Cambuslang on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cambuslang ( sco, Cammuslang, from gd, Camas Lang) is a town on the south-eastern outskirts of
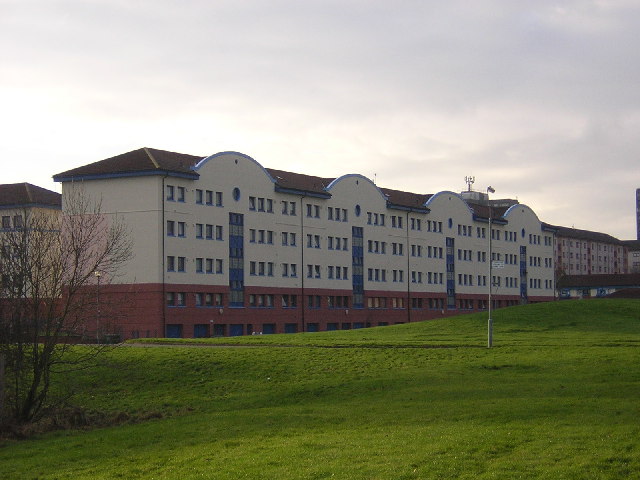
 Because of its relative prosperity, Cambuslang has been intimately concerned in the politics of the country (through the Hamilton connection) and of the local Church. Bishop John Cameron of Glasgow, and
Because of its relative prosperity, Cambuslang has been intimately concerned in the politics of the country (through the Hamilton connection) and of the local Church. Bishop John Cameron of Glasgow, and
South Lanarkshire Council were directly linked to similar movements in North America. The Scottish Enlightenment was well represented in the person of Rev Dr James Meek, the Minister. His troubles with his parishioners foreshadowed the split in the Church of Scotland during the 19th century. The manufacturing industries that grew up from the agricultural and mineral resources attracted immigrants from all over Scotland and Ireland and other European countries. Cambuslang benefited at all times from its closeness to the burgeoning city of Glasgow, brought closer in the 18th century by a
Edel Kenealy, Daily Record, 8 September 2016Shock stats show Rutherglen has more unemployment, highest rate of alcohol and drug admissions and more social work referrals than anywhere else in South Lanarkshire
Daily Record, 19 December 2018Rutherglen and Cambuslang areas among Scotland's poorest, according to Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation stats
Daily Record, 12 February 2020 *South Lanarkshire Council election results detailing local wards:
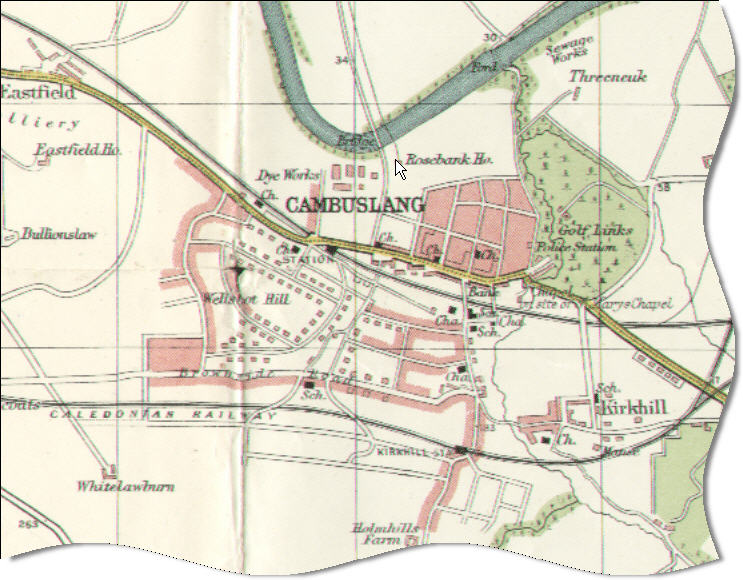
 Cambuslang is located on a lengthy bend on the
Cambuslang is located on a lengthy bend on the
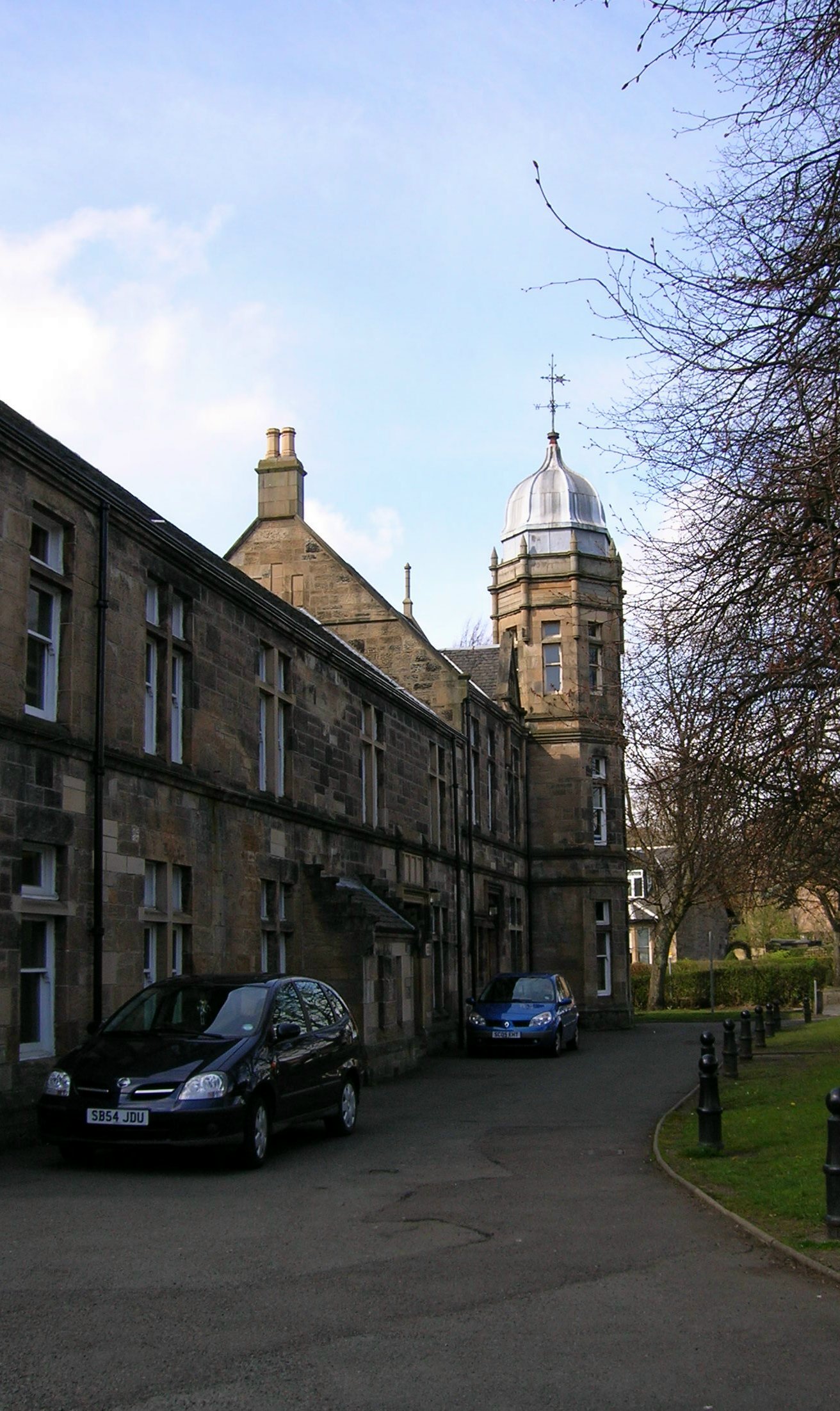 Cambuslang has an interesting range of churches, public buildings, schools, industrial and commercial buildings (see Buildings of Cambuslang). Its domestic buildings range from 19th-century mansions, villas and tenements to modern flats and detached houses, along with sheltered and nursing homes.
Cambuslang has an interesting range of churches, public buildings, schools, industrial and commercial buildings (see Buildings of Cambuslang). Its domestic buildings range from 19th-century mansions, villas and tenements to modern flats and detached houses, along with sheltered and nursing homes.
 Cambuslang College of the Building Trades was a specialist college established in the mid-twentieth century but it gradually expanded to teach other trades and academic subjects. It became Cambuslang College of Further Education in the 1960s, and went on to open a campus in East Kilbride, as well as facilities in Hamilton and Wishaw. A substantial annexe remained in Cambuslang on Hamilton Road, by now located in the former Gateside School. Reflecting its wider geographical coverage, it became South Lanarkshire College in 2000. In 2008, the Cambuslang campus closed and all South Lanarkshire College facilities were moved to a new, custom-built campus in East Kilbride.
South Lanarkshire College has links with University of the West of Scotland, Hamilton Campus, a degree-awarding higher education institution, away in Hamilton, so that local students can progress through to degrees.
As well as hosting the headquarters of the
Cambuslang College of the Building Trades was a specialist college established in the mid-twentieth century but it gradually expanded to teach other trades and academic subjects. It became Cambuslang College of Further Education in the 1960s, and went on to open a campus in East Kilbride, as well as facilities in Hamilton and Wishaw. A substantial annexe remained in Cambuslang on Hamilton Road, by now located in the former Gateside School. Reflecting its wider geographical coverage, it became South Lanarkshire College in 2000. In 2008, the Cambuslang campus closed and all South Lanarkshire College facilities were moved to a new, custom-built campus in East Kilbride.
South Lanarkshire College has links with University of the West of Scotland, Hamilton Campus, a degree-awarding higher education institution, away in Hamilton, so that local students can progress through to degrees.
As well as hosting the headquarters of the
 The original Cambuslang Public School can be seen on Greenlees Road, where it is now Greenlees Care Home. It had been for some time the Cambuslang College of the Building Trades, which became part of Cambuslang College (now South Lanarkshire College ). An even earlier school is now a Gospel Hall in Bushiehill Street.
The original Cambuslang Public School can be seen on Greenlees Road, where it is now Greenlees Care Home. It had been for some time the Cambuslang College of the Building Trades, which became part of Cambuslang College (now South Lanarkshire College ). An even earlier school is now a Gospel Hall in Bushiehill Street.
 The Cambuslang Subscription School of 1848 provided basic education to the children of miners and weavers in return for a few coppers. It was attractive to those who did not like the influence of the gentry and the minister on the parish school.
The Cambuslang Subscription School of 1848 provided basic education to the children of miners and weavers in return for a few coppers. It was attractive to those who did not like the influence of the gentry and the minister on the parish school.
 * Sir Thomas Lipton (1850–1931) of tea fame lived in the Johnstone Villa in Cambuslang, which was named after his mother's family.
* J. B. Lockhart
* Sir Thomas Lipton (1850–1931) of tea fame lived in the Johnstone Villa in Cambuslang, which was named after his mother's family.
* J. B. Lockhart
Views of Old Cambuslang
ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070724075703/http://stat-acc-scot.edina.ac.uk/stat-acc-scot/stat-acc-scot.asp The Statistical Accounts of Scotland
for an extract on Cambuslang from ''Rambles Round Glasgow'' by Hugh MacLelland
{{Authority control Towns in South Lanarkshire Civil parishes of Scotland Mining communities in Scotland
Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
, Scotland. With approximately 30,000 residents, it is the 27th largest town in Scotland by population, although, never having had a town hall, it may also be considered the largest village in Scotland. It is within the local authority area of South Lanarkshire
gd, Siorrachd Lannraig a Deas
, image_skyline =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms_slanarkshire.jpg
, image_blank_emblem = Slanarks.jpg
, blank_emblem_type = Council logo
, image_map ...
and directly borders the town of Rutherglen to the west. Historically, it was a large civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of Parish (administrative division), administrative parish used for Local government in England, local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below district ...
incorporating the nearby hamlets of Newton, Flemington, Westburn and Halfway
Halfway or Half Way may refer to:
Places Canada
*Halfway, New Brunswick, a community in Durham Parish
* Halfway, Ontario, a community in Madawaska Valley
Ireland
*Halfway, County Cork, a village in the Republic of Ireland
United Kingdom
* Halfwa ...
.
Cambuslang is located just south of the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
and about southeast of the centre of Glasgow. It has a long history of coal mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
, from at least 1490, iron and steel making, and ancillary engineering works, most recently The Hoover Company (in the town from 1946 to 2005). The Clydebridge Steelworks and other smaller manufacturing businesses continue but most employment in the area comes from the distribution or service industries. The headquarters of the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service
The Scottish Fire and Rescue Service (SFRS; gd, Seirbheis Smàlaidh agus Teasairginn na h-Alba) is the national fire and rescue service of Scotland. It was formed by the merger of eight regional fire services in the country on 1 April 2013. ...
is in Cambuslang.
History
The local geography of Cambuslang explains a great deal of its history. It has been very prosperous over time, depending first upon its agricultural land, (supplying food, thenwool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
...
, then linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
), then the mineral resources under its soil (limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
, and, to some extent, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
). These were jealously guarded by the medieval Church, and later by the local aristocracy, particularly the Duke of Hamilton
Duke of Hamilton is a title in the Peerage of Scotland, created in April 1643. It is the senior dukedom in that peerage (except for the Dukedom of Rothesay held by the Sovereign's eldest son), and as such its holder is the premier peer of Sc ...
(previously Barons of Cadzow and Earls of Arran Earl of Arran may refer to:
* Earl of Arran (Scotland), a title in the Peerage of Scotland
*Earl of Arran (Ireland)
Earl of Arran is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It is not to be confused with the title Earl of Arran in the Peerage of Sc ...
).

 Because of its relative prosperity, Cambuslang has been intimately concerned in the politics of the country (through the Hamilton connection) and of the local Church. Bishop John Cameron of Glasgow, and
Because of its relative prosperity, Cambuslang has been intimately concerned in the politics of the country (through the Hamilton connection) and of the local Church. Bishop John Cameron of Glasgow, and Cardinal Beaton
David Beaton (also Beton or Bethune; 29 May 1546) was Archbishop of St Andrews and the last Scottish cardinal prior to the Reformation.
Career
Cardinal Beaton was the sixth and youngest son of eleven children of John Beaton (Bethune) of Ba ...
, were both Rectors of Cambuslang. This importance continued following the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. From then until the Glorious Revolution a stream of Ministers of Cambuslang came, were expelled, or were re-instated, according to whether supporters of the King, Covenanters
Covenanters ( gd, Cùmhnantaich) were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland, and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. The name is derived from '' Covenan ...
, or Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
were in power. The religious movements of the 18th century, including the Cambuslang Wark,Local and family history: Cambuslang and King ArthurSouth Lanarkshire Council were directly linked to similar movements in North America. The Scottish Enlightenment was well represented in the person of Rev Dr James Meek, the Minister. His troubles with his parishioners foreshadowed the split in the Church of Scotland during the 19th century. The manufacturing industries that grew up from the agricultural and mineral resources attracted immigrants from all over Scotland and Ireland and other European countries. Cambuslang benefited at all times from its closeness to the burgeoning city of Glasgow, brought closer in the 18th century by a
turnpike road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
then, in the 19th century, by a railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
. In the 21st century, it continues to derive benefit from its proximity to Glasgow and to wider communication networks, particularly via the M74 motorway system. Its increasing (and increasingly diverse) population posed problems, over the centuries, of employment and housing as well as of schooling and health, not all of which have been solved; in this regard, it is fairly typical of most Scottish towns.
In sport, Cambuslang F.C.
Cambuslang Football Club was a Scottish football club, based in the Cambuslang area (Greater Glasgow). Cambuslang was one of the founding members of the Scottish Football League, but left the league after just two seasons.
History
The club ...
were founder members of the Scottish Football League whose most notable achievement was being the runners-up in the 1887–88 Scottish Cup
The 1887–88 Scottish Cup was the 15th season of Scotland's most prestigious football knockout competition. Renton won the competition for the second time after they beat Cambuslang 6–1 in the final. The result set a new record as the largest m ...
. They folded by the early 20th century, as did Scottish Junior Cup
The Scottish Junior Cup is an annual football competition organised by the Scottish Junior Football Association. The competition has been held every year since the inception of the SJFA in 1886 and, as of the 2022–23 edition, 108 teams compete ...
winners Cambuslang Hibernian
Cambuslang Hibernian F.C., also known as the Cambuslang Hibs, was a football club based in the town of Cambuslang, Scotland which was founded in 1884 and dissolved in 1908. They competed in regional competitions and the Scottish Cup during the ...
, but a new team Cambuslang Rangers F.C. was established and continues to this day – they enjoyed great success in the 1970s.
Governance
Westminster
Cambuslang is in the Rutherglen and Hamilton West Constituency for elections to theHouse of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buck ...
.
Gerard Killen
Gerard Killen (born 1 May 1986), known as Ged Killen, is a Scottish Labour and Co-operative politician who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Rutherglen and Hamilton West from 2017 to 2019.
Early life
Killen was born in Glasgow, living in ...
won the seat for the Scottish Labour and Co-operative Party in the June 2017 election, replacing Margaret Ferrier of the Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from ...
who had won in 2015. In the 2019 election, Ferrier re-gained the seat; following until an incident relating to a breach of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
regulations in October 2020, the SNP whip
A whip is a tool or weapon designed to strike humans or other animals to exert control through pain compliance or fear of pain. They can also be used without inflicting pain, for audiovisual cues, such as in equestrianism. They are generally ...
was withdrawn and she ignored calls to resign, continuing in office as an independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independe ...
.
Holyrood
Cambuslang was originally in the Glasgow Rutherglen Constituency for theScottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holy ...
at Holyrood. In 2011 the boundaries were redrawn and the new constituency renamed simply '' Rutherglen'', despite its boundaries taking in not only Cambuslang but also Blantyre.
In the 2016 elections, Clare Haughey won the seat for the SNP with 15,222 votes, giving a majority of 11.4%, replacing James Kelly who had been elected both in 2007
File:2007 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Steve Jobs unveils Apple's first iPhone; TAM Airlines Flight 3054 overruns a runway and crashes into a gas station, killing almost 200 people; Former Pakistani Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto ...
and 2011. Kelly remained in the Parliament as a 'list member' elected on a regional proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
basis.
South Lanarkshire Council
Administratively, the town centre is within the Cambuslang West ward of South Lanarkshire Council, which has a population of around 15,000. Taking another ward encompassing the eastern parts of the town into consideration, its overall population was approximately 30,000 in 2016. With neighbouring Rutherglen's figures being very similar, the many services and amenities shared between the towns should provide for 60,000 residents, many assessed as living in economic hardship.Rutherglen and Cambuslang communities at top of list of most deprived areas in ScotlandEdel Kenealy, Daily Record, 8 September 2016Shock stats show Rutherglen has more unemployment, highest rate of alcohol and drug admissions and more social work referrals than anywhere else in South Lanarkshire
Daily Record, 19 December 2018Rutherglen and Cambuslang areas among Scotland's poorest, according to Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation stats
Daily Record, 12 February 2020 *South Lanarkshire Council election results detailing local wards:
1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake strike ...
, 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school s ...
; 2003
File:2003 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The crew of STS-107 perished when the Space Shuttle Columbia Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, disintegrated during reentry into Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere; SARS became an 2002– ...
; 2007
File:2007 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Steve Jobs unveils Apple's first iPhone; TAM Airlines Flight 3054 overruns a runway and crashes into a gas station, killing almost 200 people; Former Pakistani Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto ...
; 2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gather ...
; 2017
File:2017 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The War Against ISIS at the Battle of Mosul (2016-2017); aftermath of the Manchester Arena bombing; The Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017 ("Great American Eclipse"); North Korea tests a ser ...
.
Geography

 Cambuslang is located on a lengthy bend on the
Cambuslang is located on a lengthy bend on the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
, south-east of Glasgow. The town is accessible from the nearby M74; the nearby A724 links to Glasgow city centre and Hamilton; the town is also accessible by car from East Kilbride
East Kilbride (; gd, Cille Bhrìghde an Ear ) is the largest town in South Lanarkshire in Scotland and the country's sixth-largest locality by population. It was also designated Scotland's first new town on 6 May 1947. The area lies on a raise ...
by the A725, A749 and then the B759. The town's railway station, Cambuslang, lies on the Argyle Line between central Glasgow and Lanark
Lanark (; gd, Lannraig ; sco, Lanrik) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Hamilton. The town lies on the River Clyde, at its confluence with Mouse Water. In 2016, the town had a population of 9 ...
.
The Reverend Dr John Robertson, Minister of Cambuslang Kirk, described the Parish in the Second Statistical Account of Scotland 1845. ''"It is bounded by the Clyde on the north, which separates it from the Parish of Old Monkland
Monklands (''Bad nam Manach'' in Scottish Gaelic) was, between 1975 and 1996, one of nineteen local government districts in the Strathclyde region of Scotland.
The district was formed by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 from:
*The burg ...
; by the Calder on the east, which separates it from Blantyre; by part of Blantyre and Kilbryde, on the south; and by Carmunnock and Rutherglen on the west."'' The highest points in this low-lying Parish are Dechmont Hill
Dechmont (Gaelic: ''Deagh Mhonadh'') is a small village located near Uphall, West Lothian in Scotland. Bangour Village Hospital is located to the west of Dechmont. It has an approximate population of 989 people. Its postal code is EH52. An alleg ...
(602 ft) and Turnlaw (or Turnlea) Hill (553 ft.) There are remains of an Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
fort on Dechmont.
Landmarks
Sites
Cambuslang Park spans encompassing the contrast of open parkland and the Borgie Glen, which is a steep tree-lined ravine, containing a complex network of pathways. The park also features a pond, sports pitches, war memorial (depicting a soldier in a kilt), woodland areas and the Bandstand, which is a natural amphitheatre, near where the famous Cambuslang Wark took place in the 18th century.Education
There is a range of schools in Cambuslang, and a history of further education colleges, although there are no longer any in the town.Primary schools
Primary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
s (''2022–23 pupil roll in parentheses'':
*Cairns Primary School (333)
*Hallside Primary School (254)
*James Aiton Primary School (148)
*Newton Farm Primary School (639)
*Park View Primary School (206)
*St Bride's Primary School (273)
*St Cadoc's Primary School (140)
*St Charles' Primary School (350)
* West Coats Primary School (409)
Secondary schools
*Cathkin High School
Cathkin High School is a state secondary school in Cambuslang, South Lanarkshire (Greater Glasgow), Scotland.
History
The original school was built at a cost of £1.25million and opened in November 1970 (official duties being performed by pol ...
(1006)
* Trinity High School (1186)
* Rutherglen High School (additional support needs) (110)
Some parts of Cambuslang are within the catchment area of Stonelaw High School, which is situated in Rutherglen, the adjoining town. Uddingston Grammar School, one train stop from Cambuslang on the Motherwell
Motherwell ( sco, Mitherwall, gd, Tobar na Màthar) is a town and former burgh in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, United Kingdom, south east of Glasgow. It has a population of around 32,120. Historically in the parish of Dalziel and part of Lana ...
via Bellshill line, includes Newton Farm Primary in its catchment.
Colleges
 Cambuslang College of the Building Trades was a specialist college established in the mid-twentieth century but it gradually expanded to teach other trades and academic subjects. It became Cambuslang College of Further Education in the 1960s, and went on to open a campus in East Kilbride, as well as facilities in Hamilton and Wishaw. A substantial annexe remained in Cambuslang on Hamilton Road, by now located in the former Gateside School. Reflecting its wider geographical coverage, it became South Lanarkshire College in 2000. In 2008, the Cambuslang campus closed and all South Lanarkshire College facilities were moved to a new, custom-built campus in East Kilbride.
South Lanarkshire College has links with University of the West of Scotland, Hamilton Campus, a degree-awarding higher education institution, away in Hamilton, so that local students can progress through to degrees.
As well as hosting the headquarters of the
Cambuslang College of the Building Trades was a specialist college established in the mid-twentieth century but it gradually expanded to teach other trades and academic subjects. It became Cambuslang College of Further Education in the 1960s, and went on to open a campus in East Kilbride, as well as facilities in Hamilton and Wishaw. A substantial annexe remained in Cambuslang on Hamilton Road, by now located in the former Gateside School. Reflecting its wider geographical coverage, it became South Lanarkshire College in 2000. In 2008, the Cambuslang campus closed and all South Lanarkshire College facilities were moved to a new, custom-built campus in East Kilbride.
South Lanarkshire College has links with University of the West of Scotland, Hamilton Campus, a degree-awarding higher education institution, away in Hamilton, so that local students can progress through to degrees.
As well as hosting the headquarters of the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service
The Scottish Fire and Rescue Service (SFRS; gd, Seirbheis Smàlaidh agus Teasairginn na h-Alba) is the national fire and rescue service of Scotland. It was formed by the merger of eight regional fire services in the country on 1 April 2013. ...
, the Scottish national training centre for firefighters is based in Cambuslang (having previously been located in Gullane, East Lothian
East Lothian (; sco, East Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area. The county was called Haddingtonshire until 1921.
In 1975, the hi ...
).
Early schools in Cambuslang
There has been a Parish school in Cambuslang at least since theReformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
, and probably before that. The schoolteacher was appointed and paid by the heritors, though he also charged fees. Free primary education came with the Education Act for Scotland (1871).
 The original Cambuslang Public School can be seen on Greenlees Road, where it is now Greenlees Care Home. It had been for some time the Cambuslang College of the Building Trades, which became part of Cambuslang College (now South Lanarkshire College ). An even earlier school is now a Gospel Hall in Bushiehill Street.
The original Cambuslang Public School can be seen on Greenlees Road, where it is now Greenlees Care Home. It had been for some time the Cambuslang College of the Building Trades, which became part of Cambuslang College (now South Lanarkshire College ). An even earlier school is now a Gospel Hall in Bushiehill Street.
Transport
There are three railway stations within the boundaries of Cambuslang - Cambuslang itself, on the Argyle Line section of theWest Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
, Kirkhill Kirkhill or Kirkhills may refer to a number of places.
In Canada:
*Kirkhill, Nova Scotia
*Kirkhill, Ontario
North Glengarry is a township in eastern Ontario, Canada, in the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry. It is a predominant ...
on the Newton branch of the Cathcart Circle
The Cathcart Circle Lines form a mostly suburban railway route linking Glasgow (Central) to Cathcart via a circular line, with branches to Newton and Neilston, on the south bank of the River Clyde. They are part of the Strathclyde Partnership ...
, and Newton, which is situated at a junction serving all of the aforementioned lines. Several bus routes pass through Cambuslang, with First Bus Glasgow currently operating most services between Lanarkshire and Glasgow. Several private hire taxi firms currently operate out of Cambuslang too.
National Cycle Route 75 passes through Cambuslang and extensive cycle lanes were added to the Main Street ( A724) in 2016, although these were to prove controversial.
Notable natives/residents
Cadoc
StCadoc
Saint Cadoc or Cadog ( lat-med, Cadocus; also Modern Welsh: Cattwg; born or before) was a 5th–6th-century Abbot of Llancarfan, near Cowbridge in Glamorgan, Wales, a monastery famous from the era of the British church as a centre of lear ...
(c 497 – c 580), also called "''Cadow''" or "''Cattwg''", reputedly founded a monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
on the site of the present ''Old Parish Church'' in the later sixth century. He is the patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholic Church, Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocacy, advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, ...
of Cambuslang, where there is a modern primary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
named after him. His feast day is 25 September. In medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
times, ''Cadoc'' was called on for help by (among others) deaf
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written ...
people and those suffering from cramp
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity; while generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the af ...
.
He was a Celtic saint – previously, a Prince of Glamorgan – who brought succour to the native Christians against the invading Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
. Cambuslang is at the northernmost reach of the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
speaking Brythons, so he may well have visited here in his wanderings, or in an effort to secure help against the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
. He had travelled to Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, to Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
(to visit the Welsh-speaking monks there), Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
(the centre of Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Y� ...
) and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
(from where he brought back two altar stones that had touched the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
.
The Europe he walked through was being battered by the barbarian invasions, so it is not improbable that he managed to reach Cambuslang. However, as no mention is made in the legends of an expedition this far north, it might have been a disciple, or a pilgrim
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of ...
returning from Glamorgan with a relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tang ...
, who established the church at Cambuslang. Cadoc was cut down, while serving Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
, by a Saxon raiding party at "''Benevenna''", most probably near Weedon Bec, Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It is ...
.
St Cadoc was prestigious enough in his lifetime for local chiefs to have recourse to him to settle disputes. This reputation lasted well into the Middle Ages, where solemn bonds and oaths were sworn over his (or his followers') remains. Just before the Reformation, a wealthy Cambuslang notable expressed in his will a desire to be interred "''with the ashes of St Cadoc''", in the Parish Kirk.
David Dale
David Dale (1739–1806) was a Scottish industrialist and philanthropist. His efforts to establish a cotton-spinning factory at Flemington failed but he was very successful as co-founder of the New Lanark Mills in 1786. Dale owned the estate of Rosebank in Cambuslang, which he used as a summer retreat from his townhouse (reputedly still standing) in Charlotte Street Glasgow and to where he retired and lived until his death. The estate was sold after his death to theCaledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh an ...
Company, which divided it in two to accommodate the new railway. The half to the north of the railway line, including Rosebank House, eventually became Rosebank Industrial Estate. The southern half was sold to Thomas Gray Buchanan, a Glasgow merchant, related to the Buchanan who established Buchanan Street in Glasgow, who established a country retreat at Wellshott House, but his son Michael sold off the lands to build suburban villas in the 1860s.
James Meek
Rev Dr James Meek (1739–1810) was Minister of Cambuslang from 1774 until his death. He had been Dean of the Chapel atGlasgow University
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
, when the Rector was Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January New Style">NS/nowiki> 1729 – 9 July 1797) was an Anglo-Irish people">Anglo-Irish Politician">statesman, economist, and philosopher. Born in Dublin, Burke served as a member of Parliament (MP) between 1766 and 1794 ...
and the professors included the philosopher Thomas Reid
Thomas Reid (; 7 May ( O.S. 26 April) 1710 – 7 October 1796) was a religiously trained Scottish philosopher. He was the founder of the Scottish School of Common Sense and played an integral role in the Scottish Enlightenment. In 1783 he w ...
. He was Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
The Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the minister or elder chosen to moderate (chair) the annual General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, which is held for a week in Edinburgh every year. After chairing the Asse ...
in 1795. He wrote the entry for Cambuslang in the First Statistical Account of Scotland. The cool, objective account in his report of the Cambuslang Wark remains the prime historical source for that event. He kept a detailed "''Journal and Register of the Weather''..." for each day over 29 years, with remarks on weather and events throughout Britain and the world. This Journal is still quoted in modern histories of the weather. He is buried in the ''Old Parish Church'' kirkyard, just inside the gate.
Other notable persons
* David Beaton (c. 1494–1546) was Rector of Cambuslang from 1520. He was appointed to this post by his uncle, James Beaton,Archbishop of Glasgow
The Archbishop of Glasgow is an archiepiscopal title that takes its name after the city of Glasgow in Scotland. The position and title were abolished by the Church of Scotland in 1689; and, in the Scottish Episcopal Church, it is now part of th ...
, and was a prebendary, which means he lived off the tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more ...
s and never lived there, leaving the work of a parish priest to a vicar.
* Claudius Buchanan
Claudius Buchanan FRSE (12 March 1766 – 9 February 1815) was a Scottish theologian, an ordained minister of the Church of England, and an evangelical missionary for the Church Missionary Society. He served as Vice Provost of the College of Ca ...
(1766–1815), Scottish theologian, an ordained minister of the Church of England, and an evangelical missionary to India.
* Sir George Burns
Sir George Burns, 1st Baronet (10 December 1795 – 2 June 1890) was a Scottish shipping magnate.
Burns was born in Glasgow, the son of Rev John Burns (1744–1839), a Presbyterian minister. George was the younger brother of James Burns ( ...
(1795–1890), shipping magnate and co-founder of the Cunard Line
Cunard () is a British shipping and cruise line based at Carnival House at Southampton, England, operated by Carnival UK and owned by Carnival Corporation & plc. Since 2011, Cunard and its three ships have been registered in Hamilton, Ber ...
resided at Rosebank House.
* Robert Crawford (1959–), Scottish poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems ( oral or wr ...
and Professor of Modern Scottish Literature at St Andrews University, and wrote a poem called "Cambuslang".
* William de Cambuslang (died 1361), Bishop of Dunblane (1347–1361).
* John Dunlop (1755–1820), one-time Lord Provost of Glasgow resided at Rosebank House.
* John Colin Dunlop (1785–1842), historian and son of John Dunlop, also lived at Rosebank House.
* Robert Fleming the elder (1630–1694), Presbyterian minister at Cambuslang and Rotterdam.
* Sammy Gilmore (1939–2011), shipyard trade-unionist; most notably a leader of the Upper Clyde Shipbuilders work-in in 1971.
* Duncan Munro Glen (1933–2008), prolific poet and historian, Emeritus Professor of Visual Communication at Nottingham Trent University
Nottingham Trent University (NTU) is a public research university in Nottingham, England. It was founded as a new universities, new university in 1992, although its roots go back to 1843 with the establishment of the Nottingham School of Desi ...
.
* William Hamilton of Gilbertfield (1665–1751), wrote a metrical abridgement, in 18th-century Scots
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
* Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland
* Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland
* Scoti, a Latin na ...
, of Blind Harry's poem '' The Actes and Deidis of the Illustre and Vallyeant Campioun Schir William Wallace'' on Sir William Wallace, whose 17th-century castle remains, though in ruins. He corresponded with Allan Ramsay Allan Ramsay may refer to:
*Allan Ramsay (poet) or Allan Ramsay the Elder (1686–1758), Scottish poet
*Allan Ramsay (artist) or Allan Ramsay the Younger (1713–1784), Scottish portrait painter
*Allan Ramsay (diplomat) (1937–2022), British diplom ...
and his poetry was praised in an epistle by Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who ha ...
– where he referred to him as "Gilbertfield".
* Scott Harrison (1977–), World Boxing Organisation featherweight champion for 2002.
* John Claudius Loudon (1783–1843), a famous gardener (or rather "''horticultural writer, dendrologist and designer''"), wrote the ''Encyclopaedia of Gardening'' (1822), and invented a flexible iron-bar sash which made possible such monumental greenhouses as the Palm House at Kew Gardens and the Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibitors from around ...
.
* Jimmy Jackson (1875–c. 1914), Scottish-Australian footballer.
* Robin Jenkins
John Robin Jenkins (11 September 1912 – 24 February 2005) was a Scottish writer of thirty published novels, the most celebrated being '' The Cone Gatherers''. He also published two collections of short stories.
Career
Robin Jenkins was bo ...
(1912–2005), novelist.
 * Sir Thomas Lipton (1850–1931) of tea fame lived in the Johnstone Villa in Cambuslang, which was named after his mother's family.
* J. B. Lockhart
* Sir Thomas Lipton (1850–1931) of tea fame lived in the Johnstone Villa in Cambuslang, which was named after his mother's family.
* J. B. Lockhart FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This so ...
(1886-1969) mathematician and educator.
* The Rt Rev David Lunan
David Ward Lunan is a Church of Scotland minister. On 30 October 2007 he was nominated to be the Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland for 2008-9, formally being elected as Moderator on the first day of the Assembly (15 May ...
(1944–), Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland (effective 2008).
* Mick McGahey
Michael McGahey (29 May 1925 – 30 January 1999) was a Scottish miners' leader and Communist. He had a distinctive gravelly voice, and described himself as "a product of my class and my movement".
Early life
His father, John McGahey, worked ...
(1925–1999), miners' leader.
* Sir Ian Alexander McGregor (1922–2007), malariologist who led British research in tropical medicine at the ''MRC Laboratories'' in the Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
.
* John McWhan
John McWhan FRSE (1885-1943) was a Scottish mathematician and academic. His academic range included electrical engineering.
Life
He was born in Cambuslang on 22 January 1885 the son of Maggie and John McWhan, headmaster of the local school. He was ...
FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This so ...
(1885–1943), mathematician and educator
* Dr David Forbes Martyn (1906–1970), physicist and radiographer, contributing to the development of coastal and air defence radar for Australia during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
* Brendan O'Hare
Brendan O'Hare (born 16 January 1970) is a Scottish multi-instrumentalist musician, primarily known for being the drummer in the rock band Teenage Fanclub from 1989 until early 1994, and a member of and collaborator with Mogwai.
Career
O'Hare ...
(1970–), musician.
* Dorothy Carleton Smyth (1880–1933), Scottish artist and an active supporter of the Woman's Suffrage Campaign.
* Martin Stepek (1959–), writer.
* Midge Ure
James Ure (born 10 October 1953) is a Scottish musician, singer-songwriter and record producer. His stage name, Midge, is a phonetic reversal of Jim, the diminutive form of his actual name. Ure enjoyed particular success in the 1970s and 1980 ...
(1953–), pop-singer and anti-hunger campaigner ( Band Aid and Live 8).
* Air Vice-Marshal John B. Wallace, Deputy Director-General of Medical Services, Royal Air Force from 1961-66.
* Mike Watson (1949–), previously a Labour life peer as Lord Watson of Invergowrie, was given a 16-month prison sentence in 2005 for wilful fire-raising. Though born in Cambuslang in 1949, Watson moved early to Invergowrie near Dundee.
* Robert Wilson (1907–1964), opera and concert singer (D'Oyly Carte Opera Company
The D'Oyly Carte Opera Company is a professional British light opera company that, from the 1870s until 1982, staged Gilbert and Sullivan's Savoy operas nearly year-round in the UK and sometimes toured in Europe, North America and elsewhere. T ...
) and recording artist (Parlophone
Parlophone Records Limited (also known as Parlophone Records and Parlophone) is a German–British record label founded in Germany in 1896 by the Carl Lindström Company as Parlophon. The British branch of the label was founded on 8 August 19 ...
and HMV).
See also
*Routes To Work South
Routes to Work South is a welfare-to-work subcontractor based in South Lanarkshire, Scotland. South Lanarkshire residents are often referred to the organisation by their local Job Centre, but individuals are also 'encouraged' to contact it themse ...
References
Bibliography
* Glen, Duncan ''A nation in a parish: A new historical prospect of Scotland from the parish of Cambuslang'' AKROS Publications Kirkcaldy (1995) * Glen, Duncan Munro ''New History of Cambuslang'' AKROS Publications Kirkcaldy (1998) * * Groome, Francis H. (1903). ''Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland: A Survey of Scottish Topography, Statistical, Biographical and Historical'', * * Magnusson, Magnus (1990). ''Chambers Biographical Dictionary'' W & R Chambers Ltd * * * * Williamson, Elizabeth; Riches, Anne; Higgs, Malcolm (1990). ''The Buildings of Scotland – Glasgow''. Penguin Books. . * Wilson, James Alexander OBE, MD ''A History of Cambuslang: a Clydesdale parish''. Jackson Wylie & Co Glasgow (1929)External links
Views of Old Cambuslang
ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070724075703/http://stat-acc-scot.edina.ac.uk/stat-acc-scot/stat-acc-scot.asp The Statistical Accounts of Scotland
for an extract on Cambuslang from ''Rambles Round Glasgow'' by Hugh MacLelland
{{Authority control Towns in South Lanarkshire Civil parishes of Scotland Mining communities in Scotland