Calcutta Llama on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the
—
—
—
— In the late 17th century, the three villages that predated Calcutta were ruled by the
—
—
—
— Though home to major cricketing venues and franchises, Kolkata stands out in India for being the country's centre of

 The discovery and
The discovery and  In 1712, the British completed the construction of Fort William, located on the east bank of the Hooghly River to protect their trading factory. Facing frequent skirmishes with
In 1712, the British completed the construction of Fort William, located on the east bank of the Hooghly River to protect their trading factory. Facing frequent skirmishes with  The partition of Bengal in 1905 along religious lines led to mass protests, making Calcutta a less hospitable place for the British. The capital was moved to
The partition of Bengal in 1905 along religious lines led to mass protests, making Calcutta a less hospitable place for the British. The capital was moved to
—
— The
 The
The
 Kolkata is the commercial and financial hub of East India, East and
Kolkata is the commercial and financial hub of East India, East and
—
— Flexible production has been the norm in Kolkata, which has an informal sector that employs more than 40% of the labour force. One unorganised group, Hawkers in Kolkata, roadside hawkers, generated business worth 87.72 billion ( 2 billion) in 2005. , around 0.81% of the city's workforce was employed in the Primary sector of the economy, primary sector (agriculture, forestry, mining, etc.); 15.49% worked in the Secondary sector of the economy, secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing); and 83.69% worked in the Tertiary sector of the economy, tertiary sector (service industries). , the majority of households in slums were engaged in occupations belonging to the informal sector; 36.5% were involved in servicing the urban middle class (as maids, drivers, etc.) and 22.2% were Wage labour, casual labourers. About 34% of the available labour force in Kolkata slums were unemployed. According to one estimate, almost a quarter of the population live on less than 27 rupees (equivalent to 45 US cents) per day.
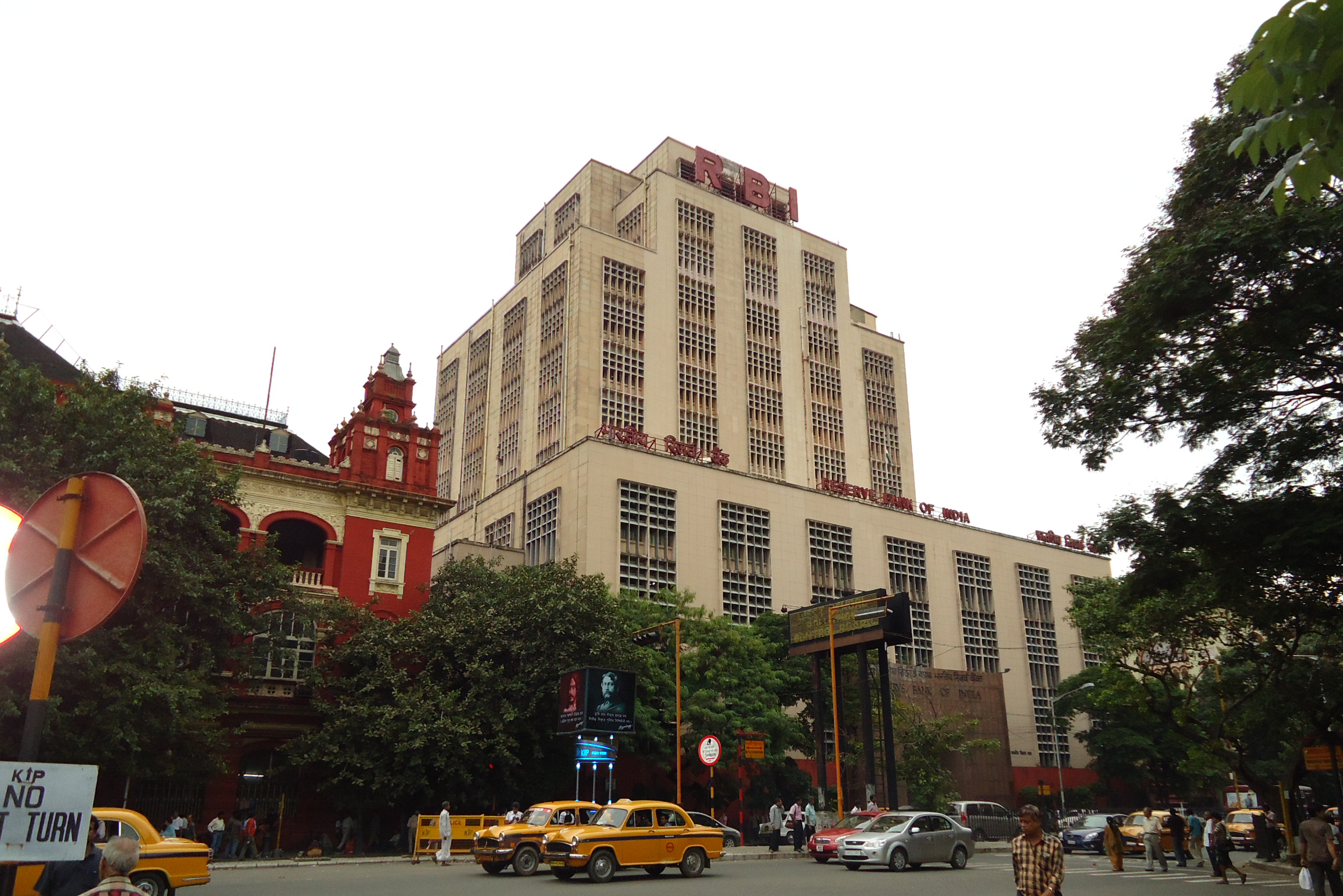
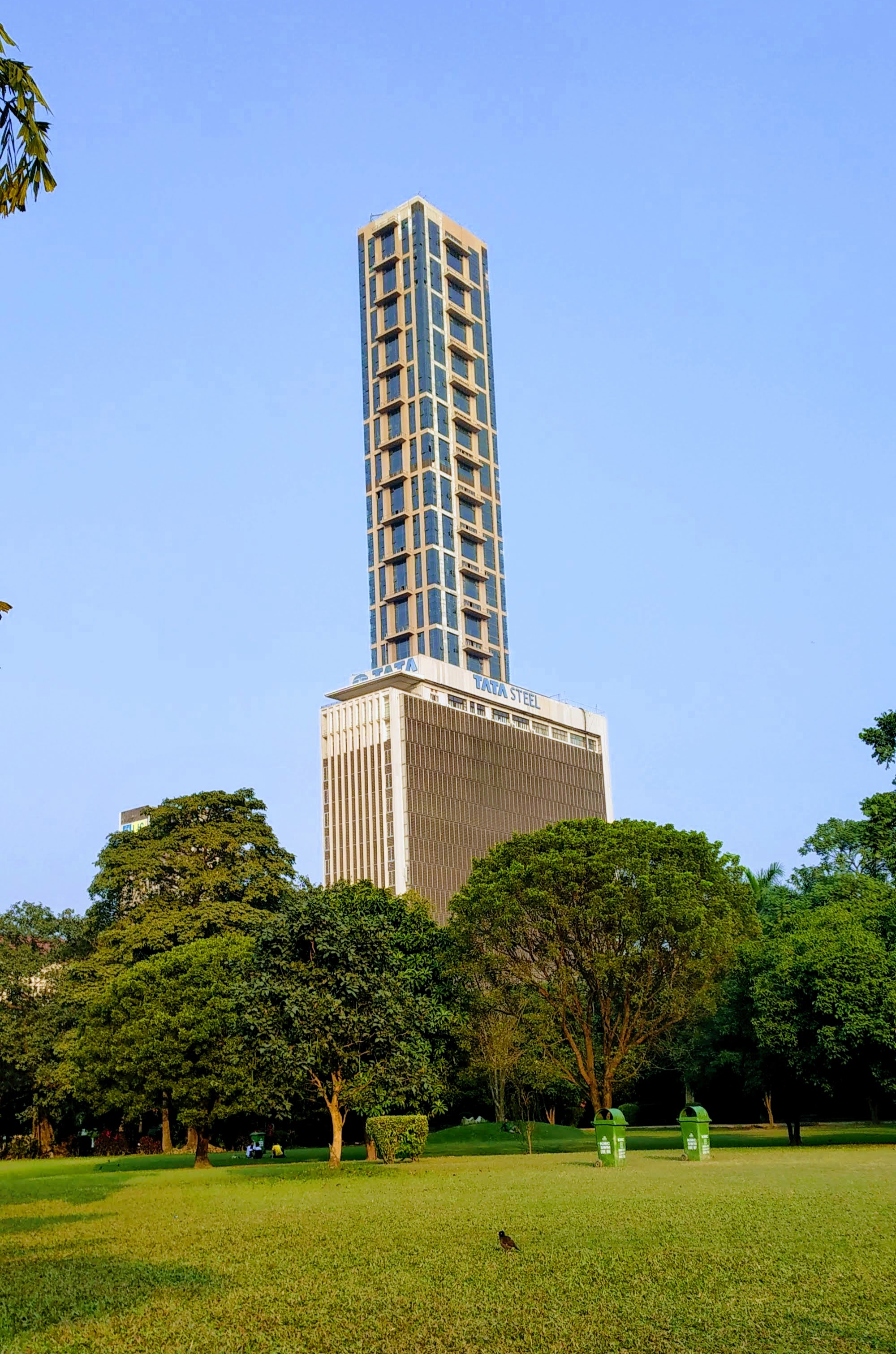
Major manufacturing companies in the city are Alstom, Larsen & Toubro, Fosroc, Videocon Telecom, Videocon. As in many other Indian cities, information technology became a high-growth sector in Kolkata starting in the late 1990s; the city's IT sector grew at 70% per annum—a rate that was twice the national average. The 2000s saw a surge of investments in the real estate, infrastructure, retail, and hospitality sectors; List of shopping malls in Kolkata, several large shopping malls and hotels were launched. Companies such as ITC Limited, CESC Limited, Exide Industries, Emami, Eveready Industries India, Lux Industries, Rupa Company, Berger Paints, Birla Corporation, Britannia Industries and Purushottam Publishers are headquartered in the city. Philips India, PricewaterhouseCoopers India, Tata Global Beverages, and Tata Steel have their registered office and zonal headquarters in Kolkata. Kolkata hosts the headquarters of three major public-sector banks: Allahabad Bank, UCO Bank, and the United Bank of India; and a private bank Bandhan Bank.
Flexible production has been the norm in Kolkata, which has an informal sector that employs more than 40% of the labour force. One unorganised group, Hawkers in Kolkata, roadside hawkers, generated business worth 87.72 billion ( 2 billion) in 2005. , around 0.81% of the city's workforce was employed in the Primary sector of the economy, primary sector (agriculture, forestry, mining, etc.); 15.49% worked in the Secondary sector of the economy, secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing); and 83.69% worked in the Tertiary sector of the economy, tertiary sector (service industries). , the majority of households in slums were engaged in occupations belonging to the informal sector; 36.5% were involved in servicing the urban middle class (as maids, drivers, etc.) and 22.2% were Wage labour, casual labourers. About 34% of the available labour force in Kolkata slums were unemployed. According to one estimate, almost a quarter of the population live on less than 27 rupees (equivalent to 45 US cents) per day.
Major manufacturing companies in the city are Alstom, Larsen & Toubro, Fosroc, Videocon Telecom, Videocon. As in many other Indian cities, information technology became a high-growth sector in Kolkata starting in the late 1990s; the city's IT sector grew at 70% per annum—a rate that was twice the national average. The 2000s saw a surge of investments in the real estate, infrastructure, retail, and hospitality sectors; List of shopping malls in Kolkata, several large shopping malls and hotels were launched. Companies such as ITC Limited, CESC Limited, Exide Industries, Emami, Eveready Industries India, Lux Industries, Rupa Company, Berger Paints, Birla Corporation, Britannia Industries and Purushottam Publishers are headquartered in the city. Philips India, PricewaterhouseCoopers India, Tata Global Beverages, and Tata Steel have their registered office and zonal headquarters in Kolkata. Kolkata hosts the headquarters of three major public-sector banks: Allahabad Bank, UCO Bank, and the United Bank of India; and a private bank Bandhan Bank.
 Kolkata is administered by several government agencies. The
Kolkata is administered by several government agencies. The
 The
The
 Public transport is provided by the Kolkata Suburban Railway, the Kolkata Metro, Trams in Kolkata, trams, rickshaws, taxis and buses. The suburban rail network connects the city's distant suburbs.
Public transport is provided by the Kolkata Suburban Railway, the Kolkata Metro, Trams in Kolkata, trams, rickshaws, taxis and buses. The suburban rail network connects the city's distant suburbs.
 According to a 2013 survey conducted by the International Association of Public Transport, in terms of a public transport system, Kolkata ranks among the top of the six Indian cities surveyed. The Kolkata Metro, in operation since 1984, is the oldest underground mass transit system in India. It spans the north–south length of the city. In 2020, part of the Second line was inaugurated to cover part of Salt Lake. This east–west line will connect Salt Lake with Howrah. The two lines cover a distance of . , four Metro rail lines were under construction.
According to a 2013 survey conducted by the International Association of Public Transport, in terms of a public transport system, Kolkata ranks among the top of the six Indian cities surveyed. The Kolkata Metro, in operation since 1984, is the oldest underground mass transit system in India. It spans the north–south length of the city. In 2020, part of the Second line was inaugurated to cover part of Salt Lake. This east–west line will connect Salt Lake with Howrah. The two lines cover a distance of . , four Metro rail lines were under construction.
 Kolkata has five long-distance railway stations, located at Howrah station, Howrah (the largest railway complex in India), Sealdah railway station, Sealdah, Kolkata Railway Station, Kolkata, Shalimar railway station, Shalimar and Santragachi railway station, Santragachi, which connect Kolkata by rail to most cities in West Bengal and to other major cities in India. The city serves as the headquarters of three railway zones out of eighteen of the Indian Railways regional divisions—the Kolkata Metro Railways, Eastern Railway Zone (India), Eastern Railway and the South Eastern Railway Zone (India), South-Eastern Railway. Kolkata has rail and road connectivity with
Kolkata has five long-distance railway stations, located at Howrah station, Howrah (the largest railway complex in India), Sealdah railway station, Sealdah, Kolkata Railway Station, Kolkata, Shalimar railway station, Shalimar and Santragachi railway station, Santragachi, which connect Kolkata by rail to most cities in West Bengal and to other major cities in India. The city serves as the headquarters of three railway zones out of eighteen of the Indian Railways regional divisions—the Kolkata Metro Railways, Eastern Railway Zone (India), Eastern Railway and the South Eastern Railway Zone (India), South-Eastern Railway. Kolkata has rail and road connectivity with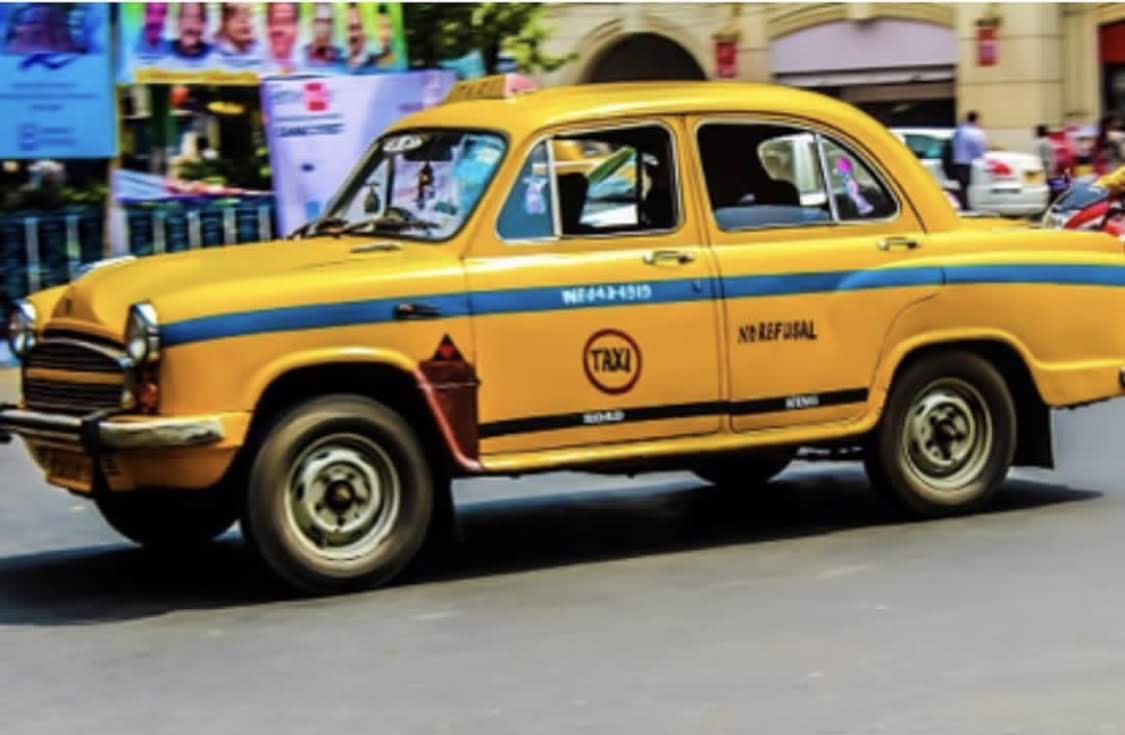  Buses, which are the most commonly used mode of transport, are run by government agencies and private operators. Kolkata is the only Indian city with a tram network, which was operated by the Calcutta Tramways Company. It has now renamed to West Bengal Transport Corporation. The slow-moving tram services are restricted to certain areas of the city. Water-logging, caused by heavy rains during the Monsoon of South Asia, summer monsoon, sometimes interrupt transportation networks. Hired public conveyances include auto rickshaws, which often ply specific routes, and yellow metered taxis. Almost all of Kolkata's taxis are antiquated Hindustan Ambassadors by make; newer air-conditioned Taxicab#Dispatching, radio taxis are in service as well. In parts of the city, cycle rickshaws and Pulled rickshaw, hand-pulled rickshaws are patronised by the public for short trips.
Buses, which are the most commonly used mode of transport, are run by government agencies and private operators. Kolkata is the only Indian city with a tram network, which was operated by the Calcutta Tramways Company. It has now renamed to West Bengal Transport Corporation. The slow-moving tram services are restricted to certain areas of the city. Water-logging, caused by heavy rains during the Monsoon of South Asia, summer monsoon, sometimes interrupt transportation networks. Hired public conveyances include auto rickshaws, which often ply specific routes, and yellow metered taxis. Almost all of Kolkata's taxis are antiquated Hindustan Ambassadors by make; newer air-conditioned Taxicab#Dispatching, radio taxis are in service as well. In parts of the city, cycle rickshaws and Pulled rickshaw, hand-pulled rickshaws are patronised by the public for short trips.
 Due to its diverse and abundant public transportation, privately owned vehicles are not as common in Kolkata as in other major Indian cities. The city has witnessed a steady increase in the number of registered vehicles; 2002 data showed an increase of 44% over a period of seven years. , after adjusting for population density, the city's "road space" was only 6% compared to 23% in Delhi and 17% in Mumbai. The Kolkata Metro has somewhat eased traffic congestion, as has the addition of new roads and Overpass, flyovers. Agencies operating long-distance bus services include the West Bengal Transport Corporation and various private operators. The city's main bus terminals are located at
Due to its diverse and abundant public transportation, privately owned vehicles are not as common in Kolkata as in other major Indian cities. The city has witnessed a steady increase in the number of registered vehicles; 2002 data showed an increase of 44% over a period of seven years. , after adjusting for population density, the city's "road space" was only 6% compared to 23% in Delhi and 17% in Mumbai. The Kolkata Metro has somewhat eased traffic congestion, as has the addition of new roads and Overpass, flyovers. Agencies operating long-distance bus services include the West Bengal Transport Corporation and various private operators. The city's main bus terminals are located at  Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, located in
Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, located in  The
The
 , the healthcare system in Kolkata consists of 48 government hospitals, mostly under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (West Bengal), Department of Health & Family Welfare, Government of West Bengal, and 366 private medical establishments; these establishments provide the city with 27,687 hospital beds. For every 10,000 people in the city, there are 61.7 hospital beds,The population (4,486,679) and hospital beds (27,687) have been used to derive this rate. which is higher than the national average of 9 hospital beds per 10,000. Ten Education in Kolkata#Medical Colleges, medical and dental colleges are located in the Kolkata metropolitan area which act as tertiary referral hospitals in the state. The Calcutta Medical College, founded in 1835, was the first institution in Asia to teach modern medicine. However, These facilities are inadequate to meet the healthcare needs of the city. More than 78% in Kolkata prefer the private medical sector over the public medical sector, due to the overburdening of the public health sector, the lack of a nearby facility, and excessive waiting times at government facilities.
According to the Indian 2005 National Family Health Survey, only a small proportion of Kolkata households were covered under any health scheme or health insurance. The total fertility rate in Kolkata was 1.4, the lowest among the eight cities surveyed. In Kolkata, 77% of the married women used contraceptives, which was the highest among the cities surveyed, but use of modern contraceptive methods was the lowest (46%). The infant mortality rate in Kolkata was live births, and the mortality rate for children under five was live births.
, the healthcare system in Kolkata consists of 48 government hospitals, mostly under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (West Bengal), Department of Health & Family Welfare, Government of West Bengal, and 366 private medical establishments; these establishments provide the city with 27,687 hospital beds. For every 10,000 people in the city, there are 61.7 hospital beds,The population (4,486,679) and hospital beds (27,687) have been used to derive this rate. which is higher than the national average of 9 hospital beds per 10,000. Ten Education in Kolkata#Medical Colleges, medical and dental colleges are located in the Kolkata metropolitan area which act as tertiary referral hospitals in the state. The Calcutta Medical College, founded in 1835, was the first institution in Asia to teach modern medicine. However, These facilities are inadequate to meet the healthcare needs of the city. More than 78% in Kolkata prefer the private medical sector over the public medical sector, due to the overburdening of the public health sector, the lack of a nearby facility, and excessive waiting times at government facilities.
According to the Indian 2005 National Family Health Survey, only a small proportion of Kolkata households were covered under any health scheme or health insurance. The total fertility rate in Kolkata was 1.4, the lowest among the eight cities surveyed. In Kolkata, 77% of the married women used contraceptives, which was the highest among the cities surveyed, but use of modern contraceptive methods was the lowest (46%). The infant mortality rate in Kolkata was live births, and the mortality rate for children under five was live births.
 Among the surveyed cities, Kolkata stood second (5%) for children who had not had any vaccinations under the Universal Immunization Programme . Kolkata ranked second with access to an ''anganwadi'' centre under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme for 57% of the children between 0 and 71 months. The proportion of malnutrition, malnourished, anaemia, anaemic and underweight children in Kolkata was less in comparison to other surveyed cities.
About 18% of the men and 30% of the women in Kolkata are obese—the majority of them belonging to the non-poor strata of society. In 2005, Kolkata had the highest percentage (55%) among the surveyed cities of Anemia, anaemic women, while 20% of the men in Kolkata were Anemia, anaemic. Diseases like diabetes, asthma, goitre and other Thyroid#Disorders, thyroid disorders were found in large numbers of people. Tropical diseases like malaria, dengue and ''chikungunya'' are prevalent in Kolkata, though their incidence is decreasing. Kolkata is one of the districts in India with HIV/AIDS in India, a high number of people with HIV/AIDS, AIDS; it has been designated a district prone to high risk. As of 2014, because of Air pollution in India, higher air pollution, the life expectancy of a person born in the city is four years fewer than in the suburbs.
Among the surveyed cities, Kolkata stood second (5%) for children who had not had any vaccinations under the Universal Immunization Programme . Kolkata ranked second with access to an ''anganwadi'' centre under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme for 57% of the children between 0 and 71 months. The proportion of malnutrition, malnourished, anaemia, anaemic and underweight children in Kolkata was less in comparison to other surveyed cities.
About 18% of the men and 30% of the women in Kolkata are obese—the majority of them belonging to the non-poor strata of society. In 2005, Kolkata had the highest percentage (55%) among the surveyed cities of Anemia, anaemic women, while 20% of the men in Kolkata were Anemia, anaemic. Diseases like diabetes, asthma, goitre and other Thyroid#Disorders, thyroid disorders were found in large numbers of people. Tropical diseases like malaria, dengue and ''chikungunya'' are prevalent in Kolkata, though their incidence is decreasing. Kolkata is one of the districts in India with HIV/AIDS in India, a high number of people with HIV/AIDS, AIDS; it has been designated a district prone to high risk. As of 2014, because of Air pollution in India, higher air pollution, the life expectancy of a person born in the city is four years fewer than in the suburbs.
 Kolkata's schools are run by the state government or private organisations, many of which are religious.
Kolkata's schools are run by the state government or private organisations, many of which are religious.  , the Kolkata urban agglomeration is home to 14 universities run by the state government. The colleges are each affiliated with a university or institution based either in Kolkata or elsewhere in India. Aliah University which was founded in 1780 as ''Mohammedan College of Calcutta'' is the oldest post-secondary educational institution of the city. The University of Calcutta, founded in 1857, is the first modern university in South Asia. Presidency College, Kolkata (formerly Hindu College between 1817 and 1855), founded in 1855, was one of the oldest colleges in India. It was affiliated with the University of Calcutta until 2010 when it was converted to Presidency University, Kolkata in 2010. Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur, Bengal Engineering and Science University (BESU) is the second oldest engineering institution of the country located in Howrah. An Institute of National Importance, BESU was converted to India's first Indian Institutes of Engineering Science and Technology, IIEST. Jadavpur University is known for its arts, science, and engineering faculties. The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta, which was the first of the Indian Institutes of Management, was established in 1961 at Joka, Kolkata, Joka, a locality in the south-western suburbs. Kolkata also houses the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, which was started here in the year 2006.
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences is one of India's Autonomous law schools in India, autonomous law schools, and the Indian Statistical Institute is a public research institute and university. State owned Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal (MAKAUT, WB), formerly West Bengal University of Technology (WBUT) is the largest Technological University in terms of student enrollment and number of Institutions affiliated by it. Private institutions include the Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute and University of Engineering & Management (UEM), Kolkata, University of Engineering & Management (UEM).
, the Kolkata urban agglomeration is home to 14 universities run by the state government. The colleges are each affiliated with a university or institution based either in Kolkata or elsewhere in India. Aliah University which was founded in 1780 as ''Mohammedan College of Calcutta'' is the oldest post-secondary educational institution of the city. The University of Calcutta, founded in 1857, is the first modern university in South Asia. Presidency College, Kolkata (formerly Hindu College between 1817 and 1855), founded in 1855, was one of the oldest colleges in India. It was affiliated with the University of Calcutta until 2010 when it was converted to Presidency University, Kolkata in 2010. Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur, Bengal Engineering and Science University (BESU) is the second oldest engineering institution of the country located in Howrah. An Institute of National Importance, BESU was converted to India's first Indian Institutes of Engineering Science and Technology, IIEST. Jadavpur University is known for its arts, science, and engineering faculties. The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta, which was the first of the Indian Institutes of Management, was established in 1961 at Joka, Kolkata, Joka, a locality in the south-western suburbs. Kolkata also houses the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, which was started here in the year 2006.
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences is one of India's Autonomous law schools in India, autonomous law schools, and the Indian Statistical Institute is a public research institute and university. State owned Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal (MAKAUT, WB), formerly West Bengal University of Technology (WBUT) is the largest Technological University in terms of student enrollment and number of Institutions affiliated by it. Private institutions include the Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute and University of Engineering & Management (UEM), Kolkata, University of Engineering & Management (UEM).
 Notable scholars who were born, worked or studied in Kolkata include physicists Satyendra Nath Bose, Meghnad Saha, and Jagadish Chandra Bose; chemist Prafulla Chandra Roy; statisticians Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis and Anil Kumar Gain; physician Upendranath Brahmachari; educator Ashutosh Mukherjee; and Nobel laureates Rabindranath Tagore, C. V. Raman, and Amartya Sen.
Notable scholars who were born, worked or studied in Kolkata include physicists Satyendra Nath Bose, Meghnad Saha, and Jagadish Chandra Bose; chemist Prafulla Chandra Roy; statisticians Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis and Anil Kumar Gain; physician Upendranath Brahmachari; educator Ashutosh Mukherjee; and Nobel laureates Rabindranath Tagore, C. V. Raman, and Amartya Sen.
 Kolkata houses many research institutes like Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB), Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Bose Institute, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP), Centre for Studies in Social Sciences, Calcutta, All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI), S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), Indian Institute of Social Welfare and Business Management (IISWBM), National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre (VECC) and Indian Centre for Space Physics. Nobel laureate Sir C. V. Raman did his groundbreaking work in Raman effect in IACS.
Kolkata houses many research institutes like Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB), Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Bose Institute, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP), Centre for Studies in Social Sciences, Calcutta, All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI), S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), Indian Institute of Social Welfare and Business Management (IISWBM), National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre (VECC) and Indian Centre for Space Physics. Nobel laureate Sir C. V. Raman did his groundbreaking work in Raman effect in IACS.
 Kolkata is known for its literary, artistic and revolutionary heritage; as the former capital of India, it was the birthplace of modern Indian literary and artistic thought. Kolkata has been called the "City of Furious, Creative Energy" as well as the "cultural [or literary] capital of India". The presence of ''para (Bengali), paras'', which are neighbourhoods that possess a strong sense of community, is characteristic of the city. Typically, each ''para'' has its own community club and on occasion, a playing field. Residents engage in ''adda (Indian), addas'', or leisurely chats, that often take the form of freestyle intellectual conversation. The city has a tradition of political graffiti depicting everything from outrageous slander to witty banter and limericks, caricatures and propaganda.
Kolkata is known for its literary, artistic and revolutionary heritage; as the former capital of India, it was the birthplace of modern Indian literary and artistic thought. Kolkata has been called the "City of Furious, Creative Energy" as well as the "cultural [or literary] capital of India". The presence of ''para (Bengali), paras'', which are neighbourhoods that possess a strong sense of community, is characteristic of the city. Typically, each ''para'' has its own community club and on occasion, a playing field. Residents engage in ''adda (Indian), addas'', or leisurely chats, that often take the form of freestyle intellectual conversation. The city has a tradition of political graffiti depicting everything from outrageous slander to witty banter and limericks, caricatures and propaganda.
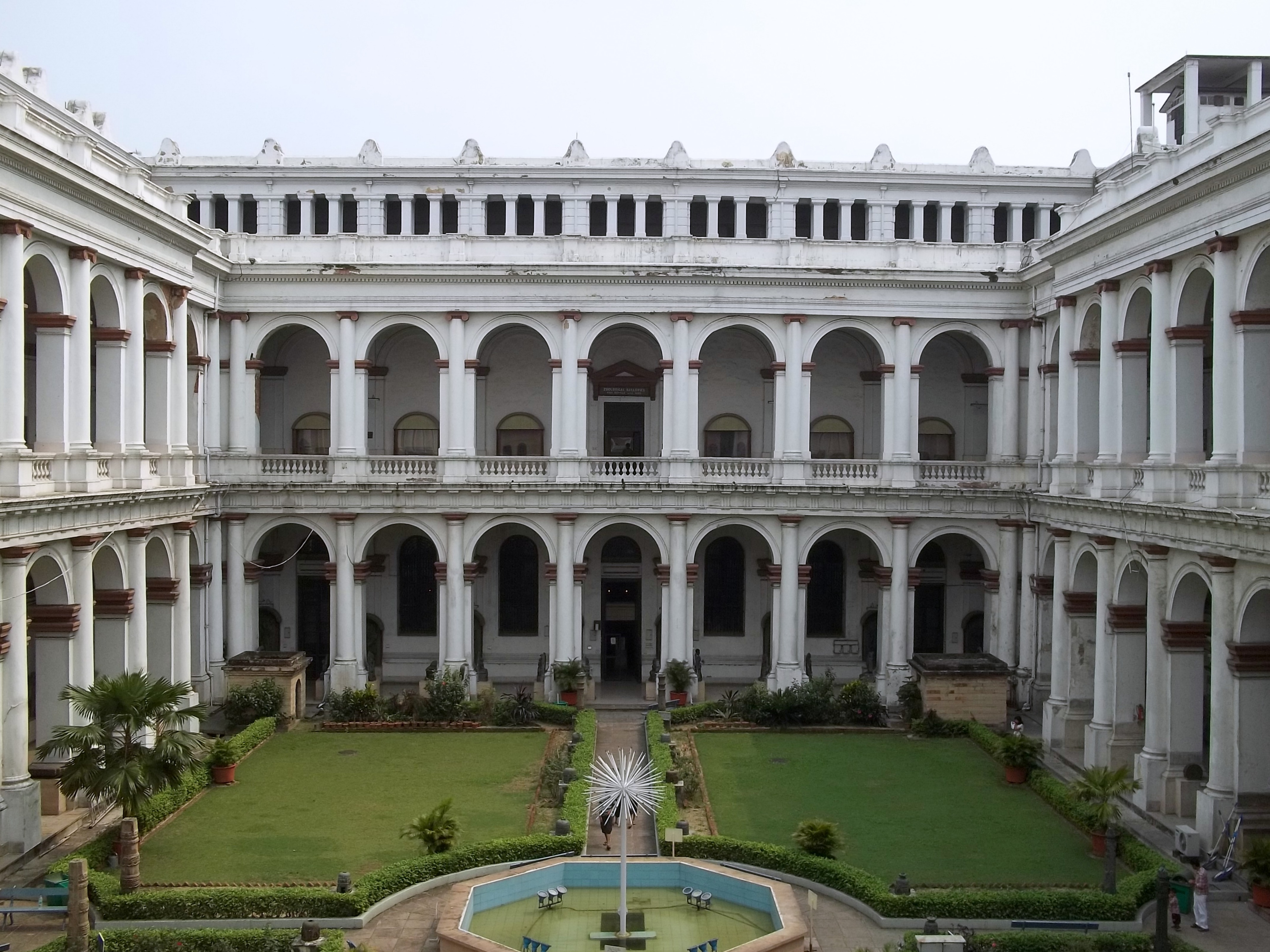 Kolkata has many buildings adorned with Indo-Islamic architecture, Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, Indo-Saracenic architectural motifs. Several well-maintained major buildings from the colonial period have been declared "heritage structures"; others are in various stages of decay. Established in 1814 as the nation's oldest museum, the
Kolkata has many buildings adorned with Indo-Islamic architecture, Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, Indo-Saracenic architectural motifs. Several well-maintained major buildings from the colonial period have been declared "heritage structures"; others are in various stages of decay. Established in 1814 as the nation's oldest museum, the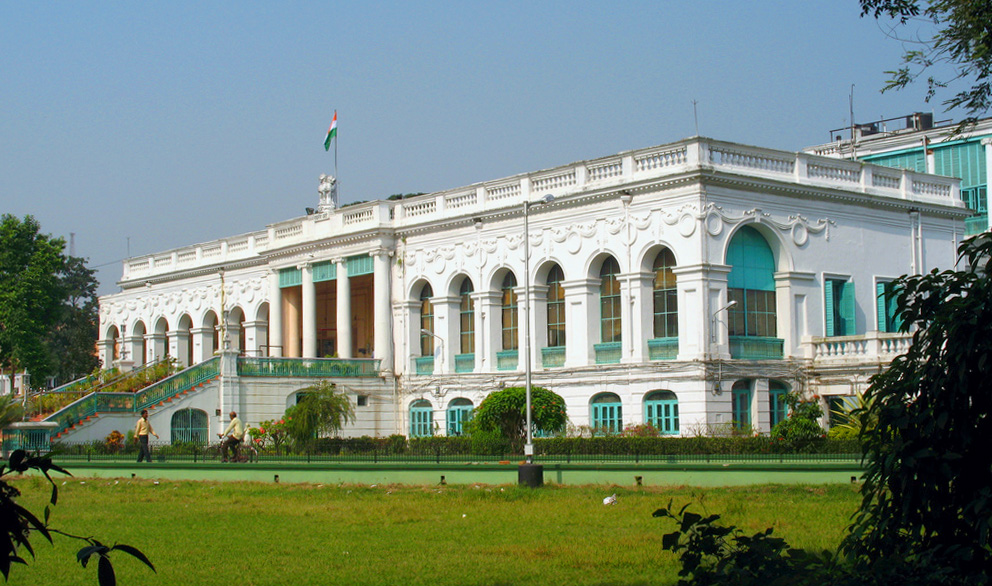  The popularity of commercial theatres in the city has declined since the 1980s. Group theatres of Kolkata, a cultural movement that started in the 1940s contrasting with the then-popular commercial theatres, are theatres that are not professional or commercial, and are centres of various experiments in theme, content, and production; group theatres use the proscenium stage to highlight socially relevant messages. Chitpur locality of the city houses multiple production companies of ''Jatra (Bengal), jatra'', a tradition of folk drama popular in rural Bengal. Kolkata is the home of the Cinema of West Bengal, Bengali cinema industry, dubbed "Tollywood" for Tollygunj, where most of the state's film studios are located. Parallel Cinema, Its long tradition of art films includes globally acclaimed film directors such as Academy Award-winning director Satyajit Ray, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen, Tapan Sinha and contemporary directors such as Aparna Sen, Buddhadeb Dasgupta, Goutam Ghose and Rituparno Ghosh. During the 19th and 20th centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Michael Madhusudan Dutt, Rabindranath Tagore, Kazi Nazrul Islam and Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay. Coupled with social reforms led by Ram Mohan Roy, Swami Vivekananda and others, this constituted a major part of the
The popularity of commercial theatres in the city has declined since the 1980s. Group theatres of Kolkata, a cultural movement that started in the 1940s contrasting with the then-popular commercial theatres, are theatres that are not professional or commercial, and are centres of various experiments in theme, content, and production; group theatres use the proscenium stage to highlight socially relevant messages. Chitpur locality of the city houses multiple production companies of ''Jatra (Bengal), jatra'', a tradition of folk drama popular in rural Bengal. Kolkata is the home of the Cinema of West Bengal, Bengali cinema industry, dubbed "Tollywood" for Tollygunj, where most of the state's film studios are located. Parallel Cinema, Its long tradition of art films includes globally acclaimed film directors such as Academy Award-winning director Satyajit Ray, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen, Tapan Sinha and contemporary directors such as Aparna Sen, Buddhadeb Dasgupta, Goutam Ghose and Rituparno Ghosh. During the 19th and 20th centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Michael Madhusudan Dutt, Rabindranath Tagore, Kazi Nazrul Islam and Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay. Coupled with social reforms led by Ram Mohan Roy, Swami Vivekananda and others, this constituted a major part of the 
 Kalighat painting originated in 19th century Kolkata as a local style that reflected a variety of themes including mythology and quotidian life. The Government College of Art & Craft, Government College of Art and Craft, founded in 1864, has been the cradle as well as workplace of eminent artists including Abanindranath Tagore, Jamini Roy and Nandalal Bose. The art college was the birthplace of the Bengal school of art that arose as an avant garde and nationalist movement reacting against the prevalent academic art styles in the early 20th century. The Academy of Fine Arts, Calcutta, Academy of Fine Arts and other art galleries hold regular art exhibitions. The city is recognised for its appreciation of ''Rabindra sangeet'' (songs written by Rabindranath Tagore) and Indian classical music, with important concerts and recitals, such as Dover Lane Music Conference, being held throughout the year; Bengali popular music, including Baul, ''baul'' folk ballads, ''kirtans'' and ''Gajan (festival), Gajan'' festival music; and modern music, including Bengali-language ''adhunik'' songs. Since the early 1990s, Indian rock#Rock scenes, new genres have emerged, including one comprising alternative folk–rock Rock music of West Bengal, Bengali bands. Another new style, ''jibonmukhi gaan'' ("songs about life"), is based on realism (arts), realism.
Kalighat painting originated in 19th century Kolkata as a local style that reflected a variety of themes including mythology and quotidian life. The Government College of Art & Craft, Government College of Art and Craft, founded in 1864, has been the cradle as well as workplace of eminent artists including Abanindranath Tagore, Jamini Roy and Nandalal Bose. The art college was the birthplace of the Bengal school of art that arose as an avant garde and nationalist movement reacting against the prevalent academic art styles in the early 20th century. The Academy of Fine Arts, Calcutta, Academy of Fine Arts and other art galleries hold regular art exhibitions. The city is recognised for its appreciation of ''Rabindra sangeet'' (songs written by Rabindranath Tagore) and Indian classical music, with important concerts and recitals, such as Dover Lane Music Conference, being held throughout the year; Bengali popular music, including Baul, ''baul'' folk ballads, ''kirtans'' and ''Gajan (festival), Gajan'' festival music; and modern music, including Bengali-language ''adhunik'' songs. Since the early 1990s, Indian rock#Rock scenes, new genres have emerged, including one comprising alternative folk–rock Rock music of West Bengal, Bengali bands. Another new style, ''jibonmukhi gaan'' ("songs about life"), is based on realism (arts), realism.
 Key elements of Bengali cuisine, Kolkata's cuisine include rice and a fish curry known as ''machher jhol'', which can be accompanied by desserts such as ''Rasgulla, roshogolla'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sandesh'', and a sweet yoghurt known as ''Mitha Dahi, mishti dohi''. Bengal's large repertoire of seafood dishes includes various preparations of ''ilish'', a fish that is a favourite among Calcuttans. Street foods such as ''beguni'' (fried battered eggplant slices), kati roll, ''kati'' roll (flatbread roll with vegetable or chicken, mutton or egg stuffing), ''Panipuri, phuchka'' (a deep-fried crêpe with tamarind sauce) and Indian Chinese cuisine from Chinatown, Kolkata, Chinatown are popular.
Key elements of Bengali cuisine, Kolkata's cuisine include rice and a fish curry known as ''machher jhol'', which can be accompanied by desserts such as ''Rasgulla, roshogolla'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sandesh'', and a sweet yoghurt known as ''Mitha Dahi, mishti dohi''. Bengal's large repertoire of seafood dishes includes various preparations of ''ilish'', a fish that is a favourite among Calcuttans. Street foods such as ''beguni'' (fried battered eggplant slices), kati roll, ''kati'' roll (flatbread roll with vegetable or chicken, mutton or egg stuffing), ''Panipuri, phuchka'' (a deep-fried crêpe with tamarind sauce) and Indian Chinese cuisine from Chinatown, Kolkata, Chinatown are popular.
 Though Bengali women traditionally wear the ''sari'', the ''shalwar kameez'' and Western attire is gaining acceptance among younger women. Western-style dress has greater acceptance among men, although the traditional ''dhoti'' and ''kurta'' are seen during festivals. Durga Puja, held in September–October, is Kolkata's most important and largest festival; it is an occasion for glamorous celebrations and artistic decorations. The Bengali New Year, known as Pohela Boishakh, Poila Boishak, as well as the harvest festival of Poush Parbon are among the city's other festivals; also celebrated are Kali Puja, Diwali, Chhath, Chhaith, Jivitputrika, Jitiya, Holi, Jagaddhatri Puja, Saraswati Puja, Rathayatra, Janmashtami, Maha Shivratri, Vishwakarma Puja, Lakshmi Puja, Ganesh Chathurthi, Makar Sankranti, Gajan (festival), Gajan, Kalpataru Day, Bhai Phonta, Maghotsab, Eid ul-Fitr, Eid, Muharram, Christmas, Buddha Purnima and Mahavir Jayanti. Cultural events include the Rabindra Jayanti, Independence Day (India), Independence Day (15 August), Republic Day (26 January), Kolkata Book Fair, the Dover Lane Music Festival, the Kolkata Film Festival, Nandikar's National Theatre Festival, Statesman Vintage & Classic Car Rally and Gandhi Jayanti.
Though Bengali women traditionally wear the ''sari'', the ''shalwar kameez'' and Western attire is gaining acceptance among younger women. Western-style dress has greater acceptance among men, although the traditional ''dhoti'' and ''kurta'' are seen during festivals. Durga Puja, held in September–October, is Kolkata's most important and largest festival; it is an occasion for glamorous celebrations and artistic decorations. The Bengali New Year, known as Pohela Boishakh, Poila Boishak, as well as the harvest festival of Poush Parbon are among the city's other festivals; also celebrated are Kali Puja, Diwali, Chhath, Chhaith, Jivitputrika, Jitiya, Holi, Jagaddhatri Puja, Saraswati Puja, Rathayatra, Janmashtami, Maha Shivratri, Vishwakarma Puja, Lakshmi Puja, Ganesh Chathurthi, Makar Sankranti, Gajan (festival), Gajan, Kalpataru Day, Bhai Phonta, Maghotsab, Eid ul-Fitr, Eid, Muharram, Christmas, Buddha Purnima and Mahavir Jayanti. Cultural events include the Rabindra Jayanti, Independence Day (India), Independence Day (15 August), Republic Day (26 January), Kolkata Book Fair, the Dover Lane Music Festival, the Kolkata Film Festival, Nandikar's National Theatre Festival, Statesman Vintage & Classic Car Rally and Gandhi Jayanti.
 The first newspaper in India, the ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette, Bengal Gazette'' started publishing from the city in 1780. Among Kolkata's widely circulated Bengali-language newspapers are ''Anandabazar Patrika'', ''Bartaman'', Ei Samay Sangbadpatra, ''Sangbad Pratidin'', ''Aajkaal'', ''Dainik Statesman'' and ''Ganashakti''. ''The Statesman (India), The Statesman'' and ''The Telegraph (Calcutta), The Telegraph'' are two major English-language newspapers that are produced and published from Kolkata. Other popular English-language newspapers published and sold in Kolkata include ''The Times of India'', ''Hindustan Times'', ''The Hindu'', ''The Indian Express'' and the ''Asian Age''. As the largest trading centre in East India, Kolkata has several high-circulation financial dailies, including ''The Economic Times'', ''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', ''Business Line'' and ''Business Standard''. Vernacular newspapers, such as those in the Hindi, Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati, Odia language, Odia, Punjabi language, Punjabi and Chinese languages, are read by minorities. Major periodicals based in Kolkata include ''Desh (magazine), Desh'', ''Sananda (magazine), Sananda'', ''Saptahik Bartaman'', ''Unish-Kuri'', ''Anandalok'' and ''Anandamela''. Historically, Kolkata has been the centre of the Little magazine movement#Bengali little magazine movement, Bengali little magazine movement.
All India Radio, the national state-owned radio broadcaster, airs several AM broadcasting, AM radio stations in the city. Kolkata has List of FM radio stations in India#Kolkata, 10 local radio stations broadcasting on frequency modulation, FM, including three from AIR. India's state-owned television broadcaster, Doordarshan, provides two free-to-air terrestrial channels, while a mix of Bengali, Hindi, English, and other regional channels are accessible via Cable television, cable subscription, direct-broadcast satellite services, or IPTV, internet-based television. List of Bengali-language television channels#News channels, Bengali-language 24-hour television news channels include ABP Ananda, News18 Bangla, Kolkata TV, Zee 24 Ghanta, TV9 Bangla and Republic Bangla.
The first newspaper in India, the ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette, Bengal Gazette'' started publishing from the city in 1780. Among Kolkata's widely circulated Bengali-language newspapers are ''Anandabazar Patrika'', ''Bartaman'', Ei Samay Sangbadpatra, ''Sangbad Pratidin'', ''Aajkaal'', ''Dainik Statesman'' and ''Ganashakti''. ''The Statesman (India), The Statesman'' and ''The Telegraph (Calcutta), The Telegraph'' are two major English-language newspapers that are produced and published from Kolkata. Other popular English-language newspapers published and sold in Kolkata include ''The Times of India'', ''Hindustan Times'', ''The Hindu'', ''The Indian Express'' and the ''Asian Age''. As the largest trading centre in East India, Kolkata has several high-circulation financial dailies, including ''The Economic Times'', ''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', ''Business Line'' and ''Business Standard''. Vernacular newspapers, such as those in the Hindi, Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati, Odia language, Odia, Punjabi language, Punjabi and Chinese languages, are read by minorities. Major periodicals based in Kolkata include ''Desh (magazine), Desh'', ''Sananda (magazine), Sananda'', ''Saptahik Bartaman'', ''Unish-Kuri'', ''Anandalok'' and ''Anandamela''. Historically, Kolkata has been the centre of the Little magazine movement#Bengali little magazine movement, Bengali little magazine movement.
All India Radio, the national state-owned radio broadcaster, airs several AM broadcasting, AM radio stations in the city. Kolkata has List of FM radio stations in India#Kolkata, 10 local radio stations broadcasting on frequency modulation, FM, including three from AIR. India's state-owned television broadcaster, Doordarshan, provides two free-to-air terrestrial channels, while a mix of Bengali, Hindi, English, and other regional channels are accessible via Cable television, cable subscription, direct-broadcast satellite services, or IPTV, internet-based television. List of Bengali-language television channels#News channels, Bengali-language 24-hour television news channels include ABP Ananda, News18 Bangla, Kolkata TV, Zee 24 Ghanta, TV9 Bangla and Republic Bangla.
 The most popular sports in Kolkata are association football, football and cricket. Unlike most parts of India, the residents show significant passion for football. Indian Football Association, the oldest football association of the country is based here. It administers football in West Bengal. Kolkata is home to the country's top football clubs such as Mohun Bagan A.C., East Bengal Club and the Mohammedan Sporting Club (Kolkata), Mohammedan Sporting Club.ATK Mohun Bagan FC and East Bengal FC are two clubs of the city compete in Indian Super League. The Calcutta Football League, which was started in 1898, is the oldest football league in Asia. Mohun Bagan A.C., one of the oldest football clubs in Asia, is the only organisation to be dubbed a "National Club of India". Football matches between Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, dubbed as the Kolkata Derby, witness large audience attendance and rivalry between patrons. The multi-use Salt Lake Stadium, also known as Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan, is India's second largest stadium by seating capacity. Most matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup were played in this stadium including both Semi-final matches and the Final match. Kolkata also accounted for 45% of total attendance in 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup with an average of 55,345 spectators. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world.
The most popular sports in Kolkata are association football, football and cricket. Unlike most parts of India, the residents show significant passion for football. Indian Football Association, the oldest football association of the country is based here. It administers football in West Bengal. Kolkata is home to the country's top football clubs such as Mohun Bagan A.C., East Bengal Club and the Mohammedan Sporting Club (Kolkata), Mohammedan Sporting Club.ATK Mohun Bagan FC and East Bengal FC are two clubs of the city compete in Indian Super League. The Calcutta Football League, which was started in 1898, is the oldest football league in Asia. Mohun Bagan A.C., one of the oldest football clubs in Asia, is the only organisation to be dubbed a "National Club of India". Football matches between Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, dubbed as the Kolkata Derby, witness large audience attendance and rivalry between patrons. The multi-use Salt Lake Stadium, also known as Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan, is India's second largest stadium by seating capacity. Most matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup were played in this stadium including both Semi-final matches and the Final match. Kolkata also accounted for 45% of total attendance in 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup with an average of 55,345 spectators. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world.
 As in the rest of India, cricket is popular in Kolkata and is played on various grounds throughout the city. Kolkata is home to Indian Premier League franchise Kolkata Knight Riders and the Bengal cricket team; the Cricket Association of Bengal, which regulates cricket in West Bengal, is also based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, football, badminton and carrom, are regularly organised here on an inter-locality or inter-club basis. The Maidan (Kolkata), Maidan, a vast field that serves as the city's largest park, hosts several minor football and cricket clubs and coaching institutes. Eden Gardens, which has a capacity of 80,000 , hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup.
Kolkata's Netaji Indoor Stadium served as host of the 1981 Asian Basketball Championship, where India's national basketball team finished 5th, ahead of teams that belong to Asia's basketball elite, such as Iran national basketball team, Iran. The city has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club, the first golf club built outside the United Kingdom. The other two are located at the Tollygunge Club and at Fort William (India), Fort William. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club hosts horse racing and polo matches. The Calcutta Polo Club is considered the oldest extant polo club in the world. The Calcutta Racket Club is a squash (sport), squash and racquet club in Kolkata. It was founded in 1793, making it one of the oldest rackets clubs in the world, and the first in the Indian subcontinent. The Calcutta South Club is a venue for national and international tennis tournaments; it held the first grass-court national championship in 1946. In the period 2005–2007, Sunfeast Open, a tier-III tournament on the Women's Tennis Association circuit, was held in the Netaji Indoor Stadium; it has since been discontinued.
The Calcutta Rowing Club hosts Sport rowing, rowing heats and training events. Kolkata, considered the leading centre of rugby union in India, gives its name to the oldest international tournament in rugby union, the Calcutta Cup. The Automobile Association of Eastern India, established in 1904, and the Bengal Motor Sports Club are involved in promoting motor sports and car rallies in Kolkata and West Bengal. The Beighton Cup, an event organised by the Bengal Hockey Association and first played in 1895, is India's oldest field hockey tournament; it is usually held on the Mohun Bagan Ground of the Maidan. Athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly, Pankaj Roy and Jhulan Goswami, who are former List of India national cricket captains, captains of the India national cricket team, Indian national cricket team; India at the Olympics, Olympic tennis bronze medalist Leander Paes, golfer Arjun Atwal, and former footballers Sailen Manna, Chuni Goswami, Pradip Kumar Banerjee, P. K. Banerjee and Subrata Bhattacharya (footballer), Subrata Bhattacharya.
As in the rest of India, cricket is popular in Kolkata and is played on various grounds throughout the city. Kolkata is home to Indian Premier League franchise Kolkata Knight Riders and the Bengal cricket team; the Cricket Association of Bengal, which regulates cricket in West Bengal, is also based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, football, badminton and carrom, are regularly organised here on an inter-locality or inter-club basis. The Maidan (Kolkata), Maidan, a vast field that serves as the city's largest park, hosts several minor football and cricket clubs and coaching institutes. Eden Gardens, which has a capacity of 80,000 , hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup.
Kolkata's Netaji Indoor Stadium served as host of the 1981 Asian Basketball Championship, where India's national basketball team finished 5th, ahead of teams that belong to Asia's basketball elite, such as Iran national basketball team, Iran. The city has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club, the first golf club built outside the United Kingdom. The other two are located at the Tollygunge Club and at Fort William (India), Fort William. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club hosts horse racing and polo matches. The Calcutta Polo Club is considered the oldest extant polo club in the world. The Calcutta Racket Club is a squash (sport), squash and racquet club in Kolkata. It was founded in 1793, making it one of the oldest rackets clubs in the world, and the first in the Indian subcontinent. The Calcutta South Club is a venue for national and international tennis tournaments; it held the first grass-court national championship in 1946. In the period 2005–2007, Sunfeast Open, a tier-III tournament on the Women's Tennis Association circuit, was held in the Netaji Indoor Stadium; it has since been discontinued.
The Calcutta Rowing Club hosts Sport rowing, rowing heats and training events. Kolkata, considered the leading centre of rugby union in India, gives its name to the oldest international tournament in rugby union, the Calcutta Cup. The Automobile Association of Eastern India, established in 1904, and the Bengal Motor Sports Club are involved in promoting motor sports and car rallies in Kolkata and West Bengal. The Beighton Cup, an event organised by the Bengal Hockey Association and first played in 1895, is India's oldest field hockey tournament; it is usually held on the Mohun Bagan Ground of the Maidan. Athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly, Pankaj Roy and Jhulan Goswami, who are former List of India national cricket captains, captains of the India national cricket team, Indian national cricket team; India at the Olympics, Olympic tennis bronze medalist Leander Paes, golfer Arjun Atwal, and former footballers Sailen Manna, Chuni Goswami, Pradip Kumar Banerjee, P. K. Banerjee and Subrata Bhattacharya (footballer), Subrata Bhattacharya.
Kolkata Municipal Corporation
*
– Incredible India
City Mayors: Richest cities in the world in 2020 by GDP
{{Authority control Kolkata, Cities and towns in Kolkata district Indian capital cities Metropolitan cities in India Port cities in India Capitals of former nations Former national capitals Former capital cities in India Populated places established in 1690 1690 establishments in Asia 1690 establishments in the British Empire 1690s establishments in India Capitals of Bengal Subdivisions of West Bengal Subdivisions in Kolkata district Cities in West Bengal
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
of the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River
The Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') or the 'Bhāgirathi-Hooghly', called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, Indi ...
west of the border with Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. It is the primary business, commercial, and financial hub of Eastern India
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha
and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha fr ...
and the main port of communication for North-East India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
. According to the 2011 Indian census, Kolkata is the seventh-most populous city in India, with a population of 45 lakh
A lakh (; abbreviated L; sometimes written lac) is a unit in the Indian numbering system equal to one hundred thousand (100,000; scientific notation: 105). In the Indian 2,2,3 convention of digit grouping, it is written as 1,00,000. For ex ...
(4.5 million) residents within the city limits, and a population of over 1.41 crore
A crore (; abbreviated cr) denotes ten million (10,000,000 or 107 in scientific notation) and is equal to 100 lakh in the Indian numbering system. It is written as 1,00,00,000 with the local 2,2,3 style of digit group separators (one lakh is e ...
(14.1 million) residents in the Kolkata Metropolitan Area
Kolkata Metropolitan Area (abbreviated KMA; formerly Calcutta Metropolitan Area), also known as Greater Kolkata, is the urban agglomeration of the city of Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the third most populous metropolitan are ...
. It is the third-most populous metropolitan area in India. In 2021, the Kolkata metropolitan area
Kolkata Metropolitan Area (abbreviated KMA; formerly Calcutta Metropolitan Area), also known as Greater Kolkata, is the urban agglomeration of the city of Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the third most populous metropolitan are ...
crossed 1.5 crore (15 million) registered voters. The Port of Kolkata
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the olde ...
is India's oldest operating port and its sole major riverine port. Kolkata is regarded as the cultural capital of India. Kolkata is the second largest Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
-speaking city after Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
. It has the highest number of nobel laureates among all cities in India.——
—
—
— In the late 17th century, the three villages that predated Calcutta were ruled by the
Nawab of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
under Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
. After the Nawab granted the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
a trading licence
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
in 1690, the area was developed by the Company into an increasingly fortified trading post known as Fort William. Nawab Siraj ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Beng ...
occupied Calcutta in 1756, and the East India Company retook it the following year. In 1793 the East India Company was strong enough to abolish native rule, and assumed full sovereignty of the region. Under company rule and later under the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
, Calcutta served as the capital of British-held territories in India until 1911. In that year, after assessing its geographical location, combined with growing nationalism in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
(Calcutta became the centre for the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
), the British moved the capital to the relatively more centrally located New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the capital of India and a part of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House ...
.
Following independence in 1947, Kolkata, which was once the premier centre of Indian commerce, culture, and politics, suffered many decades of political violence
Political violence is violence which is perpetrated in order to achieve political goals. It can include violence which is used by a state against other states (war), violence which is used by a state against civilians and non-state actors (forced ...
and economic stagnation
Economic stagnation is a prolonged period of slow economic growth (traditionally measured in terms of the GDP growth), usually accompanied by high unemployment. Under some definitions, "slow" means significantly slower than potential growth as es ...
before it rebounded. A demographically diverse global city, the culture of Kolkata
The culture of Kolkata concerns the music, art, museums, festivals, and lifestyle within Kolkata. It is the former capital of India and, , the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Geir Heierstad writes that Bengalis tend to have a special ...
features idiosyncrasies that include distinctively close-knit neighbourhoods (''paras'') and freestyle conversations (''adda''). Kolkata is home to eastern India's film industry, known as Tollywood, and cultural institutions, such as the Academy of Fine Arts
The following is a list of notable art schools.
Accredited non-profit art and design colleges
* Adelaide Central School of Art
* Alberta College of Art and Design
* Art Academy of Cincinnati
* Art Center College of Design
* The Art Institute o ...
, the Victoria Memorial
The Victoria Memorial is a large marble building on the Maidan in Central Kolkata, built between 1906 and 1921. It is dedicated to the memory of Queen Victoria, Empress of India from 1876 to 1901.
The largest monument to a monarch anywhere ...
, the Asiatic Society
The Asiatic Society is a government of India organisation founded during the Company rule in India to enhance and further the cause of "Oriental research", in this case, research into India and the surrounding regions. It was founded by the p ...
, the Indian Museum
The Indian Museum in Central Kolkata, West Bengal, India, also referred to as the Imperial Museum at Calcutta in colonial-era texts, is the ninth oldest museum in the world, the oldest and largest museum in India as well as in Asia. It has rare ...
, and the National Library of India
The National Library of India is a library located in Belvedere Estate, Alipore, Kolkata, India. It is India's largest library by volume and public record. The National Library is under Ministry of Culture (India), Ministry of Culture, Governm ...
. Among scientific institutions, Kolkata hosts the Agri Horticultural Society of India
The Agri Horticultural Society of India was founded in 1820 by William Carey (missionary), William Carey on the Alipore Road, Kolkata. It has a flower garden, greenhouses, a research laboratory and a library. It houses a massive collection of ...
, the Geological Survey of India
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India. It was founded in 1851, as a Government of India organization under the Ministry of Mines, one of the oldest of such organisations in the world and the second oldest survey ...
, the Botanical Survey of India
Botanical Survey of India (BSI) located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It was founded on 13 February 1890, is Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's organization for survey, research and conservation of plan ...
, the Calcutta Mathematical Society
The Calcutta Mathematical Society (CalMathSoc) is an association of professional mathematicians dedicated to the interests of mathematical research and education in India. The Society has its head office located at Kolkata, India.
History
C ...
, the Indian Science Congress Association
Indian Science Congress Association(ISCA) is a premier scientific organisation of India with headquarters at Kolkata, West Bengal. The association started in the year 1914 in Kolkata and it meets annually in the first week of January. It has a ...
, the Zoological Survey of India
The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), founded on 1 July 1916 by Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, as premier Indian organisation in zoological research and studies to promote the survey, exploration and r ...
, the Institution of Engineers, the Anthropological Survey of India
Anthropological Survey of India (AnSI) is the apex Indian government organisation involved in anthropological studies and field data research for human and cultural aspects, working primarily in the fields of physical anthropology and cultural ...
and the Indian Public Health Association
Indian Public Health Association shortly IPHA is a professional health organization working for the cause of Public Health in India since 1956. It is registered under Societies Registration Act
A society is a group of individuals involv ...
. Four Nobel laureates
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make ou ...
and two Nobel Memorial Prize winners are associated with the city.——
—
—
— Though home to major cricketing venues and franchises, Kolkata stands out in India for being the country's centre of
association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
and also having strong culture in other sports less widespread elsewhere.
Etymology
The word ''Kolkata'' ( bn, কলকাতা ) derives from '' Kôlikata'' ( ), theBengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second m ...
name of one of three villages that predated the arrival of the British, the other two villages were Sutanuti
Sutanuti was one of the three villages which were merged to form the city of Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) in India. The other two villages were Gobindapur and Kalikata.
See also
* European colonies in India
Colonial India was the part of th ...
and Govindapur.
There are several explanations for the etymology of this name:
*''Kolikata'' is thought to be a variation of ''Kalikkhetrô'' ( ), meaning "Field of he goddess
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
Kali
Kali (; sa, काली, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, कालिका), is a Hinduism, Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In t ...
". Similarly, it can be a variation of 'Kalikshetra' (Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
: कालीक्षेत्र, lit. "area of Goddess Kali").
*Another theory is that the name derives from Kalighat
Kalighat is a locality of Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India. One of the oldest neighbourhoods in South Kolkata, Kalighat is also densely populated — with a history of cultural intermingling with the various foreign incursions i ...
.
*Alternatively, the name may have been derived from the Bengali term ''kilkila'' ( bn, কিলকিলা), or "flat area".
*The name may have its origin in the words ''khal'' ( bn, খাল ) meaning "canal", followed by ''kaṭa'' ( bn, কাটা ), which may mean "dug".
*According to another theory, the area specialised in the production of quicklime
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ma ...
or ''koli chun'' ( bn, কলি চুন ) and coir or ''kata'' ( bn, কাতা ); hence, it was called ''Kolikata'').
Although the city's name has always been pronounced ''Kolkata'' or ''Kôlikata'' in Bengali, the anglicised form ''Calcutta'' was the official name until 2001, when it was changed to ''Kolkata'' in order to match Bengali pronunciation.
History

British colonial rule
 The discovery and
The discovery and archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
study of Chandraketugarh
Chandraketugarh is a 2,500 years old archaeological site located near the Bidyadhari river, about north-east of Kolkata, India, in the district of North 24 parganas, near the township of Berachampa and the Harua Road railhead. Once it was a ...
, north of Kolkata, provide evidence that the region in which the city stands has been inhabited for over two millennia. Kolkata's recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
began in 1690 with the arrival of the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
, which was consolidating its trade business in Bengal. Job Charnock
Job Charnock (; –1692/1693) was an English administrator with the East India Company. He is commonly regarded as the founder of the city of Kolkata (formerly Calcutta); however, this view is challenged, and in 2003 the Calcutta High Court de ...
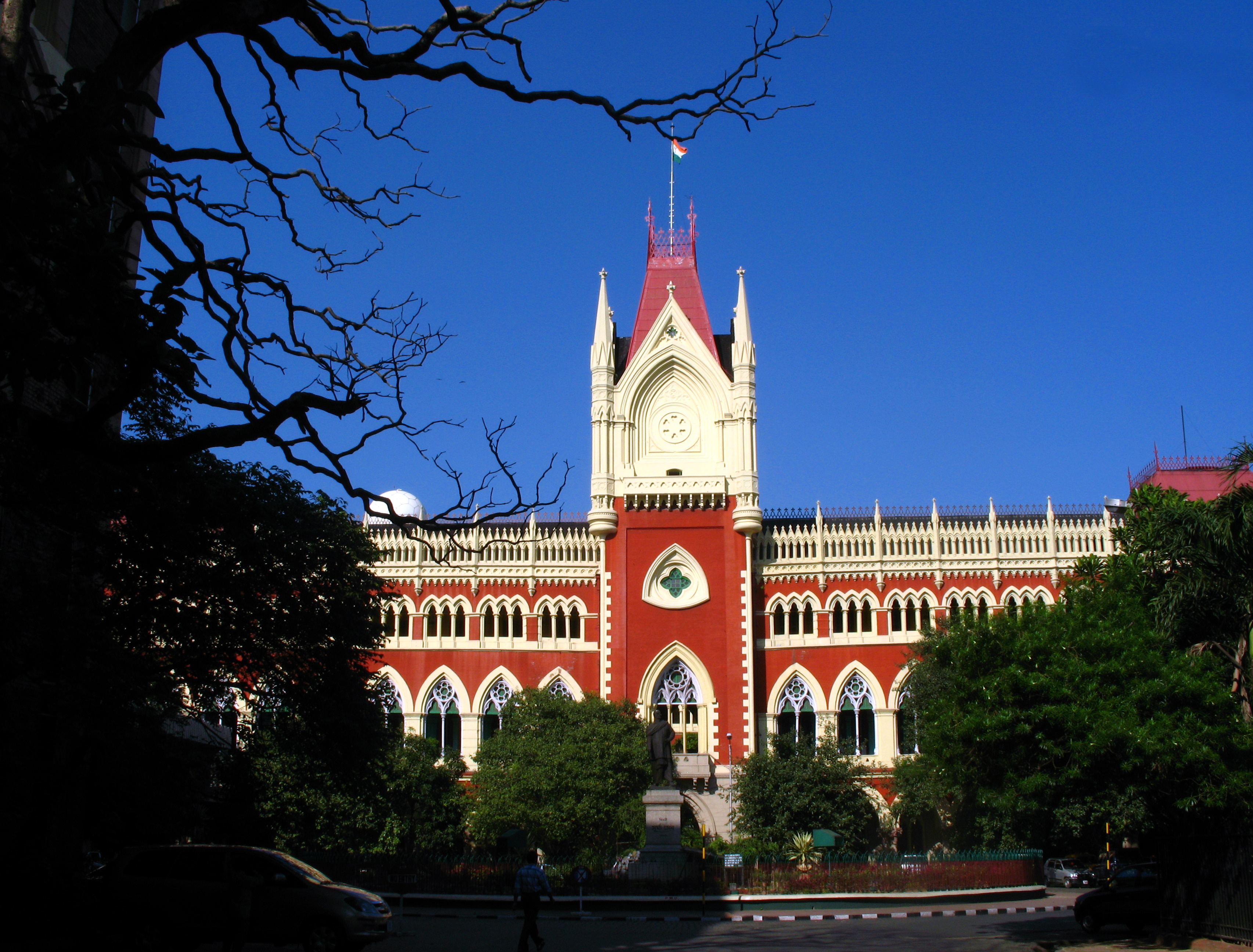
, an administrator who worked for the company, was formerly credited as the founder of the city; In response to a public petition, the Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located in B.B.D. Bagh, Kolkata, West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The High Court buildi ...
ruled in 2003 that the city does not have a founder. The area occupied by the present-day city encompassed three villages: Kalikata
Kalikata was one of the three villages which were merged to form the city of Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) in India. The other two villages were Gobindapur and Sutanuti. Job Charnock, an administrator with the British East India Company is tradit ...
, Gobindapur and Sutanuti
Sutanuti was one of the three villages which were merged to form the city of Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) in India. The other two villages were Gobindapur and Kalikata.
See also
* European colonies in India
Colonial India was the part of th ...
. Kalikata was a fishing village; Sutanuti was a riverside weavers' village. They were part of an estate belonging to the Mughal emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
; the ''jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, start ...
dari'' (a land grant bestowed by a king on his noblemen) taxation rights to the villages were held by the Sabarna Roy Choudhury
Sabarna Roy Choudhury was a Zamindar family of Mughal Bengal. They controlled significant swathes of territory, including what would later become Kolkata, prior to the sale of zamindari rights in 1698 to the East India Company.
Zamindari
E ...
family of landowners, or ''zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as a ...
s''. These rights were transferred to the East India Company in 1698.
 In 1712, the British completed the construction of Fort William, located on the east bank of the Hooghly River to protect their trading factory. Facing frequent skirmishes with
In 1712, the British completed the construction of Fort William, located on the east bank of the Hooghly River to protect their trading factory. Facing frequent skirmishes with French forces
The French Armed Forces (french: Forces armées françaises) encompass the French Army, Army, the French Navy, Navy, the French Air and Space Force, Air and Space Force and the National Gendarmerie, Gendarmerie of the French Republic. The Preside ...
, the British began to upgrade their fortifications in 1756. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah, condemned the militarisation and tax evasion by the company. His warning went unheeded, and the Nawab attacked; he captured Fort William which led to the killings of several East India company officials in the Black Hole of Calcutta
The Black Hole of Calcutta was a dungeon in Fort William, Calcutta, measuring , in which troops of Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, held British prisoners of war on the night of 20 June 1756. John Zephaniah Holwell, one of the British p ...
. A force of Company soldiers (''sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire.
In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its oth ...
s'') and British troops led by Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
recaptured the city the following year. Per the 1765 Treaty of Allahabad
The Treaty of Allahabad was signed on 12 August 1765, between the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II, son of the late Emperor Alamgir II, and Robert Clive, of the East India Company, in the aftermath of the Battle of Buxar of 23 October 1764. The tre ...
following the battle of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, led by Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, Nawab of Bengal till 1764; the Nawab of Awadh, Sh ...
, East India company was appointed imperial tax collector of the Mughal emperor in the province of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa, while Mughal-appointed Nawabs continued to rule the province. Declared a presidency city, Calcutta became the headquarters of the East India Company by 1773.
In 1793, ruling power of the Nawabs were abolished and East India company took complete control of the city and the province. In the early 19th century, the marshes surrounding the city were drained; the government area was laid out along the banks of the Hooghly River. Richard Wellesley Richard Wellesley may refer to:
* Richard Wellesley, 1st Marquess Wellesley (1760–1842), Anglo-Irish politician and colonial administrator
* Richard Wellesley (1787–1831), his son, Anglo-Irish Member of Parliament
* Richard Wellesley, 6th Earl ...
, Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William
The Governor-General of India (1773–1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 19 ...
between 1797 and 1805, was largely responsible for the development of the city and its public architecture. Throughout the late 18th and 19th century, the city was a centre of the East India Company's opium trade. A census in 1837 records the population of the city proper as 229,700, of which the British residents made up only 3,138. The same source says another 177,000 resided in the suburbs and neighbouring villages, making the entire population of greater Calcutta 406,700.
In 1864, a typhoon struck the city and killed about 60,000 in Kolkata.
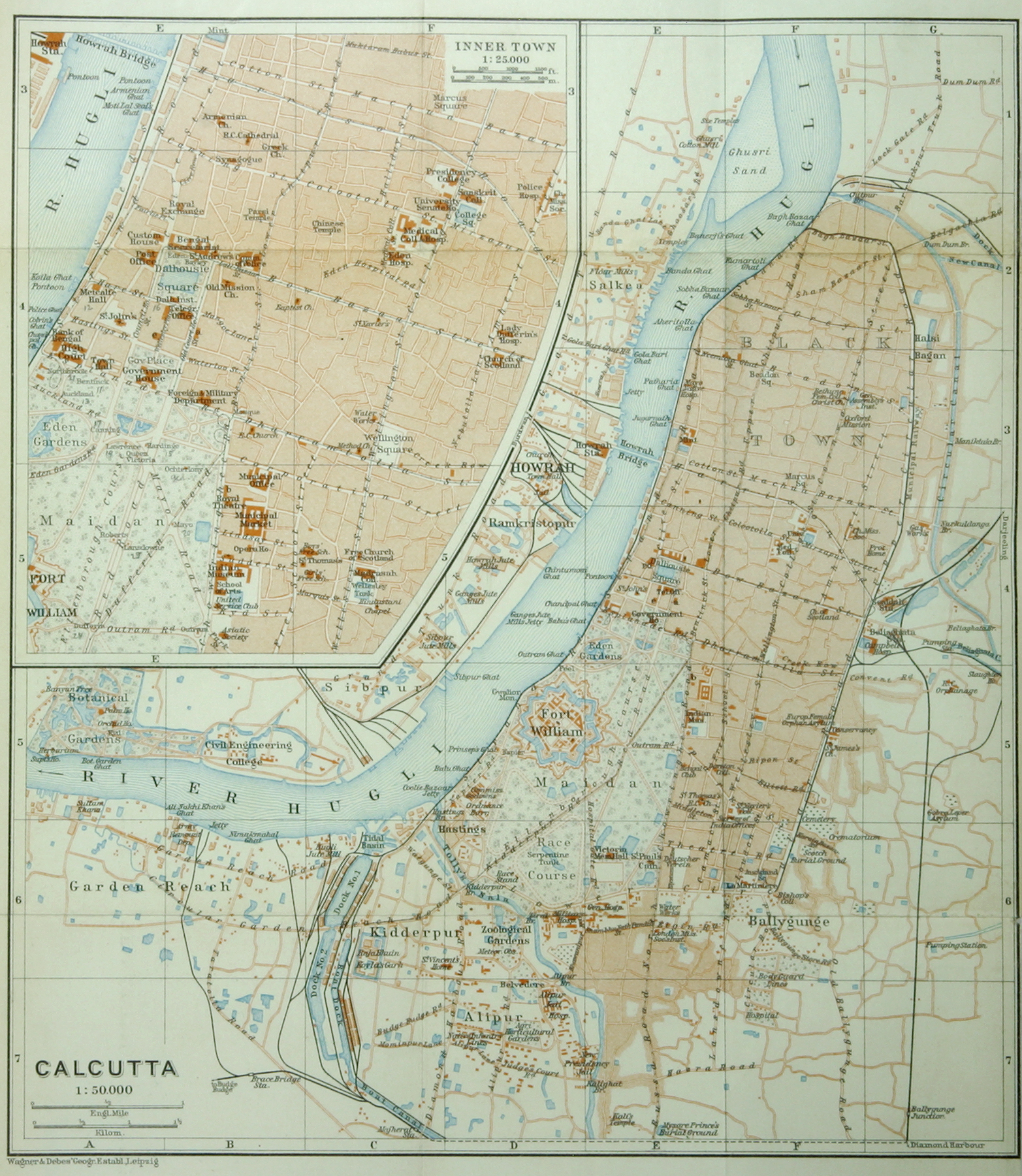
By the 1850s, Calcutta had two areas: White Town, which was primarily British and centred on Chowringhee
Chowringhee (also Chourangi) is a neighbourhood of Central Kolkata, in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. Chowringhee Road (officially Jawaharlal Nehru Road) runs on its western side. A neighbourhood steeped in history, it is a ...
and Dalhousie Square
B. B. D. Bagh, formerly called Tank Square and then Dalhousie Square (1847 to 1856), is the shortened version for Benoy-Badal-Dinesh Bagh. It is the seat of power of the state government, as well as the central business district of Kolkata in ...
; and Black Town, mainly Indian and centred on North Calcutta. The city underwent rapid industrial growth starting in the early 1850s, especially in the textile and jute industries; this encouraged British companies to massively invest in infrastructure projects, which included telegraph connections and Howrah railway station
Howrah railway station, also known as Howrah Junction, is a railway station located in the city of Howrah, West Bengal, India. It is also the oldest and largest existing railway complex in India. It is one of the busiest train stations in the w ...
. The coalescence of British and Indian culture resulted in the emergence of a new '' babu'' class of urbane Indians, whose members were often bureaucrats, professionals, newspaper readers, and Anglophiles; they usually belonged to upper-caste Hindu communities. In the 19th century, the Bengal Renaissance
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
brought about an increased sociocultural sophistication among city denizens. In 1883, Calcutta was host to the first national conference of the Indian National Association
The Indian Association was the first avowed nationalist organization founded in British India by Surendranath Banerjee and Ananda Mohan Bose in 1876. The objectives of this Association were "promoting by every legitimate means the political, in ...
, the first avowed nationalist organisation in India.
 The partition of Bengal in 1905 along religious lines led to mass protests, making Calcutta a less hospitable place for the British. The capital was moved to
The partition of Bengal in 1905 along religious lines led to mass protests, making Calcutta a less hospitable place for the British. The capital was moved to New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the capital of India and a part of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House ...
in 1911. Calcutta continued to be a centre for revolutionary organisations associated with the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
. The city and its port were bombed several times by the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
between 1942 and 1944, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Coinciding with the war, millions starved to death during the Bengal famine of 1943
The Bengal famine of 1943 was a famine in the Bengal province of British India (present-day Bangladesh, West Bengal and eastern India) during World War II. An estimated 0.8 to 3.8 million Bengalis perished, out of a population of 60.3 millio ...
due to a combination of military, administrative, and natural factors. Demands for the creation of a Muslim state led in 1946 to an episode of communal violence that killed over 4,000. The partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
led to further clashes and a demographic shift—many Muslims left for East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
(present day Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
), while hundreds of thousands of Hindus fled into the city.
Contemporary
During the 1960s and 1970s, severe power shortages, strikes and a violentMarxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
–Maoist
Maoism, officially called Mao Zedong Thought by the Chinese Communist Party, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed to realise a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of Ch ...
movement by groups known as the Naxalites damaged much of the city's infrastructure, resulting in economic stagnation.——
— The
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
of 1971 led to a massive influx of thousands of refugees, many of them penniless, that strained Kolkata's infrastructure. During the mid-1980s, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
(then called Bombay) overtook Kolkata as India's most populous city. In 1985, Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi (; 20 August 1944 – 21 May 1991) was an Indian politician who served as the sixth prime minister of India from 1984 to 1989. He took office after the 1984 assassination of his mother, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, to beco ...
dubbed Kolkata a "dying city" in light of its socio-political woes. In the period 1977–2011, West Bengal was governed from Kolkata by the Left Front, which was dominated by the Communist Party of India
Communist Party of India (CPI) is the oldest Marxist–Leninist communist party in India and one of the nine national parties in the country. The CPI was founded in modern-day Kanpur (formerly known as Cawnpore) on 26 December 1925.
H ...
(CPM). It was the world's longest-serving democratically elected communist government, during which Kolkata was a key base for Indian communism
Communism in India has existed as a social or political ideology as well as a political movement since at least as early as the 1920s. In its early years, communist ideology was harshly suppressed through legal prohibitions and criminal prosecut ...
. In the 2011 West Bengal Legislative Assembly election
Assembly election was held in Indian state of West Bengal in 2011 to elect the members of West Bengal Legislative Assembly as the term of the incumbent government was about to expire naturally. It was held in six phases between 18 April and 10 ...
, Left Front was defeated by the Trinamool Congress
The All India Trinamool Congress (English: All India Grassroots Congress; AITC), colloquially the Trinamool Congress ( TMC) is an Indian political party which is predominantly active in West Bengal. The party is led by Mamata Banerjee, the cur ...
. The city's economic recovery gathered momentum after the 1990s, when India began to institute pro-market reforms. Since 2000, the information technology (IT) services sector has revitalised Kolkata's stagnant economy. The city is also experiencing marked growth in its manufacturing base.
Geography
Spread roughly north–south along the east bank of theHooghly River
The Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') or the 'Bhāgirathi-Hooghly', called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, Indi ...
, Kolkata sits within the lower Ganges Delta of eastern India approximately 75 km (47 mi) west of the international border with Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
; the city's elevation is . Much of the city was originally a wetland that was reclaimed over the decades to accommodate a burgeoning population. The remaining undeveloped areas, known as the East Kolkata Wetlands
The East Calcutta Wetlands, (22 0 27’ N 88 0 27’ E), are a complex of natural and human-made wetlands lying east of the city of Calcutta (Kolkata), of West Bengal in India. The wetlands cover 125 square kilometres and include salt marsh ...
, were designated a "wetland of international importance" by the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It i ...
(1975). As with most of the Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
, the soil and water are predominantly alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
in origin. Kolkata is located over the "Bengal basin", a pericratonic tertiary basin. Bengal basin comprises three structural units: shelf or platform in the west; central hinge or shelf/slope break; and deep basinal part in the east and southeast. Kolkata is located atop the western part of the hinge zone which is about wide at a depth of about below the surface. The shelf and hinge zones have many faults, among them some are active. Total thickness of sediment below Kolkata is nearly above the crystalline basement
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The baseme ...
; of these the top is Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
, followed by of Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
sediments, trap
A trap is a mechanical device used to capture or restrain an animal for purposes such as hunting, pest control, or ecological research.
Trap or TRAP may also refer to:
Art and entertainment Films and television
* ''Trap'' (2015 film), Fil ...
wash of Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
trap and Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
-Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
rocks. The quaternary sediments consist of clay, silt and several grades of sand and gravel. These sediments are sandwiched between two clay beds: the lower one at a depth of ; the upper one in thickness. According to the Bureau of Indian Standards
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is the National Standards Body of India under Department of Consumer affairs, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Government of India. It is established by the Bureau of Indian Standar ...
, on a scale ranging from in order of increasing susceptibility to earthquakes, the city lies inside seismic zone III.
Urban structure

 The
The Kolkata metropolitan area
Kolkata Metropolitan Area (abbreviated KMA; formerly Calcutta Metropolitan Area), also known as Greater Kolkata, is the urban agglomeration of the city of Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the third most populous metropolitan are ...
is spread over and comprises 4 municipal corporations (including Kolkata Municipal Corporation), 37 local municipalities and 24 panchayat samiti
Panchayat samiti is a rural local government (panchayat) body at the intermediate tehsil (taluka/mandal) level in India. It works for the villages of the tehsil that together are called a development block. It has been said to be the "panchayat ...
s, as of 2011. The urban agglomeration encompassed 72 cities and 527 towns and villages, as of 2006. Suburban areas in the Kolkata metropolitan area incorporate parts of the following districts: North 24 Parganas
North 24 Parganas (abv. 24 PGS (N)) or sometimes North Twenty Four Parganas is a district in southern West Bengal, of eastern India. North 24 Parganas extends in the tropical zone from latitude 22° 11′ 6″ north to 23° 15′ 2″ north and f ...
, South 24 Parganas
South 24 Parganas (Pron: pɔrɡɔnɔs; abbr. 24 PGS (S)), or sometimes South Twenty Four Parganas and Dakshin 24 Parganas, is a district in the Indian state of West Bengal, headquartered in Alipore. It is the largest district of West Bengal by ...
, Howrah
Howrah (, , alternatively spelled as Haora) is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. Howrah is located on the western bank of the Hooghly River opposite its twin city of Kolkata. Administratively it lies within Howrah district, and is th ...
, Hooghly and Nadia
Nadia is a female name. Variations include Nadja, Nadya, Nadine, Nadiya, and Nadiia. Most variations of the name are derived from Arabic, Slavic languages, or both.
In Slavic, names similar to ''Nadia'' mean "hope" in many Slavic languages: Uk ...
. Kolkata, which is under the jurisdiction of the Kolkata Municipal Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, '' ...
(KMC), has an area of . The east–west dimension of the city is comparatively narrow, stretching from the Hooghly River in the west to roughly the Eastern Metropolitan Bypass
The Eastern Metropolitan Bypass (known simply as both ''E.M. Bypass'' and ''EM Bypass'') is a (Including Kamalgazi to Baruipur extension) major road on the east side of Kolkata. It connects Ultadanga (North Kolkata) to Baruipur Puratan Baza ...
in the east—a span of . The north–south distance is greater, and its axis is used to section the city into North, Central, South and East Kolkata.
North Kolkata is the oldest part of the city. Characterised by 19th-century architecture and narrow alleyways, it includes areas such as Jorasanko
Jorasanko is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India. It is so called because of the two (''jora'') wooden or bamboo bridges (''sanko'') that spanned a small stream at this point.
History
Apart from the disting ...
, Rajabazar, Maniktala
Maniktala is a residential area of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India.
Etymology
The tomb of Manik Pir is located in lane near Maniktala crossing. Some people say, the neighbourhood is named after Manik Pir.
Others say, M ...
, Ultadanga
Ultadanga is one of the most crowded junctions in Kolkata. The place is located at the north-eastern fringe of the city and marks the limit of Kolkata district. Prominent places in Ultadanga are Telenga Bagan and Muchi Bazar.
Etymology
Ultad ...
, Shyambazar
Shyambazar is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata
North Kolkata encompasses the northern part of Kolkata, including the city's oldest neighbourhood.
Shyambazar, Bagbazar, Kumartuli, Shobhabazar, Posta, Jorasanko, Rajabazar, Phoolbagan, Mani ...
, Shobhabazar
Shobhabazar (also spelt Sovabazar; bn, শোভাবাজার) is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district, in the Indian state of West Bengal.
History
Sheths and Basaks, well-to-do traders at Saptagram, were among the first ...
, Bagbazar
Bagbazar (also spelt Baghbazar) is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. The area, under Shyampukur police station of Kolkata Police, has been, along with neighbouring Shyambazar, the citadel of ...
, Cossipore
Kashipur (also spelt Cossipur, Kashipur) is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. One of the oldest neighbourhoods of the metropolis, it has a police station.
History
The East India Company o ...
, Sinthee
Sinthee or Sinthi is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India.
History
The East India Company obtained from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar, in 1717, the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their settleme ...
etc. The north suburban areas like Dum Dum
Dum Dum is a city and a municipality of Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of Kolkata urban area and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
Etymology
During the 19th ...
, Baranagar
("City of hogs")
, settlement_type =
City
, image_seal =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, pushpin_map = India West Bengal#India3#Asia
, pushpin_label_ ...
, Belgharia
Belgharia is a locality in Kamarhati Municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA) and a vital locality in Kolkata metropol ...
, Sodepur
Sodepur or Sodpur is a locality in Panihati, Panihati Municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of West Bengal. It is close to Kolkata and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropo ...
, Khardaha
Khardaha is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is near Kolkata and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
History
Initially Khardah was a ...
, New Barrackpore
New Barrackpore is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is close to Kolkata & a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority. It is the capital of Kolkata.
Geo ...
, Madhyamgram
Madhyamgram is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is close to Kolkata and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
History
Madhyamgram w ...
, Barrackpore
Barrackpore (also known as Barrackpur) is a city and a municipality of urban Kolkata of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA ...
, Barasat
Barasat () is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of Barasat Sadar subdivision. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA) ...
etc. are also within the city of Kolkata (as a metropolitan structure). Central Kolkata hosts the central business district. It contains B. B. D. Bagh
B. B. D. Bagh, formerly called Tank Square and then Dalhousie Square (1847 to 1856), is the shortened version for Benoy-Badal-Dinesh Bagh. It is the seat of power of the state government, as well as the central business district of Kolkata in ...
, formerly known as Dalhousie Square, and the Esplanade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortress or city walls to provide cle ...
on its east; Rajiv Gandhi Sarani is on its west. The West Bengal Secretariat, General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II in 1660. ...
, Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India, chiefly known as RBI, is India's central bank and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible for ...
, Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located in B.B.D. Bagh, Kolkata, West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The High Court buildi ...
, Lalbazar
Lalbazar is a neighbourhood in Central Kolkata, earlier known as Calcutta, in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is part of the central business district adjoining B.B.D. Bagh area. The headquarters of the Kolkata Police is located here (18, Lal ...
Police Headquarters and several other government and private offices are located there. Another business hub is the area south of Park Street, which comprises thoroughfares such as Jawahar Lal Nehru Road, Abanindra Nath Tagore Sarani, Dr. Martin Luther King Sarani, Dr. Upendra Nath Brahmachari Sarani, Shakespeare Sarani
Shakespeare Sarani (earlier Theatre Road) is a street running in the central business district of Kolkata, India, from Park Circus to Chowringhee Road (Birla Planetarium). It was renamed on 24 April 1964 after William Shakespeare, to mark the f ...
and Acharay Jagadish Chandra Basu Road. South Kolkata developed after India gained independence in 1947; it includes upscale neighbourhoods such as Bhawanipore
Bhowanipore (also Bhowanipur; bn, ভবানীপুর) is a neighbourhood of South Kolkata in Kolkata district of West Bengal, India.
History
In 1717, the East India Company obtained the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their s ...
, Alipore
Alipore (Pron:ˌɑ:lɪˈpɔ:) is a neighbourhood in south Kolkata, in Kolkata district, in the Indian state of West Bengal.
It is flanked by the Tolly Nullah to the north, Bhowanipore to the east, the Diamond Harbour Road to the west and New ...
, Ballygunge
Ballygunge is a locality of South Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India.
History
The East India Company obtained from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar, in 1717, the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their settlement. Of thes ...
, Kasba, Dhakuria
Dhakuria is a locality in the city of Kolkata, (previously Calcutta), in West Bengal, India.
It is located in the southern part of the city and is surrounded by Ballygunge and Kasba in the north, Haltu in the east, Jadavpur/ Garia in the south ...
, Santoshpur, Garia, Golf Green, Tollygunge, New Alipore, Behala, Barisha, India, Barisha etc. The south suburban areas like Maheshtala, Budge Budge, Rajpur Sonarpur, Baruipur etc. are also within the city of Kolkata (as a metropolitan structure). The Maidan (Kolkata), Maidan is a large open field in the heart of the city that has been called the "lungs of Kolkata" and accommodates sporting events and public meetings. The Victoria Memorial (India), Victoria Memorial and Kolkata Race Course are located at the southern end of the Maidan. Among the other parks are Central Park (Kolkata), Central Park in Bidhannagar and Millennium Park (Kolkata), Millennium Park on Rajiv Gandhi Sarani, along the Hooghly River.
Two planned townships in the greater Kolkata region are Bidhannagar, Kolkata, Bidhannagar, also known as Salt Lake City and located north-east of the city; and Rajarhat, also called New Town, Kolkata, New Town and located east of Bidhannagar. In the 2000s, Sector 5 in Bidhannagar developed into a business hub for information technology and telecommunication companies. Both Bidhannagar and New Town are situated outside the Kolkata Municipal Corporation limits, in their own municipalities.
Climate
Kolkata is subject to a tropical savanna climate, tropical wet-and-dry climate that is designated ''Aw'' under the Köppen climate classification. According to a United Nations Development Programme report, its wind and cyclone zone is "very high damage risk".Temperature
The annual mean temperature is ; monthly mean temperatures are . Summers (March–June) are hot and humid, with temperatures in the low 30s Celsius; during dry spells, maximum temperatures sometime exceed 40 °C (104 °F) in May and June. Winter lasts for roughly months, with seasonal lows dipping to in December and January. May is the hottest month, with daily temperatures ranging from ; January, the coldest month, has temperatures varying from . The highest recorded temperature is , and the lowest is . The winter is mild and very comfortable weather pertains over the city throughout this season. Often, in April–June, the city is struck by heavy rains or dusty squalls that are followed by thunderstorms or hailstorms, bringing cooling relief from the prevailing humidity. These thunderstorms are Convection rain, convective in nature, and are known locally as ''kal bôishakhi'' (), or "Nor'westers" in English.Rainfall
Rains brought by the Bay of Bengal branch of the Southwest monsoon, south-west summer monsoon lash Kolkata between June and September, supplying it with most of its annual rainfall of about . The highest monthly rainfall total occurs in July and August. In these months often incessant rain for days brings life to a stall for the city dwellers. The city receives 2,107 hours of sunshine per year, with maximum Insolation, sunlight exposure occurring in April. Kolkata has been hit by several cyclones; these include systems occurring in 1737 Calcutta cyclone, 1737 and 1864 Calcutta cyclone, 1864 that killed thousands. More recently, Cyclone Aila in 2009 and Cyclone Amphan in 2020 caused widespread damage to Kolkata by bringing catastrophic winds and torrential rainfall.Environmental issues
Pollution is a major concern in Kolkata. , sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide annual concentration were within the national ambient air quality standards of India, but respirable Particulates, suspended particulate matter levels were high, and on an increasing trend for five consecutive years, causing smog and haze. Severe air pollution in the city has caused a rise in pollution-related respiratory ailments, such as lung cancer.Economy
 Kolkata is the commercial and financial hub of East India, East and
Kolkata is the commercial and financial hub of East India, East and North-East India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
and home to the Calcutta Stock Exchange Association Limited, Calcutta Stock Exchange. It is a major commercial and military port, and is one of five cities in eastern India (alongside Biju Patnaik Airport, Bhubaneswar, Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport, Guwahati, Imphal Airport, Imphal, and Kushinagar International Airport, Kushinagar) to have Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, an international airport. Once India's leading city, Kolkata experienced a steady economic decline in the decades following India's independence due to steep population increases and a rise in militant trade-unionism, which included frequent strikes that were backed by left-wing parties. From the 1960s to the late 1990s, several factories were closed and businesses relocated. The lack of capital and resources added to the depressed state of the city's economy and gave rise to an unwelcome sobriquet: the "dying city". The city's fortunes improved after the Economy of India, Indian economy was liberalised in the 1990s and changes in economic policy were enacted by the West Bengal state government. Recent estimates of the economy of Kolkata's metropolitan area have ranged from $150 to $250 billion (Purchasing power parity, PPP Gross domestic product, GDP), and have ranked it List of cities by GDP, third-most productive metro area of India.——
—
 Flexible production has been the norm in Kolkata, which has an informal sector that employs more than 40% of the labour force. One unorganised group, Hawkers in Kolkata, roadside hawkers, generated business worth 87.72 billion ( 2 billion) in 2005. , around 0.81% of the city's workforce was employed in the Primary sector of the economy, primary sector (agriculture, forestry, mining, etc.); 15.49% worked in the Secondary sector of the economy, secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing); and 83.69% worked in the Tertiary sector of the economy, tertiary sector (service industries). , the majority of households in slums were engaged in occupations belonging to the informal sector; 36.5% were involved in servicing the urban middle class (as maids, drivers, etc.) and 22.2% were Wage labour, casual labourers. About 34% of the available labour force in Kolkata slums were unemployed. According to one estimate, almost a quarter of the population live on less than 27 rupees (equivalent to 45 US cents) per day.
Major manufacturing companies in the city are Alstom, Larsen & Toubro, Fosroc, Videocon Telecom, Videocon. As in many other Indian cities, information technology became a high-growth sector in Kolkata starting in the late 1990s; the city's IT sector grew at 70% per annum—a rate that was twice the national average. The 2000s saw a surge of investments in the real estate, infrastructure, retail, and hospitality sectors; List of shopping malls in Kolkata, several large shopping malls and hotels were launched. Companies such as ITC Limited, CESC Limited, Exide Industries, Emami, Eveready Industries India, Lux Industries, Rupa Company, Berger Paints, Birla Corporation, Britannia Industries and Purushottam Publishers are headquartered in the city. Philips India, PricewaterhouseCoopers India, Tata Global Beverages, and Tata Steel have their registered office and zonal headquarters in Kolkata. Kolkata hosts the headquarters of three major public-sector banks: Allahabad Bank, UCO Bank, and the United Bank of India; and a private bank Bandhan Bank.
Flexible production has been the norm in Kolkata, which has an informal sector that employs more than 40% of the labour force. One unorganised group, Hawkers in Kolkata, roadside hawkers, generated business worth 87.72 billion ( 2 billion) in 2005. , around 0.81% of the city's workforce was employed in the Primary sector of the economy, primary sector (agriculture, forestry, mining, etc.); 15.49% worked in the Secondary sector of the economy, secondary sector (industrial and manufacturing); and 83.69% worked in the Tertiary sector of the economy, tertiary sector (service industries). , the majority of households in slums were engaged in occupations belonging to the informal sector; 36.5% were involved in servicing the urban middle class (as maids, drivers, etc.) and 22.2% were Wage labour, casual labourers. About 34% of the available labour force in Kolkata slums were unemployed. According to one estimate, almost a quarter of the population live on less than 27 rupees (equivalent to 45 US cents) per day.
Major manufacturing companies in the city are Alstom, Larsen & Toubro, Fosroc, Videocon Telecom, Videocon. As in many other Indian cities, information technology became a high-growth sector in Kolkata starting in the late 1990s; the city's IT sector grew at 70% per annum—a rate that was twice the national average. The 2000s saw a surge of investments in the real estate, infrastructure, retail, and hospitality sectors; List of shopping malls in Kolkata, several large shopping malls and hotels were launched. Companies such as ITC Limited, CESC Limited, Exide Industries, Emami, Eveready Industries India, Lux Industries, Rupa Company, Berger Paints, Birla Corporation, Britannia Industries and Purushottam Publishers are headquartered in the city. Philips India, PricewaterhouseCoopers India, Tata Global Beverages, and Tata Steel have their registered office and zonal headquarters in Kolkata. Kolkata hosts the headquarters of three major public-sector banks: Allahabad Bank, UCO Bank, and the United Bank of India; and a private bank Bandhan Bank. Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India, chiefly known as RBI, is India's central bank and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible for ...
has its eastern zonal office in Kolkata, and India Government Mint, Kolkata is one of the four mints in India. Some of the oldest public sector companies are headquartered in the city such as the Coal India Limited, National Insurance Company, Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers, Tea Board of India, Geological Survey of India
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India. It was founded in 1851, as a Government of India organization under the Ministry of Mines, one of the oldest of such organisations in the world and the second oldest survey ...
, Zoological Survey of India
The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), founded on 1 July 1916 by Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, as premier Indian organisation in zoological research and studies to promote the survey, exploration and r ...
, Botanical Survey of India
Botanical Survey of India (BSI) located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It was founded on 13 February 1890, is Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's organization for survey, research and conservation of plan ...
, Jute Corporation of India, National Test House, Hindustan Copper and the Ordnance Factories Board of the Ministry of Defence (India), Indian Ministry of Defence.
Demographics
Population
The demonym for residents of Kolkata are ''Calcuttan'' and ''Kolkatan''. According to provisional results of the 2011 national census, Kolkata district, which occupies an area of , had a population of 4,486,679; its population density was . This represents a decline of 1.88% during the decade 2001–11. The human sex ratio, sex ratio is 899 females per 1000 males—lower than the national average. The ratio is depressed by the influx of working males from surrounding rural areas, from the rest of West Bengal; these men commonly leave their families behind. Kolkata's literacy rate of 87.14% exceeds the national average of 74%. The final population totals of census 2011 stated the population of city as 4,496,694. The urban agglomeration had a population of 14,112,536 in 2011. , about one-third of the population, or 15 lakh (1.5 million) people, lived in 3,500 unregistered Squatting, squatter-occupied and 2,011 registered slums. The authorised slums (with access to basic services like water, latrines, trash removal by the Kolkata Municipal Corporation) can be broadly divided into two groups—''bustees'', in which slum dwellers have some long term tenancy agreement with the landowners; and ''udbastu colonies'', settlements which had been leased to refugees from present-day Bangladesh by the government. The Shanty town, unauthorised slums (devoid of basic services provided by the municipality) are occupied by squatters who started living on encroached lands—mainly along canals, railway lines and roads. According to the 2005 National Family Health Survey, around 14% of the households in Kolkata were poor, while 33% lived in slums, indicating a substantial proportion of households in slum areas were better off economically than the bottom quarter of urban households in terms of wealth status. Mother Teresa was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for founding and working with the Missionaries of Charity in Kolkata—an organisation "whose primary task was to love and care for those persons nobody was prepared to look after".Languages
Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, the official state language, is the dominant language in Kolkata. English is also used, particularly by the white-collar workforce. Hindi and Urdu are spoken by a sizeable minority. Bengali Hindus form the majority of Kolkata's population; Marwaris, Bihari people, Biharis and Urdu-speaking Muslims compose large minorities. Among Ethnic communities in Kolkata, Kolkata's smaller communities are Overseas Chinese, Chinese, Tamil people, Tamils, People of Nepal, Nepalis, Pashtuns, Pathans/Afghans (locally known as ''Kabuliwala'') Odia people, Odias, Telugu people, Telugus, Gujarati people, Gujaratis, Anglo-Indians, Armenians in India, Armenians, Bengali Muslims, Greeks, Tibetan people, Tibetans, Marathi people, Maharashtrians, Konkani people, Konkanis, Malayali, Malayalees, Punjabis and Parsi people, Parsis. The number of Armenians, Greeks, Jews and other foreign-origin groups declined during the 20th century. The History of the Jews in Kolkata, Jewish population of Kolkata was 5,000 during World War II, but declined after Independence of India, Indian independence and the establishment of Israel; by 2013, there were 25 Jews in the city. India's sole Chinatown, Kolkata, Chinatown is in eastern Kolkata; once home to 20,000 ethnic Chinese, its population dropped to around 2,000 as a result of multiple factors including repatriation and denial of Indian citizenship following the 1962 Sino-Indian War, and immigration to foreign countries for better economic opportunities. The Chinese community traditionally worked in the local tanning industry and ran Chinese restaurants.
Religions
According to the 2011 census, 76.51% of the population is Hindu, 20.60% Muslim, 0.88% Christians, Christian and 0.47% Jainism, Jain. Scroll down to "Religion in Kolkata" The remainder of the population includes Sikhs, Buddhists, and other religions which accounts for 0.45% of the population; 1.09% did not state a religion in the census. Kolkata reported 67.6% of Crime in India, Special and Local Laws crimes registered in 35 large Indian cities during 2004.Government and public services
Civic administration
 Kolkata is administered by several government agencies. The
Kolkata is administered by several government agencies. The Kolkata Municipal Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, '' ...
, or KMC, oversees and manages the civic infrastructure of the city's 16 boroughs, which together encompass 144 wards. Each ward elects a councillor to the KMC. Each borough has a committee of councillors, each of whom is elected to represent a ward. By means of the borough committees, the corporation undertakes urban planning and maintains roads, government-aided schools, hospitals, and municipal markets. As Kolkata's apex body, the corporation discharges its functions through the mayor-in-council, which comprises a mayor, a deputy mayor, and ten other elected members of the KMC. The functions of the KMC include water supply, drainage and sewerage, sanitation, solid waste management, street lighting, and building regulation.
Kolkata's administrative agencies have areas of jurisdiction that do not coincide. Listed in ascending order by area, they are: Kolkata district; the Divisions of Kolkata Police, Kolkata Police area and the Kolkata Municipal Corporation area, or "Kolkata city"; and the Kolkata metropolitan area
Kolkata Metropolitan Area (abbreviated KMA; formerly Calcutta Metropolitan Area), also known as Greater Kolkata, is the urban agglomeration of the city of Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the third most populous metropolitan are ...
, which is the city's urban agglomeration. The agency overseeing the latter, the Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority, is responsible for the statutory planning and development of greater Kolkata. The Kolkata Municipal Corporation was ranked first out of 21 cities for best governance and administrative practices in India in 2014. It scored 4.0 on 10 compared to the national average of 3.3.
The Kolkata Port Trust, an agency of the central government, manages the city's river port. , the All India Trinamool Congress controls the KMC; the mayor is Firhad Hakim, while the deputy mayor is Atin Ghosh. The city has an apolitical Titular ruler, titular post, that of the Sheriff of Kolkata, which presides over various city-related functions and conferences.
As the seat of the Government of West Bengal, Kolkata is home to not only the offices of the local governing agencies, but also the West Bengal Legislative Assembly; the state secretariat, which is housed in the Writers' Building; and the Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located in B.B.D. Bagh, Kolkata, West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The High Court buildi ...
. Most government establishments and institutions are housed in the centre of the city in B. B. D. Bagh
B. B. D. Bagh, formerly called Tank Square and then Dalhousie Square (1847 to 1856), is the shortened version for Benoy-Badal-Dinesh Bagh. It is the seat of power of the state government, as well as the central business district of Kolkata in ...
(formerly known as Dalhousie Square). The Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located in B.B.D. Bagh, Kolkata, West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The High Court buildi ...
is the oldest High Courts of India, High Court in India. It was preceded by the Supreme Court of Judicature at Fort William which was established in 1774. The Calcutta High Court has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Kolkata has lower courts: the Court of Small Causes and the City Civil Court decide civil matters; the Sessions Court rules in criminal cases. The Kolkata Police, headed by a police commissioner, is overseen by the Ministry of Home Affairs (West Bengal), West Bengal Ministry of Home Affairs. The Kolkata district elects two representatives to India's lower house, the Lok Sabha, and 11 representatives to the state legislative assembly.
The Kolkata police district registered 15,510 Indian Penal Code cases in 2010, the 8th-highest total in the country. In 2010, the crime rate was 117.3 per 100,000, below the national rate of 187.6; it was the lowest rate among India's largest cities.
Utility services
Kolkata Municipal Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, '' ...
supplies the city with potable water that is sourced from the Hooghly River
The Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') or the 'Bhāgirathi-Hooghly', called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, Indi ...
; most of it is treated and purified at the Palta pumping station located in North 24 Parganas district. Roughly 95% of the 4,000 tonnes of refuse produced daily by the city is transported to the dumping grounds in Dhapa, India, Dhapa, which is east of the town. To promote the recycling of garbage and sewer water, agriculture is encouraged on the dumping grounds. Parts of the city lack proper sewerage, leading to unsanitary methods of waste disposal.
In 1856, the Bengal Government appointed George Turnbull (civil engineer), George Turnbull to be the Commissioner of Drainage and Sewerage to improve the city's sewerage. Turnbull's main job was to be the Chief Engineer of the East Indian Railway Company responsible for building the first railway from Howrah to Varanasi (then Benares).
Electricity is supplied by the privately operated CESC Limited, Calcutta Electric Supply Corporation, or CESC, to the city proper; the West Bengal State Electricity Board supplies it in the suburbs. Fire services are handled by the West Bengal Fire Service, a state agency. , the city had 16 fire stations.
State-owned Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited, or BSNL, as well as private enterprises, among them Vodafone Idea Ltd, Vodafone Idea, Bharti Airtel, Jio, Reliance Jio are the leading telephone and cell phone service providers in the city. with Kolkata being the first city in India to have cell phone and 4G connectivity, the GSM and Code division multiple access, CDMA cellular coverage is extensive. , Kolkata has 7 percent of the total broadband internet consumers in India; BSNL, VSNL, Tata Indicom, Sify, Hathway, Airtel, and Jio are among the main vendors.
Military and diplomatic establishments
The Eastern Command (India), Eastern Command of the Indian Army is based in the city. Being one of India's major city and the largest city in eastern and north-eastern India, Kolkata hosts diplomatic missions of many countries such as List of diplomatic missions in India, Australia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Canada, People's Republic of China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Myanmar, Nepal, Russia, Sri Lanka, Switzerland, Thailand, United Kingdom and United States. The Consulate General of the United States, Kolkata, U.S Consulate in Kolkata is the United States Department of State, US Department of State's second-oldest Consulate and dates from 19 November 1792. The Diplomatic representation of more than 65 Countries and International Organization is present in Kolkata as Consulate office, honorary Consulate office, Cultural Centre, Deputy High Commission and Economic section and Trade Representation office.Transport
 Public transport is provided by the Kolkata Suburban Railway, the Kolkata Metro, Trams in Kolkata, trams, rickshaws, taxis and buses. The suburban rail network connects the city's distant suburbs.
Public transport is provided by the Kolkata Suburban Railway, the Kolkata Metro, Trams in Kolkata, trams, rickshaws, taxis and buses. The suburban rail network connects the city's distant suburbs.
 According to a 2013 survey conducted by the International Association of Public Transport, in terms of a public transport system, Kolkata ranks among the top of the six Indian cities surveyed. The Kolkata Metro, in operation since 1984, is the oldest underground mass transit system in India. It spans the north–south length of the city. In 2020, part of the Second line was inaugurated to cover part of Salt Lake. This east–west line will connect Salt Lake with Howrah. The two lines cover a distance of . , four Metro rail lines were under construction.
According to a 2013 survey conducted by the International Association of Public Transport, in terms of a public transport system, Kolkata ranks among the top of the six Indian cities surveyed. The Kolkata Metro, in operation since 1984, is the oldest underground mass transit system in India. It spans the north–south length of the city. In 2020, part of the Second line was inaugurated to cover part of Salt Lake. This east–west line will connect Salt Lake with Howrah. The two lines cover a distance of . , four Metro rail lines were under construction.
 Kolkata has five long-distance railway stations, located at Howrah station, Howrah (the largest railway complex in India), Sealdah railway station, Sealdah, Kolkata Railway Station, Kolkata, Shalimar railway station, Shalimar and Santragachi railway station, Santragachi, which connect Kolkata by rail to most cities in West Bengal and to other major cities in India. The city serves as the headquarters of three railway zones out of eighteen of the Indian Railways regional divisions—the Kolkata Metro Railways, Eastern Railway Zone (India), Eastern Railway and the South Eastern Railway Zone (India), South-Eastern Railway. Kolkata has rail and road connectivity with
Kolkata has five long-distance railway stations, located at Howrah station, Howrah (the largest railway complex in India), Sealdah railway station, Sealdah, Kolkata Railway Station, Kolkata, Shalimar railway station, Shalimar and Santragachi railway station, Santragachi, which connect Kolkata by rail to most cities in West Bengal and to other major cities in India. The city serves as the headquarters of three railway zones out of eighteen of the Indian Railways regional divisions—the Kolkata Metro Railways, Eastern Railway Zone (India), Eastern Railway and the South Eastern Railway Zone (India), South-Eastern Railway. Kolkata has rail and road connectivity with Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
, the capital of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
.
 Buses, which are the most commonly used mode of transport, are run by government agencies and private operators. Kolkata is the only Indian city with a tram network, which was operated by the Calcutta Tramways Company. It has now renamed to West Bengal Transport Corporation. The slow-moving tram services are restricted to certain areas of the city. Water-logging, caused by heavy rains during the Monsoon of South Asia, summer monsoon, sometimes interrupt transportation networks. Hired public conveyances include auto rickshaws, which often ply specific routes, and yellow metered taxis. Almost all of Kolkata's taxis are antiquated Hindustan Ambassadors by make; newer air-conditioned Taxicab#Dispatching, radio taxis are in service as well. In parts of the city, cycle rickshaws and Pulled rickshaw, hand-pulled rickshaws are patronised by the public for short trips.
Buses, which are the most commonly used mode of transport, are run by government agencies and private operators. Kolkata is the only Indian city with a tram network, which was operated by the Calcutta Tramways Company. It has now renamed to West Bengal Transport Corporation. The slow-moving tram services are restricted to certain areas of the city. Water-logging, caused by heavy rains during the Monsoon of South Asia, summer monsoon, sometimes interrupt transportation networks. Hired public conveyances include auto rickshaws, which often ply specific routes, and yellow metered taxis. Almost all of Kolkata's taxis are antiquated Hindustan Ambassadors by make; newer air-conditioned Taxicab#Dispatching, radio taxis are in service as well. In parts of the city, cycle rickshaws and Pulled rickshaw, hand-pulled rickshaws are patronised by the public for short trips.
Esplanade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortress or city walls to provide cle ...
and Babughat. The Kolkata–Delhi and Kolkata–Chennai prongs of the Golden Quadrilateral, and National Highway 12 (India), National Highway 12 start from the city.
 Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, located in
Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport, located in Dum Dum
Dum Dum is a city and a municipality of Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of Kolkata urban area and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
Etymology
During the 19th ...
, about north-east of the city centre, operates domestic and international flights. In 2013, the airport was upgraded to handle increased air traffic.
 The
The Port of Kolkata
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the olde ...
, established in 1870, is India's oldest and the only major river port. The Kolkata Port Trust manages docks in Kolkata and Haldia. The port hosts passenger services to Port Blair, capital of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; freighter service to ports throughout India and around the world is operated by the Shipping Corporation of India. Ferry services connect Kolkata with its twin city of Howrah, located across the Hooghly River.
Healthcare
 Among the surveyed cities, Kolkata stood second (5%) for children who had not had any vaccinations under the Universal Immunization Programme . Kolkata ranked second with access to an ''anganwadi'' centre under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme for 57% of the children between 0 and 71 months. The proportion of malnutrition, malnourished, anaemia, anaemic and underweight children in Kolkata was less in comparison to other surveyed cities.
About 18% of the men and 30% of the women in Kolkata are obese—the majority of them belonging to the non-poor strata of society. In 2005, Kolkata had the highest percentage (55%) among the surveyed cities of Anemia, anaemic women, while 20% of the men in Kolkata were Anemia, anaemic. Diseases like diabetes, asthma, goitre and other Thyroid#Disorders, thyroid disorders were found in large numbers of people. Tropical diseases like malaria, dengue and ''chikungunya'' are prevalent in Kolkata, though their incidence is decreasing. Kolkata is one of the districts in India with HIV/AIDS in India, a high number of people with HIV/AIDS, AIDS; it has been designated a district prone to high risk. As of 2014, because of Air pollution in India, higher air pollution, the life expectancy of a person born in the city is four years fewer than in the suburbs.
Among the surveyed cities, Kolkata stood second (5%) for children who had not had any vaccinations under the Universal Immunization Programme . Kolkata ranked second with access to an ''anganwadi'' centre under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme for 57% of the children between 0 and 71 months. The proportion of malnutrition, malnourished, anaemia, anaemic and underweight children in Kolkata was less in comparison to other surveyed cities.
About 18% of the men and 30% of the women in Kolkata are obese—the majority of them belonging to the non-poor strata of society. In 2005, Kolkata had the highest percentage (55%) among the surveyed cities of Anemia, anaemic women, while 20% of the men in Kolkata were Anemia, anaemic. Diseases like diabetes, asthma, goitre and other Thyroid#Disorders, thyroid disorders were found in large numbers of people. Tropical diseases like malaria, dengue and ''chikungunya'' are prevalent in Kolkata, though their incidence is decreasing. Kolkata is one of the districts in India with HIV/AIDS in India, a high number of people with HIV/AIDS, AIDS; it has been designated a district prone to high risk. As of 2014, because of Air pollution in India, higher air pollution, the life expectancy of a person born in the city is four years fewer than in the suburbs.
Education
 Kolkata's schools are run by the state government or private organisations, many of which are religious.
Kolkata's schools are run by the state government or private organisations, many of which are religious. Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and English are the primary languages of instruction; Urdu and Hindi are also used, particularly in central Kolkata. Schools in Kolkata follow the Education in India, "10+2+3" plan. After completing their secondary education, students typically enroll in schools that have a higher secondary facility and are affiliated with the West Bengal Council of Higher Secondary Education, the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education, ICSE, or the Central Board of Secondary Education, CBSE. They usually choose a focus on liberal arts, business, or science. Vocational programs are also available. Some Kolkata schools, for example South Point School, La Martiniere Calcutta, Calcutta Boys' School, St. James' School (Kolkata), St. Xavier's Collegiate School and Loreto House, have been ranked amongst the best schools in the country.
 , the Kolkata urban agglomeration is home to 14 universities run by the state government. The colleges are each affiliated with a university or institution based either in Kolkata or elsewhere in India. Aliah University which was founded in 1780 as ''Mohammedan College of Calcutta'' is the oldest post-secondary educational institution of the city. The University of Calcutta, founded in 1857, is the first modern university in South Asia. Presidency College, Kolkata (formerly Hindu College between 1817 and 1855), founded in 1855, was one of the oldest colleges in India. It was affiliated with the University of Calcutta until 2010 when it was converted to Presidency University, Kolkata in 2010. Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur, Bengal Engineering and Science University (BESU) is the second oldest engineering institution of the country located in Howrah. An Institute of National Importance, BESU was converted to India's first Indian Institutes of Engineering Science and Technology, IIEST. Jadavpur University is known for its arts, science, and engineering faculties. The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta, which was the first of the Indian Institutes of Management, was established in 1961 at Joka, Kolkata, Joka, a locality in the south-western suburbs. Kolkata also houses the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, which was started here in the year 2006.
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences is one of India's Autonomous law schools in India, autonomous law schools, and the Indian Statistical Institute is a public research institute and university. State owned Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal (MAKAUT, WB), formerly West Bengal University of Technology (WBUT) is the largest Technological University in terms of student enrollment and number of Institutions affiliated by it. Private institutions include the Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute and University of Engineering & Management (UEM), Kolkata, University of Engineering & Management (UEM).
, the Kolkata urban agglomeration is home to 14 universities run by the state government. The colleges are each affiliated with a university or institution based either in Kolkata or elsewhere in India. Aliah University which was founded in 1780 as ''Mohammedan College of Calcutta'' is the oldest post-secondary educational institution of the city. The University of Calcutta, founded in 1857, is the first modern university in South Asia. Presidency College, Kolkata (formerly Hindu College between 1817 and 1855), founded in 1855, was one of the oldest colleges in India. It was affiliated with the University of Calcutta until 2010 when it was converted to Presidency University, Kolkata in 2010. Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur, Bengal Engineering and Science University (BESU) is the second oldest engineering institution of the country located in Howrah. An Institute of National Importance, BESU was converted to India's first Indian Institutes of Engineering Science and Technology, IIEST. Jadavpur University is known for its arts, science, and engineering faculties. The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta, which was the first of the Indian Institutes of Management, was established in 1961 at Joka, Kolkata, Joka, a locality in the south-western suburbs. Kolkata also houses the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade, which was started here in the year 2006.
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences is one of India's Autonomous law schools in India, autonomous law schools, and the Indian Statistical Institute is a public research institute and university. State owned Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal (MAKAUT, WB), formerly West Bengal University of Technology (WBUT) is the largest Technological University in terms of student enrollment and number of Institutions affiliated by it. Private institutions include the Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute and University of Engineering & Management (UEM), Kolkata, University of Engineering & Management (UEM).
 Kolkata houses many research institutes like Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB), Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Bose Institute, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP), Centre for Studies in Social Sciences, Calcutta, All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI), S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), Indian Institute of Social Welfare and Business Management (IISWBM), National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre (VECC) and Indian Centre for Space Physics. Nobel laureate Sir C. V. Raman did his groundbreaking work in Raman effect in IACS.
Kolkata houses many research institutes like Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB), Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Bose Institute, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP), Centre for Studies in Social Sciences, Calcutta, All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI), S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), Indian Institute of Social Welfare and Business Management (IISWBM), National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre (VECC) and Indian Centre for Space Physics. Nobel laureate Sir C. V. Raman did his groundbreaking work in Raman effect in IACS.
Culture
 Kolkata is known for its literary, artistic and revolutionary heritage; as the former capital of India, it was the birthplace of modern Indian literary and artistic thought. Kolkata has been called the "City of Furious, Creative Energy" as well as the "cultural [or literary] capital of India". The presence of ''para (Bengali), paras'', which are neighbourhoods that possess a strong sense of community, is characteristic of the city. Typically, each ''para'' has its own community club and on occasion, a playing field. Residents engage in ''adda (Indian), addas'', or leisurely chats, that often take the form of freestyle intellectual conversation. The city has a tradition of political graffiti depicting everything from outrageous slander to witty banter and limericks, caricatures and propaganda.
Kolkata is known for its literary, artistic and revolutionary heritage; as the former capital of India, it was the birthplace of modern Indian literary and artistic thought. Kolkata has been called the "City of Furious, Creative Energy" as well as the "cultural [or literary] capital of India". The presence of ''para (Bengali), paras'', which are neighbourhoods that possess a strong sense of community, is characteristic of the city. Typically, each ''para'' has its own community club and on occasion, a playing field. Residents engage in ''adda (Indian), addas'', or leisurely chats, that often take the form of freestyle intellectual conversation. The city has a tradition of political graffiti depicting everything from outrageous slander to witty banter and limericks, caricatures and propaganda.
 Kolkata has many buildings adorned with Indo-Islamic architecture, Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, Indo-Saracenic architectural motifs. Several well-maintained major buildings from the colonial period have been declared "heritage structures"; others are in various stages of decay. Established in 1814 as the nation's oldest museum, the
Kolkata has many buildings adorned with Indo-Islamic architecture, Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, Indo-Saracenic architectural motifs. Several well-maintained major buildings from the colonial period have been declared "heritage structures"; others are in various stages of decay. Established in 1814 as the nation's oldest museum, the Indian Museum
The Indian Museum in Central Kolkata, West Bengal, India, also referred to as the Imperial Museum at Calcutta in colonial-era texts, is the ninth oldest museum in the world, the oldest and largest museum in India as well as in Asia. It has rare ...
houses large collections that showcase Indian natural history and Indian art. Marble Palace (Kolkata), Marble Palace is a classic example of a European mansion that was built in the city. The Victoria Memorial (India), Victoria Memorial, a places of interest in Kolkata, place of interest in Kolkata, has a museum documenting the city's history. The National Library of India
The National Library of India is a library located in Belvedere Estate, Alipore, Kolkata, India. It is India's largest library by volume and public record. The National Library is under Ministry of Culture (India), Ministry of Culture, Governm ...
is the leading public library in the country while Science City Kolkata, Science City is the largest science centre in the Indian subcontinent.
 The popularity of commercial theatres in the city has declined since the 1980s. Group theatres of Kolkata, a cultural movement that started in the 1940s contrasting with the then-popular commercial theatres, are theatres that are not professional or commercial, and are centres of various experiments in theme, content, and production; group theatres use the proscenium stage to highlight socially relevant messages. Chitpur locality of the city houses multiple production companies of ''Jatra (Bengal), jatra'', a tradition of folk drama popular in rural Bengal. Kolkata is the home of the Cinema of West Bengal, Bengali cinema industry, dubbed "Tollywood" for Tollygunj, where most of the state's film studios are located. Parallel Cinema, Its long tradition of art films includes globally acclaimed film directors such as Academy Award-winning director Satyajit Ray, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen, Tapan Sinha and contemporary directors such as Aparna Sen, Buddhadeb Dasgupta, Goutam Ghose and Rituparno Ghosh. During the 19th and 20th centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Michael Madhusudan Dutt, Rabindranath Tagore, Kazi Nazrul Islam and Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay. Coupled with social reforms led by Ram Mohan Roy, Swami Vivekananda and others, this constituted a major part of the
The popularity of commercial theatres in the city has declined since the 1980s. Group theatres of Kolkata, a cultural movement that started in the 1940s contrasting with the then-popular commercial theatres, are theatres that are not professional or commercial, and are centres of various experiments in theme, content, and production; group theatres use the proscenium stage to highlight socially relevant messages. Chitpur locality of the city houses multiple production companies of ''Jatra (Bengal), jatra'', a tradition of folk drama popular in rural Bengal. Kolkata is the home of the Cinema of West Bengal, Bengali cinema industry, dubbed "Tollywood" for Tollygunj, where most of the state's film studios are located. Parallel Cinema, Its long tradition of art films includes globally acclaimed film directors such as Academy Award-winning director Satyajit Ray, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen, Tapan Sinha and contemporary directors such as Aparna Sen, Buddhadeb Dasgupta, Goutam Ghose and Rituparno Ghosh. During the 19th and 20th centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Michael Madhusudan Dutt, Rabindranath Tagore, Kazi Nazrul Islam and Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay. Coupled with social reforms led by Ram Mohan Roy, Swami Vivekananda and others, this constituted a major part of the Bengal Renaissance
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. The middle and latter parts of the 20th century witnessed the arrival of post-modernism, as well as literary movements such as those espoused by the ''Kallol'' movement, Hungry generation, hungryalists and the Little magazine movement#Bengali little magazine movement, little magazines. Large majority of publishers of the city is concentrated in and around College Street (Kolkata), College Street, "... a half-mile of bookshops and bookstalls spilling over onto the pavement", selling new and used books.

 Kalighat painting originated in 19th century Kolkata as a local style that reflected a variety of themes including mythology and quotidian life. The Government College of Art & Craft, Government College of Art and Craft, founded in 1864, has been the cradle as well as workplace of eminent artists including Abanindranath Tagore, Jamini Roy and Nandalal Bose. The art college was the birthplace of the Bengal school of art that arose as an avant garde and nationalist movement reacting against the prevalent academic art styles in the early 20th century. The Academy of Fine Arts, Calcutta, Academy of Fine Arts and other art galleries hold regular art exhibitions. The city is recognised for its appreciation of ''Rabindra sangeet'' (songs written by Rabindranath Tagore) and Indian classical music, with important concerts and recitals, such as Dover Lane Music Conference, being held throughout the year; Bengali popular music, including Baul, ''baul'' folk ballads, ''kirtans'' and ''Gajan (festival), Gajan'' festival music; and modern music, including Bengali-language ''adhunik'' songs. Since the early 1990s, Indian rock#Rock scenes, new genres have emerged, including one comprising alternative folk–rock Rock music of West Bengal, Bengali bands. Another new style, ''jibonmukhi gaan'' ("songs about life"), is based on realism (arts), realism.
Kalighat painting originated in 19th century Kolkata as a local style that reflected a variety of themes including mythology and quotidian life. The Government College of Art & Craft, Government College of Art and Craft, founded in 1864, has been the cradle as well as workplace of eminent artists including Abanindranath Tagore, Jamini Roy and Nandalal Bose. The art college was the birthplace of the Bengal school of art that arose as an avant garde and nationalist movement reacting against the prevalent academic art styles in the early 20th century. The Academy of Fine Arts, Calcutta, Academy of Fine Arts and other art galleries hold regular art exhibitions. The city is recognised for its appreciation of ''Rabindra sangeet'' (songs written by Rabindranath Tagore) and Indian classical music, with important concerts and recitals, such as Dover Lane Music Conference, being held throughout the year; Bengali popular music, including Baul, ''baul'' folk ballads, ''kirtans'' and ''Gajan (festival), Gajan'' festival music; and modern music, including Bengali-language ''adhunik'' songs. Since the early 1990s, Indian rock#Rock scenes, new genres have emerged, including one comprising alternative folk–rock Rock music of West Bengal, Bengali bands. Another new style, ''jibonmukhi gaan'' ("songs about life"), is based on realism (arts), realism.
Media
 The first newspaper in India, the ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette, Bengal Gazette'' started publishing from the city in 1780. Among Kolkata's widely circulated Bengali-language newspapers are ''Anandabazar Patrika'', ''Bartaman'', Ei Samay Sangbadpatra, ''Sangbad Pratidin'', ''Aajkaal'', ''Dainik Statesman'' and ''Ganashakti''. ''The Statesman (India), The Statesman'' and ''The Telegraph (Calcutta), The Telegraph'' are two major English-language newspapers that are produced and published from Kolkata. Other popular English-language newspapers published and sold in Kolkata include ''The Times of India'', ''Hindustan Times'', ''The Hindu'', ''The Indian Express'' and the ''Asian Age''. As the largest trading centre in East India, Kolkata has several high-circulation financial dailies, including ''The Economic Times'', ''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', ''Business Line'' and ''Business Standard''. Vernacular newspapers, such as those in the Hindi, Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati, Odia language, Odia, Punjabi language, Punjabi and Chinese languages, are read by minorities. Major periodicals based in Kolkata include ''Desh (magazine), Desh'', ''Sananda (magazine), Sananda'', ''Saptahik Bartaman'', ''Unish-Kuri'', ''Anandalok'' and ''Anandamela''. Historically, Kolkata has been the centre of the Little magazine movement#Bengali little magazine movement, Bengali little magazine movement.
All India Radio, the national state-owned radio broadcaster, airs several AM broadcasting, AM radio stations in the city. Kolkata has List of FM radio stations in India#Kolkata, 10 local radio stations broadcasting on frequency modulation, FM, including three from AIR. India's state-owned television broadcaster, Doordarshan, provides two free-to-air terrestrial channels, while a mix of Bengali, Hindi, English, and other regional channels are accessible via Cable television, cable subscription, direct-broadcast satellite services, or IPTV, internet-based television. List of Bengali-language television channels#News channels, Bengali-language 24-hour television news channels include ABP Ananda, News18 Bangla, Kolkata TV, Zee 24 Ghanta, TV9 Bangla and Republic Bangla.
The first newspaper in India, the ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette, Bengal Gazette'' started publishing from the city in 1780. Among Kolkata's widely circulated Bengali-language newspapers are ''Anandabazar Patrika'', ''Bartaman'', Ei Samay Sangbadpatra, ''Sangbad Pratidin'', ''Aajkaal'', ''Dainik Statesman'' and ''Ganashakti''. ''The Statesman (India), The Statesman'' and ''The Telegraph (Calcutta), The Telegraph'' are two major English-language newspapers that are produced and published from Kolkata. Other popular English-language newspapers published and sold in Kolkata include ''The Times of India'', ''Hindustan Times'', ''The Hindu'', ''The Indian Express'' and the ''Asian Age''. As the largest trading centre in East India, Kolkata has several high-circulation financial dailies, including ''The Economic Times'', ''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', ''Business Line'' and ''Business Standard''. Vernacular newspapers, such as those in the Hindi, Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati, Odia language, Odia, Punjabi language, Punjabi and Chinese languages, are read by minorities. Major periodicals based in Kolkata include ''Desh (magazine), Desh'', ''Sananda (magazine), Sananda'', ''Saptahik Bartaman'', ''Unish-Kuri'', ''Anandalok'' and ''Anandamela''. Historically, Kolkata has been the centre of the Little magazine movement#Bengali little magazine movement, Bengali little magazine movement.
All India Radio, the national state-owned radio broadcaster, airs several AM broadcasting, AM radio stations in the city. Kolkata has List of FM radio stations in India#Kolkata, 10 local radio stations broadcasting on frequency modulation, FM, including three from AIR. India's state-owned television broadcaster, Doordarshan, provides two free-to-air terrestrial channels, while a mix of Bengali, Hindi, English, and other regional channels are accessible via Cable television, cable subscription, direct-broadcast satellite services, or IPTV, internet-based television. List of Bengali-language television channels#News channels, Bengali-language 24-hour television news channels include ABP Ananda, News18 Bangla, Kolkata TV, Zee 24 Ghanta, TV9 Bangla and Republic Bangla.
Sports
 The most popular sports in Kolkata are association football, football and cricket. Unlike most parts of India, the residents show significant passion for football. Indian Football Association, the oldest football association of the country is based here. It administers football in West Bengal. Kolkata is home to the country's top football clubs such as Mohun Bagan A.C., East Bengal Club and the Mohammedan Sporting Club (Kolkata), Mohammedan Sporting Club.ATK Mohun Bagan FC and East Bengal FC are two clubs of the city compete in Indian Super League. The Calcutta Football League, which was started in 1898, is the oldest football league in Asia. Mohun Bagan A.C., one of the oldest football clubs in Asia, is the only organisation to be dubbed a "National Club of India". Football matches between Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, dubbed as the Kolkata Derby, witness large audience attendance and rivalry between patrons. The multi-use Salt Lake Stadium, also known as Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan, is India's second largest stadium by seating capacity. Most matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup were played in this stadium including both Semi-final matches and the Final match. Kolkata also accounted for 45% of total attendance in 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup with an average of 55,345 spectators. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world.
The most popular sports in Kolkata are association football, football and cricket. Unlike most parts of India, the residents show significant passion for football. Indian Football Association, the oldest football association of the country is based here. It administers football in West Bengal. Kolkata is home to the country's top football clubs such as Mohun Bagan A.C., East Bengal Club and the Mohammedan Sporting Club (Kolkata), Mohammedan Sporting Club.ATK Mohun Bagan FC and East Bengal FC are two clubs of the city compete in Indian Super League. The Calcutta Football League, which was started in 1898, is the oldest football league in Asia. Mohun Bagan A.C., one of the oldest football clubs in Asia, is the only organisation to be dubbed a "National Club of India". Football matches between Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, dubbed as the Kolkata Derby, witness large audience attendance and rivalry between patrons. The multi-use Salt Lake Stadium, also known as Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan, is India's second largest stadium by seating capacity. Most matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup were played in this stadium including both Semi-final matches and the Final match. Kolkata also accounted for 45% of total attendance in 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup with an average of 55,345 spectators. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world.
 As in the rest of India, cricket is popular in Kolkata and is played on various grounds throughout the city. Kolkata is home to Indian Premier League franchise Kolkata Knight Riders and the Bengal cricket team; the Cricket Association of Bengal, which regulates cricket in West Bengal, is also based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, football, badminton and carrom, are regularly organised here on an inter-locality or inter-club basis. The Maidan (Kolkata), Maidan, a vast field that serves as the city's largest park, hosts several minor football and cricket clubs and coaching institutes. Eden Gardens, which has a capacity of 80,000 , hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup.
Kolkata's Netaji Indoor Stadium served as host of the 1981 Asian Basketball Championship, where India's national basketball team finished 5th, ahead of teams that belong to Asia's basketball elite, such as Iran national basketball team, Iran. The city has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club, the first golf club built outside the United Kingdom. The other two are located at the Tollygunge Club and at Fort William (India), Fort William. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club hosts horse racing and polo matches. The Calcutta Polo Club is considered the oldest extant polo club in the world. The Calcutta Racket Club is a squash (sport), squash and racquet club in Kolkata. It was founded in 1793, making it one of the oldest rackets clubs in the world, and the first in the Indian subcontinent. The Calcutta South Club is a venue for national and international tennis tournaments; it held the first grass-court national championship in 1946. In the period 2005–2007, Sunfeast Open, a tier-III tournament on the Women's Tennis Association circuit, was held in the Netaji Indoor Stadium; it has since been discontinued.
The Calcutta Rowing Club hosts Sport rowing, rowing heats and training events. Kolkata, considered the leading centre of rugby union in India, gives its name to the oldest international tournament in rugby union, the Calcutta Cup. The Automobile Association of Eastern India, established in 1904, and the Bengal Motor Sports Club are involved in promoting motor sports and car rallies in Kolkata and West Bengal. The Beighton Cup, an event organised by the Bengal Hockey Association and first played in 1895, is India's oldest field hockey tournament; it is usually held on the Mohun Bagan Ground of the Maidan. Athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly, Pankaj Roy and Jhulan Goswami, who are former List of India national cricket captains, captains of the India national cricket team, Indian national cricket team; India at the Olympics, Olympic tennis bronze medalist Leander Paes, golfer Arjun Atwal, and former footballers Sailen Manna, Chuni Goswami, Pradip Kumar Banerjee, P. K. Banerjee and Subrata Bhattacharya (footballer), Subrata Bhattacharya.
As in the rest of India, cricket is popular in Kolkata and is played on various grounds throughout the city. Kolkata is home to Indian Premier League franchise Kolkata Knight Riders and the Bengal cricket team; the Cricket Association of Bengal, which regulates cricket in West Bengal, is also based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, football, badminton and carrom, are regularly organised here on an inter-locality or inter-club basis. The Maidan (Kolkata), Maidan, a vast field that serves as the city's largest park, hosts several minor football and cricket clubs and coaching institutes. Eden Gardens, which has a capacity of 80,000 , hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup.
Kolkata's Netaji Indoor Stadium served as host of the 1981 Asian Basketball Championship, where India's national basketball team finished 5th, ahead of teams that belong to Asia's basketball elite, such as Iran national basketball team, Iran. The city has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club, the first golf club built outside the United Kingdom. The other two are located at the Tollygunge Club and at Fort William (India), Fort William. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club hosts horse racing and polo matches. The Calcutta Polo Club is considered the oldest extant polo club in the world. The Calcutta Racket Club is a squash (sport), squash and racquet club in Kolkata. It was founded in 1793, making it one of the oldest rackets clubs in the world, and the first in the Indian subcontinent. The Calcutta South Club is a venue for national and international tennis tournaments; it held the first grass-court national championship in 1946. In the period 2005–2007, Sunfeast Open, a tier-III tournament on the Women's Tennis Association circuit, was held in the Netaji Indoor Stadium; it has since been discontinued.
The Calcutta Rowing Club hosts Sport rowing, rowing heats and training events. Kolkata, considered the leading centre of rugby union in India, gives its name to the oldest international tournament in rugby union, the Calcutta Cup. The Automobile Association of Eastern India, established in 1904, and the Bengal Motor Sports Club are involved in promoting motor sports and car rallies in Kolkata and West Bengal. The Beighton Cup, an event organised by the Bengal Hockey Association and first played in 1895, is India's oldest field hockey tournament; it is usually held on the Mohun Bagan Ground of the Maidan. Athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly, Pankaj Roy and Jhulan Goswami, who are former List of India national cricket captains, captains of the India national cricket team, Indian national cricket team; India at the Olympics, Olympic tennis bronze medalist Leander Paes, golfer Arjun Atwal, and former footballers Sailen Manna, Chuni Goswami, Pradip Kumar Banerjee, P. K. Banerjee and Subrata Bhattacharya (footballer), Subrata Bhattacharya.
Notable people
Sister cities
*Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
* Kunming, China (October 2013)
* Thessaloniki, Greece (January 2005)
* Naples, Italy
* Karachi, Pakistan
* Incheon, South Korea
* Odessa, Ukraine
* Jersey City, New Jersey, United States
* Long Beach, California, United States
* Dallas, Texas, United States
See also
*List of children's museums in India *List of people from Kolkata *List of tallest buildings in Kolkata *West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Kolkata Municipal Corporation
*
– Incredible India
City Mayors: Richest cities in the world in 2020 by GDP
{{Authority control Kolkata, Cities and towns in Kolkata district Indian capital cities Metropolitan cities in India Port cities in India Capitals of former nations Former national capitals Former capital cities in India Populated places established in 1690 1690 establishments in Asia 1690 establishments in the British Empire 1690s establishments in India Capitals of Bengal Subdivisions of West Bengal Subdivisions in Kolkata district Cities in West Bengal