Calais Lace Museum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the
INSEE Calais overlooks the

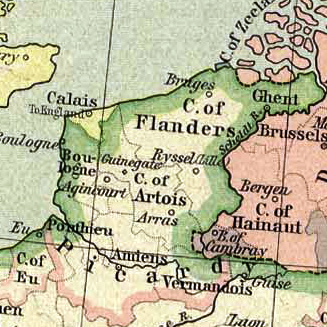 In 1360 the
In 1360 the
 Calais remained an important maritime city and smuggling centre throughout the 17th century. However, during the next century, the port of Calais began to stagnate gradually, as the nearby ports of
Calais remained an important maritime city and smuggling centre throughout the 17th century. However, during the next century, the port of Calais began to stagnate gradually, as the nearby ports of
Pas-de-Calais
Pas-de-Calais (, " strait of Calais"; pcd, Pas-Calés; also nl, Nauw van Kales) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments ...
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
, of which it is a subprefecture
A subprefecture is an administrative division of a country that is below prefecture or province.
Albania
There are twelve Counties of Albania, Albanian counties or prefectures, each of which is divided into several Districts of Albania, district ...
. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
is its third-largest city of Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
. The population of the city proper is 72,929; that of the urban area is 149,673 (2018).Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Calais (073), Commune de Calais (62193)INSEE Calais overlooks the
Strait of Dover
The Strait of Dover or Dover Strait (french: Pas de Calais - ''Strait of Calais''), is the strait at the narrowest part of the English Channel, marking the boundary between the Channel and the North Sea, separating Great Britain from continent ...
, the narrowest point in the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, which is only wide here, and is the closest French town to England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. The White Cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposi ...
can easily be seen on a clear day from Calais. Calais is a major port for ferries between France and England, and since 1994, the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
has linked nearby Coquelles
Coquelles (; vls, Kalkwelle, lang) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department near Calais in northern France.
The town comprises a shopping centre, hotels and farm in Vieille Coquelles (old Coquelles), part of the L'Européenne autoroute ( ...
to Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20t ...
by rail.
Due to its position, Calais since the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
has been a major port and a very important centre for transport and trading with England. Calais came under English control after Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ro ...
captured the city in 1347, followed by a treaty in 1360 that formally assigned Calais to English rule. Calais grew into a thriving centre for wool production, and came to be called the "brightest jewel in the English crown" owing to its great importance as the gateway for the tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
and wool trades (or "staples"). Calais remained under English control until its capture by France in 1558. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the town was virtually razed to the ground: in May 1940, it was a strategic bombing target of the invading German forces who took it during the siege of Calais. The Germans built massive bunkers along the coast in preparation for launching missiles at England.
The old part of the town, Calais proper (known as Calais-Nord), is situated on an artificial island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those tha ...
surrounded by canals and harbours. The modern part of the town, St-Pierre, lies to the south and south-east. In the centre of the old town is the Place d'Armes, in which stands the Tour du Guet, or watch-tower, a structure built in the 13th century, which was used as a lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
until 1848 when a new lighthouse was built by the port. South east of the Place is the church of Notre-Dame, built during the English occupancy of Calais. Arguably, it is the only church built in the English perpendicular style in all of France. In this church, former French President Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
married Yvonne Vendroux. South of the Place and opposite the Parc St Pierre is the Hôtel-de-ville (the town hall), and the belfry from the early 20th century. Today, Calais is visited by more than 10 million annually. Aside from being a key transport hub, Calais is also a notable fishing port and a centre for fish marketing, and some 3,000 people are still employed in the lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
industry for which the town is also famed.
History
Early history
The early history of habitation in the area is limited. It is sometimes claimed that the Romans called the settlement ''Caletum'' and that it was the departure point forJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
's invasion of Britain. However, the name ''Caletum'' does not appear in Caeser's accounts of the invasion. Caesar describes his departure point as ''Portus Itius'', which is believed to have been near Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
. At that time Calais was an island in the North Sea.Adrian Goldsworthy Caesar, page 338
Calais was an English outpost for many centuries while it was an island surrounded by marshes, and difficult to attack from the mainland. At some time before the 10th century, it would have been a Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
-speaking fishing village on a sandy beach backed by pebbles and a creek, with a natural harbour at the west edge of the early medieval estuary of the river Aa. As the pebble and sand ridge extended eastward from Calais, the haven behind it developed into fen
A fen is a type of peat-accumulating wetland fed by mineral-rich ground or surface water. It is one of the main types of wetlands along with marshes, swamps, and bogs. Bogs and fens, both peat-forming ecosystems, are also known as mires. T ...
, as the estuary progressively filled with silt and peat. Afterwards, canals were cut between Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer (; vls, Sint-Omaars) is a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department in France.
It is west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais, and is located in the Artois province. The town is named after Saint Audomar, ...
, the trading centre formerly at the head of the estuary, and three places to the west, centre and east on the newly formed coast: respectively Calais, Gravelines
Gravelines (, ; ; ) is a commune in the Nord department in Northern France. It lies at the mouth of the river Aa southwest of Dunkirk. It was formed in the 12th century around the mouth of a canal built to connect Saint-Omer with the sea. As ...
and Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Count of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the co ...
in 997 and fortified by the Count of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne was a historical title in the Kingdom of France. The city of Boulogne-sur-Mer became the centre of the county of Boulogne during the ninth century. Little is known of the early counts, but the first holder of the title is recor ...
in 1224.
The first document mentioning the existence of this community is the town charter granted by Mathieu d'Alsace, Count of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne was a historical title in the Kingdom of France. The city of Boulogne-sur-Mer became the centre of the county of Boulogne during the ninth century. Little is known of the early counts, but the first holder of the title is recor ...
, in 1181 to Gerard de Guelders; Calais thus became part of the county of Boulogne. In 1189, Richard the Lionheart
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overl ...
is documented to have landed at Calais on his journey to the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity (Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
.
14th–15th century; the Pale of Calais

English wool trade
The medieval English wool trade was one of the most important factors in the medieval English economy. The medievalist John Munro notes that " form of manufacturing had a greater impact upon the economy and society of medieval Britain than did tho ...
interests and King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
's claims to be heir to the Kingdom of France led to the Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King EdwardIII. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France du ...
between England and France in 1346, followed by Edward's siege and capture of Calais in 1347. Angered, the English king demanded reprisals against the town's citizens for holding out for so long ("obstinate defense") and ordered that the town's population be killed ''en masse''. He agreed, however, to spare them, on condition that six of the principal citizens would come to him, bareheaded and barefooted and with ropes around their necks, and give themselves up to death. On their arrival he ordered their execution, but pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the ju ...
ed them when his queen, Philippa of Hainault
Philippa of Hainault (sometimes spelled Hainaut; Middle French: ''Philippe de Hainaut''; 24 June 1310 (or 1315) – 15 August 1369) was Queen of England as the wife and political adviser of King Edward III. She acted as regent in 1346,Strickla ...
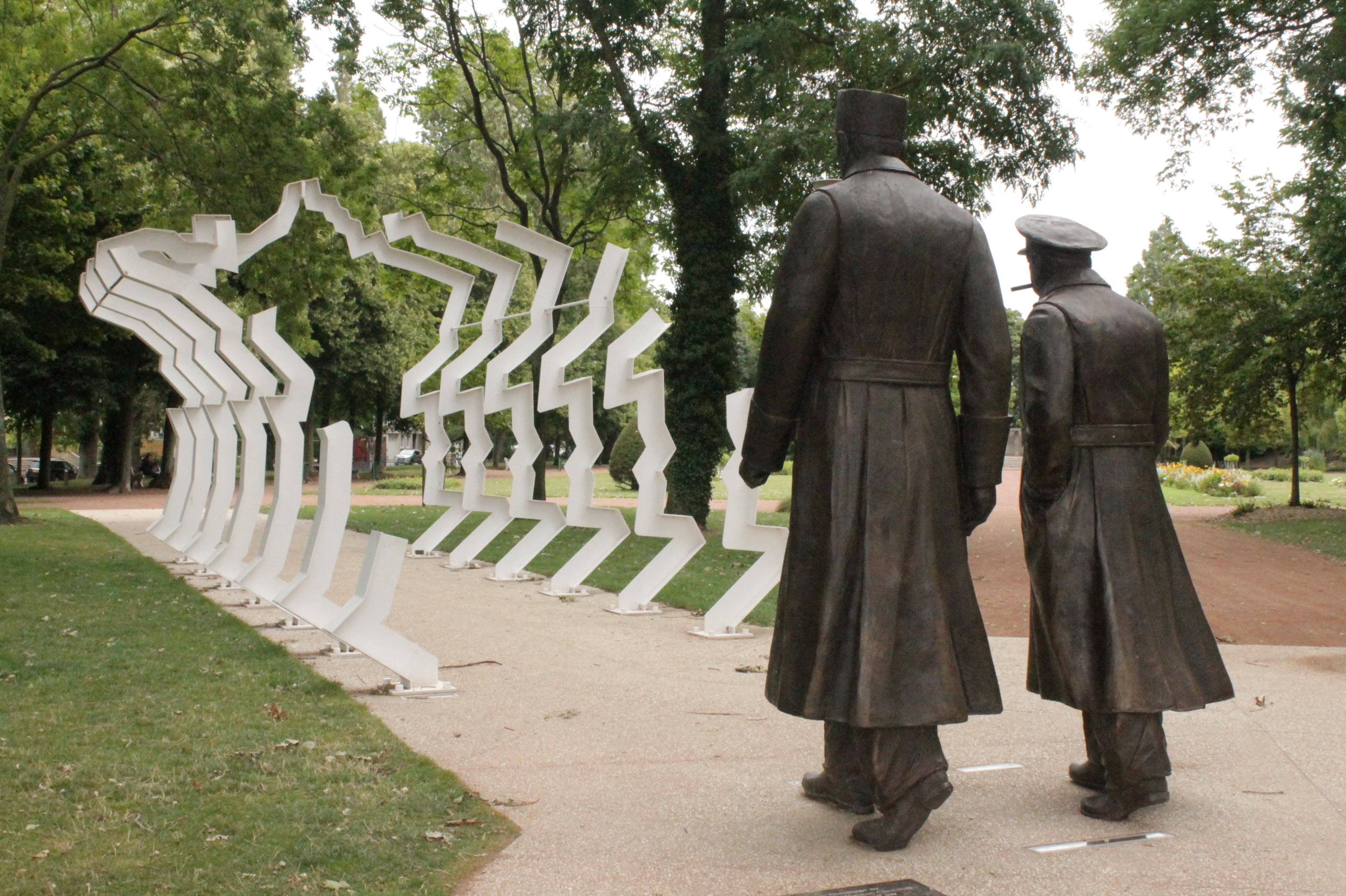
, begged him to spare their lives. This event is commemorated in ''The Burghers of Calais
''The Burghers of Calais'' (french: Les Bourgeois de Calais) is a sculpture by Auguste Rodin in twelve original castings and numerous copies. It commemorates an event during the Hundred Years' War, when Calais, a French port on the English Cha ...
'' (''Les Bourgeois de Calais''), one of the most famous sculptures by Auguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor, generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a uniqu ...
, erected in the city in 1895. Though sparing the lives of the delegation members, King Edward drove out most of the French inhabitants, and settled the town with English. The municipal charter of Calais, previously granted by the Countess of Artois
The count of Artois (French: Comtes d'Artois, Dutch: Graven van Artesië) was the ruler over the County of Artois from the 9th century until the abolition of the countship by the French Revolution, French revolutionaries in 1790.
House of Artois
...
, was reconfirmed by Edward that year (1347).
 In 1360 the
In 1360 the Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between Kings Edward III of England and John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' ...
assigned Guînes
Guînes (; vls, Giezene, lang; pcd, Guinne) is a commune in the northern French department of Pas-de-Calais. Historically it was spelt ''Guisnes''.
On 7 January 1785, Jean-Pierre Blanchard, a French pioneer in hydrogen-balloon flight, complete ...
, Marck and Calais—collectively the "Pale of Calais
The Pale of Calais was a territory in Northern France ruled by the monarchs of England for more than two hundred years from 1347 to 1558. The area, which was taken following the Battle of Crécy in 1346 and the subsequent Siege of Calais (1346� ...
"—to English rule in perpetuity, but this assignment was informally and only partially implemented. On 9 February 1363 the town was made a staple port. It remained part of the Diocese of Thérouanne
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
from 1379, keeping an ecclesiastical tie with France.
The town came to be called the "brightest jewel in the English crown" owing to its great importance as The Staple In European historiography, the term "staple" refers to the entire medieval system of trade and its taxation; its French equivalent is ''étape'', and its German equivalent ''stapeln'', words deriving from Late Latin ' with the same meaning, derived ...
a gateway port for the tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
and wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
trades (or "staples"). Its customs revenues amounted at times to a third of the English government's revenue, with wool being the most important element by far. Of its population of about 12,000 people, as many as 5,400 were recorded as having been connected with the wool trade. The governorship or Captaincy of Calais was a lucrative and highly prized public office; the famous Dick Whittington
Richard Whittington (c. 1354–1423) of the parish of St Michael Paternoster Royal, City of London, was an English merchant and a politician of the late medieval period. He is also the real-life inspiration for the English folk tale ''Dick ...
was simultaneously Lord Mayor of the City of London
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are ...
and Mayor of the Staple in 1407.
Calais was regarded for many years as being an integral part of the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On 1 ...
, with its representatives sitting in the English Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. The continued English hold on Calais however depended on expensively maintained fortifications, as the town lacked any natural defences. Maintaining Calais was a costly business that was frequently tested by the forces of France and the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
, with the Franco-Burgundian border running nearby. The British historian Geoffrey Elton
Sir Geoffrey Rudolph Elton (born Gottfried Rudolf Otto Ehrenberg; 17 August 1921 – 4 December 1994) was a German-born British political and constitutional historian, specialising in the Tudor period. He taught at Clare College, Cambridge, and w ...
once remarked "Calais—expensive and useless—was better lost than kept". The duration of the English hold over Calais was, to a large extent, the result of the feud between Burgundy and France: both sides coveted the town, but preferred to see England control it rather than their domestic rivals. The stalemate was broken by the victory of the French crown over Burgundy following Joan of Arc
Joan of Arc (french: link=yes, Jeanne d'Arc, translit= �an daʁk} ; 1412 – 30 May 1431) is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronati ...
's final battle in the siege of Compiègne
The siege of Compiègne (1430) was conducted by Duke Philip III of Burgundy after the town of Compiègne had refused to transfer allegiance to him under the terms of a treaty with Charles VII. The siege is perhaps best known for Joan of Arc's ca ...
in 1430, and the later incorporation of the duchy into France.
16th century
In 1532, the English KingHenry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
visited Calais and his men calculated that the town had about 2400 beds and stabling to keep some 2000 horses. Following the royal visit, the town's governance was reformed in 1536, aiming to strengthen ties with England. As part of this move, Calais became a parliamentary borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
sending burgesses to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
of the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised t ...
.
In September 1552, the English adventurer Thomas Stukley
Thomas Stucley (c. 15254 August 1578), also written Stukeley or Stukley and known as the Lusty Stucley,Vivian 1895, p. 721, pedigree of Stucley was an English mercenary who fought in France, Ireland, and at the Battle of Lepanto (1571) and ...
, who had been for some time in the French service, betrayed to the authorities in London some French plans for the capture of Calais, to be followed by a descent upon England. Stukley himself might have been the author of these plans.
On 7 January 1558, King Henry II of France
Henry II (french: Henri II; 31 March 1519 – 10 July 1559) was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder bro ...
sent forces led by Francis, Duke of Guise
Francis de Lorraine II, the first Prince of Joinville, also Duke of Guise and Duke of Aumale (french: François de Lorraine; 17 February 1519 – 24 February 1563), was a French general and statesman. A prominent leader during the Italian War of ...
, who laid siege to Calais. When the French attacked, they were able to surprise the English at the critical strongpoint of Fort Nieulay and the sluice gates, which could have flooded the attackers, remained unopened. The loss was regarded by Queen Mary I of England
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. Sh ...
as a dreadful misfortune. When she heard the news, she reportedly said, "When I am dead and opened, you shall find 'Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
' er husbandand 'Calais' lying in my heart." The region around Calais, then-known as the ''Calaisis
The Pale of Calais was a territory in Northern France ruled by the monarchs of England for more than two hundred years from 1347 to 1558. The area, which was taken following the Battle of Crécy in 1346 and the subsequent siege of Calais, was ...
'', was renamed the ''Pays Reconquis'' ("Reconquered Country") in commemoration of its recovery by the French. Use of the term is reminiscent of the Spanish Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid ...
, with which the French were certainly familiar—and, since it occurred in the context of a war with Spain (Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
was at the time Queen Mary's consort), might have been intended as a deliberate snub.
The town was captured by the Spanish on 24 April 1596 in an invasion mounted from the nearby Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
by Archduke Albert of Austria, but it was returned to France under the Treaty of Vervins
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
in May 1598.
17th century to World War I
 Calais remained an important maritime city and smuggling centre throughout the 17th century. However, during the next century, the port of Calais began to stagnate gradually, as the nearby ports of
Calais remained an important maritime city and smuggling centre throughout the 17th century. However, during the next century, the port of Calais began to stagnate gradually, as the nearby ports of Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
and Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.aborted invasion of Britain.
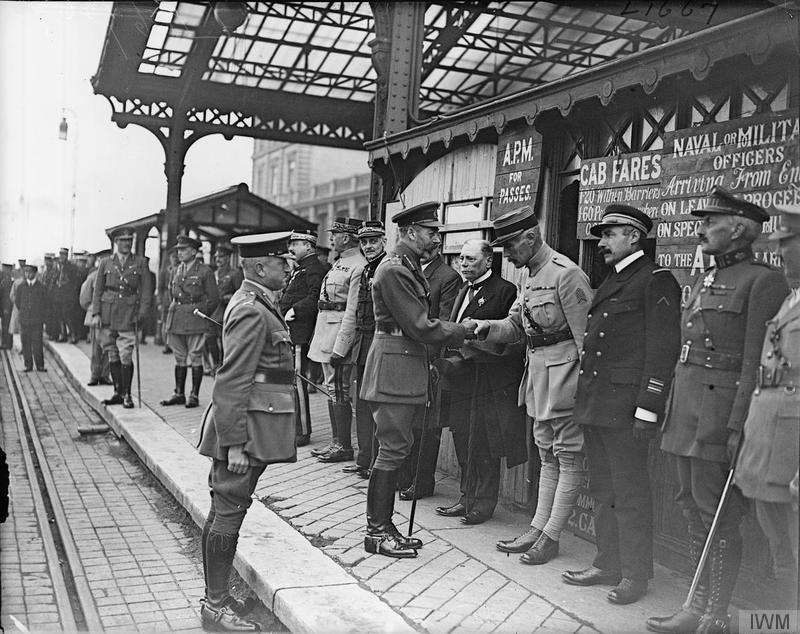
From October to December 1818, the British army used Calais as their departing port to return home after occupying post-Waterloo France. General Murray appointed Sir
Reference E60/IV/14
The Old Barracks, Harold Street,


 Calais was virtually razed to the ground during
Calais was virtually razed to the ground during
 The city's proximity to England has made it a major port for centuries. It is the principal ferry crossing point between England and France, with the vast majority of Channel crossings being made between Dover and Calais. Companies operating from Calais include SeaFrance (currently in liquidation), DFDS Seaways, and P&O Ferries. The French end of the
The city's proximity to England has made it a major port for centuries. It is the principal ferry crossing point between England and France, with the vast majority of Channel crossings being made between Dover and Calais. Companies operating from Calais include SeaFrance (currently in liquidation), DFDS Seaways, and P&O Ferries. The French end of the
 Calais is part of Pas-de-Calais's 7th constituency. The local Member of Parliament (France), MP is The Republicans (France), Republican Pierre-Henri Dumont.
The mayor of Calais has been Natacha Bouchart since 2008, first for the Union for a Popular Movement and then its successor The Republicans. From 1971 to 2008, the mayor was a member of the French Communist Party (PCF): Jean-Jacques Barthe (1971–2000) and Jacky Hénin (2000–2008).
Calais is part of Pas-de-Calais's 7th constituency. The local Member of Parliament (France), MP is The Republicans (France), Republican Pierre-Henri Dumont.
The mayor of Calais has been Natacha Bouchart since 2008, first for the Union for a Popular Movement and then its successor The Republicans. From 1971 to 2008, the mayor was a member of the French Communist Party (PCF): Jean-Jacques Barthe (1971–2000) and Jacky Hénin (2000–2008).
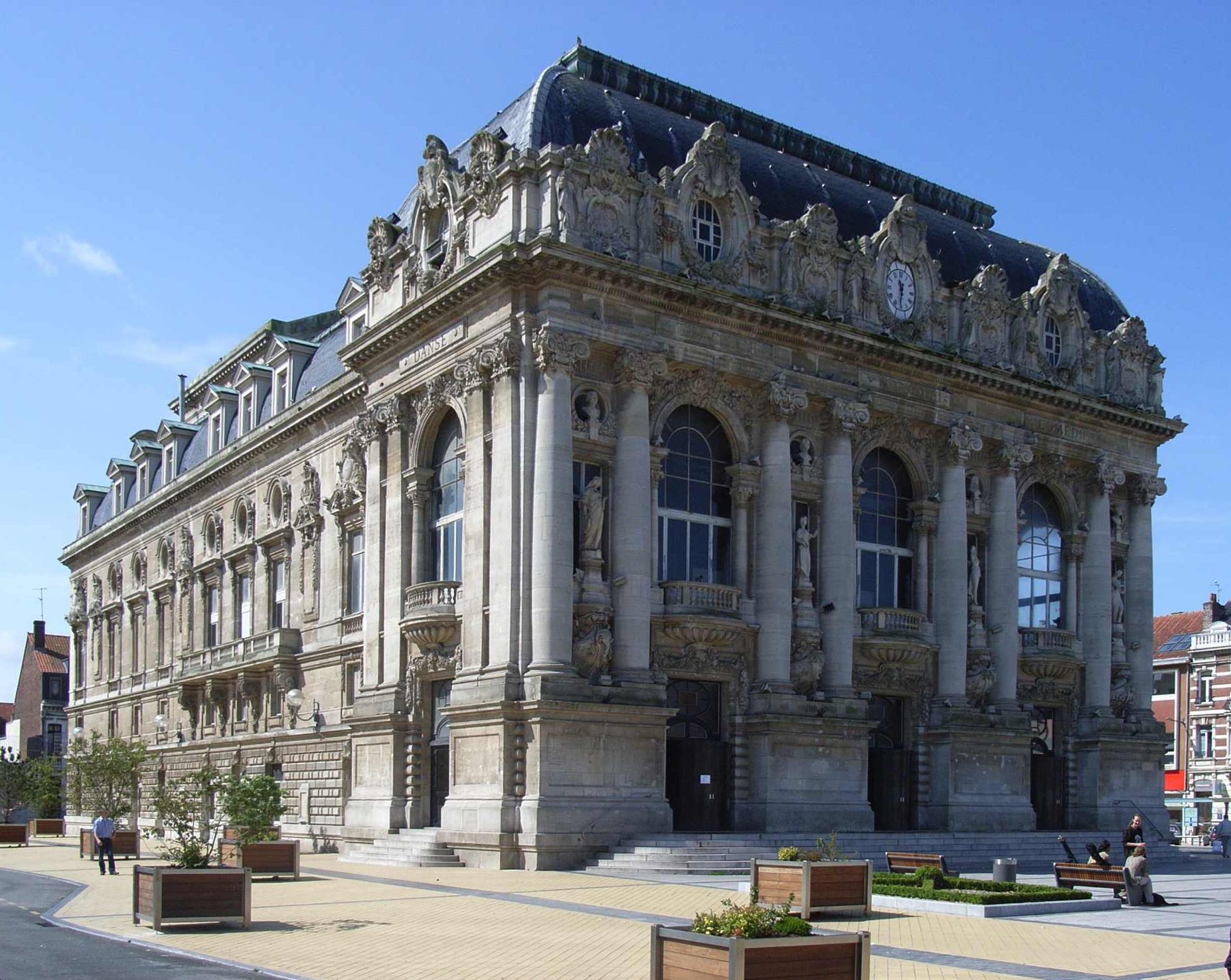
 The town centre, which has seen significant regeneration over the past decade, is dominated by its distinctive town hall (Calais City Hall, Hôtel de Ville) at Place du Soldat Inconnu. It was built in the Flemish Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style between 1911 and 1925 to commemorate the unification of the cities of Calais and Saint Pierre in 1885. A previous town hall had been erected in 1818. One of the most elegant landmarks in the city, its ornate 74-metre (246 ft) high clock tower and belfry can be seen from out to sea and chimes throughout the day and has been protected by UNESCO since 2005 as part of Belfries of Belgium and France, a series of belfries across the region. The building parts have also been listed as a series of historic monuments by government decree of 26 June 2003, including its roofs and belfry, main hall, glass roof, the staircase, corridor serving the first floor, the rooms on the first floor (including decoration): the wedding room, the VIP lounge, the lounge of the council and the cabinet room. The hall has stained glass windows and numerous paintings and exquisite decor. It houses police offices.
The town centre, which has seen significant regeneration over the past decade, is dominated by its distinctive town hall (Calais City Hall, Hôtel de Ville) at Place du Soldat Inconnu. It was built in the Flemish Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style between 1911 and 1925 to commemorate the unification of the cities of Calais and Saint Pierre in 1885. A previous town hall had been erected in 1818. One of the most elegant landmarks in the city, its ornate 74-metre (246 ft) high clock tower and belfry can be seen from out to sea and chimes throughout the day and has been protected by UNESCO since 2005 as part of Belfries of Belgium and France, a series of belfries across the region. The building parts have also been listed as a series of historic monuments by government decree of 26 June 2003, including its roofs and belfry, main hall, glass roof, the staircase, corridor serving the first floor, the rooms on the first floor (including decoration): the wedding room, the VIP lounge, the lounge of the council and the cabinet room. The hall has stained glass windows and numerous paintings and exquisite decor. It houses police offices.
 Église Notre-Dame de Calais, Église Notre-Dame is a great church which was originally built in the late 13th century and its tower was added in the late 14th or early 15th century. Like the town hall it is one of the city's most prominent landmarks. It was arguably the only church in the English perpendicular style in France. Much of the current 1400 capacity church dates to 1631–1635. It contains elements of Flemish, Gothic, Anglo-Norman and Tudor architecture. In 1691, an 1800 cubic metre cistern was added to the church under orders by Vauban. The church is dedicated to the Virgin, and built in the form of a cross, consisting of a nave and four aisles— The old grand altar dated to 1628 and was built from Carrara marble wrecked on the coast, during its transit from Genoa to Antwerp. It contained eighteen figures, the two standing on either side of the altar-piece—representing St. Louis and Charlemagne. The organ—of a deep and mellow tone, and highly ornamented by figures in relief—was built at Canterbury sometime around 1700. The pulpit and reading-desk, richly sculptured in oak, is another well-executed piece of ecclesiastical workmanship from Saint-Omer, St. Omer. The altar-piece, the Assumption, was often attributed to Anthony van Dyck, though in reality it is by Gerard Seghers; whilst the painting over the side altar, once believed to be by Peter Paul Rubens is in fact by Pieter Van Mol. A high and strongly built wall, partaking more of the fortress than a cathedral in its aspect, flanks the building, and protects it from the street where formerly ran the old river, in its course through Calais to the sea.
The square, massive Norman tower has three-arched belfry windows on each face, surmounted by corner turrets, and a conically shaped tower of octagonal proportions, topped again by a short steeple. The tower was a main viewing point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) which linked the Paris Observatory with the Royal Greenwich Observatory using trigonometry. Cross-channel sightings were made of signal lights at Dover Castle and Fairlight, East Sussex.
The church was assigned as a historic monument by decree of 10 September 1913, only to have its stained glass smashed during a Zeppelin bombardment on 15 January 1915, falling through the roof. General de Gaulle married Yvonne Vendroux on 6 April 1921 at the cathedral. The building experienced extensive damage during World War II, and was partially rebuilt, although much of the old altar and furnishings were not replaced.
Église Notre-Dame de Calais, Église Notre-Dame is a great church which was originally built in the late 13th century and its tower was added in the late 14th or early 15th century. Like the town hall it is one of the city's most prominent landmarks. It was arguably the only church in the English perpendicular style in France. Much of the current 1400 capacity church dates to 1631–1635. It contains elements of Flemish, Gothic, Anglo-Norman and Tudor architecture. In 1691, an 1800 cubic metre cistern was added to the church under orders by Vauban. The church is dedicated to the Virgin, and built in the form of a cross, consisting of a nave and four aisles— The old grand altar dated to 1628 and was built from Carrara marble wrecked on the coast, during its transit from Genoa to Antwerp. It contained eighteen figures, the two standing on either side of the altar-piece—representing St. Louis and Charlemagne. The organ—of a deep and mellow tone, and highly ornamented by figures in relief—was built at Canterbury sometime around 1700. The pulpit and reading-desk, richly sculptured in oak, is another well-executed piece of ecclesiastical workmanship from Saint-Omer, St. Omer. The altar-piece, the Assumption, was often attributed to Anthony van Dyck, though in reality it is by Gerard Seghers; whilst the painting over the side altar, once believed to be by Peter Paul Rubens is in fact by Pieter Van Mol. A high and strongly built wall, partaking more of the fortress than a cathedral in its aspect, flanks the building, and protects it from the street where formerly ran the old river, in its course through Calais to the sea.
The square, massive Norman tower has three-arched belfry windows on each face, surmounted by corner turrets, and a conically shaped tower of octagonal proportions, topped again by a short steeple. The tower was a main viewing point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) which linked the Paris Observatory with the Royal Greenwich Observatory using trigonometry. Cross-channel sightings were made of signal lights at Dover Castle and Fairlight, East Sussex.
The church was assigned as a historic monument by decree of 10 September 1913, only to have its stained glass smashed during a Zeppelin bombardment on 15 January 1915, falling through the roof. General de Gaulle married Yvonne Vendroux on 6 April 1921 at the cathedral. The building experienced extensive damage during World War II, and was partially rebuilt, although much of the old altar and furnishings were not replaced.
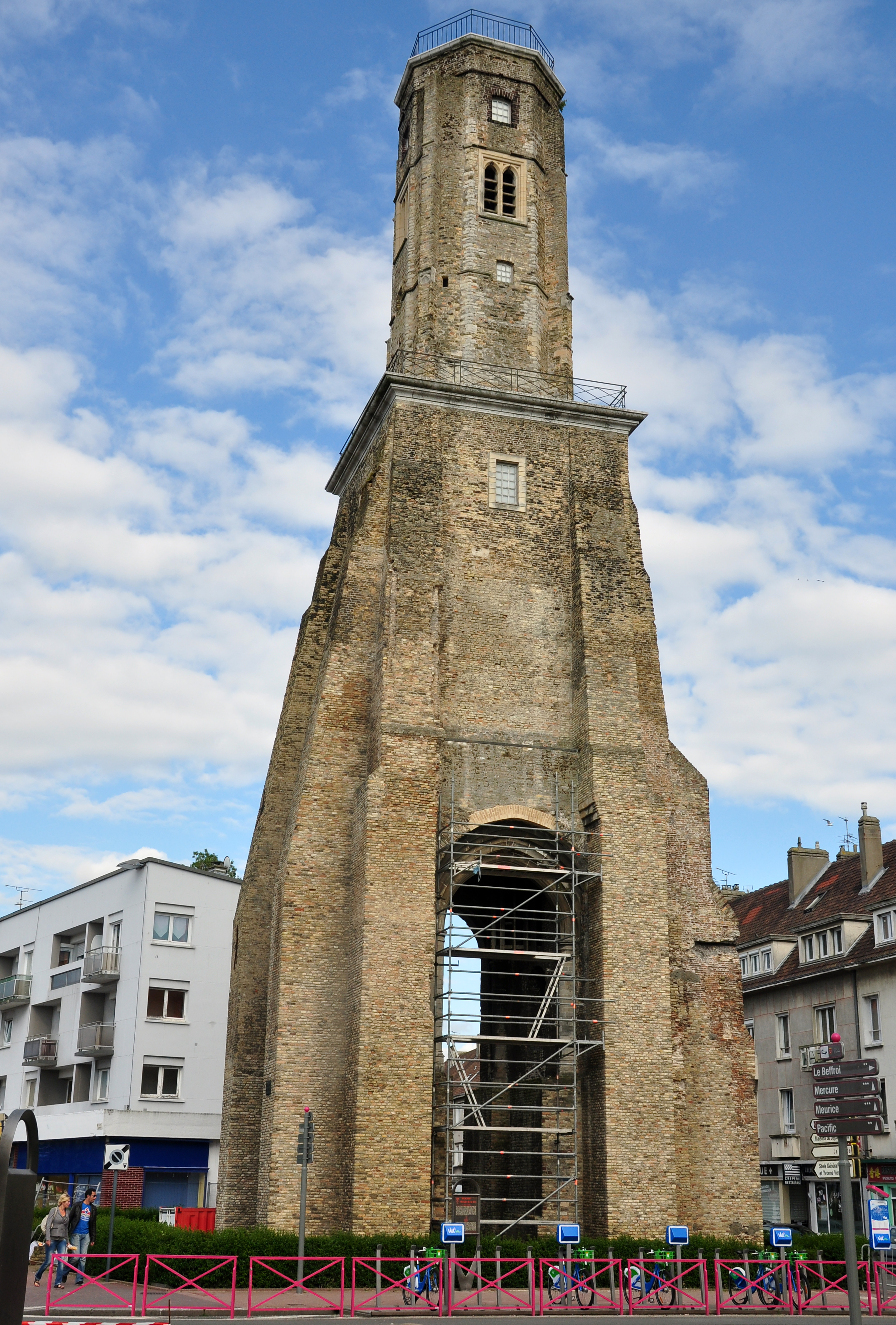 The Tour du Guet (Watch Tower), situated in Calais Nord on the Places d'Armes, is one of the few surviving pre-war buildings. Dating from 1229, when Philip I, Count of Boulogne, built the fortifications of Calais, it is one of the oldest monuments of Calais, although the oldest remaining traces date to 1302. It has a height of 35–39 metres (sources differ). An 1580 Dover Straits earthquake, earthquake in 1580 split the tower in two, and at one time it threatened to collapse completely. The tower was repaired in 1606, and then had the purpose of serving as a hall to accommodate the merchants of Calais. It was damaged in 1658 when a young stable boy set fire to it, while it was temporarily being used as royal stables during a visit of King Louis XIV. It was not repaired for some 30 years. In 1770, a bell identical to the original bell of 1348 was cast. Due to its height, from the late 17th century it became an important watchout post for the city for centuries until 1905; the last keeper of the tower was forced to leave in 1926. Abraham Chappe (a brother of Ignace Chappe) installed a telegraph office in the tower in 1816 and operated for 32 years. It was this office which announced the death of Napoleon I to the French public in 1821. It also had the dual function as lighthouse with a rotating beacon fuelled by oil from 1818. The lantern was finally replaced by a new lighthouse on 15 October 1848. During the First World War, it served as a military observation post and narrowly missed destruction during World War II. This tower has been classified as a historic monument since 6 November 1931.
The Calais Lighthouse (Le phare de Calais) was built in 1848, replacing the old watch tower as the lighthouse of the port. The tower was electrified in 1883 and automated in 1992. The staircase has 271 steps leading up to the lantern. By day it is easily distinguishable from other coastal lighthouses by its white color and black lantern. The lighthouse was classified as a historical monument on 22 November 2010.
The Tour du Guet (Watch Tower), situated in Calais Nord on the Places d'Armes, is one of the few surviving pre-war buildings. Dating from 1229, when Philip I, Count of Boulogne, built the fortifications of Calais, it is one of the oldest monuments of Calais, although the oldest remaining traces date to 1302. It has a height of 35–39 metres (sources differ). An 1580 Dover Straits earthquake, earthquake in 1580 split the tower in two, and at one time it threatened to collapse completely. The tower was repaired in 1606, and then had the purpose of serving as a hall to accommodate the merchants of Calais. It was damaged in 1658 when a young stable boy set fire to it, while it was temporarily being used as royal stables during a visit of King Louis XIV. It was not repaired for some 30 years. In 1770, a bell identical to the original bell of 1348 was cast. Due to its height, from the late 17th century it became an important watchout post for the city for centuries until 1905; the last keeper of the tower was forced to leave in 1926. Abraham Chappe (a brother of Ignace Chappe) installed a telegraph office in the tower in 1816 and operated for 32 years. It was this office which announced the death of Napoleon I to the French public in 1821. It also had the dual function as lighthouse with a rotating beacon fuelled by oil from 1818. The lantern was finally replaced by a new lighthouse on 15 October 1848. During the First World War, it served as a military observation post and narrowly missed destruction during World War II. This tower has been classified as a historic monument since 6 November 1931.
The Calais Lighthouse (Le phare de Calais) was built in 1848, replacing the old watch tower as the lighthouse of the port. The tower was electrified in 1883 and automated in 1992. The staircase has 271 steps leading up to the lantern. By day it is easily distinguishable from other coastal lighthouses by its white color and black lantern. The lighthouse was classified as a historical monument on 22 November 2010.
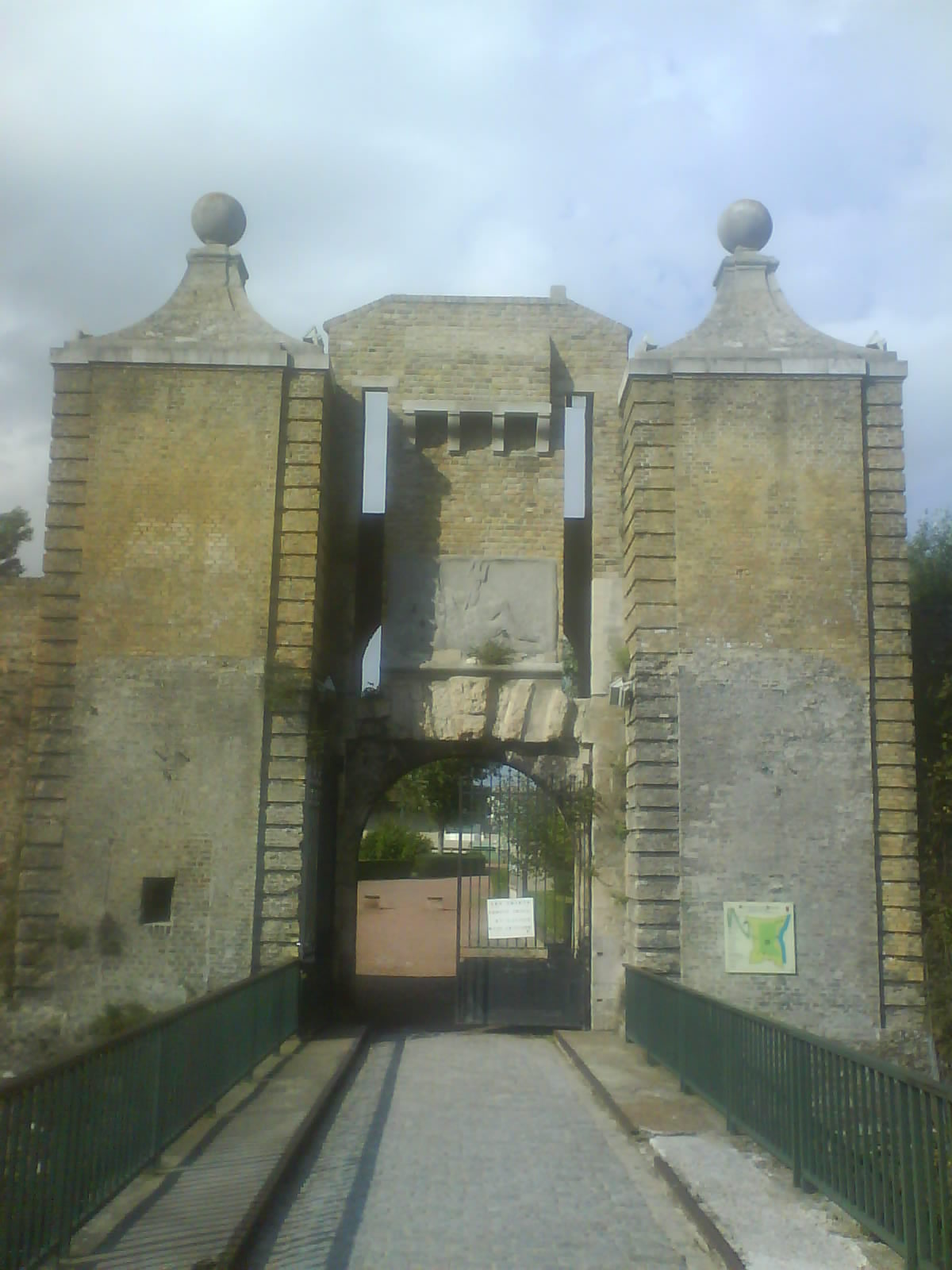 The Citadel of Calais, Citadel, located on the Avenue Pierre Coubertin, was built between 1560 and 1571 on the site of a former medieval castle which was built in 1229 by Philippe de Hureprel. Its purpose of its construction was to fend off would-be invaders, but it wasn't long until the city was successfully invaded by Archduke Albert of Austria on 24 April 1596. Both Louis XIII and Cardinal Richelieu at one time considered expanding the citadel and Calais into a great walled city for military harbour purposes but the proposals came to nothing.
Fort Risban, located on the coast on the Avenue Raymond Poincaré at the port entrance, was built by the English to prevent supplies reaching Calais by sea during the siege in November 1346 and continued to be occupied by them until 1558 when Calais was restored to France. In 1596, the fort was captured by the Spanish Netherlands until May 1598 when it was returned to the French following the Peace of Vervins, Treaty of Vervins. It was rebuilt in 1640. Vauban, who visited the fort some time in the 1680s, described it as "a home for owls, and place to hold the Sabbath" rather than a fortification. During World War II it served as an air raid shelter. It contains the Lancaster Tower, a name often given to the fort itself.
Fort Nieulay, located along the Avenue Roger Salengro originally dated to the 12th or 13th century. During the English invasion in 1346, sluices gates were added as water defences and a fort was built up around it in 1525 on the principle that the people of the fort could defend the town by flooding it. In April and May 1677, Louis XIV and Vauban visited Calais and ordered a complete rebuilding of Fort Nieulay. It was completed in 1679, with the purpose to protect the bridge of Nieulay crossing the Hames River. By 1815 the fort had fallen into a ruined state and it wasn't until 1903 that it was sold and improved by its farmer tenants. The fort was briefly the site of a low-key scuffle with Germans in May 1940.
The Citadel of Calais, Citadel, located on the Avenue Pierre Coubertin, was built between 1560 and 1571 on the site of a former medieval castle which was built in 1229 by Philippe de Hureprel. Its purpose of its construction was to fend off would-be invaders, but it wasn't long until the city was successfully invaded by Archduke Albert of Austria on 24 April 1596. Both Louis XIII and Cardinal Richelieu at one time considered expanding the citadel and Calais into a great walled city for military harbour purposes but the proposals came to nothing.
Fort Risban, located on the coast on the Avenue Raymond Poincaré at the port entrance, was built by the English to prevent supplies reaching Calais by sea during the siege in November 1346 and continued to be occupied by them until 1558 when Calais was restored to France. In 1596, the fort was captured by the Spanish Netherlands until May 1598 when it was returned to the French following the Peace of Vervins, Treaty of Vervins. It was rebuilt in 1640. Vauban, who visited the fort some time in the 1680s, described it as "a home for owls, and place to hold the Sabbath" rather than a fortification. During World War II it served as an air raid shelter. It contains the Lancaster Tower, a name often given to the fort itself.
Fort Nieulay, located along the Avenue Roger Salengro originally dated to the 12th or 13th century. During the English invasion in 1346, sluices gates were added as water defences and a fort was built up around it in 1525 on the principle that the people of the fort could defend the town by flooding it. In April and May 1677, Louis XIV and Vauban visited Calais and ordered a complete rebuilding of Fort Nieulay. It was completed in 1679, with the purpose to protect the bridge of Nieulay crossing the Hames River. By 1815 the fort had fallen into a ruined state and it wasn't until 1903 that it was sold and improved by its farmer tenants. The fort was briefly the site of a low-key scuffle with Germans in May 1940.
 Calais contains several museums. These include the Musée des Beaux-Arts et de la Dentelle de Calais, Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais and the Musée de la Seconde Guerre Mondiale (World War II museum). Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais is a lace and fashion museum located in an old Boulart factory on the canalside and contains workshops, a library and a restaurant and regularly puts on fashion shows. The World War II museum is located at Parc St Pierre opposite the town hall and south of the train station. The building is a former Nazi bunker and wartime military headquarters, built in 1941 by the Todt Organisation. The 194-metre-long structure contains twenty rooms with relics and photographs related to World War II, and one room dedicated to World War I.
Theatres and cultural centres include Le théâtre municipal, Le Centre Culturel Gérard Philipe, Le Conservatoire à rayonnement départemental (CRD), L'auditorium Didier Lockwood, L'École d'Art de Calais, Le Channel, Le Cinéma Alhambra and La Médiathèque municipale. Le théâtre municipal or Calais Theatre is located on the Boulevard Lafayette and was built in 1903 on a plot of land which was used as a cemetery between 1811 and 1871. The theatre opened in 1905. On the first floor of the façade are statues which represent the performing arts subjects of Poetry, Comedy, Dance and Music.
Calais contains several museums. These include the Musée des Beaux-Arts et de la Dentelle de Calais, Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais and the Musée de la Seconde Guerre Mondiale (World War II museum). Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais is a lace and fashion museum located in an old Boulart factory on the canalside and contains workshops, a library and a restaurant and regularly puts on fashion shows. The World War II museum is located at Parc St Pierre opposite the town hall and south of the train station. The building is a former Nazi bunker and wartime military headquarters, built in 1941 by the Todt Organisation. The 194-metre-long structure contains twenty rooms with relics and photographs related to World War II, and one room dedicated to World War I.
Theatres and cultural centres include Le théâtre municipal, Le Centre Culturel Gérard Philipe, Le Conservatoire à rayonnement départemental (CRD), L'auditorium Didier Lockwood, L'École d'Art de Calais, Le Channel, Le Cinéma Alhambra and La Médiathèque municipale. Le théâtre municipal or Calais Theatre is located on the Boulevard Lafayette and was built in 1903 on a plot of land which was used as a cemetery between 1811 and 1871. The theatre opened in 1905. On the first floor of the façade are statues which represent the performing arts subjects of Poetry, Comedy, Dance and Music.
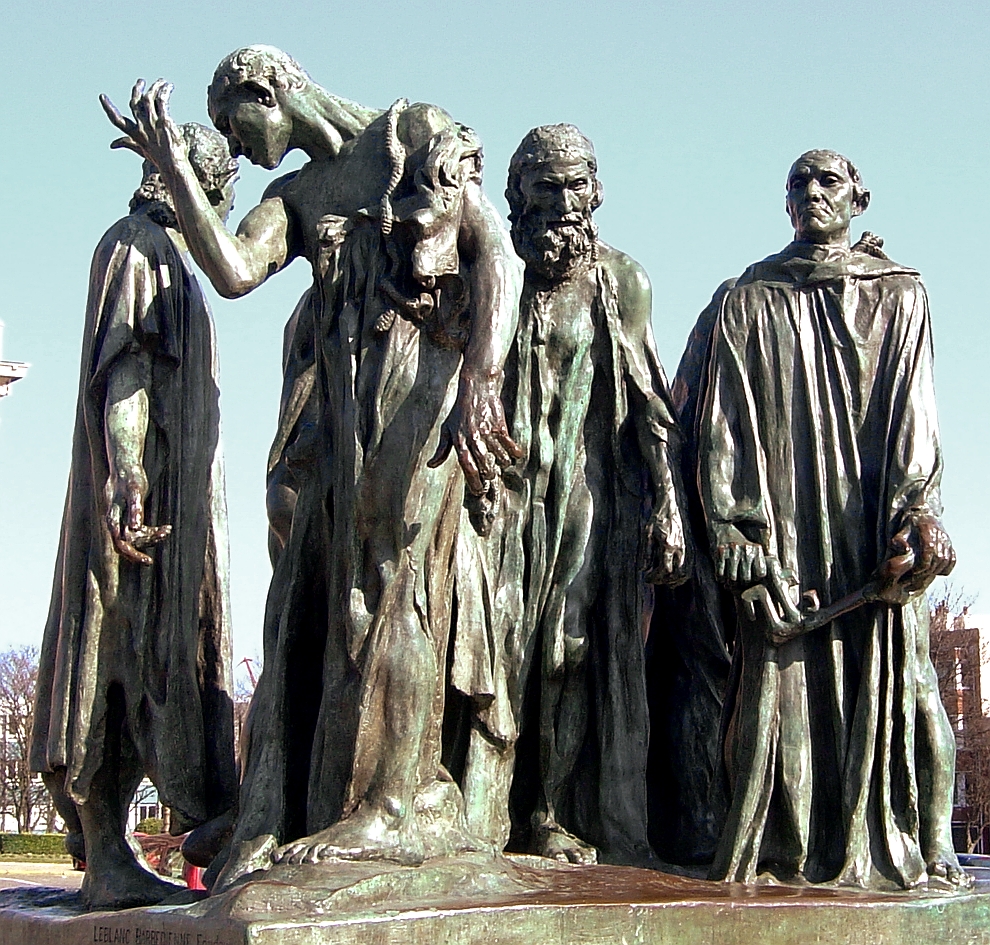
 Directly in front of the town hall is a bronze cast of ''Les Bourgeois de Calais'' ("
Directly in front of the town hall is a bronze cast of ''Les Bourgeois de Calais'' ("


Agglomération
Info about the port and city
Info about the port and city
{{Authority control Calais, Ephemeral islands Communes of Pas-de-Calais Former islands of France France–United Kingdom border crossings Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast Port cities and towns of the North Sea Pale of Calais Vauban fortifications in France
Manley Power
Lieutenant-General Sir Manley Power, KCB, ComTE (1773 – 7 July 1826) was a British military leader who fought in a number of campaigns for Britain and rose to the rank of Lieutenant-General. He is chiefly remembered for leading a brigade o ...
to oversee the evacuation of British troops from France. Cordial relations had been restored by that time and on 3 December, the mayor of Calais wrote a letter to Power to express thanks for his "considerate treatment of the French and of the town of Calais during the embarkation."Herefordshire Record OfficeReference E60/IV/14
The Old Barracks, Harold Street,
Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population ...
, HR1 2QX
The population in 1847 was 12,580, many of whom were English. It was one of the main ports for British travellers to Europe.
In World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
the British Expeditionary Force or BEF arrived in Calais on its way to the nearby frontline cutting through Nord-Pas-de-Calais
Nord-Pas-de-Calais (); pcd, Nord-Pas-Calés); is a former administrative region of France. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Hauts-de-France. It consisted of the departments of Nord and Pas-de-Calais. Nord-Pas-de-Cala ...
and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
. Calais was a key port for the supply of arms and reinforcements to the Western Front. In the 1930s, the town was known for being a politically socialist stronghold.
World War II


 Calais was virtually razed to the ground during
Calais was virtually razed to the ground during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. In May 1940, it was a key objective of the invading German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
forces and became the scene of a last-ditch defence—the siege of Calais—which diverted a sizable amount of German forces for several days immediately prior to the Battle of Dunkirk
The Battle of Dunkirk (french: Bataille de Dunkerque, link=no) was fought around the French port of Dunkirk (Dunkerque) during the Second World War, between the Allies and Nazi Germany. As the Allies were losing the Battle of France on ...
. A total of 3,000 British and 800 French troops, assisted by Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
warships, held out from 22 to 27 May 1940 against the 10th Panzer Division. The town was flattened by artillery and precision dive bombing
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact throughou ...
and only 30 of the 3800-strong defending force were evacuated before the town fell. This may have helped Operation Dynamo
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
, the evacuation of Allied forces at Dunkirk, as 10th Panzer would have been involved on the Dunkirk perimeter had it not been busy at Calais. Between 26 May and 4 June 1940, some 330,000 Allied troops escaped from the Germans at Dunkirk.
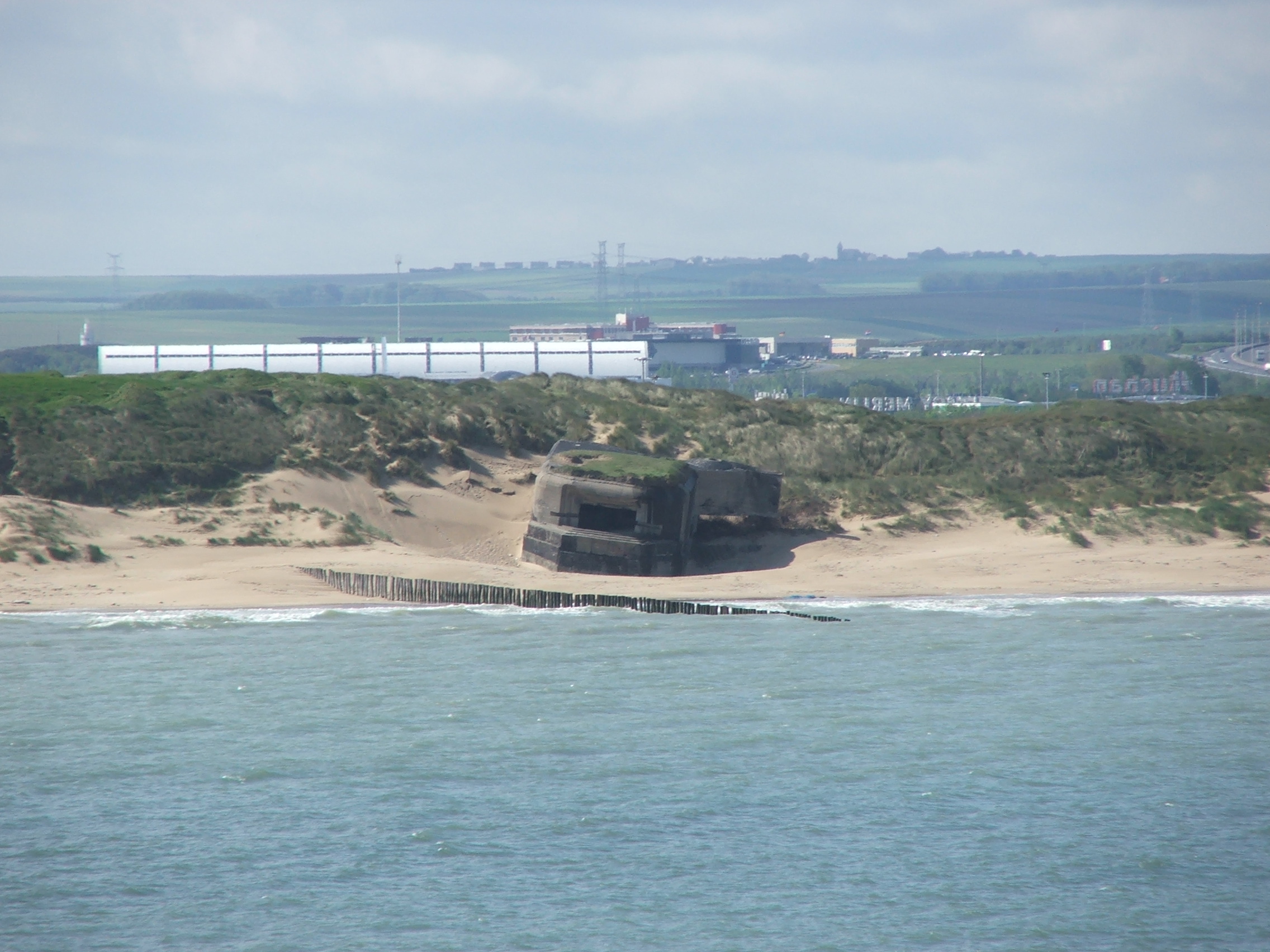
During the ensuing German occupation, it became the command post for German forces in the Pas-de-Calais/Flanders region and was very heavily fortified, as the Germans generally believed that the Allies would invade there. It was also used as a launch site for V1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buzz bomb or doodlebug and in Germany a ...
s and for much of the war, the Germans used the region as the site for railway gun
A railway gun, also called a railroad gun, is a large artillery piece, often surplus naval artillery, mounted on, transported by, and fired from a specially designed railroad car, railway wagon. Many countries have built railway guns, but the ...
s to bombard the south-eastern corner of England. In 1943 they built massive bunkers along the coast in preparation for launching missiles on the southeast of England. Despite heavy preparations for defence against an amphibious assault, the Allied invasion took place well to the west in Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
on D-Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
. Calais was very heavily bombed and shelled in a successful effort to disrupt German communications and persuade them that the Allies would target the Pas-de-Calais for invasion (rather than Normandy). The town, by then largely in ruins, was laid siege to and liberated by General Daniel Spry's 3rd Canadian Infantry Division between 25 September and 1 October 1944. On 27 February 1945 Calais experienced its last bombing raid—this time by Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
bombers who mistook the town for Dunkirk, which was at that time still occupied by German forces. After the war there was little rebuilding of the historic city and most buildings were modern ones.
21st century – migration issues
Since 1999 or earlier, an increasingly large number ofillegal immigrant
Illegal immigration is the migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country or the continued residence without the legal right to live in that country. Illegal immigration tends to be financially upwar ...
s and asylum seeker
An asylum seeker is a person who leaves their country of residence, enters another country and applies for asylum (i.e., international protection) in that other country. An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and mi ...
s started to arrive in the vicinity of Calais, living in the Calais jungle, the nickname given to a series of makeshift camps. The people lived there while attempting to enter the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
by stowing away on lorries, ferries, cars, or trains travelling through the Port of Calais
The Port of Calais in northern France is the fourth largest port in France and the largest for passenger traffic. It accounts for more than a third of economic activity in the town of Calais.
Background
The Port of Calais was the first cable ...
or the Eurotunnel Calais Terminal
The Eurotunnel Calais Terminal (also known as the Charles Dickens Terminal or Coquelles Terminal) is a railway terminal built for the transport of road-going vehicles on specially constructed trains through the Channel Tunnel. The terminal i ...
, or while waiting for their French asylum claims to be processed. The people were a mix of asylum seeker
An asylum seeker is a person who leaves their country of residence, enters another country and applies for asylum (i.e., international protection) in that other country. An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and mi ...
s and economic migrant
An economic migrant is someone who emigrates from one region to another, including crossing international borders, seeking an improved standard of living, because the conditions or job opportunities in the migrant's own region are insufficient. Th ...
s from Darfur
Darfur ( ; ar, دار فور, Dār Fūr, lit=Realm of the Fur) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju ( ar, دار داجو, Dār Dājū, links=no) while ruled by the Daju, ...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
and other Least Developed Countries, underdeveloped or conflict-stricken countries in Africa and Asia.
The Calais migrant crisis led to escalating tension between the UK and France in the summer of 2015. The UK blamed France for not doing enough to stop migrants from entering the Channel Tunnel or attempting to scale fences built along the border. The British Prime Minister David Cameron released a statement saying that illegal immigrants would be removed from the UK even if they reached the island. To discourage migrants and refugees from jumping on train shuttles at Calais, the UK government supplied fencing to be installed around the Eurotunnel complex, where the vehicles are loaded onto train shuttles in Calais.
On 26 October 2016, French authorities announced that the camp had been cleared. By January 2017, 500–1,000 migrants, mostly unaccompanied minors, had returned and were Homelessness, living rough in Calais and there has been a presence ever since.
Geography and climate
Calais is located on the Pas de Calais, which marks the boundary between theEnglish Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
and North Sea and located at the opposite end of the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
, from Dover. On a clear day the White cliffs of Dover can be viewed across the channel. Aside from being an important port and boarding point between France and England, it is at the nucleus of many major railway and highway networks and connected by road to Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
, Lens, Pas-de-Calais, Lens, Béthune and Saint-Omer, St. Omer. Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Coquelles
Coquelles (; vls, Kalkwelle, lang) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department near Calais in northern France.
The town comprises a shopping centre, hotels and farm in Vieille Coquelles (old Coquelles), part of the L'Européenne autoroute ( ...
to the west, Coulogne to the south and Marck to the east. The core area of the city is divided into the Old Town area within the old city walls, and the younger suburbs of St. Pierre, which are connected by a boulevard.
Calais is part of the Côte d'Opale (Opal Coast), a cliff-lined section of northern French coast that parallels the White cliffs of Dover, white cliffs on the British coast and is part of the same Formation (stratigraphy), geological formation. It is known for its scenic cliffs such as Cape Blanc Nez and Cape Gris Nez and for its wide area of dunes. Many artists have been inspired by its landscapes, among them the composer Henri Dutilleux, the writers Victor Hugo and Charles Dickens, and the painters J. M. W. Turner, Carolus-Duran, Maurice Boitel and Eugène Boudin. It was the painter who coined the name for this area in 1911 to describe the distinctive quality of its light.
Calais has a temperate oceanic climate (''Cfb'' in the Köppen climate classification). Temperature ranges are moderate and the winters are cool with unstable weather. It rains on average about per year.
The commune of Calais is divided into 13 ''quartier''s :
* Quartier du Beau Marais (Calais), Beau Marais
* Quartier du Cailloux (Calais), Cailloux
* Quartier du Calais-Nord (Calais), Calais-nord
*
* Quartier des Fontinettes (Calais), Fontinettes
* Quartier du Fort-Nieulay (Calais), Fort-Nieulay
* Quartier Gambetta (Calais), Gambetta
* Quartier de Nouvelle-France (Calais), Nouvelle-France
* Quartier de la Mi-Voix (Calais), Mi-voix
* Quartier du Petit-Courgain (Calais), Petit Courgain
* Quartier Plage (Calais), Plage
* Quartier du Pont-du-Leu (Calais), Pont-du-Leu
* Quartier Saint-Pierre (Calais), Saint-Pierre
Demographics
Changes in the number of inhabitants is known throughout the population censuses conducted since 1793 in Calais. Note the massive growth in population from 13,529 in 1881 to 58,969 in 1886, a growth of 335.9%; this is because the city of Saint-Pierre-lès-Calais merged with Calais in 1885. According to the National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies, INSEE census of 2017, Calais has 73,911 people (a decrease of 4.4% from 1999). The town's population ranked 60th nationally, down from 53rd in 1999.Economy
 The city's proximity to England has made it a major port for centuries. It is the principal ferry crossing point between England and France, with the vast majority of Channel crossings being made between Dover and Calais. Companies operating from Calais include SeaFrance (currently in liquidation), DFDS Seaways, and P&O Ferries. The French end of the
The city's proximity to England has made it a major port for centuries. It is the principal ferry crossing point between England and France, with the vast majority of Channel crossings being made between Dover and Calais. Companies operating from Calais include SeaFrance (currently in liquidation), DFDS Seaways, and P&O Ferries. The French end of the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
is situated in the vicinity of Calais, in Coquelles
Coquelles (; vls, Kalkwelle, lang) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department near Calais in northern France.
The town comprises a shopping centre, hotels and farm in Vieille Coquelles (old Coquelles), part of the L'Européenne autoroute ( ...
some to the west of the town. Calais possesses direct rail links to Paris, to the south. More than 10 million people visit Calais annually.
From medieval times, English companies thrived in Calais. Calais was a particularly important centre in the production and trade of wool and cloth, which outweighed the costs of maintaining the town as part of England. In 1830 some 113 manufacturers were based in Calais and the St Pierre suburbs, the majority of which were English. There are still two major lace factories in Calais with around 700 looms and 3000 employees.Ruler (2011), p.69 The town exports in the early 20th century were lace, chemicals, paper, wines, especially champagne, spirits, hay, straw, wool, potatoes, woven goods, fruit, glass-ware, lace and metal-ware.Encyclopædia Britannica 11th ed. 1911 Principal imports in the early 20th century included cotton and silk goods, coal, iron and steel, petroleum, timber, raw wool, cotton yarn and cork. During the five years 1901–1905 the average annual value of exports was £8,388,000 (£6,363,000 in the years 1896–1900), of imports £4,145,000 (£3,759,000 in 1896–1900).
As a fishing port, Calais has several notable fishing markets including Les Délices de la Mer and Huîtrière Calaisenne on the Boulevard La Fayette, the latter of which is noted for its oysters, lobster and crabs from Brittany. The Emile Fournier et Fils market on the Rue Mouron sells mainly smoked fish including salmon, trout, herring and halibut.
Politics
 Calais is part of Pas-de-Calais's 7th constituency. The local Member of Parliament (France), MP is The Republicans (France), Republican Pierre-Henri Dumont.
The mayor of Calais has been Natacha Bouchart since 2008, first for the Union for a Popular Movement and then its successor The Republicans. From 1971 to 2008, the mayor was a member of the French Communist Party (PCF): Jean-Jacques Barthe (1971–2000) and Jacky Hénin (2000–2008).
Calais is part of Pas-de-Calais's 7th constituency. The local Member of Parliament (France), MP is The Republicans (France), Republican Pierre-Henri Dumont.
The mayor of Calais has been Natacha Bouchart since 2008, first for the Union for a Popular Movement and then its successor The Republicans. From 1971 to 2008, the mayor was a member of the French Communist Party (PCF): Jean-Jacques Barthe (1971–2000) and Jacky Hénin (2000–2008).
Notable landmarks
Place d'Armes
Place d'Armes is one of the largest squares in the city of Calais. It adjoins the watchtower, and during medieval times was once the heart of the city. While Calais was a territory of England (1347–1558), it became known as Market Square (place du Marché). Only at the end of English rule did it take the name of Place d'Armes. After the reconquest of Calais in 1558 by Francis, Duke of Guise, Francis II gave Calais the right to hold a fair twice a year on the square, which still exists today, as well as a bustling Wednesday and Saturday market.Hôtel de Ville
 The town centre, which has seen significant regeneration over the past decade, is dominated by its distinctive town hall (Calais City Hall, Hôtel de Ville) at Place du Soldat Inconnu. It was built in the Flemish Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style between 1911 and 1925 to commemorate the unification of the cities of Calais and Saint Pierre in 1885. A previous town hall had been erected in 1818. One of the most elegant landmarks in the city, its ornate 74-metre (246 ft) high clock tower and belfry can be seen from out to sea and chimes throughout the day and has been protected by UNESCO since 2005 as part of Belfries of Belgium and France, a series of belfries across the region. The building parts have also been listed as a series of historic monuments by government decree of 26 June 2003, including its roofs and belfry, main hall, glass roof, the staircase, corridor serving the first floor, the rooms on the first floor (including decoration): the wedding room, the VIP lounge, the lounge of the council and the cabinet room. The hall has stained glass windows and numerous paintings and exquisite decor. It houses police offices.
The town centre, which has seen significant regeneration over the past decade, is dominated by its distinctive town hall (Calais City Hall, Hôtel de Ville) at Place du Soldat Inconnu. It was built in the Flemish Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style between 1911 and 1925 to commemorate the unification of the cities of Calais and Saint Pierre in 1885. A previous town hall had been erected in 1818. One of the most elegant landmarks in the city, its ornate 74-metre (246 ft) high clock tower and belfry can be seen from out to sea and chimes throughout the day and has been protected by UNESCO since 2005 as part of Belfries of Belgium and France, a series of belfries across the region. The building parts have also been listed as a series of historic monuments by government decree of 26 June 2003, including its roofs and belfry, main hall, glass roof, the staircase, corridor serving the first floor, the rooms on the first floor (including decoration): the wedding room, the VIP lounge, the lounge of the council and the cabinet room. The hall has stained glass windows and numerous paintings and exquisite decor. It houses police offices.
Église Notre-Dame
 Église Notre-Dame de Calais, Église Notre-Dame is a great church which was originally built in the late 13th century and its tower was added in the late 14th or early 15th century. Like the town hall it is one of the city's most prominent landmarks. It was arguably the only church in the English perpendicular style in France. Much of the current 1400 capacity church dates to 1631–1635. It contains elements of Flemish, Gothic, Anglo-Norman and Tudor architecture. In 1691, an 1800 cubic metre cistern was added to the church under orders by Vauban. The church is dedicated to the Virgin, and built in the form of a cross, consisting of a nave and four aisles— The old grand altar dated to 1628 and was built from Carrara marble wrecked on the coast, during its transit from Genoa to Antwerp. It contained eighteen figures, the two standing on either side of the altar-piece—representing St. Louis and Charlemagne. The organ—of a deep and mellow tone, and highly ornamented by figures in relief—was built at Canterbury sometime around 1700. The pulpit and reading-desk, richly sculptured in oak, is another well-executed piece of ecclesiastical workmanship from Saint-Omer, St. Omer. The altar-piece, the Assumption, was often attributed to Anthony van Dyck, though in reality it is by Gerard Seghers; whilst the painting over the side altar, once believed to be by Peter Paul Rubens is in fact by Pieter Van Mol. A high and strongly built wall, partaking more of the fortress than a cathedral in its aspect, flanks the building, and protects it from the street where formerly ran the old river, in its course through Calais to the sea.
The square, massive Norman tower has three-arched belfry windows on each face, surmounted by corner turrets, and a conically shaped tower of octagonal proportions, topped again by a short steeple. The tower was a main viewing point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) which linked the Paris Observatory with the Royal Greenwich Observatory using trigonometry. Cross-channel sightings were made of signal lights at Dover Castle and Fairlight, East Sussex.
The church was assigned as a historic monument by decree of 10 September 1913, only to have its stained glass smashed during a Zeppelin bombardment on 15 January 1915, falling through the roof. General de Gaulle married Yvonne Vendroux on 6 April 1921 at the cathedral. The building experienced extensive damage during World War II, and was partially rebuilt, although much of the old altar and furnishings were not replaced.
Église Notre-Dame de Calais, Église Notre-Dame is a great church which was originally built in the late 13th century and its tower was added in the late 14th or early 15th century. Like the town hall it is one of the city's most prominent landmarks. It was arguably the only church in the English perpendicular style in France. Much of the current 1400 capacity church dates to 1631–1635. It contains elements of Flemish, Gothic, Anglo-Norman and Tudor architecture. In 1691, an 1800 cubic metre cistern was added to the church under orders by Vauban. The church is dedicated to the Virgin, and built in the form of a cross, consisting of a nave and four aisles— The old grand altar dated to 1628 and was built from Carrara marble wrecked on the coast, during its transit from Genoa to Antwerp. It contained eighteen figures, the two standing on either side of the altar-piece—representing St. Louis and Charlemagne. The organ—of a deep and mellow tone, and highly ornamented by figures in relief—was built at Canterbury sometime around 1700. The pulpit and reading-desk, richly sculptured in oak, is another well-executed piece of ecclesiastical workmanship from Saint-Omer, St. Omer. The altar-piece, the Assumption, was often attributed to Anthony van Dyck, though in reality it is by Gerard Seghers; whilst the painting over the side altar, once believed to be by Peter Paul Rubens is in fact by Pieter Van Mol. A high and strongly built wall, partaking more of the fortress than a cathedral in its aspect, flanks the building, and protects it from the street where formerly ran the old river, in its course through Calais to the sea.
The square, massive Norman tower has three-arched belfry windows on each face, surmounted by corner turrets, and a conically shaped tower of octagonal proportions, topped again by a short steeple. The tower was a main viewing point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) which linked the Paris Observatory with the Royal Greenwich Observatory using trigonometry. Cross-channel sightings were made of signal lights at Dover Castle and Fairlight, East Sussex.
The church was assigned as a historic monument by decree of 10 September 1913, only to have its stained glass smashed during a Zeppelin bombardment on 15 January 1915, falling through the roof. General de Gaulle married Yvonne Vendroux on 6 April 1921 at the cathedral. The building experienced extensive damage during World War II, and was partially rebuilt, although much of the old altar and furnishings were not replaced.
Towers
 The Tour du Guet (Watch Tower), situated in Calais Nord on the Places d'Armes, is one of the few surviving pre-war buildings. Dating from 1229, when Philip I, Count of Boulogne, built the fortifications of Calais, it is one of the oldest monuments of Calais, although the oldest remaining traces date to 1302. It has a height of 35–39 metres (sources differ). An 1580 Dover Straits earthquake, earthquake in 1580 split the tower in two, and at one time it threatened to collapse completely. The tower was repaired in 1606, and then had the purpose of serving as a hall to accommodate the merchants of Calais. It was damaged in 1658 when a young stable boy set fire to it, while it was temporarily being used as royal stables during a visit of King Louis XIV. It was not repaired for some 30 years. In 1770, a bell identical to the original bell of 1348 was cast. Due to its height, from the late 17th century it became an important watchout post for the city for centuries until 1905; the last keeper of the tower was forced to leave in 1926. Abraham Chappe (a brother of Ignace Chappe) installed a telegraph office in the tower in 1816 and operated for 32 years. It was this office which announced the death of Napoleon I to the French public in 1821. It also had the dual function as lighthouse with a rotating beacon fuelled by oil from 1818. The lantern was finally replaced by a new lighthouse on 15 October 1848. During the First World War, it served as a military observation post and narrowly missed destruction during World War II. This tower has been classified as a historic monument since 6 November 1931.
The Calais Lighthouse (Le phare de Calais) was built in 1848, replacing the old watch tower as the lighthouse of the port. The tower was electrified in 1883 and automated in 1992. The staircase has 271 steps leading up to the lantern. By day it is easily distinguishable from other coastal lighthouses by its white color and black lantern. The lighthouse was classified as a historical monument on 22 November 2010.
The Tour du Guet (Watch Tower), situated in Calais Nord on the Places d'Armes, is one of the few surviving pre-war buildings. Dating from 1229, when Philip I, Count of Boulogne, built the fortifications of Calais, it is one of the oldest monuments of Calais, although the oldest remaining traces date to 1302. It has a height of 35–39 metres (sources differ). An 1580 Dover Straits earthquake, earthquake in 1580 split the tower in two, and at one time it threatened to collapse completely. The tower was repaired in 1606, and then had the purpose of serving as a hall to accommodate the merchants of Calais. It was damaged in 1658 when a young stable boy set fire to it, while it was temporarily being used as royal stables during a visit of King Louis XIV. It was not repaired for some 30 years. In 1770, a bell identical to the original bell of 1348 was cast. Due to its height, from the late 17th century it became an important watchout post for the city for centuries until 1905; the last keeper of the tower was forced to leave in 1926. Abraham Chappe (a brother of Ignace Chappe) installed a telegraph office in the tower in 1816 and operated for 32 years. It was this office which announced the death of Napoleon I to the French public in 1821. It also had the dual function as lighthouse with a rotating beacon fuelled by oil from 1818. The lantern was finally replaced by a new lighthouse on 15 October 1848. During the First World War, it served as a military observation post and narrowly missed destruction during World War II. This tower has been classified as a historic monument since 6 November 1931.
The Calais Lighthouse (Le phare de Calais) was built in 1848, replacing the old watch tower as the lighthouse of the port. The tower was electrified in 1883 and automated in 1992. The staircase has 271 steps leading up to the lantern. By day it is easily distinguishable from other coastal lighthouses by its white color and black lantern. The lighthouse was classified as a historical monument on 22 November 2010.
Forts
Museums, theatres and cultural centres
 Calais contains several museums. These include the Musée des Beaux-Arts et de la Dentelle de Calais, Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais and the Musée de la Seconde Guerre Mondiale (World War II museum). Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais is a lace and fashion museum located in an old Boulart factory on the canalside and contains workshops, a library and a restaurant and regularly puts on fashion shows. The World War II museum is located at Parc St Pierre opposite the town hall and south of the train station. The building is a former Nazi bunker and wartime military headquarters, built in 1941 by the Todt Organisation. The 194-metre-long structure contains twenty rooms with relics and photographs related to World War II, and one room dedicated to World War I.
Theatres and cultural centres include Le théâtre municipal, Le Centre Culturel Gérard Philipe, Le Conservatoire à rayonnement départemental (CRD), L'auditorium Didier Lockwood, L'École d'Art de Calais, Le Channel, Le Cinéma Alhambra and La Médiathèque municipale. Le théâtre municipal or Calais Theatre is located on the Boulevard Lafayette and was built in 1903 on a plot of land which was used as a cemetery between 1811 and 1871. The theatre opened in 1905. On the first floor of the façade are statues which represent the performing arts subjects of Poetry, Comedy, Dance and Music.
Calais contains several museums. These include the Musée des Beaux-Arts et de la Dentelle de Calais, Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais and the Musée de la Seconde Guerre Mondiale (World War II museum). Cité internationale de la Dentelle et de la Mode de Calais is a lace and fashion museum located in an old Boulart factory on the canalside and contains workshops, a library and a restaurant and regularly puts on fashion shows. The World War II museum is located at Parc St Pierre opposite the town hall and south of the train station. The building is a former Nazi bunker and wartime military headquarters, built in 1941 by the Todt Organisation. The 194-metre-long structure contains twenty rooms with relics and photographs related to World War II, and one room dedicated to World War I.
Theatres and cultural centres include Le théâtre municipal, Le Centre Culturel Gérard Philipe, Le Conservatoire à rayonnement départemental (CRD), L'auditorium Didier Lockwood, L'École d'Art de Calais, Le Channel, Le Cinéma Alhambra and La Médiathèque municipale. Le théâtre municipal or Calais Theatre is located on the Boulevard Lafayette and was built in 1903 on a plot of land which was used as a cemetery between 1811 and 1871. The theatre opened in 1905. On the first floor of the façade are statues which represent the performing arts subjects of Poetry, Comedy, Dance and Music.
Monuments and memorials

The Burghers of Calais
''The Burghers of Calais'' (french: Les Bourgeois de Calais) is a sculpture by Auguste Rodin in twelve original castings and numerous copies. It commemorates an event during the Hundred Years' War, when Calais, a French port on the English Cha ...
"), a sculpture by Auguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor, generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a uniqu ...
to commemorate six men who were to have been executed by Edward III in 1347. The cast was erected in 1895, funded by a public grant of 10,000 francs. Rodin (who based his design on a fourteenth-century account by Jean Froissart) intended to evoke the viewer's sympathy by emphasizing the pained expressions of the faces of the six men about to be executed.
The ''Monument des Sauveteurs'' ("Rescuers' Monument") was installed in 1899 on Boulevard des Alliés, and transferred to the Quartier of Courgain in 1960. It is a bronze sculpture, attributed to Edward Lormier. The ''Monument Le Pluviôse'' is a bronze monument built in 1912 by Émile Oscar Guillaume on the centre of the roundabout near the beach of Calais, commemorating the accidental sinking of the submarine ''French submarine Pluviôse (Q51), Pluviôse'' in May 1910, off the beach by the steamer ''Pas de Calais''. Armand Fallières, president of the Republic, and his government came to Calais for a state funeral for its 27 victims. One of these victims, Delpierre Auguste, (1889–1910), drowned at age 21 before the beach at Calais; a dock in the city is named for him. The monument was dedicated on 22 June 1913.
Monument "Jacquard" was erected on the square in 1910, opposite the entrance to the Calais theatre. It commemorates Joseph Marie Jacquard, popular in Calais because of his contribution to the development of lace through his invention of the Jacquard loom. A tall Louis XVIII column, column in the Courgain area of the city commemorates a visit by Louis XVIII.
''Parc Richelieu'', a garden behind the war memorial, was built in 1862 on the old city ramparts and redesigned in 1956. It contains a statue designed by Yves de Coëtlogon in 1962, remembering both world wars with an allegorical figure, representing Peace, which clutches an olive branch to her breast. Another monument in the Parc Richelieu, erected on 23 April 1994, marks the approximate site of Emma, Lady Hamilton's last resting place. She died in Calais on 15 January 1815.Brayne, Martin (2016), ''Gone to the Continent: the British in Calais, 1760–1860''
Hotels and nightclubs
For many years the most famous hotel in Calais was the Hôtel d'Angleterre, often called Dessin's or Dessein's, after the family which owned it for almost a hundred years. Its popularity increased after Laurence Sterne set the early chapters of his 1768 novel ''A Sentimental Journey through France and Italy'' there. With the arrival of the railway fewer British visitors stopped in Calais and Dessin's closed in 1860. Hôtel Meurice de Calais is a hotel, established in 1771 as Le Chariot Royal by the French postmaster, Charles-Augustin Meurice, who would later establish the five-star Hôtel Meurice, one of Paris' most famous luxury hotels. It was one of the earliest hotels on the continent of Europe to specifically cater for the British elite. The hotel was rebuilt in 1954–55. It has 41 en-suite rooms. The main centre of night activity in Calais is at the Casino Le Touquet's on the Rue Royale and at the 555 Club. Every month, Casino Le Touquet hosts a dinner and dance cabaret. The casino features slot machines, blackjack, roulette, and poker facilities.Education
There are several schools in Calais. These include Groupe Scolaire Coubertin, Eglise Saint-Pierre, Universite du Littoral, Centre Universitaire, Lycée HQE Léonard de Vinci on Rue du Pasteur Martin Luther-King, École d'Art de Calais on Rue des Soupirants, and the Centre Scolaire Saint-Pierre on Rue du Four à Chaux which provides education in the primary grades, high school, and vocational school. There are at least seven colleges in the city, such as Collège Martin Luther King on Rue Martin Luther King, Collège Nationalisé Lucien Vadez on Avenue Yervant Toumaniantz, Collège Les Dentelliers on Rue Gaillard, College Jean Mace on Rue Maréchaux, Collège République on Place République, Collège Vauban on Rue Orléansville, and Collège Privé Mixte Jeanne d'Arc on Rue Champailler.Sport
Calais was represented in association football by the Calais RUFC, who competed in the Championnat National. The club was founded 1902 as Racing Club de Calais and in 1974 was renamed as Calais Racing Union Football Club. Calais RUFC had a good reputation in French cup competitions and went as far as 2000 Coupe de France Final, the final in the 1999/2000 season, losing out finally to FC Nantes Atlantique, Nantes. Since 2008 they played at the Stade de l'Épopée, a stadium which holds about 12,000 spectators. Calais Racing Union was liquidated in September 2017. The rugby club in Calais is Amicale Rugby Calaisien. Basketball is popular in Calais with the teams Calais Basket (male) and COB Calais (female) as is volleyball with the Lis Calais (male) and Stella Calais (female) teams. There is also the SOC (sports club), SOC club which caters in a range of sports including athletics, handball and football and Yacht Club de Calais, a yachting club. Calais also has Les Seagulls, an American football team.Transport

Sea
ThePort of Calais
The Port of Calais in northern France is the fourth largest port in France and the largest for passenger traffic. It accounts for more than a third of economic activity in the town of Calais.
Background
The Port of Calais was the first cable ...
was the first cable ship port in Europe and is the fourth largest port in France and the largest for passenger traffic. The port accounts for more than a third of economic activity of the town of Calais. Cargo traffic has tripled over the past two decades. In 2007 more than 41.5 million tonnes of traffic passed through Calais with some 11.52 million passengers, 1.4 million trucks and trailers, 2.249 million cars and 4,700 crossings a year. Passenger numbers for the Dover to Calais route in 2018 were 9,168,000. On average, ships sail from the port every 30 minutes. A new 400 million euro project is underway at the port to create a breakwater protecting a pool of 700 meters long, thus allowing virtually all types of ships to stop at Calais.
Rail
As well as the large port, the town is served by three railway stations: Calais-Fréthun station, Gare de Calais-Fréthun, Gare de Calais-Ville, and Gare des Fontinettes, the former being the first stop on mainland Europe of the Eurostar line. Gare de Calais-Ville is the nearest station to the port with trains to Gare de Boulogne-Ville and either Gare de Lille Flandres or Gare de Lille Europe.Road
Local bus services are provided by STCE. Free car parking facilities are available in front of the Calais ferry terminal and the maximum stay is three days.Air
Calais is served by an airport and an airfield. Calais–Dunkerque Airport is located at Marck, east north east of Calais. Saint-Inglevert Airfield is located at Saint-Inglevert, south west of Calais.Notable people
International relations
Calais is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Bardejov, Slovakia ''(since 6 September 2002)'' * Brăila, Romania ''(since 8 May 2002)'' * Duisburg, Germany ''(since 25 June 1964)'' * Dover, Kent,United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
''(since June 1973)''
* Wismar, Germany ''(since December 1971)''
* Xiangtan, China
See also
* Communes of the Pas-de-Calais department * France–UK borderReferences
Notes
Bibliography
* ''This article incorporates public domain text from the 1911 edition of the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' and Robert Bell Calton's ''Annals and Legends of Calais'' (1852)''. ;Books * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Agglomération
Info about the port and city
Info about the port and city
{{Authority control Calais, Ephemeral islands Communes of Pas-de-Calais Former islands of France France–United Kingdom border crossings Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast Port cities and towns of the North Sea Pale of Calais Vauban fortifications in France