Cilician Armenia-en on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilicia plain. The region includes the provinces of
page 680
, founder of the dynasty that ruled ''Cilicia Pedias'' was Mopsus,Fox, Robin Lane (2009) ''Travelling Heroes: In the Epic Age of Homer'' Alfred A. Knopf, New York
pages 211-224
, identifiable in Phoenician sources as ''Mpš'',Fox, Robin Lane (2009) ''Travelling Heroes: In the Epic Age of Homer'' Alfred A. Knopf, New York
page 216
, Edwards, I. E. S. (editor) (2006) ''The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 2, Part 2, History of the Middle East and the Aegean Region c. 1380–1000 B.C.'' (3rd edition) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England
page 364
, the founder of Mopsuestia who gave his name to an oracle nearby. Homer mentions the people of Mopsus, identified as Cilices (Κίλικες), as from the Troad in the northwestern-most part of Anatolia. The English spelling ''Cilicia'' is the same as the Latin, as it was transliterated directly from the Greek form Κιλικία. The palatalization of c occurring in the west in later
 The Cilicians appear as '' Hilikku'' in Assyrian inscriptions, and in the early part of the first millennium BC was one of the four chief powers of Western Asia. Homer mentions the plain as the "Aleian plain" in which
The Cilicians appear as '' Hilikku'' in Assyrian inscriptions, and in the early part of the first millennium BC was one of the four chief powers of Western Asia. Homer mentions the plain as the "Aleian plain" in which
 Under the Persian empire, Cilicia (in peo, Karka) was said to be governed by tributary native kings who bore a Hellenized name or the title of "Syennesis", and it was officially included in the fourth satrapy by
Under the Persian empire, Cilicia (in peo, Karka) was said to be governed by tributary native kings who bore a Hellenized name or the title of "Syennesis", and it was officially included in the fourth satrapy by
 Cilicia Trachea became the haunt of
Cilicia Trachea became the haunt of  It was reorganized by
It was reorganized by
 During the time of the First Crusade, the area was controlled by the
During the time of the First Crusade, the area was controlled by the
 Hetoum I (r. 1226–1270) made an alliance with the Mongols, sending his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in person. The Mongols then assisted with the defence of Cilicia from the Mamluks of Egypt, until the Mongols themselves converted to Islam.
Hetoum I (r. 1226–1270) made an alliance with the Mongols, sending his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in person. The Mongols then assisted with the defence of Cilicia from the Mamluks of Egypt, until the Mongols themselves converted to Islam.
 In 1359, Mamluk Sultanate Army marched into Cilicia and took over Adana and Tarsus, two major cities of the plain, leaving few castles to Armenians. In 1375, Mamluks gained the control of the remaining areas of Cilicia, thus ending the three centuries rule of Armenians. Cilicia Pedias became part of the Mamluk Sultanate in 1375.
The Karamanid Principality, one of the
In 1359, Mamluk Sultanate Army marched into Cilicia and took over Adana and Tarsus, two major cities of the plain, leaving few castles to Armenians. In 1375, Mamluks gained the control of the remaining areas of Cilicia, thus ending the three centuries rule of Armenians. Cilicia Pedias became part of the Mamluk Sultanate in 1375.
The Karamanid Principality, one of the
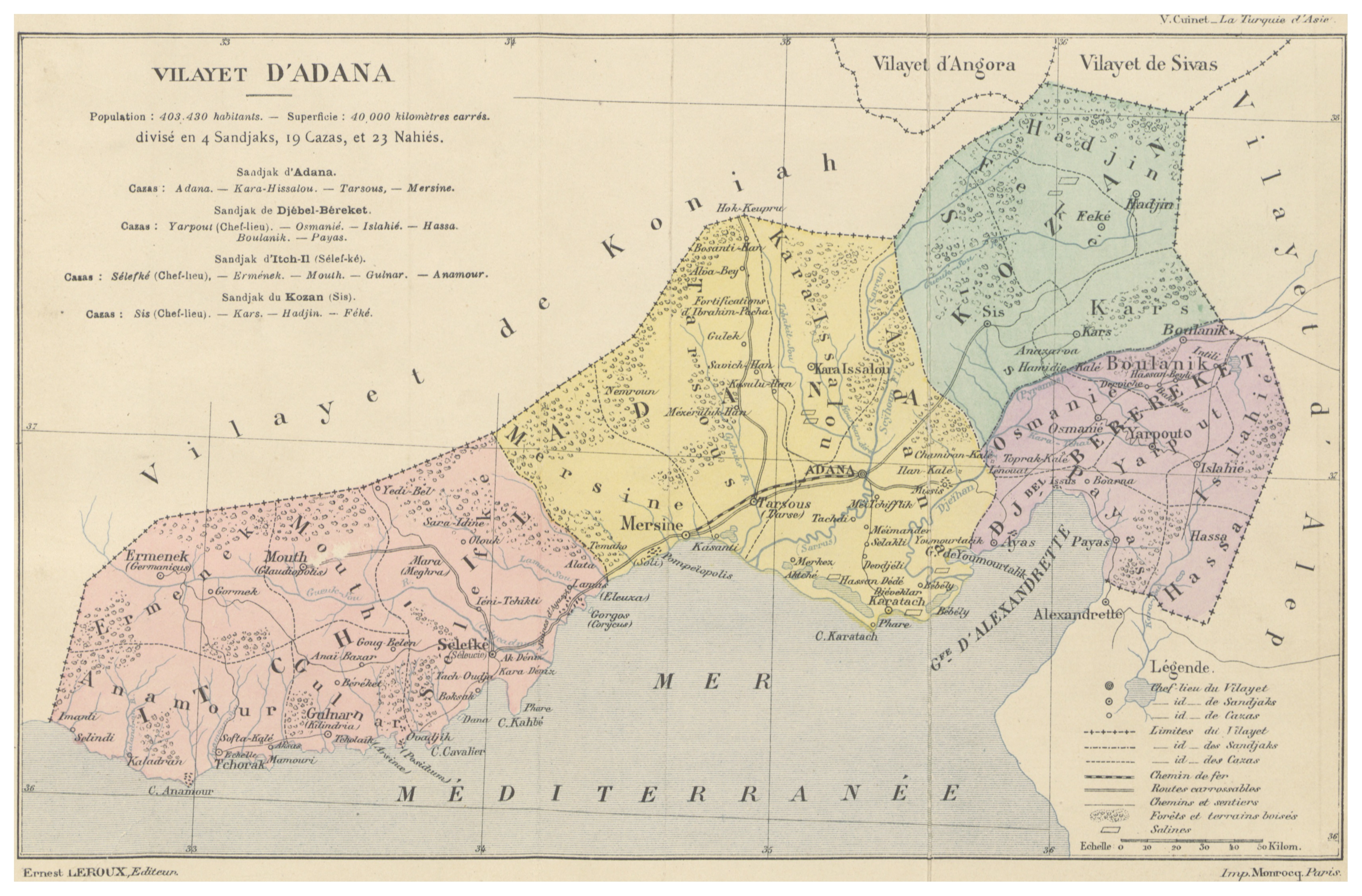
 Armistice of Mudros that was signed on 30 October 1918 to end the World War I, ceded the control of Cilicia to France. French Government sent four battalions of the
Armistice of Mudros that was signed on 30 October 1918 to end the World War I, ceded the control of Cilicia to France. French Government sent four battalions of the  With the changing political environment and interests, French further reversed their policy: The repatriation was halted, and the French ultimately abandoned all pretensions to Cilicia, which they had originally hoped to attach to their mandate over Syria. Cilicia Peace Treaty was signed on 9 March 1921 between France and Turkish Grand National Assembly. The treaty did not achieve the intended goals and was replaced with the
With the changing political environment and interests, French further reversed their policy: The repatriation was halted, and the French ultimately abandoned all pretensions to Cilicia, which they had originally hoped to attach to their mandate over Syria. Cilicia Peace Treaty was signed on 9 March 1921 between France and Turkish Grand National Assembly. The treaty did not achieve the intended goals and was replaced with the
 Lying at a crossroads of three major religions, namely Judaism, Christianity and
Lying at a crossroads of three major religions, namely Judaism, Christianity and
Das frühe Christentum im kilikisch-isaurischen Bergland. Die Christen der Kalykadnos-Region in den ersten fünf Jahrhunderten
(PDF; 27,4 MB)'' (Texte und Untersuchungen zur Geschichte der altchristlichen Literatur, vol. 184). Berlin/Boston: De Gruyter (). *''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 282/283, Symposium: Chalcolithic Cyprus. pp. 167–175. *Engels, David. 2008. "Cicéron comme proconsul en Cilicie et la guerre contre les Parthes", '' Revue Belge de Philologie et d'Histoire'' 86, pp. 23–45. *Pilhofer, Susanne. 2006
''Romanisierung in Kilikien? Das Zeugnis der Inschriften''
(Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt 46). Munich: Herbert Utz Verlag (). And: 2., erweiterte Auflage, mit einem Nachwort von Philipp Pilhofer (Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt 60) Munich: Herbert Utz Verlag ()
Ancient Cilicia - texts, photographs, maps, inscriptions
Photographs and Plans of the Churches and Fortifications in the Armenian Kingdom of CiliciaPilgrimages to Historic Armenia and Cilicia
{{Armenian diaspora Anatolia Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Ancient Greek geography Geography of Adana Province Historical regions of Anatolia History of Adana Province Historical regions Regions of Asia
Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
, Adana, Osmaniye, along with parts of Hatay
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province o ...
and Antalya.
Geography
Cilicia is extended along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separates it fromSyria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. North and east of Cilicia lie the rugged Taurus Mountains that separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, which are pierced by a narrow gorge called in antiquity the Cilician Gates. Ancient Cilicia was naturally divided into Cilicia Trachea and Cilicia Pedias by the Limonlu River. Salamis, the city on the east coast of Cyprus, was included in its administrative jurisdiction. The Greeks invented for Cilicia an eponymous Hellene founder in the purely mythical Cilix, but the historicEdwards, I. E. S. (editor) (2006) ''The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 2, Part 2, History of the Middle East and the Aegean Region c. 1380–1000 B.C.'' (3rd edition) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Englandpage 680
, founder of the dynasty that ruled ''Cilicia Pedias'' was Mopsus,Fox, Robin Lane (2009) ''Travelling Heroes: In the Epic Age of Homer'' Alfred A. Knopf, New York
pages 211-224
, identifiable in Phoenician sources as ''Mpš'',Fox, Robin Lane (2009) ''Travelling Heroes: In the Epic Age of Homer'' Alfred A. Knopf, New York
page 216
, Edwards, I. E. S. (editor) (2006) ''The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 2, Part 2, History of the Middle East and the Aegean Region c. 1380–1000 B.C.'' (3rd edition) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England
page 364
, the founder of Mopsuestia who gave his name to an oracle nearby. Homer mentions the people of Mopsus, identified as Cilices (Κίλικες), as from the Troad in the northwestern-most part of Anatolia. The English spelling ''Cilicia'' is the same as the Latin, as it was transliterated directly from the Greek form Κιλικία. The palatalization of c occurring in the west in later
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
(c. 500–700) accounts for its modern pronunciation in English.
Cilicia Trachea ("rugged Cilicia"— Greek: Κιλικία Τραχεῖα; the Assyrian ''Hilakku
Hilakku was one of the Neo-Hittite states during the Iron Age in southern Anatolia during the 1st millennium BC.
Hilakku was south of the Neo-Hittite state of Tabal, west of Que, and north of the Mediterranean sea. It covered the land of Cilicia ...
'', classical "Cilicia") is a rugged mountain district formed by the spurs of Taurus, which often terminate in rocky headlands with small sheltered harbours,Rife, Joseph L. (2002) "Officials of the Roman Provinces in Xenophon's "Ephesiaca"" ''Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik'' 138: pp. 93–108 , page 96 a feature which, in classical times, made the coast a string of havens for pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
and, in the Middle Ages, outposts for Genoese
Genoese may refer to:
* a person from Genoa
* Genoese dialect, a dialect of the Ligurian language
* Republic of Genoa (–1805), a former state in Liguria
See also
* Genovese, a surname
* Genovesi, a surname
*
*
*
*
* Genova (disambiguati ...
and Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
traders. The district is watered by the Calycadnus and was covered in ancient times by forests that supplied timber to Phoenicia and Egypt. Cilicia lacked large cities.
Cilicia Pedias ("flat Cilicia"— grc, Κιλικία Πεδιάς; Assyrian ''Kue''), to the east, included the rugged spurs of Taurus and a large coastal plain, with rich loamy soil, known to the Greeks such as Xenophon, who passed through with his mercenary group of the Ten Thousand, for its abundance (''euthemia''), filled with sesame
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
and millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
and olives and pasturage for the horses imported by Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
. Many of its high places were fortified. The plain is watered by the three great rivers, the Cydnus (Tarsus Çay Berdan River), the Sarus (Seyhan
Seyhan is a district-municipality in the Adana Province of Turkey, core of the Adana urban area. Seyhan is home to 35 percent of the residents of Adana Province and almost half of the residents of the city of Adana. It is the fifth most populous ...
), and the Pyramus (Ceyhan River
The Ceyhan River (historically Pyramos or Pyramus ( el, Πύραμος), Leucosyrus ( el, Λευκόσυρος) or Jihun) is a river in Anatolia in the south of Turkey.
Course of the river
The Ceyhan River (Pyramus) has its source (known as ' ...
), each of which brings down much silt from the deforested interior and which fed extensive wetlands. The Sarus now enters the sea almost due south of Tarsus, but there are clear indications that at one period it joined the Pyramus, and that the united rivers ran to the sea west of Kara-tash. Through the rich plain of Issus ran the great highway that linked east and west, on which stood the cities of Tarsus (Tarsa) on the Cydnus, Adana (Adanija) on the Sarus, and Mopsuestia (Missis) on the Pyramus.
Climate
The climate of Cilicia shows significant differences between the mountains and the lower plains. At the lower plains, the climate reflects a typical Mediterranean; summers are hot while winters are mild, making the land, particularly, the eastern plains, fertile. In the coldest month (January), the average temperature is 9 °C, and in the warmest month (August), the average temperature is 28 °C. The mountains of Cilicia have an inland climate with snowy winters. The average annual precipitation in the region is 647mm and the average number of rainy days in a year is 76.Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
and surrounding areas have the highest average temperature in Cilicia. Mersin also has high annual precipitation (1096mm) and 85 rainy days in a year.
Geology
The Mountains of Cilicia are formed from ancient limestones,conglomerate
Conglomerate or conglomeration may refer to:
* Conglomerate (company)
* Conglomerate (geology)
* Conglomerate (mathematics)
In popular culture:
* The Conglomerate (American group), a production crew and musical group founded by Busta Rhymes
** Co ...
, marlstone, and similar materials. The Taurus Mountains are composed of karstic limestone while its soil is also limestone-derived with pockets of volcanic soil. The lower plain is the largest alluvial plain
An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the sma ...
in Turkey. Expansion of limestone formations and fourth era alluvials brought by the rivers Seyhan
Seyhan is a district-municipality in the Adana Province of Turkey, core of the Adana urban area. Seyhan is home to 35 percent of the residents of Adana Province and almost half of the residents of the city of Adana. It is the fifth most populous ...
and Ceyhan, formed the plains of the region over the course of time.
Akyatan, Akyayan, Salt Lake, Seven lakes at Aladağ, and Karstik Dipsiz lake near Karaisalı are the lakes of the region. The reservoirs in the region are Seyhan, Çatalan, Yedigöze, Kozan and Mehmetli.
The major rivers in Cilicia are Seyhan
Seyhan is a district-municipality in the Adana Province of Turkey, core of the Adana urban area. Seyhan is home to 35 percent of the residents of Adana Province and almost half of the residents of the city of Adana. It is the fifth most populous ...
, Ceyhan, Berdan (Tarsus), Asi and Göksu
The Göksu ( Turkish for "sky water" also called ''Geuk Su'', ''Goksu Nehri''; la, Saleph, grc, Καλύκαδνος, translit=Calycadnus) is a river on the Taşeli plateau (Turkey). Both its sources arise in the Taurus Mountains—the northern ...
.
* Seyhan River emerges from the confluence of Zamantı and Göksu rivers which originate from Kayseri Province and flows into the Gulf of Mersin Gulf of Mersin ( tr, Mersin Körfezi) is one of the widest gulfs in Turkey. It is in the northeast of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost ...
. The river is 560 km long.
*Ceyhan River
The Ceyhan River (historically Pyramos or Pyramus ( el, Πύραμος), Leucosyrus ( el, Λευκόσυρος) or Jihun) is a river in Anatolia in the south of Turkey.
Course of the river
The Ceyhan River (Pyramus) has its source (known as ' ...
emerges from the confluence of the Aksu and Hurman rivers and flows towards Cape Hürmüz at the Gulf of İskenderun. It is 509 km long and it forms the Akyayan, Akyatan, and Kakarat lakes before flowing into the Mediterranean.
* Berdan River originates from the Taurus Mountains and flows into the Mediterranean, south of Tarsus.
*Göksu
The Göksu ( Turkish for "sky water" also called ''Geuk Su'', ''Goksu Nehri''; la, Saleph, grc, Καλύκαδνος, translit=Calycadnus) is a river on the Taşeli plateau (Turkey). Both its sources arise in the Taurus Mountains—the northern ...
river originates from the Taurus Mountains and flows into the Mediterranean, 16 km southeast of Silifke. It forms the delta of Göksu, including Akgöl Lake and Paradeniz Lagoon.
History
Neolithic to Neo-Assyrian period
Cilicia was settled from the Neolithic period onwards.Mellink, M.J. 1991.'' Anatolian Contacts with Chalcolithic Cyprus''. Dating of the ancient settlements of the region from Neolithic to Bronze Age is as follows: Aceramic/Neolithic: 8th and 7th millennia BC; Early Chalcolithic: 5800 BC; Middle Chalcolithic (correlated with Halaf and Ubaid developments in the east): c. 5400–4500 BC; Late Chalcolithic: 4500 – c. 3400 BC; and Early Bronze Age IA: 3400–3000 BC; EBA IB: 3000–2700 BC; EBA II: 2700–2400 BC; EBA III A-B: 2400–2000 BC. The area had been known as Kizzuwatna in the earlier Hittite era (2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC.
In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era:
The first half of the mil ...
). The region was divided into two parts, Uru Adaniya (flat Cilicia), a well-watered plain, and "rough" Cilicia (Tarza), in the mountainous west.
 The Cilicians appear as '' Hilikku'' in Assyrian inscriptions, and in the early part of the first millennium BC was one of the four chief powers of Western Asia. Homer mentions the plain as the "Aleian plain" in which
The Cilicians appear as '' Hilikku'' in Assyrian inscriptions, and in the early part of the first millennium BC was one of the four chief powers of Western Asia. Homer mentions the plain as the "Aleian plain" in which Bellerophon
Bellerophon (; Ancient Greek: Βελλεροφῶν) or Bellerophontes (), born as Hipponous, was a hero of Greek mythology. He was "the greatest hero and slayer of monsters, alongside Cadmus and Perseus, before the days of Heracles", and his ...
wandered, but he transferred the Cilicians far to the west and north and made them allies of Troy. The Cilician cities unknown to Homer already bore their pre-Greek names: Tarzu (Tarsus), Ingira ( Anchiale), Danuna-Adana, which retains its ancient name, Pahri (perhaps Mopsuestia), Kundu (Kyinda, then Anazarbus
Anazarbus ( grc, Ἀναζαρβός, medieval Ain Zarba; modern Anavarza; ar, عَيْنُ زَرْبَة) was an ancient Cilician city. Under the late Roman Empire, it was the capital of Cilicia Secunda. Roman emperor Justinian I rebuilt ...
) and Azatiwataya (today's Karatepe).
There exists evidence that circa 1650 BC both Hittite kings Hattusili I and Mursili I enjoyed the freedom of movement along the Pyramus River (now the Ceyhan River in southern Turkey), proving they exerted strong control over Cilicia in their battles with Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. After the death of Murshili around 1595 BC, Hurrians
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern Mes ...
wrested control from the Hitties, and Cilicia was free for two centuries. The first king of free Cilicia, Išputahšu, son of Pariyawatri
Isputahsu (also transliterated as Išputaḫšu) was a king of Kizzuwatna, probably during the mid 15th century BC ( short chronology). He signed a treaty of alliance with the Hittite king Telepinu.
Family
His father was Pariyawatri, who maybe w ...
, was recorded as a "great king" in both cuneiform and Hittite hieroglyphs. Another record of Hittite origins, a treaty between Išputahšu and Telipinu, king of the Hittites, is recorded in both Hittite and Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
.
In the next century, the Cilician king Pilliya
Pilliya was a king of Kizzuwatna ca. the 15th century BC (short chronology). He signed a treaty with Idrimi
Idrimi was the king of Alalakh c. 1490–1465 BC, or around 1450 BC. He is known, mainly, from an inscription on his statue found at Alal ...
finalized treaties with both King Zidanta II of the Hittites and Idrimi
Idrimi was the king of Alalakh c. 1490–1465 BC, or around 1450 BC. He is known, mainly, from an inscription on his statue found at Alalakh by Leonard Woolley in 1939.Longman III, Tremper, (1991)Fictional Akkadian Autobiography: A Generic and Co ...
of Alalakh, in which Idrimi mentions that he had assaulted several military targets throughout Eastern Cilicia. Niqmepa, who succeeded Idrimi as king of Alalakh, went so far as to ask for help from a Hurrian rival, Shaushtatar of Mitanni, to try and reduce Cilicia's power in the region. It was soon apparent, however, that increased Hittite power would soon prove Niqmepa's efforts to be futile, as the city of Kizzuwatna soon fell to the Hittites, threatening all of Cilicia. Soon after, King Sunassura II was forced to accept vassalization under the Hittites, becoming the last king of ancient Cilicia. After the death of Mursili I, which led to a power struggle among rival claimants to the throne, eventually leading to the collapse of Hittite supremacy, Cilicia appeared to have regained its independence.
In the 13th century BC a major population shift occurred as the Sea Peoples overran Cilicia. The Hurrians that resided there deserted the area and moved northeast towards the Taurus Mountains, where they settled in the area of Cappadocia. In the 8th century BC, the region was unified under the rule of the dynasty of Mukšuš, whom the Greeks rendered Mopsos and credited as the founder of Mopsuestia, though the capital was Adana. Mopsuestia's multicultural character is reflected in the bilingual inscriptions of the ninth and eighth centuries, written both in Indo-European hieroglyphic Luwian and West Semitic Phoenician. In the ninth century BC, it became part of Assyria and remained so until the late seventh century BC.
Kingdom of Cilicia and Persian period
Before the early foundings of the kingdom, Cilicians had to protect themselves from Assyrian domination. After the dissolution of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 612 BC, they established an independent kingdom from Syria. Given the fact that Cilicia was a strategically significant location, Cilicians were able to expand their kingdom as far north as the Halys River in a short period of time. With these expansions, the Cilician Kingdom became as strong asBabylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
, one of the contemporary powerhouses.
The Syennesis dynasty emerged in Cilicia and seemed to have been based in its western part during the reign of Appuašu. The peaceful governance of the Syennesis dynasty sustained the kingdom and prevented the Achaemenid Empire from attacking Lydians after the Achaemenid invasions of Median lands. Appuašu, the son of Syennesis, defended the country against the Babylonian king Neriglissar, whose army reached Cilicia and crossed the Taurus mountain range.
The Achaemenids defeated the Lydians, and Appuašu had to recognize the authority of the Persians in 549 BC to keep the local administration with the Cilicians. Cilicia became an autonomous satrapy under the reign of Cyrus II. Cilicians were independent in their internal affairs and kept this autonomy for almost 150 years. In 401, Syennesis III and his wife Epyaxa supported the revolt of Cyrus the Younger against his brother Artaxerxes II Mnemon. This was sound policy because otherwise, Cilicia would have been looted by the rebel army. However, after the defeat of Cyrus at Cunaxa, keeping Syennesis' position was difficult. Most scholars assume that this behavior marked the end of the independence of Cilicia. After 400, it became a normal satrapy.
 Under the Persian empire, Cilicia (in peo, Karka) was said to be governed by tributary native kings who bore a Hellenized name or the title of "Syennesis", and it was officially included in the fourth satrapy by
Under the Persian empire, Cilicia (in peo, Karka) was said to be governed by tributary native kings who bore a Hellenized name or the title of "Syennesis", and it was officially included in the fourth satrapy by Darius
Darius may refer to:
Persian royalty
;Kings of the Achaemenid Empire
* Darius I (the Great, 550 to 487 BC)
* Darius II (423 to 404 BC)
* Darius III (Codomannus, 380 to 330 BC)
;Crown princes
* Darius (son of Xerxes I), crown prince of Persia, ma ...
. Xenophon found a queen in power, and no opposition was offered to the takeover of Cyrus the Younger
Cyrus the Younger ( peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ''Kūruš''; grc-gre, Κῦρος ; died 401 BC) was an Achaemenid prince and general. He ruled as satrap of Lydia and Ionia from 408 to 401 BC. Son of Darius II and Parysatis, he died in 401 BC i ...
.
Roads
The great highway from the west existed before Cyrus conquered Cilicia. On its long rough descent from the Anatolian plateau to Tarsus, it ran through the narrow pass between walls of rock called the Cilician Gates. After crossing the low hills east of the Pyramus it passed through a masonry (Cilician) gate, Demir Kapu, and entered the plain of Issus. From that plain one road ran southward through another masonry (Syrian) gate to Alexandretta, and thence crossed Mt. Amanus by the Syrian Gate, Beilan Pass, eventually to Antioch and Syria. Another road ran northwards through a masonry (Armenian) gate, south of Toprak Kale, and crossed Mt. Amanus by the Armenian Gate, Baghche Pass, to northern Syria and the Euphrates. By the last pass, which was apparently unknown to Alexander, Darius crossed the mountains prior to the battle of Issus. Both passes are short and easy and connect Cilicia Pedias geographically and politically with Syria rather than with Anatolia.Hellenistic period
Alexander forded the Halys River in the summer of 333 BC, ending up on the border of southeasternPhrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
and Cilicia. He knew well the writings of Xenophon, and how the Cilician Gates had been "impassable if obstructed by the enemy". Alexander reasoned that by force alone he could frighten the defenders and breakthrough, and he gathered his men to do so. In the cover of night, they attacked, startling the guards and sending them and their satrap into full flight, setting their crops aflame as they made for Tarsus. This good fortune allowed Alexander and his army to pass unharmed through the Gates and into Cilicia. After Alexander's death it was long a battleground of the rival Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
monarchs and kingdoms, and for a time fell under Ptolemaic dominion (i.e., Egypt), but finally came to the Seleucids, who, however, never held effectually more than the eastern half. During the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
era, numerous cities were established in Cilicia, which minted coins showing the badges (gods, animals, and objects) associated with each polis.
Roman and Byzantine periods
 Cilicia Trachea became the haunt of
Cilicia Trachea became the haunt of pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
, who were subdued by Pompey in 67 BC following a Battle of Korakesion
The Battle of Korakesion, also known as the Battle of Coracaesium, was a naval battle fought in 67 BC between the Cilician Pirates and the Roman Republic. It was the culmination of Pompey the Great's campaign against the pirates of the Mediterrane ...
(modern Alanya), and Tarsus was made the capital of the Roman province of Cilicia. Cilicia Pedias became Roman territory in 103 BC first conquered by Marcus Antonius Orator in his campaign against pirates, with Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had ...
acting as its first governor, foiling an invasion of Mithridates
Mithridates or Mithradates ( Old Persian 𐎷𐎡𐎰𐎼𐎭𐎠𐎫 ''Miθradāta'') is the Hellenistic form of an Iranian theophoric name, meaning "given by the Mithra". Its Modern Persian form is Mehrdad. It may refer to:
Rulers
*Of Cius (al ...
, and the whole was organized by Pompey, 64 BC, into a province which, for a short time, extended to and included part of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
.
 It was reorganized by
It was reorganized by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
, 47 BC, and about 27 BC became part of the province Syria-Cilicia Phoenice. At first, the western district was left independent under native kings or priest-dynasts, and a small kingdom, under Tarcondimotus I, was left in the east; but these were finally united to the province by Vespasian, AD 72. Containing 47 known cities, it had been deemed important enough to be governed by a proconsul.
Under Emperor Diocletian's Tetrarchy (c. 297), Cilicia was governed by a '' consularis''; with Isauria and the Syrian, Mesopotamian, Egyptian and Libyan provinces, formed the Diocesis Orientis
The Diocese of the East ( la, Dioecesis Orientis; el, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of the majo ...
(in the late 4th century the African component was split off as Diocese of Egypt), part of the pretorian prefecture also called ''Oriens'' ('the East', also including the dioceses of Asiana and Pontica, both in Anatolia, and Thraciae
The Diocese of Thrace ( la, Dioecesis Thraciae, el, Διοίκησις Θρᾴκης) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the eastern Balkan Peninsula (comprising territories in modern south-eastern Romania, c ...
in the Balkans), the rich bulk of the eastern Roman Empire. After the division of the Roman Empire, Cilicia became part of the eastern Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire. Cilicia was one of the most important regions of the classical world and can be considered as the birthplace of Christianity.
Early Islamic period
In the 7th century Cilicia was invaded by the Muslim Arabs. The area was for some time an embattled no-man's land. The Arabs succeeded in conquering the area in the early 8th century. Under the Abbasid Caliphate, Cilicia was resettled and transformed into a fortified frontier zone ('' thughur''). Tarsus, re-built in 787/788, quickly became the largest settlement in the region and the Arabs' most important base in their raids across the Taurus Mountains into Byzantine-held Anatolia. The Muslims held the country until it was reoccupied by the Emperor Nicephorus II in 965. From this period onward, the area increasingly came to be settled by Armenians, especially as Imperial rule pushed deeper into the Caucasus over the course of the 11th century.Armenian Cilicia and the Crusades
Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, ...
. The Seljuk Turk
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
ish invasions of Armenia were followed by an exodus of Armenians migrating westward into the Byzantine Empire, and in 1080 Ruben, a relative of the last king of Ani, founded in the heart of the Cilician Taurus a small principality which gradually expanded into the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, ...
. This Christian state, surrounded by Muslim states hostile to its existence, had a stormy history of about 300 years, giving valuable support to the Crusaders, and trading with the great commercial cities of Italy.
It prospered for three centuries due to the vast network of fortifications which secured all the major roads as well as the three principal harbours at Ayas
Ayas may refer to:
Ayas
* Ayas(आयस), Sanskrit for metal, see history of metallurgy in the Indian subcontinent
* Ayas, Armenian metal band
* Aya, Adana, the ancient city of Aegeae and medieval Ajazzo or Laiazzo, now Yumurtalık, Adana Prov ...
, Koŕikos, and Mopsuestia. Through their complex alliances with the Crusader states, the Armenian barons and kings often invited Crusaders to maintain castles in and along the borders of the Kingdom, including Bagras, Trapessac, T‛il Hamtun, Harunia, Selefkia, Amouda
The castle of Amouda Crusader castle, formerly in the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, and today close to the village of Gökçedam in the Turkish Province of Osmaniye. The castle was deeded by the Armenian king Levon I to the Teutonic Knights in 12 ...
, and Sarvandikar.
Gosdantin (r. 1095 – c. 1100) assisted the Crusaders on their march to Antioch, and was created knight and marquis
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
. Thoros I (r. c. 1100 – 1129), in alliance with the Christian princes of Syria, waged successful wars against the Byzantines and Seljuk Turks. Levon II
Leo II or Leon II (occasionally numbered Leo III; , ''Levon II''; c. 1236 – 1289) was king of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, ruling from 1269''Cambridge Medieval History'', Volume IV, p. 634/1270 to 1289. He was the son of King Hetoum I ...
(Leo the Great (r. 1187–1219)), extended the kingdom beyond Mount Taurus and established the capital at Sis. He assisted the Crusaders, was crowned King by the Archbishop of Mainz
The Elector of Mainz was one of the seven Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire. As both the Archbishop of Mainz and the ruling prince of the Electorate of Mainz, the Elector of Mainz held a powerful position during the Middle Ages. The Archb ...
, and married one of the Lusignans of the Crusader Kingdom of Cyprus.
Mongols
 Hetoum I (r. 1226–1270) made an alliance with the Mongols, sending his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in person. The Mongols then assisted with the defence of Cilicia from the Mamluks of Egypt, until the Mongols themselves converted to Islam.
Hetoum I (r. 1226–1270) made an alliance with the Mongols, sending his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in person. The Mongols then assisted with the defence of Cilicia from the Mamluks of Egypt, until the Mongols themselves converted to Islam.
Turkmens
The Ilkhanate lost cohesion after the death ofAbu Sa'id
Abu or ABU may refer to:
Places
* Abu (volcano), a volcano on the island of Honshū in Japan
* Abu, Yamaguchi, a town in Japan
* Ahmadu Bello University, a university located in Zaria, Nigeria
* Atlantic Baptist University, a Christian universi ...
(r. 1316–1335), and thus could not support the Armenian Kingdom in guarding Cilicia. Internal conflicts within the Armenian Kingdom and the devastation caused by the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
that arrived in 1348, led nomadic Türkmens to turn their eyes towards unstable Cilicia. In 1352, Ramazan Beg led Turkmens settled south of Çaldağı and founded their first settlement, Camili. Later that year, Ramazan Beg visited Cairo and was assented by the Sultan to establish the new frontier ''Turkmen Emirate'' in Cilicia.
Collapse
When Levon V died (1342), John of Lusignan was crowned king as Gosdantin IV; but he and his successors alienated the native Armenians by attempting to make them conform to the Roman Church, and by giving all posts of honour toLatins
The Latins were originally an Italic tribe in ancient central Italy from Latium. As Roman power and colonization spread Latin culture during the Roman Republic.
Latins culturally "Romanized" or "Latinized" the rest of Italy, and the word Latin ...
, until at last the kingdom, falling prey to internal dissensions, ceded Cilicia Pedias to the Ramadanid
The Ramadanid Emirate ( Modern Turkish: ''Ramazanoğulları Beyliği'') was an autonomous administration and a ''de facto'' independent emirate that existed from 1352 to 1608 in Cilicia, taking over the rule of the region from the Armenian Kingd ...
-supported Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt in 1375.
Mamluk and Turkmen rule
Turkmen
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
Anatolian beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A secon ...
emerged after the collapse of the Anatolian Seljuks, took over the rule of Cilicia Thracea.
Ottoman period
In 1516, Selim I incorporated the beylik into the Ottoman Empire after his conquest of the Mamluk state. The beys of Ramadanids held the administration of the Ottoman sanjak of Adana in a hereditary manner until 1608, with the last 92 years as a vassal of the Ottomans.
Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
ended the Ramadanid administration of Adana sanjak in 1608, and ruled it directly from Constantinople then after. The autonomous sanjak was then split from the Aleppo Eyalet and established as a new province under the name of Adana Eyalet. A governor was appointed to administer the province. In late 1832, Eyalet of Egypt
The Eyalet of Egypt (, ) operated as an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire from 1517 to 1867. It originated as a result of the conquest of Mamluk Egypt by the Ottomans in 1517, following the Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–17) and th ...
Vali Muhammad Ali Pasha invaded Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, and reached Cilicia. The Convention of Kütahya
The Convention of Kütahya, also known as the Peace Agreement of Kütahya, ended the Egyptian–Ottoman War (1831–1833) in May 1833.
Information
At the Convention, the Ottoman provinces of Syria and Adana were ceded to Egypt, and Ibrahim Pash ...
that was signed on 14 May 1833, ceded Cilicia to the ''de facto'' independent Egypt. After the Oriental crisis
The Oriental Crisis of 1840 was an episode in the Egyptian–Ottoman War in the eastern Mediterranean, triggered by the self-declared Khedive of Egypt and Sudan Muhammad Ali Pasha's aims to establish a personal empire in the Ottoman province ...
, the Convention of Alexandria that was signed on 27 November 1840, required the return of Cilicia to Ottoman sovereignty. The American Civil War that broke out in 1861 disturbed the cotton flow to Europe and directed European cotton traders to fertile Cilicia. The region became the centre of cotton trade and one of the most economically strong regions of the Empire within decades. In 1869, Adana Eyalet was re-established as Adana Vilayet, after the re-structuring in the Ottoman Administration.
Thriving regional economy, doubling of Cilician Armenian population due to flee from Hamidian massacres
The Hamidian massacres also called the Armenian massacres, were massacres of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire in the mid-1890s. Estimated casualties ranged from 100,000 to 300,000, Akçam, Taner (2006) '' A Shameful Act: The Armenian Genocide an ...
, the end of autocratic Abdulhamid ʻAbd al-Ḥamīd ( ALA-LC romanization of ar, عبد الحميد) is a Muslim male given name, and in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' ʻabd'' and ''al-Ḥamīd'', one of the names of God in the Qur'an, which gave rise ...
rule with the revolution of 1908, empowered the Armenian community and envisioned an autonomous Cilicia. Enraged supporters of Abdulhamid that organized under Cemiyet-i Muhammediye amidst the countercoup, led to a series of anti-Armenian pogroms in 14–27 April 1909. The Adana massacre resulted in the deaths of roughly 25,000 Armenians, orphaned 3500 children and caused heavy destruction of Christian neighbourhoods in the entire Vilayet.
Cilicia section of the Berlin–Baghdad railway
The Baghdad railway, also known as the Berlin–Baghdad railway ( tr, Bağdat Demiryolu, german: Bagdadbahn, ar, سكة حديد بغداد, french: Chemin de Fer Impérial Ottoman de Bagdad), was started in 1903 to connect Berlin with the ...
were opened in 1912, connecting the region to Middle East. Over the course of Armenian genocide, Ottoman telegraph was received by the Governor to deport the more than 70,000 Armenians of the Adana Vilayet to Syria. Armenians of Zeitun had organized a successful resistance against the Ottoman onslaught. In order to finally subjugate Zeitun, the Ottomans had to resort to treachery by forcing an Armenian delegation from Marash to ask the ''Zeituntsi''s to put down their arms. Both the Armenian delegation, and later, the inhabitants of Zeitun, were left with no choice.
Modern era
 Armistice of Mudros that was signed on 30 October 1918 to end the World War I, ceded the control of Cilicia to France. French Government sent four battalions of the
Armistice of Mudros that was signed on 30 October 1918 to end the World War I, ceded the control of Cilicia to France. French Government sent four battalions of the Armenian Legion
The Armenian Legion (german: Armenische Legion; hy, Հայկական լեգիոն ''Haykakan legion'') was a military unit in the German Army during World War II. It primarily consisted of Soviet Armenians, who wanted to fight the Russians for an ...
in December to take over and oversee the repatriation of more than 170,000 Armenians to Cilicia.
On May 4, 1920 Armenian people declared the independence of Cilicia under the French mandate.
The French forces were spread too thinly in the region and, as they came under withering attacks by Muslim elements both opposed and loyal to Mustafa Kemal Pasha, eventually reversed their policies in the region. A truce arranged on May 28 between the French and the Kemalists, led to the retreat of the French forces south of the Mersin-Osmaniye railroad.
 With the changing political environment and interests, French further reversed their policy: The repatriation was halted, and the French ultimately abandoned all pretensions to Cilicia, which they had originally hoped to attach to their mandate over Syria. Cilicia Peace Treaty was signed on 9 March 1921 between France and Turkish Grand National Assembly. The treaty did not achieve the intended goals and was replaced with the
With the changing political environment and interests, French further reversed their policy: The repatriation was halted, and the French ultimately abandoned all pretensions to Cilicia, which they had originally hoped to attach to their mandate over Syria. Cilicia Peace Treaty was signed on 9 March 1921 between France and Turkish Grand National Assembly. The treaty did not achieve the intended goals and was replaced with the Treaty of Ankara Treaty of Ankara may refer to:
*Treaty of Ankara (1921)
*Treaty of Ankara (1926)
The Treaty of Ankara (1926), also known as The Frontier Treaty of 1926 ( tr, Ankara Anlaşması), was signed 5 June 1926 in Ankara by Turkey, United Kingdom and M ...
that was signed on 20 October 1921. Based on the terms of the agreement, France recognized the end of the Cilicia War
The Franco–Turkish War, known as the Cilicia Campaign (french: La campagne de Cilicie) in France and as the Southern Front ( tr, Güney Cephesi) of the Turkish War of Independence in Turkey, was a series of conflicts fought between France (the ...
, and French troops together with the remaining Armenian volunteers withdrew from the region in early January 1922.
Republic of Turkey
The region become part of theRepublic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
in 1921 with the signing of the Treaty of Ankara. On 15 April 1923, just before the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conflic ...
, the Turkish government enacted the "Law of Abandoned Properties" which confiscated properties of Armenians and Greeks who were not present on their property. Cilicia were one of the regions with the most confiscated property, thus muhacirs (en: immigrants) from Balkans and Crete were relocated in the old Armenian and Greek neighbourhoods and villages of the region. All types of properties, lands, houses and workshops were distributed to them. Also during this period, there was a property rush of Muslims from Kayseri
Kayseri (; el, Καισάρεια) is a large Industrialisation, industrialised List of cities in Turkey, city in Central Anatolia, Turkey, and the capital of Kayseri Province, Kayseri province. The Kayseri Metropolitan Municipality area is comp ...
and Darende to Cilicia who were granted the ownership of large farms, factories, stores and mansions. Within a decade, Cilicia had a sharp change demographically, socially and economically and lost its diversity by turning into solely Muslim/Turkish.
Administrative divisions
The modern Cilicia is split into four administrative provinces:Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
, Adana, Osmaniye and Hatay
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province o ...
. Each province is governed by the Central Government in Ankara through an appointed Provincial governor. Provinces are then divided into districts governed by the District Governors who are under the provincial governors.
Population
Cilicia is heavily populated due to its abundant resources, climate and plain geography. The population of Cilicia as of December 31, 2021 is 6,378,242. Hatay is the most rural province of Cilicia and also Hatay is the only province that the rural population is rising and the urban population is declining. The major reason is the mountainous geography of Hatay. Significant Christian communities (Antiochian Greek Christians
Antiochian Greek Christians (also known as Antiochian Rum (endonym), Rūm) are a Levantine Arabic-speaking ethnoreligious Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian group residing in the Levant region. They are either members of the Greek Orthodox Chu ...
and Armenians) found in Adana, İskenderun, and Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
.
Adana Province is the most urbanized province, with most of the population centred in the city of Adana. Mersin Province has a larger rural population than Adana Province, owing to its long and narrow stretch of flat land in between the Taurus Mountains and the Mediterranean.
Economy
Cilicia is well known for the vast fertile land and highly productive agriculture. The region is also industrialized; Tarsus, Adana and Ceyhan host numerous plants.Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
and İskenderun seaports provide transportation of goods manufactured in Central, South and Southeast Anatolia. Ceyhan hosts oil, natural gas terminals as well as refineries and shipbuilders.
Natural resources
Agriculture
The Cilicia plain has some of the most fertile soil in the world in which 3 harvests can be taken each year. The region has the second richest flora in the world and it is the producer of all agricultural products of Turkey except hazelnut and tobacco. Cilicia leads Turkey in soy, peanuts and corn harvest and is a major producer of fruits and vegetables. Half of Turkey's citrus export is from Cilicia. Anamur is the only sub-tropical area of Turkey where bananas, mango, kiwi and other sub-tropical produce can be harvested. Cilicia is the second largest honey producer in Turkey after the Muğla–Aydın
Aydın ( ''EYE-din''; ; formerly named ''Güzelhisar'', Ancient and Modern Greek: Τράλλεις /''Tralleis''/) is a city in and the seat of Aydın Province in Turkey's Aegean Region. The city is located at the heart of the lower valley of B ...
region. Samandağ
Samandağ ( ar, السويدية, ''as-Sūwaydīyah''), formerly known as Süveydiye, is a town and district in Hatay Province of southern Turkey, at the mouth of the Asi River on the Mediterranean coast, near Turkey's border with Syria, from t ...
, Yumurtalık, Karataş and Bozyazı are some of the towns in the region where fishing is the major source of income. Gray mullet, red mullet, sea bass, lagos, calamari and gilt-head bream are some of the most popular fish in the region. There are aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
farms in Akyatan, Akyağan, Yumurtalık lakes and at Seyhan Reservoir. While not as common as other forms of agriculture, dairy and livestock are also produced throughout the region.
Mining
* Zinc and lead: Kozan-Horzum seam is the major source. *Chrome
Chrome may refer to:
Materials
* Chrome plating, a process of surfacing with chromium
* Chrome alum, a chemical used in mordanting and photographic film
Computing
* Google Chrome, a web browser developed by Google
** ChromeOS, a Google Chrome- ...
is found around Aladağlar.
*Baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
resources are around Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
and Adana.
* Iron is found around Feke and Saimbeyli
Saimbeyli, alternatively known as Hadjin ( hy, Հաճըն, translit=Hajěn), is a township and a district in the Adana Province, Turkey. The township is located at the Taurus mountains of Cilicia region, 157 km north of the city of Adana. The dist ...
.
*Asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
mines are mostly in Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of A ...
.
* Limestone reserves are very rich in Cilicia. The region is home to four lime manufacturing plants.
* Pumice resources are the richest in Turkey. 14% of country's reserves are in Cilicia.
Manufacturing
Cilicia is one of the first industrialized regions of Turkey. With the improvements in agriculture and the spike of agricultural yield, agriculture-based industries are built in large numbers. Today, the manufacturing industry is mainly concentrated around Tarsus, Adana and Ceyhan. Textile, leather tanning and food processing plants are plentiful. İsdemir is a large steel plant located in İskenderun. The petrochemical industry is rapidly developing in the region with the investments around the Ceyhan Oil Terminal. Petroleum refineries are being built in the area. Ceyhan is also expected to host the shipbuilding industry.Commerce
Adana is the commercial centre of the region where many of the public and private institutions have their regional offices.Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
and Antakya are also home to regional offices of public institutions. Many industry fairs and congresses are held in the region at venues such as the TÜYAP Congress and Exhibition Centre in Adana and the Mersin Congress Centre.
Mersin Seaport is the third largest seaport in Turkey, after Istanbul and İzmir. There are 45 piers in the port. The total area of the port is 785 square kilometres (194,000 acres), and the capacity is 6,000 ships per year.
İskenderun Seaport is used mostly for transfers to Middle East and Southeastern Turkey.
Ceyhan Oil Terminal is a marine transport terminal for the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline (the "BTC"), the Kirkuk–Ceyhan Oil Pipeline
The Kirkuk–Ceyhan Oil Pipeline, also known as the Iraq–Turkey Crude Oil Pipeline, is a pipeline that runs from Kirkuk in Iraq to Ceyhan in Turkey. It is Iraq's largest crude oil export line.
Technical description
The pipeline consists two pi ...
, the planned Samsun-Ceyhan and the Ceyhan-Red Sea pipelines. Ceyhan will also be a natural gas terminal for a planned pipeline to be constructed parallel to the Kirkuk-Ceyhan oil pipeline, and for a planned extension of the Blue Stream Gas Pipeline from Samsun to Ceyhan.
Dörtyol Oil Terminal is a marine transport terminal for Batman-Dörtyol oil pipeline which started operating in 1967 to market Batman
Batman is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by artist Bob Kane and writer Bill Finger, and debuted in Detective Comics 27, the 27th issue of the comic book ''Detective Comics'' on ...
oil. The pipeline is 511 km long and has an annual capacity of 3.5 million tons.
Tourism
While the region has a long coastline, international tourism is not at the level of the neighbouring Antalya Province. There are a small number of hotels between Erdemli and Anamur that attracts tourists. Cilicia tourism is mostly cottage tourism serving the Cilicia locals as well as residents ofKayseri
Kayseri (; el, Καισάρεια) is a large Industrialisation, industrialised List of cities in Turkey, city in Central Anatolia, Turkey, and the capital of Kayseri Province, Kayseri province. The Kayseri Metropolitan Municipality area is comp ...
, Gaziantep and surrounding areas. Between Silifke and Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
, high-rise and low-rise cottages line the coast, leaving almost no vacant land. The coastline from Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
to Karataş is mostly farmland. This area is zoned for resort tourism and is expected to have a rapid development within the next 20 years. Karataş and Yumurtalık coasts are home to cottages with a bird conservatory between the two areas. Arsuz is a seaside resort that is mostly frequented by Antakya and İskenderun residents.
Plateaus on the Taurus mountains are cooler escapes for the locals who wants to chill out from hot and humid summers of the lower plains. Gözne and Çamlıyayla (Namrun) in Mersin Province, Tekir, Bürücek and Kızıldağ in Adana Province, Zorkun in Osmaniye Province and Soğukoluk in Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of A ...
are the popular high plain resorts of Cilicia which are often crowded in summer. There are a few hotels and camping sites in the Tekir plateau.
Balneary tourism
The region is a popular destination forthermal springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by c ...
. Hamamat Thermal Spring, located on midway from Kırıkhan
Kırıkhan is a town and district in the northeastern part of Hatay Province, Turkey. The name ''Kırıkhan'' means "broken inn" in the Turkish language, perhaps a reference to one of the many lodgings that once lined the road. The town stands at ...
to Reyhanlı, has a very high sulphur ratio, making it the second in the world after a thermal spring in India. It is the largest spa in the region and attracts many Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
ns due to proximity. Haruniye Thermal Spring is located on the banks of the Ceyhan River
The Ceyhan River (historically Pyramos or Pyramus ( el, Πύραμος), Leucosyrus ( el, Λευκόσυρος) or Jihun) is a river in Anatolia in the south of Turkey.
Course of the river
The Ceyhan River (Pyramus) has its source (known as ' ...
near Düziçi town and has a serene environment. Thermal springs are a hot spot for people with rheumatism. Kurttepe, Alihocalı and Ilıca mineral springs, all located in Adana Province, are popular for toxic cleansing. Ottoman Palace Thermal Resort & Spa in Antakya is one of Turkey's top resorts for revitalization.
Religious tourism
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, the region is home to numerous landmarks that are important for people of faith. Tarsus is the birthplace of St. Paul, who returned to the city after his conversion. The city was a stronghold of Christians after his death. Ashab-ı Kehf cavern, one of the locations claimed to be the resting place of the legendary Seven Sleepers, holy to Christians and Muslims, is located north of Tarsus. Tarsus was the birthplace of Paul the Apostle
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
.
Antakya is another destination for the spiritual world, where the followers of Jesus Christ were first called Christians. It is the home of Saint Peter, one of the 12 apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary Disciple (Christianity), disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. Dur ...
of Jesus. Antioch was called "the cradle of Christianity" as a result of its longevity and the pivotal role that it played in the emergence of both Hellenistic Judaism and early Christianity, The Christian New Testament asserts that the name "Christian" first emerged in Antioch. the Church of Saint Peter near Antakya ( Antioch) is one of Christianity's oldest churches.
Places of interest
Ancient sites
Kizkalesi (Maiden Castle), a fort on a small island across Kızkalesi township, was built during the early 12th century by Armenian kings of the Rubeniyan dynasty, to defend the city of Korykos (today Kızkalesi). Heaven & Hell, situated on a large hill north of Narlıkuyu, consists of the grabens result from assoil of furrings for thousands of years. Natural phenomena of thegraben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic contex ...
s is named 'Hell & Heaven' because of the exotic effects on people. From an ancient path, 260 meter long mythological giant Typhon's cave can be accessible.
The ancient Roman town of Soloi-Pompeiopolis, near the city of Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
.
Yılanlı Kale (Castle of Serpents), an 11th-century crusader castle built on a historical road connecting Taurus mountains to the city of Antakya. Castle has 8 round towers, and there ıs a military guardhouse and a church in the castle. Castle is located 5 km. west of Ceyhan.
Anazarbus
Anazarbus ( grc, Ἀναζαρβός, medieval Ain Zarba; modern Anavarza; ar, عَيْنُ زَرْبَة) was an ancient Cilician city. Under the late Roman Empire, it was the capital of Cilicia Secunda. Roman emperor Justinian I rebuilt ...
Castle was built in the 3rd century and served as the centre of the ancient metropolis of Anavarza. The city was built on a hill and had a strategic importance, controlling the Cilicia plain. Main castle and the city walls are remains of the city. City wall is 1500m. long and 8-10m. high and there are 4 entrances to the city. Castle is located 80 km. northeast of Adana.
Şar (Comona), ancient city located in northernmost Cilicia, some 200 km. north of Adana, near Tufanbeyli
Tufanbeyli is small city and a district in Adana Province of Turkey, 196 km north-east of the city of Adana, on an uneven, sloping plateau high in the Tahtalı range of the Toros mountains. It has been bounded economically to Kayseri, 178 km ...
. It is a historical centre of Hittites. Remaining structures today are, the amphitheatre built during Roman period, ruins of a church from Byzantine and rock works from Hittites.
Church of St. Peter in Antakya, was converted into a church while it was a cave on the slopes of Habibi Neccar mountain. The church is known as the first Christians' traditional meeting place. The church was declared a "Place of Pilgrimage" for Christians by Pope Paul VI in 1963, and since then a special ceremony is held on the 29 of June of each year.
St. Simeon Monastery, a 6th-century giant structure built on a desolate hill 18 km south of Antakya. The most striking features of this monastery are its cisterns, its storage compartment, and the walls. It is believed that St. Simeon Saint Simeon, Saint Symeon or Saint-Siméon may refer to:
People
* Simon Peter, 1st century AD; first of the Apostles, saint, martyr, first bishop of Antioch and Rome, calls himself "Simeon" in 2 Peter 1:1
* Simeon (Gospel of Luke), the Jerusal ...
resided here atop a 20-meter stone column for 45 years.
Parks and conservation areas
Akyatan Lagoon is a large wildlife refuge which acts as a stopover for migratory birds voyaging from Africa to Europe. The wildlife refuge has a area made up of forests, lagoon, marsh, sandy and reedy lands. Akyatan lake is a natural wonder with endemic plants and endangered bird species living in it together with other species of plants and animals. 250 species of birds are observed during a study in 1990. The conservation area is located 30 km south of Adana, near Tuzla. Yumurtalık Nature Reserve covers an area of 16,430 hectares within the Seyhan-Ceyhan delta, with its lakes, lagoons and wide collection of plant and animal species. The area is an important location for many species of migrating birds, the number gets higher during the winters when the lakes become a shelter when other lakes further north freeze. Aladağlar National Park, located north of Adana, is a huge park of around 55,000 hectares, the summit of Demirkazik at 3756 m is the highest point in the middle Taurus mountain range. There is a huge range of flora and fauna, and visitors may fish in the streams full of trout. Wildlife includes wild goats, bears, lynx and sable. The most common species of plant life is black pine and cluster pine trees, with some cedar dotted between, and fir trees in the northern areas with higher humidity. The Alpine region, from the upper borders of the forest, has pastures with rocky areas and little variety of plant life because of the high altitude and slope.Karatepe-Aslantaş National Park
Karatepe-Aslantaş National Park ( tr, Karatepe-Aslantaş Milli Parkı), established in 1958, is a national park in southern Turkey. Situated on the banks of a dam reservoir, it contains an archaeological open-air museum.
Location
Karatepe-Aslan ...
located on the west bank of Ceyhan River
The Ceyhan River (historically Pyramos or Pyramus ( el, Πύραμος), Leucosyrus ( el, Λευκόσυρος) or Jihun) is a river in Anatolia in the south of Turkey.
Course of the river
The Ceyhan River (Pyramus) has its source (known as ' ...
in Osmaniye Province. The park includes the Karatepe Hittite fortress and an open-air museum.
Tekköz-Kengerlidüz Nature Reserve, located 30 km north of Dörtyol, is known for having an ecosystem different from the Mediterranean. The main species of trees around Kengerliduz are beech, oak and fir, and around Tekkoz are hornbeam, ash, beach, black pine and silver birch. The main animal species in the area are wild goat, roe deer, bear, hyena, wild cat, wagtail, wolf, jackal and fox.
Habibi Neccar Dağı Nature Reserve is famous for its cultural as well as natural value, especially for St Pierre Church, which was carved into the rocks. The Charon monument, 200 m north of the church, is huge sculpture of Haron, known as Boatman of Hell in mythology, carved into the rocks. The main species of tree are cluster pine, oaks and sandalwood. The mountain is also home to foxes, rabbits, partridges and stock doves. Nature reserve is 10 km east of Antakya and can be accessible by public transport.
Education
There are numerous private primary and high schools besides the state schools in the region. Most popular high school in the region is Tarsus American College, founded as a missionary school in 1888 to serve Armenian community and then became a secular school in 1923. Adana Anatolian High School and Adana Science High School most important high schools in the Cilicia. In other cities, Anatolian High School and School for Science are the most popular high schools of the city. The region is home to five state and two foundation universities.Çukurova University
Çukurova University ( tr, Çukurova Üniversitesi) is a public university in Adana, Turkey. The university has sixteen faculties, three colleges, seven vocational colleges, three institutes and twenty six research and application centers ...
is a state university founded in 1973 with the union of the faculties of Agriculture and Medicine.. Main campus is in the city of Adana, and the College of Tourism Administration is in Karataş. There is an engineering faculty in Ceyhan, and vocational schools in Kozan, Karaisalı, Pozantı and Yumurtalık. The university is one of the well-developed universities of Turkey with many cultural, social and athletic facilities, currently enrolls 40,000 students.
Mersin University is a state university founded in 1992, and currently serving with 11 faculties, 6 colleges and 9 vocational schools. The university employs more than 2100 academicians and enrolls 26,980 students. Main campus is in the city of Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
. In Tarsus, there is Faculty of Technical Education and Applied Technology and Management College. In Silifke and Erdemli, university has colleges and vocational schools. There are also vocational schools in Anamur, Aydıncık, Gülnar, and Mut.
Mustafa Kemal University is a state university located in Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of A ...
. University was founded in 1992, currently has 9 faculties, 4 colleges and 7 vocational schools. Main campus is in Antakya and Faculty of Engineering is in İskenderun. The university employs 708 academicians and 14,439 students as of 2007.
Korkut Ata University was founded in 2007 as a state university with the union of colleges and vocational schools in Osmaniye Province and began enrollment in 2009. The university has 3 faculties and a vocational school at the main campus in the city of Osmaniye and vocational schools in Kadirli, Bahçe, Düziçi and Erzin. University employs 107 academicians and enrolled 4000 students in 2009.
Adana Science and Technology University
Adana (; ; ) is a major city in southern Turkey. It is situated on the Seyhan River, inland from the Mediterranean Sea. The administrative seat of Adana province, it has a population of 2.26 million.
Adana lies in the heart of Cilicia, whi ...
is a recently founded state university that is planned to have ten faculties, two institutions and a college. It will accommodate 1,700 academic, 470 administrative staff, and it is expected to enroll students by 2012.
Çağ University
The Çağ University is a private non-profit university in Mersin Province, Turkey. It was established officially on 9 July 1997 by Bayboğan Education Foundation ( tr, Bayboğan Eğitim Vakfı) in Adana. "Çağ" means "epoch".
Situated on the st ...
is a not-for-profit tuition based university founded in 1997. It is located on midway from Adana to Tarsus. University holds around 2500 students, most of them commuting from Adana, Tarsus and Mersin.
Toros University
Toros University (Turkish:''Toros Üniversitesi'') is a private university, founded by a foundation ( tr, vakıf). It is located in Mersin; a city on the Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey, famous for Turkey's largest seaport.
Description ...
is a not-for-profit tuition based university located in Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
. The university started enrolling students in 2010.
Sports
Football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
is the most popular sport in Cilicia, professionally represented at all levels of the Football in Turkey.
Transportation
Cilicia has a well-developed transportation system with two airports, two major seaports, motorways and railway lines on the historical route connecting Europe to Middle East.Air
Cilicia is served by two airports. Adana Şakirpaşa Airport is an international airport that have flights to European destinations. There are daily domestic flights to Istanbul, Ankara, İzmir, Antalya and Trabzon. Adana Şakirpaşa Airport serves the provinces ofMersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
, Adana and Osmaniye.
Hatay Airport, opened in 2007, is a domestic airport, and currently has flights to Istanbul, Ankara and Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
, TRNC
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recog ...
. Hatay Airport mostly serves Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of A ...
.
Another under construction airport is Çukurova Regional Airport
Çukurova Regional Airport ( tr, Çukurova Bölgesel Havalimanı) is a projected airport being built in the Tarsus district of Mersin Province, southern Turkey. It will serve the provinces of Mersin and Adana, as well as the rest of the region of ...
, According to the newspaper Hürriyet, the project's cost will be 357 million Euro. When finished, it will serve to 15 million people, and the capacity will be doubled in the future.
Sea
There are daily seabus and vehicle-passenger ferry services fromTaşucu
__NOTOC__
Taşucu ( Greek: Ὅλμοι, Holmoi) is a small town of Silifke, Mersin Province, Turkey. It obtained the status of Municipality after the local elections in Turkey, 1955. By the new regulations on the constitution, it legally got th ...
to Kyrenia, Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
. From Mersin
Mersin (), also known as İçel, is a large city and a port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of Mersin Province, Mersin (İçel) Province. It is made up of four municipalities and dis ...
port, there are ferry services to Famagusta
Famagusta ( , ; el, Αμμόχωστος, Ammóchostos, ; tr, Gazimağusa or ) is a city on the east coast of Geography of Cyprus, Cyprus. It is located east of Nicosia District, Nicosia and possesses the deepest harbour of the island. Duri ...
.
Road
The O50 - O59 motorways crosses Cilicia. Motorways of Cilicia extends toNiğde
Niğde (; grc, Νίγδη; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and the capital of Niğde province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey at an elevation of 1,299 m. In 2017 the city population was 141,010 people.
The city is small with plenty ...
on the north, Erdemli on the west and Şanlıurfa on the east, and İskenderun on the south. State road D-400 connects Cilicia to Antalya on the west. Adana– Kozan, Adana– Karataş, İskenderun– Antakya–Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
double roads are other regional roads.
Railway
Parallel to the highway network in Cilicia, there is an extensive railway network. Adana-Mersin train runs as a commuter train between Mersin, Tarsus and Adana. There are also regional trains from Adana to Ceyhan, Osmaniye and İskenderun.Society
Cilicia was one of the most important regions for the Ottoman Armenians because it managed very well to preserve Armenian character throughout the years. In fact, the Cilician highlands were densely populated by Armenian peasants in small but prosperous towns and villages such as Hadjin and Zeitun, two mountainous areas where autonomy was maintained until the 19th century.Bournoutian, Ani Atamian. "Cilician Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times, Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century''. Ed. Richard G. Hovannisian. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997, pp. 283-290. . In ports and cities of the Adana plain, commerce and industry were almost entirely in the hands of the Armenians and they remained so thanks to a constant influx of Armenians from the highlands. Their population was continuously increasing in numbers in Cilicia in contrast to other parts of the Ottoman Empire, where it was, since 1878, decreasing due to repression.Mythological namesake
Greek mythology mentions another Cilicia, as a small region situated immediately southeast of the Troad in northwestern Anatolia, facing the Gulf of Adramyttium. The connection (if any) between this Cilicia and the better-known and well-defined region mentioned above is unclear. This Trojan Cilicia is mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'' andStrabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
's ''Geography'', and contained localities such as Thebe
Thebe may refer to:
* Any of several female characters in Greek mythology - see List of mythological figures named Thebe
* Thebe (moon), a moon of Jupiter
* Thebe (currency), 1/100 of a Botswana pula
* Thebe, an Amazon
* Thebe, alternate name ...
, Lyrnessus and Chryse (home to Chryses and Chryseis). These three cities were all attacked and sacked by Achilles during the Trojan War.
In '' Prometheus Bound'' (v 353), Aeschylus mentions the Cilician caves (probably Cennet and Cehennem
Cennet and Cehennem ( en, heaven and hell) are the names of two large sinkholes in the Taurus Mountains, in Mersin Province, Turkey. The sinkholes are among the tourist attractions of the province.
Geography
Cennet and Cehennem are situated ne ...
), where the earth-born, hundred-headed monster Typhon dwelt before he withstood the gods and was stricken and charred by Zeus's thunderbolt.
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
*Rutishauser, Susanne. 2020. ''Siedlungskammer Kilikien. Studien zur Kultur- und Landschaftsgeschichte des Ebenen Kilikien''. Schriften zur Vorderasiatischen Archäologie Bd. 16. Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. ISBN 978-3-447-11397-7. *Pilhofer, Philipp. 2018.Das frühe Christentum im kilikisch-isaurischen Bergland. Die Christen der Kalykadnos-Region in den ersten fünf Jahrhunderten
(PDF; 27,4 MB)'' (Texte und Untersuchungen zur Geschichte der altchristlichen Literatur, vol. 184). Berlin/Boston: De Gruyter (). *''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 282/283, Symposium: Chalcolithic Cyprus. pp. 167–175. *Engels, David. 2008. "Cicéron comme proconsul en Cilicie et la guerre contre les Parthes", '' Revue Belge de Philologie et d'Histoire'' 86, pp. 23–45. *Pilhofer, Susanne. 2006
''Romanisierung in Kilikien? Das Zeugnis der Inschriften''
(Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt 46). Munich: Herbert Utz Verlag (). And: 2., erweiterte Auflage, mit einem Nachwort von Philipp Pilhofer (Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt 60) Munich: Herbert Utz Verlag ()
External links
Ancient Cilicia - texts, photographs, maps, inscriptions
{{Armenian diaspora Anatolia Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Ancient Greek geography Geography of Adana Province Historical regions of Anatolia History of Adana Province Historical regions Regions of Asia