|
Kikai Caldera
(alternatively Kikaiga-shima, Kikai Caldera Complex) is a massive, mostly submerged caldera up to in diameter in the Ōsumi Islands of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. Geology Caldera formation has been dated from about 95,000 years ago and has involved rhyolite, basalt, and andesite phases. The Kikai Caldera Complex has twin ovoid caldera by in diameter. Yahazu-dake (north west part of Satsuma Io-jima) and Takeshima, located on the caldera rim, are pre-caldera volcanoes. Kikai-Tozurahara eruption This was about 95,000 years before the present and erupted Kikai-Tozurahara (K-Tz) tephra. Various dating techniques give ages between 70,000 to 100,000 years before present. This was distributed all over Japan but did not reach South Korea. Akahoya eruption The caldera was the source of the Akahoya eruption, one of the largest eruptions during the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present) that produced the Kikai-Akahoya (K-Ah) tephra. Between 7,200 to 7,300 years ago, pyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
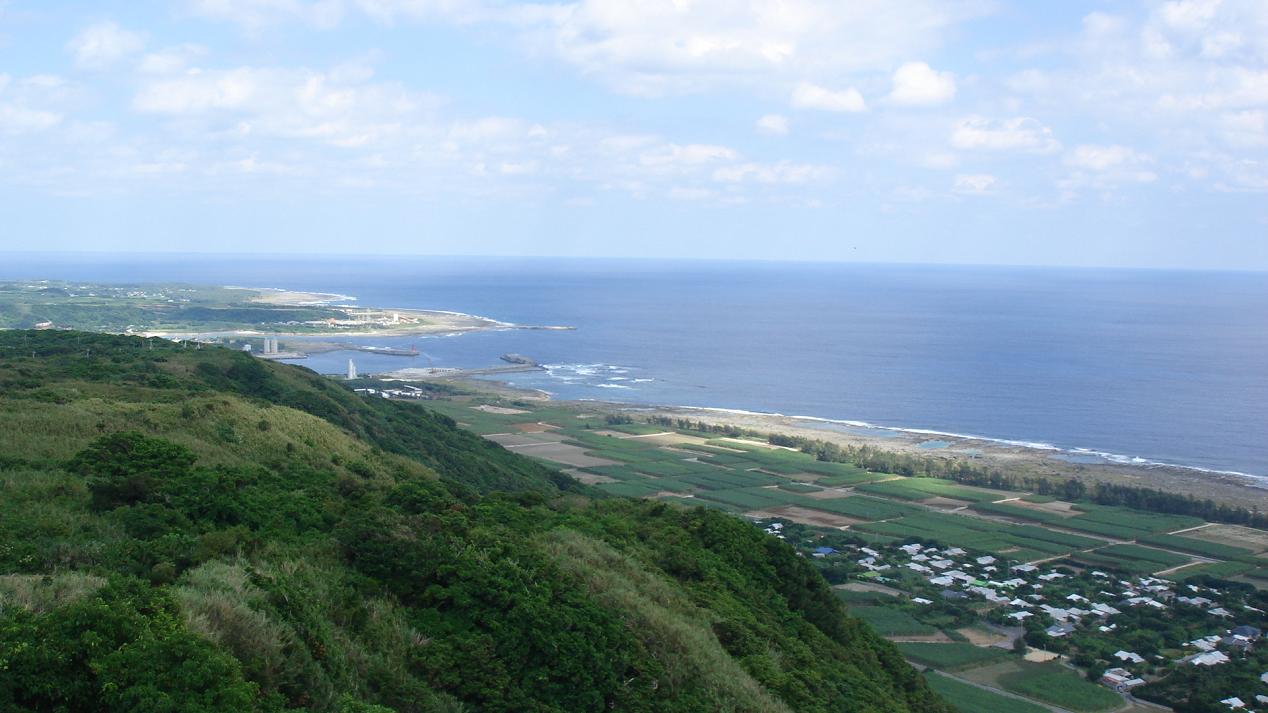
Kikaijima
is one of the Satsunan Islands, classed with the Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa. The island, in area, has a population of approximately 7,657 persons. Administratively the island forms the town of Kikai, Kagoshima Prefecture. Much of the island is within the borders of the Amami Guntō Quasi-National Park. Geography Kikaijima is isolated from the other Amami islands, and is located approximately east of Amami Ōshima and approximately south of the southern tip of Kyūshū. It is the easternmost island in the Amami chain. Compared with Amami Ōshima and Tokunoshima, Kikaijima is a relatively flat island, with its highest point at above sea level. It is a raised coral island with limestone cliffs, and draws the attention of geologists as it is one of the fastest rising coral islands in the world. Climate The climate of Kikaijima is classified as has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') with very warm summers and mild wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which paleoenvironmental or archaeological records can be placed. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the fossil and its place within the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
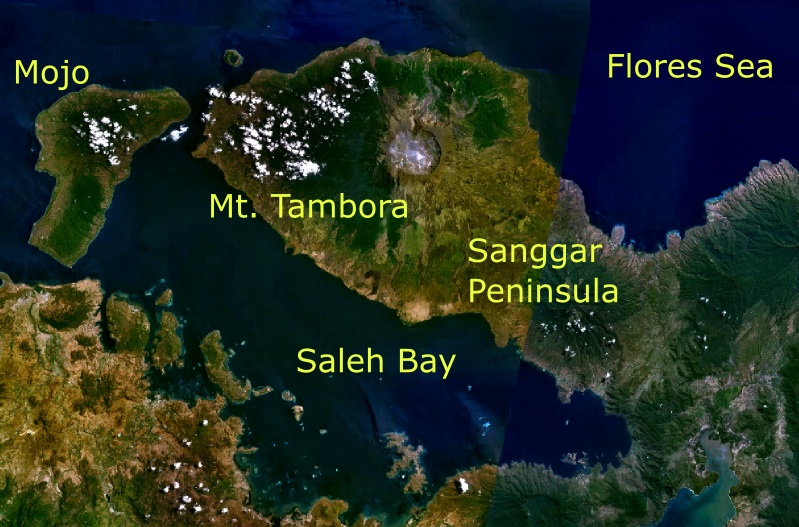
Mount Tambora
Mount Tambora, or Tomboro, is an active stratovolcano in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Located on Sumbawa in the Lesser Sunda Islands, it was formed by the active subduction zones beneath it. Before 1815, its elevation reached more than high, making it one of the tallest peaks in the Indonesian archipelago. Tambora violently erupted in a series of eruptions beginning 5 April, 1815, culminating in the largest eruption in recorded human history and the largest of the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present). The magma chamber under Tambora had been drained by previous eruptions and underwent several centuries of dormancy as it refilled. Volcanic activity reached a peak that year, culminating in an explosive eruption. The explosion was heard on Sumatra island, more than away. Heavy volcanic ash rains were observed as far away as Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, and Maluku islands, and the maximum elevation of Tambora was reduced from about to . Although estimates vary, the dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Segara Anak
Segara Anak is a crater lake in the caldera that formed during the explosive volcanic eruption of Mount Samalas in 1257. The caldera is next to Mount Rinjani on Lombok Island in Indonesia. "Segara Anak" means "child of the sea" and refers to the blue lake's resemblance to the sea. The volcanic cone Gunung Barujari is at the eastern end of the lake and is responsible for its crescent shape. The lake temperature is , which is 5-7 °C (9-13 °F) higher than normal for a lake at its altitude. Hot magma below the lake is responsible for this anomaly. Gas bubbles escape from the lake floor, helping the lake to have a pH of 7-8. The surface of Segara Anak is above mean sea level (AMSL) and is Indonesia's second-highest caldera lake with an active volcano. The peak of Gunung Baru Jari is AMSL. The lake covers , with dimensions of , and has a maximum depth of . Fish breeding There were no fish in Segara Anak. In 1969, volcanologists from the Geological Society of London examined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurile Lake
Kurile Lake (russian: Кури́льское о́зеро, Kuríl'skoye Ózero) is a caldera and crater lake in Kamchatka, Russia. It is also known as Kurilskoye Lake or Kuril Lake. It is part of the Eastern Volcanic Zone of Kamchatka which, together with the Sredinny Range, forms one of the volcanic belts of Kamchatka. These volcanoes form from the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Okhotsk Plate and the Asian Plate. Before the Kurile Lake caldera formed, the Pauzhetka caldera was active during the Pleistocene, and was the origin of the 443,000 ± 8,000 years old Golygin ignimbrite. The Kurile Lake caldera erupted 41,500 years ago, and another small eruption occurred between 9,000 and 10,000 years ago; then 6460–6414 BC a very large eruption took place, forming the present-day caldera and the Kurile Lake ignimbrite and deposited ash as far as away. This eruption has a volume of , making it a VEI 7-class eruption and one of the largest during the Holocene. Subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crater Lake
Crater Lake (Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a caldera that was formed around 7,700 (± 150) years ago by the collapse of the volcano Mount Mazama. There are no rivers flowing into or out of the lake; the evaporation is compensated for by rain and snowfall at a rate such that the total amount of water is replaced every 250 years. With a depth of , the lake is the deepest in the United States. In the world, it ranks ninth for maximum depth, and third for mean (average) depth. Crater Lake features two small islands. Wizard Island, located near the western shore of the lake, is a cinder cone approximately 316 acres (128 ha) in size. Phantom Ship, a natural rock pillar, is located near the southern shore. Since 2002, one of Oregon's regular-issue license plate designs has featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paektu Mountain
Paektu Mountain (), also known as Baekdu Mountain and in China as Changbai Mountain ( zh, s=长白山, t=長白山; Manchu: Golmin Šanggiyan Alin), is an active stratovolcano on the Chinese–North Korean border. At , it is the highest mountain of the Baekdudaegan and Changbai ranges. Koreans assign a mythical quality to the volcano and its caldera lake, considering it to be their country's spiritual home. It is the highest mountain in North Korea and Northeast China. A large crater lake, called Heaven Lake, is in the caldera atop the mountain. The caldera was formed by the VEI 7 "Millennium" or "Tianchi" eruption of 946, which erupted about of tephra. This was one of the largest and most violent eruptions in the last 5,000 years (alongside the Minoan eruption, the Hatepe eruption of Lake Taupō in around AD 180, the 1257 eruption of Mount Samalas near Mount Rinjani and the 1815 eruption of Tambora). The mountain plays an important mythological and cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santorini
Santorini ( el, Σαντορίνη, ), officially Thira (Greek: Θήρα ) and classical Greek Thera ( English pronunciation ), is an island in the southern Aegean Sea, about 200 km (120 mi) southeast from the Greek mainland. It is the largest island of a small circular archipelago, which bears the same name and is the remnant of a caldera. It forms the southernmost member of the Cyclades group of islands, with an area of approximately 73 km2 (28 sq mi) and a 2011 census population of 15,550. The municipality of Santorini includes the inhabited islands of Santorini and Therasia, as well as the uninhabited islands of Nea Kameni, Palaia Kameni, Aspronisi and Christiana. The total land area is 90.623 km2 (34.990 sq mi). Santorini is part of the Thira regional unit. The island was the site of one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded history: the Minoan eruption (sometimes called the Thera eruption), which occurred about 3,60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Japan Times
''The Japan Times'' is Japan's largest and oldest English-language daily newspaper. It is published by , a subsidiary of News2u Holdings, Inc.. It is headquartered in the in Kioicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo. History ''The Japan Times'' was launched by Motosada Zumoto on 22 March 1897, with the goal of giving Japanese people an opportunity to read and discuss news and current events in English to help Japan to participate in the international community. The newspaper was independent of government control, but from 1931 onward, the paper's editors experienced mounting pressure from the Japanese government to submit to its policies. In 1933, the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs appointed Hitoshi Ashida, former ministry official, as chief editor. During World War II, the newspaper served as an outlet for Imperial Japanese government communication and editorial opinion. It was successively renamed ''The Japan Times and Mail'' (1918–1940) following its merger with ''The Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkaidō
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel. The largest city on Hokkaidō is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about 43 kilometers (26 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. Hokkaidō was formerly known as '' Ezo'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yesso''. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaidō" in Although there were Japanese settlers who ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was considered foreign territory that was inhabited by the indigenous people of the island, known as the Ainu people. While geographers such as Mogami Tokunai and Mamiya Rinzō explored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |