Caldera (band) Albums on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
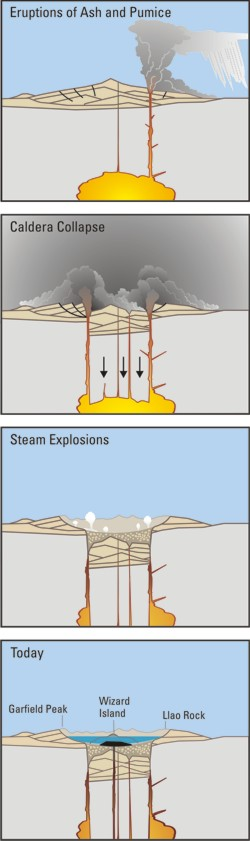 A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a
 A collapse is triggered by the emptying of the magma chamber beneath the volcano, sometimes as the result of a large explosive
A collapse is triggered by the emptying of the magma chamber beneath the volcano, sometimes as the result of a large explosive
 Some calderas are known to host rich ore deposits. Metal-rich fluids can circulate through the caldera, forming hydrothermal ore deposits of metals such as lead, silver, gold, mercury, lithium, and uranium. One of the world's best-preserved mineralized calderas is the Sturgeon Lake Caldera in
Some calderas are known to host rich ore deposits. Metal-rich fluids can circulate through the caldera, forming hydrothermal ore deposits of metals such as lead, silver, gold, mercury, lithium, and uranium. One of the world's best-preserved mineralized calderas is the Sturgeon Lake Caldera in
crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
*Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
*Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surfac ...
, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
, as it is formed through subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. Hi ...
, Hawaii in 2018.
Etymology
The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', andLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
', meaning "cooking pot". In some texts the English term ''cauldron'' is also used, though in more recent work the term ''cauldron'' refers to a caldera that has been deeply eroded to expose the beds under the caldera floor. The term ''caldera'' was introduced into the geological vocabulary by the German geologist Leopold von Buch when he published his memoirs of his 1815 visit to the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, where he first saw the Las Cañadas caldera on Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of Janu ...
, with Mount Teide
Teide, or Mount Teide, ( es, El Teide, Pico del Teide, , "Peak of Teide") is a volcano on Tenerife in the Canary Islands, Spain. Its summit (at ) is the highest point in Spain and the highest point above sea level in the islands of the Atlan ...
dominating the landscape, and then the Caldera de Taburiente on La Palma.
Caldera formation

 A collapse is triggered by the emptying of the magma chamber beneath the volcano, sometimes as the result of a large explosive
A collapse is triggered by the emptying of the magma chamber beneath the volcano, sometimes as the result of a large explosive volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
(see Tambora in 1815), but also during effusive eruptions on the flanks of a volcano (see Piton de la Fournaise
Piton de la Fournaise (; en, "Peak of the Furnace") is a shield volcano on the eastern side of Réunion island (a French overseas department and region) in the Indian Ocean. It is currently one of the most active volcanoes in the world, along ...
in 2007) or in a connected fissure system (see Bárðarbunga in 2014–2015). If enough magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
is ejected, the emptied chamber is unable to support the weight of the volcanic edifice above it. A roughly circular fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
, the "ring fault", develops around the edge of the chamber. Ring fractures serve as feeders for fault intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s which are also known as ring dikes. Secondary volcanic vents may form above the ring fracture. As the magma chamber empties, the center of the volcano within the ring fracture begins to collapse. The collapse may occur as the result of a single cataclysmic eruption, or it may occur in stages as the result of a series of eruptions. The total area that collapses may be hundreds of square kilometers.
Mineralization in calderas
 Some calderas are known to host rich ore deposits. Metal-rich fluids can circulate through the caldera, forming hydrothermal ore deposits of metals such as lead, silver, gold, mercury, lithium, and uranium. One of the world's best-preserved mineralized calderas is the Sturgeon Lake Caldera in
Some calderas are known to host rich ore deposits. Metal-rich fluids can circulate through the caldera, forming hydrothermal ore deposits of metals such as lead, silver, gold, mercury, lithium, and uranium. One of the world's best-preserved mineralized calderas is the Sturgeon Lake Caldera in northwestern Ontario
Northwestern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north and west of Lake Superior and west of Hudson Bay and James Bay. It includes most of subarctic Ontario. Its western boundary is the ...
, Canada, which formed during the Neoarchean era
An era is a span of time defined for the purposes of chronology or historiography, as in the regnal eras in the history of a given monarchy, a calendar era used for a given calendar, or the geological eras defined for the history of Earth.
Compa ...
about 2.7 billion years ago. In the San Juan volcanic field
The San Juan volcanic field is part of the San Juan Mountains in southwestern Colorado. It consists mainly of volcanic rocks that form the largest remnant of a major composite volcanic field that covered most of the southern Rocky Mountains in t ...
, ore veins were emplaced in fractures associated with several calderas, with the greatest mineralization taking place near the youngest and most silicic intrusions associated with each caldera.
Types of caldera
Explosive caldera eruptions
Explosive caldera eruptions are produced by a magma chamber whosemagma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
is rich in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
. Silica-rich magma has a high viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, and therefore does not flow easily like basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
. The magma typically also contains a large amount of dissolved gases, up to 7 wt% for the most silica-rich magmas. When the magma approaches the surface of the Earth, the drop in confining pressure
Pressure is force magnitude applied over an area. Overburden pressure is a geology term that denotes the pressure caused by the weight of the overlying layers of material at a specific depth under the earth's surface. Overburden pressure is also ca ...
causes the trapped gases to rapidly bubble out of the magma, fragmenting the magma to produce a mixture of volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcano, volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used t ...
and other tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they rem ...
with the very hot gases.
The mixture of ash and volcanic gases initially rises into the atmosphere as an eruption column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated ash and tephra suspended in gases emitted during an explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or plume that may rise many kilometers into the air a ...
. However, as the volume of erupted material increases, the eruption column is unable to entrain enough air to remain buoyant, and the eruption column collapses into a tephra fountain that falls back to the surface to form pyroclastic flows. Eruptions of this type can spread ash over vast areas, so that ash flow tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock cont ...
s emplaced by silicic caldera eruptions are the only volcanic product with volumes rivaling those of flood basalts. For example, when Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corn ...
last erupted some 650,000 years ago, it released about 1,000 km3 of material (as measured in dense rock equivalent (DRE)), covering a substantial part of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
in up to two metres of debris.
Eruptions forming even larger calderas are known, such as the La Garita Caldera
La Garita Caldera is a large caldera in the San Juan volcanic field in the San Juan Mountains near the town of Creede in southwestern Colorado, United States.
It is west of La Garita, Colorado. The eruption that created the La Garita Caldera ...
in the San Juan Mountains of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, where the Fish Canyon Tuff
The Fish Canyon Tuff is the large volcanic ash flow or ignimbrite deposit resulting from one of the largest known Explosive eruption, explosive eruptions on Earth, estimated at . (see List of largest volcanic eruptions). The Fish Canyon Tuff erupti ...
was blasted out in eruptions about 27.8 million years ago.
The caldera produced by such eruptions is typically filled in with tuff, rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
, and other igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main The three types of rocks, rock types, the others being Sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rock ...
s. The caldera is surrounded by an outflow sheet of ash flow tuff (also called an ash flow sheet).
If magma continues to be injected into the collapsed magma chamber, the center of the caldera may be uplifted in the form of a ''resurgent dome
In geology, a resurgent dome is a dome formed by swelling or rising of a caldera floor due to movement in the magma chamber beneath it. Unlike a lava dome, a resurgent dome is not formed by the extrusion of highly viscous lava onto the surfac ...
'' such as is seen at the Valles Caldera, Lake Toba
Lake Toba ( id, Danau Toba) ( Toba Batak: ᯖᯀᯬ ᯖᯬᯅ; romanized: ''Tao Toba'') is a large natural lake in North Sumatra, Indonesia, occupying the caldera of a supervolcano. The lake is located in the middle of the northern part of the ...
, the San Juan volcanic field, Cerro Galán
Cerro is Spanish for "hill" or "mountain".
Toponyms
;Bolivia:
* Cerro Rico, the "Rich Mountain" containing silver ore near Potosi, Bolivia
;Brazil:
*Cerro Branco, a municipality of Rio Grande do Sul
*Cerro Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, a municipa ...
, Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
, and many other calderas.
Because a silicic caldera may erupt hundreds or even thousands of cubic kilometers of material in a single event, it can cause catastrophic environmental effects. Even small caldera-forming eruptions, such as Krakatoa in 1883 or Mount Pinatubo in 1991, may result in significant local destruction and a noticeable drop in temperature around the world. Large calderas may have even greater effects. The ecological effects of the eruption of a large caldera can be seen in the record of the Lake Toba
Lake Toba ( id, Danau Toba) ( Toba Batak: ᯖᯀᯬ ᯖᯬᯅ; romanized: ''Tao Toba'') is a large natural lake in North Sumatra, Indonesia, occupying the caldera of a supervolcano. The lake is located in the middle of the northern part of the ...
eruption in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
At some points in geological time
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
, rhyolitic calderas have appeared in distinct clusters. The remnants of such clusters may be found in places such as the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
Rum Complex of Scotland, the San Juan Mountains of Colorado (formed during the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
, Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
, and Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Saint Francois Mountain Range of
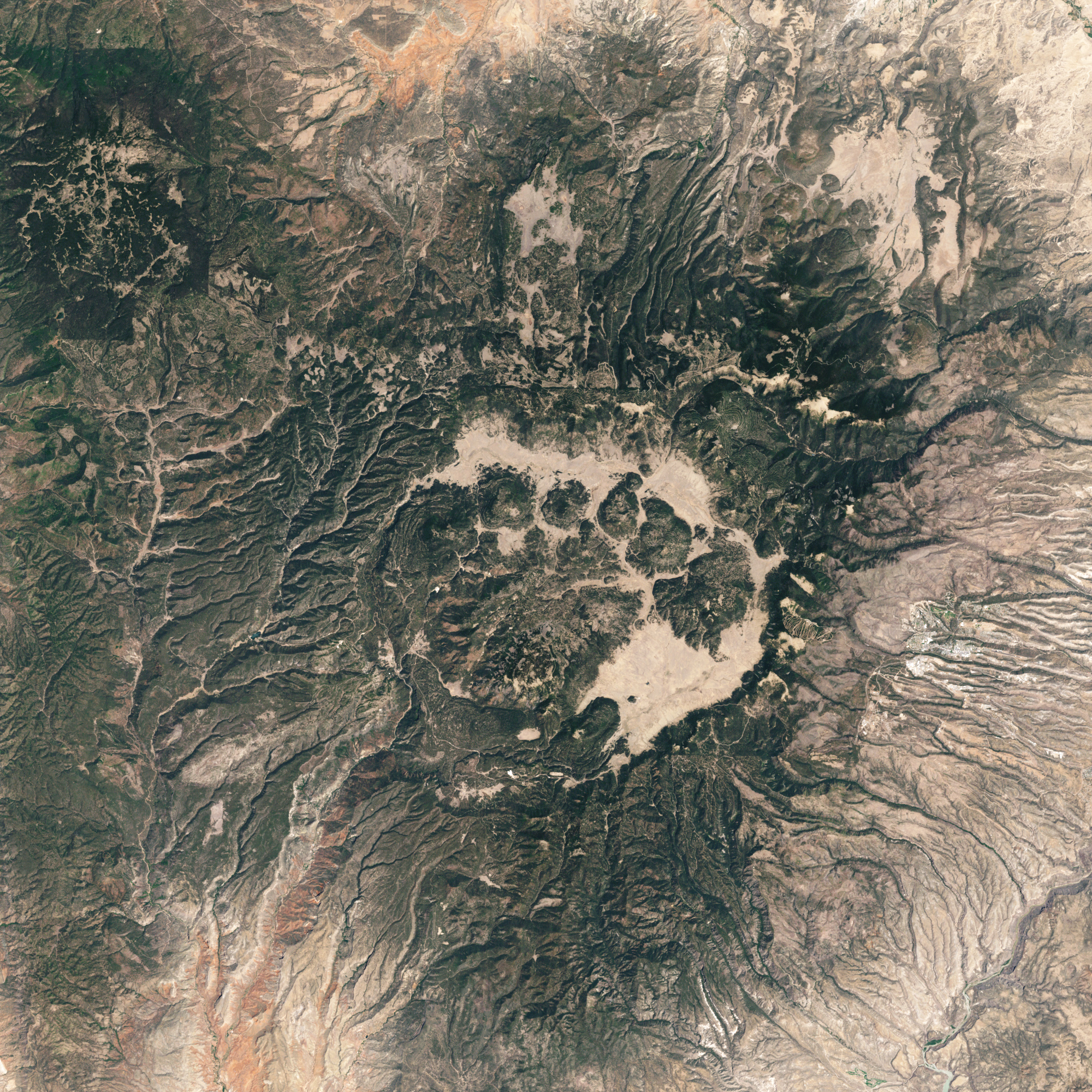 For their 1968 paper that first introduced the concept of a resurgent caldera to geology, R.L. Smith and R.A. Bailey chose the Valles caldera as their model. Although the Valles caldera is not unusually large, it is relatively young (1.25 million years old) and unusually well preserved, and it remains one of the best studied examples of a resurgent caldera. The ash flow tuffs of the Valles caldera, such as the Bandelier Tuff, were among the first to be thoroughly characterized.
For their 1968 paper that first introduced the concept of a resurgent caldera to geology, R.L. Smith and R.A. Bailey chose the Valles caldera as their model. Although the Valles caldera is not unusually large, it is relatively young (1.25 million years old) and unusually well preserved, and it remains one of the best studied examples of a resurgent caldera. The ash flow tuffs of the Valles caldera, such as the Bandelier Tuff, were among the first to be thoroughly characterized.


 Some volcanoes, such as the large
Some volcanoes, such as the large

 ***
***  *** Lake Ilopango
*** Lake Coatepeque
**
*** Lake Ilopango
*** Lake Coatepeque
**  *** Apolaki Caldera (
*** Apolaki Caldera ( *** Akademia Nauk ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Golovnin ( Kuril Islands)
*** Karymsky Caldera ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
***
*** Akademia Nauk ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Golovnin ( Kuril Islands)
*** Karymsky Caldera ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** 

 **
**  **
**
USGS page on calderas
List of Caldera Volcanoes
Collection of references on collapse calderas
(43 pages)
* ttp://www.bbc.co.uk/science/horizon/1999/supervolcanoes_script.shtml Supervolcanoes
Time-lapse video of Kīlauea caldera collapse, 2018
{{Authority control Depressions (geology) Igneous rocks Volcanism Volcanic landforms .
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
(erupted during the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
eon).
Valles
 For their 1968 paper that first introduced the concept of a resurgent caldera to geology, R.L. Smith and R.A. Bailey chose the Valles caldera as their model. Although the Valles caldera is not unusually large, it is relatively young (1.25 million years old) and unusually well preserved, and it remains one of the best studied examples of a resurgent caldera. The ash flow tuffs of the Valles caldera, such as the Bandelier Tuff, were among the first to be thoroughly characterized.
For their 1968 paper that first introduced the concept of a resurgent caldera to geology, R.L. Smith and R.A. Bailey chose the Valles caldera as their model. Although the Valles caldera is not unusually large, it is relatively young (1.25 million years old) and unusually well preserved, and it remains one of the best studied examples of a resurgent caldera. The ash flow tuffs of the Valles caldera, such as the Bandelier Tuff, were among the first to be thoroughly characterized.
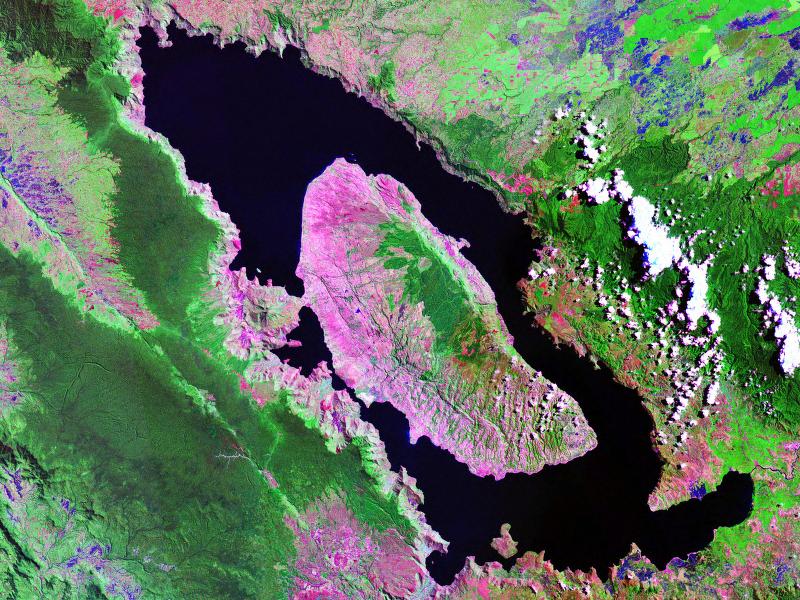
Toba
About 74,000 years ago, this Indonesian volcano released aboutdense-rock equivalent
Dense-rock equivalent (DRE) is a volcanologic calculation used to estimate volcanic eruption volume. One of the widely accepted measures of the size of a historic or prehistoric eruption is the volume of magma ejected as pumice and volcanic ash, k ...
of ejecta. This was the largest known eruption during the ongoing Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
period (the last 2.6 million years) and the largest known explosive eruption during the last 25 million years. In the late 1990s, anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and ...
Stanley Ambrose proposed that a volcanic winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosiv ...
induced by this eruption reduced the human population to about 2,000–20,000 individuals, resulting in a population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violen ...
. More recently, Lynn Jorde
Lynn B. Jorde is an American human geneticist. He is a professor in, and chair of, the Department of Human Genetics at the University of Utah School of Medicine, where he holds a H.A. and Edna Benning Presidential Endowed Chair.
Career
Jorde joi ...
and Henry Harpending
Henry Cosad Harpending (January 13, 1944 – April 3, 2016) was an American anthropologist and writer. He was a distinguished professor at the University of Utah, and formerly taught at Penn State and the University of New Mexico. He was a membe ...
proposed that the human species was reduced to approximately 5,000–10,000 people. There is no direct evidence, however, that either theory is correct, and there is no evidence for any other animal decline or extinction, even in environmentally sensitive species. There is evidence that human habitation continued in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
after the eruption.

Non-explosive calderas
 Some volcanoes, such as the large
Some volcanoes, such as the large shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
es Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. Hi ...
and Mauna Loa on the island of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, form calderas in a different fashion. The magma feeding these volcanoes is basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
, which is silica poor. As a result, the magma is much less viscous
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inter ...
than the magma of a rhyolitic volcano, and the magma chamber is drained by large lava flows rather than by explosive events. The resulting calderas are also known as subsidence calderas and can form more gradually than explosive calderas. For instance, the caldera atop Fernandina Island collapsed in 1968 when parts of the caldera floor dropped .
Extraterrestrial calderas
Since the early 1960s, it has been known that volcanism has occurred on other planets and moons in theSolar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
. Through the use of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft, volcanism has been discovered on Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, and Io, a satellite of Jupiter. None of these worlds have plate tectonics, which contributes approximately 60% of the Earth's volcanic activity (the other 40% is attributed to hotspot
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
volcanism). Caldera structure is similar on all of these planetary bodies, though the size varies considerably. The average caldera diameter on Venus is . The average caldera diameter on Io is close to , and the mode is ; Tvashtar Paterae
Tvashtar Paterae compose an active volcanic region of Jupiter's moon Io located near its north pole. It is a series of paterae, or volcanic craters. It is named after Tvashtar, the Hindu god of blacksmiths. Tvashtar was discovered in IRTF imag ...
is likely the largest caldera with a diameter of . The average caldera diameter on Mars is , smaller than Venus. Calderas on Earth are the smallest of all planetary bodies and vary from as a maximum.
The Moon
TheMoon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
has an outer shell of low-density crystalline rock that is a few hundred kilometers thick, which formed due to a rapid creation. The craters of the Moon have been well preserved through time and were once thought to have been the result of extreme volcanic activity, but are currently believed to have been formed by meteorites, nearly all of which took place in the first few hundred million years after the Moon formed. Around 500 million years afterward, the Moon's mantle was able to be extensively melted due to the decay of radioactive elements. Massive basaltic eruptions took place generally at the base of large impact craters. Also, eruptions may have taken place due to a magma reservoir at the base of the crust. This forms a dome, possibly the same morphology of a shield volcano where calderas universally are known to form. Although caldera-like structures are rare on the Moon, they are not completely absent. The Compton-Belkovich Volcanic Complex on the far side of the Moon is thought to be a caldera, possibly an ash-flow caldera.
Mars
The volcanic activity ofMars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
is concentrated in two major provinces: Tharsis and Elysium
Elysium (, ), otherwise known as the Elysian Fields ( grc, Ἠλύσιον πεδίον, ''Ēlýsion pedíon'') or Elysian Plains, is a conception of the afterlife that developed over time and was maintained by some Greek religious and philos ...
. Each province contains a series of giant shield volcanoes that are similar to what we see on Earth and likely are the result of mantle hot spots. The surfaces are dominated by lava flows, and all have one or more collapse calderas. Mars has the largest volcano in the Solar System, Olympus Mons
Olympus Mons (; Latin for Mount Olympus) is a large shield volcano on Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21.9 km (13.6 mi or 72,000 ft) as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a h ...
, which is more than three times the height of Mount Everest, with a diameter of 520 km (323 miles). The summit of the mountain has six nested calderas.
Venus
Because there is no plate tectonics onVenus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
, heat is mainly lost by conduction through the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
. This causes enormous lava flows, accounting for 80% of Venus' surface area. Many of the mountains are large shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
es that range in size from in diameter and high. More than 80 of these large shield volcanoes have summit calderas averaging across.
Io
Io, unusually, is heated by solid flexing due to the tidal influence of Jupiter and Io's orbital resonance with neighboring large moons Europa and Ganymede, which keep its orbit slightly eccentric. Unlike any of the planets mentioned, Io is continuously volcanically active. For example, the NASA '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'' spacecraft detected nine erupting volcanoes while passing Io in 1979. Io has many calderas with diameters tens of kilometers across.List of volcanic calderas
* Africa ** Ngorongoro Crater (Tanzania) ** Menengai Crater (Kenya) **Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
(Uganda/Kenya)
** Mount Fogo (Cape Verde)
** Mount Longonot (Kenya)
** Mount Meru (Tanzania)
** Erta Ale (Ethiopia)
** Nabro Volcano (Eritrea)
** Mallahle (Eritrea)
** ''See ''Europe'' for calderas in the Canary Islands
* Americas
** Argentina
*** Aguas Calientes Agua Caliente, Aguas Calientes or Aguascalientes (Spanish for 'hot/warm water(s)' or 'hot spring(s)') may refer to:
Places Central America
* Agua Caliente, El Salvador
* San Antonio Aguas Calientes, Guatemala
Mexico
* Aguascalientes, a state in M ...
, Salta Province
Salta () is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Boliv ...
*** Caldera del Atuel, Mendoza Province
*** Galán, Catamarca Province
Catamarca () is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. The province had a population of 334,568 as per the , and covers an area of 102,602 km2. Its literacy rate is 95.5%. Neighbouring provinces are (clockwise, fr ...
** Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
*** Pastos Grandes
** United States 
 ***
*** Mount Aniakchak
Mount Aniakchak (russian: Аниакчак) is a 3,700-year-old volcanic caldera approximately in diameter, located in the Aleutian Range of Alaska, United States. Although a stratovolcano by composition, the pre-existing mountain collapsed i ...
(Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve
Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve is a U.S. National Monument and National Preserve, consisting of the region around the Aniakchak volcano on the Aleutian Range of south-western Alaska. The monument is one of the least-visited places in ...
) ( Alaska)
*** Crater Lake on Mount Mazama ( Crater Lake National Park, Oregon)
*** Mount Katmai (Alaska)
*** Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. Hi ...
( Hawaii)
*** Mauna Loa ( Hawaii)
*** La Garita Caldera
La Garita Caldera is a large caldera in the San Juan volcanic field in the San Juan Mountains near the town of Creede in southwestern Colorado, United States.
It is west of La Garita, Colorado. The eruption that created the La Garita Caldera ...
(Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
)
*** Long Valley ( California)
*** Henry's Fork Caldera ( Idaho)
*** Island Park Caldera (Idaho, Wyoming)
*** Newberry Volcano (Oregon)
*** McDermitt Caldera (Oregon)
*** Medicine Lake Volcano (California)
*** Mount Okmok
Mount Okmok is the highest point on the rim of Okmok Caldera (Unmagim Anatuu in Aleut) on the northeastern part of Umnak Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands of Alaska. This wide circular caldera truncates the top of a large shield volcano. The ...
(Alaska)
*** Valles Caldera ( New Mexico)
*** Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corn ...
(Wyoming)
** Canada
*** Silverthrone Caldera ( British Columbia)
*** Mount Edziza (British Columbia)
*** Bennett Lake Volcanic Complex (British Columbia/ Yukon)
*** Mount Pleasant Caldera ( New Brunswick)
*** Sturgeon Lake Caldera ( Ontario)
*** Mount Skukum Volcanic Complex
The Mount Skukum Volcanic Complex is an early Eocene caldera complex, located 43 km west of Carcross and 32 km northeast of Mount Porsild in the Yukon Territory, Canada. The complex composes the Skukum Group. It is a northeast-trending ...
(Yukon)
*** Blake River Megacaldera Complex
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex is a giant subaqueous caldera cluster or a nested caldera system that spans across the Ontario–Quebec border in Canada.
The caldera complex is around 2.7 billion years old, consisting of a series of overlappi ...
( Quebec/Ontario)
**** New Senator Caldera
The New Senator Caldera is a large Archean caldera complex within the heart of the Blake River Megacaldera Complex, Quebec, Canada. It has a diameter of 15-30 kilometers and is made of thick massive mafic sequences. The caldera complex has infe ...
(Quebec)
**** Misema Caldera
The Misema Caldera is a 2,704-2,707 million year old caldera in Ontario and Quebec, Canada.
Geographic extent
It is the caldera that forms the Blake River Megacaldera ComplexNoranda Caldera
The Noranda Caldera is a well-known large subaqueous Archean caldera complex within the Blake River Megacaldera Complex, Quebec, Canada. The caldera contains a 7-to-9-km-thick succession of bimodal mafic-felsic tholeiitic to calc-alkaline volcan ...
(Quebec)
** Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
*** Arenas crater caldera, Nevado del Ruiz volcano, Caldas Department
*** Laguna Verde caldera, Azufral volcano, Narino Department
** Mexico
*** La primavera Caldera (Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal En ...
)
*** Amealco Caldera (Querétaro
Querétaro (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Querétaro ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Querétaro, links=no; Otomi language, Otomi: ''Hyodi Ndämxei''), is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. I ...
)
*** Las Cumbres Caldera ( Veracruz-Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
)
*** Los Azufres Caldera (Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
)
*** Los Humeros Caldera (Veracruz-Puebla)
*** Mazahua Caldera ( Mexico State)
** Chile
*** Chaitén
*** Cordillera Nevada Caldera
*** Laguna del Maule
*** Pacana Caldera
*** Sollipulli
Sollipulli (; in the Mapuche language) is an ice-filled volcanic caldera and volcanic complex, which lies southeast of the small town of Melipeuco in the La Araucanía Region, Chile. It is part of the Southern Volcanic Zone of the Andes, on ...
** Ecuador
*** Pululahua Geobotanical Reserve
*** Cuicocha
Cuicocha (Kichwa: ''Kuykucha'', "lake of guinea pigs" or ''Kuychikucha'', "rainbow lake") is a wide caldera and crater lake at the foot of Cotacachi Volcano in the Cordillera Occidental of the Ecuadorian Andes.
Its name comes from the Kichwa in ...
*** Quilotoa
Quilotoa () is a water-filled crater lake and the most western volcano in the Ecuadorian Andes. The -wide caldera was formed by the collapse of this dacite volcano following a catastrophic VEI-6 eruption about 800 years ago, which produced pyroc ...
*** Fernandina Island, Galápagos Islands
*** Sierra Negra (Galápagos)
*** Chacana Caldera
** El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
 *** Lake Ilopango
*** Lake Coatepeque
**
*** Lake Ilopango
*** Lake Coatepeque
** Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
*** Lake Amatitlán
*** Lake Atitlán
*** Xela
*** Barahona
** Other
*** Masaya (Nicaragua)
* Asia
** East Asia
*** Dakantou Caldera (大墈头) (Shanhuyan Village, Taozhu Town, Linhai
Linhai (; Tai-chow dialect: Lin-he) is a county-level city in Taizhou, Zhejiang Province situated on the banks of the Lin River in Eastern China.
As of the 2020 census, its population was 1,114,146 inhabitants even though its built-up (''or met ...
, Zhejiang, China)
*** Ma'anshan Caldera (马鞍山) (Shishan Town (石山镇), Xiuying, Hainan, China)
*** Yiyang Caldera (宜洋) (Shuangxi Town (双溪镇宜洋村), Pingnan County, Fujian, China)
*** Aira Caldera (Kagoshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
)
*** Kussharo ( Hokkaido, Japan)
*** Kuttara (Hokkaido, Japan)
*** Mashū (Hokkaido, Japan)
*** Aso Caldera, Mount Aso ( Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan)
*** Kikai Caldera (Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan)
*** Towada
is a city in Aomori Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 60,697, and a population density of 84 persons per km2 in 27,677 households. The total area of the city is .
Geography
Towada is in the foothills of the Hakkōda M ...
( Aomori Prefecture, Japan)
*** Tazawa (Akita Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Provinces and prefectures" in ; "Tōhoku" in . Its population is approximately 966,000 (as of 1 October 2019) and its ge ...
, Japan)
*** Hakone ( Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan)
*** Mount Halla ( Jeju-do, South Korea)
*** Heaven Lake ( Baekdu Mountain, North Korea/ Changbai Mountains, China)
** Southeast Asia  *** Apolaki Caldera (
*** Apolaki Caldera (Benham Rise
The Benham Rise, officially known as Philippine Rise, is an extinct volcanic ridge located in the Philippine Sea approximately east of the northern coastline of Dinapigue, Isabela. The rise has been known to the people of Catanduanes as Kalip ...
, Philippines)
*** Corregidor Caldera (Manila Bay, Philippines)
*** Mount Pinatubo ( Luzon, Philippines)
*** Taal Volcano (Luzon, Philippines)
*** Laguna Caldera (Luzon, Philippines)
*** Irosin Caldera (Luzon, Philippines)
*** Batur (Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
, Indonesia)
*** Krakatoa (Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java island, Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean.
Etymology
The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the weste ...
, Indonesia)
*** Lake Maninjau (Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Indonesia)
*** Lake Toba
Lake Toba ( id, Danau Toba) ( Toba Batak: ᯖᯀᯬ ᯖᯬᯅ; romanized: ''Tao Toba'') is a large natural lake in North Sumatra, Indonesia, occupying the caldera of a supervolcano. The lake is located in the middle of the northern part of the ...
(Sumatra, Indonesia)
*** Mount Rinjani ( Lombok, Indonesia)
*** Mount Tondano
Mount Tondano in the province of North Sulawesi, Sulawesi, Indonesia, has a 20 × 30 km wide caldera which was formed in the Late Miocene or Early Pliocene by a massive eruption. Post caldera activity includes pyroclastic cones, obsidian flow ...
(Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
, Indonesia)
*** Mount Tambora ( Sumbawa, Indonesia)
*** Tengger Caldera ( Java, Indonesia)
** Southwest Asia
*** Derik (Mardin
Mardin ( ku, Mêrdîn; ar, ماردين; syr, ܡܪܕܝܢ, Merdīn; hy, Մարդին) is a city in southeastern Turkey. The capital of Mardin Province, it is known for the Artuqid architecture of its old city, and for its strategic location on ...
, Turkey)
*** Nemrut (volcano)
Nemrut ( tr, Nemrut Dağı, hy, Սարակն ''Sarakn'', "Mountain spring", , ku, Çiyayê Nemrudê) is a dormant volcano in Eastern Turkey, close to Lake Van. The volcano is named after King Nimrod who is said to have ruled this area in about ...
(Turkey)
** Russia  *** Akademia Nauk ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Golovnin ( Kuril Islands)
*** Karymsky Caldera ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
***
*** Akademia Nauk ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Golovnin ( Kuril Islands)
*** Karymsky Caldera ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Karymshina
Karymshina is a large volcanic caldera located in the southern Kamchatka Peninsula of Russia. It was discovered in 2006 by Vladimir L Leonov and Aleksey N. Rogozin.http://www.geothermal-energy.org/pdf/IGAstandard/WGC/2010/1238.pdf
Location
Kar ...
( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Khangar
Khangar (russian: Хангар) is a stratovolcano located in the central part of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It is the southernmost volcano of the Sredinny Range. Its 2 km-wide caldera is now filled by a lake.
See also
* List of volcano ...
( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Ksudach ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Kurile Lake ( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Pauzhetka caldera (hosts Kurile Lake caldera, Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Lvinaya Past
Moekeshiwan, also known as Lvinaya Past (russian: Львиная Пасть, literally "''Lion's Maw''", after a rock that emerges from the sea and resembles a sleeping lion), is a volcano in the southern part of Iturup in the Kuril Islands, clai ...
( Kuril Islands)
*** Tao-Rusyr Caldera ( Kuril Islands)
*** Uzon
Uzon (russian: Узон) is a 9 by 12 km volcanic caldera located in the eastern part of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. Together with the Geyzernaya caldera it hosts the largest geothermal field in the Kamchatka Peninsula. The calderas were ...
( Kamchatka Peninsula)
*** Zavaritski Caldera
Zavaritski Caldera (russian: Вулкан Заварицкого, ''Vulkan Zavaritskogo'') is a caldera located in the central part of Simushir Island, Kuril Islands, Russia. Lake Biryuzovoe partially fills the youngest of three nested calderas o ...
( Kuril Islands)
*** Yankicha/Ushishir ( Kuril Islands)
*** Chegem Caldera ( Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, North Caucasus)
* Europe 

Banská Štiavnica
Banská Štiavnica (; german: Schemnitz; hu, Selmecbánya (Selmec), ) is a town in central Slovakia, in the middle of an immense caldera created by the collapse of an ancient volcano. For its size, the caldera is known as the Štiavnica Mountain ...
(Slovakia)
** Bakuriani/Didveli Caldera (Georgia)
** Samsari (Georgia)
** Santorini
Santorini ( el, Σαντορίνη, ), officially Thira (Greek: Θήρα ) and classical Greek Thera (English pronunciation ), is an island in the southern Aegean Sea, about 200 km (120 mi) southeast from the Greek mainland. It is the ...
(Greece)
** Nisyros (Greece)
** Askja (Iceland)
** Grímsvötn (Iceland)
** Bárðarbunga (Iceland)
** Katla (Iceland)
** Krafla (Iceland)
** Phlegraean Fields (Italy)
** Lake Bracciano (Italy)
** Lake Bolsena (Italy)
** Mount Somma which contains Mount Vesuvius (Italy)
** Las Cañadas
Teide, or Mount Teide, ( es, El Teide, Pico del Teide, , "Peak of Teide") is a volcano on Tenerife in the Canary Islands, Spain. Its summit (at ) is the highest point in Spain and the highest point above sea level in the islands of the Atlan ...
(Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of Janu ...
, Spain)
** Glen Coe (Scotland)
** Scafell Caldera (Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
, England)
** Laacher See (Germany)
** Lagoa das Sete Cidades Lagoa (Portuguese for ''lagoon'') may refer to the following:
People
*Barbara Lagoa, Cuban-American federal judge
Places Brazil
*Campina da Lagoa, Paraná
* Lagoa, Paraíba, Paraíba
*Lagoa, Rio de Janeiro, a quarter of Rio de Janeiro
* Lagoa Al ...
& Furnas ( São Miguel, the Azores, Portugal)
** Caldeira do Faial ( Faial, Portugal)
** Caldeirão do Corvo ( Corvo, Portugal)
* Oceania  **
** Cerberean Cauldron
This is a sortable summary of the pages Timeline of volcanism on Earth, List of Quaternary volcanic eruptions, and Large volume volcanic eruptions in the Basin and Range Province. Uncertainties as to dates and tephra volumes are not restated, a ...
(Australia)
** Dakataua
The Dakataua Caldera is located at the northern tip of the Willaumez Peninsula, New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The peninsula includes the 350 m high andesitic Mount Makalia stratovolcano. The last major collapse of Dakataua was during the Holoce ...
(Papua New Guinea)
** Kapenga (New Zealand)
** Kilauea ( Hawaii, US)
** Lake Ohakuri (New Zealand)
** Lake Okataina (New Zealand)
** Lake Rotorua (New Zealand)
** Lake Taupo (New Zealand)
** Maroa (New Zealand)
** Moku‘āweoweo Caldera on Mauna Loa (Hawaii, US)
** Mount Warning (Australia)
** Prospect Hill (Australia)
** Rano Kau ( Easter Island, Chile)
** Reporoa caldera (New Zealand)
* Antarctica
** Deception Island
* Indian Ocean
** Cirque de Mafate, Cirque de Salazie, Enclos Fouqué, and Cirque de Cilaos on Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
Extraterrestrial volcanic calderas
*Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
** Olympus Mons
Olympus Mons (; Latin for Mount Olympus) is a large shield volcano on Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21.9 km (13.6 mi or 72,000 ft) as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a h ...
caldera
* Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
** Maat Mons caldera
Erosion calderas
* Americas **Guaichane-Mamuta
Guaichane-Mamuta is a volcano in Chile. It is formed by a caldera and lava flows which form two separate systems. The volcano is of Miocene age.
Guaichane-Mamuta lies northeast of Pisagua. One half is formed by the wide and deep erosion calde ...
(Chile)
** Mount Tehama ( California, US)
* Europe
** Caldera de Taburiente (Spain)
* Oceania
** Tweed Valley ( New South Wales, Queensland, Australia)
* Asia
** Chegem Caldera ( Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, Northern Caucasus Region, Russia)
** Taal volcano (Philippines) Batangas Province
See also
* * * * *Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * * Kokelaar, B. P; and Moore, I. D; 2006. ''Glencoe caldera volcano, Scotland''. . Pub. British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottinghamshire. There is an associated 1:25000 solid geology map. * Lipman, P; 1999. "Caldera". In Haraldur Sigurdsson, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Volcanoes''. Academic Press. *External links
USGS page on calderas
List of Caldera Volcanoes
Collection of references on collapse calderas
(43 pages)
* ttp://www.bbc.co.uk/science/horizon/1999/supervolcanoes_script.shtml Supervolcanoes
Time-lapse video of Kīlauea caldera collapse, 2018
{{Authority control Depressions (geology) Igneous rocks Volcanism Volcanic landforms .