Biological Crop Protection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation,
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation,


 Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation,
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs.
There are three basic strategies for biological pest control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment.
Natural enemies of insect pests, also known as biological control agents, include predators, parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable str ...
s, pathogens, and competitors. Biological control agents of plant diseases are most often referred to as antagonists. Biological control agents of weeds include seed predators, herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s, and plant pathogens.
Biological control can have side-effects on biodiversity through attacks on non-target species by any of the above mechanisms, especially when a species is introduced without a thorough understanding of the possible consequences.
History
The term "biological control" was first used byHarry Scott Smith
Harry Scott Smith (November 29, 1883 – November 28, 1957), an entomologist and professor at University of California, Riverside (UCR), was a pioneer in the field of biological pest control.
United States Department of Agriculture
Smith gre ...
at the 1919 meeting of the Pacific Slope Branch of the American Association of Economic Entomologists, in Riverside, California. It was brought into more widespread use by the entomologist Paul H. DeBach (1914–1993) who worked on citrus crop pests throughout his life. However, the practice has previously been used for centuries. The first report of the use of an insect species to control an insect pest comes from " Nanfang Caomu Zhuang" (南方草木狀 ''Plants of the Southern Regions'') (), attributed to Western Jin dynasty botanist ''Ji Han'' (嵇含, 263–307), in which it is mentioned that "'' Jiaozhi people sell ants and their nests attached to twigs looking like thin cotton envelopes, the reddish-yellow ant being larger than normal. Without such ants, southern citrus fruits will be severely insect-damaged''". The ants used are known as ''huang gan'' (''huang'' = yellow, ''gan'' = citrus) ants ('' Oecophylla smaragdina''). The practice was later reported by Ling Biao Lu Yi (late Tang Dynasty or Early Five Dynasties), in ''Ji Le Pian'' by ''Zhuang Jisu'' (Southern Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
), in the ''Book of Tree Planting'' by Yu Zhen Mu ( Ming Dynasty), in the book ''Guangdong Xing Yu'' (17th century), ''Lingnan'' by Wu Zhen Fang (Qing Dynasty), in ''Nanyue Miscellanies'' by Li Diao Yuan, and others.
Biological control techniques as we know them today started to emerge in the 1870s. During this decade, in the US, the Missouri State Entomologist C. V. Riley and the Illinois State Entomologist W. LeBaron began within-state redistribution of parasitoids to control crop pests. The first international shipment of an insect as a biological control agent was made by Charles V. Riley in 1873, shipping to France the predatory mites ''Tyroglyphus phylloxera'' to help fight the grapevine phylloxera ( ''Daktulosphaira vitifoliae'') that was destroying grapevines in France. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) initiated research in classical biological control following the establishment of the Division of Entomology in 1881, with C. V. Riley as Chief. The first importation of a parasitoidal wasp into the United States was that of the braconid '' Cotesia glomerata'' in 1883–1884, imported from Europe to control the invasive cabbage white butterfly, '' Pieris rapae''. In 1888–1889 the vedalia beetle, ''Rodolia cardinalis
''Novius cardinalis'' (common names vedalia beetle or cardinal ladybird) is a species of ladybird beetle native to Australia. It was formerly placed in the genus ''Rodolia'', but that genus was synonymized under the genus '' Novius'' in 2020.Pan ...
'', a lady beetle, was introduced from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
to California to control the cottony cushion scale, '' Icerya purchasi''. This had become a major problem for the newly developed citrus industry in California, but by the end of 1889, the cottony cushion scale population had already declined. This great success led to further introductions of beneficial insects into the US.Coulson, J. R.; Vail, P. V.; Dix M.E.; Nordlund, D.A.; Kauffman, W.C.; Eds. 2000. 110 years of biological control research and development in the United States Department of Agriculture: 1883–1993. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. pages=3–11
In 1905 the USDA initiated its first large-scale biological control program, sending entomologists to Europe and Japan to look for natural enemies of the spongy moth, '' Lymantria dispar dispar'', and the brown-tail moth, ''Euproctis chrysorrhoea'', invasive pests of trees and shrubs. As a result, nine parasitoids (solitary wasps) of the spongy moth, seven of the brown-tail moth, and two predators of both moths became established in the US. Although the spongy moth was not fully controlled by these natural enemies, the frequency, duration, and severity of its outbreaks were reduced and the program was regarded as successful. This program also led to the development of many concepts, principles, and procedures for the implementation of biological control programs.

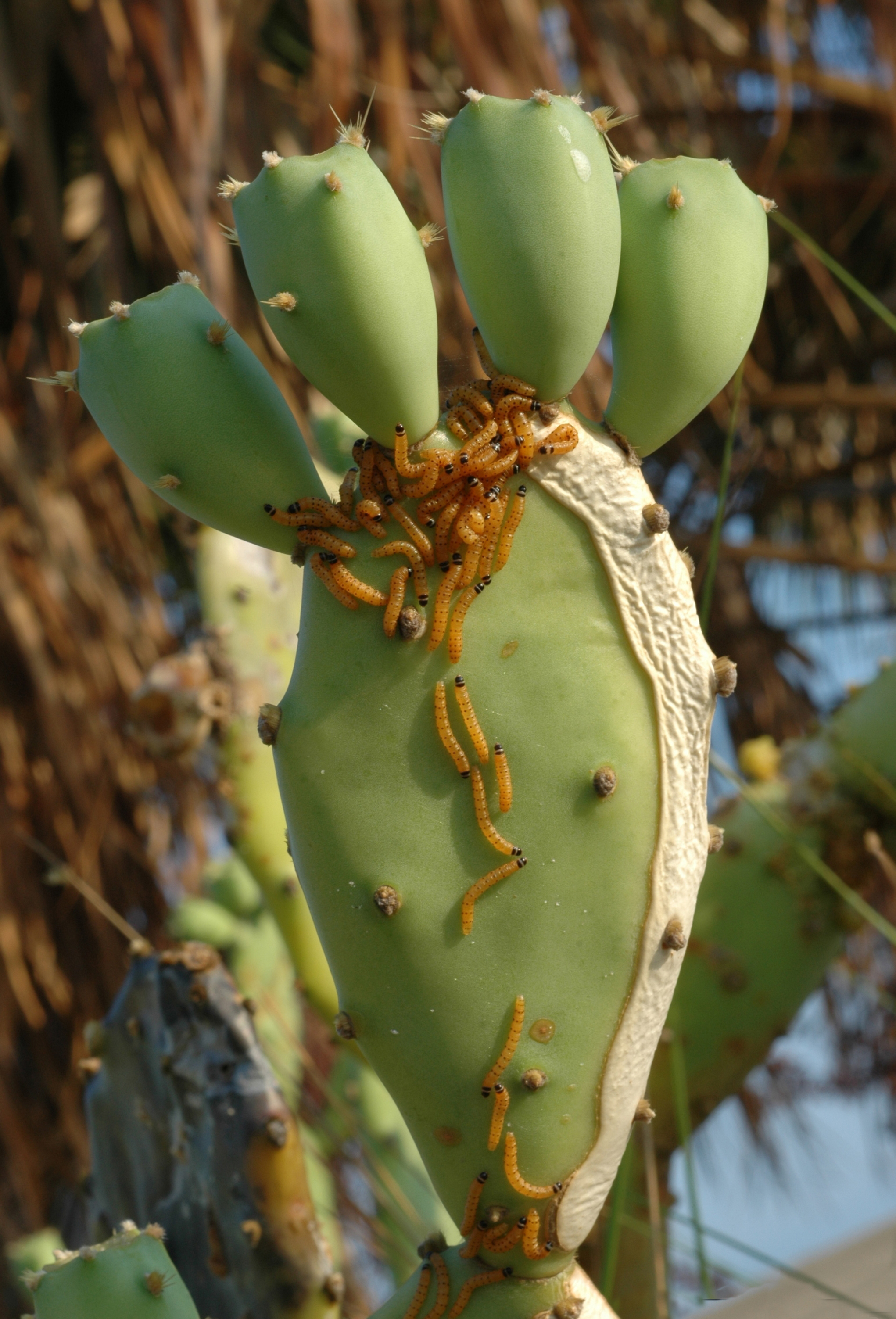
Prickly pear cacti
''Opuntia'', commonly called prickly pear or pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Prickly pears are also known as ''tuna'' (fruit), ''sabra'', ''nopal'' (paddle, plural ''nopales'') from the Nahuatl word f ...
were introduced into Queensland, Australia as ornamental plants, starting in 1788. They quickly spread to cover over 25 million hectares of Australia by 1920, increasing by 1 million hectares per year. Digging, burning, and crushing all proved ineffective. Two control agents were introduced to help control the spread of the plant, the cactus moth ''Cactoblastis cactorum
''Cactoblastis cactorum'', the cactus moth, South American cactus moth or nopal moth, is native to Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay and southern Brazil. It is one of five species in the genus '' Cactoblastis'' that inhabit South America, where many pa ...
'', and the scale insect '' Dactylopius''. Between 1926 and 1931, tens of millions of cactus moth eggs were distributed around Queensland with great success, and by 1932, most areas of prickly pear had been destroyed.
The first reported case of a classical biological control attempt in Canada involves the parasitoidal wasp '' Trichogramma minutum''. Individuals were caught in New York State and released in Ontario gardens in 1882 by William Saunders, a trained chemist and first Director of the Dominion Experimental Farms, for controlling the invasive currantworm ''Nematus ribesii
''Nematus ribesii'' is a species of sawfly in the family Tenthredinidae. English names include common gooseberry sawfly
Importation or classical biological control involves the introduction of a pest's natural enemies to a new locale where they do not occur naturally. Early instances were often unofficial and not based on research, and some introduced species became serious pests themselves.
To be most effective at controlling a pest, a biological control agent requires a colonizing ability which allows it to keep pace with changes to the habitat in space and time. Control is greatest if the agent has temporal persistence so that it can maintain its population even in the temporary absence of the target species, and if it is an opportunistic forager, enabling it to rapidly exploit a pest population.
One of the earliest successes was in controlling '' Icerya purchasi'' (cottony cushion scale) in Australia, using a predatory insect ''
 Augmentation involves the supplemental release of natural enemies that occur in a particular area, boosting the naturally occurring populations there. In inoculative release, small numbers of the control agents are released at intervals to allow them to reproduce, in the hope of setting up longer-term control and thus keeping the pest down to a low level, constituting prevention rather than cure. In inundative release, in contrast, large numbers are released in the hope of rapidly reducing a damaging pest population, correcting a problem that has already arisen. Augmentation can be effective, but is not guaranteed to work, and depends on the precise details of the interactions between each pest and control agent.
An example of inoculative release occurs in the horticultural production of several crops in
Augmentation involves the supplemental release of natural enemies that occur in a particular area, boosting the naturally occurring populations there. In inoculative release, small numbers of the control agents are released at intervals to allow them to reproduce, in the hope of setting up longer-term control and thus keeping the pest down to a low level, constituting prevention rather than cure. In inundative release, in contrast, large numbers are released in the hope of rapidly reducing a damaging pest population, correcting a problem that has already arisen. Augmentation can be effective, but is not guaranteed to work, and depends on the precise details of the interactions between each pest and control agent.
An example of inoculative release occurs in the horticultural production of several crops in
 Cropping systems can be modified to favor natural enemies, a practice sometimes referred to as habitat manipulation. Providing a suitable habitat, such as a
Cropping systems can be modified to favor natural enemies, a practice sometimes referred to as habitat manipulation. Providing a suitable habitat, such as a
 Predators are mainly free-living species that directly consume a large number of prey during their whole lifetime. Given that many major crop pests are insects, many of the predators used in biological control are insectivorous species. Lady beetles, and in particular their larvae which are active between May and July in the northern hemisphere, are voracious predators of aphids, and also consume
Predators are mainly free-living species that directly consume a large number of prey during their whole lifetime. Given that many major crop pests are insects, many of the predators used in biological control are insectivorous species. Lady beetles, and in particular their larvae which are active between May and July in the northern hemisphere, are voracious predators of aphids, and also consume  Several species of entomopathogenic nematode are important predators of insect and other invertebrate pests. Entomopathogenic nematodes form a stress–resistant stage known as the infective juvenile. These spread in the soil and infect suitable insect hosts. Upon entering the insect they move to the hemolymph where they recover from their stagnated state of development and release their bacterial
Several species of entomopathogenic nematode are important predators of insect and other invertebrate pests. Entomopathogenic nematodes form a stress–resistant stage known as the infective juvenile. These spread in the soil and infect suitable insect hosts. Upon entering the insect they move to the hemolymph where they recover from their stagnated state of development and release their bacterial  For rodent pests, cats are effective biological control when used in conjunction with reduction of "harborage"/hiding locations. While cats are effective at preventing rodent "population explosions", they are not effective for eliminating pre-existing severe infestations. Barn owls are also sometimes used as biological rodent control. Although there are no quantitative studies of the effectiveness of barn owls for this purpose, they are known rodent predators that can be used in addition to or instead of cats; they can be encouraged into an area with nest boxes.
In Honduras, where the mosquito '' Aedes aegypti'' was transmitting
For rodent pests, cats are effective biological control when used in conjunction with reduction of "harborage"/hiding locations. While cats are effective at preventing rodent "population explosions", they are not effective for eliminating pre-existing severe infestations. Barn owls are also sometimes used as biological rodent control. Although there are no quantitative studies of the effectiveness of barn owls for this purpose, they are known rodent predators that can be used in addition to or instead of cats; they can be encouraged into an area with nest boxes.
In Honduras, where the mosquito '' Aedes aegypti'' was transmitting
 Entomopathogenic fungi, which cause disease in insects, include at least 14 species that attack aphids. ''
Entomopathogenic fungi, which cause disease in insects, include at least 14 species that attack aphids. ''
 Vertebrate animals tend to be generalist feeders, and seldom make good biological control agents; many of the classic cases of "biocontrol gone awry" involve vertebrates. For example, the cane toad (''Rhinella marina'') was intentionally introduced to
Vertebrate animals tend to be generalist feeders, and seldom make good biological control agents; many of the classic cases of "biocontrol gone awry" involve vertebrates. For example, the cane toad (''Rhinella marina'') was intentionally introduced to
Introduction to Biological Control
. Midwest Institute for Biological Control, Illinois. * * * *
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20071123044914/http://www.biotechnologyonline.gov.au/enviro/canetoad.cfm Cane toad: a case study 2003. * Humphrey, J. and Hyatt. 2004. CSIRO Australian Animal Health Laboratory. ''Biological Control of the Cane Toad Bufo marinus in Australia'' * * Johnson, M. 2000. Nature and Scope of Biological Control. ''Biological Control of Pests''.
Association of Natural Biocontrol ProducersInternational Organization for Biological Control
{{DEFAULTSORT:Biological Pest Control American inventions Chinese inventions Insects in culture
Rodolia cardinalis
''Novius cardinalis'' (common names vedalia beetle or cardinal ladybird) is a species of ladybird beetle native to Australia. It was formerly placed in the genus ''Rodolia'', but that genus was synonymized under the genus '' Novius'' in 2020.Pan ...
'' (the vedalia beetle). This success was repeated in California using the beetle and a parasitoidal fly, ''Cryptochaetum
''Cryptochetum'' is a genus of scale parasite flies in the family Cryptochetidae. There are more than 30 described species in ''Cryptochetum''.
Species
These 35 species belong to the genus ''Cryptochetum'':
*'' C. acuticornutum'' (Yang & Yang, ...
iceryae''. Other successful cases include the control of '' Antonina graminis'' in Texas by '' Neodusmetia sangwani'' in the 1960s.
Damage from '' Hypera postica'', the alfalfa weevil, a serious introduced pest of forage, was substantially reduced by the introduction of natural enemies. 20 years after their introduction the population of weevils in the alfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as w ...
area treated for alfalfa weevil in the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
remained 75 percent down.
Alligator weed was introduced to the United States from South America. It takes root in shallow water, interfering with navigation, irrigation, and flood control. The alligator weed flea beetle and two other biological controls were released in Florida, greatly reducing the amount of land covered by the plant. Another aquatic weed, the giant salvinia ('' Salvinia molesta'') is a serious pest, covering waterways, reducing water flow and harming native species. Control with the salvinia weevil ('' Cyrtobagous salviniae'') and the salvinia stem-borer moth ('' Samea multiplicalis)'' is effective in warm climates, and in Zimbabwe, a 99% control of the weed was obtained over a two-year period.
Small commercially reared parasitoidal wasps, '' Trichogramma ostriniae'', provide limited and erratic control of the European corn borer (''Ostrinia nubilalis''), a serious pest. Careful formulations of the bacterium ''Bacillus thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflie ...
'' are more effective. The O. nubilalis integrated control releasing Tricogramma brassicae (egg parasitoiod) and later Bacillus thuringiensis subs. kurstaki (larvicidae effect) reduce pest damages as better than insecticide treatments
The population of ''Levuana iridescens
The levuana moth (''Levuana iridescens'') is an extinct species of moth in the family Zygaenidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Levuana''.
The levuana moth became a serious pest for coconut plants in 1877, in Viti Levu, Fiji. On the islan ...
'', the Levuana moth, a serious coconut pest in Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, was brought under control by a classical biological control program in the 1920s.
Augmentation
 Augmentation involves the supplemental release of natural enemies that occur in a particular area, boosting the naturally occurring populations there. In inoculative release, small numbers of the control agents are released at intervals to allow them to reproduce, in the hope of setting up longer-term control and thus keeping the pest down to a low level, constituting prevention rather than cure. In inundative release, in contrast, large numbers are released in the hope of rapidly reducing a damaging pest population, correcting a problem that has already arisen. Augmentation can be effective, but is not guaranteed to work, and depends on the precise details of the interactions between each pest and control agent.
An example of inoculative release occurs in the horticultural production of several crops in
Augmentation involves the supplemental release of natural enemies that occur in a particular area, boosting the naturally occurring populations there. In inoculative release, small numbers of the control agents are released at intervals to allow them to reproduce, in the hope of setting up longer-term control and thus keeping the pest down to a low level, constituting prevention rather than cure. In inundative release, in contrast, large numbers are released in the hope of rapidly reducing a damaging pest population, correcting a problem that has already arisen. Augmentation can be effective, but is not guaranteed to work, and depends on the precise details of the interactions between each pest and control agent.
An example of inoculative release occurs in the horticultural production of several crops in greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
s. Periodic releases of the parasitoidal wasp, '' Encarsia formosa'', are used to control greenhouse whitefly, while the predatory mite ''Phytoseiulus persimilis
''Phytoseiulus'' is a genus of mites in the Phytoseiidae family. A predatory mite, this is the mite predator most frequently used to control two-spotted spider mites in greenhouses and outdoor crops grown in mild environments. This mite was acci ...
'' is used for control of the two-spotted spider mite.
The egg parasite '' Trichogramma'' is frequently released inundatively to control harmful moths. New way for inundative releases are now introduced i.e. use of drones. Egg parasitoids are able to find the eggs of the target host by means of several cues. Kairomones were found on moth scales. Similarly, ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' and other microbial insecticides are used in large enough quantities for a rapid effect. Recommended release rates for ''Trichogramma'' in vegetable or field crops range from 5,000 to 200,000 per acre (1 to 50 per square metre) per week according to the level of pest infestation. Similarly, nematodes that kill insects (that are entomopathogenic) are released at rates of millions and even billions per acre for control of certain soil-dwelling insect pests.
Conservation
The conservation of existing natural enemies in an environment is the third method of biological pest control. Natural enemies are already adapted to the habitat and to the target pest, and their conservation can be simple and cost-effective, as when nectar-producing crop plants are grown in the borders of rice fields. These provide nectar to support parasitoids and predators of planthopper pests and have been demonstrated to be so effective (reducing pest densities by 10- or even 100-fold) that farmers sprayed 70% less insecticides and enjoyed yields boosted by 5%. Predators of aphids were similarly found to be present in tussock grasses by field boundary hedges in England, but they spread too slowly to reach the centers of fields. Control was improved by planting a meter-wide strip of tussock grasses in field centers, enabling aphid predators to overwinter there. Cropping systems can be modified to favor natural enemies, a practice sometimes referred to as habitat manipulation. Providing a suitable habitat, such as a
Cropping systems can be modified to favor natural enemies, a practice sometimes referred to as habitat manipulation. Providing a suitable habitat, such as a shelterbelt
A windbreak (shelterbelt) is a planting usually made up of one or more rows of trees or shrubs planted in such a manner as to provide shelter from the wind and to protect soil from erosion. They are commonly planted in hedgerows around the edges ...
, hedgerow
A hedge or hedgerow is a line of closely spaced shrubs and sometimes trees, planted and trained to form a barrier or to mark the boundary of an area, such as between neighbouring properties. Hedges that are used to separate a road from adjoini ...
, or beetle bank where beneficial insects such as parasitoidal wasps can live and reproduce, can help ensure the survival of populations of natural enemies. Things as simple as leaving a layer of fallen leaves or mulch in place provides a suitable food source for worms and provides a shelter for insects, in turn being a food source for such beneficial mammals as hedgehogs and shrews. Compost piles and stacks of wood can provide shelter for invertebrates and small mammals. Long grass and ponds support amphibians. Not removing dead annuals and non-hardy plants in the autumn allow insects to make use of their hollow stems during winter. In California, prune trees are sometimes planted in grape vineyards to provide an improved overwintering habitat or refuge for a key grape pest parasitoid. The providing of artificial shelters in the form of wooden caskets, boxes or flowerpots is also sometimes undertaken, particularly in gardens, to make a cropped area more attractive to natural enemies. For example, earwigs are natural predators that can be encouraged in gardens by hanging upside-down flowerpots filled with straw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
or wood wool. Green lacewings can be encouraged by using plastic bottles with an open bottom and a roll of cardboard inside. Birdhouses enable insectivorous birds to nest; the most useful birds can be attracted by choosing an opening just large enough for the desired species.
In cotton production, the replacement of broad-spectrum insecticides with selective control measures such as Bt cotton can create a more favorable environment for natural enemies of cotton pests due to reduced insecticide exposure risk. Such predators or parasitoids
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionary strategies within parasitis ...
can control pests not affected by the Bt protein. Reduced prey quality and abundance associated with increased control from Bt cotton can also indirectly decrease natural enemy populations in some cases, but the percentage of pests eaten or parasitized in Bt and non-Bt cotton are often similar.
Biological control agents
Predators
 Predators are mainly free-living species that directly consume a large number of prey during their whole lifetime. Given that many major crop pests are insects, many of the predators used in biological control are insectivorous species. Lady beetles, and in particular their larvae which are active between May and July in the northern hemisphere, are voracious predators of aphids, and also consume
Predators are mainly free-living species that directly consume a large number of prey during their whole lifetime. Given that many major crop pests are insects, many of the predators used in biological control are insectivorous species. Lady beetles, and in particular their larvae which are active between May and July in the northern hemisphere, are voracious predators of aphids, and also consume mites
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
, scale insect
Scale insects are small insects of the order Hemiptera, suborder Sternorrhyncha. Of dramatically variable appearance and extreme sexual dimorphism, they comprise the infraorder Coccomorpha which is considered a more convenient grouping than the ...
s and small caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s. The spotted lady beetle (''Coleomegilla maculata
''Coleomegilla maculata'', commonly known as the spotted lady beetle, pink spotted lady beetle or twelve-spotted lady beetle, is a large coccinellid beetle native to North America. The adults and larvae feed primarily on aphids and the species ...
'') is also able to feed on the eggs and larvae of the Colorado potato beetle (''Leptinotarsa decemlineata'').
The larvae of many hoverfly species principally feed upon aphids, one larva devouring up to 400 in its lifetime. Their effectiveness in commercial crops has not been studied.
The running crab spider '' Philodromus cespitum'' also prey heavily on aphids, and act as a biological control agent in European fruit orchards.
 Several species of entomopathogenic nematode are important predators of insect and other invertebrate pests. Entomopathogenic nematodes form a stress–resistant stage known as the infective juvenile. These spread in the soil and infect suitable insect hosts. Upon entering the insect they move to the hemolymph where they recover from their stagnated state of development and release their bacterial
Several species of entomopathogenic nematode are important predators of insect and other invertebrate pests. Entomopathogenic nematodes form a stress–resistant stage known as the infective juvenile. These spread in the soil and infect suitable insect hosts. Upon entering the insect they move to the hemolymph where they recover from their stagnated state of development and release their bacterial symbionts
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
. The bacterial symbionts reproduce and release toxins, which then kill the host insect. ''Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita
''Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita'' is a Facultative parasite, facultative parasitic nematode that can kill slugs and snails.Genena, M. A., Mostafa, F. A., Fouly, A. H., & Yousef, A. A. (2011). First record for the slug parasitic nematode, Phasmarh ...
'' is a microscopic nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
that kills slugs. Its complex life cycle includes a free-living, infective stage in the soil where it becomes associated with a pathogenic bacteria such as '' Moraxella osloensis''. The nematode enters the slug through the posterior mantle region, thereafter feeding and reproducing inside, but it is the bacteria that kill the slug. The nematode is available commercially in Europe and is applied by watering onto moist soil. Entomopathogenic nematodes have a limited shelf life because of their limited resistance to high temperature and dry conditions. The type of soil they are applied to may also limit their effectiveness.
Species used to control spider mites include the predatory mites ''Phytoseiulus persimilis
''Phytoseiulus'' is a genus of mites in the Phytoseiidae family. A predatory mite, this is the mite predator most frequently used to control two-spotted spider mites in greenhouses and outdoor crops grown in mild environments. This mite was acci ...
'', '' Neoseilus californicus,'' and ''Amblyseius
''Amblyseius'' is a large genus of predatory mites belonging to the family Phytoseiidae.de Moraes, G. J. (2005)Phytoseiidae Species Listing Biology Catalog, Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 19, 2010. Many members of this genus feed on ...
cucumeris'', the predatory midge '' Feltiella acarisuga'', and a ladybird ''Stethorus punctillum
''Stethorus punctillum'', known generally as the lesser mite destroyer or spider mite destroyer, is a species of lady beetle in the family Coccinellidae
Coccinellidae () is a widespread family of small beetles ranging in size from . They a ...
''. The bug '' Orius insidiosus'' has been successfully used against the two-spotted spider mite
''Tetranychus urticae'' ( common names include red spider mite and two-spotted spider mite) is a species of plant-feeding mite generally considered to be a pest. It is the most widely known member of the family Tetranychidae or spider mites. ...
and the western flower thrips (''Frankliniella occidentalis'').
Predators including ''Cactoblastis cactorum'' (mentioned above) can also be used to destroy invasive plant species. As another example, the poison hemlock moth (''Agonopterix alstroemeriana)'' can be used to control poison hemlock (''Conium maculatum''). During its larval stage, the moth strictly consumes its host plant, poison hemlock, and can exist at hundreds of larvae per individual host plant, destroying large swathes of the hemlock.
 For rodent pests, cats are effective biological control when used in conjunction with reduction of "harborage"/hiding locations. While cats are effective at preventing rodent "population explosions", they are not effective for eliminating pre-existing severe infestations. Barn owls are also sometimes used as biological rodent control. Although there are no quantitative studies of the effectiveness of barn owls for this purpose, they are known rodent predators that can be used in addition to or instead of cats; they can be encouraged into an area with nest boxes.
In Honduras, where the mosquito '' Aedes aegypti'' was transmitting
For rodent pests, cats are effective biological control when used in conjunction with reduction of "harborage"/hiding locations. While cats are effective at preventing rodent "population explosions", they are not effective for eliminating pre-existing severe infestations. Barn owls are also sometimes used as biological rodent control. Although there are no quantitative studies of the effectiveness of barn owls for this purpose, they are known rodent predators that can be used in addition to or instead of cats; they can be encouraged into an area with nest boxes.
In Honduras, where the mosquito '' Aedes aegypti'' was transmitting dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characterist ...
and other infectious diseases, biological control was attempted by a community action plan; copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s, baby turtles, and juvenile tilapia were added to the wells and tanks where the mosquito breeds and the mosquito larvae were eliminated.
Even amongst arthropods usually thought of as obligate predators of animals (especially other arthropods), floral
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism ...
food sources (nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists ...
and to a lesser degree pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
) are often useful adjunct sources. It had been noticed in one study that adult '' Adalia bipunctata'' (predator and common biocontrol of '' Ephestia kuehniella'') could survive on flowers but never completed its life cycle, so a meta-analysis was done to find such an overall trend in previously published data, if it existed. In some cases floral resources are outright necessary. Overall, floral resources (and an imitation, i.e. sugar water) increase longevity
The word " longevity" is sometimes used as a synonym for "life expectancy" in demography. However, the term ''longevity'' is sometimes meant to refer only to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is always d ...
and fecundity, meaning even predatory population numbers can depend on non-prey food abundance. Thus biocontrol population maintenance - and success - may depend on nearby flowers.
Parasitoids
Parasitoids lay their eggs on or in the body of an insect host, which is then used as a food for developing larvae. The host is ultimately killed. Most insectparasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable str ...
s are wasps or flies, and many have a very narrow host range. The most important groups are the ichneumonid wasps, which mainly use caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s as hosts; braconid wasps, which attack caterpillars and a wide range of other insects including aphids; chalcidoid wasps, which parasitize eggs and larvae of many insect species; and tachinid flies, which parasitize a wide range of insects including caterpillars, beetle adults and larvae, and true bugs. Parasitoids are most effective at reducing pest populations when their host organisms have limited refuges to hide from them.
Parasitoids are among the most widely used biological control agents. Commercially, there are two types of rearing systems: short-term daily output with high production of parasitoids per day, and long-term, low daily output systems. In most instances, production will need to be matched with the appropriate release dates when susceptible host species at a suitable phase of development will be available. Larger production facilities produce on a yearlong basis, whereas some facilities produce only seasonally. Rearing facilities are usually a significant distance from where the agents are to be used in the field, and transporting the parasitoids from the point of production to the point of use can pose problems. Shipping conditions can be too hot, and even vibrations from planes or trucks can adversely affect parasitoids.
'' Encarsia formosa'' is a small parasitoid wasp attacking whiteflies, sap-feeding insects which can cause wilting and black sooty moulds in glasshouse vegetable and ornamental crops. It is most effective when dealing with low level infestations, giving protection over a long period of time. The wasp lays its eggs in young whitefly 'scales', turning them black as the parasite larvae pupate. '' Gonatocerus ashmeadi'' (Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order (biology), order of insects, comprising the sawfly, sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are Par ...
: Mymaridae) has been introduced to control the glassy-winged sharpshooter
The glassy-winged sharpshooter (''Homalodisca vitripennis'', formerly known as ''H. coagulata'') is a large leafhopper (family Cicadellidae), similar to other species of sharpshooter.
Description
These sharpshooters are about in length. Thei ...
''Homalodisca vitripennis'' (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) in French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
and has successfully controlled ~95% of the pest density.
The eastern spruce budworm is an example of a destructive insect in fir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
and spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
forests. Birds are a natural form of biological control, but the ''Trichogramma minutum'', a species of parasitic wasp, has been investigated as an alternative to more controversial chemical controls.
There are a number of recent studies pursuing sustainable methods for controlling urban cockroaches using parasitic wasps. Since most cockroaches remain in the sewer system and sheltered areas which are inaccessible to insecticides, employing active-hunter wasps is a strategy to try and reduce their populations.
Pathogens
Pathogenic micro-organisms include bacteria, fungi, and viruses. They kill or debilitate their host and are relatively host-specific. Variousmicrobial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
insect diseases occur naturally, but may also be used as biological pesticides. When naturally occurring, these outbreaks are density-dependent in that they generally only occur as insect populations become denser.
The use of pathogens against aquatic weed Aquatic plant management involves the science and methodologies used to control invasive and non-invasive aquatic plant species in waterways. Methods used include spraying herbicide, biological controls, mechanical removal as well as habitat modifi ...
s was unknown until a groundbreaking 1972 proposal by Zettler and Freeman. Up to that point biocontrol of any kind had not been used against any water weeds. In their review of the possibilities, they noted the lack of interest and information thus far, and listed what was known of pests-of-pests - whether pathogens or not. They proposed that this should be relatively straightfoward to apply in the same way as other biocontrols. And indeed in the decades since, the same biocontrol methods that are routine on land have become common in the water.
Bacteria
Bacteria used for biological control infect insects via their digestive tracts, so they offer only limited options for controlling insects with sucking mouth parts such as aphids and scale insects. ''Bacillus thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflie ...
'', a soil-dwelling bacterium, is the most widely applied species of bacteria used for biological control, with at least four sub-species used against Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order (biology), order of insects that includes butterfly, butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 Family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic r ...
n ( moth, butterfly), Coleoptera
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
n (beetle) and Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
n (true fly) insect pests. The bacterium is available to organic farmers in sachets of dried spores which are mixed with water and sprayed onto vulnerable plants such as brassicas and fruit trees. Genes from ''B. thuringiensis'' have also been incorporated into transgenic crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
, making the plants express some of the bacterium's toxins, which are proteins. These confer resistance to insect pests and thus reduce the necessity for pesticide use. If pests develop resistance to the toxins in these crops, ''B. thuringiensis'' will become useless in organic farming also.
The bacterium ''Paenibacillus popilliae
''Paenibacillus popilliae'' (formerly ''Bacillus popilliae'') is a soil-dwelling, Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-positive, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacterium. It is responsible for a disease (commonly called milky spore) of the white grubs of ...
'' which causes milky spore disease has been found useful in the control of Japanese beetle, killing the larvae. It is very specific to its host species and is harmless to vertebrates and other invertebrates.
'' Bacillus'' spp.,p.94-5, II. Biocontrol Modes of Action fluorescent Pseudomonads, and Streptomycete
The ''Streptomycetaceae'' are a family of ''Actinomycetota'', making up the monotypic order ''Streptomycetales''. It includes the important genus ''Streptomyces''. This was the original source of many antibiotics, namely streptomycin, the first a ...
s are controls of various fungal pathogens.p.94
Fungi
 Entomopathogenic fungi, which cause disease in insects, include at least 14 species that attack aphids. ''
Entomopathogenic fungi, which cause disease in insects, include at least 14 species that attack aphids. ''Beauveria bassiana
''Beauveria bassiana'' is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the entomopathogenic fungi. It is used as a biological ...
'' is mass-produced and used to manage a wide variety of insect pests including whiteflies, thrips, aphids and weevils. ''Lecanicillium
''Lecanicillium'' is a genus of fungi in the order Hypocreales and is described as anamorphic Cordycipitaceae; 21 species are currently described. Some of these entomopathogenic fungus species were previously widely known as ''Verticillium leca ...
'' spp. are deployed against white flies, thrips and aphids. '' Metarhizium'' spp. are used against pests including beetles, locusts
Locusts (derived from the Vulgar Latin ''locusta'', meaning grasshopper) are various species of short-horned grasshoppers in the family Acrididae that have a swarming phase. These insects are usually solitary, but under certain circumst ...
and other grasshoppers, Hemiptera
Hemiptera (; ) is an order (biology), order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, Reduviidae, assassin bugs, Cimex, bed bugs, and shield bugs. ...
, and spider mite
Spider mites are members of the Tetranychidae family, which includes about 1,200 species. They are part of the subclass Acari (mites). Spider mites generally live on the undersides of leaves of plants, where they may spin protective silk webs, a ...
s. ''Paecilomyces fumosoroseus
''Isaria fumosorosea'' is an entomopathogenic fungus, formerly known as ''Paecilomyces fumosoroseus''. It shows promise as a biological pesticide with an extensive host range.
Life cycle
When a conidium or blastospore of ''Isaria fumosorosea'' ...
'' is effective against white flies, thrips and aphids; '' Purpureocillium lilacinus'' is used against root-knot nematodes, and 89 ''Trichoderma
''Trichoderma'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts. This ...
'' species against certain plant pathogens.p.93 '' Trichoderma viride'' has been used against Dutch elm disease, and has shown some effect in suppressing silver leaf, a disease of stone fruits caused by the pathogenic fungus '' Chondrostereum purpureum''.
Pathogenic fungi may be controlled by other fungi, or bacteria or yeasts, such as: '' Gliocladium'' spp., mycoparasitic '' Pythium'' spp., binucleate
Binucleated cells are cells that contain two nuclei. This type of cell is most commonly found in cancer cells and may arise from a variety of causes. Binucleation can be easily visualized through staining and microscopy. In general, binucleati ...
types of '' Rhizoctonia'' spp., and '' Laetisaria'' spp.
The fungi ''Cordyceps
''Cordyceps'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi (sac fungi) that includes about 600 species. Most ''Cordyceps'' species are endoparasitoids, parasitic mainly on insects and other arthropods (they are thus entomopathogenic fungi); a few are parasiti ...
'' and '' Metacordyceps'' are deployed against a wide spectrum of arthropods. ''Entomophaga
''Entomophaga'' is a genus of flies in the family Tachinidae. It was reviewed by T. Tachi and H. Shima in 2006 and was found to be paraphyletic; it was also found to form a monophyletic group with '' Proceromyia''.
Species
*'' E. exoleta'' ( Me ...
'' is effective against pests such as the green peach aphid
''Myzus persicae'', known as the green peach aphid, greenfly, or the peach-potato aphid, is a small green aphid belonging to the order Hemiptera. It is the most significant aphid pest of peach trees, causing decreased growth, shrivelling of the ...
.
Several members of Chytridiomycota and Blastocladiomycota have been explored as agents of biological control. From Chytridiomycota, '' Synchytrium solstitiale'' is being considered as a control agent of the yellow star thistle
''Centaurea solstitialis'', the yellow star-thistle, is a species of thorny plant in the genus ''Centaurea'', which is part of the family Asteraceae. A winter annual, it is native to the Mediterranean Basin region and invasive in many other ...
(''Centaurea solstitialis'') in the United States.
Viruses
Baculoviruses
''Baculoviridae'' is a family of viruses. Arthropods, among the most studied being Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera, serve as natural hosts. Currently, 85 species are placed in this family, assigned to four genera.
Baculoviruses are kno ...
are specific to individual insect host species and have been shown to be useful in biological pest control. For example, the Lymantria dispar multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus
Lymantria dispar multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus or LdMNPV is a viral infection in spongy moths (''Lymantria dispar'') that causes infected larvae to die and disintegrate. Infected larvae climb to the top of a tree and die. The larvae the ...
has been used to spray large areas of forest in North America where larvae of the spongy moth are causing serious defoliation. The moth larvae are killed by the virus they have eaten and die, the disintegrating cadavers leaving virus particles on the foliage to infect other larvae.
A mammalian virus, the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus was introduced to Australia to attempt to control the European rabbit populations there. It escaped from quarantine and spread across the country, killing large numbers of rabbits. Very young animals survived, passing immunity to their offspring in due course and eventually producing a virus-resistant population. Introduction into New Zealand in the 1990s was similarly successful at first, but a decade later, immunity had developed and populations had returned to pre-RHD levels.
RNA mycovirus
Mycoviruses (Ancient Greek: μύκης ' ("fungus") + Latin '), also known as mycophages, are viruses that infect fungi. The majority of mycoviruses have double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genomes and isometric particles, but approximately 30% have po ...
es are controls of various fungal pathogens.
Oomycota
'' Lagenidium giganteum'' is a water-borne mold that parasitizes the larval stage of mosquitoes. When applied to water, the motile spores avoid unsuitable host species and search out suitable mosquito larval hosts. This mold has the advantages of a dormant phase, resistant to desiccation, with slow-release characteristics over several years. Unfortunately, it is susceptible to many chemicals used in mosquito abatement programmes.Competitors
Thelegume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock f ...
vine ''Mucuna pruriens
''Mucuna pruriens'' is a tropical legume native to Africa and tropical Asia and widely naturalized and cultivated. Its English common names include monkey tamarind, velvet bean, Bengal velvet bean, Florida velvet bean, Mauritius velvet bean, Yo ...
'' is used in the countries of Benin and Vietnam as a biological control for problematic '' Imperata cylindrica'' grass: the vine is extremely vigorous and suppresses neighbouring plants by out-competing them for space and light. ''Mucuna pruriens'' is said not to be invasive outside its cultivated area. '' Desmodium uncinatum'' can be used in push-pull farming to stop the parasitic plant, witchweed ('' Striga'').
The Australian bush fly, ''Musca vetustissima
''Musca vetustissima'', commonly known as the Australian bush fly, is a species of fly found in Australia. It is the specific fly that has given rise to the expression " Aussie salute".
Description
The Australian bush fly is a dung fly that ...
'', is a major nuisance pest in Australia, but native decomposers found in Australia are not adapted to feeding on cow dung, which is where bush flies breed. Therefore, the Australian Dung Beetle Project
The Australian Dung Beetle Project (1965–1985), conceived and led by Dr George Bornemissza of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), was an international scientific research and biological control project with ...
(1965–1985), led by George Bornemissza of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, released forty-nine species of dung beetle, to reduce the amount of dung and therefore also the potential breeding sites of the fly.
Combined use of parasitoids and pathogens
In cases of massive and severe infection of invasive pests, techniques of pest control are often used in combination. An example is the emerald ash borer, ''Agrilus planipennis
The emerald ash borer (''Agrilus planipennis''), also known by the acronym EAB, is a green buprestid or jewel beetle native to north-eastern Asia that feeds on ash species. Females lay eggs in bark crevices on ash trees, and larvae feed undern ...
'', an invasive beetle from China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, which has destroyed tens of millions of ash trees in its introduced range in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. As part of the campaign against it, from 2003 American scientists and the Chinese Academy of Forestry searched for its natural enemies in the wild, leading to the discovery of several parasitoid wasps, namely ''Tetrastichus planipennisi'', a gregarious larval endoparasitoid, ''Oobius agrili
''Oobius agrili'' is a parasitic non-stinging wasp of family Encyrtidae which is native to North Asia. It is a parasitoid of the emerald ash borer ('' Agrilus planipennis'' Fairmaire, family Buprestidae), an invasive species which has destroye ...
'', a solitary, parthenogenic egg parasitoid, and ''Spathius agrili
''Spathius agrili'' is a parasitic non-stinging wasp of family Braconidae which is native to North Asia. It is a parasitoid of the emerald ash borer (''Agrilus planipennis'' Fairmaire), an invasive species which has destroyed tens of millions of ...
'', a gregarious larval ectoparasitoid. These have been introduced and released into the United States of America as a possible biological control of the emerald ash borer. Initial results for ''Tetrastichus planipennisi'' have shown promise, and it is now being released along with ''Beauveria bassiana
''Beauveria bassiana'' is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the entomopathogenic fungi. It is used as a biological ...
'', a fungal pathogen with known insecticidal properties.
Target pests
Fungal pests
'' Botrytis cinerea'' on lettuce, by '' Fusarium'' spp. and '' Penicillium claviforme'', on grape andstrawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
by ''Trichoderma
''Trichoderma'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts. This ...
'' spp., on strawberry by '' Cladosporium herbarum'', on Chinese cabbage by '' Bacillus brevis'', and on various other crops by various yeasts and bacteria. '' Sclerotinia sclerotiorum'' by several fungal biocontrols. Fungal pod infection of snap bean by '' Trichoderma hamatum'' if before or concurrent with infection.p.93-4 '' Cryphonectria parasitica'', ''Gaeumannomyces graminis
''Gaeumannomyces graminis'' var. ''graminis'' is a plant pathogen. This fungal pathogen produces extensive damage on the sheath of rice, causing black spots which protrude from the infected. This pathogen also generates a discoloration in the fol ...
'', '' Sclerotinia'' spp., and '' Ophiostoma novo-ulmi'' by viruses. Various powdery mildews and rusts by various '' Bacillus'' spp. and fluorescent Pseudomonads. '' Colletotrichum orbiculare'' will suppress further infection by itself if manipulated to produce plant-induced systemic resistance by infected the lowest leaf.p.95-6
Difficulties
Many of the most important pests are exotic, invasive species that severely impact agriculture, horticulture, forestry, and urban environments. They tend to arrive without their co-evolved parasites, pathogens and predators, and by escaping from these, populations may soar. Importing the natural enemies of these pests may seem a logical move but this may have unintended consequences; regulations may be ineffective and there may be unanticipated effects on biodiversity, and the adoption of the techniques may prove challenging because of a lack of knowledge among farmers and growers.Side effects
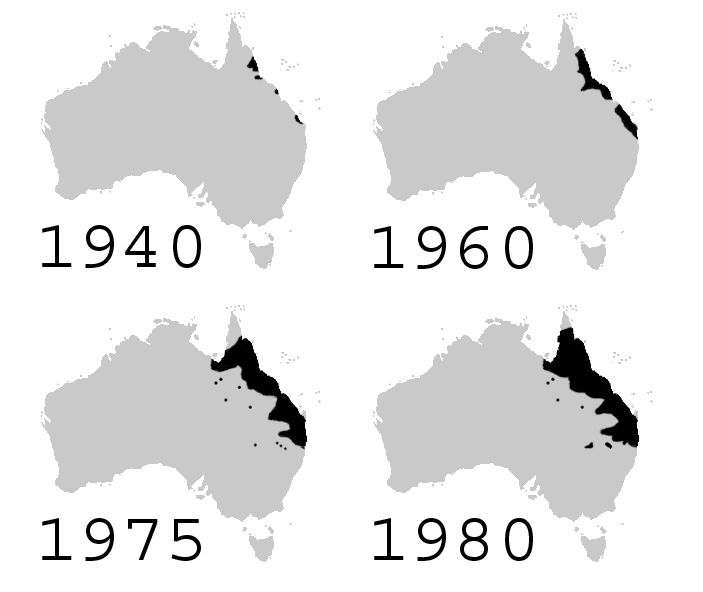
Biological control can affect biodiversity through predation, parasitism, pathogenicity, competition, or other attacks on non-target species. An introduced control does not always target only the intended pest species; it can also target native species. In Hawaii during the 1940s parasitic wasps were introduced to control a lepidopteran pest and the wasps are still found there today. This may have a negative impact on the native ecosystem; however, host range and impacts need to be studied before declaring their impact on the environment. Vertebrate animals tend to be generalist feeders, and seldom make good biological control agents; many of the classic cases of "biocontrol gone awry" involve vertebrates. For example, the cane toad (''Rhinella marina'') was intentionally introduced to
Vertebrate animals tend to be generalist feeders, and seldom make good biological control agents; many of the classic cases of "biocontrol gone awry" involve vertebrates. For example, the cane toad (''Rhinella marina'') was intentionally introduced to Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
to control the greyback cane beetle (''Dermolepida albohirtum''), and other pests of sugar cane. 102 toads were obtained from Hawaii and bred in captivity to increase their numbers until they were released into the sugar cane fields of the tropic north in 1935. It was later discovered that the toads could not jump very high and so were unable to eat the cane beetles which stayed on the upper stalks of the cane plants. However, the toad thrived by feeding on other insects and soon spread very rapidly; it took over native amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
habitat and brought foreign disease to native toads and frogs, dramatically reducing their populations. Also, when it is threatened or handled, the cane toad releases poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
from parotoid glands on its shoulders; native Australian species such as goannas, tiger snakes, dingo
The dingo (''Canis familiaris'', ''Canis familiaris dingo'', ''Canis dingo'', or ''Canis lupus dingo'') is an ancient (Basal (phylogenetics), basal) lineage of dog found in Australia (continent), Australia. Its taxonomic classification is de ...
s and northern quolls that attempted to eat the toad were harmed or killed. However, there has been some recent evidence that native predators are adapting, both physiologically and through changing their behaviour, so in the long run, their populations may recover.
'' Rhinocyllus conicus'', a seed-feeding weevil, was introduced to North America to control exotic musk thistle
''Carduus nutans'', with the common names musk thistle, nodding thistle, and nodding plumeless thistle, is a biennial plant in the daisy and sunflower family Asteraceae. It is native to regions of Eurasia.
Description
''Carduus nutans'' is usua ...
(''Carduus nutans'') and Canadian thistle (''Cirsium arvense''). However, the weevil also attacks native thistles, harming such species as the endemic Platte thistle (''Cirsium neomexicanum'') by selecting larger plants (which reduced the gene pool), reducing seed production and ultimately threatening the species' survival. Similarly, the weevil '' Larinus planus'' was also used to try to control the Canadian thistle, but it damaged other thistles as well. This included one species classified as threatened.
The small Asian mongoose Small Asian mongoose is a common name applied to two mammals which were formerly considered to be a single species:
*Javan mongoose
*Small Indian mongoose
The small Indian mongoose (''Urva auropunctata'') is a mongoose species native to Iraq and ...
(''Herpestus javanicus'') was introduced to Hawaii in order to control the rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
population. However, the mongoose was diurnal, and the rats emerged at night; the mongoose, therefore, preyed on the endemic birds of Hawaii, especially their eggs, more often than it ate the rats, and now both rats and mongooses threaten the birds. This introduction was undertaken without understanding the consequences of such an action. No regulations existed at the time, and more careful evaluation should prevent such releases now.
The sturdy and prolific eastern mosquitofish (''Gambusia holbrooki'') is a native of the southeastern United States and was introduced around the world in the 1930s and '40s to feed on mosquito larvae and thus combat malaria. However, it has thrived at the expense of local species, causing a decline of endemic fish and frogs through competition for food resources, as well as through eating their eggs and larvae. In Australia, control of the mosquitofish is the subject of discussion; in 1989 researchers A. H. Arthington and L. L. Lloyd stated that "biological population control is well beyond present capabilities".
Grower education
A potential obstacle to the adoption of biological pest control measures is that growers may prefer to stay with the familiar use of pesticides. However, pesticides have undesired effects, including the development of resistance among pests, and the destruction of natural enemies; these may in turn enable outbreaks of pests of other species than the ones originally targeted, and on crops at a distance from those treated with pesticides. One method of increasing grower adoption of biocontrol methods involves letting them learn by doing, for example showing them simple field experiments, enabling them to observe the live predation of pests, or demonstrations of parasitised pests. In the Philippines, early-season sprays against leaf folder caterpillars were common practice, but growers were asked to follow a 'rule of thumb' of not spraying against leaf folders for the first 30 days after transplanting; participation in this resulted in a reduction of insecticide use by 1/3 and a change in grower perception of insecticide use.Related techniques
Related to biological pest control is the technique of introducing sterile individuals into the native population of some organism. This technique is widely practised with insects: a large number of males sterilized byradiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
are released into the environment, which proceed to compete with the native males for females. Those females that copulate with the sterile males will lay infertile eggs, resulting in a decrease in the size of the population. Over time, with repeated introductions of sterile males, this could result in a significant decrease in the size of the organism's population. A similar technique has recently been applied to weeds using irradiated pollen, resulting in deformed seeds that do not sprout.
See also
* Beneficial insects *Biological control of gorse in New Zealand
Biological control programs for gorse in New Zealand have existed since the introduction of the gorse seed weevil (''Exapion ulicis'') in 1928. Biological pest control is the use of natural mechanisms such as predation to limit the growth and preva ...
* Chitosan
* Companion planting
* Insectary plants
Insectary plants are those that attract insects. As such, beneficial insectary plants are intentionally introduced into an ecosystem to increase pollen and nectar resources required by the natural enemies of the harmful or unwanted insects pest ( ...
* International Organization for Biological Control
The International Organization for Biological and Integrated Control (IOBC), is an organization, affiliated with the International Union of Biological Sciences (IUBS), organised to promote and study biological pest control, integrated pest manage ...
* Inundative application
Inundative application of a biological control or natural enemy of a pest refers to the release of overwhelming numbers of a mass-produced biological control agent in the expectation of either achieving a rapid reduction of a pest (animal), pest ...
* Mating disruption
Mating disruption (MD) is a pest management technique designed to control certain insect pests by introducing artificial stimuli that confuse the individuals and disrupt mate localization and/or courtship, thus preventing mating and blocking the ...
* Nematophagous fungus
* Organic gardening
Organic horticulture is the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture in soil building and conservation, pest management, and heirloom variety preserva ...
* Organic farming
* Permaculture zone 5
* Sustainable farming
Sustainable agriculture is farming in sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem se ...
* Sustainable gardening
* Zero Budget Farming
Natural farming ( 自然農法, shizen nōhō),1975 1978 re-presentation ''The One-Straw Revolution: An Introduction to Natural Farming''. also referred to as "the Fukuoka Method", "the natural way of farming" or "do-nothing farming", is an ec ...
References
* :*Chapter 6,Further reading
General
* Wiedenmann, R. (2000)Introduction to Biological Control
. Midwest Institute for Biological Control, Illinois. * * * *
Effects on native biodiversity
* * Weeden, C. R.; Shelton, A. M.; Hoffman, M. P* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20071123044914/http://www.biotechnologyonline.gov.au/enviro/canetoad.cfm Cane toad: a case study 2003. * Humphrey, J. and Hyatt. 2004. CSIRO Australian Animal Health Laboratory. ''Biological Control of the Cane Toad Bufo marinus in Australia'' * * Johnson, M. 2000. Nature and Scope of Biological Control. ''Biological Control of Pests''.
Economic effects
* *External links
Association of Natural Biocontrol Producers
{{DEFAULTSORT:Biological Pest Control American inventions Chinese inventions Insects in culture