|
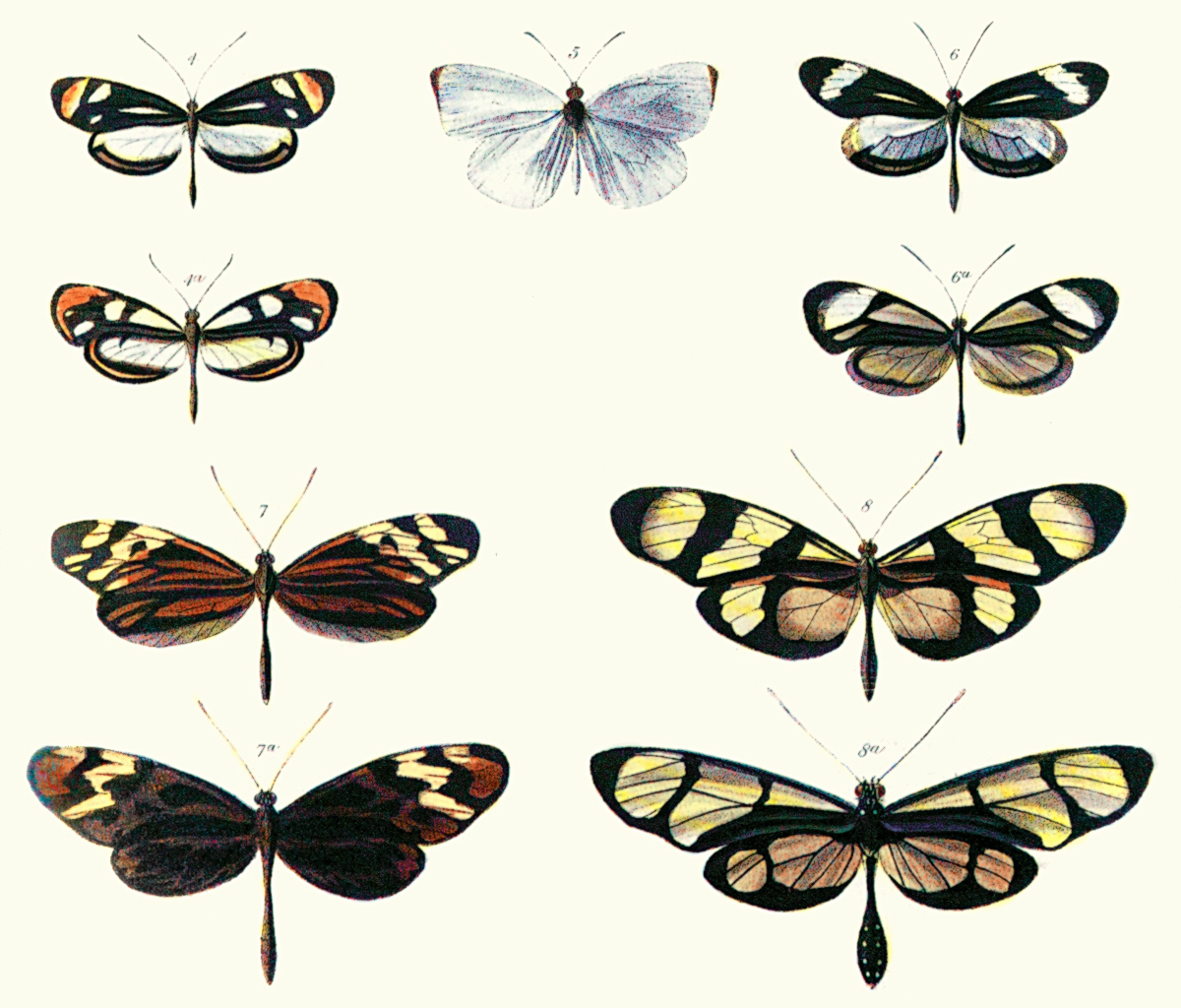
Distractive Markings
Distractive markings serve to camouflage animals or military vehicles by drawing the observer's attention away from the object as a whole, such as noticing its outline. This delays recognition. The markings necessarily have high contrast and are thus in themselves conspicuous. The mechanism therefore relies, as does camouflage as a whole, on deceiving the cognition of the observer, not in blending with the background. Distractive markings were first noticed by the American artist Abbott Handerson Thayer in 1909, but the mechanism was for a century confused with disruptive coloration, another mechanism for delaying recognition that also relies on conspicuous markings. Distractive markings however need to be small and to avoid outlines, to avoid drawing attention to them, whereas disruptive markings work best when they touch the outline, breaking it up. Distractive camouflage marks are sometimes called dazzle markings, but the mechanism differs from motion dazzle. History The Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubo Scandiacus Male Muskegon (cropped)
A bubo (Greek βουβών, ''boubṓn'', 'groin') is adenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes and is an example of reactive lymphadenopathy. Classification Buboes are a symptom of bubonic plague and occur as painful swellings in the thighs, neck, groin or armpits. They are caused by ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria spreading from flea bites through the bloodstream to the lymph nodes, where the bacteria replicate, causing the nodes to swell. Plague buboes may turn black and Necrosis, necrotic, rotting away the surrounding tissue, or they may rupture, discharging large amounts of pus. Infection can spread from buboes around the body, resulting in other forms of the disease such as pneumonic plague. Management Plague patients whose buboes swell to such a size that they burst tend to survive the disease. Before the discovery of antibiotics, doctors often Incision and drainage, drained buboes to save patients. Buboes are also symptoms of other diseases, such as chancroid and lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowy Owl
The snowy owl (''Bubo scandiacus''), also known as the polar owl, the white owl and the Arctic owl, is a large, white owl of the true owl family. Snowy owls are native to the Arctic regions of both North America and the Palearctic, breeding mostly on the tundra. It has a number of unique adaptations to its habitat and lifestyle, which are quite distinct from other extant owls. One of the largest species of owl, it is the only owl with mainly white plumage. Males tend to be a purer white overall while females tend to more have more extensive flecks of dark brown.Holt, D. W., M. D. Larson, N. Smith, D. L. Evans, and D. F. Parmelee (2020)Snowy Owl (''Bubo scandiacus'') version 1.0. In Birds of the World (S. M. Billerman, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. Juvenile male snowy owls have dark markings that may appear similar to females until maturity, at which point they typically turn whiter. The composition of brown markings about the wing, although not foolproof, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Cott
Hugh Bamford Cott (6 July 1900 – 18 April 1987) was a British zoologist, an authority on both natural and military camouflage, and a scientific illustrator and photographer. Many of his field studies took place in Africa, where he was especially interested in the Nile crocodile, the evolution of pattern and colour in animals. During the World War II, Second World War, Cott worked as a camouflage expert for the British Army and helped to influence War Office policy on camouflage. His book ''Adaptive Coloration in Animals'' (1940), popular among serving soldiers, was the major textbook on camouflage in zoology of the twentieth century. After the war, he became a Fellow of Selwyn College, Cambridge. As a Fellow of the Zoological Society of London, he undertook expeditions to Africa and the Amazon to collect specimens, mainly reptiles and amphibians. Life and career Cott was born in Ashby Magna, Leicestershire, England, on 6 July 1900; his father was the Rector (ecclesiastical), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Image
Prey detection is the process by which predators are able to detect and locate their prey via sensory signals. This article treats predation in its broadest sense, i.e. where one organism eats another. Evolutionary struggle and prey defenses Predators are in an evolutionary arms race with their prey, for which advantageous mutations are constantly preserved by natural selection. In turn, predators, too, are subject to such selective pressure, those most successful in locating prey passing on their genes in greater number to the next generation's gene pool. Adaptations of prey that allow them to avoid predators are widespread, those that make them hard to find being collectively known as crypsis. Crypsis may involve temporal evasion such as nocturnality, behavioral methods such as hiding, and non-behavioral adaptations such as camouflage. Antipredator adaptations include methods other than crypsis, such as aposematism and the ability to fight. Often behavioral and passive charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Spatial Attention
Visual spatial attention is a form of visual attention that involves directing attention to a location in space. Similar to its temporal counterpart visual temporal attention, these attention modules have been widely implemented in video analytics in computer vision to provide enhanced performance and human interpretable explanation of deep learning models. Spatial attention allows humans to selectively process visual information through prioritization of an area within the visual field. A region of space within the visual field is selected for attention and the information within this region then receives further processing. Research shows that when spatial attention is evoked, an observer is typically faster and more accurate at detecting a target that appears in an expected location compared to an unexpected location. Attention is guided even more quickly to unexpected locations, when these locations are made salient by external visual inputs (such as a sudden flash). According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Tit
The Eurasian blue tit (''Cyanistes caeruleus'') is a small passerine bird in the tit family, Paridae. It is easily recognisable by its blue and yellow plumage and small size. Eurasian blue tits, usually resident and non-migratory birds, are widespread and a common resident breeder throughout temperate and subarctic Europe and the western Palearctic in deciduous or mixed woodlands with a high proportion of oak. They usually nest in tree holes, although they easily adapt to nest boxes where necessary. Their main rival for nests and in the search for food is the larger and more common great tit. The Eurasian blue tit prefers insects and spiders for its diet. Outside the breeding season, they also eat seeds and other vegetable-based foods. The birds are famed for their acrobatic skills, as they can hold on to the outermost branches of trees and shrubs and hang upside down when looking for food. Taxonomy The Eurasian blue tit was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the 10th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masquerade (biology)
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innes Cuthill
Innes C. Cuthill (born 1960) is a professor of behavioural ecology at the University of Bristol. His main research interest is in camouflage, in particular how it evolves in response to the colour vision of other animals such as predators. Life Innes Cuthill was educated at University College School, London. He read zoology at the University of Cambridge, graduating in 1982 and gained his D.Phil. at the University of Oxford in 1985. He worked at Oxford until 1989 when he became a lecturer at the University of Bristol. He became a professor there in 1998 and was head of the School of Biological Sciences there from 2008 to 2012. He describes himself as "wear ngtwo hats, behavioural ecologist and sensory ecologist", unified by seeking to explain the "design, through natural selection, of animal form and function." He states that his main research interest is in the evolution of camouflage of one kind of animal, such as prey, in response to the colour vision of another kind of animal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disruptive Versus Distractive Camouflage Markings
Disruption, disruptive, or disrupted may refer to: Business *Creative disruption, disruption concept in a creative context, introduced in 1992 by TBWA's chairman Jean-Marie Dru *Disruptive innovation, Clayton Christensen's theory of industry disruption by new technology or products Psychology and sociology *Disruptive behavior disorders, a class of mental health disorders *Disruptive physician, a physician whose obnoxious behaviour upsets patients or other staff *Social disruption, a radical alteration, transformation, dysfunction or breakdown of social life Other uses *Cell disruption is a method or process in cell biology for releasing biological molecules from inside a cell *'' Disrupted: My Misadventure in the Start Up Bubble'', a 2016 book by Daniel Lyons *Disruption (adoption) is also the term for the cancellation of an adoption of a child before it is legally completed *Disruption (of schema), in the field of computer genetic algorithms *Disruption of 1843, the divergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Bunting
The snow bunting (''Plectrophenax nivalis'') is a passerine bird in the family Calcariidae. It is an Arctic specialist, with a circumpolar Arctic breeding range throughout the northern hemisphere. There are small isolated populations on a few high mountain tops south of the Arctic region, including the Cairngorms in central Scotland and the Saint Elias Mountains on the southern Alaska-Yukon border, as well as the Cape Breton Highlands. The snow bunting is the most northerly recorded passerine in the world. Taxonomy The snow bunting was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it with the buntings in the genus ''Emberiza'' and coined the binomial name ''Emberiza nivalis''. He specified the locality as Lapland. It is now placed in the genus ''Plectrophenax'' that was introduced in 1882 by the Norwegian born zoologist Leonhard Stejneger with the snow bunting as the type species. The genus name ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chameleons and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)