three families. This way, he could establish a centralized government. However, Confucius relied solely on diplomacy as he had no military authority himself. In , Hou Fan—the governor of Hou—revolted against his lord of the Shu family. Although the Meng and Shu families unsuccessfully besieged Hou, a loyalist official rose up with the people of Hou and forced Hou Fan to flee to the Qi state. The situation may have been in favor for Confucius as this likely made it possible for Confucius and his disciples to convince the aristocratic families to dismantle the fortifications of their cities. Eventually, after a year and a half, Confucius and his disciples succeeded in convincing the Shu family to raze the walls of Hou, the Ji family in razing the walls of Bi, and the Meng family in razing the walls of Cheng. First, the Shu family led an army towards their city Hou and tore down its walls in . Soon thereafter, Gongshan Furao (also known as Gongshan Buniu), a retainer of the Ji family, revolted and took control of the forces at Bi. He immediately launched an attack and entered the capital Lu. Earlier, Gongshan had approached Confucius to join him, which Confucius considered as he wanted the opportunity to put his principles into practice but he gave up on the idea in the end. Confucius disapproved the use of a violent revolution by principle, even though the Ji family dominated the Lu state by force for generations and had exiled the previous duke. Creel (1949) states that, unlike the rebel Yang Hu before him, Gongshan may have sought to destroy the three hereditary families and restore the power of the duke. However, Dubs (1946) is of the view that Gongshan was encouraged by Viscount Ji Huan to invade the Lu capital in an attempt to avoid dismantling the Bi fortified walls. Whatever the situation may have been, Gongshan was considered an upright man who continued to defend the state of Lu, even after he was forced to flee. During the revolt by Gongshan, Zhong You had managed to keep the duke and the three viscounts together at the court. Zhong You was one of the disciples of Confucius and Confucius had arranged for him to be given the position of governor by the Ji family. When Confucius heard of the raid, he requested that Viscount Ji Huan allow the duke and his court to retreat to a stronghold on his palace grounds. Thereafter, the heads of the three families and the duke retreated to the Ji's palace complex and ascended the Wuzi Terrace.. Confucius ordered two officers to lead an assault against the rebels. At least one of the two officers was a retainer of the Ji family, but they were unable to refuse the orders while in the presence of the duke, viscounts, and court. The rebels were pursued and defeated at Gu. Immediately after the revolt was defeated, the Ji family razed the Bi city walls to the ground. The attackers retreated after realizing that they would have to become rebels against the state and their lord. Through Confucius' actions, the Bi officials had inadvertently revolted against their own lord, thus forcing Viscount Ji Huan's hand in having to dismantle the walls of Bi (as it could have harbored such rebels) or confess to instigating the event by going against proper conduct and righteousness as an official. Dubs (1949) suggests that the incident brought to light Confucius' foresight, practical political ability, and insight into human character. When it was time to dismantle the city walls of the Meng family, the governor was reluctant to have his city walls torn down and convinced the head of the Meng family not to do so. The '' Zuozhuan'' recalls that the governor advised against razing the walls to the ground as he said that it made Cheng vulnerable to the Qi state and cause the destruction of the Meng family. Even though Viscount Meng Yi gave his word not to interfere with an attempt, he went back on his earlier promise to dismantle the walls. Later in , Duke Ding personally went with an army to lay siege to Cheng in an attempt to raze its walls to the ground, but he did not succeed. Thus, Confucius could not achieve the idealistic reforms that he wanted including restoration of the legitimate rule of the duke. He had made powerful enemies within the state, especially with Viscount Ji Huan, due to his successes so far.. According to accounts in the '' Zuozhuan'' and '' Shiji'', Confucius departed his homeland in after his support for the failed attempt of dismantling the fortified city walls of the powerful Ji, Meng, and Shu families. He left the state of Lu without resigning, remaining in self-exile and unable to return as long as Viscount Ji Huan was alive.Exile
 The '' Shiji'' stated that the neighboring Qi state was worried that Lu was becoming too powerful while Confucius was involved in the government of the Lu state. According to this account, Qi decided to sabotage Lu's reforms by sending 100 good horses and 80 beautiful dancing girls to the duke of Lu. The duke indulged himself in pleasure and did not attend to official duties for three days. Confucius was disappointed and resolved to leave Lu and seek better opportunities, yet to leave at once would expose the misbehavior of the duke and therefore bring public humiliation to the ruler Confucius was serving. Confucius therefore waited for the duke to make a lesser mistake. Soon after, the duke neglected to send to Confucius a portion of the sacrificial meat that was his due according to custom, and Confucius seized upon this pretext to leave both his post and the Lu state.
After Confucius's resignation, he began a long journey or set of journeys around the principality states of north-east and central China including
The '' Shiji'' stated that the neighboring Qi state was worried that Lu was becoming too powerful while Confucius was involved in the government of the Lu state. According to this account, Qi decided to sabotage Lu's reforms by sending 100 good horses and 80 beautiful dancing girls to the duke of Lu. The duke indulged himself in pleasure and did not attend to official duties for three days. Confucius was disappointed and resolved to leave Lu and seek better opportunities, yet to leave at once would expose the misbehavior of the duke and therefore bring public humiliation to the ruler Confucius was serving. Confucius therefore waited for the duke to make a lesser mistake. Soon after, the duke neglected to send to Confucius a portion of the sacrificial meat that was his due according to custom, and Confucius seized upon this pretext to leave both his post and the Lu state.
After Confucius's resignation, he began a long journey or set of journeys around the principality states of north-east and central China including Wey
Wey may refer to:
Places
*Wey (state) (衞), or Wei, ancient Chinese state during the Zhou Dynasty
*River Wey, river in Surrey, Hampshire and West Sussex, England
*River Wey (Dorset), river of Dorset, south west England
*Wey and Arun Canal, canal ...
, Song, Zheng, Cao, Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BC–223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BC–202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BC–70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
, Qi, Chen, and Cai (and a failed attempt to go to Jin). At the courts of these states, he expounded his political beliefs but did not see them implemented.
Return home
 According to the '' Zuozhuan'', Confucius returned home to his native Lu when he was 68, after he was invited to do so by Ji Kangzi, the chief minister of Lu. The ''Analects'' depict him spending his last years teaching 72 or 77
According to the '' Zuozhuan'', Confucius returned home to his native Lu when he was 68, after he was invited to do so by Ji Kangzi, the chief minister of Lu. The ''Analects'' depict him spending his last years teaching 72 or 77 disciples
A disciple is a follower and student of a mentor, teacher, or other figure. It can refer to:
Religion
* Disciple (Christianity), a student of Jesus Christ
* Twelve Apostles of Jesus, sometimes called the Twelve Disciples
* Seventy disciples in ...
and transmitting the old wisdom via a set of texts called the Five Classics.
During his return, Confucius sometimes acted as an advisor to several government officials in Lu, including Ji Kangzi, on matters including governance and crime.
Burdened by the loss of both his son and his favorite disciples, he died at the age of 71 or 72 from natural causes. Confucius was buried in Kong Lin cemetery which lies in the historical part of Qufu in the Shandong Province. The original tomb erected there in memory of Confucius on the bank of the Sishui River had the shape of an axe. In addition, it has a raised brick platform at the front of the memorial for offerings such as sandalwood incense and fruit.
Philosophy
Although Confucianism is often followed in a religious manner by the Chinese, many argue that its values are secular and that it is, therefore, less a religion than a secular morality. Proponents argue, however, that despite the secular nature of Confucianism's teachings, it is based on a worldview that is religious. Confucianism discusses elements of theafterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving ess ...
and views concerning Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
, but it is relatively unconcerned with some spiritual matters often considered essential to religious thought, such as the nature of souls.
In the ''Analects
The ''Analects'' (; ; Old Chinese: '' ŋ(r)aʔ''; meaning "Selected Sayings"), also known as the ''Analects of Confucius'', the ''Sayings of Confucius'', or the ''Lun Yu'', is an ancient Chinese book composed of a large collection of sayings a ...
'', Confucius presents himself as a "transmitter who invented nothing". He puts the greatest emphasis on the importance of study, and it is the Chinese character for study () that opens the text. Far from trying to build a systematic or formalist theory, he wanted his disciples to master and internalize older classics, so that their deep thought and thorough study would allow them to relate the moral problems of the present to past political events (as recorded in the ''Annals'') or the past expressions of commoners' feelings and noblemen's reflections (as in the poems of the '' Book of Odes'').
Ethics
 One of the deepest teachings of Confucius may have been the superiority of personal exemplification over explicit rules of behavior. His moral teachings emphasized self-cultivation, emulation of moral exemplars, and the attainment of skilled judgment rather than knowledge of rules. Confucian ethics may, therefore, be considered a type of virtue ethics. His teachings rarely rely on reasoned argument, and ethical ideals and methods are conveyed indirectly, through allusion, innuendo, and even tautology. His teachings require examination and context to be understood. A good example is found in this famous anecdote:
By not asking about the horses, Confucius demonstrates that the sage values human beings over property (which animals seem to represent in this example); readers are led to reflect on whether their response would follow Confucius's and to pursue self-improvement if it would not have.
One of his teachings was a variant of the Golden Rule, sometimes called the " Silver Rule" owing to its negative form:
Often overlooked in Confucian ethics are the virtues to the self: sincerity and the cultivation of knowledge. Virtuous action towards others begins with virtuous and sincere thought, which begins with knowledge. A virtuous disposition without knowledge is susceptible to corruption, and virtuous action without sincerity is not true righteousness. Cultivating knowledge and sincerity is also important for one's own sake; the superior person loves learning for the sake of learning and righteousness for the sake of righteousness.
The Confucian theory of ethics as exemplified in '' lǐ'' () is based on three important conceptual aspects of life: (a) ceremonies associated with sacrifice to ancestors and deities of various types, (b) social and political institutions, and (c) the etiquette of daily behavior. Some believed that ''lǐ'' originated from the heavens, but Confucius stressed the development of ''lǐ'' through the actions of sage leaders in human history. His discussions of ''lǐ'' seem to redefine the term to refer to all actions committed by a person to build the ideal society, rather than those conforming with canonical standards of ceremony.
In the early Confucian tradition, ''lǐ'' was doing the proper thing at the proper time; balancing between maintaining existing norms to perpetuate an ethical social fabric, and violating them in order to accomplish ethical good. Training in the ''lǐ'' of past sages, cultivates virtues in people that include ethical judgment about when ''lǐ'' must be adapted in light of situational contexts.
In Confucianism, the concept of ''li'' is closely related to ''yì'' (), which is based upon the idea of reciprocity. ''Yì'' can be translated as righteousness, though it may mean what is ethically best to do in a certain context. The term contrasts with action done out of self-interest. While pursuing one's own self-interest is not necessarily bad, one would be a better, more righteous person if one's life was based upon following a path designed to enhance the greater good. Thus an outcome of ''yì'' is doing the right thing for the right reason.
Just as action according to '' lǐ'' should be adapted to conform to the aspiration of adhering to ''yì'', so ''yì'' is linked to the core value of ''rén'' ().'' Rén'' consists of five basic virtues: seriousness, generosity, sincerity, diligence, and kindness.. ''Rén'' is the virtue of perfectly fulfilling one's responsibilities toward others, most often translated as "benevolence" or "humaneness"; translator Arthur Waley calls it "Goodness" (with a capital ''G''), and other translations that have been put forth include "authoritativeness" and "selflessness". Confucius's moral system was based upon empathy and understanding others, rather than divinely ordained rules. To develop one's spontaneous responses of ''rén'' so that these could guide action intuitively was even better than living by the rules of ''yì''. Confucius asserts that virtue is a mean between extremes. For example, the properly generous person gives the right amount – not too much and not too little.
One of the deepest teachings of Confucius may have been the superiority of personal exemplification over explicit rules of behavior. His moral teachings emphasized self-cultivation, emulation of moral exemplars, and the attainment of skilled judgment rather than knowledge of rules. Confucian ethics may, therefore, be considered a type of virtue ethics. His teachings rarely rely on reasoned argument, and ethical ideals and methods are conveyed indirectly, through allusion, innuendo, and even tautology. His teachings require examination and context to be understood. A good example is found in this famous anecdote:
By not asking about the horses, Confucius demonstrates that the sage values human beings over property (which animals seem to represent in this example); readers are led to reflect on whether their response would follow Confucius's and to pursue self-improvement if it would not have.
One of his teachings was a variant of the Golden Rule, sometimes called the " Silver Rule" owing to its negative form:
Often overlooked in Confucian ethics are the virtues to the self: sincerity and the cultivation of knowledge. Virtuous action towards others begins with virtuous and sincere thought, which begins with knowledge. A virtuous disposition without knowledge is susceptible to corruption, and virtuous action without sincerity is not true righteousness. Cultivating knowledge and sincerity is also important for one's own sake; the superior person loves learning for the sake of learning and righteousness for the sake of righteousness.
The Confucian theory of ethics as exemplified in '' lǐ'' () is based on three important conceptual aspects of life: (a) ceremonies associated with sacrifice to ancestors and deities of various types, (b) social and political institutions, and (c) the etiquette of daily behavior. Some believed that ''lǐ'' originated from the heavens, but Confucius stressed the development of ''lǐ'' through the actions of sage leaders in human history. His discussions of ''lǐ'' seem to redefine the term to refer to all actions committed by a person to build the ideal society, rather than those conforming with canonical standards of ceremony.
In the early Confucian tradition, ''lǐ'' was doing the proper thing at the proper time; balancing between maintaining existing norms to perpetuate an ethical social fabric, and violating them in order to accomplish ethical good. Training in the ''lǐ'' of past sages, cultivates virtues in people that include ethical judgment about when ''lǐ'' must be adapted in light of situational contexts.
In Confucianism, the concept of ''li'' is closely related to ''yì'' (), which is based upon the idea of reciprocity. ''Yì'' can be translated as righteousness, though it may mean what is ethically best to do in a certain context. The term contrasts with action done out of self-interest. While pursuing one's own self-interest is not necessarily bad, one would be a better, more righteous person if one's life was based upon following a path designed to enhance the greater good. Thus an outcome of ''yì'' is doing the right thing for the right reason.
Just as action according to '' lǐ'' should be adapted to conform to the aspiration of adhering to ''yì'', so ''yì'' is linked to the core value of ''rén'' ().'' Rén'' consists of five basic virtues: seriousness, generosity, sincerity, diligence, and kindness.. ''Rén'' is the virtue of perfectly fulfilling one's responsibilities toward others, most often translated as "benevolence" or "humaneness"; translator Arthur Waley calls it "Goodness" (with a capital ''G''), and other translations that have been put forth include "authoritativeness" and "selflessness". Confucius's moral system was based upon empathy and understanding others, rather than divinely ordained rules. To develop one's spontaneous responses of ''rén'' so that these could guide action intuitively was even better than living by the rules of ''yì''. Confucius asserts that virtue is a mean between extremes. For example, the properly generous person gives the right amount – not too much and not too little.
Politics
Confucius's political thought is based upon his ethical thought. He argued that the best government is one that rules through "rites" (''lǐ'') and people'snatural morality
Natural morality refers to morality that is based on human nature, rather than acquired from societal norms or religious teachings. Charles Darwin's theory of evolution is central to many modern conceptions of natural morality, but the concept goe ...
, and ''not'' by using bribery and coercion. He explained that this is one of the most important analects: "If the people be led by laws, and uniformity sought to be given them by punishments, they will try to avoid the punishment, but have no sense of shame. If they be led by virtue, and uniformity sought to be given them by the rules of propriety, they will have the sense of the shame, and moreover will become good." (''Analects'' 2.3, tr. Legge). This "sense of shame" is an internalisation of duty
A duty (from "due" meaning "that which is owing"; fro, deu, did, past participle of ''devoir''; la, debere, debitum, whence "debt") is a commitment or expectation to perform some action in general or if certain circumstances arise. A duty may ...
, where the punishment precedes the evil action, instead of following it in the form of laws as in Legalism.
Confucius looked nostalgically upon earlier days, and urged the Chinese, particularly those with political power, to model themselves on earlier examples. In times of division, chaos, and endless wars between feudal states, he wanted to restore the Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, ''Tian'') – which embodies the natural ...
() that could unify the "world" (, "all under Heaven") and bestow peace and prosperity on the people. Because his vision of personal and social perfections was framed as a revival of the ordered society of earlier times, Confucius is often considered a great proponent of conservatism, but a closer look at what he proposes often shows that he used (and perhaps twisted) past institutions and rites to push a new political agenda of his own: a revival of a unified royal state, whose rulers would succeed to power on the basis of their moral merits instead of lineage. These would be rulers devoted to their people, striving for personal and social perfection, and such a ruler would spread his own virtues to the people instead of imposing proper behavior with laws and rules.
While Confucius supported the idea of government ruling by a virtuous king, his ideas contained a number of elements to limit the power of rulers. He argued for representing truth in language, and honesty was of paramount importance. Even in facial expression, truth must always be represented. Confucius believed that if a ruler is to lead correctly, by action, that orders would be unnecessary in that others will follow the proper actions of their ruler. In discussing the relationship between a king and his subject (or a father and his son), he underlined the need to give due respect to superiors. This demanded that the subordinates must advise their superiors if the superiors are considered to be taking a course of action that is wrong. Confucius believed in ruling by example, if you lead correctly, orders by force or punishment are not necessary.
Music and poetry
 Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar Li Zehou argued that Confucianism is based on the idea of rites. Rites serve as the starting point for each individual and that these sacred social functions allow each person's human nature to be harmonious with reality. Given this, Confucius believed that "music is the harmonization of heaven and earth; the rites is the order of heaven and earth". Thus the application of music in rites creates the order that makes it possible for society to prosper.
The Confucian approach to music was heavily inspired by the Shijing and the Classic of Music, which was said to be the sixth Confucian classic until it was lost during the Han Dynasty. The Shijing serves as one of the current Confucian classics and is a book on poetry that contains a diversified variety of poems as well as folk songs. Confucius is traditionally ascribed with compiling these classics within his school. In the Analects, Confucius described the importance of the art in the development of society:
Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar Li Zehou argued that Confucianism is based on the idea of rites. Rites serve as the starting point for each individual and that these sacred social functions allow each person's human nature to be harmonious with reality. Given this, Confucius believed that "music is the harmonization of heaven and earth; the rites is the order of heaven and earth". Thus the application of music in rites creates the order that makes it possible for society to prosper.
The Confucian approach to music was heavily inspired by the Shijing and the Classic of Music, which was said to be the sixth Confucian classic until it was lost during the Han Dynasty. The Shijing serves as one of the current Confucian classics and is a book on poetry that contains a diversified variety of poems as well as folk songs. Confucius is traditionally ascribed with compiling these classics within his school. In the Analects, Confucius described the importance of the art in the development of society:
Legacy
 Confucius's teachings were later turned into an elaborate set of rules and practices by his numerous disciples and followers, who organized his teachings into the Analects. Confucius's disciples and his only grandson, Zisi, continued his philosophical school after his death. These efforts spread Confucian ideals to students who then became officials in many of the royal courts in China, thereby giving Confucianism the first wide-scale test of its dogma.
Two of Confucius's most famous later followers emphasized radically different aspects of his teachings. In the centuries after his death,
Confucius's teachings were later turned into an elaborate set of rules and practices by his numerous disciples and followers, who organized his teachings into the Analects. Confucius's disciples and his only grandson, Zisi, continued his philosophical school after his death. These efforts spread Confucian ideals to students who then became officials in many of the royal courts in China, thereby giving Confucianism the first wide-scale test of its dogma.
Two of Confucius's most famous later followers emphasized radically different aspects of his teachings. In the centuries after his death, Mencius
Mencius ( ); born Mèng Kē (); or Mèngzǐ (; 372–289 BC) was a Chinese Confucianism, Confucian Chinese philosophy, philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, second to Confucius himself. He is part of Confuc ...
() and Xun Zi () both composed important teachings elaborating in different ways on the fundamental ideas associated with Confucius. Mencius
Mencius ( ); born Mèng Kē (); or Mèngzǐ (; 372–289 BC) was a Chinese Confucianism, Confucian Chinese philosophy, philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, second to Confucius himself. He is part of Confuc ...
() articulated the innate goodness in human beings as a source of the ethical intuitions that guide people towards ''rén'', ''yì'', and ''lǐ'', while Xun Zi () underscored the realistic and materialistic aspects of Confucian thought, stressing that morality was inculcated in society through tradition and in individuals through training. In time, their writings, together with the ''Analects'' and other core texts came to constitute the philosophical corpus of Confucianism.
This realignment in Confucian thought was parallel to the development of Legalism, which saw filial piety as self-interest and not a useful tool for a ruler to create an effective state. A disagreement between these two political philosophies came to a head in when the Qin state conquered all of China. Li Si, Prime Minister of the Qin dynasty, convinced Qin Shi Huang to abandon the Confucians' recommendation of awarding fiefs akin to the Zhou Dynasty before them which he saw as being against to the Legalist idea of centralizing the state around the ruler. When the Confucian advisers pressed their point, Li Si had many Confucian scholars killed and their books burned—considered a huge blow to the philosophy and Chinese scholarship.
Under the succeeding Han and Tang dynasties, Confucian ideas gained even more widespread prominence. Under Wudi, the works of Confucius were made the official imperial philosophy and required reading for civil service examinations in which was continued nearly unbroken until the end of the 19th century. As Mohism
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and science developed by the academic scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (c. 470 BC – c. 391 BC), embodied in an epony ...
lost support by the time of the Han, the main philosophical contenders were Legalism, which Confucian thought somewhat absorbed, the teachings of Laozi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state
...
, whose focus on more spiritual ideas kept it from direct conflict with Confucianism, and the new Buddhist religion, which gained acceptance during the Southern and Northern Dynasties era. Both Confucian ideas and Confucian-trained officials were relied upon in the Ming Dynasty and even the Yuan Dynasty, although Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
distrusted handing over provincial control to them.
During the Song dynasty, the scholar Zhu Xi () added ideas from Daoism and Buddhism into Confucianism. In his life, Zhu Xi was largely ignored, but not long after his death, his ideas became the new orthodox view of what Confucian texts actually meant. Modern historians view Zhu Xi as having created something rather different and call his way of thinking '' Neo-Confucianism''. Neo-Confucianism held sway in China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam until the 19th century.
 The works of Confucius were first translated into European languages by Jesuit missionaries in the 16th century during the late Ming dynasty. The first known effort was by Michele Ruggieri, who returned to Italy in 1588 and carried on his translations while residing in
The works of Confucius were first translated into European languages by Jesuit missionaries in the 16th century during the late Ming dynasty. The first known effort was by Michele Ruggieri, who returned to Italy in 1588 and carried on his translations while residing in Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
. Matteo Ricci
Matteo Ricci, SJ (; la, Mattheus Riccius; 6 October 1552 – 11 May 1610), was an Italians, Italian Society of Jesus, Jesuit Priesthood in the Catholic Church, priest and one of the founding figures of the Jesuit China missions. He create ...
started to report on the thoughts of Confucius, and a team of Jesuits—Prospero Intorcetta
Prospero Intorcetta (1626–1696), known to the Chinese as Yin Duoze, was an Italian Jesuit missionary to the Qing Empire. The first to translate the works of Confucius in Europe.
Life
Prospero Intorcetta was born in Piazza Armerina in 1626.
...
, Philippe Couplet
Philippe or Philip Couplet (1623–1693), known in China as Bai Yingli, was a Flemish Jesuit missionary to the Qing Empire. He worked with his fellow missionaries to compile the influential ''Confucius, Philosopher of the Chinese'', published in ...
, and two others—published a translation of several Confucian works and an overview of Chinese history
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapter ...
in Paris in 1687.. François Noël, after failing to persuade ClementXI that Chinese veneration of ancestors
Chinese ancestor veneration, also called Chinese ancestor worship, is an aspect of the Chinese folk religion, Chinese traditional religion which revolves around the ritual celebration of the deification, deified ancestors and tutelary deities ...
and Confucius did not constitute idolatry, completed the Confucian canon at Prague in 1711, with more scholarly treatments of the other works and the first translation of the collected works of Mencius
Mencius ( ); born Mèng Kē (); or Mèngzǐ (; 372–289 BC) was a Chinese Confucianism, Confucian Chinese philosophy, philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, second to Confucius himself. He is part of Confuc ...
. It is thought that such works had considerable importance on European thinkers of the period, particularly among the Deists and other philosophical groups of the Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
who were interested by the integration of the system of morality of Confucius into Western civilization.
In the modern era Confucian movements, such as New Confucianism, still exist, but during the Cultural Revolution, Confucianism was frequently attacked by leading figures in the Chinese Communist Party. This was partially a continuation of the condemnations of Confucianism by intellectuals and activists in the early 20th century as a cause of the ethnocentric close-mindedness and refusal of the Qing Dynasty to modernize that led to the tragedies that befell China in the 19th century.
Confucius's works are studied by scholars in many other Asian countries, particularly those in the Chinese cultural sphere, such as Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. Many of those countries still hold the traditional memorial ceremony every year.
Among Tibetans, Confucius is often worshipped as a holy king and master of magic, divination and astrology. Tibetan Buddhists see him as learning divination from the Buddha Manjushri
Mañjuśrī (Sanskrit: मञ्जुश्री) is a ''bodhisattva'' associated with '' prajñā'' (wisdom) in Mahāyāna Buddhism. His name means "Gentle Glory" in Sanskrit. Mañjuśrī is also known by the fuller name of Mañjuśrīkumārab ...
(and that knowledge subsequently reaching Tibet through Princess Wencheng), while Bon practitioners see him as being a reincarnation of Tonpa Shenrab Miwoche, the legendary founder of Bon.
The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community believes Confucius was a Divine Prophet of God, as were Lao-Tzu and other eminent Chinese personages.
In modern times, Asteroid 7853, "Confucius", was named after the Chinese thinker.
Disciples
Confucius began teaching after he turned 30, and taught more than 3,000 students in his life, about 70 of whom were considered outstanding. His disciples and the early Confucian community they formed became the most influential intellectual force in the Warring States period. The Han dynasty historianSima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years b ...
dedicated a chapter in his '' Records of the Grand Historian'' to the biographies of Confucius's disciples, accounting for the influence they exerted in their time and afterward. Sima Qian recorded the names of 77 disciples in his collective biography, while '' Kongzi Jiayu'', another early source, records 76, not completely overlapping. The two sources together yield the names of 96 disciples. Twenty-two of them are mentioned in the ''Analects
The ''Analects'' (; ; Old Chinese: '' ŋ(r)aʔ''; meaning "Selected Sayings"), also known as the ''Analects of Confucius'', the ''Sayings of Confucius'', or the ''Lun Yu'', is an ancient Chinese book composed of a large collection of sayings a ...
'', while the ''Mencius
Mencius ( ); born Mèng Kē (); or Mèngzǐ (; 372–289 BC) was a Chinese Confucianism, Confucian Chinese philosophy, philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, second to Confucius himself. He is part of Confuc ...
'' records 24.
Confucius did not charge any tuition, and only requested a symbolic gift of a bundle of dried meat from any prospective student. According to his disciple Zigong, his master treated students like doctors treated patients and did not turn anybody away. Most of them came from Lu, Confucius's home state, with 43 recorded, but he accepted students from all over China, with six from the state of Wey
Wey may refer to:
Places
*Wey (state) (衞), or Wei, ancient Chinese state during the Zhou Dynasty
*River Wey, river in Surrey, Hampshire and West Sussex, England
*River Wey (Dorset), river of Dorset, south west England
*Wey and Arun Canal, canal ...
(such as Zigong), three from Qin, two each from Chen and Qi, and one each from Cai, Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BC–223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BC–202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BC–70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
, and Song. Confucius considered his students' personal background irrelevant, and accepted noblemen, commoners, and even former criminals such as Yan Zhuoju and Gongye Chang
Gongye Chang (), courtesy name Zichang (), was a major disciple and the son-in-law of Confucius. Little is known about his life, but Chinese legends attribute to him the ability to understand birds' language.
Life
Gongye Chang's years of birth ...
. His disciples from richer families would pay a sum commensurate with their wealth which was considered a ritual donation.
Confucius's favorite disciple was Yan Hui, most probably one of the most impoverished of them all. Sima Niu, in contrast to Yan Hui, was from a hereditary noble family hailing from the Song state. Under Confucius's teachings, the disciples became well learned in the principles and methods of government. He often engaged in discussion and debate with his students and gave high importance to their studies in history, poetry, and ritual. Confucius advocated loyalty to principle rather than to individual acumen, in which reform was to be achieved by persuasion rather than violence. Even though Confucius denounced them for their practices, the aristocracy was likely attracted to the idea of having trustworthy officials who were studied in morals as the circumstances of the time made it desirable. In fact, the disciple Zilu even died defending his ruler in Wey
Wey may refer to:
Places
*Wey (state) (衞), or Wei, ancient Chinese state during the Zhou Dynasty
*River Wey, river in Surrey, Hampshire and West Sussex, England
*River Wey (Dorset), river of Dorset, south west England
*Wey and Arun Canal, canal ...
.
Yang Hu, who was a subordinate of the Ji family, had dominated the Lu government from 505 to 502 and even attempted a coup, which narrowly failed. As a likely consequence, it was after this that the first disciples of Confucius were appointed to government positions. A few of Confucius's disciples went on to attain official positions of some importance, some of which were arranged by Confucius. By the time Confucius was 50 years old, the Ji family had consolidated their power in the Lu state over the ruling ducal house. Even though the Ji family had practices with which Confucius disagreed and disapproved, they nonetheless gave Confucius's disciples many opportunities for employment. Confucius continued to remind his disciples to stay true to their principles and renounced those who did not, all the while being openly critical of the Ji family.
Visual portraits
 No contemporary painting or sculpture of Confucius survives, and it was only during the Han Dynasty that he was portrayed visually. Carvings often depict his legendary meeting with
No contemporary painting or sculpture of Confucius survives, and it was only during the Han Dynasty that he was portrayed visually. Carvings often depict his legendary meeting with Laozi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state
...
. Since that time there have been many portraits of Confucius as the ideal philosopher. An early verbal portrayal of Confucius is found in the chapter "External Things" () of the book '' Zhuangzi'' (), finished in about 3rd BCE, long after Confucius's death. The oldest known portrait of Confucius has been unearthed in the tomb of the Han dynasty ruler Marquis of Haihun (died ). The picture was painted on the wooden frame to a polished bronze mirror.
In former times, it was customary to have a portrait in Confucius Temples; however, during the reign of Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398.
As famine, plagues and peasant revolts in ...
(Taizu) of the Ming dynasty, it was decided that the only proper portrait of Confucius should be in the temple in his home town, Qufu in Shandong. In other temples, Confucius is represented by a memorial tablet. In 2006, the China Confucius Foundation commissioned a standard portrait of Confucius based on the Tang dynasty portrait by Wu Daozi.
The South Wall Frieze in the courtroom of the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
depicts Confucius as a teacher of harmony, learning, and virtue.
Fictional portrayals
There have been two film adaptations of Confucius' life: the 1940 film ''Confucius'' starring Tang Huaiqiu, and the 2010 film ''Confucius'' starring Chow Yun-fat.Memorials

 Soon after Confucius's death, Qufu, his home town, became a place of devotion and remembrance. The Han dynasty '' Records of the Grand Historian'' records that it had already become a place of pilgrimage for ministers. It is still a major destination for cultural tourism, and many people visit his grave and the surrounding temples. In Sinic cultures, there are many temples where representations of the Buddha,
Soon after Confucius's death, Qufu, his home town, became a place of devotion and remembrance. The Han dynasty '' Records of the Grand Historian'' records that it had already become a place of pilgrimage for ministers. It is still a major destination for cultural tourism, and many people visit his grave and the surrounding temples. In Sinic cultures, there are many temples where representations of the Buddha, Laozi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state
...
, and Confucius are found together. There are also many temples dedicated to him, which have been used for Confucian ceremonies.
Followers of Confucianism have a tradition of holding spectacular memorial ceremonies of Confucius () every year, using ceremonies that supposedly derived from Zhou Li () as recorded by Confucius, on the date of Confucius's birth. In the 20th century, this tradition was interrupted for several decades in mainland China, where the official stance of the Communist Party and the State was that Confucius and Confucianism represented reactionary feudalist beliefs which held that the subservience of the people to the aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At t ...
is a part of the natural order. All such ceremonies and rites were therefore banned. Only after the 1990s did the ceremony resume. As it is now considered a veneration of Chinese history and tradition, even Communist Party members may be found in attendance.
In Taiwan, where the Nationalist Party ( Kuomintang) strongly promoted Confucian beliefs in ethics and behavior, the tradition of the memorial ceremony of Confucius () is supported by the government and has continued without interruption. While not a national holiday, it does appear on all printed calendars, much as Father's Day or Christmas Day do in the Western world.
In South Korea, a grand-scale memorial ceremony called Seokjeon Daeje is held twice a year on Confucius's birthday and the anniversary of his death, at Confucian academies
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
across the country and Sungkyunkwan in Seoul.
Descendants
Confucius's descendants were repeatedly identified and honored by successive imperial governments with titles of nobility and official posts. They were honored with the rank of amarquis
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
35 times since Gaozu of the Han dynasty, and they were promoted to the rank of duke 42 times from the Tang dynasty to the Qing dynasty. Emperor Xuanzong of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was the seventh emperor of the Tang dynasty in China, reigning from 712 to 756 CE. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. In the early ...
first bestowed the title of "Duke Wenxuan" on Kong Suizhi of the 35th generation. In 1055, Emperor Renzong of Song
Emperor Renzong of Song (30 May 1010 – 30 April 1063), personal name Zhao Zhen, was the fourth emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned for about 41 years from 1022 to his death in 1063, and was the longest reigning Song dynasty empe ...
first bestowed the title of " Duke Yansheng" on Kong Zongyuan of the 46th generation.
During the Southern Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
, the Duke Yansheng Kong Duanyou fled south with the Song Emperor to Quzhou
Quzhou is a prefecture-level city in western Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. Sitting on the upper course of the Qiantang River, it borders Hangzhou to the north, Jinhua to the east, Lishui to the southeast, and the provinces o ...
in Zhejiang, while the newly established Jin dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (,
; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin
in ...
in the north appointed Kong Duanyou's brother Kong Duancao who remained in Qufu as Duke Yansheng. From that time up until the Yuan dynasty, there were two Duke Yanshengs, one in the north in Qufu and the other in the south at Quzhou. An invitation to come back to Qufu was extended to the southern Duke Yansheng Kong Zhu by the Yuan-dynasty Emperor Kublai Khan. The title was taken away from the southern branch after Kong Zhu rejected the invitation, so the northern branch of the family kept the title of Duke Yansheng. The southern branch remained in Quzhou where they live to this day. Confucius's descendants in Quzhou alone number 30,000. The Hanlin Academy
The Hanlin Academy was an academic and administrative institution of higher learning founded in the 8th century Tang China by Emperor Xuanzong in Chang'an.
Membership in the academy was confined to an elite group of scholars, who performed sec ...
rank of Wujing boshi 五經博士 was awarded to the southern branch at Quzhou by a Ming Emperor while the northern branch at Qufu held the title Duke Yansheng. The leader of the southern branch is 孔祥楷 Kong Xiangkai.
In 1351, during the reign of Emperor Toghon Temür of the Yuan dynasty, 53rd-generation descendant Kong Huan ()'s second son Kong Shao () moved from China to Korea during the Goryeo Dynasty
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean kingdom founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korean Peninsula until 1392. Goryeo achieved what has been called a "true national unificati ...
, and was received courteously by Princess Noguk
Princess Supreme Noguk (; d. 8 March 1365; ), also known as Queen Indeok () and Queen Mother Indeok () during her stepson, King U of Goryeo's reign, was a Yuan dynasty imperial family member as the great-granddaughter of Darmabala and niece of ...
(the Mongolian-born wife of the future king Gongmin). After being naturalized as a Korean citizen, he changed the hanja of his name from "昭" to "紹" (both pronounced ''so'' in Korean), married a Korean woman and bore a son (Gong Yeo (), 1329–1397), therefore establishing the Changwon Gong clan (), whose ancestral seat was located in Changwon
Changwon () is the capital city of Gyeongsangnam-do, on the southeast coast of South Korea. With a population of 1.07 million , Changwon is South Korea's ninth-most populous city.
A port city, Changwon is bordered by Masan Bay to the south ...
, South Gyeongsang Province. The clan then received an aristocratic rank during the succeeding Joseon dynasty. In 1794, during the reign of King Jeongjo, the clan then changed its name to Gokbu Gong clan
The Gokbu Gong clan () is one of the Korean clans originally from China. Their Bon-gwan () are in Qufu, Shandong in China, which was also Confucius's birthplace. Qufu is known as Gokbu () in Korean. According to the South Korean 2000 census, t ...
() in honor of Confucius's birthplace Qufu ().
Famous descendants include actors such as Gong Yoo (real name Gong Ji-cheol (공지철)) and Gong Hyo-jin (공효진); and artists such as male idol group B1A4 member Gongchan (real name Gong Chan-sik (공찬식)), singer-songwriter Minzy (real name Gong Min-ji (공민지)), as well as her great aunt, traditional folk dancer (공옥진).
Despite repeated dynastic change in China, the title of Duke Yansheng was bestowed upon successive generations of descendants until it was abolished by the Nationalist government in 1935. The last holder of the title, Kung Te-cheng of the 77th generation, was appointed Sacrificial Official to Confucius. Kung Te-cheng died in October 2008, and his son, Kung Wei-yi, the 78th lineal descendant, died in 1989. Kung Te-cheng's grandson, Kung Tsui-chang
Kung Tsui-chang (, born 1 July 1975) is the Sacrificial Official to Confucius in the Republic of China (Taiwan) and Senior Advisor to the President of the Republic of China.
Kung is the 79th-generation descendant of Confucius in the main li ...
, the 79th lineal descendant, was born in 1975; his great-grandson, Kung Yu-jen, the 80th lineal descendant, was born in Taipei on January 1, 2006. Te-cheng's sister, Kong Demao, lives in mainland China and has written a book about her experiences growing up at the family estate in Qufu. Another sister, Kong Deqi, died as a young woman.. Many descendants of Confucius still live in Qufu today.
A descendant of Confucius, H. H. Kung, was the Premier of the Republic of China. One of his sons, (孔令傑), married Debra Paget who gave birth to Gregory Kung ().
Confucius's family, the Kongs, have the longest recorded extant pedigree in the world today. The father-to-son family tree, now in its 83rd generation, has been recorded since the death of Confucius. According to the Confucius Genealogy Compilation Committee (CGCC), he has two million known and registered descendants, and there are an estimated three million in all.. Of these, several tens of thousands live outside of China. In the 14th century, a Kong descendant went to Korea, where an estimated 34,000 descendants of Confucius live today. One of the main lineages fled from the Kong ancestral home in Qufu during the Chinese Civil War in the 1940s and eventually settled in Taiwan. There are also branches of the Kong family who have converted to Islam after marrying Muslim women, in Dachuan in Gansu province in the 1800s, and in 1715 in Xuanwei in Yunnan province. Many of the Muslim Confucius descendants are descended from the marriage of Ma Jiaga (), a Muslim woman, and Kong Yanrong (), 59th generation descendant of Confucius in the year 1480, and are found among the Hui and Dongxiang peoples. The new genealogy includes the Muslims. Kong Dejun () is a prominent Islamic scholar and Arabist from Qinghai province and a 77th generation descendant of Confucius.
Because of the huge interest in the Confucius family tree, there was a project in China to test the DNA of known family members of the collateral branches in mainland China. Among other things, this would allow scientists to identify a common Y chromosome in male descendants of Confucius. If the descent were truly unbroken, father-to-son, since Confucius's lifetime, the males in the family would all have the same Y chromosome as their direct male ancestor, with slight mutations due to the passage of time. The aim of the genetic test was to help members of collateral branches in China who lost their genealogical records to prove their descent. However, in 2009, many of the collateral branches decided not to agree to DNA testing.. Bryan Sykes, professor of genetics at Oxford University, understands this decision: "The Confucius family tree has an enormous cultural significance ... It's not just a scientific question." The DNA testing was originally proposed to add new members, many of whose family record books were lost during 20th century upheavals, to the Confucian family tree. The main branch of the family which fled to Taiwan was never involved in the proposed DNA test at all.
In 2013 a DNA test performed on multiple different families who claimed descent from Confucius found that they shared the same Y chromosome as reported by Fudan University.
The fifth and most recent edition of the Confucius genealogy was printed by the CGCC. It was unveiled in a ceremony at Qufu on September 24, 2009.. Women are now included for the first time..
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
''See and for extensive bibliographies'' * Clements, Jonathan (2008). ''Confucius: A Biography''. Stroud, Gloucestershire, England: Sutton Publishing. . * Confucius (1997). ''Lun yu'', (in English ''The Analects of Confucius''). Translation and notes by Simon Leys. New York: W.W. Norton. . * Confucius (2003). ''Confucius: Analects – With Selections from Traditional Commentaries''. Translated by E. Slingerland. Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing. (Original work published c. ) . * Creel, Herrlee Glessner (1949). ''Confucius and the Chinese Way''. New York: Harper. * * Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2005). "Confucianism: An Overview". In Encyclopedia'' of Religion'' (Vol. C, pp. 1890–1905). Detroit: MacMillan Reference * * * * * Sterckx, Roel. ''Chinese Thought. From Confucius to Cook Ding.'' London: Penguin, 2019. * Van Norden, B.W., ed. (2001). ''Confucius and the Analects: New Essays''. New York: Oxford University Press. .External links
* * *Multilingual web site on Confucius and the Analects
The Dao of Kongzi
introduction to the thought of Confucius. * * *
Confucian Analects
(Project Gutenberg release of James Legge's Translation)
in the ''Analects of Confucius''. {{Authority control 551 BC births 479 BC deaths 6th-century BC historians 6th-century BC Chinese philosophers 6th-century BC Chinese writers 5th-century BC historians 5th-century BC Chinese philosophers 5th-century BC Chinese writers Aphorists Chinese educational theorists Chinese ethicists Chinese logicians Chinese political philosophers Classical humanists Confucianism Cultural critics Deified Chinese people Education theory Educators from Shandong Epistemologists Founders of philosophical traditions Founders of religions Gong clan of Qufu Guqin players Historians from Shandong Moral philosophers People from Qufu Politicians from Jining Philosophers from Lu (state) Philosophers from Shandong Philosophers of culture Philosophers of education Philosophers of ethics and morality Philosophers of law Chinese social commentators Social critics Social philosophers Writers from Jining Zhou dynasty historians Zhou dynasty philosophers Zhou dynasty politicians 5th-century BC Chinese musicians 6th-century BC Chinese musicians 6th-century BC religious leaders 5th-century BC religious leaders