Cardiff University Rowing Club Rowing Blade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and
 Until the Roman conquest of Britain, Cardiff was part of the territory of the Silures – a Celtic British tribe that flourished in the
Until the Roman conquest of Britain, Cardiff was part of the territory of the Silures – a Celtic British tribe that flourished in the
 In 1081 William I, King of England, began work on the castle keep within the walls of the old Roman fort. Cardiff Castle has been at the heart of the city ever since. The castle was substantially altered and extended during the Victorian period by John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, and the architect
In 1081 William I, King of England, began work on the castle keep within the walls of the old Roman fort. Cardiff Castle has been at the heart of the city ever since. The castle was substantially altered and extended during the Victorian period by John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, and the architect
 In 1536, the
In 1536, the 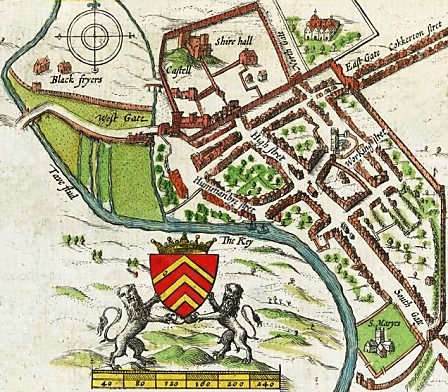 A disastrous flood in the Bristol Channel on 30 January 1607 (now believed to have been a tidal wave) changed the course of the River Taff and ruined St Mary's Parish Church, which was replaced by a chapel of ease dedicated to St John the Baptist.
During the
A disastrous flood in the Bristol Channel on 30 January 1607 (now believed to have been a tidal wave) changed the course of the River Taff and ruined St Mary's Parish Church, which was replaced by a chapel of ease dedicated to St John the Baptist.
During the
 The town grew rapidly from the 1830s onwards, when the Marquess of Bute built a dock, which eventually linked to the
The town grew rapidly from the 1830s onwards, when the Marquess of Bute built a dock, which eventually linked to the

 The East Moors Steelworks closed in 1978 and Cardiff lost population in the 1980s, consistent with a wider pattern of counter-urbanisation in Britain. However, it recovered to become one of the few cities outside London where population grew in the 1990s. During this period the
The East Moors Steelworks closed in 1978 and Cardiff lost population in the 1980s, consistent with a wider pattern of counter-urbanisation in Britain. However, it recovered to become one of the few cities outside London where population grew in the 1990s. During this period the
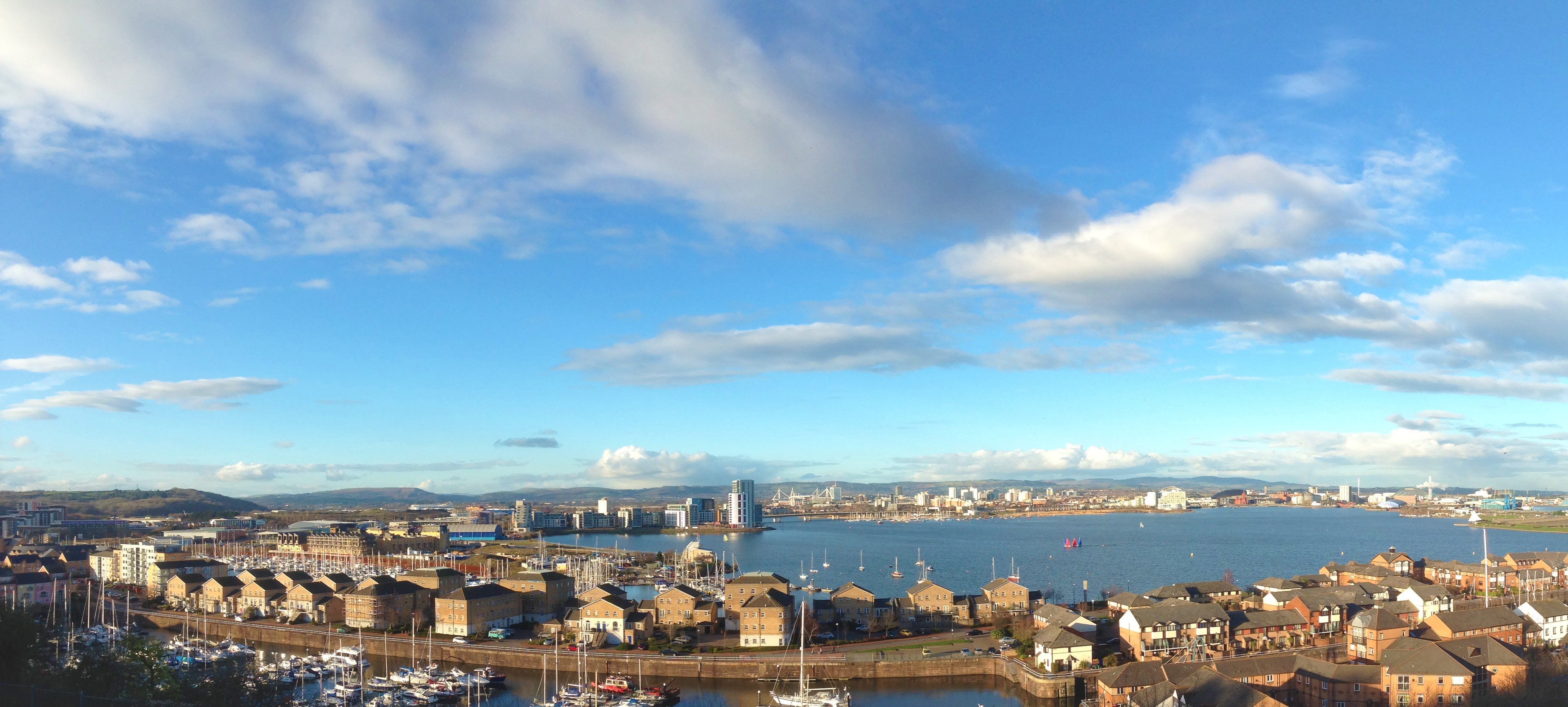


 "Inner Cardiff" consists of the wards of
"Inner Cardiff" consists of the wards of
For Wales, the temperatures average (July) and (February). Cardiff has 1,518 hours of sunshine in an average year (Wales 1,388.7 hours). Cardiff is sunniest in July, with an average 203.4 hours during the month (Wales 183.3 hours), and least sunny in December with 44.6 hours (Wales 38.5 hours). Cardiff experiences less rainfall than average for Wales. It falls on 146 days in an average year, with total annual rainfall of . Monthly rainfall patterns show that from October to January, average monthly rainfall in Cardiff exceeds each month, the wettest month being December with and the driest from April to June, with average monthly rainfall fairly consistent between .
 Official census estimates of the city's total population have been disputed. The city council published two articles arguing that the 2001 census seriously under-reported the population of Cardiff, and in particular the ethnic minority population of some inner city areas.
The Welsh Government's official mid-year estimate of the population of the Cardiff local authority area in 2019 was 366,903. At the 2011, census the official population of the Cardiff Built Up Area (BUA) was put at 447,287. The BUA is not contiguous with the local authority boundary and aggregates data at a lower level; for Cardiff this includes the urban part of Cardiff, Penarth/Dinas Powys, Caerphilly and Pontypridd.
Cardiff has an ethnically diverse population due to past trading connections, post-war
Official census estimates of the city's total population have been disputed. The city council published two articles arguing that the 2001 census seriously under-reported the population of Cardiff, and in particular the ethnic minority population of some inner city areas.
The Welsh Government's official mid-year estimate of the population of the Cardiff local authority area in 2019 was 366,903. At the 2011, census the official population of the Cardiff Built Up Area (BUA) was put at 447,287. The BUA is not contiguous with the local authority boundary and aggregates data at a lower level; for Cardiff this includes the urban part of Cardiff, Penarth/Dinas Powys, Caerphilly and Pontypridd.
Cardiff has an ethnically diverse population due to past trading connections, post-war
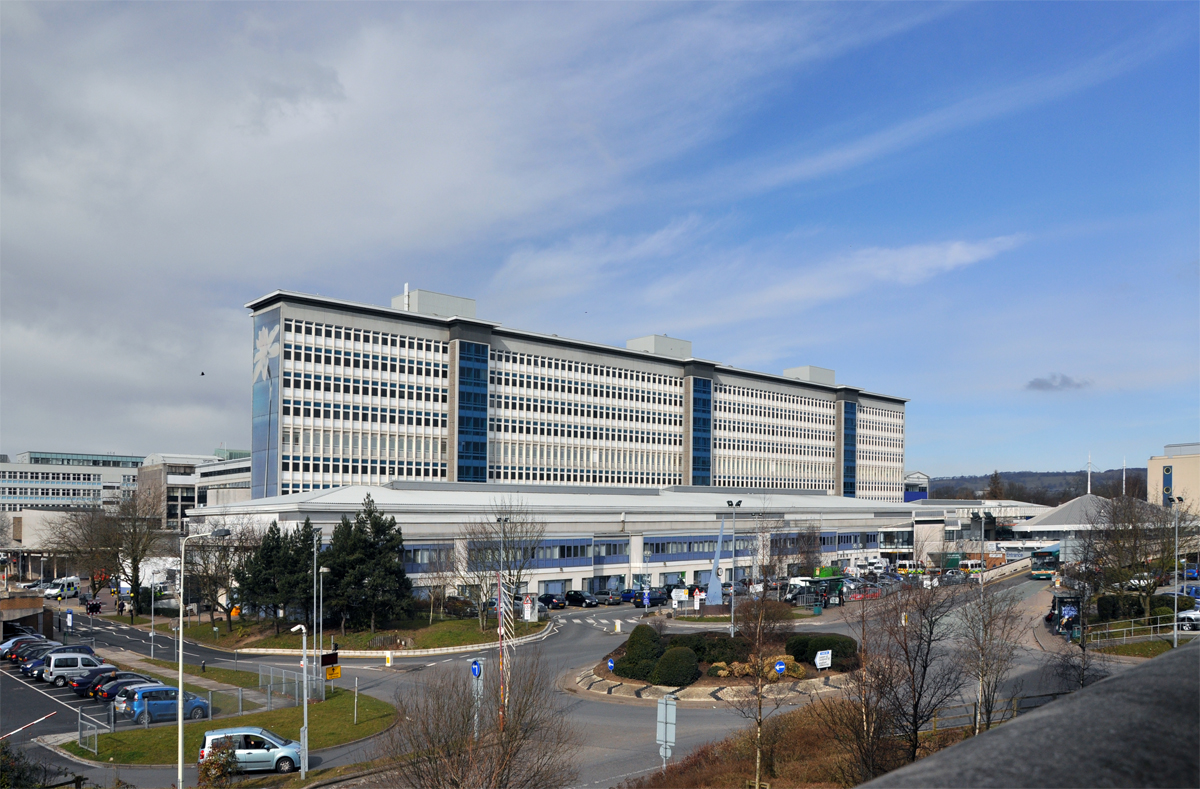 There are seven NHS hospitals in the city, the largest being the
There are seven NHS hospitals in the city, the largest being the
 Cardiff has a chequered linguistic history with
Cardiff has a chequered linguistic history with
 As the capital city of Wales, Cardiff is the main engine of growth in the Welsh economy. Though the population of Cardiff is about 10% of the Welsh population, the economy of Cardiff makes up nearly 20% of Welsh GDP and 40% of the city's workforce are daily in-commuters from the surrounding South Wales area.
Industry has played a major part in Cardiff's development for many centuries. The main catalyst for its transformation from a small town into a big city was the demand for coal required in making iron and later steel, brought to sea by packhorse from Merthyr Tydfil. This was first achieved by building a canal from Merthyr ( above sea level) to the Taff Estuary at Cardiff. Eventually the
As the capital city of Wales, Cardiff is the main engine of growth in the Welsh economy. Though the population of Cardiff is about 10% of the Welsh population, the economy of Cardiff makes up nearly 20% of Welsh GDP and 40% of the city's workforce are daily in-commuters from the surrounding South Wales area.
Industry has played a major part in Cardiff's development for many centuries. The main catalyst for its transformation from a small town into a big city was the demand for coal required in making iron and later steel, brought to sea by packhorse from Merthyr Tydfil. This was first achieved by building a canal from Merthyr ( above sea level) to the Taff Estuary at Cardiff. Eventually the  Cardiff today is the main finance and business
Cardiff today is the main finance and business
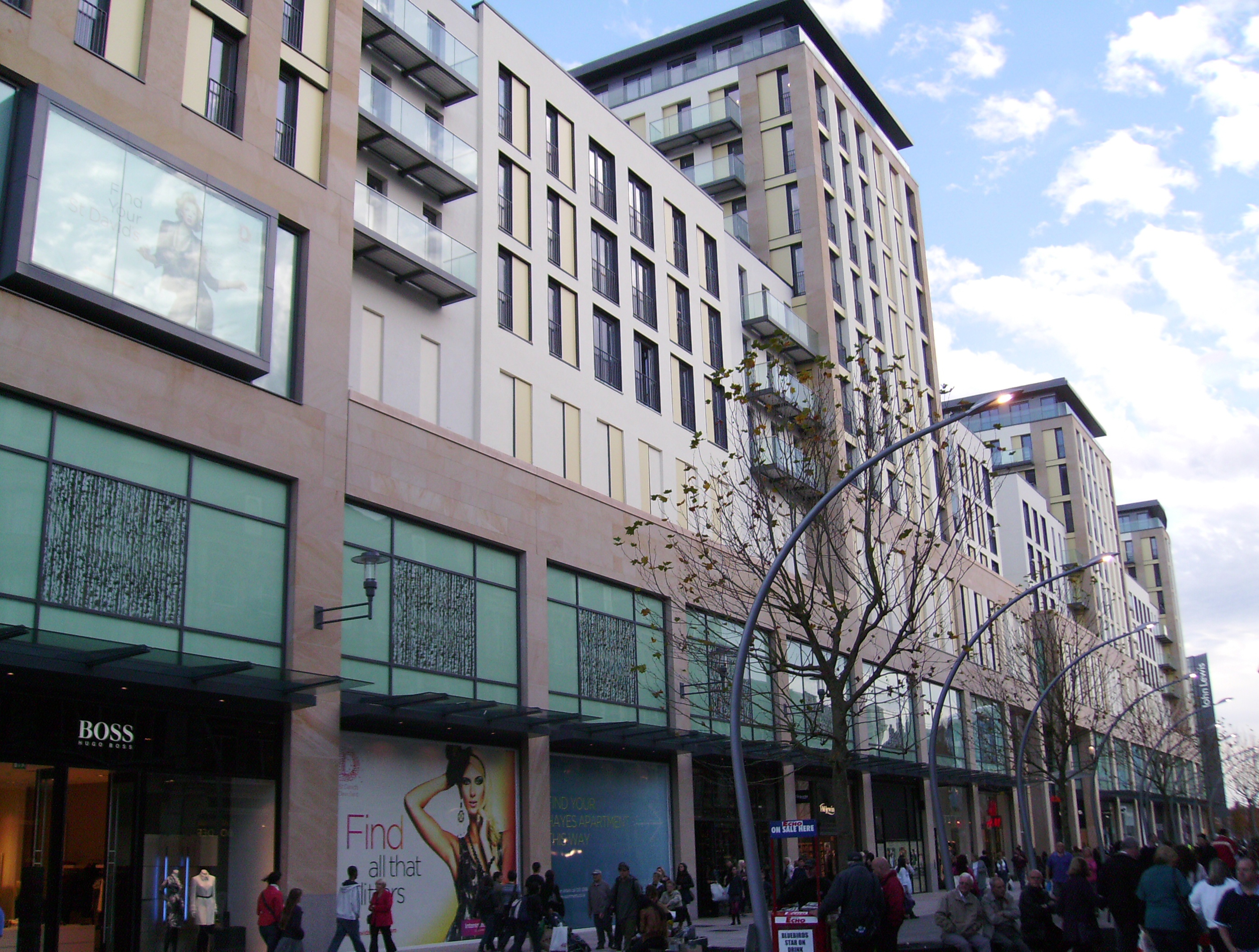 Most of Cardiff's shopping portfolio is in the city centre around Queen Street, St. Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street and High Street, with large suburban retail parks in Cardiff Bay,
Most of Cardiff's shopping portfolio is in the city centre around Queen Street, St. Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street and High Street, with large suburban retail parks in Cardiff Bay,  The Castle Quarter (Cardiff), Castle Quarter is a commercial area in the north of the city centre, which includes some of Cardiff's Victorian and Edwardian arcades: Castle Arcade, Morgan Arcade and Royal Arcade, Cardiff, Royal Arcade, and principal shopping streets: St Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street, High Street, The Hayes, and Queen Street.
The Castle Quarter (Cardiff), Castle Quarter is a commercial area in the north of the city centre, which includes some of Cardiff's Victorian and Edwardian arcades: Castle Arcade, Morgan Arcade and Royal Arcade, Cardiff, Royal Arcade, and principal shopping streets: St Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street, High Street, The Hayes, and Queen Street.
File:Cardiff Central station (26526139271).jpg, Cardiff Central railway station
File:Gorsaf Heol y Frenhines, Caerdydd.JPG, Cardiff Queen Street railway station
File:Cardiff Airport (Oct 2010).jpg, Cardiff Airport
File:Cardiff Bus double decker (Central Bus Station).jpg, Cardiff Bus has the most bus services operating in the Cardiff area.
File:Cycle lane in Excalibur Drive, Cardiff.jpg, Typical cycle lane in Cardiff
File:Aquabushydro1.jpg, Aquabus
 Cardiff is home to four major institutions of higher education: Cardiff University, Cardiff Metropolitan University, University of South Wales and the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama.
Cardiff University was founded by a royal charter in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire, is a member of the Russell Group of leading research led universities, having most of its campus in
Cardiff is home to four major institutions of higher education: Cardiff University, Cardiff Metropolitan University, University of South Wales and the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama.
Cardiff University was founded by a royal charter in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire, is a member of the Russell Group of leading research led universities, having most of its campus in  The total number of higher education students in the city is around 43,900. The city also has two further education colleges: Cardiff and Vale College and St David's Catholic College, St David's College. The former is the result of a merger, completed in August 2011, between Coleg Glan Hafren and Barry College. Further education is also offered at most high schools in the city.
Cardiff has three state nursery schools (one bilingual), 98 state primary schools (two bilingual, fifteen Welsh medium education, Welsh medium), and 19 state secondary schools (three Welsh medium). There are also several independent schools in the city, including St John's College, Cardiff, St John's College, The Cathedral School, Llandaff, Llandaff Cathedral School, Cardiff Sixth Form College, Kings Monkton School and Howell's School Llandaff, Howell's School, a single-sex girls' school (until sixth form). In 2013 Cardiff Sixth Form College came top of the independent senior schools in the UK, which were based on the percentage of A* and A at GCE Advanced Level, Advanced Level. Also in the top 100 were St John's College and Howell's School.
Notable schools include Whitchurch High School (the largest secondary school in Wales), Fitzalan High School (one of the most multi-cultural state schools in the UK), and Ysgol Gyfun Gymraeg Glantaf (the largest Welsh medium secondary school in Wales).
As well as academic institutions, Cardiff is also home to other educational and learning organisations such as Techniquest, a hands-on science discovery centre that now has franchises throughout Wales, and is part of the Wales Gene Park in collaboration with Cardiff University, NHS Wales and the
The total number of higher education students in the city is around 43,900. The city also has two further education colleges: Cardiff and Vale College and St David's Catholic College, St David's College. The former is the result of a merger, completed in August 2011, between Coleg Glan Hafren and Barry College. Further education is also offered at most high schools in the city.
Cardiff has three state nursery schools (one bilingual), 98 state primary schools (two bilingual, fifteen Welsh medium education, Welsh medium), and 19 state secondary schools (three Welsh medium). There are also several independent schools in the city, including St John's College, Cardiff, St John's College, The Cathedral School, Llandaff, Llandaff Cathedral School, Cardiff Sixth Form College, Kings Monkton School and Howell's School Llandaff, Howell's School, a single-sex girls' school (until sixth form). In 2013 Cardiff Sixth Form College came top of the independent senior schools in the UK, which were based on the percentage of A* and A at GCE Advanced Level, Advanced Level. Also in the top 100 were St John's College and Howell's School.
Notable schools include Whitchurch High School (the largest secondary school in Wales), Fitzalan High School (one of the most multi-cultural state schools in the UK), and Ysgol Gyfun Gymraeg Glantaf (the largest Welsh medium secondary school in Wales).
As well as academic institutions, Cardiff is also home to other educational and learning organisations such as Techniquest, a hands-on science discovery centre that now has franchises throughout Wales, and is part of the Wales Gene Park in collaboration with Cardiff University, NHS Wales and the
 Cardiff has many landmark buildings such as the Principality Stadium, Pierhead Building the Welsh National Museum and the Senedd building, the home of the Welsh Parliament. Cardiff is also famous for Cardiff Castle, St David's Hall,
Cardiff has many landmark buildings such as the Principality Stadium, Pierhead Building the Welsh National Museum and the Senedd building, the home of the Welsh Parliament. Cardiff is also famous for Cardiff Castle, St David's Hall,
 Cardiff has many cultural sites varying from the historical Cardiff Castle and out of town Castell Coch to the more modern
Cardiff has many cultural sites varying from the historical Cardiff Castle and out of town Castell Coch to the more modern
 A large number of concerts are held in the city, the larger ones at St David's Hall, the Motorpoint Arena Cardiff, Motorpoint Arena (previously known as the Cardiff International Arena) and occasionally the Principality Stadium. A number of festivals are also held in Cardiff, the largest being the Cardiff big weekend, Cardiff Big Weekend Festival, held annually in the city centre in the summer and playing host to free musical performances (from artists such as Ash (band), Ash, Jimmy Cliff, Cerys Matthews, the Fun Loving Criminals, Soul II Soul and the Magic Numbers), fairground rides and cultural events such as a Children's Festival that takes place in the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The annual festival claims to be the UK's largest free outdoor festival, attracting over 250,000 visitors in 2007.
Cardiff hosted the National Eisteddfod in 1883, 1899, 1938, 1960, 1978, 2008 and 2018. Cardiff is unique in Wales in having two permanent stone circles used by the Gorsedd of Bards during Eisteddfodau. The original circle stands in Gorsedd Gardens in front of the National Museum while its 1978 replacement is situated in Bute Park. Since 1983, Cardiff has hosted the BBC Cardiff Singer of the World competition, a world-renowned event on the opera calendar which is held every two years. The city also hosts smaller events.
The
A large number of concerts are held in the city, the larger ones at St David's Hall, the Motorpoint Arena Cardiff, Motorpoint Arena (previously known as the Cardiff International Arena) and occasionally the Principality Stadium. A number of festivals are also held in Cardiff, the largest being the Cardiff big weekend, Cardiff Big Weekend Festival, held annually in the city centre in the summer and playing host to free musical performances (from artists such as Ash (band), Ash, Jimmy Cliff, Cerys Matthews, the Fun Loving Criminals, Soul II Soul and the Magic Numbers), fairground rides and cultural events such as a Children's Festival that takes place in the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The annual festival claims to be the UK's largest free outdoor festival, attracting over 250,000 visitors in 2007.
Cardiff hosted the National Eisteddfod in 1883, 1899, 1938, 1960, 1978, 2008 and 2018. Cardiff is unique in Wales in having two permanent stone circles used by the Gorsedd of Bards during Eisteddfodau. The original circle stands in Gorsedd Gardens in front of the National Museum while its 1978 replacement is situated in Bute Park. Since 1983, Cardiff has hosted the BBC Cardiff Singer of the World competition, a world-renowned event on the opera calendar which is held every two years. The city also hosts smaller events.
The
 Cardiff has strong nightlife. Most clubs and bars are situated in the city centre, especially St Mary Street. More recently Cardiff Bay has built up a strong night scene, with many modern bars and restaurants. The Brewery Quarter on St Mary Street is a recently developed venue for bars and restaurant with a central courtyard. Charles Street is also a popular part of the city.
Cardiff has strong nightlife. Most clubs and bars are situated in the city centre, especially St Mary Street. More recently Cardiff Bay has built up a strong night scene, with many modern bars and restaurants. The Brewery Quarter on St Mary Street is a recently developed venue for bars and restaurant with a central courtyard. Charles Street is also a popular part of the city.
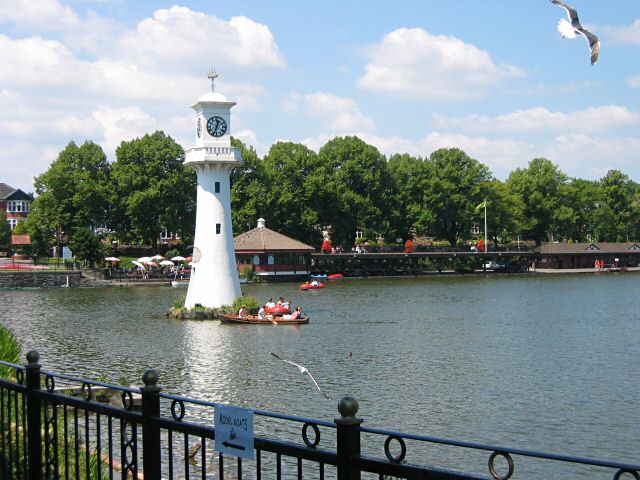 Cardiff is known for its extensive parks and other green spaces covering around 10% of the city's total area. Cardiff's main park, Bute Park (which was formerly the castle grounds) extends northwards from the top of one of Cardiff's main shopping street (Queen Street); when combined with the adjacent Llandaff Fields and Pontcanna Fields to the north-west it produces a massive open space skirting the River Taff. Other popular parks include Roath Park in the north, donated to the city by the John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, 3rd Marquess of Bute in 1887, which includes a popular boating lake; Victoria Park, Cardiff's first official park; and Thompson's Park, formerly home to an aviary removed in the 1970s. Wild open spaces include Howardian Local Nature Reserve, of the lower Rhymney valley in Penylan noted for its orchids, and Forest Farm Country Park, over along the River Taff in Whitchurch.
Cardiff is one of the top ten retail destinations in the UK with Queen Street and St. Mary Street as the two main shopping streets with the three shopping arcades, St. David's Centre, Queens Arcade and the Capitol Centre, Cardiff, Capitol Centre. The current expansion of St. David's Centre as part of the St David's 2 project has made it one of the largest shopping centres in the UK. As well as the modern shopping arcades, the city is home to Victorian shopping centres, such as High Street Arcade, Castle Arcade, Wyndham Arcade, Royal Arcade and Morgan Arcade. Also of note is The Hayes, home to Spillers Records, the world's oldest record shop. Cardiff has a number of markets, including the vast Victorian indoor Cardiff Market, Cardiff Central Market and the newly established Riverside Community Market, which specialises in locally produced organic produce. Several out-of-town retail parks exist, such as Newport Road, Culverhouse Cross, Cardiff Gate and Cardiff Bay.
Cardiff is known for its extensive parks and other green spaces covering around 10% of the city's total area. Cardiff's main park, Bute Park (which was formerly the castle grounds) extends northwards from the top of one of Cardiff's main shopping street (Queen Street); when combined with the adjacent Llandaff Fields and Pontcanna Fields to the north-west it produces a massive open space skirting the River Taff. Other popular parks include Roath Park in the north, donated to the city by the John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, 3rd Marquess of Bute in 1887, which includes a popular boating lake; Victoria Park, Cardiff's first official park; and Thompson's Park, formerly home to an aviary removed in the 1970s. Wild open spaces include Howardian Local Nature Reserve, of the lower Rhymney valley in Penylan noted for its orchids, and Forest Farm Country Park, over along the River Taff in Whitchurch.
Cardiff is one of the top ten retail destinations in the UK with Queen Street and St. Mary Street as the two main shopping streets with the three shopping arcades, St. David's Centre, Queens Arcade and the Capitol Centre, Cardiff, Capitol Centre. The current expansion of St. David's Centre as part of the St David's 2 project has made it one of the largest shopping centres in the UK. As well as the modern shopping arcades, the city is home to Victorian shopping centres, such as High Street Arcade, Castle Arcade, Wyndham Arcade, Royal Arcade and Morgan Arcade. Also of note is The Hayes, home to Spillers Records, the world's oldest record shop. Cardiff has a number of markets, including the vast Victorian indoor Cardiff Market, Cardiff Central Market and the newly established Riverside Community Market, which specialises in locally produced organic produce. Several out-of-town retail parks exist, such as Newport Road, Culverhouse Cross, Cardiff Gate and Cardiff Bay.
 Cardiff is the Welsh base for the main national broadcasters (BBC Cymru Wales, ITV Wales and S4C). A locally based television station, ''Made in Cardiff'', is also based in the city centre. Major filming studios in Cardiff include the BBC's Roath Lock Studios and Pinewood Studios Wales.
Several contemporary television programmes and films are filmed in and/or set in Cardiff such as ''Casualty (TV series), Casualty'', '' Doctor Who'', ''The Sarah Jane Adventures'', ''
Cardiff is the Welsh base for the main national broadcasters (BBC Cymru Wales, ITV Wales and S4C). A locally based television station, ''Made in Cardiff'', is also based in the city centre. Major filming studios in Cardiff include the BBC's Roath Lock Studios and Pinewood Studios Wales.
Several contemporary television programmes and films are filmed in and/or set in Cardiff such as ''Casualty (TV series), Casualty'', '' Doctor Who'', ''The Sarah Jane Adventures'', ''
 Cardiff hosts many high-profile sporting events at local, national and international level and in recognition of the city's commitment to sport for all was awarded the title of European Capital of Sport 2014. Organised sports have been held in the city since the early 19th century. national home sporting fixtures are nearly always played in the city. All Wales' multi-sports agencies and many of the Countries of the United Kingdom, country's Governing bodies of sports in Wales, sports governing bodies have their headquarters in Cardiff and the city's many top quality venues have attracted world-famous sports events, sometimes unrelated to Cardiff or to Wales. In 2008/09, 61% of Cardiff residents regularly participated in sport and active recreation, the highest percentage in ll 22 local authorities in Wales.
Rugby union fans around the world have long been familiar with the old National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, and its successor the Principality Stadium, which hosted the FA Cup for six years (from 2001 to 2006) it took to rebuild Wembley Stadium. In 2009, Cardiff hosted the first Australian cricket team in England in 2009, Ashes cricket test between England and Australia to be held in Wales. Cardiff hosted eight football matches of the London 2012 Olympics.
Cardiff hosts many high-profile sporting events at local, national and international level and in recognition of the city's commitment to sport for all was awarded the title of European Capital of Sport 2014. Organised sports have been held in the city since the early 19th century. national home sporting fixtures are nearly always played in the city. All Wales' multi-sports agencies and many of the Countries of the United Kingdom, country's Governing bodies of sports in Wales, sports governing bodies have their headquarters in Cardiff and the city's many top quality venues have attracted world-famous sports events, sometimes unrelated to Cardiff or to Wales. In 2008/09, 61% of Cardiff residents regularly participated in sport and active recreation, the highest percentage in ll 22 local authorities in Wales.
Rugby union fans around the world have long been familiar with the old National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, and its successor the Principality Stadium, which hosted the FA Cup for six years (from 2001 to 2006) it took to rebuild Wembley Stadium. In 2009, Cardiff hosted the first Australian cricket team in England in 2009, Ashes cricket test between England and Australia to be held in Wales. Cardiff hosted eight football matches of the London 2012 Olympics.
 Cardiff City F.C. (founded 1899 as Riverside AFC) played their home games at Ninian Park from 1910 until the end of the 2008–09 season. The club's new home is the Cardiff City Stadium, which they initially rented to the Cardiff Blues, the city's professional rugby union team, the Blues returning to the Arms Park in 2012. Cardiff City have played in the English The Football League, Football League since the 1920–21 season, climbing to Division 1 after one season. Cardiff City are the only non-English team to have won the FA Cup, beating Arsenal F.C., Arsenal in the 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927 final at Wembley Stadium (1923), Wembley Stadium. They were runners up to Portsmouth F.C., Portsmouth in the 2008 FA Cup Final, 2008 final, losing 1–0 at the new Wembley Stadium. In the 2013/14 and 2018/19 seasons Cardiff City played in the English Premier League.
Cardiff Metropolitan University F.C. of the Athletic Union of Cardiff Metropolitan University, based in Cyncoed, play in the Cymru Premier, having been promoted from Welsh League Division One in 2016. They were winners of the Welsh League Cup for the 2018–19 season.
Cardiff has numerous smaller clubs including Bridgend Street A.F.C., Caerau (Ely) A.F.C., Cardiff Corinthians F.C., Cardiff Grange Harlequins A.F.C., and Ely Rangers A.F.C., which all play in the Welsh football league system.
Cardiff City F.C. (founded 1899 as Riverside AFC) played their home games at Ninian Park from 1910 until the end of the 2008–09 season. The club's new home is the Cardiff City Stadium, which they initially rented to the Cardiff Blues, the city's professional rugby union team, the Blues returning to the Arms Park in 2012. Cardiff City have played in the English The Football League, Football League since the 1920–21 season, climbing to Division 1 after one season. Cardiff City are the only non-English team to have won the FA Cup, beating Arsenal F.C., Arsenal in the 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927 final at Wembley Stadium (1923), Wembley Stadium. They were runners up to Portsmouth F.C., Portsmouth in the 2008 FA Cup Final, 2008 final, losing 1–0 at the new Wembley Stadium. In the 2013/14 and 2018/19 seasons Cardiff City played in the English Premier League.
Cardiff Metropolitan University F.C. of the Athletic Union of Cardiff Metropolitan University, based in Cyncoed, play in the Cymru Premier, having been promoted from Welsh League Division One in 2016. They were winners of the Welsh League Cup for the 2018–19 season.
Cardiff has numerous smaller clubs including Bridgend Street A.F.C., Caerau (Ely) A.F.C., Cardiff Corinthians F.C., Cardiff Grange Harlequins A.F.C., and Ely Rangers A.F.C., which all play in the Welsh football league system.
 In addition to men's football teams Cardiff City Ladies F.C., Cardiff City Ladies of the FA Women's Premier League Southern Division are based in the city. Teams in the Welsh Premier Women's Football League are Cardiff Met. Ladies F.C., Cardiff Met. Ladies, Cyncoed Ladies F.C., Cyncoed Ladies and Cardiff City F.C. (women), Cardiff City.
During the 1990s, London-based football club Wimbledon FC expressed interest in relocating to Cardiff, having been without a home of their own since exiting Plough Lane (1912–98), Plough Lane stadium in 1991 and sharing with Crystal Palace FC at Selhurst Park. The relocation of the club to Cardiff did not happen; in 2003, the club moved to Milton Keynes and a year later rebranded as Milton Keynes Dons FC, Milton Keynes Dons.
Cardiff Arms Park ( cy, Parc yr Arfau Caerdydd), in central Cardiff, is among the world's most famous venues—being the scene of three Welsh Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slams in the 1970s (1971 Five Nations Championship, 1971, 1976 Five Nations Championship, 1976 and 1978 Five Nations Championship, 1978) and six Six Nations Championship, Five Nations titles in nine years—and was the venue for Wales' games in the 1991 Rugby World Cup. The Arms Park has a sporting history dating back to at least the 1850s, when Cardiff Cricket Club (formed 1819) relocated to the site. The ground was donated to Cardiff CC in 1867 by the Marquess of Bute. Cardiff Cricket Club shared the ground with Cardiff Rugby Football Club (founded 1876) — forming Cardiff Athletic Club between them — until 1966, when the cricket section moved to Sophia Gardens. Cardiff Athletic Club and the Welsh Rugby Union established two stadia on the site—Cardiff RFC played at their stadium at the northern end of the site, and the Wales national rugby union team played international matches at the National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, which opened in 1970. The National Stadium was replaced by the 74,500 capacity Millennium Stadium ( cy, Stadiwm y Mileniwm) in 1999—in time for the 1999 Rugby World Cup—and is home stadium to the Wales national rugby union team, Wales national rugby and Wales national football team, football teams for international matches. In addition to Wales' Six Nations Championship and other international games, the Principality Stadium held four matches in the 2007 Rugby World Cup and six FA Cup finals (from the 2001–02 FA Cup, 2001–02 to 2005–06 FA Cup, 2005–06 seasons) while Wembley Stadium was being rebuilt.
In addition to men's football teams Cardiff City Ladies F.C., Cardiff City Ladies of the FA Women's Premier League Southern Division are based in the city. Teams in the Welsh Premier Women's Football League are Cardiff Met. Ladies F.C., Cardiff Met. Ladies, Cyncoed Ladies F.C., Cyncoed Ladies and Cardiff City F.C. (women), Cardiff City.
During the 1990s, London-based football club Wimbledon FC expressed interest in relocating to Cardiff, having been without a home of their own since exiting Plough Lane (1912–98), Plough Lane stadium in 1991 and sharing with Crystal Palace FC at Selhurst Park. The relocation of the club to Cardiff did not happen; in 2003, the club moved to Milton Keynes and a year later rebranded as Milton Keynes Dons FC, Milton Keynes Dons.
Cardiff Arms Park ( cy, Parc yr Arfau Caerdydd), in central Cardiff, is among the world's most famous venues—being the scene of three Welsh Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slams in the 1970s (1971 Five Nations Championship, 1971, 1976 Five Nations Championship, 1976 and 1978 Five Nations Championship, 1978) and six Six Nations Championship, Five Nations titles in nine years—and was the venue for Wales' games in the 1991 Rugby World Cup. The Arms Park has a sporting history dating back to at least the 1850s, when Cardiff Cricket Club (formed 1819) relocated to the site. The ground was donated to Cardiff CC in 1867 by the Marquess of Bute. Cardiff Cricket Club shared the ground with Cardiff Rugby Football Club (founded 1876) — forming Cardiff Athletic Club between them — until 1966, when the cricket section moved to Sophia Gardens. Cardiff Athletic Club and the Welsh Rugby Union established two stadia on the site—Cardiff RFC played at their stadium at the northern end of the site, and the Wales national rugby union team played international matches at the National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, which opened in 1970. The National Stadium was replaced by the 74,500 capacity Millennium Stadium ( cy, Stadiwm y Mileniwm) in 1999—in time for the 1999 Rugby World Cup—and is home stadium to the Wales national rugby union team, Wales national rugby and Wales national football team, football teams for international matches. In addition to Wales' Six Nations Championship and other international games, the Principality Stadium held four matches in the 2007 Rugby World Cup and six FA Cup finals (from the 2001–02 FA Cup, 2001–02 to 2005–06 FA Cup, 2005–06 seasons) while Wembley Stadium was being rebuilt.
 Cardiff Cricket Club was formed in 1819 and Glamorgan CCC, Glamorgan County Cricket Club has competed as a first-class county since 1921. Its headquarters and ground is the SWALEC Stadium, Sophia Gardens, since moving from Cardiff Arms Park in 1966. The Sophia Gardens stadium underwent multimillion-pound improvements since being selected to host the first England cricket team, "England" v Australia national cricket team, Australia Test cricket, Test match of the Australian cricket team in England in 2009, 2009 Ashes series. The Hundred (cricket), The Hundred franchise team Welsh Fire is also based at the stadium.
Cardiff has a long association with boxing, from Jim Driscoll, 'Peerless' Jim Driscoll — born in Cardiff in 1880 — to more recent, high-profile fights staged in the city. These include the World Boxing Council, WBC Lennox Lewis vs. Frank Bruno heavyweight championship fight at the Arms Park in 1993, and many of Joe Calzaghe's fights, between 2003 and 2007.
Cardiff's professional ice hockey team, the Cardiff Devils, plays in the 3,000-seat Ice Arena Wales in the Cardiff International Sports Village. It plays in the 12-team professional Elite Ice Hockey League. Founded in 1986, it was one of the most successful British teams in the 1990s.
Cardiff's only American-flag football team is the Hurricanes. It won the British Championship in 2014 after falling short by 2 points in a quarter-final to eventual winners, the London Rebels, the previous year. It is based at Roath Recreational Ground.
Cardiff Cricket Club was formed in 1819 and Glamorgan CCC, Glamorgan County Cricket Club has competed as a first-class county since 1921. Its headquarters and ground is the SWALEC Stadium, Sophia Gardens, since moving from Cardiff Arms Park in 1966. The Sophia Gardens stadium underwent multimillion-pound improvements since being selected to host the first England cricket team, "England" v Australia national cricket team, Australia Test cricket, Test match of the Australian cricket team in England in 2009, 2009 Ashes series. The Hundred (cricket), The Hundred franchise team Welsh Fire is also based at the stadium.
Cardiff has a long association with boxing, from Jim Driscoll, 'Peerless' Jim Driscoll — born in Cardiff in 1880 — to more recent, high-profile fights staged in the city. These include the World Boxing Council, WBC Lennox Lewis vs. Frank Bruno heavyweight championship fight at the Arms Park in 1993, and many of Joe Calzaghe's fights, between 2003 and 2007.
Cardiff's professional ice hockey team, the Cardiff Devils, plays in the 3,000-seat Ice Arena Wales in the Cardiff International Sports Village. It plays in the 12-team professional Elite Ice Hockey League. Founded in 1986, it was one of the most successful British teams in the 1990s.
Cardiff's only American-flag football team is the Hurricanes. It won the British Championship in 2014 after falling short by 2 points in a quarter-final to eventual winners, the London Rebels, the previous year. It is based at Roath Recreational Ground.
 The 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games were hosted by Cardiff. These involved 1,130 athletes from 35 national teams competing in 94 events. One of the venues for those Games—The Wales Empire Swimming Pool—was demolished in 1998 to make way for the Principality Stadium. The GBP32m Cardiff International Pool in Cardiff Bay, opened to the public on 12 January 2008 — part of the GBP1bn International Sports Village (ISV) — is the only Olympic-standard swimming pool in Wales. When complete, the ISV complex will provide Olympic standard facilities for sports including boxing and fencing, gymnastics, judo, white water events (including Whitewater canoeing, canoeing and Whitewater kayaking, kayaking) and wrestling as well as a Indoor skiing, snow dome with real snow for skiing and snowboarding, an Cardiff Arena, arena for public ice skating and ice hockey and a hotel. Some of the sports facilities at the ISV were to be used as training venues for the London 2012 Olympics.
The 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games were hosted by Cardiff. These involved 1,130 athletes from 35 national teams competing in 94 events. One of the venues for those Games—The Wales Empire Swimming Pool—was demolished in 1998 to make way for the Principality Stadium. The GBP32m Cardiff International Pool in Cardiff Bay, opened to the public on 12 January 2008 — part of the GBP1bn International Sports Village (ISV) — is the only Olympic-standard swimming pool in Wales. When complete, the ISV complex will provide Olympic standard facilities for sports including boxing and fencing, gymnastics, judo, white water events (including Whitewater canoeing, canoeing and Whitewater kayaking, kayaking) and wrestling as well as a Indoor skiing, snow dome with real snow for skiing and snowboarding, an Cardiff Arena, arena for public ice skating and ice hockey and a hotel. Some of the sports facilities at the ISV were to be used as training venues for the London 2012 Olympics.
 The Principality Stadium hosts motor-sport events such as the World Rally Championship, as part of Wales Rally GB. The first indoor special stages of the World Rally Championship were held at the Principality Stadium in September 2005 and have been an annual event since. The Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain, British Speedway Grand Prix, one of the World Championship events, is held at the Millennium Stadium. While the track—a temporary, purpose built, shale oval—is not universally loved, the venue is considered the best of the World Championship's 11 rounds.
The Cardiff International Sports Stadium, opened 19 January 2009, replacing the Cardiff Athletics Stadium, demolished to make way for the Cardiff City Stadium. It has a 4,953 capacity as a multi sport/special event venue, offering certificated international track and field athletics facilities, including an international standard external throws area. The stadium houses the Headquarters of Welsh Athletics, the sport's governing body for Wales. The city's indoor track and field athletics sports venue is the National Indoor Athletics Centre, an international athletics and multi sports centre at the University of Wales Institute, Cardiff Campus,
The Principality Stadium hosts motor-sport events such as the World Rally Championship, as part of Wales Rally GB. The first indoor special stages of the World Rally Championship were held at the Principality Stadium in September 2005 and have been an annual event since. The Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain, British Speedway Grand Prix, one of the World Championship events, is held at the Millennium Stadium. While the track—a temporary, purpose built, shale oval—is not universally loved, the venue is considered the best of the World Championship's 11 rounds.
The Cardiff International Sports Stadium, opened 19 January 2009, replacing the Cardiff Athletics Stadium, demolished to make way for the Cardiff City Stadium. It has a 4,953 capacity as a multi sport/special event venue, offering certificated international track and field athletics facilities, including an international standard external throws area. The stadium houses the Headquarters of Welsh Athletics, the sport's governing body for Wales. The city's indoor track and field athletics sports venue is the National Indoor Athletics Centre, an international athletics and multi sports centre at the University of Wales Institute, Cardiff Campus,
Cardiff Council siteVisit CardiffCardiff Records
the full text of the edition of historical records for Cardiff, edited by J. H. Matthews (1898–1905). Part of British History Online. {{Authority control Cardiff, Cardiff Capital cities in the United Kingdom Cities in Wales Populated coastal places in Wales Counties of Wales Glamorgan Port cities and towns in Wales Principal areas of Wales County towns in Wales Rally GB 50s establishments Populated places established in the 1st century
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. It forms a principal area {{Short description, Formal legal term for a county in England and Wales
In England and Wales local government legislation, a principal area is one of the sub-national areas established for control by a principal council. They include most of the ar ...
, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingdom. Located in the south-east of Wales and in the Cardiff Capital Region
The Cardiff Capital Region (CCR; cy, Prifddinas Ranbarth Caerdydd) is a city region in Wales, centred on the capital city of Wales, Cardiff, in the southeast of the country. It is a partnership between the ten local authorities of Blaenau Gwe ...
, Cardiff is the county town of the historic county of Glamorgan and in 1974–1996 of South Glamorgan
, Government= South Glamorgan County Council
, Status= Non-metropolitan county (1974–1996) Preserved county (1996–)
, Start= 1974
, End= 1996
, Arms=
, HQ= ...
. It belongs to the Eurocities
Eurocities is a network of large cities in Europe, established in 1986 by the mayors of six large cities: Barcelona, Birmingham, Frankfurt, Lyon, Milan and Rotterdam. Today, Eurocities members includes over 200 of Europe's major cities from 38 c ...
network of the largest European cities. A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a port for coal when mining began in the region helped its expansion. In 1905, it was ranked as a city and in 1955 proclaimed capital of Wales. Cardiff Built-up Area covers a larger area outside the county boundary, including the towns of Dinas Powys
Dinas Powys (; also spelt "Dinas Powis" in English) is a small town and community in the Vale of Glamorgan, South Wales. Its name means "fort of the provincial place" and refers to the Iron Age hillfort which overlooks the village. Dinas Powys ...
and Penarth.
Cardiff is the main commercial centre of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
as well as the base for the Senedd. At the 2021 census, the unitary authority area population was put at 362,400. The population of the wider urban area in 2011 was 479,000. In 2011, it ranked sixth in the world in a ''National Geographic'' magazine list of alternative tourist destinations. It is the most popular destination in Wales with 21.3 million visitors in 2017.
Cardiff is a major centre for television and film production (such as '' Doctor Who'', ''Torchwood
''Torchwood'' is a British science fiction television programme created by Russell T Davies. A spin-off of the 2005 revival of ''Doctor Who'', it aired from 2006 to 2011. The show shifted its broadcast channel each series to reflect its growin ...
'' and '' Sherlock'') and is the Welsh base for the main national broadcasters.
Cardiff Bay contains the Senedd building
The Senedd building () in Cardiff houses the debating chamber and three committee rooms of the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; , formerly the National Assembly for Wales). The Senedd building was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 1 March 2006, Saint ...
(home to the Senedd, the Welsh Parliament) and the Wales Millennium Centre
Wales Millennium Centre ( cy, Canolfan Mileniwm Cymru) is an arts centre located in the Cardiff Bay area of Cardiff, Wales. The site covers a total area of . Phase 1 of the building was opened during the weekend of the 26–28 November 2004 an ...
arts complex. Work continues at Cardiff Bay and in the centre, on projects such as Cardiff International Sports Village
Cardiff International Sports Village ( cy, Pentref Chwaraeon Rhyngwladol Caerdydd) is located in Cardiff Bay in the city of Cardiff, Wales. It is one of the largest Urban renewal, regeneration projects currently in the UK and is a Public-priv ...
, BBC drama village, and a new business district.
Etymology
(theWelsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
name of the city) derives from the Middle Welsh
Middle Welsh ( cy, Cymraeg Canol, wlm, Kymraec) is the label attached to the Welsh language of the 12th to 15th centuries, of which much more remains than for any earlier period. This form of Welsh developed directly from Old Welsh ( cy, Hen G ...
. The change from to shows the colloquial alteration of Welsh ''f'' and ''dd'' , and was perhaps also driven by folk etymology. This sound change had probably first occurred in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
; both forms were current in the Tudor period
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began wit ...
. has its origins in post-Roman Brythonic words meaning "the fort of the Taff
Taff may refer to:
* River Taff, a large river in Wales
* ''Taff'' (TV series), a German tabloid news programme
* Trans-Atlantic Fan Fund, an organisation for science fiction fandom
People
* a demonym for anyone from south Wales
* Jerry Taff ( ...
". The fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
probably refers to that established by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. is Welsh for ''fort'' and is in effect a form of (Taff), the river which flows by Cardiff Castle, with the showing consonant mutation
Consonant mutation is change in a consonant in a word according to its morphological or syntactic environment.
Mutation occurs in languages around the world. A prototypical example of consonant mutation is the initial consonant mutation of all ...
to and the vowel showing affection as a result of a (lost) genitive case ending.Hywel Wyn Owen and Richard Morgan, ''Dictionary of the Place-names of Wales''. University of Wales Press, 2007, , p. 70.
The anglicised ''Cardiff'' is derived from , with the Welsh ''f'' borrowed as ''ff'' , as also happens in ''Taff'' (from Welsh ) and ''Llandaff
Llandaff (; cy, Llandaf ; from 'church' and ''River Taff, Taf'') is a district, Community (Wales), community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It was incorporated into the city in 1922. It is the seat of ...
'' (from Welsh ).
The antiquarian William Camden
William Camden (2 May 1551 – 9 November 1623) was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of ''Britannia'', the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the ''Ann ...
(1551–1623) suggested that the name Cardiff may derive from * ("the Fort of Didius"), a name supposedly given in honour of , governor of a nearby province at the time when the Roman fort was established. Although some sources repeat this theory, it has been rejected on linguistic grounds by modern scholars such as Professor Pierce.
History
Origins
Archaeological evidence from sites in and around Cardiff show that people had settled in the area by at least around 6000 BC, during the early Neolithic; about 1,500 years before either Stonehenge or theGreat Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient Worl ...
was completed. These include the St Lythans burial chamber
, alternate_name =
, image = St Lythans burial chamber (4794) (cropped).jpg
, caption =
, alt = a grassy field in which three large upright stones support a stone slab roof
, location = near St Lythans and Barry ()
, region = Vale ...
near Wenvoe
Wenvoe ( cy, Gwenfô) is a village, community and electoral ward between Barry and Cardiff in the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales. Nearby are the Wenvoe Transmitter near Twyn-yr-Odyn and the site of the former HTV Wales Television Centre at Culverhouse ...
, (approximately west of Cardiff city centre); the Tinkinswood burial chamber, near St. Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-day Demre ...
(about west of Cardiff city centre), the Cae'rarfau Chambered Tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could ...
, Creigiau
Creigiau is a dormitory settlement in the north-west of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. The village currently has about 1,500 houses and a population of approximately 5,000 people. The Cardiff electoral ward is called Creigiau/St. Fagans. The ...
(about northwest of Cardiff city centre) and the Gwern y Cleppa long barrow, near Coedkernew
Coedkernew ( cy, Coedcernyw) is a community in the south west of the city of Newport, South Wales, in the Marshfield ward.
The parish is bounded by Percoed reen to the south, Nant-y-Selsig to the southwest, and Pound Hill to the west. The no ...
, Newport (about northeast of Cardiff city centre). A group of five Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
is at the summit of the Garth
Garth may refer to:
Places
* Garth, Alberta, Canada
* Garth, Bridgend, a village in south Wales
:* Garth railway station (Bridgend)
* Garth, Ceredigion, small village in Wales
* Garth, Powys, a village in mid Wales
:* Garth railway station (Powy ...
, within the county's northern boundary. Four Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
and enclosure
Enclosure or Inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or " common land" enclosing it and by doing so depriving commoners of their rights of access and privilege. Agreements to enclose land ...
sites have been identified within Cardiff's county boundaries, including Caerau Hillfort, an enclosed area of .
 Until the Roman conquest of Britain, Cardiff was part of the territory of the Silures – a Celtic British tribe that flourished in the
Until the Roman conquest of Britain, Cardiff was part of the territory of the Silures – a Celtic British tribe that flourished in the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
– whose territory included the areas that would become known as Breconshire
, image_flag=
, HQ= Brecon
, Government= Brecknockshire County Council (1889-1974)
, Origin= Brycheiniog
, Status=
, Start= 1535
, End= ...
, Monmouthshire and Glamorgan. The fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
established by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
near the mouth of the River Taff in AD 75, in what would become the north western boundary of the centre of Cardiff, was built over an extensive settlement that had been established by the Romans in the 50s AD. The fort was one of a series of military outposts associated with ''Isca Augusta
Isca, variously specified as Isca Augusta or Isca Silurum, was the site of a Roman legionary fortress and settlement or ''vicus'', the remains of which lie beneath parts of the present-day suburban village of Caerleon in the north of the city of ...
'' (Caerleon
Caerleon (; cy, Caerllion) is a town and community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman ...
) that acted as border defences. The fort may have been abandoned in the early 2nd century as the area had been subdued. However, by this time a civilian settlement, or ''vicus
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (plural ) designated a village within a rural area () or the neighbourhood of a larger settlement. During the Republican era, the four of the city of Rome were subdivided into . In the 1st century BC, Augustus ...
'', was established. It was likely made up of traders who made a living from the fort, ex-soldiers and their families. A Roman villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Typology and distribution
Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas n ...
has been discovered at Ely. Contemporary with the Saxon Shore forts
The Saxon Shore ( la, litus Saxonicum) was a military command of the late Roman Empire, consisting of a series of fortifications on both sides of the Channel. It was established in the late 3rd century and was led by the "Count of the Saxon Sho ...
of the 3rd and 4th centuries, a stone fortress was established at Cardiff. Similar to the shore forts, the fortress was built to protect Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
from raiders. Coins from the reign of Gratian
Gratian (; la, Gratianus; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and w ...
indicate that Cardiff was inhabited until at least the 4th century; the fort was abandoned towards the end of the 4th century, as the last Roman legions left the province of Britannia with Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; cy, Macsen Wledig ; died 8 August 388) was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian in 383 through negotiation with emperor Theodosius I.
He was made emperor in B ...
.
Little is known of the fort and civilian settlement in the period between the Roman departure from Britain and the Norman Conquest. The settlement probably shrank in size and may even have been abandoned. In the absence of Roman rule, Wales was divided into small kingdoms; early on, Meurig ap Tewdrig Meurig ap Tewdrig (Latin: ''Mauricius''; English: ''Maurice'') was the son of Tewdrig (St. Tewdric), and a King of the early Welsh Kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing. He is thought to have lived between 400AD and 600AD, but some sources give more spec ...
emerged as the local king in Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Name and ...
(which later became Glamorgan). The area passed through his family until the advent of the Normans in the 11th century.
Norman occupation and Middle Ages
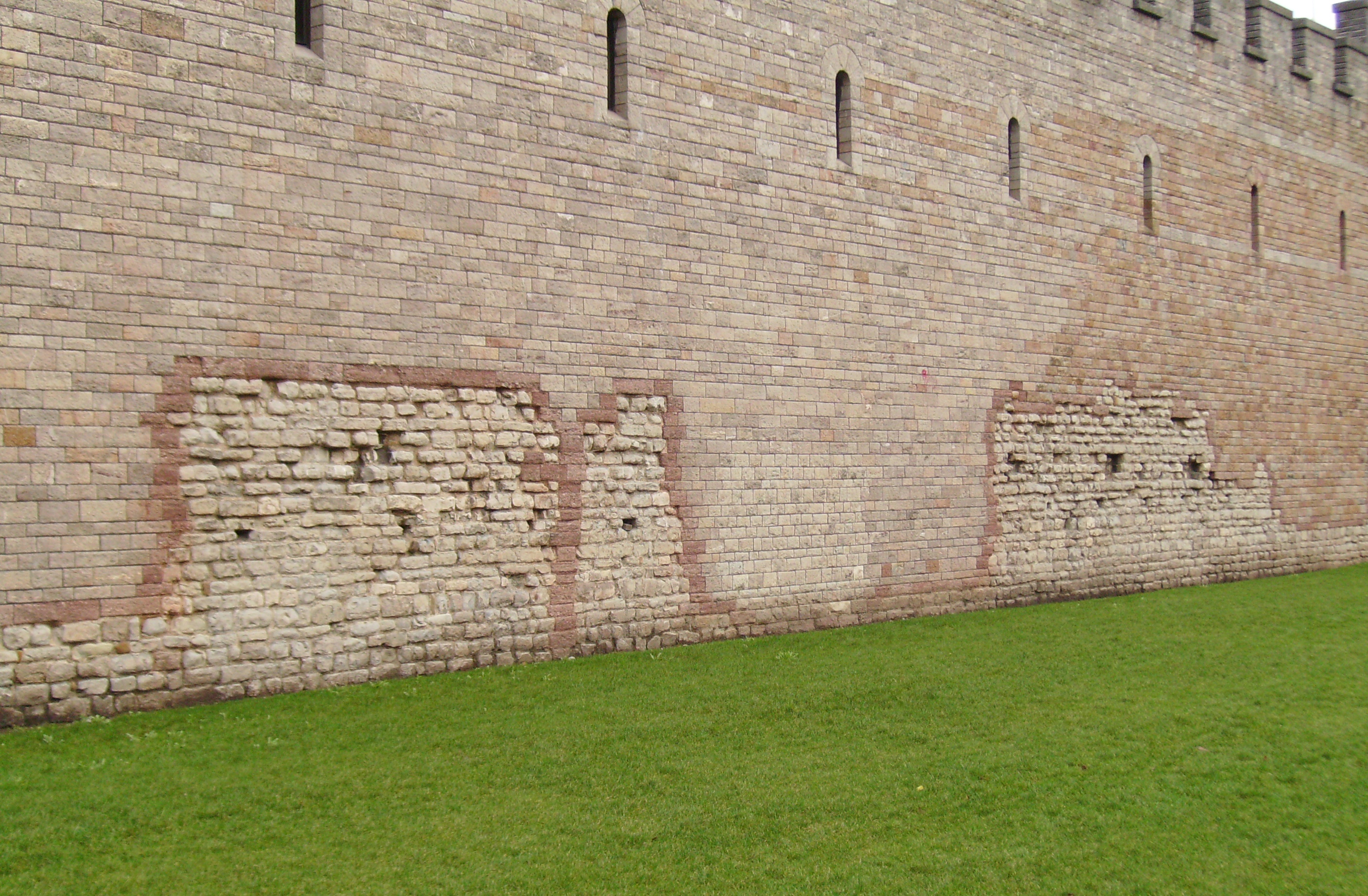
 In 1081 William I, King of England, began work on the castle keep within the walls of the old Roman fort. Cardiff Castle has been at the heart of the city ever since. The castle was substantially altered and extended during the Victorian period by John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, and the architect
In 1081 William I, King of England, began work on the castle keep within the walls of the old Roman fort. Cardiff Castle has been at the heart of the city ever since. The castle was substantially altered and extended during the Victorian period by John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, and the architect William Burges
William Burges (; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoc ...
. Original Roman work can, however, still be distinguished in the wall facings.
A town grew up under the castle, consisting mainly of settlers from England. Cardiff had a population of between 1,500 and 2,000 in the Middle Ages – a normal size for a Welsh town in the period. It was the centre of the Norman Marcher Lordship of Glamorgan. By the end of the 13th century, Cardiff was the only town in Wales with a population exceeding 2,000, although it remained relatively small compared with notable towns in England and continued to be contained within its walls, which were begun as a wooden palisade in the early 12th century. It was of sufficient size and importance to receive a series of charters, notably in 1331 from William La Zouche, Lord of Glamorgan through marriage with the de Clare family, Edward III in 1359, then Henry IV in 1400, and later Henry VI.
In 1404, Owain Glyndŵr burned Cardiff and took possession of the Castle. As many of the buildings were made of timber and tightly packed within the town walls, much of Cardiff was destroyed. His statue was erected in Cardiff Town Hall in the early 20th century, reflecting the complex, often conflicting cultural identity of Cardiff as capital of Wales. It was soon rebuilt on the same street plan and began to flourish again. Besides serving an important political role in the governance of the fertile south Glamorgan coastal plain, Cardiff was a busy port in the Middle Ages and declared a staple port in 1327.
County town of Glamorganshire

 In 1536, the
In 1536, the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542
The Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 ( cy, Y Deddfau Cyfreithiau yng Nghymru 1535 a 1542) were Acts of the Parliament of England, and were the parliamentary measures by which Wales was annexed to the Kingdom of England. Moreover, the legal sys ...
led to the creation of Glamorganshire and Cardiff was made the county town, it also became part of Kibbor hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
, around the same time the Herberts became the most powerful family in the area. In 1538, Henry VIII closed Cardiff's Dominican and Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
friaries, whose remains were used as building materials. A writer in this period noted: "The River Taff runs under the walls of his honours castle and from the north part of the town to the south part where there is a fair quay and a safe harbour for shipping."
Cardiff became a borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
in 1542 and further Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
s were granted to it by Elizabeth I in 1600 and James I in 1608. In 1573, it was made a head port for collection of customs duties. Pembrokeshire historian George Owen described Cardiff in 1602 as "the fayrest towne in Wales yett not the welthiest". It gained a second Royal Charter in 1608.
 A disastrous flood in the Bristol Channel on 30 January 1607 (now believed to have been a tidal wave) changed the course of the River Taff and ruined St Mary's Parish Church, which was replaced by a chapel of ease dedicated to St John the Baptist.
During the
A disastrous flood in the Bristol Channel on 30 January 1607 (now believed to have been a tidal wave) changed the course of the River Taff and ruined St Mary's Parish Church, which was replaced by a chapel of ease dedicated to St John the Baptist.
During the Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February to August 1648 in Kingdom of England, England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639-1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 1641� ...
St Fagans, just to the west of the town, the Battle of St Fagans, between Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
rebels and a New Model Army detachment, was a decisive victory for the Parliamentarians that allowed Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
to conquer Wales. It was the last major battle in Wales, with about 200, mostly Royalist soldiers killed.
Cardiff was at peace throughout the ensuing century. In 1766, John Stuart, 1st Marquess of Bute
John Stuart, 1st Marquess of Bute PC, FRS (30 June 1744 – 16 November 1814), styled Lord Mount Stuart until 1792 and known as The Earl of Bute between 1792 and 1794, was a British nobleman, coalfield owner, diplomat and politician who sat in ...
married into the Herbert family and was later created Baron Cardiff. In 1778, he began renovating Cardiff Castle. A racecourse
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also use ...
, printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
, bank and coffee house
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non- ...
opened in the 1790s and Cardiff gained a stagecoach service to London. Despite these improvements, Cardiff's position in the Welsh urban hierarchy
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area. Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are convention ...
declined over the 18th century. Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10 March 1747 – 18 December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclop ...
called it "an obscure and inconsiderable place" and the 1801 census found a population of only 1,870, making it only the 25th largest town in Wales, well behind Merthyr
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
and Swansea.
Building the docks
In 1793,John Crichton-Stuart, 2nd Marquess of Bute
John Crichton-Stuart, 2nd Marquess of Bute, KT, FRS (10 August 1793 – 18 March 1848), styled Lord Mount Stuart between 1794 and 1814, was a wealthy aristocrat and industrialist in Georgian and early Victorian Britain. He developed the coal ...
was born. He spent his life building the Cardiff docks and was later hailed as "the creator of modern Cardiff". A twice-weekly boat service between Cardiff and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
opened in 1815, and in 1821, the Cardiff Gas Works was established.
After the Napoleonic Wars Cardiff suffered some social and industrial unrest, starting with the trial and hanging of Dic Penderyn
Richard Lewis (1807/8 – 13 August 1831), known as Dic Penderyn, was a Welsh labourer and coal miner who lived in Merthyr Tydfil and was involved with the Merthyr Rising of 3 June 1831. In the course of the riot he was arrested alongside Lewis ...
in 1831.
 The town grew rapidly from the 1830s onwards, when the Marquess of Bute built a dock, which eventually linked to the
The town grew rapidly from the 1830s onwards, when the Marquess of Bute built a dock, which eventually linked to the Taff Vale Railway
The Taff Vale Railway (TVR) was a standard gauge railway in South Wales, built by the Taff Vale Railway Company to serve the iron and coal industries around Merthyr Tydfil and to connect them with docks in Cardiff. It was opened in st ...
. Cardiff became the main port for coal exports from the Cynon, Rhondda
Rhondda , or the Rhondda Valley ( cy, Cwm Rhondda ), is a former coal mining, coalmining area in South Wales, historically in the county of Glamorgan. It takes its name from the River Rhondda, and embraces two valleys – the larger Rhondda Fa ...
, and Rhymney valleys, and grew in population at a rate of nearly 80 per cent per decade between 1840 and 1870. Much of this was due to migration from within and outside Wales: in 1841, a quarter of Cardiff's population were English-born and more than 10 per cent born in Ireland. By the 1881 census, Cardiff had overtaken Merthyr and Swansea to become the largest town in Wales. Cardiff's status as the premier town in South Wales was confirmed when it was chosen as the site for the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire
, latin_name =
, image_name = Shield of the University of Cardiff.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms of Cardiff University
, motto = cy, Gwirionedd, Undod a Chytgord
, mottoeng = Truth, Unity and Concord
, established = 1 ...
in 1883.
A permanent military presence was established with the completion of Maindy Barracks
Maindy Barracks is a military installation in the Cathays district of Cardiff in Wales.
History
Maindy Barracks opened in 1877. Their creation took place as part of the Cardwell Reforms which encouraged the localisation of British military forces ...
in 1877.
Cardiff faced a challenge in the 1880s when David Davies of Llandinam and the Barry Railway Company promoted rival docks at Barry Barry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Barry (name), including lists of people with the given name, nickname or surname, as well as fictional characters with the given name
* Dancing Barry, stage name of Barry Richards (born c. 19 ...
. These had the advantage of being accessible in all tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s: David Davies claimed his venture would cause "grass to grow in the streets of Cardiff". From 1901 coal exports from Barry surpassed those from Cardiff, but the administration of the coal trade remained centred on Cardiff, in particular its Coal Exchange
The Coal Exchange (also known as the Exchange Building) is an historic building in Cardiff, Wales. It is designed in Renaissance Revival style. Built in 1888 as the Coal and Shipping Exchange to be used as a market floor and office building for ...
, where the price of coal on the British market was determined and the first million-pound deal was struck in 1907. The city also strengthened its industrial base when the owners of the Dowlais Ironworks
The Dowlais Ironworks was a major ironworks and steelworks located at Dowlais near Merthyr Tydfil, in Wales. Founded in the 18th century, it operated until the end of the 20th, at one time in the 19th century being the largest steel producer in ...
in Merthyr (who would later form part of Guest, Keen and Nettlefolds
GKN Ltd is a British multinational automotive and aerospace components business headquartered in Redditch, England. It is a long-running business known for many decades as Guest, Keen and Nettlefolds. It can trace its origins back to 1759 an ...
) built a steelworks close to the docks at East Moors, which Lord Bute opened on 4 February 1891.
County Borough of Cardiff
Cardiff became acounty borough
County borough is a term introduced in 1889 in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, to refer to a borough or a city independent of county council control, similar to the unitary authorities created since the 1990s. An equivalent te ...
on 1 April 1889 under the Local Government Act 1888
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
* Local government, a form of public administration, usually the lowest tier of administrat ...
. The town had grown rapidly and had a population of over 123,000. It retained its county borough status until 1974.
City and capital city status
King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria a ...
granted Cardiff city status City status is a symbolic and legal designation given by a national or subnational government. A municipality may receive city status because it already has the qualities of a city, or because it has some special purpose.
Historically, city status ...
on 28 October 1905. It acquired a Roman Catholic cathedral in 1916. Later, more national institutions came to the city, including the National Museum of Wales
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
, the Welsh National War Memorial
The Welsh National War Memorial ( cy, Cofeb ryfel Cenedlaethol Cymru) is situated in Alexandra Gardens, Cathays Park, Cardiff. The memorial was designed by Sir Ninian Comper and unveiled on 12 June 1928 by the Prince of Wales. The memorial comm ...
, and the University of Wales
, latin_name =
, image =
, caption = Coat of Arms
, motto = cy, Goreu Awen Gwirionedd
, mottoeng = The Best Inspiration is Truth
, established =
,
, type = Confederal, non-member ...
Registry Building, but it was denied the National Library of Wales, partly because the library's founder, Sir John Williams, considered Cardiff to have "a non-Welsh population".
After a brief post-war boom, Cardiff docks entered a prolonged decline in the interwar period. By 1936, trade was at less than half its value in 1913, reflecting the slump in demand for Welsh coal. Bomb damage in the Cardiff Blitz
The Cardiff Blitz ( cy, Blitz Caerdydd); refers to the bombing of Cardiff, Wales during World War II. Between 1940 and the final raid on the city in March 1944 approximately 2,100 bombs fell, killing 355 people.
Cardiff Docks became a strate ...
of World War II included the devastation of Llandaff Cathedral
Llandaff Cathedral ( cy, Eglwys Gadeiriol Llandaf) is an Anglican cathedral and parish church in Llandaff, Cardiff, Wales. It is the seat of the Bishop of Llandaff, head of the Church in Wales Diocese of Llandaff. It is dedicated to Saint Pet ...
, and in the immediate postwar years, the city's link with the Bute family came to an end.
The city was recognised as the capital city of Wales on 20 December 1955, in a written reply by the Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, otherwise known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The home secretary leads the Home Office, and is responsible for all national s ...
, Gwilym Lloyd George
Gwilym Lloyd George, 1st Viscount Tenby, (4 December 1894 – 14 February 1967) was a Welsh politician and cabinet minister. The younger son of David Lloyd George, he served as Home Secretary from 1954 to 1957.
Background, education and milit ...
. Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a royal town, community and port in Gwynedd, Wales, with a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the eastern shore of the Menai Strait, opposite the Isle of Anglesey. The city of Bangor is ...
had also vied for the title. Welsh local authorities had been divided: only 76 out of 161 chose Cardiff in a 1924 poll organised by the ''South Wales Daily News''. The subject was not debated again until 1950, and meanwhile Cardiff took steps to promote its "Welshness". The stalemate between Cardiff and cities such as Caernarfon and Aberystwyth was not broken until Cardiganshire County Council decided to support Cardiff; and in a new local authority vote, 134 out of 161 voted for Cardiff.
Cardiff therefore celebrated two important anniversaries
An anniversary is the date on which an event took place or an institution was founded in a previous year, and may also refer to the commemoration or celebration of that event. The word was first used for Catholic feasts to commemorate saints. ...
in 2005. The Encyclopedia of Wales notes that the decision to recognise the city as the capital of Wales "had more to do with the fact that it contained marginal Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
constituencies than any reasoned view of what functions a Welsh capital should have." Although the city hosted the Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games, often referred to as the Friendly Games or simply the Comm Games, are a quadrennial international multi-sport event among athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations. The event was first held in 1930, and, with the exce ...
in 1958, Cardiff only became a centre of national administration with the establishment of the Welsh Office
The Welsh Office ( cy, Swyddfa Gymreig) was a department in the Government of the United Kingdom with responsibilities for Wales. It was established in April 1965 to execute government policy in Wales, and was headed by the Secretary of State f ...
in 1964, which later prompted the creation of various other public bodies such as the Arts Council of Wales and the Welsh Development Agency
Welsh Development Agency (WDA; cy, Awdurdod Datblygu Cymru) was an executive agency (or QUANGO) and later designated an Assembly Sponsored Public Body (ASPB). Established in 1976, it was tasked with rescuing the ailing Welsh economy by encour ...
, most of which were based in Cardiff.
 The East Moors Steelworks closed in 1978 and Cardiff lost population in the 1980s, consistent with a wider pattern of counter-urbanisation in Britain. However, it recovered to become one of the few cities outside London where population grew in the 1990s. During this period the
The East Moors Steelworks closed in 1978 and Cardiff lost population in the 1980s, consistent with a wider pattern of counter-urbanisation in Britain. However, it recovered to become one of the few cities outside London where population grew in the 1990s. During this period the Cardiff Bay Development Corporation
The Cardiff Bay Development Corporation was set up by the United Kingdom Government on 3 April 1987 to redevelop one sixth of the area of Cardiff to create Cardiff Bay.
Objectives
The Secretary of State for Wales, Nicholas Edwards set out the ...
was promoting the redevelopment
Redevelopment is any new construction on a site that has pre-existing uses. It represents a process of land development uses to revitalize the physical, economic and social fabric of urban space.
Description
Variations on redevelopment include: ...
of south Cardiff; an evaluation of the regeneration of Cardiff Bay published in 2004 concluded that the project had "reinforced the competitive position of Cardiff" and "contributed to a massive improvement in the quality of the built environment, although it had "failed "to attract the major inward investors originally anticipated."
In the 1997 Welsh devolution referendum
The Welsh devolution referendum of 1997 was a pre-legislative referendum held in Wales on 18 September 1997 over whether there was support for the creation of a National Assembly for Wales, and therefore a degree of self-government. The refer ...
, Cardiff voters rejected the establishment of the National Assembly for Wales by 55.4% to 44.2% on a 47% turnout, which Denis Balsom partly ascribed to a general preference in Cardiff and some other parts of Wales for a British rather than exclusively Welsh identity
Identity may refer to:
* Identity document
* Identity (philosophy)
* Identity (social science)
* Identity (mathematics)
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Identity'' (1987 film), an Iranian film
* ''Identity'' (2003 film), ...
. The relative lack of local support for the Assembly and difficulties between the Welsh Office and Cardiff Council in acquiring the originally preferred venue, Cardiff City Hall
City Hall ( cy, Neuadd y ddinas) is a civic building in Cathays Park, Cardiff, Wales, UK. It serves as Cardiff's centre of local government. It was built as part of the Cathays Park civic centre development and opened in October 1906. Built of ...
, encouraged other local authorities to bid to house the Assembly. However, the Assembly was eventually located at Tŷ Hywel
Tŷ Hywel (Hywel House or Hywel's House) is a building in Cardiff, Wales, used by the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ; formerly the National Assembly for Wales). It is named after the medieval king (''Howell the Good''), King of Deheubarth in South W ...
in Cardiff Bay in 1999. In 2005, a new debating chamber on an adjacent site, designed by Richard Rogers, was opened.
Government
The Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ) has been based in Cardiff Bay since its formation in 1999 as the "National Assembly for Wales". The Senedd building was opened on 1 March 2006 byThe Queen
In the English-speaking world, The Queen most commonly refers to:
* Elizabeth II (1926–2022), Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 1952 until her death
The Queen may also refer to:
* Camilla, Queen Consort (born 1947), ...
. The Members of the Senedd
A Member of the Senedd (MS; plural: ''MSs''; cy, Aelodau o'r Senedd; , plural:) (AS)., group=la is a representative elected to the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ). There are sixty members, with forty members chosen to represent individual Senedd ...
(MSs), the Senedd Commission and ministerial support staff are based in Cardiff Bay.
Cardiff elects four constituency Members of the Senedd to the Senedd; the constituencies for the Senedd are the same as for the UK Parliament. All of the city's electors have an extra vote for the South Wales Central
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
regional members; this system increases proportionality to the Senedd. The most recent Senedd general election was held on 6 May 2021.
In the Senedd, Cardiff is represented by Jenny Rathbone (Labour) in Cardiff Central, Julie Morgan (Labour) in Cardiff North, Vaughan Gething
Vaughan Gething (born 15 March 1974) is a Welsh Labour and Co-operative politician serving as Minister for the Economy since 2021. He previously served as the Minister for Health and Social Services from 2016 to 2021. He has been the Membe ...
(Labour) in Cardiff South and Penarth and First Minister of Wales Mark Drakeford (Labour) in Cardiff West.
At Westminster, Cardiff is represented by four Labour MPs: Jo Stevens
Joanna Meriel Stevens (born 6 September 1966) is a Welsh politician serving as Shadow Secretary of State for Wales since 2021, and previously from 2016 to 2017. A member of the Labour Party, she has been Member of Parliament (MP) for Cardif ...
in Cardiff Central, Anna McMorrin in Cardiff North, Stephen Doughty
Stephen John Doughty (born 15 April 1980) is a Welsh Labour and Co-operative Party politician who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Cardiff South and Penarth since 2012. He has been the Shadow Minister for Africa and a Shadow M ...
in Cardiff South and Penarth, and Kevin Brennan in Cardiff West.
The Welsh Government
, image =
, caption =
, date_established =
, country = Wales
, address =
, leader_title = First Minister ()
, appointed = First Minister approved by the Senedd, ceremonially appointed ...
is headquartered in Cardiff's Cathays Park
Cathays Park ( cy, Parc Cathays) or Cardiff Civic Centre is a civic centre area in the city centre of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, consisting of a number of early 20th century buildings and a central park area, Alexandra Gardens. It i ...
, where most of its civil servants are based, with smaller numbers in other central locations: Cathays
Cathays ( ; Welsh: officially ''Cathays'' but also , 'the constant meadow') is a district and community in the centre of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It is an old suburb of Cardiff established in 1875. It is very densely populated and contain ...
, Canton, and Cardiff Bay. There are other Welsh Government offices in other parts of Wales, such as Llandudno and Aberystwyth, and there are international offices.
Local government
Between 1889 and 1974 Cardiff was a county borough governed byCardiff County Borough Council
Cardiff County Borough Council, known as Cardiff City Council after Cardiff achieved city status in 1905, was the elected local authority that administered the town (later city) and county borough of Cardiff, Glamorgan, Wales between 1889 and ...
(known as Cardiff City Council after 1905). Between 1974 and 1996, Cardiff was governed by Cardiff City Council, a district council of South Glamorgan
, Government= South Glamorgan County Council
, Status= Non-metropolitan county (1974–1996) Preserved county (1996–)
, Start= 1974
, End= 1996
, Arms=
, HQ= ...
. Since local government reorganisation in 1996, Cardiff has been governed by the City and County Council of Cardiff, based at County Hall in Atlantic Wharf, Cardiff Bay. Voters elect 75 councillors every four years.
Between the 2004 and 2012 local elections, no individual political party held a majority on Cardiff County Council. The Liberal Democrats held the largest number of seats and Cllr Rodney Berman was Leader of the council. The Liberal Democrats and Plaid Cymru formed a partnership administration. In the 2012 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 2012.
International
* 2012 United Nations Security Council election
Africa Egypt
* 2012 Egyptian presidential election
Mali
* 2012 Malian presidential election
* 2012 Malian parliamentary electio ...
the Labour Party achieved an outright majority, after gaining an additional 33 seats across the city.
Cardiff is divided into communities, several with their own community council
A community council is a public representative body in Great Britain.
In England they may be statutory parish councils by another name, under the Local Government and Public Involvement in Health Act 2007, or they may be non-statutory bodies. In ...
and the rest governed directly by Cardiff City Council. Elections are held every five years. The last contested elections would have been held at the same time as the 2017 Cardiff Council election had there been more candidates standing than available seats. Those with community councils are:
*Lisvane (10 seats)
*Old St. Mellons (9 seats)
*Pentyrch (13 seats)
*Radyr & Morganstown (13 seats)
*Tongwynlais (9 seats)
*St Fagans (9 seats)
Geography
The centre of Cardiff is relatively flat and bounded by hills to the east, north and west. Its location influenced its development as the world's largest coal port, notably its proximity and easy access to the coalfields of the South Wales Valleys. The highest point in the local authority area isGarth Hill
Garth Hill (usually called The Garth, or Garth Mountain, ''Mynydd y Garth'' in Welsh) is a hill located in between the communities of Llantwit Fardre and Pentyrch in Wales. The Garth can be seen from nearly the whole of the city of Cardiff and th ...
, above sea level.
Cardiff is built on reclaimed marshland on a bed of Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
stones. This reclaimed marshland stretches from Chepstow
Chepstow ( cy, Cas-gwent) is a town and community in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the tidal River Wye, about above its confluence with the River Severn, and adjoining the wester ...
to the Ely Estuary, which is the natural boundary of Cardiff and the Vale of Glamorgan. Triassic landscapes of this part of the world are usually shallow and low-lying, consistent with the flatness of the centre of Cardiff. The classic Triassic marl, sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
and conglomerate rocks are used predominantly throughout Cardiff as building materials. Many of these Triassic rocks are purplish, especially the coastal marl found near Penarth. One of the Triassic rocks used in Cardiff is "Radyr Stone", a freestone which as its name suggests is quarried in the Radyr district. Cardiff has also imported some materials for buildings: Devonian sandstones (the Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also exte ...
) from the Brecon Beacons has been used. Most famously, the buildings of Cathays Park
Cathays Park ( cy, Parc Cathays) or Cardiff Civic Centre is a civic centre area in the city centre of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, consisting of a number of early 20th century buildings and a central park area, Alexandra Gardens. It i ...
, the civic centre in the centre of the city, are built of Portland stone from Dorset. A widely used building stone in Cardiff is the yellow-grey Liassic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
rock of the Vale of Glamorgan, including the rare "Sutton Stone", a conglomerate of lias limestone and carboniferous limestone.
Cardiff is bordered to the west by the rural district of the Vale of Glamorgan, also known as the Garden of Cardiff, to the east by the city of Newport; to the north by the South Wales Valleys, and to the south by the Severn Estuary
The Severn Estuary ( cy, Aber Hafren) is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its high tidal range, approximately , means that it has been at the centre of discussions in t ...
and Bristol Channel. The River Taff winds through the city centre and together with the River Ely
The River Ely ( cy, Afon Elái) is in South Wales flowing generally southeast, from Tonyrefail to Cardiff.
The river is about long. The Ely's numerous sources lie in the mountains to the south of Tonypandy, near the town of Tonyrefail, ri ...
flows into the freshwater Cardiff Bay. A third river, the Rhymney, flows through the east of the city directly into the Severn Estuary.
Cardiff lies near the Glamorgan Heritage Coast, stretching westward from Penarth and Barry – commuter town
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many ...
s of Cardiff – with striped yellow-blue Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
limestone cliffs. The Glamorgan coast is the only part of the Celtic Sea
The Celtic Sea ; cy, Y Môr Celtaidd ; kw, An Mor Keltek ; br, Ar Mor Keltiek ; french: La mer Celtique is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits includ ...
with exposed Jurassic (blue lias
The Blue Lias is a geological formation in southern, eastern and western England and parts of South Wales, part of the Lias Group. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone and shale layers, laid down in latest Triassic and early Jurassi ...
) geology. This stretch of coast with its reefs, sandbanks and serrated cliffs was a ship graveyard
A ship graveyard or ship cemetery is a location where the hulls of scrapped ships are left to decay and disintegrate, or left in reserve. Such a practice is now less common due to waste regulations and so some dry docks where ships are brok ...
; many ships sailing to Cardiff during the industrial era were wrecked on this hostile coastline during west/south-westerly gales. Smuggling, deliberate shipwrecking and attacks on ships were also common.
Cityscape


 "Inner Cardiff" consists of the wards of
"Inner Cardiff" consists of the wards of Plasnewydd
Plasnewydd (meaning ''New Manor'' or ''New Place'' in English) is an electoral ward (and formerly the name of a community) of Cardiff, Wales. It falls within the parliamentary constituency of Cardiff Central. It is bounded by the electoral wa ...
, Gabalfa
Gabalfa (, ) is a district and community in the north of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It is characterised by a four-lane fly over road at the Gabalfa Interchange, where the A48 road meets the A470 road (North Road) which leads from C ...
, Roath
Roath ( cy, Y Rhath) is a district and community to the north-east of the city centre of Cardiff, capital of Wales.
There is no community council for the area which is mostly covered by the Plasnewydd electoral ward, and stretches from Adamsdo ...
, Cathays
Cathays ( ; Welsh: officially ''Cathays'' but also , 'the constant meadow') is a district and community in the centre of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It is an old suburb of Cardiff established in 1875. It is very densely populated and contain ...
, Adamsdown
Adamsdown ( cy, Waunadda or ) is an inner city area and community in the south of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales. Adamsdown is generally located between Newport Road, to the north and the mainline railway to the south. The area includes ...
and Splott
Splott ( cy, Y Sblot) is a district and community in the south of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales, just east of the city centre. It was built up in the late 19th century on the land of two farms of the same name: Upper Splott and Lower Spl ...
ward on the north and east of the city centre, and Butetown
Butetown (or ''The Docks'', cy, Tre-biwt) is a district and community in the south of the city of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. It was originally a model housing estate built in the early 19th century by the 2nd Marquess of Bute, for whose t ...
, Grangetown, Riverside and Canton to the south and west. The inner-city areas to the south of the A4161 road
The A4161 is a main road in Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom. The main purpose of the road is to link the city centre with the M4 motorway in the west at junction 33, and in the east with the A48(M) motorway at St Mellons.
History
The 1923 ro ...
, known as the "Southern Arc", are with the exception of Cardiff Bay some of the poorest districts of Wales, with low levels of economic activity. On the other hand, Gabalfa, Plasnewydd and Cathays north of the 'arc' have large student populations, and Pontcanna (north of Riverside and alongside Canton) is a favourite for students and young professionals. Penylan
Penylan is a district and community in the east of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, known for its Edwardian era period houses and spacious tree lined roads and avenues.
Situated to both the north and south of the A48 dual carriageway, it ...
, to the north east of Roath Park, is an affluent area popular with older parents and the retired.
To the west lie Ely and Caerau, which have some of the largest housing estates in the United Kingdom. With the exception of some outlying privately built estates at Michaelston-super-Ely
Michaelston-super-Ely is a village, to the west of the city of Cardiff, Wales.
Its Welsh name is Llanfihangel-ar-Elai (where ''llan'' church + ''Mihangel'' Saint Michael + ''Elai'' River Ely).
It is approximately half a mile from the boundar ...
, this is an economically disadvantaged area with high numbers of unemployed households. Culverhouse Cross
Culverhouse Cross ( cy, Croes Cwrlwys) is a district straddling the boundary between Cardiff and the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales, in the community of Wenvoe.
The district is centred on a major traffic roundabout that links West Cardiff to the M4 mo ...
is a more affluent western area of the city. Fairwater, Heath
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler a ...
, Birchgrove, Gabalfa
Gabalfa (, ) is a district and community in the north of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It is characterised by a four-lane fly over road at the Gabalfa Interchange, where the A48 road meets the A470 road (North Road) which leads from C ...
, Mynachdy, Llandaff North
Llandaff North ( cy, Ystum Taf), is a district, community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales.
Description
It is located in the north of Cardiff and can be considered a two-part ward, each containin ...
, Llandaff
Llandaff (; cy, Llandaf ; from 'church' and ''River Taff, Taf'') is a district, Community (Wales), community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It was incorporated into the city in 1922. It is the seat of ...
, Llanishen
Llanishen (Welsh language, Welsh Llanisien ''llan'' church + ''Isien'' Saint Isan) is a district and Community (Wales), community in the north of Cardiff, Wales. Its population as of the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census was 17,417. Lla ...
, Radyr, Whitchurch & Tongwynlais
is a village and Community (Wales), community in the north of Cardiff, Wales, north of the M4 motorway in the River Taff, Taff Valley. It is notable as the location of the hillside landmark, . The population as of the 2011 census was 1871.
Top ...
, Rhiwbina
Rhiwbina ( cy, Rhiwbeina, also ''Rhiwbina'') is a suburb and community in the north of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. Formerly a small hamlet within the parish of Whitchurch, Rhiwbina was developed throughout the twentieth century, and is now a ...
, Thornhill, Lisvane
Lisvane ( cy, Llys-faen) is an affluent community in the north of Cardiff, the capital of Wales, located north of the city centre. Lisvane is generally considered to be one of the wealthiest residential areas of Wales, with an average house ...
and Cyncoed
Cyncoed ( ); is an affluent and exclusive community in the northeast of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. With many properties in the area fetching over £1 million, Cyncoed is considered to have some of the highest property prices in the country. Cy ...
lie in an arc from the north-west to the north-east of the centre. Lisvane, Cyncoed, Radyr and Rhiwbina contain some of the most expensive housing in Wales.
Further east lie the wards of Pontprennau and Old St Mellons, Rumney, Pentwyn, Llanrumney
Llanrumney ( cy, Llanrhymni) is a suburb, community and electoral ward in east Cardiff, Wales.
Llanrumney was in Monmouthshire until it was incorporated into Cardiff in 1938.
History
The land where modern Llanrumney stands was left to Keynsham ...
, Llanedeyrn
Llanedeyrn ( cy, Llanedern) is a former village, now a district and community, in the east of the city of Cardiff, Wales, located around 3.5 miles from the city centre. The parish of Llanedeyrn rests on the banks of the river Rhymney and is visi ...
and Trowbridge
Trowbridge ( ) is the county town of Wiltshire, England, on the River Biss in the west of the county. It is near the border with Somerset and lies southeast of Bath, 31 miles (49 km) southwest of Swindon and 20 miles (32 km) southeas ...
. The last four are largely public housing stock, although much new private housing is being built in Trowbridge. Pontprennau
Pontprennau is a ward and community in the north of the city of Cardiff, Wales, lying north of Pentwyn and Cyncoed, between the village of Old St Mellons and the farmlands east of Lisvane. The community had a population of 7,353 in 2011.
Histo ...
is the newest "suburb" of Cardiff, while Old St Mellons
Old St Mellons ( cy, Pentre Llaneirwg) is a village, a community and a civil parish on the eastern edge of Cardiff, Wales. Lying to the east of the Rhymney River, it forms part of the historic county of Monmouthshire. It is separated from the m ...
has a history going back to the 11th-century Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
. The region that may be called "Rural Cardiff" contains the villages of St Fagans, Creigiau, Pentyrch
Pentyrch ( cy, Pen-tyrch) is a village and community located on the western outskirts of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales. The village gives its name to a Cardiff local authority electoral ward, Pentyrch, which covers the village and immediat ...
, Tongwynlais
is a village and Community (Wales), community in the north of Cardiff, Wales, north of the M4 motorway in the River Taff, Taff Valley. It is notable as the location of the hillside landmark, . The population as of the 2011 census was 1871.
Top ...
and Gwaelod-y-garth
Gwaelod-y-garth ( Welsh for ''Foot of the Garth'') is a village in the community of Pentyrch, Cardiff in Wales.
Location
Gwaelod-y-garth is located in Taff Valley at the foot of Garth Hill, north of central Cardiff and south of Pontypridd ...
. In 2017, plans were approved for a new suburb of 7,000 homes between Radyr and St Fagans, known as Plasdŵr. St Fagans, home to the Museum of Welsh Life
St Fagans National Museum of History ( ; cy, Sain Ffagan: Amgueddfa Werin Cymru, links=no), commonly referred to as St Fagans after the village where it is located, is an open-air museum in Cardiff chronicling the historical lifestyle, cultur ...
, is protected from further development.
Since 2000, there has been a marked change of scale and building height in Cardiff, with the development of the city centre's first purpose-built high-rise apartments. Tall buildings
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ri ...
have been built in the city centre and Cardiff Bay, and more are planned.
Climate
Cardiff, in thenorth temperate zone
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
, has a maritime climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: Cfb) marked by mild weather that is often cloudy, wet and windy. Summers tend to be warm and sunny, with average maxima between . Winters are fairly wet, but excessive rainfall as well as frost are rare. Spring and autumn feel similar and the temperatures tend to stay above – also the average annual daytime temperature. Rain is unpredictable at any time of year, although showers tend to be shorter in summer.
The northern part of the county, being higher and inland, tends to be cooler and wetter than the city centre.
Cardiff's maximum and minimum monthly temperatures average (July) and (February).For Wales, the temperatures average (July) and (February). Cardiff has 1,518 hours of sunshine in an average year (Wales 1,388.7 hours). Cardiff is sunniest in July, with an average 203.4 hours during the month (Wales 183.3 hours), and least sunny in December with 44.6 hours (Wales 38.5 hours). Cardiff experiences less rainfall than average for Wales. It falls on 146 days in an average year, with total annual rainfall of . Monthly rainfall patterns show that from October to January, average monthly rainfall in Cardiff exceeds each month, the wettest month being December with and the driest from April to June, with average monthly rainfall fairly consistent between .
Demography
After a period of decline in the 1970s and 1980s, Cardiff's population is growing again. It reached 362,400 in the 2021 census, compared to a 2011 census figure of 346,100. Between mid-2007 and mid-2008, Cardiff was the fastest-growing local authority in Wales, with growth of 1.2%. According to 2001 census data, Cardiff was the 21st largesturban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
. The Cardiff Larger Urban Zone
The larger urban zone (LUZ), or functional urban area (FUA), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zone outside it.
The ...
(a Eurostat definition including the Vale of Glamorgan and a number of local authorities in the Valleys) has 841,600 people, the 10th largest LUZ in the UK. The Cardiff and South Wales Valleys metropolitan area has a population of nearly 1.1 million.
 Official census estimates of the city's total population have been disputed. The city council published two articles arguing that the 2001 census seriously under-reported the population of Cardiff, and in particular the ethnic minority population of some inner city areas.
The Welsh Government's official mid-year estimate of the population of the Cardiff local authority area in 2019 was 366,903. At the 2011, census the official population of the Cardiff Built Up Area (BUA) was put at 447,287. The BUA is not contiguous with the local authority boundary and aggregates data at a lower level; for Cardiff this includes the urban part of Cardiff, Penarth/Dinas Powys, Caerphilly and Pontypridd.
Cardiff has an ethnically diverse population due to past trading connections, post-war
Official census estimates of the city's total population have been disputed. The city council published two articles arguing that the 2001 census seriously under-reported the population of Cardiff, and in particular the ethnic minority population of some inner city areas.
The Welsh Government's official mid-year estimate of the population of the Cardiff local authority area in 2019 was 366,903. At the 2011, census the official population of the Cardiff Built Up Area (BUA) was put at 447,287. The BUA is not contiguous with the local authority boundary and aggregates data at a lower level; for Cardiff this includes the urban part of Cardiff, Penarth/Dinas Powys, Caerphilly and Pontypridd.
Cardiff has an ethnically diverse population due to past trading connections, post-war immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
and large numbers of foreign students who attend university in the city. The ethnic make-up of Cardiff's population at the 2011 census was: 84.7% White, 1.6% mixed White and Black African/Caribbean, 0.7% mixed White and Asian, 0.6% mixed other, 8.1% Asian, 2.4% Black, 1.4% Arab and 0.6% other ethnic groups. This means almost 53,000 people from a non-white ethnic group reside in the city. This diversity, especially that of the city's long-established African and Arab communities, has been celebrated in cultural exhibitions and events, along with a number of books published on this subject.
Health
 There are seven NHS hospitals in the city, the largest being the
There are seven NHS hospitals in the city, the largest being the University Hospital of Wales
University Hospital of Wales ( cy, Ysbyty Athrofaol Cymru) (UHW), also known as the Heath Hospital, is a major 1,000-bed hospital in the Heath district of Cardiff, Wales. UHW is a teaching hospital of Cardiff University School of Medicine. Constr ...
, which is the third largest hospital in the UK and deals with most accidents and emergencies. The University Dental Hospital, which provides emergency treatment, is also located on this site. Llandough Hospital
University Hospital Llandough ( cy, Ysbyty Llandochau Prifysgol) is a district general hospital in Llandough, Penarth, Wales. It is managed by the Cardiff and Vale University Health Board.
History
In the first decade the 20th century the Cardif ...
is located in the south of the city.
St. David's Hospital, the city's newest hospital, built behind the former building, is located in Canton and provides services for the elderly and children. Cardiff Royal Infirmary
Cardiff Royal Infirmary ( cy, Ysbyty Brenhinol Caerdydd) (also known as the CRI or YBC) is a hospital in central Cardiff, Wales. It is managed by the Cardiff and Vale University Health Board.
History
The hospital has its origins in the Cardiff ...
is on Newport Road, near the city centre. The majority of this hospital was closed in 1999, but the west wing remained open for clinic services, genitourinary medicine and rehabilitation treatment. Rookwood Hospital
Rookwood Hospital ( cy, Ysbyty Rookwood) is a rehabilitation hospital situated in Llandaff, in the city of Cardiff in South Wales. It is managed by Cardiff and Vale University Health Board.
History
Rookwood was built for Colonel Sir Edward Hill ...
and the Velindre Cancer Centre
The Velindre Cancer Centre ( cy, Canolfan Ganser Felindre) is a specialist facility caring for cancer patients in Whitchurch, Cardiff, Wales. It is managed by the Velindre University NHS Trust.
History
The facility was established as Velindre H ...
are also located within Cardiff. They are administered by the Cardiff and Vale University Health Board, with the exception of Velindre, which is run by a separate trust. Spire Healthcare
Spire Healthcare Group plc is the second-largest provider of private healthcare in the United Kingdom. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
History
Spire Healthcare was formed from the sale of Bu ...
, a private hospital, is in Pontprennau.
Language
 Cardiff has a chequered linguistic history with
Cardiff has a chequered linguistic history with Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
, English, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Norse and Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
French preponderant at different times. Welsh was the majority language in Cardiff from the 13th century until the city's explosive growth in the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
. As late as 1850, five of the 12 Anglican churches within the current city boundaries conducted their services exclusively in Welsh, while only two worshipped exclusively in English. By 1891, the percentage of Welsh speakers had fallen to 27.9% and only Lisvane
Lisvane ( cy, Llys-faen) is an affluent community in the north of Cardiff, the capital of Wales, located north of the city centre. Lisvane is generally considered to be one of the wealthiest residential areas of Wales, with an average house ...
, Llanedeyrn
Llanedeyrn ( cy, Llanedern) is a former village, now a district and community, in the east of the city of Cardiff, Wales, located around 3.5 miles from the city centre. The parish of Llanedeyrn rests on the banks of the river Rhymney and is visi ...
and Creigiau
Creigiau is a dormitory settlement in the north-west of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. The village currently has about 1,500 houses and a population of approximately 5,000 people. The Cardiff electoral ward is called Creigiau/St. Fagans. The ...
remained as majority Welsh-speaking communities. The Welsh language became grouped around a small cluster of chapels and churches, the most notable of which is Tabernacl in the city centre, one of four UK churches chosen to hold official services to commemorate the new millennium.
The city's first Welsh-language school (Ysgol Gymraeg Bryntaf) was established in the 1950s. Welsh has since regained ground. Aided by Welsh-medium education
Education delivered through the medium of the Welsh language is known as Welsh-medium education ().
Welsh-medium education should be distinguished from the teaching of the Welsh language itself as an academic subject.
16% of pupils in Wales atte ...
and migration from other parts of Wales, there are now many more Welsh speakers: their numbers doubled between the 1991 and 2011 censuses, from 18,071 (6.6%) to 36,735 (11.1%) residents aged three years and above. The LSOA
ONS codes are geocodes maintained by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics to represent a wide range of geographical areas of the UK, for use in tabulating census and other statistical data. These codes are also known as GSS codes, wh ...
(Lower Layer Super Output Area) with the highest percentage of Welsh speakers in the city centre is found in Canton, at 25.5%. The LSOA with the highest percentage of Welsh speakers in the whole of Cardiff is Whitchurch, at 26%.
Cardiff City Council adopted a five-year Welsh-language strategy in 2017, aimed at increasing the number of Welsh speakers (aged 3+) in Cardiff by 15.9%, from 36,735 in 2011 to 42,584 residents by the 2021 Census. The ONS estimated that in December 2020, 89,900 (24.8%) of Cardiff's population could speak Welsh.
In addition to English and Welsh, the diversity of Cardiff's population (including foreign students) means that many other languages are spoken. One study has found that Cardiff has speakers of at least 94 languages, with Somali, Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Bengali Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to: *something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia * Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region * Bengali language, the language they speak ** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and '' Bengali Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to: *something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia * Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region * Bengali language, the language they speak ** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
being the most commonly spoken foreign ones.
The modern Cardiff accent is distinct from that of nearby South Wales Valleys. It is marked primarily by:
*Substitution of by
*''here'' iːəpronounced as in the broader form
*The vowel of ''start'' may be realised as or even , so that ''Cardiff'' is pronounced .
Language schools
Due to its diversity and large student population, more people now come to the city to learn English. Foreign students from Arab states and other European countries are a common sight on the streets of Cardiff. TheBritish Council
The British Council is a British organisation specialising in international cultural and educational opportunities. It works in over 100 countries: promoting a wider knowledge of the United Kingdom and the English language (and the Welsh lan ...
has an office in the city centre and there are six accredited schools in the area.
Religion
Since 1922, Cardiff has includedLlandaff
Llandaff (; cy, Llandaf ; from 'church' and ''River Taff, Taf'') is a district, Community (Wales), community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It was incorporated into the city in 1922. It is the seat of ...
within its boundary, along with the Anglican Llandaff Cathedral
Llandaff Cathedral ( cy, Eglwys Gadeiriol Llandaf) is an Anglican cathedral and parish church in Llandaff, Cardiff, Wales. It is the seat of the Bishop of Llandaff, head of the Church in Wales Diocese of Llandaff. It is dedicated to Saint Pet ...
, the parish church of Llandaff and the seat of the Bishop of Llandaff
The Bishop of Llandaff is the ordinary of the Church in Wales Diocese of Llandaff.
Area of authority
The diocese covers most of the County of Glamorgan. The bishop's seat is in the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul (the site of ...
, head of the Church in Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The p ...
and the Diocese of Llandaff
The Diocese of Llandaff is an Anglican (Church in Wales) diocese that traces its roots to pre-Reformation times as heir of a Catholic bishopric. It is headed by the Bishop of Llandaff, whose seat is located at the Cathedral Church of Saint Pet ...
.
There is a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
in the city. Since 1916, Cardiff has been the seat of a Catholic archbishop, but there appears to have been a fall in the estimated Catholic population, with numbers in 2006 around 25,000 fewer than in 1980. Likewise, the Jewish population appears to have fallen – there are two synagogues in Cardiff, one in Cyncoed and one in Moira Terrace, as opposed to seven at the turn of the 20th century. There are several nonconformist
Nonconformity or nonconformism may refer to:
Culture and society
* Insubordination, the act of willfully disobeying an order of one's superior
*Dissent, a sentiment or philosophy of non-agreement or opposition to a prevailing idea or entity
** ...
chapels, an early 20th century Greek Orthodox church and 11 mosques. In the 2001 census, 66.9% of Cardiff's population described itself as Christian, a percentage point below the Welsh and UK averages.
The oldest of the non-Christian communities in Wales is Judaism. Jews were not permitted to live in England and Wales between the 1290 Edict of Expulsion
The Edict of Expulsion was a royal decree issued by King Edward I of England on 18 July 1290 expelling all Jews from the Kingdom of England. Edward advised the sheriffs of all counties he wanted all Jews expelled by no later than All Saints' D ...
and the 17th century. A Welsh Jewish community was re-established in the 18th century. There was once a fairly substantial Jewish population in South Wales, most of which has disappeared. The Orthodox Jewish
Orthodox Judaism is the collective term for the traditionalist and theologically conservative branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Written and Oral, as revealed by God to Moses on M ...
community congregations are consolidated in the Cardiff United Synagogue in Cyncoed, which was dedicated by Chief Rabbi Jonathan Sacks
Jonathan Henry Sacks, Baron Sacks ( he, יונתן הנרי זקס, translit=Yona'tan Henry Zaks; 8 March 19487 November 2020) was an English Orthodox rabbi, philosopher, theologian, and author. Sacks served as the Chief Rabbi of the United ...
in 2003. The Cardiff Reform Synagogue is in Adamsdown.
Cardiff's Muslim population is much above the Welsh average and the longest established in the UK, being started by Yemeni and Somali sailors settling in the 19th century. Cardiff now has over 11,000 Muslims with various national affiliations – nearly 52 per cent of the Muslim population in Wales.
The proportion of Cardiff residents declaring themselves Hindu, Sikh and Jewish were all considerably higher than the Welsh averages, but lower than the UK figures. The city has had a Hindu community since Indian immigrants settled in the 1950s and 1960s. The first Hindu temple in the city was opened in Grangetown on 6 April 1979 on the site of an abandoned synagogue. The 25th anniversary of the founding was celebrated in September 2007 with a parade of over 3,000 people through the city centre, including Hindus from across the United Kingdom and members of Cardiff's other religious communities. There are over 2,000 Hindus in Cardiff, worshiping at three temples.
In the 2001 census 18.8% of the city's population stated they had no religion, while 8.6% did not state a religion.
Economy
 As the capital city of Wales, Cardiff is the main engine of growth in the Welsh economy. Though the population of Cardiff is about 10% of the Welsh population, the economy of Cardiff makes up nearly 20% of Welsh GDP and 40% of the city's workforce are daily in-commuters from the surrounding South Wales area.
Industry has played a major part in Cardiff's development for many centuries. The main catalyst for its transformation from a small town into a big city was the demand for coal required in making iron and later steel, brought to sea by packhorse from Merthyr Tydfil. This was first achieved by building a canal from Merthyr ( above sea level) to the Taff Estuary at Cardiff. Eventually the
As the capital city of Wales, Cardiff is the main engine of growth in the Welsh economy. Though the population of Cardiff is about 10% of the Welsh population, the economy of Cardiff makes up nearly 20% of Welsh GDP and 40% of the city's workforce are daily in-commuters from the surrounding South Wales area.
Industry has played a major part in Cardiff's development for many centuries. The main catalyst for its transformation from a small town into a big city was the demand for coal required in making iron and later steel, brought to sea by packhorse from Merthyr Tydfil. This was first achieved by building a canal from Merthyr ( above sea level) to the Taff Estuary at Cardiff. Eventually the Taff Vale Railway
The Taff Vale Railway (TVR) was a standard gauge railway in South Wales, built by the Taff Vale Railway Company to serve the iron and coal industries around Merthyr Tydfil and to connect them with docks in Cardiff. It was opened in st ...
replaced the canal barges and massive marshalling yards sprang up as new docks were developed in Cardiff – all prompted by the soaring worldwide demand for coal from the South Wales valleys.
At its peak, Cardiff's port area, known as Tiger Bay
Tiger Bay ( cy, Bae Teigr) was the local name for an area of Cardiff which covered Butetown and Cardiff Docks. Following the building of the Cardiff Barrage, which dams the tidal rivers, Ely and Taff, to create a body of water, it is re ...
, became the busiest port in the world and – for some time – the world's most important coal port. In the years leading up to the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, more than 10 million tonnes of coal was exported annually from Cardiff Docks
Cardiff Docks ( cy, Dociau Caerdydd) is a port in southern Cardiff, Wales. At its peak, the port was one of the largest dock systems in the world with a total quayage of almost . Once the main port for the export of South Wales coal, the Port ...
. In 1907, Cardiff's Coal Exchange
The Coal Exchange (also known as the Exchange Building) is an historic building in Cardiff, Wales. It is designed in Renaissance Revival style. Built in 1888 as the Coal and Shipping Exchange to be used as a market floor and office building for ...
was the first host to a business deal for a million pounds Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and ...
. The high demand for Welsh coal and specifically Welsh artificial fuel, named Patent Fuel, is shown by the numberous factories producing this fuel, with the same recipe, in the region of Cardiff. Most well known factories were the Star Patent fuel Co., the Crown Patent fuel, the Cardiff Patent fuel etc. After a period of decline, due to low demand on coal, Cardiff's port has started to grow again – over 3 million tonnes of cargo passed through the docks in 2007.
 Cardiff today is the main finance and business
Cardiff today is the main finance and business services
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a p ...
centre in Wales, with strong representation of finance and business services in the local economy. This sector, combined with the public administration, education and health sectors, have accounted for about 75% of Cardiff's economic growth since 1991. The city was recently placed seventh overall in the top 50 European cities in the fDI 2008 Cities of the Future list published by the fDi magazine
''fDi Intelligence'' is an English-language bi-monthly news and foreign direct investment (FDI) publication, providing an up-to-date review of global investment activity. The A4 glossy pages reach a circulation of 15,488 ABC audited, active corpo ...
, and ranked seventh in terms of attracting foreign investment. Notable companies such as Legal & General
Legal & General Group plc, commonly known as Legal & General, is a British multinational financial services and asset management company headquartered in London, England. Its products and services include investment management, lifetime mortg ...
, Admiral Insurance, HBOS
HBOS plc was a banking and insurance company in the United Kingdom, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Lloyds Banking Group, having been taken over in January 2009. It was the holding company for Bank of Scotland plc, which operated the Ba ...
, Zurich, ING Direct
The ING Group ( nl, ING Groep) is a Dutch multinational banking and financial services corporation headquartered in Amsterdam. Its primary businesses are retail banking, direct banking, commercial banking, investment banking, wholesale bankin ...
, The AA
AA Limited, trading as The AA (formerly The Automobile Association), is a British motoring association.
Founded in 1905, it provides vehicle insurance, driving lessons, breakdown cover, loans, motoring advice, road maps and other services. Th ...
, Principality Building Society
The Principality Building Society ( cy, Cymdeithas Adeiladu'r Principality) is a building society based in Cardiff, Wales. With assets of £10bn it is the largest building society in Wales and the sixth largest in the United Kingdom. Principali ...
, 118118, British Gas
British Gas (trading as Scottish Gas in Scotland) is an energy and home services provider in the United Kingdom. It is the trading name of British Gas Services Limited and British Gas New Heating Limited, both subsidiaries of Centrica. Servi ...
, Brains
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, SWALEC Energy and BT, all operate large national or regional headquarters and contact centres in the city, some of them based in Cardiff's office towers such as Capital Tower, Cardiff, Capital Tower and Brunel House. Other major employers include NHS Wales and the Senedd. On 1 March 2004, Cardiff was granted Fairtrade City status.
Cardiff is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the United Kingdom, receiving 18.3 million visitors in 2010 and generating £852 million for the city's economy. One result is that one in five employees in Cardiff is based in the distribution, hotels and restaurants sector, highlighting the growing retail and tourism industries in the city. The city has many hotels of varying sizes and standards, providing almost 9,000 available beds.
Cardiff is home to the Welsh media and a large media sector with BBC Cymru Wales, S4C and ITV Wales & West, ITV Wales all having studios in the city. There is a large independent TV production industry sector of over 600 companies, employing around 6,000, with a turnover estimated at £350 million. Just to the north-west of the city, in Rhondda Cynon Taff, the first completely new film studios in the UK for 30 years are being built, to be named Valleywood. The studios are set to be the biggest in the UK. In 2011 the BBC completed the Roath Lock studios in Cardiff Bay to film dramas such as ''Casualty'', ''Doctor Who'', and ''Pobol y Cwm''.
Cardiff has several regeneration projects, such as St David's 2 Centre and surrounding areas of the city centre, and the £1.4 billion International Sports Village in Cardiff Bay, which played a part in the 2012 Summer Olympics, London 2012 Olympics. It features the only Olympic-size swimming pool, Olympic-standard swimming pool in Wales, the Cardiff International Pool, which opened on 12 January 2008.
According to the Welsh Rugby Union, the Principality Stadium contributed £1 billion to the Welsh economy in the ten years after it opened in 1999, with around 85% of that staying in the Cardiff area.
Shopping
 Most of Cardiff's shopping portfolio is in the city centre around Queen Street, St. Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street and High Street, with large suburban retail parks in Cardiff Bay,
Most of Cardiff's shopping portfolio is in the city centre around Queen Street, St. Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street and High Street, with large suburban retail parks in Cardiff Bay, Culverhouse Cross
Culverhouse Cross ( cy, Croes Cwrlwys) is a district straddling the boundary between Cardiff and the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales, in the community of Wenvoe.
The district is centred on a major traffic roundabout that links West Cardiff to the M4 mo ...
, Leckwith, Penylan, Newport Road and Pontprennau
Pontprennau is a ward and community in the north of the city of Cardiff, Wales, lying north of Pentwyn and Cyncoed, between the village of Old St Mellons and the farmlands east of Lisvane. The community had a population of 7,353 in 2011.
Histo ...
, together with markets in the city centre and Splott
Splott ( cy, Y Sblot) is a district and community in the south of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales, just east of the city centre. It was built up in the late 19th century on the land of two farms of the same name: Upper Splott and Lower Spl ...
. A £675 million regeneration programme for Cardiff's St. David's Centre was completed in 2009, providing a total of of shopping space, making it one of the largest shopping centres in the United Kingdom. The centre was named the international shopping centre of the year in 2010 by Retail Leisure International (RLI).
 The Castle Quarter (Cardiff), Castle Quarter is a commercial area in the north of the city centre, which includes some of Cardiff's Victorian and Edwardian arcades: Castle Arcade, Morgan Arcade and Royal Arcade, Cardiff, Royal Arcade, and principal shopping streets: St Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street, High Street, The Hayes, and Queen Street.
The Castle Quarter (Cardiff), Castle Quarter is a commercial area in the north of the city centre, which includes some of Cardiff's Victorian and Edwardian arcades: Castle Arcade, Morgan Arcade and Royal Arcade, Cardiff, Royal Arcade, and principal shopping streets: St Mary Street/High Street, St Mary Street, High Street, The Hayes, and Queen Street.
Transport
Rail
Cardiff Central railway station is the largest railway station in Wales, with nine platforms coping with over 12.5 million passengers a year. It provides direct services to Bridgend railway station, Bridgend and Newport railway station, Newport, long-distance, cross-Wales services to Wrexham General railway station, Wrexham and Holyhead railway station, Holyhead, and services to Bristol Temple Meads railway station, Bristol, Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester and Paddington railway station, London. Cardiff Central Station is situated within the southern border of what was known Temperance Town, Cardiff, Temperance Town, a former residential area within central Cardiff. Cardiff Queen Street railway station is the second busiest in Wales and the hub for the Valley Lines services that connect the South Wales Valleys and the Cardiff suburbs with the city centre. It is located at the eastern end of the city centre and provides services to Cardiff Bay. Cardiff has a Commuter rail in the United Kingdom, suburban rail system known as the Valleys & Cardiff Local Routes, operated by Transport for Wales Rail, Transport for Wales. There are eight lines that serve 20 stations in the city, 26 in the wider urban area (including Taffs Well, Penarth and Dinas Powys) and more than 60 in the South Wales valleys and the Vale of Glamorgan.Metro
The South Wales Metro is an integrated public transport system under development in south-east Wales, centred on Cardiff. The project is to include the electrification of some of the existing railway lines. Four lines are under construction with a further three planned. The first lines will link and to , , and , with plans to also serve , St Mellons and Porth Teigr. Alongside this, current commuter services will be improved with a near-tripling in capacity on some routes to and .Air
Domestic and international air links to Cardiff and South & West Wales are provided from Cardiff Airport, Cardiff Airport (CWL), the only international airport in Wales. The airport lies in the village of Rhoose, west of the city. There are regular bus services linking the airport with Cardiff Central bus station, and a train service from Rhoose Cardiff International Airport railway station to Cardiff Central.Road and bus
The M4 motorway connects Cardiff with Swansea to the west and Newport and London to the east, with four junctions on the M4, including one with the A48(M) motorway, A48(M). The A470 road, A470 provides an important link from the city to the A465 road, Heads of the Valleys road. When completed, the A4232 road, A4232 – also known as the Peripheral Distributor Road – will form part of the Cardiff ring-road system, along with the M4 motorway between junctions 30 and 33. Cardiff has a comprehensive bus network, whose providers include the municipal bus companies, municipal bus company Cardiff Bus (routes within the city and to Newport, Barry and Penarth), NAT Group (cross-city and to Cardiff Airport), Stagecoach South Wales (to the South Wales Valleys) and First Cymru (to Cowbridge and Bridgend). National Express Coaches, National Express and Megabus (Europe), Megabus provides direct services to major cities such asBristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
, London, Newcastle upon Tyne and Manchester.
Cycle
The Taff Trail is a walkway, walking and cycle path running for between Cardiff Bay and Brecon in the Brecon Beacons National Park. It runs through Bute Park, Sophia Gardens and many other green areas within Cardiff. It is possible to cycle the entire distance of the Trail almost completely off-road, as it largely follows the River Taff and many of the disused railways of the Glamorganshire valleys. Nextbike have operated a public bike-hire scheme in the city since March 2018.Water
The Aquabus water taxi runs every hour between the city centre (Taff Mead Embankment) and Cardiff Bay (Mermaid Quay), and between Cardiff Bay and Penarth Cardiff Bay Barrage. Throughout the year, Cardiff Waterbus sail between the Pierhead on The Waterfront and the Penarth end of the Cardiff Bay Barrage with short sightseeing cruises. Between March and October boats depart from Cardiff Bay for Flat Holm Island. The ''PS Waverley'' and ''MV Balmoral (1949), MV Balmoral'' sail from Britannia Quay (in Roath Basin) to various destinations in the Bristol Channel.Telecommunications
029 is the current telephone dialling code for Cardiff, as well as for the neighbouring towns of Penarth, Dinas Powys and Caerphilly. The dialling code is optional when dialling within the area: one can dial between any two phones within the 09 code using only the eight-digit local number. Prior to the Big Number Change on 22 April 2000 the area had shorter, six-digit local numbers with an area code of 01222. This was 0222 before May 1995, derived from 0 (indicating it was a trunk call), 22 (CA on a telephone pad, for CArdiff) and 2 (as 220 was used for CAmbridge and 221 for BAth). Before the introduction of automated trunk call dialling, non-local numbers were accessed through a system of manual telephone exchanges, in common with rest if the United Kingdom. There remains a common misconception that local numbers are still six digits long and that the code is 02920, even though there are newer Cardiff numbers in the ranges (029) 21xx xxxx and (029) 22xx xxxx.Education
 Cardiff is home to four major institutions of higher education: Cardiff University, Cardiff Metropolitan University, University of South Wales and the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama.
Cardiff University was founded by a royal charter in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire, is a member of the Russell Group of leading research led universities, having most of its campus in
Cardiff is home to four major institutions of higher education: Cardiff University, Cardiff Metropolitan University, University of South Wales and the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama.
Cardiff University was founded by a royal charter in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire, is a member of the Russell Group of leading research led universities, having most of its campus in Cathays
Cathays ( ; Welsh: officially ''Cathays'' but also , 'the constant meadow') is a district and community in the centre of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It is an old suburb of Cardiff established in 1875. It is very densely populated and contain ...
and the city centre. Cardiff Metropolitan University (formerly UWIC) has campuses in the Llandaff, Cyncoed
Cyncoed ( ); is an affluent and exclusive community in the northeast of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. With many properties in the area fetching over £1 million, Cyncoed is considered to have some of the highest property prices in the country. Cy ...
and city centre areas, and is part of the confederal University of Wales
, latin_name =
, image =
, caption = Coat of Arms
, motto = cy, Goreu Awen Gwirionedd
, mottoeng = The Best Inspiration is Truth
, established =
,
, type = Confederal, non-member ...
. The Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama is a music school, conservatoire established in 1949 and is based in the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The University of South Wales's Cardiff campus, Atrium (Cardiff), Atrium, is home to the Cardiff School of Creative & Cultural Industries and is located in the city centre.
 The total number of higher education students in the city is around 43,900. The city also has two further education colleges: Cardiff and Vale College and St David's Catholic College, St David's College. The former is the result of a merger, completed in August 2011, between Coleg Glan Hafren and Barry College. Further education is also offered at most high schools in the city.
Cardiff has three state nursery schools (one bilingual), 98 state primary schools (two bilingual, fifteen Welsh medium education, Welsh medium), and 19 state secondary schools (three Welsh medium). There are also several independent schools in the city, including St John's College, Cardiff, St John's College, The Cathedral School, Llandaff, Llandaff Cathedral School, Cardiff Sixth Form College, Kings Monkton School and Howell's School Llandaff, Howell's School, a single-sex girls' school (until sixth form). In 2013 Cardiff Sixth Form College came top of the independent senior schools in the UK, which were based on the percentage of A* and A at GCE Advanced Level, Advanced Level. Also in the top 100 were St John's College and Howell's School.
Notable schools include Whitchurch High School (the largest secondary school in Wales), Fitzalan High School (one of the most multi-cultural state schools in the UK), and Ysgol Gyfun Gymraeg Glantaf (the largest Welsh medium secondary school in Wales).
As well as academic institutions, Cardiff is also home to other educational and learning organisations such as Techniquest, a hands-on science discovery centre that now has franchises throughout Wales, and is part of the Wales Gene Park in collaboration with Cardiff University, NHS Wales and the
The total number of higher education students in the city is around 43,900. The city also has two further education colleges: Cardiff and Vale College and St David's Catholic College, St David's College. The former is the result of a merger, completed in August 2011, between Coleg Glan Hafren and Barry College. Further education is also offered at most high schools in the city.
Cardiff has three state nursery schools (one bilingual), 98 state primary schools (two bilingual, fifteen Welsh medium education, Welsh medium), and 19 state secondary schools (three Welsh medium). There are also several independent schools in the city, including St John's College, Cardiff, St John's College, The Cathedral School, Llandaff, Llandaff Cathedral School, Cardiff Sixth Form College, Kings Monkton School and Howell's School Llandaff, Howell's School, a single-sex girls' school (until sixth form). In 2013 Cardiff Sixth Form College came top of the independent senior schools in the UK, which were based on the percentage of A* and A at GCE Advanced Level, Advanced Level. Also in the top 100 were St John's College and Howell's School.
Notable schools include Whitchurch High School (the largest secondary school in Wales), Fitzalan High School (one of the most multi-cultural state schools in the UK), and Ysgol Gyfun Gymraeg Glantaf (the largest Welsh medium secondary school in Wales).
As well as academic institutions, Cardiff is also home to other educational and learning organisations such as Techniquest, a hands-on science discovery centre that now has franchises throughout Wales, and is part of the Wales Gene Park in collaboration with Cardiff University, NHS Wales and the Welsh Development Agency
Welsh Development Agency (WDA; cy, Awdurdod Datblygu Cymru) was an executive agency (or QUANGO) and later designated an Assembly Sponsored Public Body (ASPB). Established in 1976, it was tasked with rescuing the ailing Welsh economy by encour ...
(WDA). Cardiff is also home of the largest regional office of the International Baccalaureate Organisation (IBO). This office is home to the organisation's curriculum and assessment centre, which is responsible for overseeing the creation and grading of various IBDP assessments.
Landmarks and attractions
 Cardiff has many landmark buildings such as the Principality Stadium, Pierhead Building the Welsh National Museum and the Senedd building, the home of the Welsh Parliament. Cardiff is also famous for Cardiff Castle, St David's Hall,
Cardiff has many landmark buildings such as the Principality Stadium, Pierhead Building the Welsh National Museum and the Senedd building, the home of the Welsh Parliament. Cardiff is also famous for Cardiff Castle, St David's Hall, Llandaff Cathedral
Llandaff Cathedral ( cy, Eglwys Gadeiriol Llandaf) is an Anglican cathedral and parish church in Llandaff, Cardiff, Wales. It is the seat of the Bishop of Llandaff, head of the Church in Wales Diocese of Llandaff. It is dedicated to Saint Pet ...
and the Wales Millennium Centre
Wales Millennium Centre ( cy, Canolfan Mileniwm Cymru) is an arts centre located in the Cardiff Bay area of Cardiff, Wales. The site covers a total area of . Phase 1 of the building was opened during the weekend of the 26–28 November 2004 an ...
.
Cardiff Castle is a major tourist attraction in the city and is situated in the heart of the city centre. The St Fagans National History Museum, National History Museum at St Fagans in Cardiff is a large open-air museum housing dozens of buildings from throughout Welsh history that have been moved to the site in Cardiff. The Civic Centre in Cathays Park
Cathays Park ( cy, Parc Cathays) or Cardiff Civic Centre is a civic centre area in the city centre of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, consisting of a number of early 20th century buildings and a central park area, Alexandra Gardens. It i ...
comprises a collection of Edwardian architecture, Edwardian buildings such as the City Hall, Cardiff, City Hall, National Museum Cardiff, National Museum and Gallery of Wales, Cardiff Crown Court, and buildings forming part of Cardiff University, together with more modern civic buildings. These buildings are laid out around the Queen Alexandra Gardens, a formal park which contains the Welsh National War Memorial
The Welsh National War Memorial ( cy, Cofeb ryfel Cenedlaethol Cymru) is situated in Alexandra Gardens, Cathays Park, Cardiff. The memorial was designed by Sir Ninian Comper and unveiled on 12 June 1928 by the Prince of Wales. The memorial comm ...
and a number of other, smaller memorials.
In addition to Cardiff Castle, Castell Coch is a castle in Tongwynlais
is a village and Community (Wales), community in the north of Cardiff, Wales, north of the M4 motorway in the River Taff, Taff Valley. It is notable as the location of the hillside landmark, . The population as of the 2011 census was 1871.
Top ...
, in the north of the city. The current castle is an elaborately decorated Victorian folly designed by William Burges
William Burges (; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoc ...
for the Marquess and built in the 1870s, as an occasional retreat. However, the Victorian castle stands on the footings of a much older medieval castle possibly built by Ifor Bach, a regional baron with links to Cardiff Castle also. The exterior has become a popular location for film and television productions. It rarely fulfilled its intended role as a retreat for the Butes, who seldom stayed there. For the Marquess, the pleasure had been in its creation, a pleasure lost following Burges's death in 1881.
Cardiff claims the largest concentration of castles of any city in the world. As well as Cardiff Castle and Castell Coch, there are the remains of two motte-and-bailey castles in Morganstown and Rhiwbina
Rhiwbina ( cy, Rhiwbeina, also ''Rhiwbina'') is a suburb and community in the north of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. Formerly a small hamlet within the parish of Whitchurch, Rhiwbina was developed throughout the twentieth century, and is now a ...
, known as Morganstown Castle Mound and Twmpath Castle or Twmpath Motte (also known as cy, Caer Cynwrig) respectively. Twmpath being a Welsh word for a small mound), which along with a castle at Whitchurch (known as Treoda and destroyed by housing in the 1960s) formed an arc of fortifications which divided the Norman lordship from the Welsh lordship of Senghenydd. Further up the Cefn Cibwr ridge on the boundary with Caerphilly there is also another ruined castle, known as Morgraig Castle ( cy, Castell Morgraig). Archaeological evidence suggests this castle was never finished, and it is debated whether the fortification was of Norman or Welsh origin. The concentration of castles indicates the moveable nature of the border between the Norman lordship of Glamorgan, centred at Cardiff, and its Welsh neighbours to the north.
There is also the ruined Bishop's Palace, Llandaff, Llandaff Bishop's Palace, also known as Llandaff Castle, which was the home of the medieval bishops, which was destroyed about 1403–1404 by the Welsh leader Owain Glyndŵr. Now only the ruined gatehouse remains. Not strictly a castle in the historical sense, St Fagans National History Museum, Saint Fagans Castle is a preserved 17th-century manor house, once the seat of the Earl of Plymouth, Earls of Plymouth.
Other major tourist attractions are the Cardiff Bay regeneration sites, which include the recently opened Wales Millennium Centre and the Senedd building, and many other cultural and sites of interest, including the Cardiff Bay Barrage and the famous Coal Exchange
The Coal Exchange (also known as the Exchange Building) is an historic building in Cardiff, Wales. It is designed in Renaissance Revival style. Built in 1888 as the Coal and Shipping Exchange to be used as a market floor and office building for ...
. The New Theatre (Cardiff), New Theatre was founded in 1906 and refurbished in the 1980s. Until the opening of the Wales Millennium Centre in 2004, it was the premier venue in Wales for touring theatre and dance companies. Other venues popular for concerts and sporting events include Motorpoint Arena Cardiff, Motorpoint Arena, St David's Hall and the Principality Stadium. Cardiff Story, a museum documenting the city's history, has been open to the public since the spring of 2011.
Cardiff has over 1,000 listed buildings, ranging from the more prominent buildings such as the castles, to smaller buildings, houses and structures. Cathedral Road was developed by the 3rd Marquis of Bute and is lined by fine villas, some backing on to Sophia Gardens.
Cardiff has walks of special interest for tourists and Walking, ramblers alike, such as the Cardiff Centenary Walk, Centenary Walk, which runs for within Cardiff city centre. This route passes through many of Cardiff's landmarks and historic buildings. The Animal Wall, designed by William Burges
William Burges (; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoc ...
in 1866, marks the south edge of Bute Park on Castle Street. It bears 15 carved animal statues.
Culture and recreation
 Cardiff has many cultural sites varying from the historical Cardiff Castle and out of town Castell Coch to the more modern
Cardiff has many cultural sites varying from the historical Cardiff Castle and out of town Castell Coch to the more modern Wales Millennium Centre
Wales Millennium Centre ( cy, Canolfan Mileniwm Cymru) is an arts centre located in the Cardiff Bay area of Cardiff, Wales. The site covers a total area of . Phase 1 of the building was opened during the weekend of the 26–28 November 2004 an ...
and Cardiff Bay. Cardiff was a finalist in the European Capital of Culture 2008. In recent years Cardiff has grown in stature as a tourist destination, with recent accolades including Cardiff being voted the eighth favourite UK city by readers of the ''Guardian''.
The city was also listed as one of the top 10 destinations in the UK on the official British tourist boards website Visit Britain, and US travel guide Frommers have listed Cardiff as one of 13 top destinations worldwide for 2008. Annual events in Cardiff that have become regular appearances in Cardiff's calendar include Sparks in the Park, The Great British Cheese Festival, Pride Cymru (formerly Cardiff Mardi Gras), Cardiff Winter Wonderland, Cardiff Festival and Made in Roath.
Music and performing arts
 A large number of concerts are held in the city, the larger ones at St David's Hall, the Motorpoint Arena Cardiff, Motorpoint Arena (previously known as the Cardiff International Arena) and occasionally the Principality Stadium. A number of festivals are also held in Cardiff, the largest being the Cardiff big weekend, Cardiff Big Weekend Festival, held annually in the city centre in the summer and playing host to free musical performances (from artists such as Ash (band), Ash, Jimmy Cliff, Cerys Matthews, the Fun Loving Criminals, Soul II Soul and the Magic Numbers), fairground rides and cultural events such as a Children's Festival that takes place in the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The annual festival claims to be the UK's largest free outdoor festival, attracting over 250,000 visitors in 2007.
Cardiff hosted the National Eisteddfod in 1883, 1899, 1938, 1960, 1978, 2008 and 2018. Cardiff is unique in Wales in having two permanent stone circles used by the Gorsedd of Bards during Eisteddfodau. The original circle stands in Gorsedd Gardens in front of the National Museum while its 1978 replacement is situated in Bute Park. Since 1983, Cardiff has hosted the BBC Cardiff Singer of the World competition, a world-renowned event on the opera calendar which is held every two years. The city also hosts smaller events.
The
A large number of concerts are held in the city, the larger ones at St David's Hall, the Motorpoint Arena Cardiff, Motorpoint Arena (previously known as the Cardiff International Arena) and occasionally the Principality Stadium. A number of festivals are also held in Cardiff, the largest being the Cardiff big weekend, Cardiff Big Weekend Festival, held annually in the city centre in the summer and playing host to free musical performances (from artists such as Ash (band), Ash, Jimmy Cliff, Cerys Matthews, the Fun Loving Criminals, Soul II Soul and the Magic Numbers), fairground rides and cultural events such as a Children's Festival that takes place in the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The annual festival claims to be the UK's largest free outdoor festival, attracting over 250,000 visitors in 2007.
Cardiff hosted the National Eisteddfod in 1883, 1899, 1938, 1960, 1978, 2008 and 2018. Cardiff is unique in Wales in having two permanent stone circles used by the Gorsedd of Bards during Eisteddfodau. The original circle stands in Gorsedd Gardens in front of the National Museum while its 1978 replacement is situated in Bute Park. Since 1983, Cardiff has hosted the BBC Cardiff Singer of the World competition, a world-renowned event on the opera calendar which is held every two years. The city also hosts smaller events.
The Wales Millennium Centre
Wales Millennium Centre ( cy, Canolfan Mileniwm Cymru) is an arts centre located in the Cardiff Bay area of Cardiff, Wales. The site covers a total area of . Phase 1 of the building was opened during the weekend of the 26–28 November 2004 an ...
hosts performances of opera, ballet, dance, comedy, musicals and is home to the BBC National Orchestra of Wales. St David's Hall (which hosts the Singer of the World competition) has regular performances of classical music and ballet as well as music of other genres. The largest of Cardiff's theatres is the New Theatre (Cardiff), New Theatre, situated in the city centre just off Queen Street. Other such venues include the Sherman Theatre, Chapter Arts Centre and the Gate Arts Centre.
The Cardiff music scene is established and wide-ranging: home to the BBC National Orchestra of Wales and the Welsh National Opera; has produced several leading acts; has acted as a springboard for Welsh bands to become famous. Acts hailing from Cardiff include Charlotte Church, Shirley Bassey, Iwan Rheon, the Oppressed, Kids In Glass Houses, Los Campesinos, the Hot Puppies, The School (UK), the School, We're No Heroes, Budgie (band), Budgie and Shakin' Stevens. Also, performers such as the Automatic, Manic Street Preachers, Lostprophets, Super Furry Animals, Catatonia (band), Catatonia and Bullet for My Valentine have links with the city and are associated with the Cardiff music scene. In 2010, Cardiff was named the UK's second "most musical" city by PRS for Music.
Visual arts
Cardiff has held a photomarathon in the city each year since 2004, in which photographers compete to take the best 12 pictures of 12 previously unknown topics in 12 hours. An exhibition of winners and other entries is held in June/July each year.Sporting venues
Sporting venues include the Millennium Stadium, Principality Stadium – the national stadium and home of the Wales national rugby union team – Sophia Gardens (cricket ground), Sophia Gardens for Glamorgan County Cricket Club), Cardiff City Stadium for Cardiff City F.C. and the Wales national football team, Wales football team), Cardiff International Sports Stadium, home of Cardiff Amateur Athletic Club), Cardiff Arms Park for Cardiff Blues and Cardiff RFC rugby union teams, and Ice Arena Wales for Cardiff Devils ice hockey team. It hosted the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games and was dubbed European City of Sport for its role in international sporting events in 2009 and again in 2014. The Principality Stadium hosted 11 football matches during the 2012 Summer Olympics, including the opening event and the men's bronze medal match.Recreation
 Cardiff has strong nightlife. Most clubs and bars are situated in the city centre, especially St Mary Street. More recently Cardiff Bay has built up a strong night scene, with many modern bars and restaurants. The Brewery Quarter on St Mary Street is a recently developed venue for bars and restaurant with a central courtyard. Charles Street is also a popular part of the city.
Cardiff has strong nightlife. Most clubs and bars are situated in the city centre, especially St Mary Street. More recently Cardiff Bay has built up a strong night scene, with many modern bars and restaurants. The Brewery Quarter on St Mary Street is a recently developed venue for bars and restaurant with a central courtyard. Charles Street is also a popular part of the city.
 Cardiff is known for its extensive parks and other green spaces covering around 10% of the city's total area. Cardiff's main park, Bute Park (which was formerly the castle grounds) extends northwards from the top of one of Cardiff's main shopping street (Queen Street); when combined with the adjacent Llandaff Fields and Pontcanna Fields to the north-west it produces a massive open space skirting the River Taff. Other popular parks include Roath Park in the north, donated to the city by the John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, 3rd Marquess of Bute in 1887, which includes a popular boating lake; Victoria Park, Cardiff's first official park; and Thompson's Park, formerly home to an aviary removed in the 1970s. Wild open spaces include Howardian Local Nature Reserve, of the lower Rhymney valley in Penylan noted for its orchids, and Forest Farm Country Park, over along the River Taff in Whitchurch.
Cardiff is one of the top ten retail destinations in the UK with Queen Street and St. Mary Street as the two main shopping streets with the three shopping arcades, St. David's Centre, Queens Arcade and the Capitol Centre, Cardiff, Capitol Centre. The current expansion of St. David's Centre as part of the St David's 2 project has made it one of the largest shopping centres in the UK. As well as the modern shopping arcades, the city is home to Victorian shopping centres, such as High Street Arcade, Castle Arcade, Wyndham Arcade, Royal Arcade and Morgan Arcade. Also of note is The Hayes, home to Spillers Records, the world's oldest record shop. Cardiff has a number of markets, including the vast Victorian indoor Cardiff Market, Cardiff Central Market and the newly established Riverside Community Market, which specialises in locally produced organic produce. Several out-of-town retail parks exist, such as Newport Road, Culverhouse Cross, Cardiff Gate and Cardiff Bay.
Cardiff is known for its extensive parks and other green spaces covering around 10% of the city's total area. Cardiff's main park, Bute Park (which was formerly the castle grounds) extends northwards from the top of one of Cardiff's main shopping street (Queen Street); when combined with the adjacent Llandaff Fields and Pontcanna Fields to the north-west it produces a massive open space skirting the River Taff. Other popular parks include Roath Park in the north, donated to the city by the John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, 3rd Marquess of Bute in 1887, which includes a popular boating lake; Victoria Park, Cardiff's first official park; and Thompson's Park, formerly home to an aviary removed in the 1970s. Wild open spaces include Howardian Local Nature Reserve, of the lower Rhymney valley in Penylan noted for its orchids, and Forest Farm Country Park, over along the River Taff in Whitchurch.
Cardiff is one of the top ten retail destinations in the UK with Queen Street and St. Mary Street as the two main shopping streets with the three shopping arcades, St. David's Centre, Queens Arcade and the Capitol Centre, Cardiff, Capitol Centre. The current expansion of St. David's Centre as part of the St David's 2 project has made it one of the largest shopping centres in the UK. As well as the modern shopping arcades, the city is home to Victorian shopping centres, such as High Street Arcade, Castle Arcade, Wyndham Arcade, Royal Arcade and Morgan Arcade. Also of note is The Hayes, home to Spillers Records, the world's oldest record shop. Cardiff has a number of markets, including the vast Victorian indoor Cardiff Market, Cardiff Central Market and the newly established Riverside Community Market, which specialises in locally produced organic produce. Several out-of-town retail parks exist, such as Newport Road, Culverhouse Cross, Cardiff Gate and Cardiff Bay.
Media
 Cardiff is the Welsh base for the main national broadcasters (BBC Cymru Wales, ITV Wales and S4C). A locally based television station, ''Made in Cardiff'', is also based in the city centre. Major filming studios in Cardiff include the BBC's Roath Lock Studios and Pinewood Studios Wales.
Several contemporary television programmes and films are filmed in and/or set in Cardiff such as ''Casualty (TV series), Casualty'', '' Doctor Who'', ''The Sarah Jane Adventures'', ''
Cardiff is the Welsh base for the main national broadcasters (BBC Cymru Wales, ITV Wales and S4C). A locally based television station, ''Made in Cardiff'', is also based in the city centre. Major filming studios in Cardiff include the BBC's Roath Lock Studios and Pinewood Studios Wales.
Several contemporary television programmes and films are filmed in and/or set in Cardiff such as ''Casualty (TV series), Casualty'', '' Doctor Who'', ''The Sarah Jane Adventures'', ''Torchwood
''Torchwood'' is a British science fiction television programme created by Russell T Davies. A spin-off of the 2005 revival of ''Doctor Who'', it aired from 2006 to 2011. The show shifted its broadcast channel each series to reflect its growin ...
'', ''Merlin (TV series), Merlin'', ''Class (2016 TV series), Class'', ''The Valleys (TV series), The Valleys'', ''Upstairs Downstairs (2010 TV series), Upstairs Downstairs'', ''A Discovery of Witches (TV series), A Discovery of Witches'', ''His Dark Materials (TV series), His Dark Materials'', ''Being Human (British TV series), Being Human'', ''The Story of Tracy Beaker (TV series), The Story of Tracy Beaker'', ''Wizards vs Aliens'', ''Sex Education (TV series), Sex Education'' and '' Sherlock''.
The main local newspaper is the ''South Wales Echo''; the national paper is the ''Western Mail (Wales), Western Mail''. Both are based in Park Street in the city centre. ''Capital Times'', ''Echo Extra'' and the South Wales edition of ''Metro (Associated Metro Limited), Metro'' are also based and distributed in the city. There are several magazines, including ''Primary Times'' and a monthly ''papur bro'', and a Welsh-language community newsletter called ''Y Dinesydd'' (The Citizen). Radio stations serving the city and based in Cardiff include 97.4 & 103.2 Capital FM South Wales, Capital South Wales, Heart South Wales, BBC Radio Wales, BBC Radio Cymru, Nation Radio Wales, Radio Cardiff, Smooth Wales and Xpress Radio.
The Principality Stadium was one of the first six British landmarks to be fully mapped on Google street view, Google Street View as a 360-degree virtual tour.
Sport
 Cardiff hosts many high-profile sporting events at local, national and international level and in recognition of the city's commitment to sport for all was awarded the title of European Capital of Sport 2014. Organised sports have been held in the city since the early 19th century. national home sporting fixtures are nearly always played in the city. All Wales' multi-sports agencies and many of the Countries of the United Kingdom, country's Governing bodies of sports in Wales, sports governing bodies have their headquarters in Cardiff and the city's many top quality venues have attracted world-famous sports events, sometimes unrelated to Cardiff or to Wales. In 2008/09, 61% of Cardiff residents regularly participated in sport and active recreation, the highest percentage in ll 22 local authorities in Wales.
Rugby union fans around the world have long been familiar with the old National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, and its successor the Principality Stadium, which hosted the FA Cup for six years (from 2001 to 2006) it took to rebuild Wembley Stadium. In 2009, Cardiff hosted the first Australian cricket team in England in 2009, Ashes cricket test between England and Australia to be held in Wales. Cardiff hosted eight football matches of the London 2012 Olympics.
Cardiff hosts many high-profile sporting events at local, national and international level and in recognition of the city's commitment to sport for all was awarded the title of European Capital of Sport 2014. Organised sports have been held in the city since the early 19th century. national home sporting fixtures are nearly always played in the city. All Wales' multi-sports agencies and many of the Countries of the United Kingdom, country's Governing bodies of sports in Wales, sports governing bodies have their headquarters in Cardiff and the city's many top quality venues have attracted world-famous sports events, sometimes unrelated to Cardiff or to Wales. In 2008/09, 61% of Cardiff residents regularly participated in sport and active recreation, the highest percentage in ll 22 local authorities in Wales.
Rugby union fans around the world have long been familiar with the old National Stadium, Cardiff Arms Park, and its successor the Principality Stadium, which hosted the FA Cup for six years (from 2001 to 2006) it took to rebuild Wembley Stadium. In 2009, Cardiff hosted the first Australian cricket team in England in 2009, Ashes cricket test between England and Australia to be held in Wales. Cardiff hosted eight football matches of the London 2012 Olympics.
 Cardiff City F.C. (founded 1899 as Riverside AFC) played their home games at Ninian Park from 1910 until the end of the 2008–09 season. The club's new home is the Cardiff City Stadium, which they initially rented to the Cardiff Blues, the city's professional rugby union team, the Blues returning to the Arms Park in 2012. Cardiff City have played in the English The Football League, Football League since the 1920–21 season, climbing to Division 1 after one season. Cardiff City are the only non-English team to have won the FA Cup, beating Arsenal F.C., Arsenal in the 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927 final at Wembley Stadium (1923), Wembley Stadium. They were runners up to Portsmouth F.C., Portsmouth in the 2008 FA Cup Final, 2008 final, losing 1–0 at the new Wembley Stadium. In the 2013/14 and 2018/19 seasons Cardiff City played in the English Premier League.
Cardiff Metropolitan University F.C. of the Athletic Union of Cardiff Metropolitan University, based in Cyncoed, play in the Cymru Premier, having been promoted from Welsh League Division One in 2016. They were winners of the Welsh League Cup for the 2018–19 season.
Cardiff has numerous smaller clubs including Bridgend Street A.F.C., Caerau (Ely) A.F.C., Cardiff Corinthians F.C., Cardiff Grange Harlequins A.F.C., and Ely Rangers A.F.C., which all play in the Welsh football league system.
Cardiff City F.C. (founded 1899 as Riverside AFC) played their home games at Ninian Park from 1910 until the end of the 2008–09 season. The club's new home is the Cardiff City Stadium, which they initially rented to the Cardiff Blues, the city's professional rugby union team, the Blues returning to the Arms Park in 2012. Cardiff City have played in the English The Football League, Football League since the 1920–21 season, climbing to Division 1 after one season. Cardiff City are the only non-English team to have won the FA Cup, beating Arsenal F.C., Arsenal in the 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927 final at Wembley Stadium (1923), Wembley Stadium. They were runners up to Portsmouth F.C., Portsmouth in the 2008 FA Cup Final, 2008 final, losing 1–0 at the new Wembley Stadium. In the 2013/14 and 2018/19 seasons Cardiff City played in the English Premier League.
Cardiff Metropolitan University F.C. of the Athletic Union of Cardiff Metropolitan University, based in Cyncoed, play in the Cymru Premier, having been promoted from Welsh League Division One in 2016. They were winners of the Welsh League Cup for the 2018–19 season.
Cardiff has numerous smaller clubs including Bridgend Street A.F.C., Caerau (Ely) A.F.C., Cardiff Corinthians F.C., Cardiff Grange Harlequins A.F.C., and Ely Rangers A.F.C., which all play in the Welsh football league system.
 Cardiff Cricket Club was formed in 1819 and Glamorgan CCC, Glamorgan County Cricket Club has competed as a first-class county since 1921. Its headquarters and ground is the SWALEC Stadium, Sophia Gardens, since moving from Cardiff Arms Park in 1966. The Sophia Gardens stadium underwent multimillion-pound improvements since being selected to host the first England cricket team, "England" v Australia national cricket team, Australia Test cricket, Test match of the Australian cricket team in England in 2009, 2009 Ashes series. The Hundred (cricket), The Hundred franchise team Welsh Fire is also based at the stadium.
Cardiff has a long association with boxing, from Jim Driscoll, 'Peerless' Jim Driscoll — born in Cardiff in 1880 — to more recent, high-profile fights staged in the city. These include the World Boxing Council, WBC Lennox Lewis vs. Frank Bruno heavyweight championship fight at the Arms Park in 1993, and many of Joe Calzaghe's fights, between 2003 and 2007.
Cardiff's professional ice hockey team, the Cardiff Devils, plays in the 3,000-seat Ice Arena Wales in the Cardiff International Sports Village. It plays in the 12-team professional Elite Ice Hockey League. Founded in 1986, it was one of the most successful British teams in the 1990s.
Cardiff's only American-flag football team is the Hurricanes. It won the British Championship in 2014 after falling short by 2 points in a quarter-final to eventual winners, the London Rebels, the previous year. It is based at Roath Recreational Ground.
Cardiff Cricket Club was formed in 1819 and Glamorgan CCC, Glamorgan County Cricket Club has competed as a first-class county since 1921. Its headquarters and ground is the SWALEC Stadium, Sophia Gardens, since moving from Cardiff Arms Park in 1966. The Sophia Gardens stadium underwent multimillion-pound improvements since being selected to host the first England cricket team, "England" v Australia national cricket team, Australia Test cricket, Test match of the Australian cricket team in England in 2009, 2009 Ashes series. The Hundred (cricket), The Hundred franchise team Welsh Fire is also based at the stadium.
Cardiff has a long association with boxing, from Jim Driscoll, 'Peerless' Jim Driscoll — born in Cardiff in 1880 — to more recent, high-profile fights staged in the city. These include the World Boxing Council, WBC Lennox Lewis vs. Frank Bruno heavyweight championship fight at the Arms Park in 1993, and many of Joe Calzaghe's fights, between 2003 and 2007.
Cardiff's professional ice hockey team, the Cardiff Devils, plays in the 3,000-seat Ice Arena Wales in the Cardiff International Sports Village. It plays in the 12-team professional Elite Ice Hockey League. Founded in 1986, it was one of the most successful British teams in the 1990s.
Cardiff's only American-flag football team is the Hurricanes. It won the British Championship in 2014 after falling short by 2 points in a quarter-final to eventual winners, the London Rebels, the previous year. It is based at Roath Recreational Ground.
 The 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games were hosted by Cardiff. These involved 1,130 athletes from 35 national teams competing in 94 events. One of the venues for those Games—The Wales Empire Swimming Pool—was demolished in 1998 to make way for the Principality Stadium. The GBP32m Cardiff International Pool in Cardiff Bay, opened to the public on 12 January 2008 — part of the GBP1bn International Sports Village (ISV) — is the only Olympic-standard swimming pool in Wales. When complete, the ISV complex will provide Olympic standard facilities for sports including boxing and fencing, gymnastics, judo, white water events (including Whitewater canoeing, canoeing and Whitewater kayaking, kayaking) and wrestling as well as a Indoor skiing, snow dome with real snow for skiing and snowboarding, an Cardiff Arena, arena for public ice skating and ice hockey and a hotel. Some of the sports facilities at the ISV were to be used as training venues for the London 2012 Olympics.
The 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games were hosted by Cardiff. These involved 1,130 athletes from 35 national teams competing in 94 events. One of the venues for those Games—The Wales Empire Swimming Pool—was demolished in 1998 to make way for the Principality Stadium. The GBP32m Cardiff International Pool in Cardiff Bay, opened to the public on 12 January 2008 — part of the GBP1bn International Sports Village (ISV) — is the only Olympic-standard swimming pool in Wales. When complete, the ISV complex will provide Olympic standard facilities for sports including boxing and fencing, gymnastics, judo, white water events (including Whitewater canoeing, canoeing and Whitewater kayaking, kayaking) and wrestling as well as a Indoor skiing, snow dome with real snow for skiing and snowboarding, an Cardiff Arena, arena for public ice skating and ice hockey and a hotel. Some of the sports facilities at the ISV were to be used as training venues for the London 2012 Olympics.
 The Principality Stadium hosts motor-sport events such as the World Rally Championship, as part of Wales Rally GB. The first indoor special stages of the World Rally Championship were held at the Principality Stadium in September 2005 and have been an annual event since. The Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain, British Speedway Grand Prix, one of the World Championship events, is held at the Millennium Stadium. While the track—a temporary, purpose built, shale oval—is not universally loved, the venue is considered the best of the World Championship's 11 rounds.
The Cardiff International Sports Stadium, opened 19 January 2009, replacing the Cardiff Athletics Stadium, demolished to make way for the Cardiff City Stadium. It has a 4,953 capacity as a multi sport/special event venue, offering certificated international track and field athletics facilities, including an international standard external throws area. The stadium houses the Headquarters of Welsh Athletics, the sport's governing body for Wales. The city's indoor track and field athletics sports venue is the National Indoor Athletics Centre, an international athletics and multi sports centre at the University of Wales Institute, Cardiff Campus,
The Principality Stadium hosts motor-sport events such as the World Rally Championship, as part of Wales Rally GB. The first indoor special stages of the World Rally Championship were held at the Principality Stadium in September 2005 and have been an annual event since. The Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain, British Speedway Grand Prix, one of the World Championship events, is held at the Millennium Stadium. While the track—a temporary, purpose built, shale oval—is not universally loved, the venue is considered the best of the World Championship's 11 rounds.
The Cardiff International Sports Stadium, opened 19 January 2009, replacing the Cardiff Athletics Stadium, demolished to make way for the Cardiff City Stadium. It has a 4,953 capacity as a multi sport/special event venue, offering certificated international track and field athletics facilities, including an international standard external throws area. The stadium houses the Headquarters of Welsh Athletics, the sport's governing body for Wales. The city's indoor track and field athletics sports venue is the National Indoor Athletics Centre, an international athletics and multi sports centre at the University of Wales Institute, Cardiff Campus, Cyncoed
Cyncoed ( ); is an affluent and exclusive community in the northeast of Cardiff, the capital of Wales. With many properties in the area fetching over £1 million, Cyncoed is considered to have some of the highest property prices in the country. Cy ...
.
Notable people
Many notable people have hailed from Cardiff, ranging from historical figures such as the 12th-century Welsh leader Ifor Bach to more recent figures such as Roald Dahl, Ken Follett, Griff Rhys Jones, Catrin Dafydd, and the former Blue Peter presenter Gethin Jones. The notable actors include Ioan Gruffudd (notable film performances such as Lancelot in ''King Arthur (2004 film), King Arthur'' (2004), Mister Fantastic (Reed Richards) in ''Fantastic 4 (2005 film), Fantastic 4'' (2005) and its sequel ''Fantastic 4: Rise of the Silver Surfer'' (2007)) and Iwan Rheon. Also notable is Siân Grigg, BAFTA winner and Oscar nominated Hollywood make-up artist. In particular, the city has been the birthplace of sports stars such as Tanni Grey-Thompson and Colin Jackson, as well as many Premier League, The Football League, Football League and international footballers, such as Craig Bellamy, Gareth Bale, Ryan Giggs, Joe Ledley, and former managers of the Wales national football team Terry Yorath and John Toshack. International rugby league players from Cardiff include Frank Whitcombe, Billy Boston, David Willicombe and Colin Dixon. International rugby union players include Sam Warburton, Jamie Roberts, Jamie Robinson (rugby player), Jamie Robinson, Nicky Robinson (rugby player), Nicky Robinson, Rhys Patchell, and baseball internationals include George Whitcombe and Ted Peterson. Saint Teilo (c. 500 – 9 February c. 560) is the patron saint of Cardiff. He was a British Christian monk, bishop, and founder of monasteries and churches. Reputed to be a cousin, friend, and disciple of Saint David, he was Bishop of Llandaff and founder of the first church at Llandaff Cathedral, where his tomb is. His Saint's Day is 9 February. Cardiff is also well known for its musicians. Ivor Novello inspired the Ivor Novello Awards. Idloes Owen, founder of the Welsh National Opera, lived in Llandaff. Dame Shirley Bassey was born and raised in Cardiff. Charlotte Church is famous as a crossover classical/pop singer. Shakin' Stevens was one of the top-selling male artists in the UK during the 1980s. Tigertailz, a popular glam metal act in the 1980s, also hailed from Cardiff. A number of Cardiff-based bands, such as Catatonia (band), Catatonia and Super Furry Animals, were popular in the 1990s.Twinning
*Luhansk, Ukraine *Hordaland, Hordaland county, Norway *Sucre, Bolivia *Nantes, France *Stuttgart, Germany *Xiamen, China *Lima, PeruNamesake
Cardiff-by-the-Sea in Encinitas, California was named after Cardiff in Wales.Diplomatic presence
A total of 28 countries have a diplomatic presence in Cardiff. Many of these, such as Germany, Italy, Switzerland, Denmark, Canada, Thailand and the Czech Republic, are represented by consul (representative), honorary consulates. The United States Embassy to the UK operates a satellite office.Freedom of the City
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the City of Cardiff; they are listed with the date that they received the honour.Individuals
Military units
*The Welch Regiment: 10 June 1944 *The Welsh Guards: 27 April 1957 *The Royal Regiment of Wales: 11 June 1969 *The Royal Welch Fusiliers: 7 November 1973 *The 1st The Queen's Dragoon Guards: 29 July 1985 *HMS Cardiff (D108), HMS Cardiff, Royal Navy, RN: 3 February 1988 *The Merchant Navy (United Kingdom), Merchant Navy Association (Wales): 3 September 2001 *203 (Welsh) Field Hospital Army Reserve (United Kingdom), (Volunteers) Royal Army Medical Corps, RAMC: 21 April 2014 *HMS Dragon (D35), HMS Dragon, Royal Navy, RN: 18 May 2014See also
*Cardiff city centre *Cardiff music scene *List of cultural venues in Cardiff *List of parliamentary constituencies in South Glamorgan *List of places in Cardiff *List of places of worship in Cardiff *List of streets and squares in Cardiff * SeneddReferences
External links
Cardiff Council site
the full text of the edition of historical records for Cardiff, edited by J. H. Matthews (1898–1905). Part of British History Online. {{Authority control Cardiff, Cardiff Capital cities in the United Kingdom Cities in Wales Populated coastal places in Wales Counties of Wales Glamorgan Port cities and towns in Wales Principal areas of Wales County towns in Wales Rally GB 50s establishments Populated places established in the 1st century