Bharat Broadband Network Limited on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
BharatNet, also known as Bharat Broadband Network Limited, is a central public sector undertaking, set up by the Department of Telecommunications, a department under
/ref> which is built under the Make in India initiative with no involvement of foreign companies. It is both an enabler and a beneficiary of other key government schemes, such as Digital India, Make in India, the
STL
etc. BharatNet collaborated with other government entities such as C-DOT,
Economic Times, 17 November 2017. As per study by th
ICRIER
every 10% increase in the usage of internet in India will add leading to a 3.3% increase in GDP of India, a number that will go up after the completion of Phase-II in March 2019. By the end of BharatNet Phase-II in March 2019, the total current fibre optical network will grow by 100% to 10 million kilometres. This 100% increment in the fibre optic network would result in several hundred percent increment in the internet usage when in addition to 625,000 villages (each with minimum 100 Mbit/s), 2,500,000 government institutions and 5,000,000 households will also be connected to the BharatNet broadband by the time it is completed."422.2M Internet connections in India; Maharashtra (excluding Mumbai) had highest broadband connections."MediaNama.Com
July 2017.
To put the potential gains things in perspective, during the early phase of the project in 2018, India had a population of 1.3 billion people (1.36 billion in 2021), 1.23 billion Aadhaar digital biometric identities, 1.21 billion mobile phones, 446 million smartphones, 560 million internet users (800 million in 2021), 35% internet penetration (57% in 2021), and 51% growth in e-commerce.Govt will soon make Aadhaar-driving licence linking mandatory: Ravi Shankar Prasad
Indian Express, 7 Jan 2019. BharatNet has stated goal of 100 Mbit/s internet speed, and in Q1 2020 India ranked 3rd with 15.34 Mbit/s wireless/mobile internet speed and 70th with 55.76 Mbit/s fixed broadband speed (also see countries by Internet connection speed). BharatNet will expedite broadband and smartphone penetration and speed and their multiplier impact on the economy.
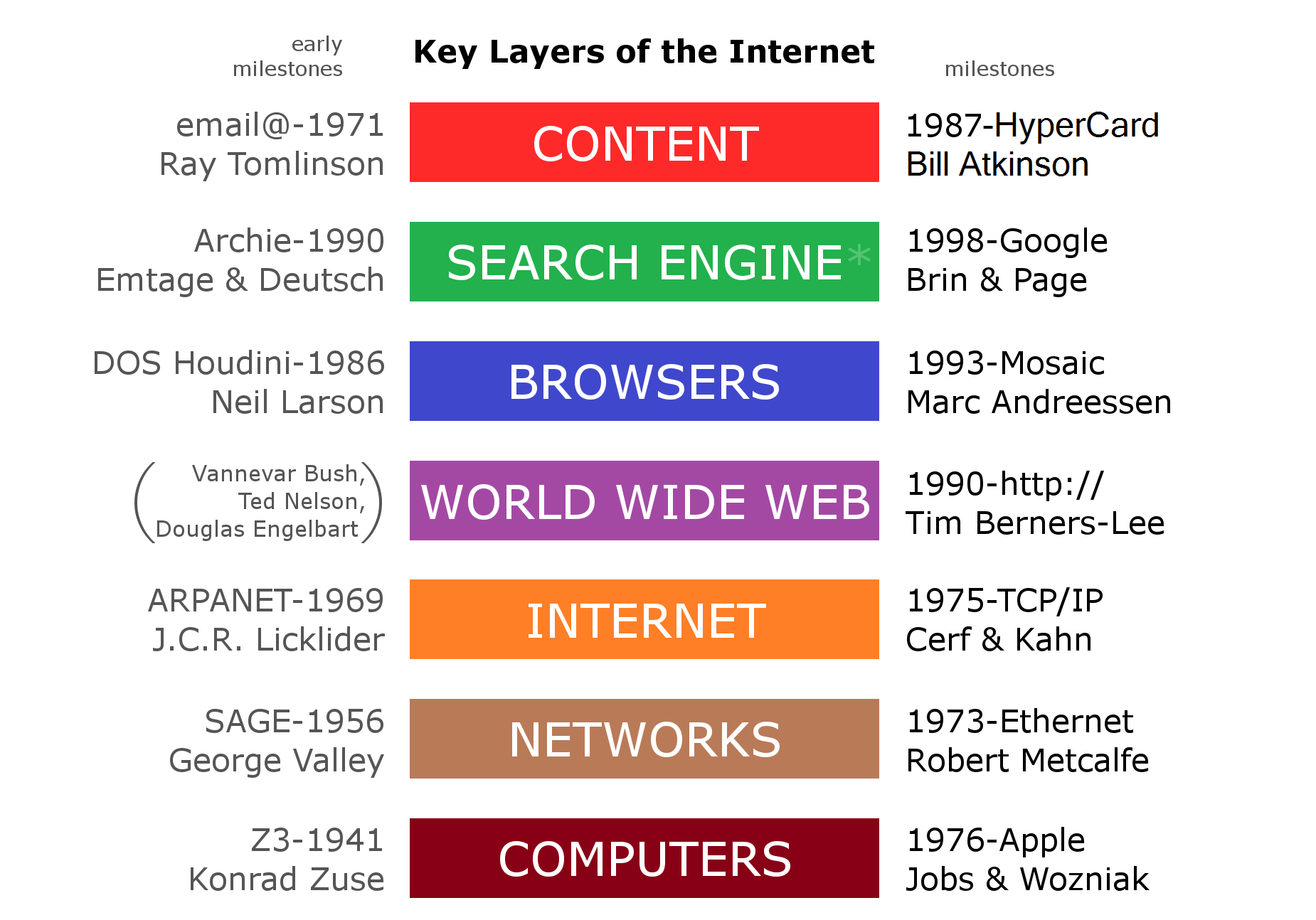 BharatNet is the "internet" layer in the "Internet Key Layers" diagram and it is
BharatNet is the "internet" layer in the "Internet Key Layers" diagram and it is
concept diagram
are as follows.
Passive optical network network architecture brings fibre cabling and digital signals to the homes, using the point-to-multipoint communication design that enables a single optical fibre to serve multiple premises. Design based on the
OLT device installed at each
The connectivity from OLT at Subdistrict-Block-level to each
The beam splitter (downstream; upstream is called the "combiner") is an optical device that splits a beam of light in two, thus providing the ability to connect multiple gram panchayats along the way to the single optical fibre cable. Use of the "passive" (unpowered) fibre optic splitter reduces the operational cost of equipment compared to the point-to-point technology (Wi-Fi, requires power). #
ONT, also called ONU, are the devices that transmit signals to the customer premises (each gram panchayat in this case) using fibre optic technology in a fibre-to-the-premises system. BharatNet will sign contracts with
Each gram panchayat is connected by the low-maintenance fibre optic technology, and each village under the gram panchayat is connected by a Wi-Fi hotspot tower of up to 15-meter height with a range of 5 to 7 km installed by ISP telecom companies by using short-range 5.48 GHz unused radiofrequency. Comparatively easier and faster to deploy higher-maintenance wireless technology, for Wi-Fi Hotspots in each village under the gram panchayat, is used only for the last mile connectivity. Wi-Fi router and
The Local service providers provide broadband connections to individual homes, offering employment and entrepreneurship opportunities to village youth. Once all the gram panchayats have been connected by the dedicated fibre optical network, the last mile connectivity to all villages will be provided by the commercial telecom operators by expanding the current national network of 38,000 Wi-Fi hotspots to 700,000 Wi-Fi hotspots to cover all 625,000 villages in India. , union government subsidy support will be given to the telecom service operators for rolling out Wi-Fi hotspots in commercially non-viable villages. BharatNet has offered the bulk broadband bandwidth at 75% discounted rates to the commercial telecom operators so that they can offer deeply discounted monetised competitive deals to the rural wireless broadband customers. Commercial operators Reliance Jio,
Economic Times, 14 November 2017."What is BharatNet project and why it's a big boost for PM Narendra Modi's Digital India dream?."
Economic Times, 7 Jan 2018. HRD ministry has instructed 50,000 colleges and technical in India to offer free Wi-Fi to students and staff with capped free data quota, after which data will have to be purchased. Out of these Reliance Jio has offered to deploy free Wi-Fi connectivity to 38,000 colleges, which has been supported by Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) and the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).HRD ministry asks colleges to provide free Wi-Fi on campus
Economic Times, 16 Jan 2018.
Money Control, 20 July 2021.
/ref> 13 states and UTs in this phase were:
The Tribune, 13 Jan 2018. To provide the last mile connectivity for the 100,000-gram panchayats in Phase-I, contracts were signed to connect 30,500 village panchayats by Vodafone, 30,000 village panchayats by Reliance Jio. 2,000 by Vodafone and 1,000 by Idea Cellular, these Wi-Fi hotspots were activated after connecting BharatNet fibre optics OLT to commercial operator's cell phone base stations.
Latest weekly update
Business Standard, 16 Jan 2018.
Official live current overall summary status report
Official Phase-I status breakdown by statePhase-II Planning
Collection of Scripts to analyse the district wise data of the progress.
{{Telecommunication companies of India Telecommunications companies of India Government-owned companies of India Proposed infrastructure in India
Ministry of Communications
A Communications Ministry or Department of Communications is a ministry or other government agency charged with communication. Communications responsibilities includes regulating telecommunications, postal services, broadcasting and print media. T ...
of the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, c ...
for the establishment, management, and operation of the National Optical Fibre Network to provide a minimum of 100 Mbit/s broadband
In telecommunications, broadband is wide bandwidth data transmission which transports multiple signals at a wide range of frequencies and Internet traffic types, that enables messages to be sent simultaneously, used in fast internet connections. ...
connectivity to all 250,000-gram panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bod ...
s in the country, covering nearly 625,000 villages, by improving the middle layer of nation-wide broadband internet in India to achieve the goal of Digital India
Digital India is a campaign launched by the Government of India in order to ensure that the Government's services are made available to citizens electronically by improved online infrastructure and by increasing Internet connectivity or making ...
."Only 'Made in India' equipment for BharatNet: Govt."The Hindu
''The Hindu'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper owned by The Hindu Group, headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It began as a weekly in 1878 and became a daily in 1889. It is one of the Indian newspapers of record and the secon ...
, 12 November 2017."Govt to launch second phase of BharatNet, to connect 1.5 lakh panchayats with internet."The News Minute
''The News Minute'' is an Indian digital news platform based in Bangalore, Karnataka. It was founded by Dhanya Rajendran, Chitra Subramaniam and Vignesh Vellore in 2014. Apart from Karnataka, it also has bureaus in the states of Telangana, And ...
, 13 November 2017.
BharatNet Phase-I, connecting 100,000 village councils covering 300,000 villages, was completed by December 2017. BharatNet Phase-II will be completed by 31 March 2023 to connect the remaining 150,000 village councils covering 325,000 villages in 16 states (July 2021 update). The last mile
Last mile may refer to:
* Last mile (telecommunications), the final leg of the telecommunications networks that deliver services to retail end-users
* Last mile (transportation), the final leg the movement of people and goods from a transportation ...
connectivity, with a total of 700,000 Wi-Fi hotspots to cover all 625,000 villages of India by adding 2 to 5 Wi-Fi hotspots per gram panchayat and a minimum of one Wi-Fi hotspot per village, have been created by connecting high-speed 4G base tower stations of commercial telecom operators to BharatNet, whereby commercially non-viable Wi-Fi hotspots will be subsidized by the union government grant of to sustain the operation.
BharatNet is the world's largest rural broadband connectivity program,BharatNet FAQ/ref> which is built under the Make in India initiative with no involvement of foreign companies. It is both an enabler and a beneficiary of other key government schemes, such as Digital India, Make in India, the
National e-Governance Plan
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) is an initiative of the Government of India to make all government services available to the citizens of India via electronic media. NeGP was formulated by the Department of Electronics and Information Techno ...
, UMANG, Bharatmala
The Bharatmala Pariyojna ( 'India garland project') is an ecosystem of road development which includes development of tunnels, bridges, elevated corridors, flyovers, overpass, interchanges, bypasses, ring roads etc. to provide shortest, jam f ...
, Sagarmala
The Sagarmala Programme () is an initiative by the Government of India to enhance the performance of the country's logistics sector. The programme envisages unlocking the potential of waterways and the coastline to minimize infrastructural inv ...
, Parvatmala, the dedicated freight corridors, industrial corridors, and UDAN-RCS.
History
Origin and slow pace of implementation (2011)
On 25 October 2011, the Government of India approved the National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) initiative, later renamed as BharatNet, to connect all 250,000 gram panchayats in the country covering nearly 625,000 villages, by utilizing the existing optical fibre network and extending it to the gram panchayats. To achieve this, Bharat Broadband Network was incorporated as a Special Purpose Vehicle(SPV) on 25 February 2012 under Companies Act of 1956. Between 2011 and 2014, project did not take off as planned, and only 350 km of optical fibre, out of 300,000 km optical fibre network needed for the Phase-I, was laid. Between 2014 and 2017, the original Phase-I target of laying 300,000 km of optical fibre was completed under the new BJP government.Implementation boost in 2014
The BharatNet project picked up pace under the Digital India initiative after Prime MinisterNarendra Modi
Narendra Damodardas Modi (; born 17 September 1950) is an Indian politician serving as the 14th and current Prime Minister of India since 2014. Modi was the Chief Minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Parliament from ...
came to power, he renamed the project as the "BharatNet", made several changes to expedite the project, significantly enhanced the BharatNet funding to several billion dollars under the Digital India
Digital India is a campaign launched by the Government of India in order to ensure that the Government's services are made available to citizens electronically by improved online infrastructure and by increasing Internet connectivity or making ...
, set ambitious time-bound implementations deadlines, appointed government public sector units (BSNL, RailTel, and PowerGrid Corp) for the swift implementation and monitoring, and to bypass the right of way
Right of way is the legal right, established by grant from a landowner or long usage (i.e. by prescription), to pass along a specific route through property belonging to another.
A similar ''right of access'' also exists on land held by a gov ...
issues for laying the optical fibre cable network the existing government-owned roads, rail lines, and power lines were used. Bangalore based United Telecoms Limited won the bid, being almost 80% lower than the second-lowest bidder ITI Limited followed by TejasSTL
etc. BharatNet collaborated with other government entities such as C-DOT,
Telecommunications Consultants India Limited
Telecommunications Consultants India Limited (TCIL) is a central public sector undertaking. It is under the ownership of the Department of Telecommunications , Ministry of Communications, Government of India. It was set up in 1978 to give con ...
and National Informatics Centre
The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is an Indian government department under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY). The NIC provides infrastructure, IT Consultancy, IT Services including but not limited to architecti ...
for the design and rollout plan of BharatNet NOFN Project. BharatNet assigned the execution work of network roll out to several other Government of India Public Sector Units, namely BSNL, RailTel
RailTel Corporation of India Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India. It provides broadband and VPN services. RailTel was formed in September 2000 with the objective of creating a nati ...
and Power Grid Corporation of India
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited is an Indian central public sector undertaking under the ownership of Ministry of Power, Government of India. It is engaged mainly in transmission of bulk power across different states of India. It is ...
. Project was rolled out as a collaboration between the Union Government (to provide broadband connectivity at sub-district Block-level), state governments (optical fibre to gram panchayat level) and private sector companies (Wi-Fi hotspots in each village and connections to the individual homes). Union government total share is , the rest will be funded by the respective state governments.
Implementation partners
There are 36states and union territories of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
, including 28 states and 9 UTs. BSNL was awarded work for 18 of these, RailTel received work in 8 and Power Grid Corporation of India in 5. BSNL was awarded work for 18+ states and UTs, namely Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
, Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which al ...
, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
, Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
, Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siligur ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
(divided into two projects, UP East and UP West), Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
and West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
. RailTel was awarded work for 8+ states and UTs, namely Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares int ...
, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
, Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanm ...
, Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo people, Mizo", the endonym, self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo ...
, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of As ...
, Puducherry and Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east a ...
. Power Grid Corporation of India was awarded work for 5 states, namely Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . It ...
, Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
and Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
. Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
is included with Phase-I BSNL work for Haryana. Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
is also included with Phase-I BSNL work for Maharastra. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu are included with Phase-II work for RailTel. Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east a ...
is likely included with Phase-II RailTel work for the Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
.
Project features
Benefits
BharatNet will provide more employment opportunities, improved service delivery (online e-gram panchayat services, e-governance, e-education, e-health, e-medicine, e-grievances, e-agriculture, e-citizen, etc.), and an impetus to the Make in India,Digital India
Digital India is a campaign launched by the Government of India in order to ensure that the Government's services are made available to citizens electronically by improved online infrastructure and by increasing Internet connectivity or making ...
and Startup India
Startup India is an initiative of the Government of India. The campaign was first announced by Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi during his speech on 15 August 2015.
The action plan of this initiative is focussing on three areas:
# Simplif ...
initiatives. According to Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is an American multinational investment management and financial services company headquartered at 1585 Broadway in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. With offices in more than 41 countries and more than 75,000 employees, the fir ...
's research, of India's 33% internet penetration in November 2017 only 15% and 2% of total internet users use online shopping and retail shopping respectively, estimated to go up to 78% penetration, 62% online shoppers and 15% online retail shopper respectively by 2027."."Economic Times, 17 November 2017. As per study by th
ICRIER
every 10% increase in the usage of internet in India will add leading to a 3.3% increase in GDP of India, a number that will go up after the completion of Phase-II in March 2019. By the end of BharatNet Phase-II in March 2019, the total current fibre optical network will grow by 100% to 10 million kilometres. This 100% increment in the fibre optic network would result in several hundred percent increment in the internet usage when in addition to 625,000 villages (each with minimum 100 Mbit/s), 2,500,000 government institutions and 5,000,000 households will also be connected to the BharatNet broadband by the time it is completed."422.2M Internet connections in India; Maharashtra (excluding Mumbai) had highest broadband connections."
July 2017.
Indian Express, 7 Jan 2019. BharatNet has stated goal of 100 Mbit/s internet speed, and in Q1 2020 India ranked 3rd with 15.34 Mbit/s wireless/mobile internet speed and 70th with 55.76 Mbit/s fixed broadband speed (also see countries by Internet connection speed). BharatNet will expedite broadband and smartphone penetration and speed and their multiplier impact on the economy.
Funding
The government has discounted the bulk BharatNet bandwidth rates to the commercial telecom operators by 76% to enable them to offer the highly discounted, affordable, competitive, and commercially viable BharatNet-enabled wireless cellular 4G broadband deals to the rural customers. The union government share of funding will come from the Universal Services Obligation Fund of the Department of Telecommunications. It will be rolled out with the additional funding by state governments to connect all gram panchayats in India.Make in India
Both theoptical fibre
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
and the Gigabit-capable passive optical network broadband
In telecommunications, broadband is wide bandwidth data transmission which transports multiple signals at a wide range of frequencies and Internet traffic types, that enables messages to be sent simultaneously, used in fast internet connections. ...
equipment, made to account for the dust and power outage issues in the rural areas, are made in India by C-DOT with no involvement of foreign companies. GPON products (see below) supplied by United Telecoms Limited (UTL) which are manufactured in India and the technology is indigenously developed by Centre for Development of Telematics
The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) is an Indian Government owned telecommunications technology development centre. It was established in 1984 with initial mandate of designing and developing digital exchanges. C-DOT has expanded to ...
(C-DOT).
Bharat Net as middle layer
 BharatNet is the "internet" layer in the "Internet Key Layers" diagram and it is
BharatNet is the "internet" layer in the "Internet Key Layers" diagram and it is designed
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ...
to provide first four layers of the OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that 'provides a common basis for the coordination of SOstandards development for the purpose of systems interconnection'. In the OSI reference model, the communications ...
, namely the physical layer, data link layer, network layer, and transport layer.
The components of the BharatNet architecture in thconcept diagram
are as follows.
National level connectivity: GPON technology
The ''"Gigabit passive optical network:'' (GPON)technology at the national level:Passive optical network network architecture brings fibre cabling and digital signals to the homes, using the point-to-multipoint communication design that enables a single optical fibre to serve multiple premises. Design based on the
ITU
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
standard G.984
G.984,
commonly known as GPON (gigabit-capable passive optical network), is a standard for passive optical networks (PON) published by the ITU-T. It is commonly used to implement the outermost link to the customer (last kilometre or last mile) o ...
and TEC spec GR no.PON-01/02 Apr 2008 provides higher bandwidth and efficiency due to the bigger variable-length network packets, allowing more efficient packaging of user traffic with segmented frame, offering higher quality of service (QoS) and low latency for delay-sensitive voice and video traffic.
A GPON brings fibre cabling and signals to the home using a point-to-multipoint scheme that enables a single optical fibre to serve multiple premises. Encryption maintains data security in this shared environment. The architecture uses passive (unpowered) optical splitters, reducing the cost of equipment compared to point-to-point architectures.http://www.bbnl.nic.in/content/page/technology.php
The GPON standard differs from other passive optical network standards in that it achieves higher bandwidth and higher efficiency using larger, variable-length packets. GPON offers efficient packaging of user traffic, with frame segmentation allowing higher quality of service (QoS) for delay-sensitive voice and video communications traffic. The main components of GPON technology are OLT
Olt or OLT may refer to:
People:
* Károly Olt (1904–1985), Hungarian politician
* Mike Olt (born 1988), American baseball player
Places:
* Olt County, a county (județ) of Romania
* Olt (river), a river in Romania
** Olt Defile, a defile that ...
, ONT/ ONU, Fiber-optic splitter
A fiber-optic splitter, also known as a beam splitter, is based on a quartz substrate of an integrated waveguide optical power distribution device, similar to a coaxial cable transmission system. The optical network system uses an optical sig ...
and Optical Fibre Cables. The ITU
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
standard G-984 series as well as TEC spec GR no.PON-01/02 Apr 2008 define the GPON technology.
C-DOT has also inked technology transfer pacts with six Indian vendors which include Indian Telephone Industries Limited (ITI Ltd), Tejas Networks
Tejas Networks is an optical, broadband and data networking products company based in India. The company designs develops and sells its products to telecom service providers, internet service providers, utilities, security and government entities i ...
, VMC, Sai Systems, UTL and SM Creative to manufacture the gear on winning the contracts.
UTL emerged as the competitive bid winner and obtained the GPON supply contract for a value of approximately Rs 1000 Cr. The companies like ITI Ltd, Tejas Networks
Tejas Networks is an optical, broadband and data networking products company based in India. The company designs develops and sells its products to telecom service providers, internet service providers, utilities, security and government entities i ...
, Sterlite, ZTE
ZTE Corporation is a Chinese partially state-owned technology company that specializes in telecommunication. Founded in 1985, ZTE is listed on both the Hong Kong and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges.
ZTE's core business is wireless, exchange, optic ...
and Larsen & Toubro lost this deal to UTL. The rollout of GPON is being carried out and it is expected that by March 2015 around 60000 villages will be connected.
Community Development Block level connectivity
#Optical line terminal {{unreferenced, date=April 2016
An optical line termination (OLT), also called an optical line terminal, is a device which serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network. It provides two main functions:
# to perform conversio ...
at subdistrict block level: OLT device installed at each
Block (district subdivision)
A block is an administrative division of some South Asian countries.
Bhutan
In Bhutan, a block is called a gewog. It is essentially for oil a group of villages. Gewogs are official administrative units of Bhutan. The country is composed of ...
will serve as the BharatNet's national-level service provider's endpoint of a passive optical network and perform a conversion between the electrical signals used by the service provider's equipment and the fibre optic signals used by the passive optical network.
Gram panchayat level level connectivity
# Optical fibre cable to each gram panchayat:The connectivity from OLT at Subdistrict-Block-level to each
gram panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bod ...
is provided by the optical fibre
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
point of presence. Optical fibre technology provides high bandwidth, low maintenance, and a scalable network but requires time to roll out the physical network. End-to-end encryption is used to ensure data security in this shared network.
# Beam splitter
A beam splitter or ''beamsplitter'' is an optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as interferometers, also finding wide ...
s and combiners: The beam splitter (downstream; upstream is called the "combiner") is an optical device that splits a beam of light in two, thus providing the ability to connect multiple gram panchayats along the way to the single optical fibre cable. Use of the "passive" (unpowered) fibre optic splitter reduces the operational cost of equipment compared to the point-to-point technology (Wi-Fi, requires power). #
Optical network terminal
upTwo simple NIDs, carrying six lines each, on the outside of a building
upA German copper phone line termination box called '' Abschlusspunkt LinienTechnik'' (APL, " Demarcation point")
In telecommunications, a network interface device (NID; ...
s at gram panchayat level: ONT, also called ONU, are the devices that transmit signals to the customer premises (each gram panchayat in this case) using fibre optic technology in a fibre-to-the-premises system. BharatNet will sign contracts with
internet service provider
An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides services for accessing, using, or participating in the Internet. ISPs can be organized in various forms, such as commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or otherwise private ...
(ISP) telecom companies to set up Wi-Fi hotspots (connected to fibre optic network via ONT), and also to provide optical fibre connections to the individual houses or institutes needing relatively much higher speed dedicated connection. As throughput requirements of a village, institute, or house increase, they will require dedicated fibre optical connections instead of village-level shared Wi-Fi. Each house or institute with a dedicated fibre optical connection will also require its own ONT installed by the service provider, though within the house or institute they can have their own Wi-Fi setup. A Common Service Centre panchayat kiosk for the online government e-services will be provided at each gram panchayat level.
Last mile connectivity
# Hotspot (Wi-Fi) at each village-level within the gram panchayat:Each gram panchayat is connected by the low-maintenance fibre optic technology, and each village under the gram panchayat is connected by a Wi-Fi hotspot tower of up to 15-meter height with a range of 5 to 7 km installed by ISP telecom companies by using short-range 5.48 GHz unused radiofrequency. Comparatively easier and faster to deploy higher-maintenance wireless technology, for Wi-Fi Hotspots in each village under the gram panchayat, is used only for the last mile connectivity. Wi-Fi router and
Antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
require continuous supply of power, hence an emergency power system is needed during the power blackout
A power outage (also called a powercut, a power out, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, or a blackout) is the loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.
There are many causes of power failures in an electricity ...
, e.g. power inverter with a backup battery A backup battery provides power to a system when the primary source of power is unavailable. Backup batteries range from small single cells to retain clock time and date in computers, up to large battery room facilities that power uninterruptible po ...
that may be recharged by the solar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
. Reliance Jio, Idea Cellular, Airtel, and Vodafone have already connected their 4G Base Towers to BharatNet fibre optic OLT to provide last mile wireless coverage.
# Connectivity to the individual homes: The Local service providers provide broadband connections to individual homes, offering employment and entrepreneurship opportunities to village youth. Once all the gram panchayats have been connected by the dedicated fibre optical network, the last mile connectivity to all villages will be provided by the commercial telecom operators by expanding the current national network of 38,000 Wi-Fi hotspots to 700,000 Wi-Fi hotspots to cover all 625,000 villages in India. , union government subsidy support will be given to the telecom service operators for rolling out Wi-Fi hotspots in commercially non-viable villages. BharatNet has offered the bulk broadband bandwidth at 75% discounted rates to the commercial telecom operators so that they can offer deeply discounted monetised competitive deals to the rural wireless broadband customers. Commercial operators Reliance Jio,
Bharti Airtel
Bharti Airtel Limited, commonly known as (d/b/a) Airtel, is an Indian multinational telecommunications services company based in New Delhi. It operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa, as well as the Channel Islands. Currently, ...
, Idea Cellular and Vodafone
Vodafone Group Public limited company, plc () is a British Multinational corporation, multinational Telephone company, telecommunications company. Its registered office and Headquarters, global headquarters are in Newbury, Berkshire, England. It ...
have already connected their 4G-based-broadband base towers to BharatNet at various locations to provide the high speed last mile wireless broadband connectivity."Bharat turns new telco battleground."Daily News and Analysis
Publications established in 2005
Newspapers published in Mumbai
English-language newspapers published in India
Daily newspapers published in India
Essel Group
2005 establishments in Maharashtra ...
, 14 November 2017."Jio, Airtel take lead in signing up for BharatNet connectivity."Economic Times, 14 November 2017."What is BharatNet project and why it's a big boost for PM Narendra Modi's Digital India dream?."
The Financial Express (India)
''The Financial Express'' is an Indian English-language business newspaper owned by The Indian Express Group. It has been published by the Indian Express
''The Indian Express'' is an English-language Indian daily newspaper founded in 19 ...
, 14 November 2017.
The central government will set up sufficient Wi-Fi hotspots to cover 100 million citizens by 2020, and tender will be floated for this soon (as of November 2017). Additionally, Indian Railways
Indian Railways (IR) is a statutory body under the ownership of Ministry of Railways, Government of India that operates India's national railway system. It manages the fourth largest national railway system in the world by size, with a tot ...
will provide Wi-Fi hotspots, limited free access, and unlimited paid access, at 600 major stations by March 2018 and all of its 8,500 stations by March 2019 with an outlay of , with 1,200 large stations catering to the rail passengers and the remaining 7,300 stations catering to both rail passengers and local population in remote and rural areas, including facilities to access government services or e-purchase of commercial products (c. 7 Jan 2018).Indian Railways to equip all 8,500 stations with Wi-FiEconomic Times, 7 Jan 2018. HRD ministry has instructed 50,000 colleges and technical in India to offer free Wi-Fi to students and staff with capped free data quota, after which data will have to be purchased. Out of these Reliance Jio has offered to deploy free Wi-Fi connectivity to 38,000 colleges, which has been supported by Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) and the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).HRD ministry asks colleges to provide free Wi-Fi on campus
Hindustan Times
''Hindustan Times'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper based in Delhi. It is the flagship publication of HT Media, an entity controlled by the KK Birla family, and is owned by Shobhana Bhartia.
It was founded by Sunder Singh Lyall ...
, 18 Jan 2018.
Some Startups, such as Velmenni Research, under the Startup India
Startup India is an initiative of the Government of India. The campaign was first announced by Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi during his speech on 15 August 2015.
The action plan of this initiative is focussing on three areas:
# Simplif ...
, are working on solutions to offer Li-Fi
Li-Fi (also written as LiFi) is a wireless communication technology which utilizes light to transmit data and position between devices. The term was first introduced by Harald Haas during a 2011 TEDGlobal talk in Edinburgh.
Li-Fi is a light comm ...
access via LED lights at homes at a speed 100 faster than ordinary WI-FI bandwidth.Forget Wi-Fi: This startup tech can power the Internet using light bulbs and is 100 times fasterEconomic Times, 16 Jan 2018.
Implementation
BharatNet is a middle layer for providing broadband connectivity across allCommunity Development Block
In India, a Community development block (CD block) or simply Block is a sub-division of Tehsil, administratively earmarked for planning and development. The area is administered by a Block Development Officer (BDO), supported by several technic ...
s (CDB), 250,000 village gram panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bod ...
s covering 630,000 inhabited villages of states and union territories of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
. As of July 2021, Phase-I was complete and 150,000 Gram Panchayats and associated villages had been service ready with 5.09 lakh km of Optical Fibre Cable already laid, the 29,500 crore (US$4 billion) PPP tender for remaining nearly 100,000 gram panchayats and all the individual inhabited villages under hose panchayats spread across 16 states was floated in 2021 with target date for broadband connectivity of 2023.Global tenders worth rs 29500 crore invited for bharatnetMoney Control, 20 July 2021.
BharatNet Phase-I (Completed: Dec 2017)
BharatNet Phase-I, across 13 states and UTs was completed in December 2017 with the Phase-I union government funding share of . It connected 100,000 gram panchayat, covering 300,000 villages by laying 300,000 km of optical fibre network.BharatNet Phase-II planIIT Bombay
The Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay or IITB) is a public research university and technical institute in Powai, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It is considered as one of the best engineering universities in India and is top ranked ...
.BharatNet Phase-I status by states and UT./ref> 13 states and UTs in this phase were:
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
, Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which al ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
, Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanm ...
, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of As ...
, Puducherry, Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siligur ...
and West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
.BSNL lays 11,005-km optical fibre cable in stateThe Tribune, 13 Jan 2018. To provide the last mile connectivity for the 100,000-gram panchayats in Phase-I, contracts were signed to connect 30,500 village panchayats by Vodafone, 30,000 village panchayats by Reliance Jio. 2,000 by Vodafone and 1,000 by Idea Cellular, these Wi-Fi hotspots were activated after connecting BharatNet fibre optics OLT to commercial operator's cell phone base stations.
Latest weekly update
BharatNet Phase-II (Target: March 2023)
BharatNet Phase-II, will connect the remaining nearly 145,000 gram panchayats covering 325,000 villages through additional 1 million km of optical fibre. Phase-II commenced with the union government funding share of , with the current 250 km per day pace of optical fibre network roll out which needs to be raised to 500 km per day to achieve the completion target of March 2019. DoT will invest on BharatNet inNortheast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
, including erecting 6,673 towers to connect 8,621 villages at the cost of and additional 4,240 gram panchayats by satellite broadband connectivity.DoT to spend Rs 10,743 cr to improve connectivity in NEBusiness Standard, 16 Jan 2018.
Merger of BSNL and BBNL
On 27th July 2022. The cabinet decided to merge state owned Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited and Bharat Broadband Network LimitedSee also
* Internet in India * List of countries by Internet connection speeds * List of countries by number of broadband Internet subscriptions * List of countries by number of Internet users * List of countries by smartphone penetrationReferences
Citations
External links
*Official live current overall summary status report
Official Phase-I status breakdown by state
IIT Bombay
The Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay or IITB) is a public research university and technical institute in Powai, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It is considered as one of the best engineering universities in India and is top ranked ...
Collection of Scripts to analyse the district wise data of the progress.
{{Telecommunication companies of India Telecommunications companies of India Government-owned companies of India Proposed infrastructure in India