impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
when a large asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic o ...
, about in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be in diameter and in depth. It is the second largest confirmed impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring
A peak ring crater is a type of complex crater, which is different from a multi-ringed basin or central-peak crater. A central peak is not seen; instead, a roughly circular ring or plateau, possibly discontinuous, surrounds the crater's center, ...
is intact and directly accessible for scientific research.
The crater was discovered by Antonio Camargo and Glen Penfield, geophysicists who had been looking for petroleum in the Yucatán Peninsula during the late 1970s. Penfield was initially unable to obtain evidence that the geological feature was a crater and gave up his search. Later, through contact with Alan R. Hildebrand in 1990, Penfield obtained samples that suggested it was an impact feature. Evidence for the crater's impact origin includes shocked quartz
Shocked quartz is a form of quartz that has a microscopic structure that is different from normal quartz. Under intense pressure (but limited temperature), the crystalline structure of quartz is deformed along planes inside the crystal. These pl ...
, a gravity anomaly
The gravity anomaly at a location on the Earth's surface is the difference between the observed value of gravity and the value predicted by a theoretical model. If the Earth were an ideal oblate spheroid of uniform density, then the gravity mea ...
, and tektite
Tektites (from grc, τηκτός , meaning 'molten') are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Fra ...
s in surrounding areas.
The date of the impact coincides with the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary, formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) boundary, is a geological signature, usually a thin band of rock containing much more iridium than other bands. The K–Pg boundary marks the end ...
(commonly known as the K–Pg or K–T boundary). It is now widely accepted that the resulting devastation and climate disruption was the cause of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million y ...
, a mass extinction
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. I ...
of 75% of plant and animal species on Earth, including all non-avian dinosaurs.
Discovery
In the late 1970s, geologistWalter Alvarez
Walter Alvarez (born October 3, 1940) is a professor in the Earth and Planetary Science department at the University of California, Berkeley. He is most widely known for the theory that dinosaurs were killed by an asteroid impact, developed in co ...
and his father, Nobel Prize-winning scientist Luis Walter Alvarez
Luis Walter Alvarez (June 13, 1911 – September 1, 1988) was an American experimental physicist, inventor, and professor who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1968 for his discovery of resonance states in particle physics using the ...
, put forth their theory that the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction was caused by an impact event. The main evidence of such an impact was contained in a thin layer of clay present in the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary, formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) boundary, is a geological signature, usually a thin band of rock containing much more iridium than other bands. The K–Pg boundary marks the end ...
(K–Pg boundary) in Gubbio, Italy
Gubbio () is an Italian town and ''comune'' in the far northeastern part of the Italian province of Perugia (Umbria). It is located on the lowest slope of Mt. Ingino, a small mountain of the Apennines.
History
The city's origins are very ancient. ...
. The Alvarezes and colleagues reported that it contained an abnormally high concentration of iridium, a chemical element rare on Earth but common in asteroids. Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density of ...
levels in this layer were as much as 160 times above the background level. It was hypothesized that the iridium was spread into the atmosphere when the impactor was vaporized
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon. ...
and settled across Earth's surface among other material thrown up by the impact, producing the layer of iridium-enriched clay. At the time, there was no consensus on what caused the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction and the boundary layer, with theories including a nearby supernova, climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, or a geomagnetic reversal
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged (not to be confused with geographic north and geographic south). The Earth's field has alternated be ...
. The Alvarezes' impact hypothesis was rejected by many paleontologists, who believed that the lack of fossils found close to the K–Pg boundary—the "three-meter problem"—suggested a more gradual die-off of fossil species.
The Alvarezes, joined by Frank Asaro
Frank Asaro (born Francesco Asaro, July 31, 1927 – June 10, 2014) was an Emeritus Senior Scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory associated with the University of California at Berkeley. He is best known as the chemist who discove ...
and Helen Michel from University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
, published their paper on the iridium anomaly in ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
'' in June 1980. Their paper was followed by other reports of similar iridium spikes at the K–Pg boundary across the globe, and sparked wide interest in the cause of the K–Pg extinction; over 2,000 papers were published in the 1980s on the topic. There were no known impact craters that were the right age and size, spurring a search for a suitable candidate. Recognizing the scope of the work, Lee Hunt and Lee Silver organized a cross-discipline meeting in Snowbird, Utah
Snowbird is an unincorporated community in Little Cottonwood Canyon in the Wasatch Range of the Rocky Mountains near Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It is most famous for Snowbird Ski and Summer Resort, an alpine skiing and snowboarding are ...
, in 1981. Unknown to them, evidence of the crater they were looking for was being presented the same week, and would be largely missed by the scientific community.
 In 1978, geophysicists Glen Penfield and Antonio Camargo were working for the Mexican state-owned oil company Petróleos Mexicanos (
In 1978, geophysicists Glen Penfield and Antonio Camargo were working for the Mexican state-owned oil company Petróleos Mexicanos (Pemex
Pemex (a portmanteau of Petróleos Mexicanos, which translates to ''Mexican Petroleum'' in English; ) is the Mexican state-owned petroleum company managed and operated by the Mexican government. It was formed in 1938 by nationalization and expr ...
) as part of an airborne magnetic survey of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
north of the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
. Penfield's job was to use geophysical data to scout possible locations for oil drilling. In the offshore magnetic data, Penfield noted anomalies whose depth he estimated and mapped. He then obtained onshore gravity data from the 1940s. When the gravity maps and magnetic anomalies
In geophysics, a magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping of variation over an area is valuable in detecting structures obscured by overlying ...
were compared, Penfield described a shallow "bullseye", in diameter, appearing on the otherwise non-magnetic and uniform surroundings—clear evidence to him of an impact feature. A decade earlier, the same map had suggested a crater to contractor Robert Baltosser, but Pemex corporate policy prevented him from publicizing his conclusion.
Penfield presented his findings to Pemex, who rejected the crater theory, instead deferring to findings that ascribed the feature to volcanic activity. Pemex disallowed release of specific data, but let Penfield and Camargo present the results at the 1981 Society of Exploration Geophysicists
The Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) is a learned society dedicated to promoting the science and education of exploration geophysics in particular and geophysics in general. The Society fosters the expert and ethical practice of geophys ...
conference. That year's conference was under-attended and their report attracted scant attention, with many experts on impact craters and the K–Pg boundary attending the Snowbird conference instead. Carlos Byars, a ''Houston Chronicle
The ''Houston Chronicle'' is the largest daily newspaper in Houston, Texas, United States. , it is the third-largest newspaper by Sunday circulation in the United States, behind only ''The New York Times'' and the ''Los Angeles Times''. With i ...
'' journalist who was familiar with Penfield and had seen the gravitational and magnetic data himself, wrote a story on Penfield and Camargo's claim, but the news did not disseminate widely.
Although Penfield had plenty of geophysical data sets, he had no rock cores or other physical evidence of an impact. He knew Pemex had drilled exploratory wells in the region. In 1951, one bored into what was described as a thick layer of andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
about down. This layer could have resulted from the intense heat and pressure of an Earth impact, but at the time of the borings it was dismissed as a lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruption ...
—a feature uncharacteristic of the region's geology. Penfield was encouraged by William C. Phinney
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conques ...
, curator of the lunar rocks at the Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late ...
, to find these samples to support his hypothesis. Penfield tried to secure site samples, but was told they had been lost or destroyed. When attempts to return to the drill sites to look for corroborating rocks proved fruitless, Penfield abandoned his search, published his findings and returned to his Pemex work. Seeing the 1980 ''Science'' paper, Penfield wrote to Walter Alvarez about the Yucatán structure, but received no response.
Alvarez and other scientists continued their search for the crater, although they were searching in oceans based on incorrect analysis of glassy spherule
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the ...
s from the K–Pg boundary that suggested the impactor had landed in open water. Unaware of Penfield's discovery, University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory. ...
graduate student Alan R. Hildebrand and faculty adviser William V. Boynton looked for a crater near the Brazos River
The Brazos River ( , ), called the ''Río de los Brazos de Dios'' (translated as "The River of the Arms of God") by early Spanish explorers, is the 11th-longest river in the United States at from its headwater source at the head of Blackwater ...
in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. Their evidence included greenish-brown clay with surplus iridium, containing shocked quartz
Shocked quartz is a form of quartz that has a microscopic structure that is different from normal quartz. Under intense pressure (but limited temperature), the crystalline structure of quartz is deformed along planes inside the crystal. These pl ...
grains and small weathered glass beads that looked to be tektite
Tektites (from grc, τηκτός , meaning 'molten') are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Fra ...
s. Thick, jumbled deposits of coarse rock fragments were also present, thought to have been scoured from one place and deposited elsewhere by an impact event. Such deposits occur in many locations but seemed concentrated in the Caribbean Basin
In Geography, the Caribbean Basin is generally defined as the area running from Florida westward along the Gulf coast, then south along the Mexican coast through Central America and then eastward across the northern coast of South America. This ...
at the K–Pg boundary. When Haitian professor Florentine Morás discovered what he thought to be evidence of an ancient volcano on Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, Hildebrand suggested it could be a telltale feature of a nearby impact. Tests on samples retrieved from the K–Pg boundary revealed more tektite glass, formed only in the heat of asteroid impacts and high-yield nuclear detonations.
In 1990, Carlos Byars told Hildebrand of Penfield's earlier discovery of a possible impact crater. Hildebrand contacted Penfield and the pair soon secured two drill samples from the Pemex wells, which had been stored in New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Hildebrand's team tested the samples, which clearly showed shock-metamorphic materials. A team of California researchers surveying satellite images found a
 The impactor's velocity was estimated at . The
The impactor's velocity was estimated at . The
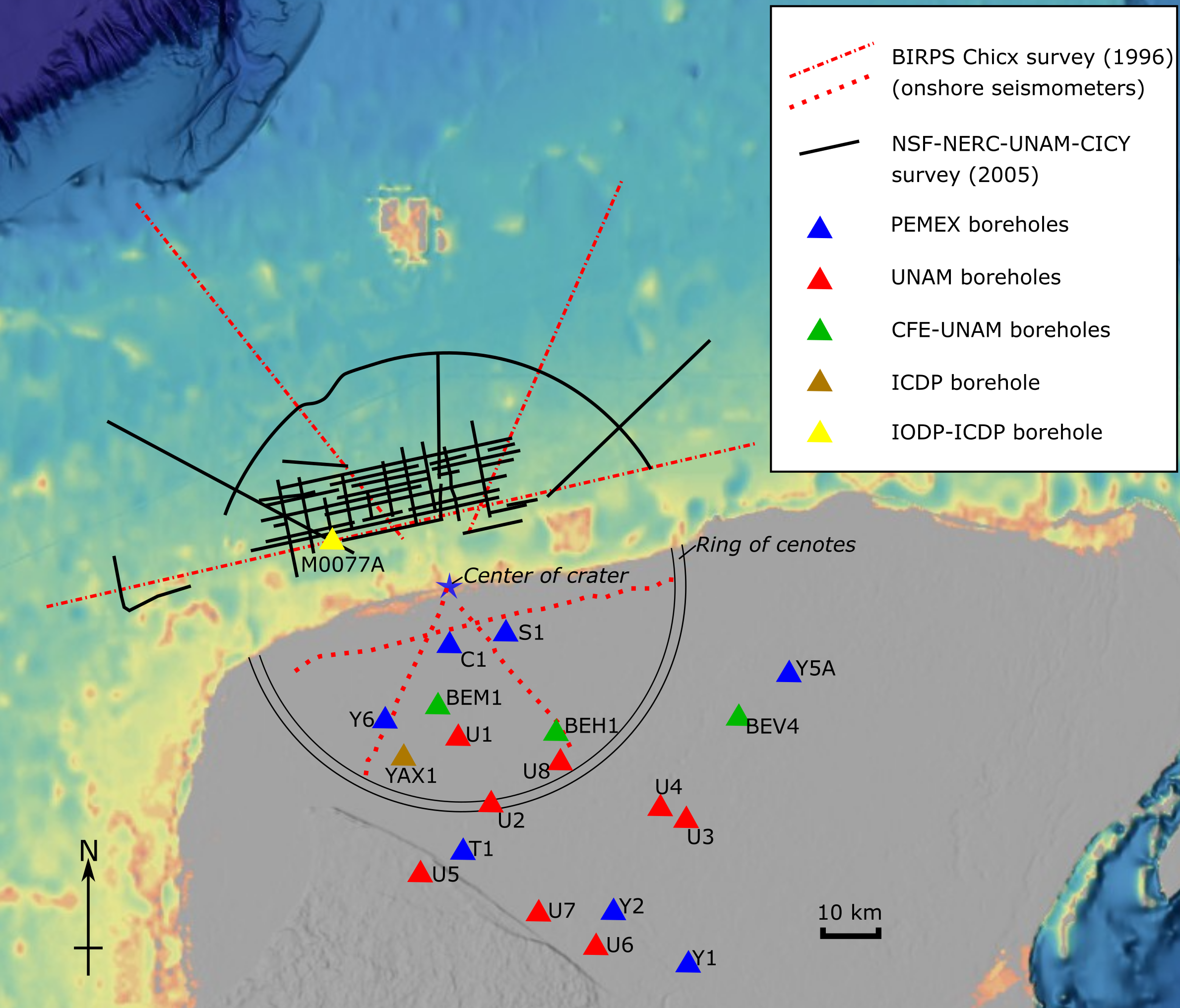
 The form and structure (morphology) of the Chicxulub crater is known mainly from geophysical data. It has a well-defined concentric multi-ring structure. The outermost ring was identified using seismic reflection data. It is up to from the crater center, and is a ring of
The form and structure (morphology) of the Chicxulub crater is known mainly from geophysical data. It has a well-defined concentric multi-ring structure. The outermost ring was identified using seismic reflection data. It is up to from the crater center, and is a ring of
 Before the impact, the geology of the Yucatán area, sometimes referred to as the "target rocks", consisted of a sequence of mainly Cretaceous limestones, overlying
Before the impact, the geology of the Yucatán area, sometimes referred to as the "target rocks", consisted of a sequence of mainly Cretaceous limestones, overlying
Chicxulub Crater
(Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA)
"Doubts on Dinosaurs"
– ''
Papers and presentations resulting from the 2016 Chicxulub drilling project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicxulub Crater Cretaceous impact craters Extinction events Impact craters of Mexico Mérida, Yucatán Natural history of the Caribbean Natural history of the Yucatán Peninsula Oceans Prehistoric dinosaurs
cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting from the collapse of limestone bedrock that exposes groundwater. The regional term is specifically associated with the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where cenotes were commonly used for ...
(sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
) ring centered on the town of Chicxulub Puerto that matched the one Penfield saw earlier; the cenotes were thought to be caused by subsidence of bolide
A bolide is normally taken to mean an exceptionally bright meteor, but the term is subject to more than one definition, according to context. It may refer to any large crater-forming body, or to one that explodes in the atmosphere. It can be a ...
-weakened lithostratigraphy
Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geological science associated with the study of strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology.
In general, strata are primarily ign ...
around the impact crater wall. More recent evidence suggests the crater is wide, and the ring is an inner wall of it. Hildebrand, Penfield, Boynton, Camargo, and others published their paper identifying the crater in 1991. The crater was named for the nearby town of Chicxulub. Penfield also recalled that part of the motivation for the name was "to give the academics and NASA naysayers a challenging time pronouncing it" after years of dismissing its existence.
In March 2010, forty-one experts from many countries reviewed the available evidence: twenty years' worth of data spanning a variety of fields. They concluded that the impact at Chicxulub triggered the mass extinctions at the K–Pg boundary. Dissenters, notably Gerta Keller
Gerta Keller (born 7 March 1945) is a geologist and paleontologist who contests the Alvarez hypothesis that the impact of the Chicxulub impactor, or another large celestial body, directly caused the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Keller ...
of Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the n ...
, have proposed an alternate culprit: the eruption of the Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood ...
in what is now the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
. This period of intense volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the Earth#Surface, surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the su ...
occurred before and after the Chicxulub impact; dissenting studies argue that the worst of the volcanic activity occurred ''before'' the impact, and the role of the Deccan Traps was instead shaping the evolution of surviving species post-impact. A 2013 study compared isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass number ...
s in impact glass
Impactite is rock created or modified by one or more impacts of a meteorite. Impactites are considered metamorphic rock, because their source materials were modified by the heat and pressure of the impact. On Earth, impactites consist primarily o ...
from the Chicxulub impact with isotopes in ash from the K–Pg boundary, concluding that they were dated almost exactly the same within experimental error.
Impact specifics
A 2013 study published in ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
'' estimated the age of the impact as 66,043,000 ± 11,000 years ago (± 43,000 years ago considering systematic error), based on multiple lines of evidence, including argon–argon dating
Argon–argon (or 40Ar/39Ar) dating is a radiometric dating method invented to supersede potassiumargon (K/Ar) dating in accuracy. The older method required splitting samples into two for separate potassium and argon measurements, while the newer ...
of tektites from Haiti and bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-m ...
horizons overlying the impact horizon in northeastern Montana
Montana () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West List of regions of the United States#Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions, division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North ...
, United States. This date was supported by a 2015 study based on argon–argon dating of tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they re ...
found in lignite beds in the Hell Creek
The Hell Creek Formation is an intensively studied division of mostly Upper Cretaceous and some lower Paleocene rocks in North America, named for exposures studied along Hell Creek, near Jordan, Montana. The formation stretches over portions of ...
and overlying Fort Union formations in northeastern Montana. A 2018 study based on argon–argon dating of spherules from Gorgonilla Island, Colombia, obtained a slightly different result of 66,051,000 ± 31,000 years ago. The impact has been interpreted to have occurred in Northern Hemisphere spring based on annual isotope curves in sturgeon and paddlefish
Paddlefish (family Polyodontidae) are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their titular elongl ...
bones found in an ejecta-bearing sedimentary unit at the Tanis site in southwestern North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, S ...
. This sedimentary unit is thought to have formed within hours of impact. A 2020 study concluded that the Chicxulub crater was formed by an inclined (45–60° to horizontal) impact from the northeast. The site of the crater at the time of impact was a marine carbonate platform
A carbonate platform is a sedimentary body which possesses topographic relief, and is composed of autochthonic calcareous deposits. Platform growth is mediated by sessile organisms whose skeletons build up the reef or by organisms (usually mic ...
. The water depth at the impact site varied from on the western edge of the crater to over on the northeastern edge. The seafloor rocks consisted of a sequence of Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
–Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
marine sediments, thick. They were predominantly carbonate rock
Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone, which is composed of calcite or aragonite (different crystal forms of CaCO3), and dolomite rock (also known as doloston ...
, including dolomite (35–40% of total sequence) and limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
(25–30%), along with evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as oce ...
s (anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with t ...
25–30%), and minor amounts of shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especia ...
and sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
(3–4%) underlain by approximately of continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial' ...
, composed of igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
crystalline basement
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The baseme ...
including granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
.
There is broad consensus that the Chicxulub impactor was an asteroid with a carbonaceous chondrite
Carbonaceous chondrites or C chondrites are a class of chondritic meteorites comprising at least 8 known groups and many ungrouped meteorites. They include some of the most primitive known meteorites. The C chondrites represent only a small prop ...
composition, rather than a comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma, and sometimes also a Comet ta ...
. In 1998, a meteorite was described from the North Pacific from sediments spanning the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary; it was suggested to represent a fragment of the Chicxulub impactor. Analysis suggested that it best fitted the criteria of the CV, CO and CR groups of carbonaceous chondrites. A 2021 paper suggested, based on geochemical evidence including the excess of chromium isotope 54Cr and the ratios of platinum group metals found in marine impact layers, that the impactor was either a CM or CR carbonaceous chondrite C-type asteroid
C-type (carbonaceous) asteroids are the most common variety, forming around 75% of known asteroids. They are volatile-rich and distinguished by a very low albedo because their composition includes a large amount of carbon, in addition to rocks ...
. The impactor was around in diameter—large enough that, if set at sea level, it would have reached taller than Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation (snow ...
.
Effects
 The impactor's velocity was estimated at . The
The impactor's velocity was estimated at . The kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its a ...
of the impact was estimated at . The impact created winds in excess of near the blast's center, and created a transient cavity wide and deep that later collapsed. This formed a crater mainly under the sea and covered by of sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
by the 21st century. The impact, expansion of water after filling the crater, and related seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
activity spawned megatsunami
A megatsunami is a very large wave created by a large, sudden displacement of material into a body of water.
Megatsunamis have quite different features from ordinary tsunamis. Ordinary tsunamis are caused by underwater tectonic activity (movemen ...
s over tall, with one simulation suggesting the immediate waves from the impact may have reached up to high. The waves scoured the sea floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
, leaving ripples underneath what is now Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a U.S. state, state in the Deep South and South Central United States, South Central regions of the United States. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-smal ...
with average wavelengths of and average wave heights of , the largest ripples documented. Material shifted by subsequent earthquakes and the waves reached to what are now Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
and Florida, and may have disturbed sediments as far as from the impact site., , The impact triggered a seismic event with an estimated magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of 9–11 at the impact site.
A cloud of hot dust, ash and steam would have spread from the crater, with as much as 25 trillion metric tons of excavated material being ejected into the atmosphere by the blast. Some of this material escaped orbit, dispersing throughout the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
, while some of it fell back to Earth, heated to incandescence
Incandescence is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (including visible light) from a hot body as a result of its high temperature. The term derives from the Latin verb ''incandescere,'' to glow white. A common use of incandescence is ...
upon re-entry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
. The rock heated Earth's surface and ignited wildfires, estimated to have enveloped nearly 70% of the planet's forests. The devastation to living creatures even hundreds of kilometers away was immense, and much of present-day Mexico and the United States would have been devastated. Fossil evidence for an instantaneous extinction of diverse animals was found in a soil layer only thick in New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York (state), New York; on the ea ...
, away from the impact site, indicating that death and burial under debris occurred suddenly and quickly over wide distances on land. Field research from the Hell Creek Formation
The Hell Creek Formation is an intensively studied division of mostly Upper Cretaceous and some lower Paleocene rocks in North America, named for exposures studied along Hell Creek, near Jordan, Montana. The formation stretches over portions of ...
in North Dakota published in 2019 shows the simultaneous mass extinction of myriad species combined with geological and atmospheric features consistent with the impact event.
Due to the relatively shallow water, the rock that was vaporized included sulfur-rich gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and dr ...
from the lower part of the Cretaceous sequence, and this was injected into the atmosphere. This global dispersal of dust and sulfates would have led to a sudden and catastrophic effect on the climate worldwide, instigating large temperature drops and devastating the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), d ...
. The researchers stated that the impact generated an environmental calamity that extinguished life, but it also induced a vast subsurface hydrothermal system that became an oasis for the recovery of life. Researchers using seismic images of the crater in 2008 determined that the impactor landed in deeper water than previously assumed, which may have resulted in increased sulfate aerosols in the atmosphere, due to more water vapor being available to react with the vaporized anhydrite. This could have made the impact even deadlier by cooling the climate and generating acid rain.
The emission of dust and particles could have covered the entire surface of Earth for several years, possibly a decade, creating a harsh environment for living things. Production of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
caused by the destruction of carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonat ...
rocks would have led to a sudden greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly ...
. Over a decade or longer, sunlight would have been blocked from reaching the surface of Earth by the dust particles in the atmosphere, cooling the surface dramatically. Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
by plants would also have been interrupted, affecting the entire food chain. A model of the event developed by Lomax et al (2001) suggests that net primary productivity
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
rates may have increased to higher than pre-impact levels over the long term because of the high carbon dioxide concentrations.
A long-term local effect of the impact was the creation of the Yucatán sedimentary basin which "ultimately produced favorable conditions for human settlement in a region where surface water is scarce".
Post-discovery investigations

Geophysical data
Twoseismic reflection
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic ...
datasets have been acquired over the offshore parts of the crater since its discovery. Older 2D seismic datasets have also been used that were originally acquired for hydrocarbon exploration. A set of three long-record 2D lines was acquired in October 1996, with a total length of , by the BIRPS
The British Institutions Reflection Profiling Syndicate, better known by its acronym BIRPS, was set up to acquire deep seismic reflection profiles around the United Kingdom Continental Shelf (UKCS). It was formed, initially as BURPS, the British U ...
group. The longest of the lines, Chicx-A, was shot parallel to the coast, while Chicx-B and Chicx-C were shot NW–SE and SSW–NNE respectively. In addition to the conventional seismic reflection imaging, data was recorded onshore to allow wide-angle refraction imaging.
In 2005, another set of profiles was acquired, bringing the total length of 2D deep-penetration seismic data up to . This survey also used ocean bottom seismometer
An ocean-bottom seismometer (OBS) is a seismometer that is designed to record the earth motion under oceans and lakes from man-made sources and natural sources.
Sensors at the sea floor are used to observe acoustic and seismic events. Seismic a ...
s and land stations to allow 3D travel time inversion to improve the understanding of the velocity structure of the crater. The data was concentrated around the interpreted offshore peak ring to help identify possible drilling locations. At the same time, gravity data were acquired along of profiles. The acquisition was funded by the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
(NSF), Natural Environment Research Council
The Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) is a British research council that supports research, training and knowledge transfer activities in the environmental sciences.
History
NERC began in 1965 when several environmental (mainly geog ...
(NERC) with logistical assistance from the National Autonomous University of Mexico
The National Autonomous University of Mexico ( es, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, UNAM) is a public research university in Mexico. It is consistently ranked as one of the best universities in Latin America, where it's also the bigge ...
(UNAM) and the Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán (CICY – Yucatán Center for Scientific Investigation).
Borehole drilling
Intermittentcore sample
A core sample is a cylindrical section of (usually) a naturally-occurring substance. Most core samples are obtained by drilling with special drills into the substance, such as sediment or rock, with a hollow steel tube, called a core drill. The ...
s from hydrocarbon exploration boreholes drilled by Pemex on the Yucatán peninsula have provided some useful data. UNAM drilled a series of eight fully-cored boreholes in 1995, three of which penetrated deeply enough to reach the ejecta deposits outside the main crater rim, UNAM-5, 6 and 7. In 2001–2002, a scientific borehole was drilled near the Hacienda Yaxcopoil
An ''hacienda'' ( or ; or ) is an estate (or ''finca''), similar to a Roman ''latifundium'', in Spain and the former Spanish Empire. With origins in Andalusia, ''haciendas'' were variously plantations (perhaps including animals or orchards), ...
, known as Yaxcopoil-1 (or more commonly Yax-1), to a depth of below the surface, as part of the International Continental Scientific Drilling Program
The International Continental Scientific Drilling Program is a multinational program to further and fund geosciences in the field of Continental Scientific Drilling. Scientific drilling is a critical tool in understanding of Earth processes and s ...
. The borehole was cored continuously, passing through of impactites. Three fully-cored boreholes were also drilled by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad
The Comisión Federal de Electricidad ( en, Federal Electricity Commission) is the state-owned electric utility of Mexico, widely known as CFE. It is the country's dominant electric company, and the country's second most powerful state-owned comp ...
(Federal Electricity Commission) with UNAM. One of them, (BEV-4), was deep enough to reach the ejecta deposits.
In 2016, a joint United Kingdom–United States team obtained the first offshore core samples, from the peak ring in the central zone of the crater with the drilling of the borehole known as M0077A, part of Expedition 364 of the International Ocean Discovery Program
The International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) is an international marine research collaboration dedicated to advancing scientific understanding of the Earth through drilling, coring, and monitoring the subseafloor. The research enabled by IODP ...
. The borehole reached below the seafloor.
Morphology
 The form and structure (morphology) of the Chicxulub crater is known mainly from geophysical data. It has a well-defined concentric multi-ring structure. The outermost ring was identified using seismic reflection data. It is up to from the crater center, and is a ring of
The form and structure (morphology) of the Chicxulub crater is known mainly from geophysical data. It has a well-defined concentric multi-ring structure. The outermost ring was identified using seismic reflection data. It is up to from the crater center, and is a ring of normal fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectoni ...
s, throwing down towards the crater center, marking the outer limit of significant crustal deformation. This makes it one of the three largest impact structures on Earth. Moving into the center, the next ring is the main crater rim, also known as the "inner rim" which correlates with ring of cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting from the collapse of limestone bedrock that exposes groundwater. The regional term is specifically associated with the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where cenotes were commonly used for ...
s onshore and a major circular Bouguer gravity gradient anomaly. This has a radius that varies between . The next ring structure, moving inwards, is the peak ring. The area between the inner rim and peak ring is described as the "terrace zone", characterized by a series of fault block
Fault blocks are very large blocks of rock, sometimes hundreds of kilometres in extent, created by tectonic and localized stresses in Earth's crust. Large areas of bedrock are broken up into blocks by faults. Blocks are characterized by rela ...
s defined by normal faults dipping towards the crater center, sometimes referred to as "slump blocks". The peak ring is about 80 km in diameter and of variable height, from above the base of the crater in the west and northwest and in the north, northeast and east. The central part of the crater lies above a zone where the mantle was uplifted such that the Moho is shallower by about compared to regional values.
The ring structures are best developed to the south, west and northwest, becoming more indistinct towards the north and northeast of the structure. This is interpreted to be a result of variable water depth at the time of impact, with less well-defined rings resulting from the areas with water depths significantly deeper than .
Geology
Pre-impact geology
 Before the impact, the geology of the Yucatán area, sometimes referred to as the "target rocks", consisted of a sequence of mainly Cretaceous limestones, overlying
Before the impact, the geology of the Yucatán area, sometimes referred to as the "target rocks", consisted of a sequence of mainly Cretaceous limestones, overlying red bed
Red beds (or redbeds) are sedimentary rocks, typically consisting of sandstone, siltstone, and shale, that are predominantly red in color due to the presence of ferric oxides. Frequently, these red-colored sedimentary strata locally contain th ...
s of uncertain age above an unconformity with the dominantly granitic basement
A basement or cellar is one or more Storey, floors of a building that are completely or partly below the storey, ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, ...
. The basement forms part of the Maya Block
The Maya Block, also known as the Maya Terrane, Yucatan Block, or YucatanChiapas Block, is a physiographic or geomorphic region and tectonic or crustal block in the southernmost portion of the North American Plate.
Extent
The Block is com ...
and information about its makeup and age in the Yucatán area has come only from drilling results around the Chicxulub crater and the analysis of basement material found as part of the ejecta at more distant K–Pg boundary sites. The Maya block is one of a group of crustal blocks found at the edge of the Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
continent. Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of th ...
ages are consistent with the presence of an underlying Grenville age crust, with large amounts of late Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and t ...
arc-related igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or l ...
s, interpreted to have formed in the Pan-African orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Or ...
. Late Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
granitoid
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz ...
s (the distinctive "pink granite") were found in the peak ring borehole M0077A, with an estimated age of 326 ± 5 million years ago ( Carboniferous). These have an adakitic
Adakites are volcanic rocks of intermediate to felsic composition that have geochemical characteristics of magma originally thought to have formed by partial melting of altered basalt that is subducted below volcanic arcs. Most magmas deriv ...
composition and are interpreted to represent the effects of slab detachment
In plate tectonics, slab detachment or slab break-off may occur during continent-continent or arc-continent collisions. When the continental margin of the subducting plate reaches the oceanic trench of the subduction zone, the more buoyant contin ...
during the Marathon-Ouachita orogeny, part of the collision between Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
and Gondwana that created the Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 millio ...
supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which lea ...
.
Red beds of variable thickness, up to , overlay the granitic basement, particularly in the southern part of the area. These continental clastic rock
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rock ...
s are thought to be of Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
-to-Jurassic age, although they may extend into the Lower Cretaceous
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
Nizhny (russian: Ни́жний; masculine), Nizhnyaya (; feminine), or Nizhneye (russian: Ни́� ...
. The lower part of the Lower Cretaceous sequence consists of dolomite with interbedded anhydrite and gypsum, with the upper part being limestone, with dolomite and anhydrite in part. The thickness of the Lower Cretaceous varies from up to in the boreholes. The Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
sequence is mainly platform limestone, with marl and interbedded anhydrite. It varies in thickness from up to . There is evidence for a Cretaceous basin within the Yucatán area that has been named the Yucatán Trough, running approximately south–north, widening northwards, explaining the observed thickness variations.
Impact rocks
The most common observed impact rocks aresuevite
Suevite is a rock consisting partly of melted material, typically forming a breccia containing glass and crystal or lithic fragments, formed during an impact event. It forms part of a group of rock types and structures that are known as i ...
s, found in many of the boreholes drilled around the Chicxulub crater. Most of the suevites were resedimented soon after the impact by the resurgence of oceanic water into the crater. This gave rise to a layer of suevite extending from the inner part of the crater out as far as the outer rim.
Impact melt rocks are thought to fill the central part of the crater, with a maximum thickness of . The samples of melt rock that have been studied have overall compositions similar to that of the basement rocks, with some indications of mixing with carbonate source, presumed to be derived from the Cretaceous carbonates. An analysis of melt rocks sampled by the M0077A borehole indicates two types of melt rock, an upper impact melt (UIM), which has a clear carbonate component as shown by its overall chemistry and the presence of rare limestone clasts and a lower impact melt-bearing unit (LIMB) that lacks any carbonate component. The difference between the two impact melts is interpreted to be a result of the upper part of the initial impact melt, represented by the LIMB in the borehole, becoming mixed with materials from the shallow part of the crust either falling back into the crater or being brought back by the resurgence forming the UIM.
The "pink granite", a granitoid rich in alkali feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
found in the peak ring borehole shows many deformation features that record the extreme strains associated with the formation of the crater and the subsequent development of the peak ring. The granitoid has an unusually low density and P-wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at an ...
velocity compared to typical granitic basement rocks. Study of the core from M0077A shows the following deformation features in apparent order of development: pervasive fracturing along and through grain boundaries, a high density of shear fault
sinistral shear sense'', Starlight Pit, Fortnum Gold Mine, Western Australia
In geology, shear is the response of a rock to deformation usually by compressive stress and forms particular textures. Shear can be homogeneous or non-homogeneous, ...
s, bands of cataclasite
Cataclasite is a cohesive granular fault rock. Comminution, also known as cataclasis, is an important process in forming cataclasites. They fall into the category of cataclastic rocks which are formed through faulting or fracturing in the uppe ...
and ultra-cataclasite and some ductile shear structures. This deformation sequence is interpreted to result from initial crater formation involving acoustic fluidization followed by shear faulting with the development of cataclasites with fault zone
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geolo ...
s containing impact melts.
The peak ring drilling below the sea floor also discovered evidence of a massive hydrothermal system, which modified approximately of Earth's crust and lasted for hundreds of thousands of years. These hydrothermal systems may provide support for the impact origin of life hypothesis for the Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a geologic eon of Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the Hadean is defined as the age of the oldest solid material ...
eon, when the entire surface of Earth was affected by impactors much larger than the Chicxulub impactor.
Post-impact geology
After the immediate effects of the impact had stopped,sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to t ...
in the Chicxulub area returned to the shallow water platform carbonate depositional environment
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will b ...
that characterised it before the impact. The sequence, which dates back as far as the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, consists of marl and limestone, reaching a thickness of about . The K–Pg boundary inside the crater is significantly deeper than in the surrounding area.
On the Yucatán peninsula, the inner rim of the crater is marked by clusters of cenotes, which are the surface expression of a zone of preferential groundwater flow, moving water from a recharge zone in the south to the coast through a karstic aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteri ...
system. From the cenote locations, the karstic aquifer is clearly related to the underlying crater rim, possibly through higher levels of fracturing,
caused by differential compaction.
Astronomical origin of impactor
In September 2007, a report published in ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
'' proposed an origin for the asteroid that created the Chicxulub crater. The authors, William F. Bottke, David Vokrouhlický, and David Nesvorný
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
, argued that a collision in the asteroid belt 160 million years ago between a 170 km (106 mi) diameter parent body and another 60 km (37 mi) diameter body, resulted in the Baptistina family
The Baptistina family (FIN: 403) is an asteroid family of more than 2500 members that was probably produced by the breakup of an asteroid across 80 million years ago following an impact with a smaller body. The two largest presumed remnants o ...
of asteroids, the largest surviving member of which is 298 Baptistina
Baptistina (minor planet designation: 298 Baptistina) is an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt. It is the namesake of the Baptistina family. It was discovered on 9 September 1890 by Auguste Charlois of Nice. The source of its name is unknow ...
. They proposed that the "Chicxulub asteroid" was also a member of this group.
The Baptistina family is not considered a likely source of the Chicxulub asteroid because a spectrographic analysis published in 2009 revealed that 298 Baptistina has a different composition more typical of an S-type asteroid
S-type asteroids are asteroids with a spectral type that is indicative of a siliceous (i.e. stony) mineralogical composition, hence the name. They have relatively high density. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the secon ...
than the presumed carbonaceous chondrite composition of the Chicxulub impactor. In 2011, data from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 2 ...
revised the date of the collision which created the Baptistina family to about 80 million years ago. This made an asteroid from this family highly improbable to be the asteroid that created the Chicxulub crater, as typically the process of resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillat ...
and collision of an asteroid takes many tens of millions of years. In 2010, another hypothesis implicated the newly discovered asteroid 354P/LINEAR, a member of the Flora family
The Flora family (''adj. Florian''; ; also known as ''Ariadne family'') is a prominent family of stony asteroids located in the inner region of the asteroid belt. It is one of the largest families with more than 13,000 known members, or appro ...
of asteroids, as a possible remnant cohort of the K–Pg impactor. In July 2021, a study reported that the impactor likely originated in the outer main part of the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called ...
, based on numerical simulations.
The original 1980 paper describing the crater suggested that it was created by an asteroid around in diameter. Two papers published in 1984 proposed the impactor to be a comet originating from the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging f ...
, and it was proposed in 1992 that tidal disruption
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenome ...
of comets could potentially increase impact rates. In February 2021, four independent laboratories reported elevated concentrations of iridium in the crater's peak ring, further corroborating the asteroid impact hypothesis. In the same month, Avi Loeb
Abraham "Avi" Loeb ( he, אברהם (אבי) לייב; born February 26, 1962) is an Israeli- American theoretical physicist who works on astrophysics and cosmology. Loeb is the Frank B. Baird Jr. Professor of Science at Harvard University. He h ...
and a colleague published a study in ''Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely t ...
'' suggesting the impactor was a fragment from a disrupted comet, rather than an asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic o ...
—the long-standing leading candidate among scientists.; This was followed by a rebuttal published in ''Astronomy & Geophysics
''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (''A&G'') is a scientific journal and trade magazine published on behalf of the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS) by Oxford University Press. It publishes a mixture of content of interest to astronomers and geophysicists: ...
'' that June, which charged that the paper ignored the fact that the mass of iridium deposited across the globe by the impact (estimated to be approximately 2.0–2.8 × 10 grams), was too large to be created by a comet impactor the size required to create the crater, and that Loeb et al. had overestimated likely comet impact rates. They found that an asteroid impactor was strongly favored by all available evidence, and that a comet impactor could be effectively ruled out.
See also
*Barberton Greenstone Belt
The Barberton Greenstone Belt is situated on the eastern edge of Kaapvaal Craton in South Africa. It is known for its gold mineralisation and for its komatiites, an unusual type of ultramafic volcanic rock named after the Komati River that flows t ...
* List of impact craters on Earth
This list of impact craters on Earth contains a selection of the 190 confirmed craters given in the Earth Impact Database as of 2017.
To keep the lists manageable, only the largest craters within a time period are included. Alphabetical lists f ...
* List of possible impact structures on Earth
This is a list of possible impact structures on Earth. More than 130 geophysical features on the surface of the Earth have been proposed as candidate sites for impact events by appearing several times in the literature and/or being endorsed by the ...
* Nadir crater
The Nadir crater is an undersea feature on the Guinea Plateau in the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Guinea. It is suggested to be an impact crater. The feature is named after the Nadir Seamount, located 100 km to the south, and is around 8.5- ...
* Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, a ...
* Timeline of Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event research
References
*External links
Chicxulub Crater
(Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA)
"Doubts on Dinosaurs"
– ''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it i ...
''
Papers and presentations resulting from the 2016 Chicxulub drilling project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicxulub Crater Cretaceous impact craters Extinction events Impact craters of Mexico Mérida, Yucatán Natural history of the Caribbean Natural history of the Yucatán Peninsula Oceans Prehistoric dinosaurs