|
International Ocean Discovery Program
The International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) is an international marine research collaboration dedicated to advancing scientific understanding of the Earth through drilling, coring, and monitoring the subseafloor. The research enabled by IODP samples and data improves scientific understanding of changing climate and ocean conditions, the origins of ancient life, risks posed by geohazards, and the structure and processes of Earth's tectonic plates and uppermost mantle. IODP began in 2013 and builds on the research of four previous scientific ocean drilling programs: Project Mohole, Deep Sea Drilling Project, Ocean Drilling Program, and Integrated Ocean Drilling Program. Together, these programs represent the longest running and most successful international Earth science collaboration. Scientific scope The scientific scope of IODP is laid out in the program's science plan, ''Illuminating Earth's Past, Present, and Future''. The science plan covers a 10-year period of opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geohazard
A geologic hazard or geohazard is an adverse geologic condition capable of causing widespread damage or loss of property and life. These hazards are geological and environmental conditions and involve long-term or short-term geological processes. Geohazards can be relatively small features, but they can also attain huge dimensions (e.g., submarine or surface landslide) and affect local and regional socio-economics to a large extent (e.g., tsunamis). Sometimes the hazard is instigated by the careless location of developments or construction in which the conditions were not taken into account. Human activities, such as drilling through overpressured zones, could result in significant risk, and as such mitigation and prevention are paramount, through improved understanding of geohazards, their preconditions, causes and implications. In other cases, particularly in montane regions, natural processes can cause catalytic events of a complex nature, such as an avalanche hitting a lake a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
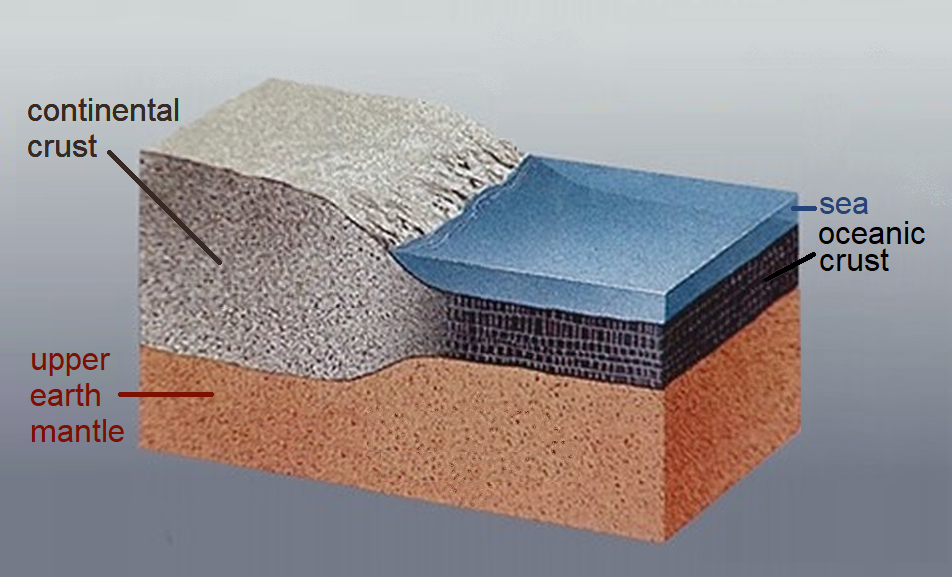
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Continental Scientific Drilling Program
The International Continental Scientific Drilling Program is a multinational program to further and fund geosciences in the field of Continental Scientific Drilling. Scientific drilling is a critical tool in understanding of Earth processes and structure. It provides direct insight into Earth processes and critically tests geological models. Results obtained from drilling projects at critical sites can be applied to other areas worldwide. It is, therefore, believed that international cooperation in continental scientific drilling is an essential component for a responsible management strategy for the Earth's natural resources and environment. The ICDP was founded in February 1996 in the German Embassy in Tokyo as a result of the German Continental Deep Drilling Program (KTB; 1987-1995). The GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences serves as the headquarters for both the current ICDP and the former KTB project. Motivation ICDP supports international science teams with a prove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Earthquake
A slow earthquake is a discontinuous, earthquake-like event that releases energy over a period of hours to months, rather than the seconds to minutes characteristic of a typical earthquake. First detected using long term strain measurements, most slow earthquakes now appear to be accompanied by fluid flow and related tremor, which can be detected and approximately located using seismometer data filtered appropriately (typically in the 1–5 Hz band). That is, they are quiet compared to a regular earthquake, but not "silent" as described in the past. Slow earthquakes should not be confused with tsunami earthquakes, in which relatively slow rupture velocity produces tsunami out of proportion to the triggering earthquake. In a tsunami earthquake, the rupture propagates along the fault more slowly than usual, but the energy release occurs on a similar timescale to other earthquakes. __TOC__ Causes Earthquakes occur as a consequence of gradual stress increases in a region, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
The Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum (PETM), alternatively (ETM1), and formerly known as the "Initial Eocene" or "", was a time period with a more than 5–8 °C global average temperature rise across the event. This climate event occurred at the time boundary of the Paleocene and Eocene geological epochs. The exact age and duration of the event is uncertain but it is estimated to have occurred around 55.5 million years ago. The associated period of massive carbon release into the atmosphere has been estimated to have lasted from 20,000 to 50,000 years. The entire warm period lasted for about 200,000 years. Global temperatures increased by 5–8 °C. The onset of the Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum has been linked to volcanism and uplift associated with the North Atlantic Igneous Province, causing extreme changes in Earth's carbon cycle and a significant temperature rise. The period is marked by a prominent negative excursion in carbon stable isotope () r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Of South Asia
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving. The unique Geography of India, geographical features of the Indian subcontinent, along with associated atmospheric, oceanic, and geophysical factors, influence the behavior of the monsoon. Because of its effect on agriculture, on flora and fauna, and on the climates of nations such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – among other economic, social, and environmental effects – the monsoon is one of the most anticipated, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
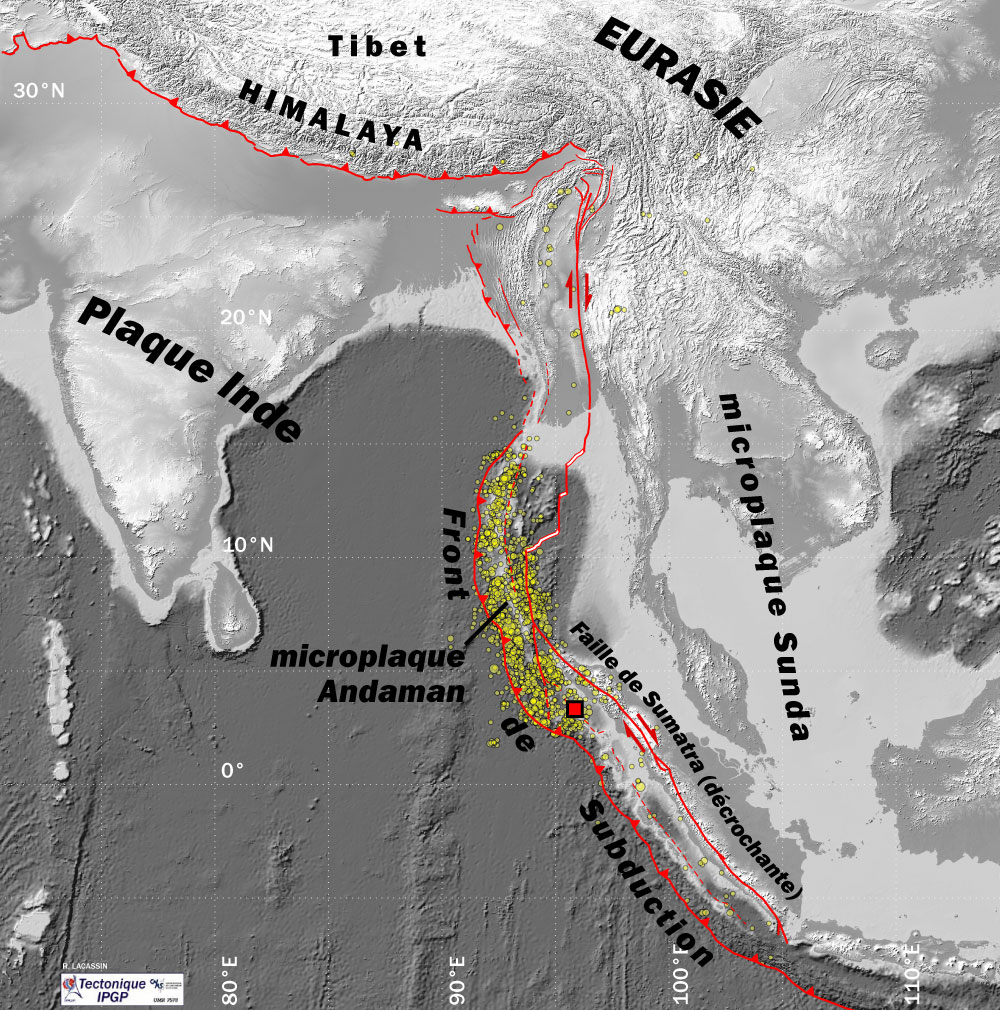
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+07:00, UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an Submarine earthquake, undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Modified Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it List of natural disasters by death toll#Ten deadliest natural disasters since 1900 excluding epidemics and famines, one of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicxulub Crater
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large asteroid, about in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be in diameter and in depth. It is the second largest confirmed impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research. The crater was discovered by Antonio Camargo and Glen Penfield, geophysicists who had been looking for petroleum in the Yucatán Peninsula during the late 1970s. Penfield was initially unable to obtain evidence that the geological feature was a crater and gave up his search. Later, through contact with Alan R. Hildebrand in 1990, Penfield obtained samples that suggested it was an impact feature. Evidence for the crater's impact origin includes shocked quartz, a gravity anomaly, and tektites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Core Complex
An oceanic core complex, or megamullion, is a seabed geologic feature that forms a long ridge perpendicular to a mid-ocean ridge. It contains smooth domes that are lined with transverse ridges like a corrugated roof. They can vary in size from 10 to 150 km in length, 5 to 15 km in width, and 500 to 1500 m in height. History, distribution and exploration The first oceanic core complexes described were identified in the Atlantic Ocean. Since then numerous such structures have been identified primarily in oceanic lithosphere formed at intermediate, slow- and ultra-slow spreading mid-ocean ridges, as well as back-arc basins. Examples include 10-1000 square km expanses of ocean floor and therefore of the oceanic lithosphere, particularly along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Southwest Indian Ridge. Some of these structures have been drilled and sampled, showing that the footwall can be composed of both mafic plutonic and ultramafic rocks (gabbro and peridotite primarily, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Indian Ridge
The Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR) is a mid-ocean ridge located along the floors of the south-west Indian Ocean and south-east Atlantic Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary separating the Somali Plate to the north from the Antarctic Plate to the south, the SWIR is characterised by ultra-slow spreading rates (only exceeding those of the Gakkel Ridge in the Arctic) combined with a fast lengthening of its axis between the two flanking triple junctions, Rodrigues () in the Indian Ocean and Bouvet () in the Atlantic Ocean. Geological setting Spreading rates The spreading rate along the SWIR varies: the transition between slow (30 mm/yr) and ultra-slow (15 mm/yr) spreading occur at magnetic anomaly C6C (ca. 24 Ma). This occurs between 54°–67°E, the deepest, and perhaps coldest and most melt-poor, part of Earth's mid-ocean ridge system. Crustal thickness decreases quickly as spreading rates drop below c. 20 mm/yr and in the SWIR there is an absence of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohorovičić Discontinuity
The Mohorovičić discontinuity ( , ), usually referred to as the Moho discontinuity or the Moho, is the boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle. It is defined by the distinct change in velocity of seismic waves as they pass through changing densities of rock. The Moho lies almost entirely within the lithosphere (the hard outer layer of the Earth, including the crust). Only beneath mid-ocean ridges does it define the lithosphere– asthenosphere boundary (the depth at which the mantle becomes significantly ductile). The Mohorovičić discontinuity is below the ocean floor, and beneath typical continental crusts, with an average of . Named after the pioneering Croatian seismologist Andrija Mohorovičić, the Moho separates both the oceanic crust and continental crust from the underlying mantle. The Mohorovičić discontinuity was first identified in 1909 by Mohorovičić, when he observed that seismograms from shallow-focus earthquakes had two sets of P-wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Biosphere
The deep biosphere is the part of the biosphere that resides below the first few meters of the surface. It extends down at least 5 kilometers below the continental surface and 10.5 kilometers below the sea surface, at temperatures that may reach beyond 120 °C, which is comparable to the maximum temperature where a metabolically active organism has been found. It includes all three domains of life and the genetic diversity rivals that on the surface. The first indications of deep life came from studies of oil fields in the 1920s, but it was not certain that the organisms were indigenous until methods were developed in the 1980s to prevent contamination from the surface. Samples are now collected in deep mines and scientific drilling programs in the ocean and on land. Deep observatories have been established for more extended studies. Near the surface, living organisms consume organic matter and breathe oxygen. Lower down, these are not available, so they make use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_sunk_1968.jpg)