Camouflage (band) Songs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the
 In ancient Greece,
In ancient Greece,
Abstract
Camouflage has been a topic of interest and research in The English zoologist
The English zoologist  The artist
The artist
 Camouflage can be achieved by different methods, described below. Most of the methods help to hide against a background; but mimesis and motion dazzle protect without hiding. Methods may be applied on their own or in combination. Many mechanisms are visual, but some research has explored the use of techniques against olfactory (scent) and acoustic (sound) detection. Methods may also apply to military equipment.
Camouflage can be achieved by different methods, described below. Most of the methods help to hide against a background; but mimesis and motion dazzle protect without hiding. Methods may be applied on their own or in combination. Many mechanisms are visual, but some research has explored the use of techniques against olfactory (scent) and acoustic (sound) detection. Methods may also apply to military equipment.
File:Lion-in-tall-grass.jpg, Lion in Kruger National Park, South Africa, blending in with the tall grass
File:Tanzania 0607 cropped Nevit.jpg, Black-faced sandgrouse is coloured like its desert background.
File:Caprimulgus aegyptius.jpg, Egyptian nightjar nests in open sand with only its camouflaged plumage to protect it.
File:Podargus papuensis - Daintree River.jpg,
File:Great male Leopard in South Afrika-JD.JPG, Leopard: a disruptively camouflaged predator
File:T-90 main battle tank (2).jpg, Russian T-90 battle tank painted in bold disruptive pattern of sand and green
File:Gaboon viper (4530693343).jpg,
 Some animals, such as the
Some animals, such as the
File:Ibexes.jpg, Three countershaded and cryptically coloured
File:Hyastenus elatus.jpg, This
 Movement catches the eye of prey animals on the lookout for predators, and of predators hunting for prey. Most methods of crypsis therefore also require suitable cryptic behaviour, such as lying down and keeping still to avoid being detected, or in the case of stalking predators such as the
Movement catches the eye of prey animals on the lookout for predators, and of predators hunting for prey. Most methods of crypsis therefore also require suitable cryptic behaviour, such as lying down and keeping still to avoid being detected, or in the case of stalking predators such as the
 Most forms of camouflage are ineffective when the camouflaged animal or object moves, because the motion is easily seen by the observing predator, prey or enemy. However, insects such as
Most forms of camouflage are ineffective when the camouflaged animal or object moves, because the motion is easily seen by the observing predator, prey or enemy. However, insects such as
File:Hoverfly August 2007-8.jpg, Male ''
File:Rock Ptarmigan (Lagopus Muta).jpg, Rock ptarmigan, changing colour in springtime. The male is still mostly in winter plumage
File:Norwegian Winter War Volunteers.jpg, Norwegian volunteer soldiers in
 Countershading uses graded colour to counteract the effect of self-shadowing, creating an illusion of flatness. Self-shadowing makes an animal appear darker below than on top, grading from light to dark; countershading 'paints in' tones which are darkest on top, lightest below, making the countershaded animal nearly invisible against a suitable background. Thayer observed that "Animals are painted by Nature, darkest on those parts which tend to be most lighted by the sky's light, and ''vice versa''". Accordingly, the principle of countershading is sometimes called ''Thayer's Law''. Countershading is widely used by terrestrial animals, such as
Countershading uses graded colour to counteract the effect of self-shadowing, creating an illusion of flatness. Self-shadowing makes an animal appear darker below than on top, grading from light to dark; countershading 'paints in' tones which are darkest on top, lightest below, making the countershaded animal nearly invisible against a suitable background. Thayer observed that "Animals are painted by Nature, darkest on those parts which tend to be most lighted by the sky's light, and ''vice versa''". Accordingly, the principle of countershading is sometimes called ''Thayer's Law''. Countershading is widely used by terrestrial animals, such as
File:Gazella-dorcas.jpg, Countershaded
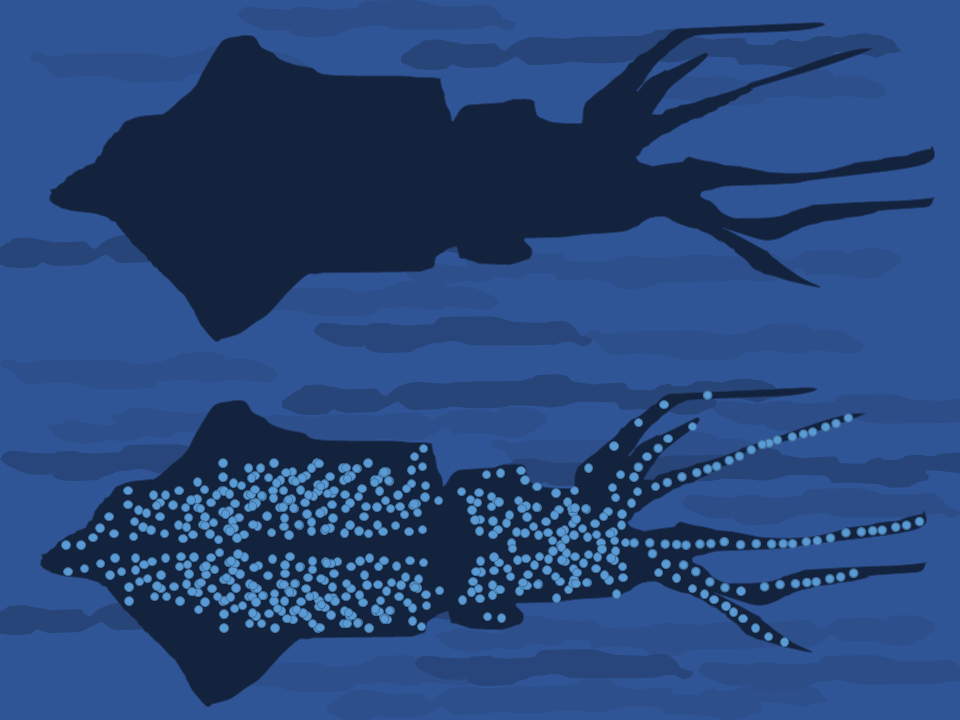 Counter-illumination means producing light to match a background that is brighter than an animal's body or military vehicle; it is a form of active camouflage. It is notably used by some species of squid, such as the
Counter-illumination means producing light to match a background that is brighter than an animal's body or military vehicle; it is a form of active camouflage. It is notably used by some species of squid, such as the
File:HMS Largs by night with incomplete Diffused Lighting Camouflage 1942.jpg, HMS ''Largs'' by night with incomplete diffused lighting camouflage, 1942, set to maximum brightness
File:HMS Largs bulwark with Diffused Lighting Camouflage fittings.jpg, Bulwark of HMS ''Largs'' showing 4 (of about 60) diffused lighting fittings, 2 lifted, 2 deployed
File:Principle of Yehudi Lights with Avenger head-on view.jpg,
 Many marine animals that float near the surface are highly
Many marine animals that float near the surface are highly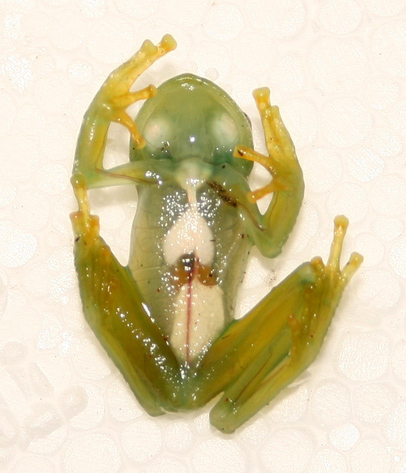  Some tissues such as muscles can be made transparent, provided either they are very thin or organised as regular layers or fibrils that are small compared to the wavelength of visible light. A familiar example is the transparency of the lens of the vertebrate eye, which is made of the protein
Some tissues such as muscles can be made transparent, provided either they are very thin or organised as regular layers or fibrils that are small compared to the wavelength of visible light. A familiar example is the transparency of the lens of the vertebrate eye, which is made of the protein

 Where transparency cannot be achieved, it can be imitated effectively by silvering to make an animal's body highly reflective. At medium depths at sea, light comes from above, so a mirror oriented vertically makes animals such as fish invisible from the side. Most fish in the upper ocean such as
Where transparency cannot be achieved, it can be imitated effectively by silvering to make an animal's body highly reflective. At medium depths at sea, light comes from above, so a mirror oriented vertically makes animals such as fish invisible from the side. Most fish in the upper ocean such as
 Some deep sea fishes have very black skin, reflecting under 0.5% of ambient light. This can prevent detection by predators or prey fish which use bioluminescence for illumination. '' Oneirodes'' had a particularly black skin which reflected only 0.044% of 480 nm wavelength light. The ultra-blackness is achieved with a thin but continuous layer of particles in the dermis,
Some deep sea fishes have very black skin, reflecting under 0.5% of ambient light. This can prevent detection by predators or prey fish which use bioluminescence for illumination. '' Oneirodes'' had a particularly black skin which reflected only 0.044% of 480 nm wavelength light. The ultra-blackness is achieved with a thin but continuous layer of particles in the dermis,
File:Biston betularia.png,
 Most forms of camouflage are made ineffective by movement: a deer or grasshopper may be highly cryptic when motionless, but instantly seen when it moves. But one method, motion dazzle, requires rapidly moving bold patterns of contrasting stripes. Motion dazzle may degrade predators' ability to estimate the prey's speed and direction accurately, giving the prey an improved chance of escape. Motion dazzle distorts speed perception and is most effective at high speeds; stripes can also distort perception of size (and so, perceived range to the target). As of 2011, motion dazzle had been proposed for military vehicles, but never applied. Since motion dazzle patterns would make animals more difficult to locate accurately when moving, but easier to see when stationary, there would be an evolutionary trade-off between motion dazzle and crypsis.
An animal that is commonly thought to be dazzle-patterned is the
Most forms of camouflage are made ineffective by movement: a deer or grasshopper may be highly cryptic when motionless, but instantly seen when it moves. But one method, motion dazzle, requires rapidly moving bold patterns of contrasting stripes. Motion dazzle may degrade predators' ability to estimate the prey's speed and direction accurately, giving the prey an improved chance of escape. Motion dazzle distorts speed perception and is most effective at high speeds; stripes can also distort perception of size (and so, perceived range to the target). As of 2011, motion dazzle had been proposed for military vehicles, but never applied. Since motion dazzle patterns would make animals more difficult to locate accurately when moving, but easier to see when stationary, there would be an evolutionary trade-off between motion dazzle and crypsis.
An animal that is commonly thought to be dazzle-patterned is the
 Ship camouflage was occasionally used in ancient times.
Ship camouflage was occasionally used in ancient times.
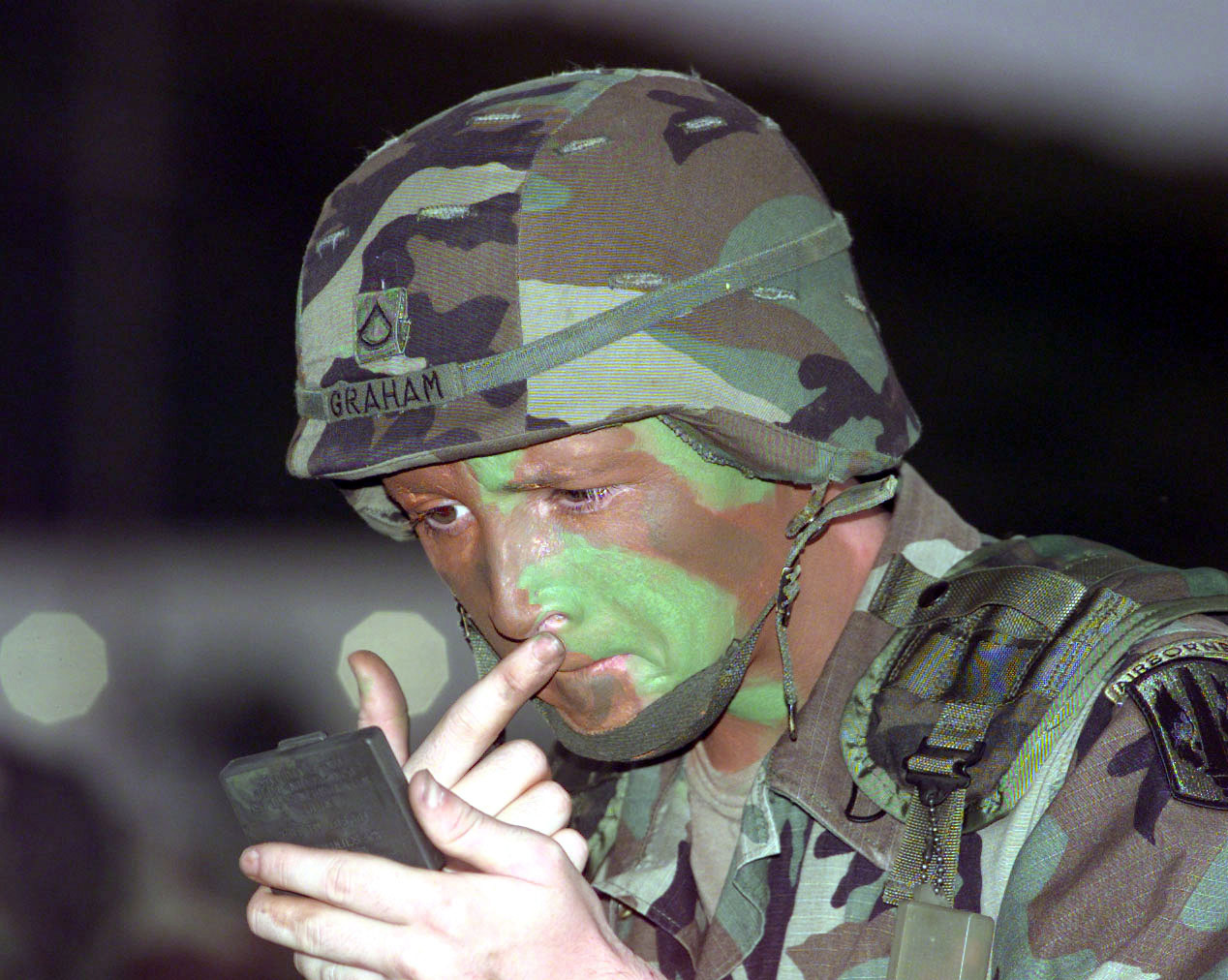
 The development of military camouflage was driven by the increasing range and accuracy of infantry firearms in the 19th century. In particular the replacement of the inaccurate musket with weapons such as the
The development of military camouflage was driven by the increasing range and accuracy of infantry firearms in the 19th century. In particular the replacement of the inaccurate musket with weapons such as the
 In the
In the
File:USS West Mahomet (ID-3681) cropped.jpg, USS ''West Mahomet'' in dazzle camouflage
File:CamouflagedAustralian9.2inchHowitzerYpres1917.jpeg, BL 9.2-inch howitzer, Siege howitzer camouflaged against observation from the air, 1917
File:Austro-Hungarian ski patrol on Italian front in snow camouflage 1915-1918.jpg, Austro-Hungarian ski patrol in two-part snow uniforms with improvised head camouflage on Italian front, 1915-1918
File:Catalina Góraszka 2008 204.JPG, Maritime patrol Consolidated PBY Catalina, Catalina, painted white to minimise visibility against the sky
File:SS Platanenmuster Sommer.jpg, 1937 summer variant of Waffen SS ''Flecktarn'' Plane tree pattern
File:USS Duluth (CL-87) underway in Hampton Roads on 10 October 1944 (NH 98363).jpg, USS Duluth (CL-87), USS ''Duluth'' in naval camouflage Measure 32, Design 11a, one of many dazzle schemes used on warships
File:Spitfire.planform.arp.jpg, A Supermarine Spitfire, Spitfire's underside 'azure' paint scheme, meant to hide it against the sky
File:Royal Air Force 1939-1945- Fighter Command CL3979.jpg, A Luftwaffe aircraft hangar built to resemble a street of village houses, Belgium, 1944
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 183-E0406-0022-001, Russland, Kesselschlacht Stalingrad.jpg, Red Army soldiers in the Battle of Stalingrad in
File:CADPAT digital camouflage pattern (Temperate Woodland variant).jpg, CADPAT was the first pixellated digital camouflage pattern to be issued, in 2002.
File:British dpm2.jpg, British Disruptive Pattern Material, issued to Special forces#United Kingdom, special forces in 1963 and universally by 1968
File:M05 snow pattern.jpg, 2007 2-colour snow variant of Finnish Defence Forces M05 pattern
File:Pla camo.svg, Main (4-colour woodland) variant of Chinese People's Liberation Army Type 99 (camouflage), Type 99 pattern, c. 2006

battledress
A combat uniform, also called field uniform, battledress or military fatigues, is a casual type of uniform used by military, police, fire and other public uniformed services for everyday fieldwork and combat duty purposes, as opposed to dress ...
of a modern soldier
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a conscripted or volunteer enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, or an officer.
Etymology
The word ''soldier'' derives from the Middle English word , from Old French ...
, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration
Disruptive coloration (also known as disruptive camouflage or disruptive patterning) is a form of camouflage that works by breaking up the outlines of an animal, soldier or military vehicle with a strongly contrasting pattern. It is often comb ...
, eliminating shadow, and countershading
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, a ...
. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination
Counter-illumination is a method of active camouflage seen in marine animals such as firefly squid and midshipman fish, and in military prototypes, producing light to match their backgrounds in both brightness and wavelength.
Marine animals of ...
on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chameleons and octopuses, are capable of actively changing their skin pattern and colours, whether for camouflage or for signalling. It is possible that some plants use camouflage to evade being eaten by herbivores.
Military camouflage
Military camouflage is the use of camouflage by an armed force to protect personnel and equipment from observation by enemy forces. In practice, this means applying colour and materials to military equipment of all kinds, including vehicles, ...
was spurred by the increasing range and accuracy of firearms in the 19th century. In particular the replacement of the inaccurate musket with the rifle made personal concealment in battle a survival skill. In the 20th century, military camouflage developed rapidly, especially during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. On land, artists such as André Mare
Charles André Mare (1885–1932), or André-Charles Mare, was a French painter and textile designer, and co-founder of the Company of French Art (''la Compagnie des Arts Français'') in 1919. He was a designer of colorful textiles, and was one o ...
designed camouflage schemes and observation posts disguised as trees. At sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
, merchant ships and troop carriers were painted in dazzle
Dazzle may refer to:
* Glare (vision), difficulty seeing in the presence of bright light
* Dazzle (fabric), a type of polyester fabric
* ''Dazzle'' (manga), a Japanese manga series by Minari Endoh
* "Dazzle" (song), a song by Siouxsie & the Bans ...
patterns that were highly visible, but designed to confuse enemy submarines as to the target's speed, range, and heading. During and after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, a variety of camouflage schemes were used for aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engine ...
and for ground vehicles in different theatres of war. The use of radar since the mid-20th century has largely made camouflage for fixed-wing military aircraft obsolete.
Non-military use of camouflage includes making cell telephone towers less obtrusive and helping hunters to approach wary game animals. Patterns derived from military camouflage are frequently used in fashion clothing, exploiting their strong designs and sometimes their symbolism. Camouflage themes recur in modern art, and both figuratively and literally in science fiction and works of literature.
History
 In ancient Greece,
In ancient Greece, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
(384–322 BC) commented on the colour-changing abilities, both for camouflage and for signalling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, of cephalopods including the octopus, in his ''Historia animalium
''History of Animals'' ( grc-gre, Τῶν περὶ τὰ ζῷα ἱστοριῶν, ''Ton peri ta zoia historion'', "Inquiries on Animals"; la, Historia Animalium, "History of Animals") is one of the major texts on biology by the ancient Gr ...
'':Aristotle (c. 350 BC). ''Historia Animalium''. IX, 622a: 2–10. Cited in Borrelli, Luciana; Gherardi, Francesca; Fiorito, Graziano (2006). ''A catalogue of body patterning in Cephalopoda''. Firenze University Press. Abstract
Camouflage has been a topic of interest and research in
zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ...
for well over a century. According to Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's 1859 theory of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
, features such as camouflage evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by providing individual animals with a reproductive advantage, enabling them to leave more offspring, on average, than other members of the same species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
. In his ''Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'', Darwin wrote:
 The English zoologist
The English zoologist Edward Bagnall Poulton
Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton, FRS HFRSE FLS (27 January 1856 – 20 November 1943) was a British evolutionary biologist, a lifelong advocate of natural selection through a period in which many scientists such as Reginald Punnett doubted its ...
studied animal coloration, especially camouflage. In his 1890 book ''The Colours of Animals
''The Colours of Animals'' is a zoology book written in 1890 by Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton (1856–1943). It was the first substantial textbook to argue the case for Darwinian selection applying to all aspects of animal coloration. The book a ...
'', he classified different types such as "special protective resemblance" (where an animal looks like another object), or "general aggressive resemblance" (where a predator blends in with the background, enabling it to approach prey). His experiments showed that swallow-tailed moth pupae
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their ...
were camouflaged to match the backgrounds on which they were reared as larvae. Poulton's "general protective resemblance" was at that time considered to be the main method of camouflage, as when Frank Evers Beddard
Frank Evers Beddard FRS FRSE (19 June 1858 – 14 July 1925) was an English zoologist. He became a leading authority on annelids, including earthworms. He won the Linnean Medal in 1916 for his book on oligochaetes.
Life
Beddard was born in ...
wrote in 1892 that "tree-frequenting animals are often green in colour. Among vertebrates numerous species of parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
s, iguana
''Iguana'' (, ) is a genus of herbivorous lizards that are native to tropical areas of Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. The genus was first described in 1768 by Austrian naturalist Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in his ...
s, tree-frogs, and the green tree-snake are examples". Beddard did however briefly mention other methods, including the "alluring coloration" of the flower mantis
Flower mantises are praying mantis species that use a special form of camouflage referred to as aggressive mimicry, which they not only use to attract prey, but avoid predators as well. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that ...
and the possibility of a different mechanism in the orange tip butterfly. He wrote that "the scattered green spots upon the under surface of the wings might have been intended for a rough sketch of the small flowerets of the plant n_umbellifer.html" ;"title="umbellifer.html" ;"title="n umbellifer">n umbellifer">umbellifer.html" ;"title="n umbellifer">n umbellifer so close is their mutual resemblance." He also explained the coloration of sea fish such as the mackerel: "Among pelagic fish it is common to find the upper surface dark-coloured and the lower surface white, so that the animal is inconspicuous when seen either from above or below."
 The artist
The artist Abbott Handerson Thayer
Abbott Handerson Thayer (August 12, 1849May 29, 1921) was an American artist, naturalist and teacher. As a painter of portraits, figures, animals and landscapes, he enjoyed a certain prominence during his lifetime, and his paintings are represen ...
formulated what is sometimes called Thayer's Law, the principle of countershading
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, a ...
. However, he overstated the case in the 1909 book ''Concealing-Coloration in the Animal Kingdom
''Concealing-Coloration in the Animal Kingdom: An Exposition of the Laws of Disguise Through Color and Pattern; Being a Summary of Abbott H. Thayer’s Discoveries'' is a book published ostensibly by Gerald H. Thayer in 1909, and revised in 191 ...
'', arguing that "All patterns and colors whatsoever of all animals that ever preyed or are preyed on are under certain normal circumstances obliterative" (that is, cryptic camouflage), and that "Not one ' mimicry' mark, not one 'warning color
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste o ...
'... nor any ' sexually selected' color, exists anywhere in the world where there is not every reason to believe it the very best conceivable device for the concealment of its wearer", and using paintings such as ''Peacock in the Woods'' (1907) to reinforce his argument. Thayer was roundly mocked for these views by critics including Teddy Roosevelt.
The English zoologist Hugh Cott
Hugh Bamford Cott (6 July 1900 – 18 April 1987) was a British zoologist, an authority on both natural and military camouflage, and a scientific illustrator and photographer. Many of his field studies took place in Africa, where he was espec ...
's 1940 book ''Adaptive Coloration in Animals
''Adaptive Coloration in Animals'' is a 500-page textbook about camouflage, warning coloration and mimicry by the Cambridge zoologist Hugh Cott, first published during the Second World War in 1940; the book sold widely and made him famous.
The ...
'' corrected Thayer's errors, sometimes sharply: "Thus we find Thayer straining the theory to a fantastic extreme in an endeavour to make it cover almost every type of coloration in the animal kingdom." Cott built on Thayer's discoveries, developing a comprehensive view of camouflage based on "maximum disruptive contrast", countershading and hundreds of examples. The book explained how disruptive camouflage worked, using streaks of boldly contrasting colour, paradoxically making objects less visible by breaking up their outlines. While Cott was more systematic and balanced in his view than Thayer, and did include some experimental evidence on the effectiveness of camouflage, his 500-page textbook was, like Thayer's, mainly a natural history narrative which illustrated theories with examples.
Experimental evidence that camouflage helps prey avoid being detected by predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
s was first provided in 2016, when ground-nesting birds (plovers
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subfa ...
and coursers
The coursers are a group of birds which together with the pratincoles make up the family Glareolidae. They have long legs, short wings and long pointed bills which curve downwards. Their most unusual feature for birds classed as waders is that ...
) were shown to survive according to how well their egg contrast matched the local environment.
Evolution
As there is a lack of evidence for camouflage in the fossil record, studying the evolution of camouflage strategies is very difficult. Furthermore, camouflage traits must be both adaptable (provide a fitness gain in a given environment) and heritable (in other words, the trait must undergo positive selection). Thus, studying the evolution of camouflage strategies requires an understanding of the genetic components and various ecological pressures that drive crypsis.Fossil history
Camouflage is a soft-tissue feature that is rarely preserved in thefossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
record, but rare fossilised skin samples from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period show that some marine reptiles were countershaded. The skins, pigmented with dark-coloured eumelanin, reveal that both leatherback turtles and mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on ...
s had dark backs and light bellies. There is fossil evidence of camouflaged insects going back over 100 million years, for example lacewings larvae that stick debris all over their bodies much as their modern descendants do, hiding them from their prey. Dinosaurs appear to have been camouflaged, as a 120 million year old fossil of a ''Psittacosaurus
''Psittacosaurus'' ( ; "parrot lizard") is a genus of extinct ceratopsian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of what is now Asia, existing between 126 and 101 million years ago. It is notable for being the most species-rich non-avian dinosaur gen ...
'' has been preserved with countershading
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, a ...
.
Genetics
Camouflage does not have a single genetic origin. However, studying the genetic components of camouflage in specific organisms illuminates the various ways that crypsis can evolve among lineages. Many cephalopods have the ability to actively camouflage themselves, controlling crypsis through neural activity. For example, the genome of the common cuttlefish includes 16 copies of the reflectin gene, which grants the organism remarkable control over coloration and iridescence. The reflectin gene is thought to have originated through transposition from symbiotic ''Aliivibrio fischeri
''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (also called ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine anim ...
'' bacteria, which provide bioluminescence to its hosts. While not all cephalopods use active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
, ancient cephalopods may have inherited the gene horizontally from symbiotic ''A. fischeri'', with divergence occurred through subsequent gene duplication (such as in the case of ''Sepia officinalis'') or gene loss (as with cephalopods with no active camouflage capabilities). /sup> This is unique as an instance of camouflage arising as an instance of horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). H ...
from an endosymbiont
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within ...
. However, other methods of horizontal gene transfer are common in the evolution of camouflage strategies in other lineages. Peppered moths and walking stick insects both have camouflage-related genes that stem from transposition events.
The Agouti
The agouti (, ) or common agouti is any of several rodent species of the genus ''Dasyprocta''. They are native to Middle America, northern and central South America, and the southern Lesser Antilles. Some species have also been introduced else ...
genes are orthologous genes involved in camouflage across many lineages. They produce yellow and red coloration (phaeomelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
), and work in competition with other genes that produce black (melanin) and brown (eumelanin) colours. In eastern deer mice, over a period of about 8000 years the single agouti gene developed 9 mutations that each made expression of yellow fur stronger under natural selection, and largely eliminated melanin-coding black fur coloration. On the other hand, all black domesticated cats have deletions of the agouti gene that prevent its expression, meaning no yellow or red color is produced. The evolution, history and widespread scope of the agouti gene shows that different organisms often rely on orthologous or even identical genes to develop a variety of camouflage strategies.
Ecology
While camouflage can increase an organism's fitness, it has genetic and energetic costs. There is a trade-off between detectability and mobility. Species camouflaged to fit a specificmicrohabitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
are less likely to be detected when in that microhabitat, but must spend energy to reach, and sometimes to remain in, such areas. Outside the microhabitat, the organism has a higher chance of detection. Generalized camouflage allows species to avoid predation over a wide range of habitat backgrounds, but is less effective. The development of generalized or specialized camouflage strategies is highly dependent on the biotic and abiotic composition of the surrounding environment.
There are many examples of the tradeoffs between specific and general cryptic patterning. '' Phestilla melanocrachia'', a species of nudibranch that feeds on stony coral
Scleractinia, also called stony corals or hard corals, are marine animals in the phylum Cnidaria that build themselves a hard skeleton. The individual animals are known as polyps and have a cylindrical body crowned by an oral disc in which a mo ...
, utilizes specific cryptic patterning in reef ecosystems. The nudibranch syphons pigments from the consumed coral into the epidermis, adopting the same shade as the consumed coral. This allows the nudibranch to change colour (mostly between black and orange) depending on the coral system that it inhabits. However, ''P. melanocrachia'' can only feed and lay eggs on the branches of host-coral, '' Platygyra carnosa'', which limits the geographical range and efficacy in nudibranch nutritional crypsis. Furthermore, the nudibranch colour change is not immediate, and switching between coral hosts when in search for new food or shelter can be costly.
The costs associated with distractive or disruptive crypsis are more complex than the costs associated with background matching. Disruptive patterns distort the body outline, making it harder to precisely identify and locate. However, disruptive patterns result in higher predation. Disruptive patterns that specifically involve visible symmetry (such as in some butterflies) reduce survivability and increase predation. Some researchers argue that because wing-shape and color pattern are genetically linked, it is genetically costly to develop asymmetric wing colorations that would enhance the efficacy of disruptive cryptic patterning. Symmetry does not carry a high survival cost for butterflies and moths that their predators views from above on a homogeneous background, such as the bark of a tree. On the other hand, natural selection drives species with variable backgrounds and habitats to move symmetrical patterns away from the centre of the wing and body, disrupting their predators' symmetry recognition.
Principles
 Camouflage can be achieved by different methods, described below. Most of the methods help to hide against a background; but mimesis and motion dazzle protect without hiding. Methods may be applied on their own or in combination. Many mechanisms are visual, but some research has explored the use of techniques against olfactory (scent) and acoustic (sound) detection. Methods may also apply to military equipment.
Camouflage can be achieved by different methods, described below. Most of the methods help to hide against a background; but mimesis and motion dazzle protect without hiding. Methods may be applied on their own or in combination. Many mechanisms are visual, but some research has explored the use of techniques against olfactory (scent) and acoustic (sound) detection. Methods may also apply to military equipment.
Resemblance to surroundings
Some animals' colours and patterns resemble a particular natural background. This is an important component of camouflage in all environments. For instance, tree-dwellingparakeet
A parakeet is any one of many small to medium-sized species of parrot, in multiple genera, that generally has long tail feathers.
Etymology and naming
The name ''parakeet'' is derived from the French wor''perroquet'' which is reflected in ...
s are mainly green; woodcock
The woodcocks are a group of seven or eight very similar living species of wading birds in the genus ''Scolopax''. The genus name is Latin for a snipe or woodcock, and until around 1800 was used to refer to a variety of waders. The English name ...
s of the forest floor are brown and speckled; reedbed bittern
Bitterns are birds belonging to the subfamily Botaurinae of the heron family Ardeidae. Bitterns tend to be shorter-necked and more secretive than other members of the family. They were called ''hæferblæte'' in Old English; the word "bittern ...
s are streaked brown and buff; in each case the animal's coloration matches the hues of its habitat. Similarly, desert animals
A xerocole (), is a general term referring to any animal that is adapted to live in a desert. The main challenges xerocoles must overcome are lack of water and excessive heat. To conserve water they avoid evaporation and concentrate excretions (i. ...
are almost all desert coloured in tones of sand, buff, ochre, and brownish grey, whether they are mammals like the gerbil
The Mongolian gerbil or Mongolian jird (''Meriones unguiculatus'') is a small rodent belonging to the subfamily Gerbillinae. Their body size is typically , with a tail, and body weight , with adult males larger than females. The animal is us ...
or fennec fox
The fennec fox (''Vulpes zerda'') is a small crepuscular fox native to the deserts of North Africa, ranging from Western Sahara to the Sinai Peninsula. Its most distinctive feature is its unusually large ears, which serve to dissipate heat and ...
, birds such as the desert lark
The desert lark (''Ammomanes deserti'') breeds in deserts and semi-deserts from Morocco to western India. It has a very wide distribution and faces no obvious threats, and surveys have shown that it is slowly increasing in numbers as it expands ...
or sandgrouse
Sandgrouse is the common name for Pteroclidae , a family of sixteen species of bird, members of the order Pterocliformes . They are traditionally placed in two genera. The two central Asian species are classified as '' Syrrhaptes'' and the othe ...
, or reptiles like the skink or horned viper. Military uniforms, too, generally resemble their backgrounds; for example khaki
The color khaki (, ) is a light shade of tan with a slight yellowish tinge.
Khaki has been used by many armies around the world for uniforms and equipment, particularly in arid or desert regions, where it provides camouflage relative to sandy ...
uniforms are a muddy or dusty colour, originally chosen for service in South Asia. Many moths show industrial melanism
Industrial melanism is an evolutionary effect prominent in several arthropods, where dark pigmentation ( melanism) has evolved in an environment affected by industrial pollution, including sulphur dioxide gas and dark soot deposits. Sulphur d ...
, including the peppered moth
The peppered moth (''Biston betularia'') is a temperate species of night-flying moth. It is mostly found in the northern hemisphere in places like Asia, Europe and North America. Peppered moth evolution is an example of population genetics an ...
which has coloration that blends in with tree bark. The coloration of these insects evolved between 1860 and 1940 to match the changing colour of the tree trunks on which they rest, from pale and mottled to almost black in polluted areas. This is taken by zoologists as evidence that camouflage is influenced by natural selection, as well as demonstrating that it changes where necessary to resemble the local background.
Papuan frogmouth
The Papuan frogmouth (''Podargus papuensis'') is a species of bird in the family Podargidae.
Taxonomy
The species was originally described by zoologist Jean René Constant Quoy and naturalist Joseph Paul Gaimard in 1830.
The three subspeci ...
resembles a broken branch.
File:Katydid camouflaged in basil plant.jpg, Bright green katydid has the colour of fresh vegetation.
Disruptive coloration
Disruptive patterns use strongly contrasting, non-repeating markings such as spots or stripes to break up the outlines of an animal or military vehicle, or to conceal telltale features, especially by masking the eyes, as in thecommon frog
The common frog or grass frog (''Rana temporaria''), also known as the European common frog, European common brown frog, European grass frog, European Holarctic true frog, European pond frog or European brown frog, is a semi-aquatic amphibian ...
. Disruptive patterns may use more than one method to defeat visual systems such as edge detection
Edge detection includes a variety of mathematical methods that aim at identifying edges, curves in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. The same problem of finding discontinuitie ...
. Predators like the leopard use disruptive camouflage to help them approach prey, while potential prey use it to avoid detection by predators. Disruptive patterning is common in military usage, both for uniforms and for military vehicles. Disruptive patterning, however, does not always achieve crypsis on its own, as an animal or a military target may be given away by factors like shape, shine, and shadow.
The presence of bold skin markings does not in itself prove that an animal relies on camouflage, as that depends on its behaviour. Roosevelt attacks Thayer on page 191, arguing that neither zebra nor giraffe are "'adequately obliterated' by countershading or coloration pattern or anything else." For example, although giraffes have a high contrast pattern that could be disruptive coloration, the adults are very conspicuous when in the open. Some authors have argued that adult giraffes are cryptic, since when standing among trees and bushes they are hard to see at even a few metres' distance. However, adult giraffes move about to gain the best view of an approaching predator, relying on their size and ability to defend themselves, even from lions, rather than on camouflage. A different explanation is implied by young giraffes being far more vulnerable to predation than adults. More than half of all giraffe calves die within a year, and giraffe mothers hide their newly born calves, which spend much of the time lying down in cover while their mothers are away feeding. The mothers return once a day to feed their calves with milk. Since the presence of a mother nearby does not affect survival, it is argued that these juvenile giraffes must be very well camouflaged; this is supported by coat markings being strongly inherited.
The possibility of camouflage in plants has been little studied until the late 20th century. Leaf variegation with white spots may serve as camouflage in forest understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but abo ...
plants, where there is a dappled background; leaf mottling is correlated with closed habitats. Disruptive camouflage would have a clear evolutionary advantage in plants: they would tend to escape from being eaten by herbivores. Another possibility is that some plants have leaves differently coloured on upper and lower surfaces or on parts such as veins and stalks to make green-camouflaged insects conspicuous, and thus benefit the plants by favouring the removal of herbivores by carnivores. These hypotheses are testable.
Gaboon viper
The Gaboon viper (''Bitis gabonica''), also called the Gaboon adder, is a viper species found in the rainforests and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa.McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. ''Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geog ...
's bold markings are powerfully disruptive.
File:Ptarmigan and five chicks.JPG, A ptarmigan
''Lagopus'' is a small genus of birds in the grouse subfamily commonly known as ptarmigans (). The genus contains three living species with numerous described subspecies, all living in tundra or cold upland areas.
Taxonomy and etymology
The ge ...
and five chicks exhibit exceptional disruptive camouflage
File:Jumping spider with prey.jpg, Jumping spider
Jumping spiders are a group of spiders that constitute the family Salticidae. As of 2019, this family contained over 600 described genera and over 6,000 described species, making it the largest family of spiders at 13% of all species. Jumping spi ...
: a disruptively camouflaged invertebrate predator
File:Saw Greenbriar - Smilax bona-nox, Colt Creek State Park, Lakeland, Florida.jpg, Many understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but abo ...
plants such as the saw greenbriar, '' Smilax bona-nox'' have pale markings, possibly disruptive camouflage.
Eliminating shadow
horned lizard
Horned lizards (''Phrynosoma''), also known as horny toads or horntoads, are a genus of North American lizards and the type genus of the family Phrynosomatidae. The common names refer directly to their horns or to their flattened, rounded bodies, ...
s of North America, have evolved elaborate measures to eliminate shadow
A shadow is a dark area where light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object. It occupies all of the three-dimensional volume behind an object with light in front of it. The cross section of a shadow is a two-dimensional silhouette, ...
. Their bodies are flattened, with the sides thinning to an edge; the animals habitually press their bodies to the ground; and their sides are fringed with white scales which effectively hide and disrupt any remaining areas of shadow there may be under the edge of the body. The theory that the body shape of the horned lizards which live in open desert is adapted to minimise shadow is supported by the one species which lacks fringe scales, the roundtail horned lizard, which lives in rocky areas and resembles a rock. When this species is threatened, it makes itself look as much like a rock as possible by curving its back, emphasizing its three-dimensional shape. Some species of butterflies, such as the speckled wood, ''Pararge aegeria
The speckled wood (''Pararge aegeria'') is a butterfly found in and on the borders of woodland areas throughout much of the Palearctic realm. The species is subdivided into multiple subspecies, including ''Pararge aegeria aegeria'', ''Pararge aeg ...
'', minimise their shadows when perched by closing the wings over their backs, aligning their bodies with the sun, and tilting to one side towards the sun, so that the shadow becomes a thin inconspicuous line rather than a broad patch. Similarly, some ground-nesting birds, including the European nightjar
The European nightjar (''Caprimulgus europaeus''), common goatsucker, Eurasian nightjar or just nightjar, is a crepuscular and nocturnal bird in the nightjar family that breeds across most of Europe and the Palearctic to Mongolia and Northwest ...
, select a resting position facing the sun. Eliminating shadow was identified as a principle of military camouflage during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
ibex
An ibex (plural ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa ...
almost invisible in the Israeli desert
File:Armoured personnel carriers, Eriboll - geograph.org.uk - 1316295.jpg, "Shape, shine, shadow" make these 'camouflaged' military vehicles easily visible.
File:Phrynosoma mcallii.jpg, The flat-tail horned lizard's body is flattened and fringed to minimise its shadow.
File:Øvelse på Evjemoen Tropp 4.2 - camouflage nettings.jpg, Camouflage netting
In law, set-off or netting are legal techniques applied between persons or businesses with mutual rights and liabilities, replacing gross positions with net positions. It permits the rights to be used to discharge the liabilities where cross cla ...
is draped away from a military vehicle to reduce its shadow.
File:Perfect Camouflage (Caterpillar on teakwood branch).jpg, A caterpillar's fringe of bristles conceals its shadow.
Distraction
Many prey animals have conspicuous high-contrast markings which paradoxically attract the predator's gaze. These distractive markings may serve as camouflage by distracting the predator's attention from recognising the prey as a whole, for example by keeping the predator from identifying the prey's outline. Experimentally, search times forblue tit
The Eurasian blue tit (''Cyanistes caeruleus'') is a small passerine bird in the tit family, Paridae. It is easily recognisable by its blue and yellow plumage and small size.
Eurasian blue tits, usually resident and non-migratory birds, ar ...
s increased when artificial prey had distractive markings.
Self-decoration
Some animals actively seek to hide by decorating themselves with materials such as twigs, sand, or pieces of shell from their environment, to break up their outlines, to conceal the features of their bodies, and to match their backgrounds. For example, acaddisfly
The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the ...
larva builds a decorated case and lives almost entirely inside it; a decorator crab
Decorator crabs are crabs of several different species, belonging to the superfamily Majoidea (not all of which are decorators), that use materials from their environment to hide from, or ward off, predators. They decorate themselves by sticking ...
covers its back with seaweed, sponges, and stones. The nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label= Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are ...
of the predatory masked bug uses its hind legs and a ' tarsal fan' to decorate its body with sand or dust. There are two layers of bristles (trichome
Trichomes (); ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a p ...
s) over the body. On these, the nymph spreads an inner layer of fine particles and an outer layer of coarser particles. The camouflage may conceal the bug from both predators and prey.
Similar principles can be applied for military purposes, for instance when a sniper wears a ghillie suit
A ghillie suit is a type of camouflage clothing designed to resemble the background environment such as foliage, snow or sand. Typically, it is a net or cloth garment covered in loose strips of burlap ( hessian), cloth, or twine, sometimes made t ...
designed to be further camouflaged by decoration with materials such as tufts of grass from the sniper's immediate environment. Such suits were used as early as 1916, the British army having adopted "coats of motley hue and stripes of paint" for snipers. Cott takes the example of the larva of the blotched emerald
The blotched emerald (''Comibaena bajularia'') is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found throughout Europe and the Near East. It has a scattered distribu ...
moth, which fixes a screen of fragments of leaves to its specially hooked bristles, to argue that military camouflage uses the same method, pointing out that the "device is ... essentially the same as one widely practised during the Great War for the concealment, not of caterpillars, but of caterpillar-tractors, unbattery positions, observation posts and so forth."
decorator crab
Decorator crabs are crabs of several different species, belonging to the superfamily Majoidea (not all of which are decorators), that use materials from their environment to hide from, or ward off, predators. They decorate themselves by sticking ...
has covered its body with sponges.
File:IDF-CombatEngineeringSniper001.jpg, Sniper in a Ghillie suit
A ghillie suit is a type of camouflage clothing designed to resemble the background environment such as foliage, snow or sand. Typically, it is a net or cloth garment covered in loose strips of burlap ( hessian), cloth, or twine, sometimes made t ...
with plant materials
File:Reduvius personatus, Masked Hunter Bug nymph camouflaged with sand grains.JPG, '' Reduvius personatus'', masked hunter bug nymph, camouflaged with sand grains
File:Battle of Lake Khasan-Camouflaged soviet tanks.jpg, Soviet tanks under netting dressed with vegetation, 1938
Cryptic behaviour
 Movement catches the eye of prey animals on the lookout for predators, and of predators hunting for prey. Most methods of crypsis therefore also require suitable cryptic behaviour, such as lying down and keeping still to avoid being detected, or in the case of stalking predators such as the
Movement catches the eye of prey animals on the lookout for predators, and of predators hunting for prey. Most methods of crypsis therefore also require suitable cryptic behaviour, such as lying down and keeping still to avoid being detected, or in the case of stalking predators such as the tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ...
, moving with extreme stealth, both slowly and quietly, watching its prey for any sign they are aware of its presence. As an example of the combination of behaviours and other methods of crypsis involved, young giraffes seek cover, lie down, and keep still, often for hours until their mothers return; their skin pattern blends with the pattern of the vegetation, while the chosen cover and lying position together hide the animals' shadows. The flat-tail horned lizard similarly relies on a combination of methods: it is adapted to lie flat in the open desert, relying on stillness, its cryptic coloration, and concealment of its shadow to avoid being noticed by predators. In the ocean, the leafy sea dragon
The leafy seadragon (''Phycodurus eques'') or Glauert's seadragon, is the only member of the genus ''Phycodurus'' and is a marine fish in the family Syngnathidae, which includes seadragons, pipefish, and seahorses.
It is found along the sou ...
sways mimetically, like the seaweeds amongst which it rests, as if rippled by wind or water currents. Swaying is seen also in some insects, like Macleay's spectre stick insect, '' Extatosoma tiaratum''. The behaviour may be motion crypsis, preventing detection, or motion masquerade, promoting misclassification (as something other than prey), or a combination of the two.
Motion camouflage
hoverflies
Hover flies, also called flower flies or syrphid flies, make up the insect family Syrphidae. As their common name suggests, they are often seen hovering or nectaring at flowers; the adults of many species feed mainly on nectar and pollen, while ...
and dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threa ...
use motion camouflage: the hoverflies to approach possible mates, and the dragonflies to approach rivals when defending territories. Motion camouflage is achieved by moving so as to stay on a straight line between the target and a fixed point in the landscape; the pursuer thus appears not to move, but only to loom larger in the target's field of vision. The same method can be used for military purposes, for example by missiles to minimise their risk of detection by an enemy. However, missile engineers, and animals such as bats, use the method mainly for its efficiency rather than camouflage.
Syritta pipiens
''Syritta pipiens,'' sometimes called the thick-legged hoverfly, is one of the most common species in the insect family Syrphidae. This fly originates from Europe and is currently distributed across Eurasia and North America. They are fast and ...
'' hoverflies use motion camouflage to approach females
File:Australian Emperor mating and laying.jpg, Male Australian Emperor dragonflies use motion camouflage to approach rivals.
Changeable skin coloration
Animals such as chameleon, frog, flatfish such as the peacock flounder, squid and octopus actively change their skin patterns and colours using specialchromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...
cells to resemble their current background, or, as in most chameleons, for signalling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
. However, Smith's dwarf chameleon
Smith's dwarf chameleon or the Elandsberg dwarf chameleon (''Bradypodion taeniabronchum'') is a species of lizard in the family Chamaeleonidae endemic to South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the ...
does use active colour change for camouflage.
Each chromatophore contains pigment of only one colour. In fish and frogs, colour change is mediated by a type of chromatophore known as melanophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in cont ...
s that contain dark pigment. A melanophore is star-shaped; it contains many small pigmented organelles which can be dispersed throughout the cell, or aggregated near its centre. When the pigmented organelles are dispersed, the cell makes a patch of the animal's skin appear dark; when they are aggregated, most of the cell, and the animal's skin, appears light. In frogs, the change is controlled relatively slowly, mainly by hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are require ...
s. In fish, the change is controlled by the brain, which sends signals directly to the chromatophores, as well as producing hormones.
The skins of cephalopods such as the octopus contain complex units, each consisting of a chromatophore with surrounding muscle and nerve cells. The cephalopod chromatophore has all its pigment grains in a small elastic sac, which can be stretched or allowed to relax under the control of the brain to vary its opacity. By controlling chromatophores of different colours, cephalopods can rapidly change their skin patterns and colours.
On a longer timescale, animals like the Arctic hare
The Arctic hare (''Lepus arcticus'') is a species of hare highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs, a small nose, fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a ...
, Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in ...
, stoat
The stoat (''Mustela erminea''), also known as the Eurasian ermine, Beringian ermine and ermine, is a mustelid native to Eurasia and the northern portions of North America. Because of its wide circumpolar distribution, it is listed as Least Conc ...
, and rock ptarmigan
The rock ptarmigan (''Lagopus muta'') is a medium-sized game bird in the grouse family. It is known simply as the ptarmigan in the UK. It is the official bird for the Canadian territory of Nunavut, where it is known as the ''aqiggiq'' (ᐊᕿ� ...
have snow camouflage
Snow camouflage is the use of a coloration or pattern for effective camouflage in winter, often combined with a different summer camouflage. Summer patterns are typically disruptively patterned combinations of shades of browns and greys, up to ...
, changing their coat colour (by moulting and growing new fur or feathers) from brown or grey in the summer to white in the winter; the Arctic fox is the only species in the dog family to do so. However, Arctic hares which live in the far north of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, where summer is very short, remain white year-round.
The principle of varying coloration either rapidly or with the changing seasons has military applications. ''Active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
'' could in theory make use of both dynamic colour change and counterillumination. Simple methods such as changing uniforms and repainting vehicles for winter have been in use since World War II. In 2011, BAE Systems announced their Adaptiv
Adaptiv is an active camouflage technology developed by BAE Systems AB to protect military vehicles from detection by far infrared night vision devices, providing infrared stealth. It consists of an array of hexagonal Peltier plates which can be ...
infrared camouflage technology. It uses about 1,000 hexagonal panels to cover the sides of a tank. The Peltier plate panels are heated and cooled to match either the vehicle's surroundings (crypsis), or an object such as a car (mimesis), when viewed in infrared.
Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
, 1940, with white camouflage overalls over their uniforms
File:Arctic Hare.jpg, Arctic hares in the low arctic change from brown to white in winter
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 101III-Roth-173-01, Russland, Raum Charkow, Jagdpanzer.jpg, Snow-camouflaged German Marder III
''Marder'' III was the name for a series of World War II German tank destroyers. They mounted either the modified ex-Soviet 76.2 mm F-22 Model 1936 divisional field gun, or the German 7.5 cm PaK 40, in an open-topped fighting compartment on ...
jagdpanzer
''Jagdpanzer'' (JgPz) is the name given in German to a heavily-armoured, tracked tank destroyer, although it may also be used for other kinds of self-propelled guns. Literally translated from German, ''Jagdpanzer'' is "hunting tank".
It typ ...
and white-overalled crew and infantry in Russia, 1943
File:Yemen Chameleon (cropped).jpg, Veiled chameleon
The veiled chameleon (''Chamaeleo calyptratus'') is a species of chameleon (family Chamaeleonidae) native to the Arabian Peninsula in Yemen and Saudi Arabia. Other common names include cone-head chameleon and Yemen chameleon. They are born pas ...
, ''Chamaeleo calyptratus'', changes colour mainly in relation to mood and for signalling.
File:Adaptiv infrared camouflage demo hiding tank as car.jpg, Adaptiv
Adaptiv is an active camouflage technology developed by BAE Systems AB to protect military vehicles from detection by far infrared night vision devices, providing infrared stealth. It consists of an array of hexagonal Peltier plates which can be ...
infrared camouflage lets an armoured vehicle mimic a car.
Countershading
gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, '' Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third ...
s and grasshoppers; marine animals, such as sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorp ...
and dolphins
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
; and birds, such as snipe
A snipe is any of about 26 wading bird species in three genera in the family Scolopacidae. They are characterized by a very long, slender bill, eyes placed high on the head, and cryptic/ camouflaging plumage. The ''Gallinago'' snipes have a ...
and dunlin
The dunlin (''Calidris alpina'') is a small wader, formerly sometimes separated with the other "stints" in the genus ''Erolia''. The English name is a dialect form of "dunling", first recorded in 1531–1532. It derives from ''dun'', "dull brown ...
.
Countershading is less often used for military camouflage, despite Second World War experiments that showed its effectiveness. English zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and d ...
Hugh Cott
Hugh Bamford Cott (6 July 1900 – 18 April 1987) was a British zoologist, an authority on both natural and military camouflage, and a scientific illustrator and photographer. Many of his field studies took place in Africa, where he was espec ...
encouraged the use of methods including countershading, but despite his authority on the subject, failed to persuade the British authorities. Soldiers often wrongly viewed camouflage netting as a kind of invisibility cloak, and they had to be taught to look at camouflage practically, from an enemy observer's viewpoint. At the same time in Australia, zoologist William John Dakin advised soldiers to copy animals' methods, using their instincts for wartime camouflage.
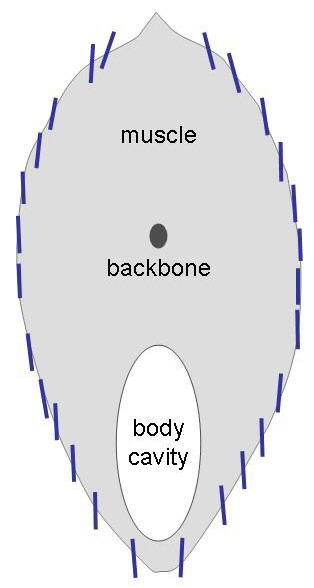
The term countershading has a second meaning unrelated to "Thayer's Law". It is that the upper and undersides of animals such as sharks, and of some military aircraft, are different colours to match the different backgrounds when seen from above or from below. Here the camouflage consists of two surfaces, each with the simple function of providing concealment against a specific background, such as a bright water surface or the sky. The body of a shark or the fuselage of an aircraft is not gradated from light to dark to appear flat when seen from the side. The camouflage methods used are the matching of background colour and pattern, and disruption of outlines.
Dorcas gazelle
The dorcas gazelle (''Gazella dorcas''), also known as the ariel gazelle, is a small and common gazelle. The dorcas gazelle stands about at the shoulder, with a head and body length of and a weight of . The numerous subspecies survive on vegeta ...
, ''Gazella dorcas''
File:Tiburón.jpg, Countershaded grey reef shark
The grey reef shark (''Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos'', sometimes misspelled ''amblyrhynchus'' or ''amblyrhinchos'') is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae. One of the most common reef sharks in the Indo-Pacific, it is found as ...
, ''Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos''
File:Thayers ships.jpg, Countershaded ship and submarine in Thayer's 1902 patent application
File:Abbott thayer countershading.jpg, Two model birds painted by Thayer: painted in background colours on the left, countershaded and nearly invisible on the right
File:Focke-Wulf Fw 190D-9 outside USAF.jpg, Countershaded Focke-Wulf Fw 190D-9
Counter-illumination
 Counter-illumination means producing light to match a background that is brighter than an animal's body or military vehicle; it is a form of active camouflage. It is notably used by some species of squid, such as the
Counter-illumination means producing light to match a background that is brighter than an animal's body or military vehicle; it is a form of active camouflage. It is notably used by some species of squid, such as the firefly squid
The firefly squid (''Watasenia scintillans''), also commonly known as the sparkling enope squid or hotaru-ika in Japan, is a species of squid in the family Enoploteuthidae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus ''Watasenia''. These tiny ...
and the midwater squid. The latter has light-producing organs (photophores
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
) scattered all over its underside; these create a sparkling glow that prevents the animal from appearing as a dark shape when seen from below. Counterillumination camouflage is the likely function of the bioluminescence of many marine organisms, though light is also produced to attract or to detect prey and for signalling.
Counterillumination has rarely been used for military purposes. " Diffused lighting camouflage" was trialled by Canada's National Research Council National Research Council may refer to:
* National Research Council (Canada), sponsoring research and development
* National Research Council (Italy), scientific and technological research, Rome
* National Research Council (United States), part of ...
during the Second World War. It involved projecting light on to the sides of ships to match the faint glow of the night sky, requiring awkward external platforms to support the lamps. The Canadian concept was refined in the American Yehudi lights
Yehudi lights are lamps of automatically controlled brightness placed on the front and leading edges of an aircraft to raise the aircraft's luminance to the average brightness of the sky, a form of active camouflage using counter-illumination. T ...
project, and trialled in aircraft including B-24 Liberators and naval Avengers. The planes were fitted with forward-pointing lamps automatically adjusted to match the brightness of the night sky. This enabled them to approach much closer to a target – within – before being seen. Counterillumination was made obsolete by radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, and neither diffused lighting camouflage nor Yehudi lights entered active service.
Yehudi Lights
Yehudi lights are lamps of automatically controlled brightness placed on the front and leading edges of an aircraft to raise the aircraft's luminance to the average brightness of the sky, a form of active camouflage using counter-illumination. T ...
raise the average brightness of the plane from a dark shape to the same as the sky.
Transparency
 Many marine animals that float near the surface are highly
Many marine animals that float near the surface are highly transparent
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to:
* Transparency (optics), the physical property of allowing the transmission of light through a material
They may also refer to:
Literal uses
* Transparency (photography), a still, ...
, giving them almost perfect camouflage. However, transparency is difficult for bodies made of materials that have different refractive indices
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
from seawater. Some marine animals such as jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrell ...
have gelatinous bodies, composed mainly of water; their thick mesogloea
Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges.
Descr ...
is acellular and highly transparent. This conveniently makes them buoyant
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pr ...
, but it also makes them large for their muscle mass, so they cannot swim fast, making this form of camouflage a costly trade-off with mobility. Gelatinous plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
ic animals are between 50 and 90 percent transparent. A transparency of 50 percent is enough to make an animal invisible to a predator such as cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
at a depth of ; better transparency is required for invisibility in shallower water, where the light is brighter and predators can see better. For example, a cod can see prey that are 98 percent transparent in optimal lighting in shallow water. Therefore, sufficient transparency for camouflage is more easily achieved in deeper waters.
 Some tissues such as muscles can be made transparent, provided either they are very thin or organised as regular layers or fibrils that are small compared to the wavelength of visible light. A familiar example is the transparency of the lens of the vertebrate eye, which is made of the protein
Some tissues such as muscles can be made transparent, provided either they are very thin or organised as regular layers or fibrils that are small compared to the wavelength of visible light. A familiar example is the transparency of the lens of the vertebrate eye, which is made of the protein crystallin
In anatomy, a crystallin is a water-soluble structural protein found in the lens and the cornea of the eye accounting for the transparency of the structure. It has also been identified in other places such as the heart, and in aggressive breast c ...
, and the vertebrate cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
which is made of the protein collagen. Other structures cannot be made transparent, notably the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
s or equivalent light-absorbing structures of eyes – they must absorb light to be able to function. The camera
A camera is an optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), with a ...
-type eye of vertebrates and cephalopods must be completely opaque. Finally, some structures are visible for a reason, such as to lure prey. For example, the nematocysts (stinging cells) of the transparent siphonophore
Siphonophorae (from Greek ''siphōn'' 'tube' + ''pherein'' 'to bear') is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 specie ...
'' Agalma okenii'' resemble small copepods. Examples of transparent marine animals include a wide variety of larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e, including radiata
Radiata or Radiates is a historical taxonomic rank that was used to classify animals with radially symmetric body plans. The term Radiata is no longer accepted, as it united several different groupings of animals that do not form a monophyletic ...
(coelenterates), siphonophores, salps
A salp (plural salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (plural salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktic tunicate. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body, one of the most efficient ...
(floating tunicate
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata (). It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time ...
s), gastropod molluscs, polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made ...
worms, many shrimplike crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s, and fish; whereas the adults of most of these are opaque and pigmented, resembling the seabed or shores where they live. Adult comb jellies
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
and jellyfish obey the rule, often being mainly transparent. Cott suggests this follows the more general rule that animals resemble their background: in a transparent medium like seawater, that means being transparent. The small Amazon river fish '' Microphilypnus amazonicus'' and the shrimps it associates with, ''Pseudopalaemon gouldingi
''Pseudopalaemon'' is a genus of shrimps belonging to the family Palaemonidae.
The species of this genus are found in Southern America.
Species:
*''Pseudopalaemon amazonensis''
*'' Pseudopalaemon bouvieri''
*''Pseudopalaemon chryseus''
*''Ps ...
'', are so transparent as to be "almost invisible"; further, these species appear to select whether to be transparent or more conventionally mottled (disruptively patterned) according to the local background in the environment.
Silvering

 Where transparency cannot be achieved, it can be imitated effectively by silvering to make an animal's body highly reflective. At medium depths at sea, light comes from above, so a mirror oriented vertically makes animals such as fish invisible from the side. Most fish in the upper ocean such as
Where transparency cannot be achieved, it can be imitated effectively by silvering to make an animal's body highly reflective. At medium depths at sea, light comes from above, so a mirror oriented vertically makes animals such as fish invisible from the side. Most fish in the upper ocean such as sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the It ...
and herring are camouflaged by silvering.
The marine hatchetfish
Marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes are small deep-sea mesopelagic ray-finned fish of the stomiiform subfamily Sternoptychinae. They should not be confused with the freshwater hatchetfishes, which are not particularly closely related T ...
is extremely flattened laterally, leaving the body just millimetres thick, and the body is so silvery as to resemble aluminium foil
Aluminium foil (or aluminum foil in North American English; often informally called tin foil) is aluminium prepared in thin metal leaves with a thickness less than ; thinner gauges down to are also commonly used. Standard household foil is typ ...
. The mirrors consist of microscopic structures similar to those used to provide structural coloration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination wi ...
: stacks of between 5 and 10 crystals of guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
spaced about of a wavelength apart to interfere constructively and achieve nearly 100 per cent reflection. In the deep waters that the hatchetfish lives in, only blue light with a wavelength of 500 nanometres percolates down and needs to be reflected, so mirrors 125 nanometres apart provide good camouflage.
In fish such as the herring which live in shallower water, the mirrors must reflect a mixture of wavelengths, and the fish accordingly has crystal stacks with a range of different spacings. A further complication for fish with bodies that are rounded in cross-section is that the mirrors would be ineffective if laid flat on the skin, as they would fail to reflect horizontally. The overall mirror effect is achieved with many small reflectors, all oriented vertically. Silvering is found in other marine animals as well as fish. The cephalopods, including squid, octopus and cuttlefish, have multilayer mirrors made of protein rather than guanine.
Ultra-blackness
 Some deep sea fishes have very black skin, reflecting under 0.5% of ambient light. This can prevent detection by predators or prey fish which use bioluminescence for illumination. '' Oneirodes'' had a particularly black skin which reflected only 0.044% of 480 nm wavelength light. The ultra-blackness is achieved with a thin but continuous layer of particles in the dermis,
Some deep sea fishes have very black skin, reflecting under 0.5% of ambient light. This can prevent detection by predators or prey fish which use bioluminescence for illumination. '' Oneirodes'' had a particularly black skin which reflected only 0.044% of 480 nm wavelength light. The ultra-blackness is achieved with a thin but continuous layer of particles in the dermis, melanosome
A melanosome is an organelle found in animal cells and is the site for synthesis, storage and transport of melanin, the most common light-absorbing pigment found in the animal kingdom. Melanosomes are responsible for color and photoprotection i ...
s. These particles both absorb most of the light, and are sized and shaped so as to scatter rather than reflect most of the rest. Modelling suggests that this camouflage should reduce the distance at which such a fish can be seen by a factor of 6 compared to a fish with a nominal 2% reflectance. Species with this adaptation are widely dispersed in various orders of the phylogenetic tree of bony fishes ( Actinopterygii), implying that natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
has driven the convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
of ultra-blackness camouflage independently many times.
Mimesis
In mimesis (also called ''masquerade''), the camouflaged object looks like something else which is of no special interest to the observer. Mimesis is common inprey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
animals, for example when a peppered moth
The peppered moth (''Biston betularia'') is a temperate species of night-flying moth. It is mostly found in the northern hemisphere in places like Asia, Europe and North America. Peppered moth evolution is an example of population genetics an ...
caterpillar mimics a twig, or a grasshopper mimics a dry leaf. It is also found in nest structures; some eusocial wasps, such as '' Leipomeles dorsata'', build a nest envelope in patterns that mimic the leaves surrounding the nest.
Mimesis is also employed by some predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
and parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s to lure their prey. For example, a flower mantis
Flower mantises are praying mantis species that use a special form of camouflage referred to as aggressive mimicry, which they not only use to attract prey, but avoid predators as well. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that ...
mimics a particular kind of flower, such as an orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowerin ...
. This tactic has occasionally been used in warfare, for example with heavily armed Q-ship
Q-ships, also known as Q-boats, decoy vessels, special service ships, or mystery ships, were heavily armed merchant ships with concealed weaponry, designed to lure submarines into making surface attacks. This gave Q-ships the chance to open f ...
s disguised as merchant ships.
The common cuckoo
The common cuckoo (''Cuculus canorus'') is a member of the cuckoo order of birds, Cuculiformes, which includes the roadrunners, the anis and the coucals.
This species is a widespread summer migrant to Europe and Asia, and winters in Africa. I ...
, a brood parasite, provides examples of mimesis both in the adult and in the egg. The female lays her eggs in nests of other, smaller species of bird, one per nest. The female mimics a sparrowhawk
Sparrowhawk (sometimes sparrow hawk) may refer to several species of small hawk in the genus ''Accipiter''. "Sparrow-hawk" or sparhawk originally referred to ''Accipiter nisus'', now called "Eurasian" or "northern" sparrowhawk to distinguish it f ...
. The resemblance is sufficient to make small birds take action to avoid the apparent predator. The female cuckoo then has time to lay her egg in their nest without being seen to do so. The cuckoo's egg itself mimics the eggs of the host species, reducing its chance of being rejected.
Peppered moth
The peppered moth (''Biston betularia'') is a temperate species of night-flying moth. It is mostly found in the northern hemisphere in places like Asia, Europe and North America. Peppered moth evolution is an example of population genetics an ...
caterpillars mimic twigs
File:Insect camouflage PP08338.png, Flower mantis
Flower mantises are praying mantis species that use a special form of camouflage referred to as aggressive mimicry, which they not only use to attract prey, but avoid predators as well. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that ...
lures its insect prey by mimicking a ''Phalaenopsis
''Phalaenopsis'' (), also known as moth orchids, is a genus of about seventy species of plants in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are monopodial epiphytes or lithophytes with long, coarse roots, short, leafy stems and long-lasti ...
'' orchid blossom
File:Hooded Grasshopper (Teratodus monticollis) W IMG 0525.jpg, Hooded grasshopper ''Teratodus monticollis'', superbly mimics a leaf with a bright orange border
File:Gumleaf grasshopper.jpg, This grasshopper hides from predators by mimicking a dry leaf
File:IWM-E-18461-Crusader-camouflaged-19421026.jpg, WWII tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
concealed in Operation Bertram
Operation Bertram was a Second World War deception operation practised by the Allied forces in Egypt led by Bernard Montgomery, in the months before the Second Battle of El Alamein in 1942. Bertram was devised by Dudley Clarke to deceive Erwin ...
by mimicking a truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
File:HMS President - geograph.org.uk - 659583.jpg, Armed WW1 Q-ship
Q-ships, also known as Q-boats, decoy vessels, special service ships, or mystery ships, were heavily armed merchant ships with concealed weaponry, designed to lure submarines into making surface attacks. This gave Q-ships the chance to open f ...
lured enemy submarines by mimicking a merchantman
File:European Cuckoo Mimics Sparrowhawk.jpg, Cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes . The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals and anis. The coucals and anis are sometimes separ ...
adult mimics sparrowhawk
Sparrowhawk (sometimes sparrow hawk) may refer to several species of small hawk in the genus ''Accipiter''. "Sparrow-hawk" or sparhawk originally referred to ''Accipiter nisus'', now called "Eurasian" or "northern" sparrowhawk to distinguish it f ...
, giving female time to lay eggs parasitically
File:Cuckoo Eggs Mimicking Reed Warbler Eggs.JPG, Cuckoo eggs mimicking smaller eggs, in this case of reed warbler
The ''Acrocephalus'' warblers are small, insectivorous passerine birds belonging to the genus ''Acrocephalus''. Formerly in the paraphyletic Old World warbler assemblage, they are now separated as the namesake of the marsh and tree warbler f ...
File:Wrap-around spider in the genus Dolophones (Family Araneidae) Camouflage View.JPG, Wrap-around spider ''Dolophones'' mimicking a stick
Motion dazzle
 Most forms of camouflage are made ineffective by movement: a deer or grasshopper may be highly cryptic when motionless, but instantly seen when it moves. But one method, motion dazzle, requires rapidly moving bold patterns of contrasting stripes. Motion dazzle may degrade predators' ability to estimate the prey's speed and direction accurately, giving the prey an improved chance of escape. Motion dazzle distorts speed perception and is most effective at high speeds; stripes can also distort perception of size (and so, perceived range to the target). As of 2011, motion dazzle had been proposed for military vehicles, but never applied. Since motion dazzle patterns would make animals more difficult to locate accurately when moving, but easier to see when stationary, there would be an evolutionary trade-off between motion dazzle and crypsis.
An animal that is commonly thought to be dazzle-patterned is the
Most forms of camouflage are made ineffective by movement: a deer or grasshopper may be highly cryptic when motionless, but instantly seen when it moves. But one method, motion dazzle, requires rapidly moving bold patterns of contrasting stripes. Motion dazzle may degrade predators' ability to estimate the prey's speed and direction accurately, giving the prey an improved chance of escape. Motion dazzle distorts speed perception and is most effective at high speeds; stripes can also distort perception of size (and so, perceived range to the target). As of 2011, motion dazzle had been proposed for military vehicles, but never applied. Since motion dazzle patterns would make animals more difficult to locate accurately when moving, but easier to see when stationary, there would be an evolutionary trade-off between motion dazzle and crypsis.
An animal that is commonly thought to be dazzle-patterned is the zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebr ...
. The bold stripes of the zebra have been claimed to be disruptive camouflage, background-blending and countershading. After many years in which the purpose of the coloration was disputed, an experimental study by Tim Caro Timothy M. Caro (born 1951) is a British evolutionary ecologist known for his work on conservation biology, animal behaviour, anti-predator defences in animals, and the function of zebra stripes. He is the author of several textbooks on these su ...
suggested in 2012 that the pattern reduces the attractiveness of stationary models to biting flies such as horseflies and tsetse flies
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies), are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glos ...
. However, a simulation study by Martin How and Johannes Zanker in 2014 suggests that when moving, the stripes may confuse observers, such as mammalian predators and biting insects, by two visual illusion
Within visual perception, an optical illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; the ...
s: the wagon-wheel effect
The wagon-wheel effect (alternatively called stagecoach-wheel effect or stroboscopic effect) is an optical illusion in which a spoked wheel appears to rotate differently from its true rotation. The wheel can appear to rotate more slowly than the ...
, where the perceived motion is inverted, and the barberpole illusion, where the perceived motion is in a wrong direction.
Applications
Military
Before 1800
 Ship camouflage was occasionally used in ancient times.
Ship camouflage was occasionally used in ancient times. Philostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostratus (; grc-gre, Φιλόστρατος ; c. 170 – 247/250 AD), called "the Athenian", was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. His father was a minor sophist of the same name. He was born probab ...
() wrote in his '' Imagines'' that Mediterranean pirate ships could be painted blue-gray for concealment. Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
() says that "Venetian blue" (sea green) was used in the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
, when Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
sent his ''speculatoria navigia'' (reconnaissance boats) to gather intelligence along the coast of Britain; the ships were painted entirely in bluish-green wax, with sails, ropes and crew the same colour. There is little evidence of military use of camouflage on land before 1800, but two unusual ceramics show men in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
's Mochica culture from before 500 AD, hunting birds with blowpipes which are fitted with a kind of shield near the mouth, perhaps to conceal the hunters' hands and faces. Another early source is a 15th-century French manuscript, ''The Hunting Book of Gaston Phebus'', showing a horse pulling a cart which contains a hunter armed with a crossbow under a cover of branches, perhaps serving as a hide for shooting game. Jamaican Maroons
Jamaican Maroons descend from Africans who freed themselves from slavery on the Colony of Jamaica and established communities of free black people in the island's mountainous interior, primarily in the eastern parishes. Africans who were ensl ...
are said to have used plant materials as camouflage in the First Maroon War
The First Maroon War was a conflict between the Jamaican Maroons and the colonial British authorities that started around 1728 and continued until the peace treaties of 1739 and 1740. It was led by self-liberated Africans who set up communities i ...
().
19th-century origins
 The development of military camouflage was driven by the increasing range and accuracy of infantry firearms in the 19th century. In particular the replacement of the inaccurate musket with weapons such as the
The development of military camouflage was driven by the increasing range and accuracy of infantry firearms in the 19th century. In particular the replacement of the inaccurate musket with weapons such as the Baker rifle
The Baker rifle (officially known as the Pattern 1800 Infantry Rifle) was a flintlock rifle used by the rifle regiments of the British Army during the Napoleonic Wars. It was the first standard-issue, British-made rifle accepted by the British ...
made personal concealment in battle essential. Two Napoleonic War
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
skirmishing units of the British Army, the Rifle Brigade (Prince Consort's Own), 95th Rifle Regiment and the 60th Rifle Regiment, were the first to adopt camouflage in the form of a rifle green jacket, while the Line regiments continued to wear scarlet tunics. A contemporary study in 1800 by the English artist and soldier Charles Hamilton Smith provided evidence that grey uniforms were less visible than green ones at a range of 150 yards.
In the American Civil War, rifle units such as the 1st United States Sharp Shooters (in the Union (American Civil War), Federal army) similarly wore green jackets while other units wore more conspicuous colours. The first British Army unit to adopt khaki (colour), khaki uniforms was the Corps of Guides (British India), Corps of Guides at Peshawar, when Harry Burnett Lumsden, Sir Harry Lumsden and his second in command, William Stephen Raikes Hodson, William Hodson introduced a "drab" uniform in 1848. Hodson wrote that it would be more appropriate for the hot climate, and help make his troops "invisible in a land of dust". Later they improvised by dyeing cloth locally. Other regiments in India soon adopted the khaki uniform, and by 1896 khaki drill uniform was used everywhere outside Europe; by the Second Boer War six years later it was used throughout the British Army.
During the late 19th century camouflage was applied to British coastal fortifications. The fortifications around Plymouth, England were painted in the late 1880s in "irregular patches of red, brown, yellow and green." From 1891 onwards British coastal artillery was permitted to be painted in suitable colours "to harmonise with the surroundings" and by 1904 it was standard practice that artillery and mountings should be painted with "large irregular patches of different colours selected to suit local conditions."
First World War
 In the
In the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the French army formed a camouflage corps, led by Lucien-Victor Guirand de Scévola, employing artists known as ''List of camoufleurs, camoufleurs'' to create schemes such as tree observation posts and covers for guns. Other armies soon followed them. The term ''wikt:camouflage, camouflage'' probably comes from ''camoufler'', a Parisian slang term meaning ''to disguise'', and may have been influenced by ''camouflet'', a French language, French term meaning ''smoke blown in someone's face''. The English zoologist John Graham Kerr, artist Solomon J. Solomon and the American artist Abbott Thayer led attempts to introduce scientific principles of countershading and disruptive patterning into military camouflage, with limited success. In early 1916 the Royal Naval Air Service began to create dummy air fields to draw the attention of enemy planes to empty land. They created decoy homes and lined fake runways with flares, which were meant to help protect real towns from night raids. This strategy was not common practice and did not succeed at first, but in 1918 it caught the Germans off guard multiple times.
Ship camouflage was introduced in the early 20th century as the range of naval guns increased, with ships painted grey all over. In April 1917, when German U-boats were sinking many British ships with torpedoes, the marine artist Norman Wilkinson (artist), Norman Wilkinson devised dazzle camouflage, which paradoxically made ships more visible but harder to target. In Wilkinson's own words, dazzle was designed "not for low visibility, but in such a way as to break up her form and thus confuse a submarine officer as to the course on which she was heading".
Second World War
In theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the zoologist Hugh Cott, a protégé of Kerr, worked to persuade the British army to use more effective camouflage methods, including countershading, but, like Kerr and Thayer in the First World War, with limited success. For example, he painted two rail-mounted coastal guns, one in conventional style, one Countershading, countershaded. In aerial photographs, the countershaded gun was essentially invisible. The power of aerial observation and attack led every warring nation to camouflage targets of all types. The Soviet Union's Red Army created the comprehensive military doctrine, doctrine of ''Russian military deception, Maskirovka'' for military deception, including the use of camouflage. For example, during the Battle of Kursk, Mikhail Katukov, General Katukov, the commander of the Soviet 1st Tank Army, remarked that the enemy "did not suspect that our well-camouflaged tanks were waiting for him. As we later learned from prisoners, we had managed to move our tanks forward unnoticed". The tanks were concealed in previously prepared defensive emplacements, with only their turrets above ground level. In the air, Second World War fighters were often painted in ground colours above and sky colours below, attempting two different camouflage schemes for observers above and below. Bombers and night fighters were often black, while maritime reconnaissance planes were usually white, to avoid appearing as dark shapes against the sky. For ships, dazzle camouflage was mainly replaced with plain grey in the Second World War, though experimentation with colour schemes continued.
As in the First World War, artists were pressed into service; for example, the surrealist painter Roland Penrose became a lecturer at the newly founded Camouflage Development and Training Centre at Farnham Castle, writing the practical ''Home Guard Manual of Camouflage''. The film-maker Geoffrey Barkas ran the Middle East Command Camouflage Directorate during the 1941–1942 war in the Western Desert, including the successful deception of Operation Bertram
Operation Bertram was a Second World War deception operation practised by the Allied forces in Egypt led by Bernard Montgomery, in the months before the Second Battle of El Alamein in 1942. Bertram was devised by Dudley Clarke to deceive Erwin ...
. Hugh Cott was chief instructor; the artist camouflage officers, who called themselves ''camoufleurs'', included Steven Sykes (artist), Steven Sykes and Tony Ayrton. In Australia, artists were also prominent in the Sydney Camouflage Group, formed under the chairmanship of Professor William John Dakin, a zoologist from Sydney University. Max Dupain, Sydney Ure Smith, and William Dobell were among the members of the group, which worked at Bankstown Airport, RAAF Base Richmond and Garden Island Dockyard. In the United States, artists like John Vassos took a certificate course in military and industrial camouflage at the American School of Design with Baron Nicholas Cerkasoff, and went on to create camouflage for the Air Force.
snow camouflage
Snow camouflage is the use of a coloration or pattern for effective camouflage in winter, often combined with a different summer camouflage. Summer patterns are typically disruptively patterned combinations of shades of browns and greys, up to ...
overalls, January 1943
After 1945
Camouflage has been used to protect military equipment such as vehicles, guns, Ship camouflage, ships, Aircraft camouflage, aircraft and buildings as well as individual soldiers and their positions. Vehicle camouflage methods begin with paint, which offers at best only limited effectiveness. Other methods for stationary land vehicles include covering with improvised materials such as blankets and vegetation, and erecting nets, screens and soft covers which may suitably reflect, scatter or absorb near infrared andradar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
waves. Some military textiles and vehicle camouflage paints also reflect infrared to help provide concealment from image intensification, night vision devices.
After the Second World War, radar made camouflage generally less effective, though coastal boats are sometimes painted like land vehicles. Aircraft camouflage too came to be seen as less important because of radar, and aircraft of different air forces, such as the Royal Air Force's English Electric Lightning, Lightning, were often uncamouflaged.
Many List of camouflage patterns, camouflaged textile patterns have been developed to suit the need to match Battledress, combat clothing to different kinds of terrain (such as woodland, snow, and desert). The design of a pattern effective in all terrains has proved elusive. The American Universal Camouflage Pattern of 2004 attempted to suit all environments, but was withdrawn after a few years of service. Terrain-specific patterns have sometimes been developed but are ineffective in other terrains. The problem of making a pattern that works at different ranges has been solved with multiscale designs, often with a pixellated appearance and designed digitally, that provide a fractal-like range of patch sizes so they appear disruptively coloured both at close range and at a distance. The first genuinely digital camouflage pattern was the Canadian Disruptive Pattern (CADPAT), issued to the army in 2002, soon followed by the American Marine pattern (MARPAT). A pixellated appearance is not essential for this effect, though it is simpler to design and to print.